Insights on the Functional Interaction between Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (mGluRI) and ErbB Receptors
Abstract
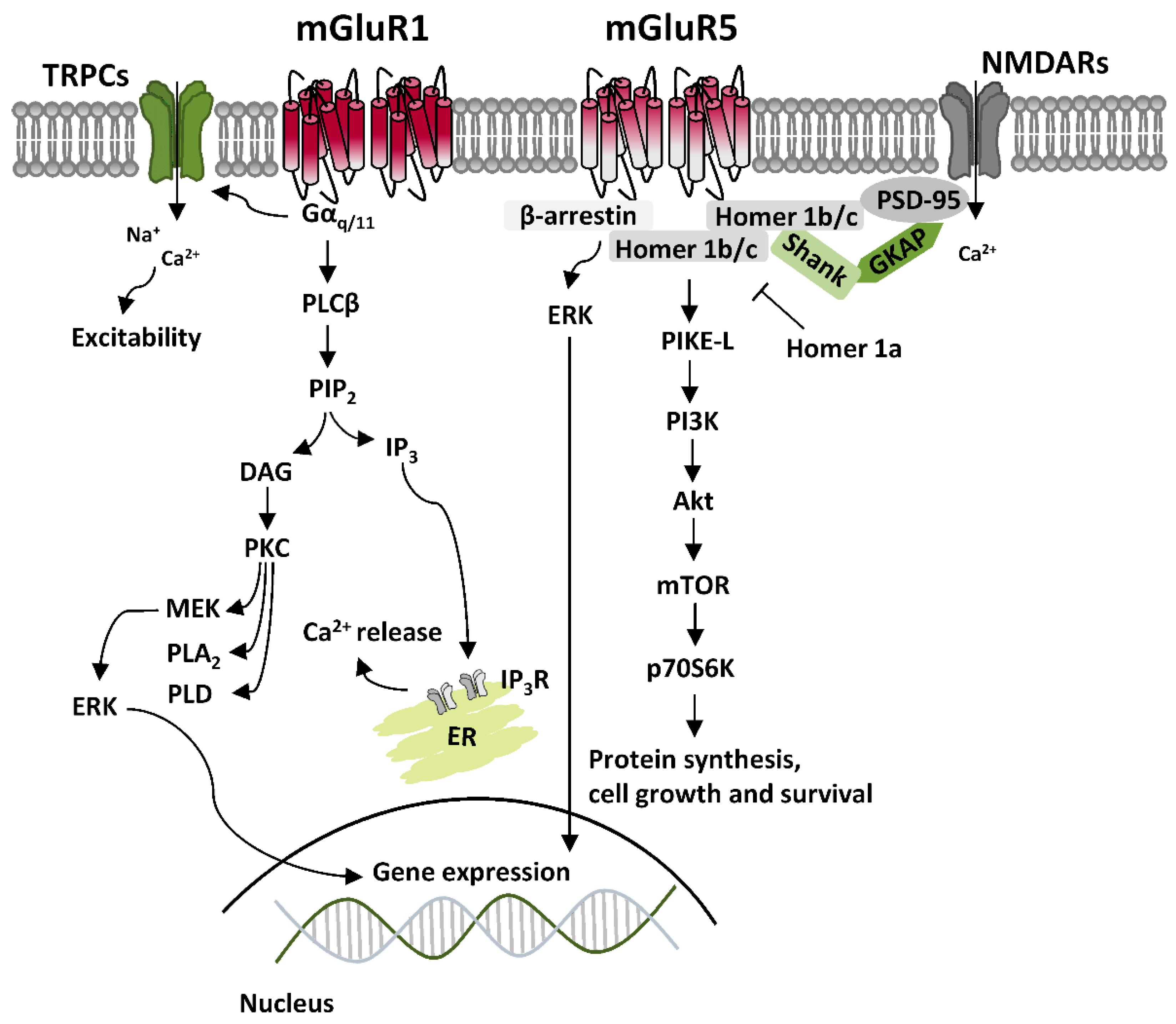
:1. Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (mGluRI)
