New Treatment Addressing the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Pathogenesis of Psoriasis
2.1. AMPs
2.2. A Disintegrin and Metalloprotease Domain Containing Thrombospondin Type 1 Motif-Like 5 (ADAMTSL5)
2.3. DCs
2.4. IL23/IL17 Axis
2.5. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR)
3. Treatment
3.1. Currently Available Oral Systemic Therapy
3.1.1. Retinoids
3.1.2. Methotrexate
3.1.3. Cyclosporine A
3.1.4. Apremilast
3.2. Currently Available Biologic Therapy
3.2.1. TNFα Inhibitors
3.2.2. IL23 Inhibitors
3.2.3. IL17 Inhibitors
3.3. RORγt Inhibitors
3.4. IL36 Receptor Antagonist
3.5. Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors
3.6. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate (S1P) Agonist
3.7. Rho-Associated Kinase (ROCK2) Inhibitor
3.8. The AhR Agonist, Tapinarof
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griffiths, C.E.; Barker, J.N. Pathogenesis and Clinical Features of Psoriasis. Lancet 2007, 370, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehncke, W.; Boehncke, S.; Tobin, A.; Kirby, B. The ‘psoriatic March’: A Concept of how Severe Psoriasis may Drive Cardiovascular Comorbidity. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, K.; Mizutani, H. “Inflammatory Skin March”: IL-1–mediated Skin Inflammation, Atopic Dermatitis, and Psoriasis to Cardiovascular Events. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 823–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Yang, X.; Liang, Y.; Xie, H.; Dai, Z.; Zheng, G. Transcription Factor Retinoid-Related Orphan Receptor γt: A Promising Target for the Treatment of Psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Gallo, R.L. AMPed up Immunity: How Antimicrobial Peptides have Multiple Roles in Immune Defense. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, E.; Sato, Y.; Minagawa, A.; Okuyama, R. Pathogenesis of Psoriasis and Development of Treatment. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rendon, A.; Schäkel, K. Psoriasis Pathogenesis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Büchau, A.S.; Gallo, R.L. Innate Immunity and Antimicrobial Defense Systems in Psoriasis. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harder, J.; Schröder, J.M. Psoriatic scales: A promising source for the isolation of human skin-derived antimicrobial proteins. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morizane, S.; Gallo, R.L. Antimicrobial Peptides in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2012, 39, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, R.L.; Broome, A.; Ruse, M.; Robinson, N.; Ryan, D.; Lee, K. S100 Proteins in the Epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.C.; Tan, X.; Luxenberg, D.P.; Karim, R.; Dunussi-Joannopoulos, K.; Collins, M.; Fouser, L.A. Interleukin (IL)-22 and IL-17 are Coexpressed by Th17 Cells and Cooperatively Enhance Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinquan, T.; Vorum, H.; Larsen, C.G.; Madsen, P.; Rasmussen, H.H.; Gesser, B.; Etzerodt, M.; Honoré, B.; Celis, J.E.; Thestrup-Pedersen, K. Psoriasin: A Novel Chemotactic Protein. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 107, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frohm, M.; Agerberth, B.; Ahangari, G.; Backdahl, M.S.; Liden, S.; Wigzell, H.; Gudmundsson, G.H. The Expression of the Gene Coding for the Antibacterial Peptide LL-37 is Induced in Human Keratinocytes during Inflammatory Disorders. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 15258–15263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lande, R.; Gregorio, J.; Facchinetti, V.; Chatterjee, B.; Wang, Y.H.; Homey, B.; Cao, W.; Wang, Y.H.; Su, B.; Nestle, F.O.; et al. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Sense Self-DNA Coupled with Antimicrobial Peptide. Nature 2007, 449, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morizane, S.; Yamasaki, K.; Mühleisen, B.; Kotol, P.F.; Murakami, M.; Aoyama, Y.; Iwatsuki, K.; Hata, T.; Gallo, R.L. Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37 in Psoriasis Enables Keratinocyte Reactivity Against TLR9 Ligands. