Intestinal Explant Cultures from Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata, L.) Allowed the Determination of Mucosal Sensitivity to Bacterial Pathogens and the Impact of a Plant Protein Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
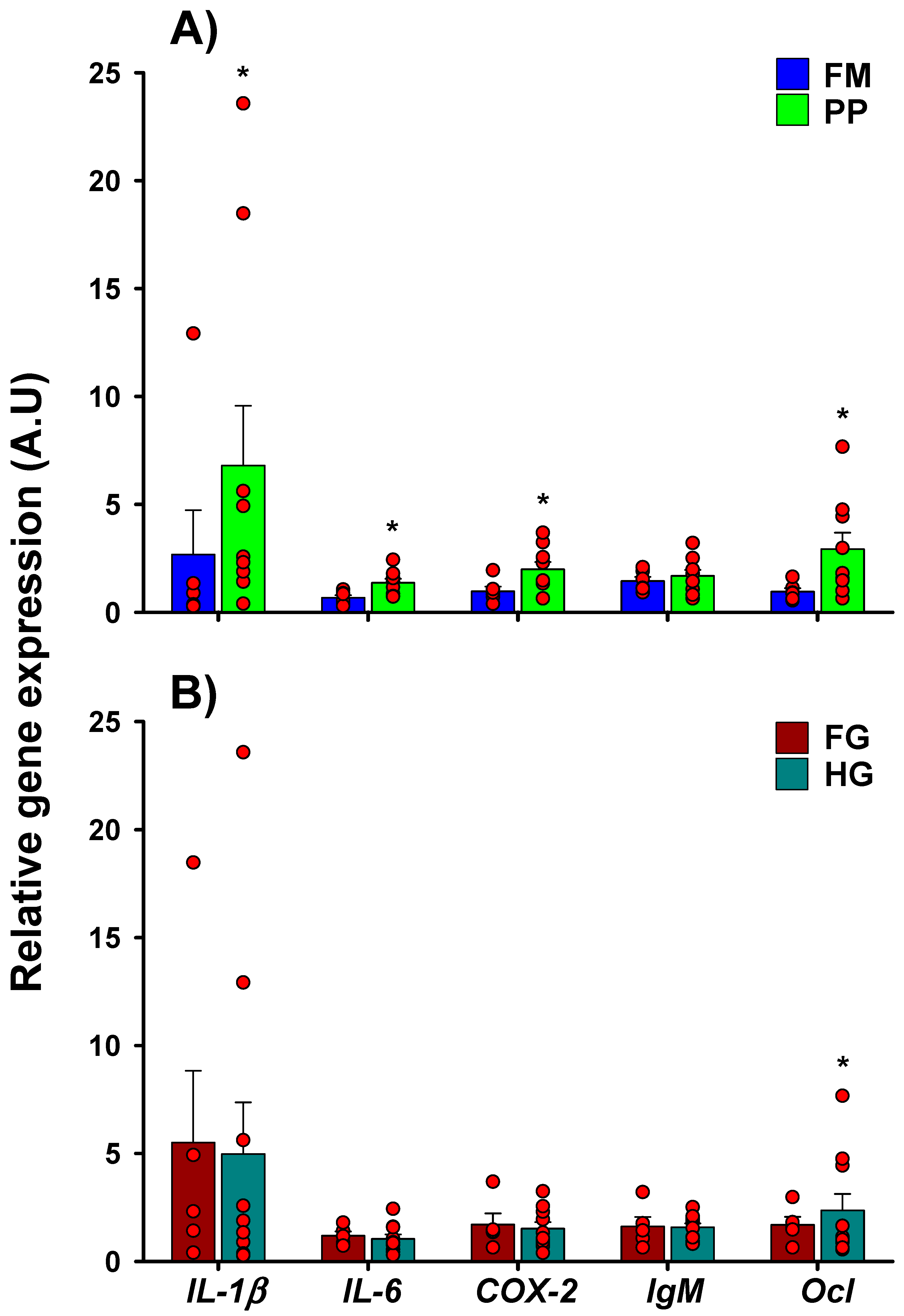
2.1. Phase I: Up to 68 g
2.1.1. Basal Gene Expression
2.1.2. Ex Vivo Assay
2.2. Phase II: Up to 250 g
2.2.1. Basal Gene Expression
2.2.2. Ex vivo Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Fish, Rearing System Conditions, Diets, and Feeding Conditions
4.3. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.4. Experimental Design
4.4.1. Phase I: Up to 68 g
4.4.2. Phase II: Up to 250 g
Ex vivo Assays and Bacterial Challenge
LDH Activity Assay
Gene Expression Assay of Intestinal Inflammatory and Immune Markers
4.5. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| AOAC | Association of Analytical Communities |
| β-Act | β-Actin |
| cDNA | Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid |
| CECT | Colección Española de Cultivos Tipo |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase 2 |
| FM | fish meal-based diet |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| EF-1α | Elongation Factor 1α |
| FG | Foregut |
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| HG | hindgut |
| IgM | immunoglobulin M |
| IL-1β | interleukin 1β |
| IL-6 | interleukin 6 |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| NADH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| Ocl | occludin |
| PP | plant protein-based diet |
| PP* | plant protein-based diet (short term) |
| qPCR | quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid; Rps18: ribosomal protein S18 |
References
- Minghetti, M.; Drieschner, C.; Bramaz, N.; Schug, H.; Schirmer, K. A fish intestinal epithelial barrier model established from the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cell line, RTgutGC. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2017, 33, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, G.D.G.; Balcázar, J.L.J. A review on the interactions between gut microbiota and innate immunity of fish. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 52, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartviksen, M.; González Vecino, J.L.; Kettunen, A.; Myklebust, R.; Ruohonen, K.; Wadsworth, S.; Ringø, E. Probiotic and Pathogen Ex-vivo Exposure of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar L.) Intestine from Fish Fed Four Different Protein Sources. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, A.; Decostere, A.; Ducatelle, R.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F. Development of a gut perfusion model as an alternative to the use of live fish. Lab. Anim. 2005, 39, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-C. Acute toxicity of ammonia on Litopenaeus vannamei Boone juveniles at different salinity levels. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2001, 259, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, A.; Pasmans, F.; Van Den Broeck, W.; Ducatelle, R.; Haesebrouck, F.; Decostere, A. Association of Flavobacterium psycrophilum strains with intestinal explants of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2005, 67, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, G.M.; Monfort, M.; Saoud, I.P.; Emery, M.J.; Mustafa, S.; Rawling, M.D.; Eynon, B.; Davies, S.J.; Merrifield, D.L. An ex vivo approach to studying the interactions of Pediococcus acidilactici and Vibrio (Listonella) anguillarum in the anterior intestine of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2011, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövmo Martinsen, L.; Salma, W.; Myklebust, R.; Mayhew, T.M.; Ringö, E. Carnobacterium maltaromaticum vs. Vibrio (Listonella) anguillarum in the midgut of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.): An ex vivo study. Aquac. Res. 2011, 42, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; He, S.; Liu, W.; Ringø, E.; Zhou, Z. Lactobacillus planarum subsp. plantarum JCM 1149 vs. Aeromonas hydrophila NJ-1 in the anterior intestine and posterior intestine of hybrid tilapia Oreochromis niloticus ♀×Oreochromis aureus ♂: An exvivo study. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resau, J.H.; Sakamoto, K.; Cottrell, J.R.; Hudson, E.A.; Meltzer, S.J. Explant organ culture: A review. Cytotechnology 1991, 7, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dame, M.K.; Bhagavathula, N.; Mankey, C.; Dasilva, M.; Paruchuri, T.; Aslam, M.N.; Varani, J. Human colon tissue in organ culture: Preservation of normal and neoplastic characteristics. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2010, 46, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäuerl, C.; Llopis, M.; Antolín, M.; Monedero, V.; Mata, M.; Zuñiga, M.; Guarner, F.; Pérez Martínez, G. Lactobacillus paracasei and Lactobacillus plantarum strains downregulate proinflammatory genes in an ex vivo system of cultured human colonic mucosa. Genes Nutr. 2013, 8, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva-Teles, A.; Enes, P.; Peres, H. Replacing Fishmeal and Fish Oil in Industrial Aquafeeds for Carnivorous Fish. In Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 203–233. ISBN 9780081005064. [Google Scholar]
- Monge-Ortíz, R.; Martínez-Llorens, S.; Márquez, L.; Moyano, F.J.; Jover-Cerdá, M.; Tomás-Vidal, A. Potential use of high levels of vegetal proteins in diets for market-sized gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 70, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva-Teles, A. Review Article Nutrition and health of aquaculture fish. J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Llorens, S.; Moñino, A.V.; Vidal, A.T.; Salvador, V.J.M.; Pla Torres, M.; Jover Cerdá, M. Soybean meal as a protein source in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) diets: Effects on growth and nutrient utilization. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Llorens, S.; Vidal, A.T.; Garcia, I.J.; Torres, M.P.; CerdÁ, M.J. Optimum dietary soybean meal level for maximizing growth and nutrient utilization of on-growing gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquac. Nutr. 2009, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogdahl, Å.; Penn, M.; Thorsen, J.; Refstie, S.; Bakke, A.M. Important antinutrients in plant feedstuffs for aquaculture: An update on recent findings regarding responses in salmonids. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogdahl, Å.; Bakke-McKellep, A.M.; Baeverfjord, G. Effects of graded levels of standard soybean meal on intestinal structure, mucosal enzyme activities, and pancreatic response in Atlantic salmon (Salmo solar L.). Aquac. Nutr. 2003, 9, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urán, P.A.; Schrama, J.W.; Jaafari, S.; Baardsen, G.; Rombout, J.H.W.M.; Koppe, W.; Verreth, J.A.J. Variation in commercial sources of soybean meal influences the severity of enteritis in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquac. Nutr. 2009, 15, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokou, F.; Sarropoulou, E.; Cotou, E.; Rigos, G.; Henry, M.; Alexis, M.; Kentouri, M. Effects of fish meal replacement by a soybean protein on growth, histology, selected immune and oxidative status markers of gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2015, 46, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.G.; Oliva-Teles, A. Evaluation of corn gluten meal as a protein source in diets for gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) juveniles. Aquac. Res. 2003, 34, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Llorens, S.; Baeza-Ariño, R.; Nogales-Mérida, S.; Jover-Cerdá, M.; Tomás-Vidal, A. Carob seed germ meal as a partial substitute in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) diets: Amino acid retention, digestibility, gut and liver histology. Aquaculture 2012, 338–341, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitjá-Bobadilla, A.; Peña-Llopis, S.; Gómez-Requeni, P.; Médale, F.; Kaushik, S.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Effect of fish meal replacement by plant protein sources on non-specific defence mechanisms and oxidative stress in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 2005, 249, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estensoro, I.; Ballester-Lozano, G.; Benedito-Palos, L.; Grammes, F.; Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; Mydland, L.T.