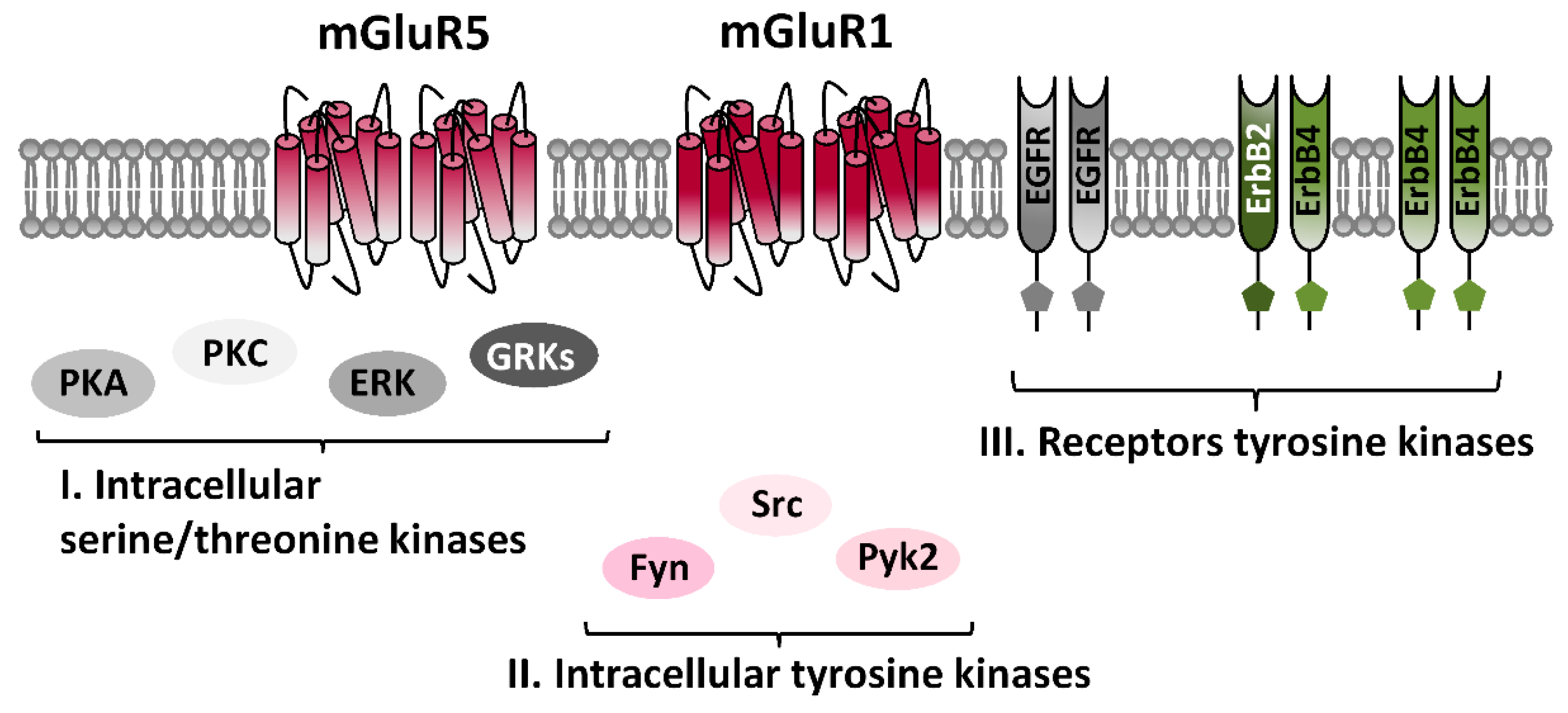
Protein Kinases-Dependent Regulation of mGluRI: Focus on Tyrosine Kinases
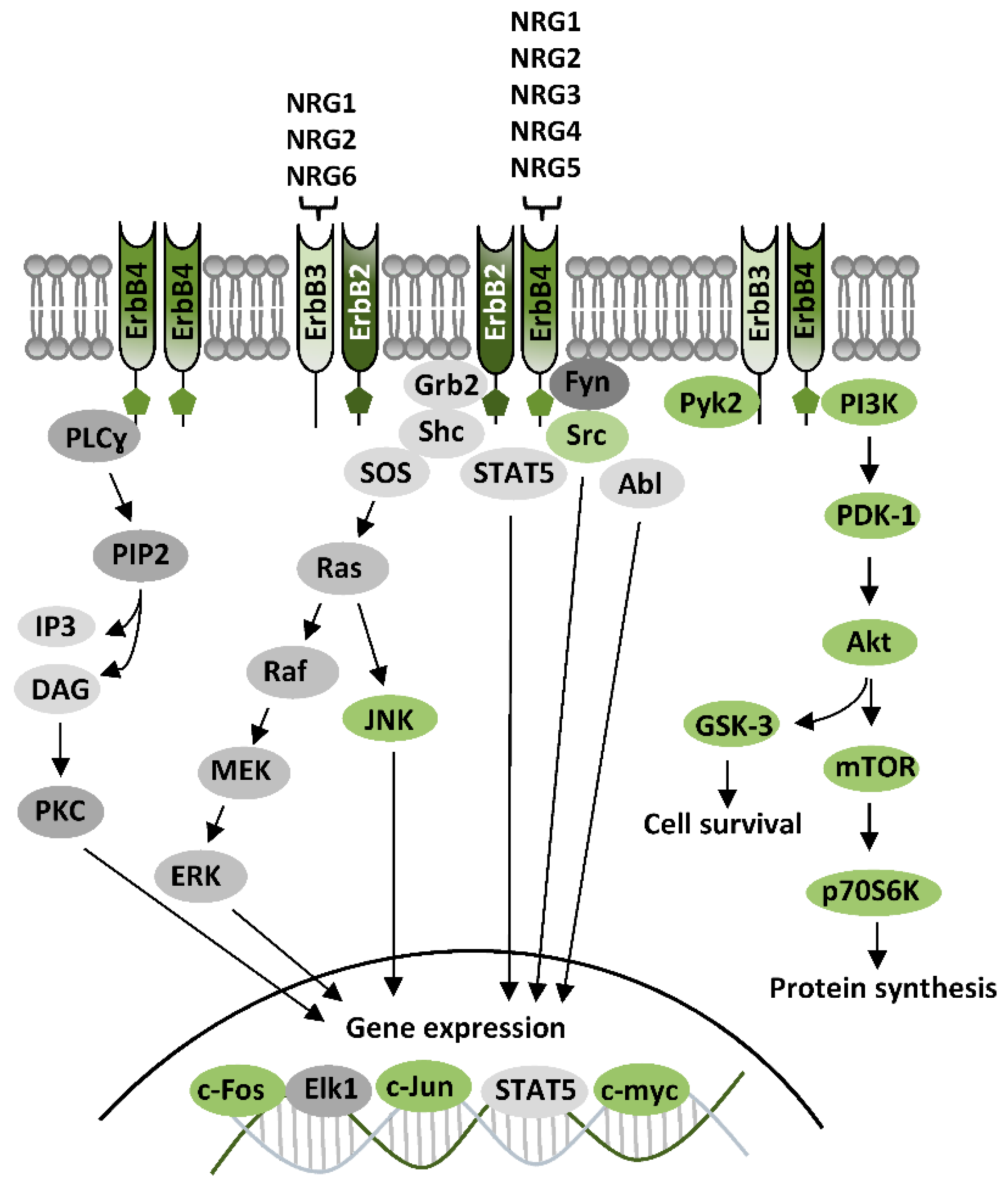
2. ErbB Receptors and Their Ligands
ErbB Signaling
3. ErbB-Dependent Regulation of mGluRI
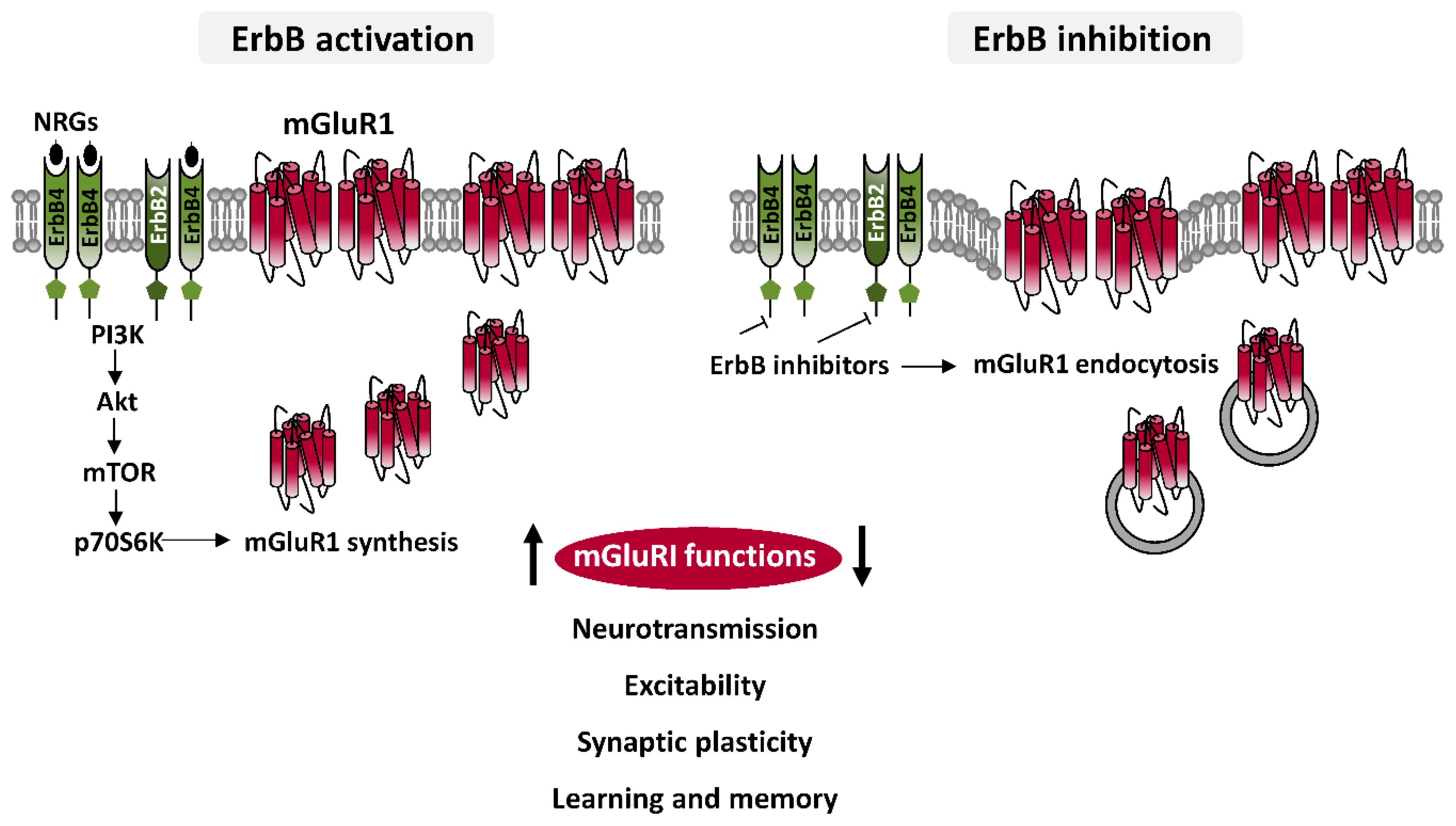
3.1. ErbB-Dependent Modulation of mGluRI: Mechanisms
3.2. ErbB-Dependent Regulation of mGluRI: Functional Implications
3.2.1. ErbB-mGluRI Interaction in Neuronal Depolarization and Excitability
3.2.2. ErbB-mGluRI Interaction in Glutamatergic Synaptic Plasticity
3.2.3. ErbB-mGluRI Interaction in Learning and Memory Processes
3.2.4. ErbB-mGluRI Interaction in the In Vivo Modulation of DA Release
3.3. ErbB-Dependent Regulation of mGluRI: Pathological Implications and Therapeutical Potential?
4. Conclusions and Open Issues
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hermans, E.; Challiss, R. Structural, signalling and regulatory properties of the group I metabotropic glutamate receptors: Prototypic family C G-protein-coupled receptors. Biochem. J. 2001, 359, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraguti, F.; Crepaldi, L.; Nicoletti, F. Metabotropic Glutamate 1 Receptor: Current Concepts and Perspectives. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 536–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, F.; Bockaert, J.; Collingridge, G.; Conn, P.; Ferraguti, F.; Schoepp, D.; Wroblewski, J.; Pin, J. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: From the workbench to the bedside. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 1017–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niswender, C.M.; Conn, P.J. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors: Physiology, Pharmacology, and Disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 295–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choe, E.S.; Wang, J.Q. Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor activation increases phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein, Elk-1, and extracellular signal-regulated kinases in rat dorsal striatum. Mol. Brain Res. 2001, 94, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, A.C.; Pshenichkin, S.; Takoudjou, G.R.; Grajkowska, E.; Wolfe, B.B.; Wroblewski, J.T. The Protective Signaling of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1 Is Mediated by Sustained, β-Arrestin-1-dependent ERK Phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 26041–26048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenti, O.; Conn, P.J.; Marino, M.J. Distinct physiological roles of the Gq-coupled metabotropic glutamate receptors co-expressed in the same neuronal populations. Rev. J. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 191, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisik, O.V.; Mannaioni, G.; Traynelis, S.; Smith, Y.; Conn, P.J. Distinct Functional Roles of the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors 1 and 5 in the Rat Globus Pallidus. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kramer, P.F.; Williams, J.T. Cocaine Decreases Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor mGluR1 Currents in Dopamine Neurons by Activating mGluR5. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagni, L.; Ango, F.; Perroy, J.; Bockaert, J. Identification and functional roles of metabotropic glutamate receptor-interacting proteins. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 15, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagni, L. Diversity of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor–Interacting Proteins and Pathophysiological Functions. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 970, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eenz, R. Metabotropic glutamate receptors and interacting proteins: Evolving drug targets. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronesi, J.A.; Huber, K.M. Homer Interactions Are Necessary for Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor-Induced Long-Term Depression and Translational Activation. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakeman, P.R.; Lanahan, A.A.; O’Brien, R.; Roche, K.; Barnes, C.A.; Huganir, R.L.; Worley, P.F. Homer: A protein that selectively binds metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nat. Cell Biol. 1997, 386, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, R.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Huang, H.; Nagata, E.; Kalman, D.; Kapp, J.A.; Tu, J.; Worley, P.F.; Snyder, S.H.; Ye, K. PI3 kinase enhancer–Homer complex couples mGluRI to PI3 kinase, preventing neuronal apoptosis. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Tu, J.C.; Petralia, R.S.; Yuan, J.P.; Doan, A.; Breder, C.D.; Ruggiero, A.; Lanahan, A.A.; Wenthold, R.J.; Worley, P.F. Homer Regulates the Association of Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors with Multivalent Complexes of Homer-Related, Synaptic Proteins. Neuron 1998, 21, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, J.C.; Xiao, B.; Yuan, J.P.; Lanahan, A.A.; Leoffert, K.; Li, M.; Linden, D.J.; Worley, P.F. Homer Binds a Novel Proline-Rich Motif and Links Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors with IP3 Receptors. Neuron 1998, 21, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, J.C.; Xiao, B.; Naisbitt, S.; Yuan, J.P.; Petralia, R.S.; Brakeman, P.; Doan, A.; Aakalu, V.K.; Lanahan, A.A.; Sheng, M.; et al. Coupling of mGluR/Homer and PSD-95 Complexes by the Shank Family of Postsynaptic Density Proteins. Neuron 1999, 23, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dale, L.B.; Bhattacharya, M.; Anborgh, P.H.; Murdoch, B.; Bhatia, M.; Nakanishi, S.; Ferguson, S.S.G. G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase-mediated Desensitization of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1A Protects against Cell Death. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 38213–38220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sallese, M.; Mariggiò, S.; D’Urbano, E.; Iacovelli, L.; De Blasi, A. Selective regulation of Gq signaling by G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2: Direct interaction of kinase N terminus with activated galphaq. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iacovelli, L.; Salvatore, L.; Capobianco, L.; Picascia, A.; Barletta, E.; Storto, M.; Mariggiò, S.; Sallese, M.; Porcellini, A.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Role of G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase 4 and β-Arrestin 1 in Agonist-stimulated Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1 Internalization and Activation of Mitogen-activated Protein Kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12433–12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sorensen, S.D.; Conn, P.J. G protein-coupled receptor kinases regulate metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 function and expression. Neuropharmacology 2003, 44, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saugstad, J.A.; Marino, M.J.; Folk, J.A.; Hepler, J.R.; Conn, P.J. RGS4 Inhibits Signaling by Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciruela, F.; Escriche, M.; Burgueño, J.; Angulo-Pueyo, E.; Casadó, V.; Soloviev, M.M.; Franco, R.; Mallol, J.; Chan, W.-Y.; Lluis, C.; et al. Metabotropic Glutamate 1α and Adenosine A1 Receptors Assemble into Functionally Interacting Complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18345–18351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabata, T.; Kano, M. Calcium Dependence of Native Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Signaling in Central Neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 2004, 29, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prézeau, L.; Rives, M.-L.; Comps-Agrar, L.; Maurel, D.; Kniazeff, J.; Pin, J.-P. Functional crosstalk between GPCRs: With or without oligomerization. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Carlsson, J.; Ambrogini, P.; Narváez, M.; Wydra, K.