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hänsel, A.; Günther, C.; Ingwersen, J.; Starke, J.; Schmitz, M.; Bachmann, M.; Meurer, M.; Rieber, E.P.; Schäkel, K. Human Slan (6-Sulfo LacNAc) Dendritic Cells are Inflammatory Dermal Dendritic Cells in Psoriasis and Drive Strong Th17/Th1 T-Cell Responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, T.; Hirayama, N. Binding Affinity and Interaction of LL-37 with HLA-C06:02 in Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1901–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arakawa, A.; Siewert, K.; Stöhr, J.; Besgen, P.; Kim, S.; Rühl, G.; Nickel, J.; Vollmer, S.; Thomas, P.; Krebs, S.; et al. Melanocyte Antigen Triggers Autoimmunity in Human Psoriasis. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, J.G. An autoimmune “attack” on melanocytes triggers psoriasis and cellular hyperplasia. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishimoto, S.; Kotani, H.; Tsuruta, S.; Shimizu, N.; Ito, M.; Shichita, T.; Morita, R.; Takahashi, H.; Amagai, M.; Yoshimura, A. Th17 Cells Carrying TCR Recognizing Epidermal Autoantigen Induce Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Romanelli, P.; Volpe, E.; Borsellino, G.; Romanelli, M. Scanning the Immunopathogenesis of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Bonifacio, K.M.; Kunjravia, N.; Hawkes, J.E.; Cueto, I.; Li, X.; Garcet, S.; Krueger, J.G. Autoantigens ADAMTSL5 and LL-37 are significantly Upregulated in Active Psoriasis and Associated with Dendritic Cells and Macrophages. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifacio, K.M.; Kunjravia, N.; Krueger, J.G.; Fuentes-Duculan, J. Cutaneous Expression of a Disintegrin-Like and Metalloprotease Domain Containing Thrombospondin Type 1 Motif-Like 5 (ADAMTSL5) in Psoriasis Goes Beyond Melanocytes. J. Pigment Disord. 2016, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Bai, Y. Dendritic Cells: The Driver of Psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macri, C.; Pang, E.S.; Patton, T.; O’Keeffe, M. Dendritic cell subsets. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2018, 84, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, M.; McGovern, N.; Haniffa, M. Human Dendritic Cell Subsets. Immunology 2013, 140, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Kolbeck, R.; Sanjuan, M.A. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells in Autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 44, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Arimura, K.; Uto, T.; Fukaya, T.; Nakamura, T.; Choijookhuu, N.; Hishikawa, Y.; Sato, K. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Orchestrate TLR7-Mediated Innate and Adaptive Immunity for the Initiation of Autoimmune Inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopfnagel, V.; Wagenknecht, S.; Harder, J.; Hofmann, K.; Kleine, M.; Buch, A.; Sodeik, B.; Werfel, T. RNase 7 Strongly Promotes TLR9-Mediated DNA Sensing by Human Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lande, R.; Chamilos, G.; Ganguly, D.; Demaria, O.; Frasca, L.; Durr, S.; Conrad, C.; Schröder, J.; Gilliet, M. Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides in Psoriatic Skin Cooperate to Break Innate Tolerance to self-DNA. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestle, F.O.; Conrad, C.; Tun-Kyi, A.; Homey, B.; Gombert, M.; Boyman, O.; Burg, G.; Liu, Y.; Gilliet, M. Plasmacytoid Predendritic Cells Initiate Psoriasis through Interferon-A Production. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lande, R.; Gilliet, M. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells: Key Players in the Initiation and Regulation of Immune Responses. Annu. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1183, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, S.M.; Lapenta, C.; Logozzi, M.; Parlato, S.; Spada, M.; Di Pucchio, T.; Belardelli, F. Type I Interferon as a Powerful Adjuvant for Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cell Development and Activity in Vitro and in Hu-PBL-SCID Mice. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsujii, K.; Furue, Y.; Imura, C.; Shichijo, M.; Yasui, K. Mechanism of Pathogenesis of Imiquimod-induced Skin Inflammation in the Mouse: A Role for Interferon-alpha in Dendritic Cell Activation by Imiquimod. J. Dermatol. 2014, 41, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohyama, M.; Yang, L.; Hanakawa, Y.; Dai, X.; Shirakata, Y.; Sayama, K. IFN-A Enhances IL-22 Receptor Expression in Keratinocytes: A Possible Role in the Development of Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1933–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Cao, X. Regulatory Dendritic Cells in Autoimmunity: A Comprehensive Review. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 63, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manicassamy, S.; Pulendran, B. Dendritic Cell Control of Tolerogenic Responses. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 241, 206–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buhl, T.; Saleh, M.M.; Schön, M.P. More Tolerance for Dendritic Cells in Psoriasis. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganguly, D.; Haak, S.; Sisirak, V.; Reizis, B. The Role of Dendritic Cells in Autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auriemma, M.; Brzoska, T.; Klenner, L.; Kupas, V.; Goerge, T.; Voskort, M.; Zhao, Z.; Sparwasser, T.; Luger, T.A.; Loser, K. A-MSH-Stimulated Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells Induce Functional Regulatory T Cells and Ameliorate Ongoing Skin Inflammation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1814–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terhorst, D.; Chelbi, R.; Wohn, C.; Malosse, C.; Tamoutounour, S.; Jorquera, A.; Bajenoff, M.; Dalod, M.; Malissen, B.; Henri, S. Dynamics and Transcriptomics of Skin Dendritic Cells and Macrophages in an Imiquimod-Induced, Biphasic Mouse Model of Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4953–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bos, J.D.; Hulsebosch, H.J.; Krieg, S.R.; Bakker, P.M.; Cormane, R.H. Immunocompetent Cells in Psoriasis. in Situ Immunophenotyping by Monoclonal Antibodies. Arch. Dermatolog. Res. 1983, 275, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, E.; Wikén, M.; Cheuk, S.; Sérézal, I.G.; Baharom, F.; Ståhle, M.; Smed-Sörensen, A.; Eidsmo, L. Dynamic Changes in Resident and Infiltrating Epidermal Dendritic Cells in Active and Resolved Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eaton, L.H.; Mellody, K.T.; Pilkington, S.M.; Dearman, R.J.; Kimber, I.; Griffiths, C.E.M. Impaired Langerhans Cell Migration in Psoriasis is due to an Altered Keratinocyte Phenotype Induced by interleukin-17. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, T.P.; Zhang, H.H.; Borek, I.; Wolf, P.; Hedrick, M.N.; Singh, S.P.; Kelsall, B.L.; Clausen, B.E.; Farber, J.M. Monocyte-Derived Inflammatory Langerhans Cells and Dermal Dendritic Cells Mediate Psoriasis-Like Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korn, T.; Bettelli, E.; Oukka, M.; Kuchroo, V.K. IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 485–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Res, P.C.M.; Piskin, G.; de Boer, O.J.; van der Loos, C.M.; Teeling, P.; Bos, J.D.; Teunissen, M.B.M. Overrepresentation of IL-17A and IL-22 Producing CD8 T Cells in Lesional Skin Suggests their Involvement in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Krueger, J.G. Highly Effective New Treatments for Psoriasis Target the IL-23 Type 17 T Cell Autoimmune Axis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2017, 68, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, J.E.; Chan, T.C.; Krueger, J.G. Psoriasis Pathogenesis and the Development of Novel Targeted Immune Therapies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Nograles, K.E.; Tian, S.; Cardinale, I.; Chimenti, S.; Krueger, J.G. Integrative Responses to IL-17 and TNF-A in Human Keratinocytes Account for Key Inflammatory Pathogenic Circuits in Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoreschi, K.; Laurence, A.; Yang, X.; Tato, C.M.; McGeachy, M.J.; Konkel, J.E.; Ramos, H.L.; Wei, L.; Davidson, T.S.; Bouladoux, N.; et al. Generation of Pathogenic TH17 Cells in the Absence of TGF-Β Signalling. Nature 2010, 467, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eyerich, S.; Eyerich, K.; Pennino, D.; Carbone, T.; Nasorri, F.; Pallotta, S.; Cianfarani, F.; Odorisio, T.