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Fuentes, J.; Karalazos, V.; Ortiz, Á.; et al. Dietary butyrate helps to restore the intestinal status of a marine teleost (Sparus aurata) fed extreme diets low in fish meal and fish oil. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokou, F.; Sarropoulou, E.; Cotou, E.; Kentouri, M.; Alexis, M.; Rigos, G. Effects of graded dietary levels of soy protein concentrate supplemented with methionine and phosphate on the immune and antioxidant responses of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 64, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couso, N.; Castro, R.; Margariños, B.; Obach, A.; Lamas, J. Effect of oral administration of glucans on the resistance of gilthead seabream to pasteurellosis. Aquaculture 2003, 219, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, I.; Romero, A.; Acerete, L.; MacKenzie, S.; Roher, N.; Callol, A.; Cano, I.; Alvarez, M.C.; Tort, L. Changes in complement responses in Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) and European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) under crowding stress, plus viral and bacterial challenges. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-becerril, M.; López-medina, T.; Ascencio-valle, F.; Ángeles, M. Fish & Shellfish Immunology Immune response of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) following experimental infection with Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzon, M.C.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Pereiro, P.; Estensoro, I.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Gómez-Casado, E.; Novoa, B.; Mulero, V.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Differential Modulation of igT and igM upon Parasitic, Bacterial, Viral, and Dietary Challenges in a Perciform Fish. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge-Ortiz, R.; Tomás-Vidal, A.; Gallardo-Álvarez, F.J.; Estruch, G.; Godoy-Olmos, S.; Jover-Cerdá, M.; Martínez-Llorens, S. Partial and total replacement of fishmeal by a blend of animal and plant proteins in diets for Seriola dumerili: Effects on performance and nutrient efficiency. Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecillas, S.; Caballero, M.J.; Mompel, D.; Montero, D.; Zamorano, M.J.; Robaina, L.; Rivero-ramírez, F.; Karalazos, V.; Kaushik, S.; Izquierdo, M. Disease resistance and response against Vibrio anguillarum intestinal infection in European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fed low fish meal and fish oil diets. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruch, G.; Collado, M.C.; Peñaranda, D.S.; Tomás Vidal, A.; Jover Cerdá, M.; Pérez Martínez, G.; Martinez-Llorens, S. Impact of fishmeal replacement in diets for gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) on the gastrointestinal microbiota determined by pyrosequencing the 16S rRNA gene. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruch, G.; Martínez-Llorens, S.; Tomás-Vidal, A.; Monge-Ortiz, R.; Jover-Cerdá, M.; Brown, P.B.; Peñaranda, D.S. Impact of high dietary plant protein with or without marine ingredients in gut mucosa proteome of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata, L.). J. Proteom. 2020, 216, 103672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruch, G.; Collado, M.C.; Monge-Ortiz, R.; Tomás-Vidal, A.; Jover-Cerdá, M.; Peñaranda, D.S.; Pérez Martínez, G.; Martínez-Llorens, S. Long-term feeding with high plant protein based diets in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata, L.) leads to changes in the inflammatory and immune related gene expression at intestinal level. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristiansen, M.; Merrifield, D.L.; Vecino, J.L.G.; Myklebust, R.; Ringø, E. Evaluation of Prebiotic and Probiotic Effects on the Intestinal Gut Microbiota and Histology of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2011, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løkka, G.; Koppang, E.O. Antigen sampling in the fish intestine. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 64, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secombes, C.J.; Wang, T.; Hong, S.; Peddie, S.; Crampe, M.; Laing, K.J. Cytokines and innate immunity of fish. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 25, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.; Sunyer, J.O.; Salinas, I. The mucosal immune system of fish: The evolution of tolerating commensals while fighting pathogens. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogdahl, A.; Bakke-McKellep, A.M.; Roed, K.H.; Baeverfjord, G. Feeding Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. soybean products: Effects on disease resistance (furunculosis), and lysozyme and IgM levels in the intestinal mucosa. Aquac. Nutr. 2000, 6, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, I.; Zhang, Y.-A.; Sunyer, J.O. Mucosal immunoglobulins and B cells of teleost fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1346–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasiotis, H.; Effendi, J.C.; Kelly, S.P. Occludin expression in goldfish held in ion-poor water. J. Comp. Physiol. B Biochem. Syst. Environ. Physiol. 2009, 179, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lozano, N.B.; Martínez-Llorens, S.; Tomás-Vidal, A.; Cerdá, M.J. Effect of high-level fish meal replacement by pea and rice concentrate protein on growth, nutrient utilization and fillet quality in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata, L.). Aquaculture 2009, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savan, R.; Sakai, M. Genomics of fish cytokines. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D 2006, 1, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrecillas, S.; Montero, D.; Caballero, M.J.; Robaina, L.; Zamorano, M.J.; Sweetman, J.; Izquierdo, M. Effects of dietary concentrated mannan oligosaccharides supplementation on growth, gut mucosal immune system and liver lipid metabolism of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 42, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, T.; Bird, S.; Sonoda, K.; Savan, R.; Secombes, C.J.; Sakai, M. Characterization and expression analysis of an interleukin-7 homologue in the Japanese pufferfish, Takifugu rubripes. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelegrín, P.; García-Castillo, J.; Mulero, V.; Meseguer, J. Interleukine-1B isolated from a marine fish reveals uo-regulated expression in macrophages following activation with lipopolysaccharide and lymphokines. Cytokine 2001, 16, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Pelegrín, P.; García-Castillo, J.; García-Ayala, A.; Mulero, V.; Meseguer, J. Acidophilic granulocytes of the marine fish gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) produce interleukin-1b following infection with Vibrio anguillarum. Cell Tissue Res. 2004, 316, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepulcre, M.P.; López-Castejón, G.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V. The activation of gilthead seabream professional phagocytes by different PAMPs underlines the behavioural diversity of the main innate immune cells of bony fish. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltaña, S.; Tridico, R.; Teles, M.; Mackenzie, S.; Tort, L. Lipopolysaccharides isolated from Aeromonas salmonicida and Vibrio anguillarum show quantitative but not qualitative differences in inflammatory outcome in Sparus aurata (Gilthead seabream). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 39, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, R.; Ciznadija, D.; Vanevski, M.; Mantamadiotis, T. Transcriptional regulation of cyclo-oxygenase expression: Three pillars of control. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2003, 16, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, R.; Seybold, J.; Liu, S.F.; Barnes, P.J. Alternate COX-2 Transcripts Are Differentially Regulated: Implications for Post-Transcriptional Control. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 234, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, C.; Röllinghoff, M.; Diefenbach, A. Reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen intermediates in innate and specific immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2000, 12, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.; Embregts, C.W.E.; Forlenza, M.; Wiegertjes, G.F. Evidence of Trained Immunity in a Fish: Conserved Features in Carp Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezuela, R.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.Á. Effects of dietary inulin, Bacillus subtilis and microalgae on intestinal gene expression in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredenburgh, L.E.; Suárez Velandia, M.M.; Ma, J.; Olszak, T.; Cernadas, M.; Englert, J.A.; Chung, S.W.; Liu, X.; Begay, C.; Padera, R.F.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 Deficiency Leads to Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction and Increased Mortality during Polymicrobial Sepsis. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 5255–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, M.; Parisi, G.; Médale, F.; Lupi, P.; Kaushik, S.J.; Poli, B.M. Effect of long-term feeding with a plant protein mixture based diet on growth and body/fillet quality traits of large rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2004, 236, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarotto, V.; Médale, F.; Larroquet, L.; Corraze, G. Long-term dietary replacement of fishmeal and fish oil in diets for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Effects on growth, whole body fatty acids and intestinal and hepatic gene expression. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Dong, X.; Yang, Q.; Chi, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Tan, B.; Zhang, S. Dietary replacement of fish meal with peanut meal in juvenile hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus ♀ × Epinephelus lanceolatus ♂): Growth performance, immune response and intestinal microbiota. Aquac. Reports 2020, 17, 100327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, I.; Martínez de Ilárduya, Ó.; Estonba, A.; Pardo, M.A. Innate immune gene expression in individual zebrafish after Listonella anguillarum inoculation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doménech, A.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.F.; Lawson, P.; García, J.A.; Cutuli, M.T.; Blanco, M.; Gibello, A.; Moreno, M.A.; Collins, M.D.; Domínguez, L. Winter disease outbreak in sea-bream (Sparus aurata) associated with Pseudomonas anguilliseptica infection. Aquaculture 1997, 156, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colorni, A.; Paperna, I.; Gordin, H. Bacterial infections in gilt-head sea bream Sparus aurata cultured at Elat. Aquaculture 1981, 23, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balebona, M.C.; Andreu, M.J.; Bordas, M.A.; Zorilla, I.; Moriñgo, M.A.; Borrego, J.J. Pathogenicity of Vibrio alginolyticus for cultured gilt-head sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 4269–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-F.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.-L.; Chen, Y.-J.; Hu, C.-J. Complete genome sequence of Vibrio alginolyticus ATCC 17749 T. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, 1500–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de la Presidencia Rd 53/2013. BOE 2013, 34, 11370–11421.
- Peres, H.; Oliva-Teles, A. The optimum dietary essential amino acid profile for gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) juveniles. Aquaculture 2009, 296, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, W.; Latimer Junior, G.W. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Analytical Chemists International; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, L.; Alegría, A.; Farré, R. Application of the 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysccinimidyl carbamate (AQC) reagent to the RP-HPLC determination of amino acids in infant foods. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 831, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, C.M.; Sibley, C.P.; Jones, C.J.P.; Turner, M.A.; Greenwood, S.L. The functional regeneration of syncytiotrophoblast in cultured explants of term placenta Downloaded from. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 280, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Tichopad, A.; Prgomet, C.; Neuvians, T.P. Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |