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Li, X.; Millon, C.; Ferraro, L.; Cuppini, R.; et al. Understanding the Role of GPCR Heteroreceptor Complexes in Modulating the Brain Networks in Health and Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, T.K.Y.; Zhai, D.; Su, P.; Jiang, A.; Boychuk, J.; Liu, F. The receptor-receptor interaction between mGluR1 receptor and NMDA receptor: A potential therapeutic target for protection against ischemic stroke. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 14423–14439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Roche, K.W. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: Phosphorylation and receptor signaling. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 86, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.-M.; Liu, X.-Y.; Zhang, G.-C.; Chu, X.-P.; Fibuch, E.E.; Wang, L.S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.Q. Phosphorylation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1/5) in vitro and in vivo. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, L.-M.; Guo, M.; Jin, D.-Z.; Fibuch, E.E.; Choe, E.S.; Wang, J.Q. Post-Translational Modification Biology of Glutamate Receptors and Drug Addiction. Front. Neuroanat. 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mao, L.-M.; Wang, Q. Phosphorylation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in drug addiction and translational research. J. Neurol. Transl. Neurosci. (Beijing) 2016, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Poisik, O.V.; Smith, Y.; Conn, P.J. D1- and D2-like dopamine receptors regulate signaling properties of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in the rat globus pallidus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, K.; Heiman, M.; Zelenina, M.; Padovan, J.; Chait, B.T.; Aperia, A.; Nishi, A.; Greengard, P. Protein kinase A directly phosphorylates metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 to modulate its function. J. Neurochem. 2015, 132, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gereau, R.W.; Heinemann, S.F. Role of protein kinase C phosphorylation in rapid desensitization of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5. Neuron 1998, 20, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francesconi, A.; Duvoisin, R.M. Opposing effects of protein kinase C and protein kinase A on metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling: Selective desensitization of the inositol trisphosphate/Ca2+ pathway by phosphorylation of the receptor-G protein-coupling domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6185–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eumemori, H. Activation of the G Protein Gq/11 Through Tyrosine Phosphorylation of the Subunit. Science 1997, 276, 1878–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, L.; Dunah, A.; Standaert, D.G.; Young, A. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 in striatal neurons. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.-M.; Wang, J.Q. Tyrosine phosphorylation of glutamate receptors by non-receptor tyrosine kinases: Roles in depression-like behavior. Neurotransmitter 2016, 3, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, D.R.; Wu, Y.-M.; Lin, S.-F. The protein tyrosine kinase family of the human genome. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5548–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heuss, C.; Scanziani, M.; Gähwiler, B.H.; Gerber, U. G-protein-independent signaling mediated by metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozzi, A.; Guatteo, E.; Caputi, L.; Bernardi, G.; Mercuri, N.B. Group I mGluRs coupled to G proteins are regulated by tyrosine kinase in dopamine neurons of the rat midbrain. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 85, 2490–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, H.; Nagao, S.; Obata, K.; Hirono, M. mGluR1-Mediated Excitation of Cerebellar GABAergic Interneurons Requires Both G Protein-Dependent and Src–ERK1/2-Dependent Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Bianchi, R.; Wang, M.; Wong, R.K.S. Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 Is Required for the Induction of Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor-Mediated Epileptiform Discharges. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canepari, M.; Ogden, D. Evidence for Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase, Tyrosine Kinase, and G-Protein Regulation of the Parallel Fiber Metabotropic Slow EPSC of Rat Cerebellar Purkinje Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 4066–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peavy, R.D.; Chang, M.S.S.; Sanders-Bush, E.; Conn, P.J. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5-Induced Phosphorylation of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase in Astrocytes Depends on Transactivation of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 9619–9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.-Z.; Mao, L.-M.; Wang, J.Q. An Essential Role of Fyn in the Modulation of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1 in Neurons. Eneuro 2017, 4, 0096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicodemo, A.A.; Pampillo, M.; Ferreira, L.T.; Dale, L.B.; Cregan, T.; Ribeiro, F.M.; Ferguson, S.S.G. Pyk2 uncouples metabotropic glutamate receptor G protein signaling but facilitates ERK1/2 activation. Mol. Brain 2010, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sitcheran, R.; Comb, W.C.; Cogswell, P.C.; Baldwin, A.S. Essential Role for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Glutamate Receptor Signaling to NF-κB. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 5061–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foley, C.M.; Moffitt, J.A.; Hay, M.; Hasser, E.M. Glutamate in the nucleus of the solitary tract activates both ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1998, 275, R1858–R1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledonne, A.; Nobili, A.; Latagliata, E.C.; Cavallucci, V.; Guatteo, E.; Puglisi-Allegra, S.; D’Amelio, M.; Mercuri, N.B. Neuregulin 1 signalling modulates mGluR1 function in mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ledonne, A.; Mercuri, N.B. mGluR1-Dependent Long Term Depression in Rodent Midbrain Dopamine Neurons Is Regulated by Neuregulin 1/ErbB Signaling. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledonne, A.; Mango, D.; Latagliata, E.C.; Chiacchierini, G.; Nobili, A.; Nisticò, R.; D’Amelio, M.; Puglisi-Allegra, S.; Mercuri, N.B. Neuregulin 1/ErbB signalling modulates hippocampal mGluRI-dependent LTD and object recognition memory. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 130, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledonne, A.; Mercuri, N.B. On the Modulatory Roles of Neuregulins/ErbB Signaling on Synaptic Plasticity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yarden, Y.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Xiong, W.-C. Neuregulin 1 in neural development, synaptic plasticity and schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, Y.; Nawa, H. ErbB1-4-dependent EGF/neuregulin signals and their cross talk in the central nervous system: Pathological implications in schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graus-Porta, D.; Beerli, R.R.; Daly, J.M.; Hynes, N.E. ErbB-2, the preferred heterodimerization partner of all ErbB receptors, is a mediator of lateral signaling. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwkowski, M.X.; Schaefer, G.; Akita, R.W.; Lofgren, A.J.; Fitzpatrick, V.D.; Nuijens, A.; Fendly, B.M.; Cerione, R.A.; Vandlen, R.L.; Carraway, K.L. Coexpression of erbB2 and erbB3 proteins reconstitutes a high affinity receptor for heregulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 14661–14665. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.-M.; Kuo, A.; Alimandi, M.; Veri, M.C.; Lee, C.-C.; Kapoor, V.; Ellmore, N.; Chen, X.-H.; Pierce, J.H. ErbB2 expression increases the spectrum and potency of ligand-mediated signal transduction through ErbB4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6809–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mei, L.; Nave, K.