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Behrendt, H.; et al. Th22 Cells Represent a Distinct Human T Cell Subset Involved in Epidermal Immunity and Remodeling. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3573–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, K.; Suh, J.W.; Lee, K.H.; Kang, J.L.; Woo, S. IL-17 and IL-22 Enhance Skin Inflammation by Stimulating the Secretion of IL-1β by Keratinocytes Via the ROS-NLRP3-Caspase-1 Pathway. Int. Immunol. 2012, 24, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, E.G.; Guo, C.; Rizzo, H.; Lillis, J.V.; Kurtz, S.E.; Skorcheva, I.; Purdy, D.; Fitch, E.; Iordanov, M.; Blauvelt, A. Th17 Cytokines Stimulate CCL20 Expression in Keratinocytes in Vitro and in Vivo: Implications for Psoriasis Pathogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2175–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heidenreich, R.; Röcken, M.; Ghoreschi, K. Angiogenesis Drives Psoriasis Pathogenesis. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2009, 90, 232–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denison, M.S.; Nagy, S.R. Activation of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor by Structurally Diverse Exogenous and Endogenous Chemicals. Annu. Rev. Pharma. Toxicol. 2003, 43, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockinger, B.; Meglio, P.D.; Gialitakis, M.; Duarte, J.H. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor: Multitasking in the Immune System. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 403–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, M.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Tsuji, G. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramirez, J.; Brembilla, N.C.; Sorg, O.; Chicheportiche, R.; Matthes, T.; Dayer, J.; Saurat, J.; Roosnek, E.; Chizzolini, C. Activation of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Reveals Distinct Requirements for IL-22 and IL-17 Production by Human T Helper Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 2450–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Qiao, H.; Fu, M.; Dang, E.; Wang, G. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Cutaneous Vascular Endothelial Cells Restricts Psoriasis Development by Negatively Regulating Neutrophil Recruitment. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chularojanamontri, L.; Silpa-archa, N.; Wongpraparut, C.; Limphoka, P. Long-term Safety and Drug Survival of Acitretin in Psoriasis: A Retrospective Observational Study. Int. J. Dermatol. 2019, 58, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogra, S.; Jain, A.; Kanwar, A.J. Efficacy and Safety of Acitretin in Three Fixed Doses of 25, 35 and 50 mg in Adult Patients with Severe Plaque Type Psoriasis: A Randomized, Double Blind, Parallel Group, Dose Ranging Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 27, e305–e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raaby, L.; Zachariae, C.; Østensen, M.; Heickendorff, L.; Thielsen, P.; Grønbæk, H.; Skov, L.; Kyvsgaard, N.; Madsen, J.; Heidenheim, M.; et al. Methotrexate Use and Monitoring in Patients with Psoriasis: A Consensus Report Based on a Danish Expert Meeting. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2017, 97, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- West, J.; Ogston, S.; Foerster, J. Safety and Efficacy of Methotrexate in Psoriasis: A Meta-Analysis of Published Trials. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maza, A.; Montaudié, H.; Sbidian, E.; Gallini, A.; Aractingi, S.; Aubin, F.; Bachelez, H.; Cribier, B.; Joly, P.; Jullien, D.; et al. Oral Cyclosporin in Psoriasis: A Systematic Review on Treatment Modalities, Risk of Kidney Toxicity and Evidence for use in Non-plaque Psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, K.; Reich, K.; Leonardi, C.L.; Kircik, L.; Chimenti, S.; Langley, R.G.; Hu, C.; Stevens, R.M.; Day, R.M.; Gordon, K.B.; et al. Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: Results of a phase III, randomized, controlled trial (Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis [ESTEEM] 1). J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariette, X.; Förger, F.; Abraham, B.; Flynn, A.D.; Moltó, A.; Flipo, R.; van Tubergen, A.; Shaughnessy, L.; Simpson, J.; Teil, M.; et al. Lack of Placental Transfer of Certolizumab Pegol during Pregnancy: Results from CRIB, a Prospective, Postmarketing, Pharmacokinetic Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, J.S.; Kalb, R.E. Infliximab for the Treatment of Plaque Psoriasis. Biologics 2008, 2, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Alwawi, E.A.; Mehlis, S.L.; Gordon, K.B. Treating Psoriasis with Adalimumab. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 345–351. [Google Scholar]
- Blauvelt, A.; Reich, K.; Lebwohl, M.; Burge, D.; Arendt, C.; Peterson, L.; Drew, J.; Rolleri, R.; Gottlieb, A.B. Certolizumab Pegol for the Treatment of Patients with Moderate-to-severe Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: Pooled Analysis of Week 16 Data from Three Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 33, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhi, D. Ustekinumab for the treatment of psoriasis: Review of three multicenter clinical trials. Drugs Today 2010, 46, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, M.; Torres, T. Guselkumab for the treatment of psoriasis—evidence to date. Drugs Context 2019, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, H.; Khatri, A.; Diderichsen, P.M.; Mandema, J.; Othman, A.A. Meta-Analyses of Clinical Efficacy of Risankizumab and Adalimumab in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: Supporting Evidence of Risankizumab Superiority. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 107, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blauvelt, A.; Sofen, H.; Papp, K.; Gooderham, M.; Tyring, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lowry, S.; Mendelsohn, A.; Parno, J.; Reich, K. Tildrakizumab efficacy and impact on quality of life up to 52 weeks in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis: A pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Ferrer, A.; Vilarrasa, E.; Puig, L. Secukinumab (AIN457) for the treatment of psoriasis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, K.A.; Leonardi, C.L.; Blauvelt, A.; Reich, K.; Korman, N.J.; Ohtsuki, M.; Paul, C.; Ball, S.; Cameron, G.S.; Erickson, J.; et al. Ixekizumab Treatment for Psoriasis: Integrated Efficacy Analysis of Three Double-Blinded, Controlled Studies (UNCOVER-1, UNCOVER-2, UNCOVER-3). Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foulkes, A.C.; Warren, R.B. Brodalumab in Psoriasis: Evidence to Date and Clinical Potential. Drugs Context 2019, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, V.B.; Kumar, S.; Sachchidanand; Sharma, R.; Desai, R.C. Combating Autoimmune Diseases with Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor-γ (RORγ or RORc) Inhibitors: Hits and Misses. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10976–10995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.G.; Wu, S.; Gupta, A.; von Mackensen, Y.L.; Siemetzki, H.; Freudenberg, J.; Wigger-Alberti, W.; Yamaguchi, Y. A phase I randomized controlled trial to evaluate safety and clinical effect of topically applied GSK2981278 ointment in a psoriasis plaque test. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, 1427–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imura, C.; Ueyama, A.; Sasaki, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Furue, Y.; Tai, N.; Tsujii, K.; Katayama, K.; Okuno, T.; Shichijo, M.; et al. A Novel RORγt Inhibitor is a Potential Therapeutic Agent for the Topical Treatment of Psoriasis with Low Risk of Thymic Aberrations. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 93, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, R.; Raymond, E.L.; Mennerich, D.; Woska, J.R.; Caviness, G.; Grimaldi, C.; Ahlberg, J.; Perez, R.; Roberts, S.; Yang, D.; et al. Generation and Functional Characterization of Anti-Human and Anti-Mouse IL-36R Antagonist Monoclonal Antibodies. mAbs 2017, 9, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bachelez, H.; Choon, S.; Marrakchi, S.; Burden, A.D.; Tsai, T.; Morita, A.; Turki, H.; Hall, D.B.; Shear, M.; Baum, P.; et al. Inhibition of the Interleukin-36 Pathway for the Treatment of Generalized Pustular Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Schwartz, D.M.; Villarino, A.V.; Gadina, M.; McInnes, I.B.; Laurence, A. The JAK-STAT Pathway: Impact on Human Disease and Therapeutic Intervention. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, D.M.; Kanno, Y.; Villarino, A.; Ward, M.; Gadina, M.; O’Shea, J.J. JAK Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy for Immune and Inflammatory Diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, K.A.; Menter, M.A.; Abe, M.; Elewski, B.; Feldman, S.R.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Langley, R.; Luger, T.; Thaci, D.; Buonanno, M.; et al. Tofacitinib, an Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitor, for the Treatment of Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: Results from Two Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Phase III Trials. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, R.; Iversen, L.; Sofen, H.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Foley, P.; Romiti, R.; Bachinsky, M.; Rottinghaus, S.T.; Tan, H.; Proulx, J.; et al. Tofacitinib Withdrawal and Retreatment in Moderate-to-severe Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 172, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachelez, H.; Kerkhof, P.C.M.; Strohal, R.; Kubanov, A.; Valenzuela, F.; Lee, J.; Yakusevich, V.; Chimenti, S.; Papacharalambous, J.; Proulx, J.; et al. Tofacitinib Versus Etanercept or Placebo in Moderate-to-Severe Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: A Phase 3 Randomised Non-Inferiority Trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tsai, T.; Lee, M.; Zheng, M.; Wang, G.; Jin, H.; Gu, J.; Li, R.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. The Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib in Asian Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: A Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 88, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papp, K.A.; Menter, A.; Strober, B.; Langley, R.G.; Buonanno, M.; Wolk, R.; Gupta, P.; Krishnaswami, S.; Tan, H.; Harness, J.A. Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib, an Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitor, in the Treatment of Psoriasis: A Phase 2b Randomized Placebo-controlled Dose-ranging Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Biehl, A.; Gadina, M.; Hasni, S.; Schwartz, D.M. JAK–STAT Signaling as a Target for Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases: Current and Future Prospects. Drugs 2017, 77, 521–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, K.M.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Suprun, M.; Zhang, W.; Garcet, S.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Li, X.; Scaramozza, M.; Kieras, E.; Banfield, C.; et al. Molecular and Cellular Responses to the TYK2/JAK1 Inhibitor PF-06700841 Reveal Reduction of Skin Inflammation in Plaque Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solimani, F.; Meier, K.; Ghoreschi, K. Emerging Topical and Systemic JAK Inhibitors in Dermatology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borodzicz, S.; Rudnicka, L.; Mirowska-Guzel, D.; Cudnoch-Jedrzejewska, A. The Role of Epidermal Sphingolipids in Dermatologic Diseases. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunkel, G.T.; Maceyka, M.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Targeting the Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Axis in Cancer, Inflammation and Beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krause, A.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Dingemanse, J. Modeling Clinical Efficacy of the S1P Receptor Modulator Ponesimod in Psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 89, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JCyster, J.G.; Schwab, S.R. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate and Lymphocyte Egress from Lymphoid Organs. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, W.S.; Wang, W.; Herr, D.R. To fingolimod and beyond: The rich pipeline of drug candidates that target S1P signaling. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piali, L.; Froidevaux, S.; Hess, P.; Nayler, O.; Bolli, M.H.; Schlosser, E.; Kohl, C.; Steiner, B.; Clozel, M. The Selective Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 1 Agonist Ponesimod Protects against Lymphocyte-Mediated Tissue Inflammation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 337, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, M.; Xue, N.; Lai, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Chen, X. Validating a Selective S1P1 Receptor Modulator Syl930 for Psoriasis Treatment. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manggau, M.; Kim, D.; Ruwisch, L.; Vogler, R.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Kleuser, B. boothe Formation of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 117, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogler, R.; Sauer, B.; Kim, D.S.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Kleuser, B.; Sch, M. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate and Its Potentially Paradoxical Effects on Critical Parameters of Cutaneous Wound Healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schüppel, M.; Kürschner, U.; Kleuser, U.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Kleuser, B. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Restrains Insulin-Mediated Keratinocyte Proliferation via Inhibition of Akt through the S1P2 Receptor Subtype. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schaper, K.; Dickhaut, J.; Japtok, L.; Kietzmann, M.; Mischke, R.; Kleuser, B.; Bäumer, W. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Exhibits Anti-Proliferative and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Mouse Models of Psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 71, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Im, D. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor Modulators and Drug Discovery. Biomol. Ther. 2017, 25, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolli, M.H.; Abele, S.; Binkert, C.; Bravo, R.; Buchmann, S.; Bur, D.; Gatfield, J.; Hess, P.; Kohl, C.; Mangold, C.; et al. 2-Imino-Thiazolidin-4-One Derivatives as Potent, Orally Active S1P1 Receptor Agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4198–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosio, D.; Freedman, M.S.; Prinz, J. Ponesimod, a Selective S1P1 Receptor Modulator: A Potential Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis and Other Immune-Mediated Diseases. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2016, 7, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaclavkova, A.; Chimenti, S.; Arenberger, P.; Hóllo, P.; Sator, P.G.; Burcklen, M.; Stefani, M.; D’Ambrosio, D. Oral ponesimod in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.; Foley, D.; Naylor, C.; Robinson, C.; Riley, J.; Epemolu, O.; Scullion, P.; Shishikura, Y.; Katz, E.; Mclean, W.H.I.; et al. Discovery of Super Soft-Drug Modulators of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 28, 3255–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riento, K.; Ridley, A.J. ROCKs. multifunctional kinases in cell behavior. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin-Zhorov, A.; Weiss, J.M.; Nyuydzefe, M.S.; Chen, W.; Scher, J.U.; Mo, R.; Depoil, D.; Rao, N.; Liu, B.; Wei, J.; et al. Selective Oral ROCK2 Inhibitor Down-Regulates IL-21 and IL-17 Secretion in Human T Cells Via STAT3-Dependent Mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16814–16819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Zheng, Y.; von Bornstadt, D.; Wei, Y.; Balcioglu, A.; Daneshmand, A.; Yalcin, N.; Yu, E.; Herisson, F.; Atalay, Y.B.; et al. Selective ROCK2 Inhibition in Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2014, 1, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flynn, R.; Paz, K.; Du, J.; Reichenbach, D.K.; Taylor, P.A.