| IL-1β | IL-6 | COX-2 | IgM | Ocl | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diet | 0.533 | 0.601 | 0.025 * | 0.120 | 0.044 * |
| Section | 0.157 | 0.138 | 0.168 | 0.864 | 0.486 |
| Stimuli | 0.003 * | 0.036 * | 0.021 * | 0.218 | 0.163 |
| Diet | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients (g kg−1) | FM | PP |
| Fish meal | 589 | |
| Wheat meal | 260 | |
| Wheat gluten | 295 | |
| Broad bean meal | 41 | |
| Soybean meal | 182 | |
| Pea meal | 41 | |
| Sunflower meal | 158 | |
| Krill meal | ||
| Squid meal | ||
| Fish oil | 38.1 | 90 |
| Soybean oil | 92.9 | 90 |
| Soy Lecithin | 10 | 10 |
| Vitamin-mineral mix 1 | 10 | 10 |
| Calcium phosphate | 38 | |
| Arginine | 5 | |
| Lysine | 10 | |
| Methionine | 7 | |
| Taurine | 20 | |
| Threonine | 3 | |
| Proximate composition (% dry weight) | ||
| Dry matter | 88.1 | 93.9 |
| Ashes | 10.1 | 7.4 |
| Crude lipid | 18.5 | 19.8 |
| Crude fiber | 0.8 | 4.3 |
| Crude protein | 44.2 | 45.0 |
| Essential amino acids (g 100 g-1) | ||
| Arginine | 3.39 | 3.30 |
| Histidine | 1.00 | 0.82 |
| Isoleucine | 1.47 | 1.17 |
| Leucine | 3.24 | 2.98 |
| Lysine | 3.68 | 2.26 |
| Methionine | 1.16 | 1.06 |
| Phenylalanine | 1.80 | 1.87 |
| Threonine | 1.98 | 1.44 |
| Valine | 2.01 | 1.47 |
| Gene 1 | GeneBank ID | Primer Forward (5′→3′) | Primer Reverse (5′→3′) | Length (pb) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REFERENCE GENES | |||||
| EF-1α | AF184170 | CTGTCAAGGAAATCCGTCGT | TGACCTGAGCGTTGAAGTTG | 87 | [35,36] |
| GAPDH | DQ641630 | CCAACGTGTCAGTGGTTGAC | AGCCTTGACGACCTTCTTGA | 80 | [37] |
| Rps18 | AM490061 | AGGGTGTTGGCAGACGTTAC | CGCTCAACCTCCTCATCAGT | 97 | [37] |
| β-Act | X89920 | TCTGTCTGGATCGGAGGCTC | AAGCATTTGCGGTGGACG | 113 | [38] |
| TARGET GENES | |||||
| IL-1β | AJ277166 | GCGACCTACCTGCCACCTACACC | TCGTCCACCGCCTCCAGATGC | 131 | [37] |
| IL-6 | AM749958 | AGGCAGGAGTTTGAAGCTGA | ATGCTGAAGTTGGTGGAAGG | 101 | [35] |
| COX-2 | AM296029 | GAGTACTGGAAGCCGAGCAC | GATATCACTGCCGCCTGAGT | 192 | [55] |
| IgM | JQ811851 | TCAGCGTCCTTCAGTGTTTATGATGCC | CAGCGTCGTCGTCAACAAGCCAAGC | 131 | [39] |
| Ocl | JK692876 | GTGCGCTCAGTACCAGCAG | TGAGGCTCCACCACACAGTA | 81 | [35,36] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peñaranda, D.S.; Bäuerl, C.; Tomás-Vidal, A.; Jover-Cerdá, M.; Estruch, G.; Pérez Martínez, G.; Martínez Llorens, S. Intestinal Explant Cultures from Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata, L.) Allowed the Determination of Mucosal Sensitivity to Bacterial Pathogens and the Impact of a Plant Protein Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207584
Peñaranda DS, Bäuerl C, Tomás-Vidal A, Jover-Cerdá M, Estruch G, Pérez Martínez G, Martínez Llorens S. Intestinal Explant Cultures from Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata, L.) Allowed the Determination of Mucosal Sensitivity to Bacterial Pathogens and the Impact of a Plant Protein Diet. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(20):7584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207584
Chicago/Turabian StylePeñaranda, David Sánchez, Christine Bäuerl, Ana Tomás-Vidal, Miguel Jover-Cerdá, Guillem Estruch, Gaspar Pérez Martínez, and Silvia Martínez Llorens. 2020. "Intestinal Explant Cultures from Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata, L.) Allowed the Determination of Mucosal Sensitivity to Bacterial Pathogens and the Impact of a Plant Protein Diet" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 20: 7584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207584
APA StylePeñaranda, D. S., Bäuerl, C., Tomás-Vidal, A., Jover-Cerdá, M., Estruch, G., Pérez Martínez, G., & Martínez Llorens, S. (2020). Intestinal Explant Cultures from Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata, L.) Allowed the Determination of Mucosal Sensitivity to Bacterial Pathogens and the Impact of a Plant Protein Diet. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(20), 7584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207584