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Vulic, A.; Luznik, L.; MacDonald, K.K.P.; Hill, G.R.; et al. Targeted Rho-Associated Kinase 2 Inhibition Suppresses Murine and Human Chronic GVHD through a Stat3-Dependent Mechanism. Blood 2016, 127, 2144–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zanin-Zhorov, A.; Weiss, J.M.; Trzeciak, A.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Nyuydzefe, M.S.; Arencibia, C.; Polimera, S.; Schueller, O.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; et al. Cutting Edge: Selective Oral ROCK2 Inhibitor Reduces Clinical Scores in Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris and Normalizes Skin Pathology via Concurrent Regulation of IL-17 and IL-10. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 3809–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, P.S.; Gupta, S.; Chang, E.; Song, L.; Stirzaker, R.A.; Liao, J.K.; Bhagat, G.; Pernis, A.B. Phosphorylation of IRF4 by ROCK2 Regulates IL-17 and IL-21 Production and the Development of Autoimmunity in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3280–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, W.H.; Schmidt, T.M.; Nealson, K.H. Identification of an anthraquinone pigment and a hydroxystilbene antibiotic from Xenorhabdus luminescens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 1602–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.H.; Jayawickreme, C.; Rickard, D.J.; Nicodeme, E.; Bui, T.; Simmons, C.; Coquery, C.M.; Neil, J.; Pryor, W.M.; Mayhew, D.; et al. Tapinarof is a Natural AhR Agonist that Resolves Skin Inflammation in Mice and Humans. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2110–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robbins, K.; Bissonnette, R.; Maeda-Chubachi, T.; Ye, L.; Peppers, J.; Gallagher, K.; Kraus, J.E. Phase 2, Randomized Dose-Finding Study of Tapinarof (GSK2894512 Cream) for the Treatment of Plaque Psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
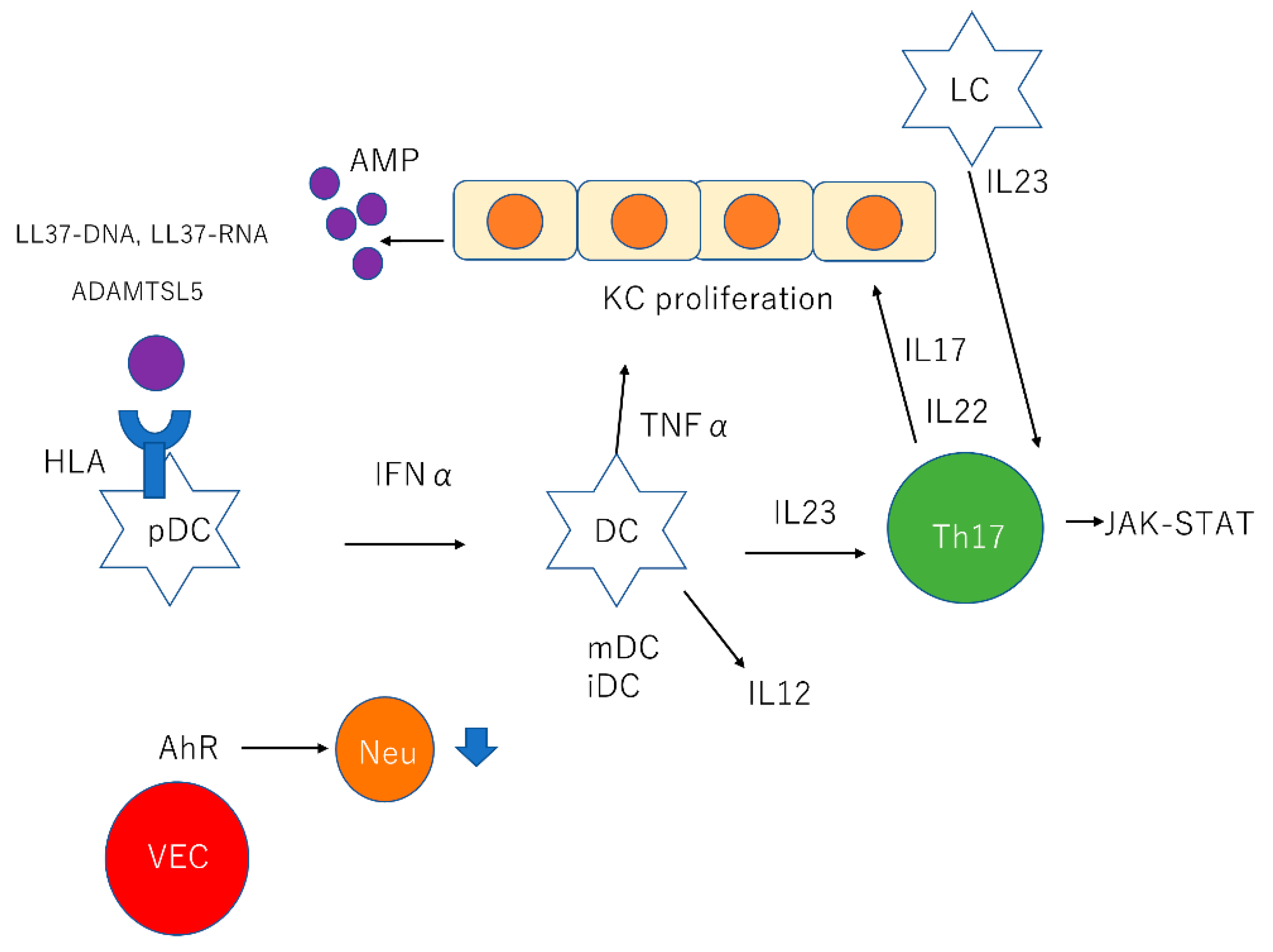

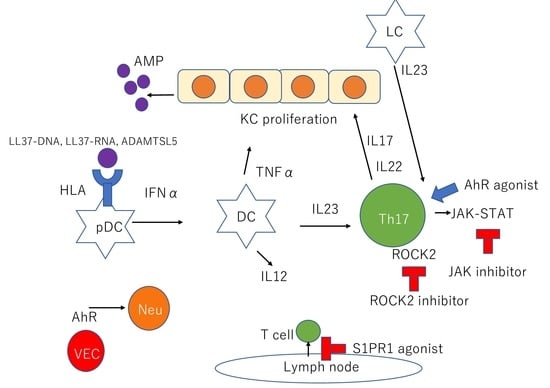
| Cell Type | Description |
|---|---|
| KCs | KCs produce AMPs such as β-defensins, S100 proteins, and cathelicidin |
| pDCs | pDCs stimulated by LL37-DNA complexes produce IFNα |
| mDCs | mDCs stimulated by LL37-RNA complexes produce TNFα, IL23, and IL12. |
| LCs | LCs produce IL23 |
| Th17 cells | Th17 cells stimulated by IL23 produce IL17 and IL22 through JAK-STAT pathway IL17 recruits neutrophil and proliferates KCs |
| VECs | AhR in cutaneous VECs downregulate neutrophil recruitment |
| Name | Target | Stage | Dosage Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| VTP-43742 | RORγt inhibitor | Phase 2 | Oral |
| GSK2981278 | RORγ inverse agonist | Phase 1 | Topical |
| BI 655130 | IL36-receptor antagonist | Phase 1 | Intravenous |
| Tofacitinib | JAK inhibitor | Phase 3 | Oral |
| Baricitinib | JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor | Phase 2 | Oral |
| BMS-986165 | TYK2 inhibitor | Phase 2 | Oral |
| PF-06700841 | TYK2/JAK1 inhibitor | Phase 2 | Topical |
| Ponesimod | S1PR1 agonist | Phase 2 | Oral |
| KD025 | ROCK2 inhibitor | Phase 2 | Oral |
| Tapinarof | AhR agonist | Phase 2 | Topical |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tokuyama, M.; Mabuchi, T. New Treatment Addressing the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7488. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207488
Tokuyama M, Mabuchi T. New Treatment Addressing the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(20):7488. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207488
Chicago/Turabian StyleTokuyama, Michio, and Tomotaka Mabuchi. 2020. "New Treatment Addressing the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 20: 7488. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207488
APA StyleTokuyama, M., & Mabuchi, T. (2020). New Treatment Addressing the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(20), 7488. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207488