-A. Neuregulin-ERBB Signaling in the Nervous System and Neuropsychiatric Diseases. Neuron 2014, 83, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia, R.A.G.; Vasudevan, K.; Buonanno, A. The neuregulin receptor ErbB-4 interacts with PDZ-containing proteins at neuronal synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3596–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Z.; Won, S.; Ali, D.W.; Wang, Q.; Tanowitz, M.; Du, Q.S.; Pelkey, K.A.; Yang, D.J.; Xiong, W.C.; Salter, M.W.; et al. Regulation of Neuregulin Signaling by PSD-95 Interacting with ErbB4 at CNS Synapses. Neuron 2000, 26, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.Z.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, W.C.; Mei, L. Erbin Is a Protein Concentrated at Postsynaptic Membranes That Interacts with PSD-95. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 19318–19326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.; Sheng, M. PDZ domain proteins of synapses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guatteo, E.; Mercuri, N.B.; Bernardi, G.; Knöpfel, T. Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors mediate an inward current in rat substantia nigra dopamine neurons that is independent from calcium mobilization. J. Neurophysiol. 1999, 82, 1974–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, C.E.; Benquet, P.; Gerber, U. Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors activate a calcium-sensitive transient receptor potential-like conductance in rat hippocampus. J. Physiol. 2003, 546, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpak, S.; Gähwiler, B.H.; Do, K.; Knöpfel, T. Potassium conductances in hippocampal neurons blocked by excitatory amino-acid transmitters. Nat. Cell Biol. 1990, 347, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, C.D.; Williams, J.T. Glutamate mediates an inhibitory postsynaptic potential in dopamine neurons. Nat. Cell Biol. 1998, 394, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.H.; Clarke, V.R.; Jane, D.E.; Collingridge, G.L. Pharmacology of postsynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptors in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurones. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 116, 1859–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prisco, S.; Natoli, S.; Bernardi, G.; Mercuri, N.B. Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors activate burst firing in rat midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Neuropharmacology 2002, 42, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lüscher, C.; Huber, K.M. Group 1 mGluR-Dependent Synaptic Long-Term Depression: Mechanisms and Implications for Circuitry and Disease. Neuron 2010, 65, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collingridge, G.L.; Peineau, S.; Howland, J.G.; Wang, Y.T. Long-term depression in the CNS. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, K.M.; Gallagher, S.M.; Warren, S.T.; Bear, M.F. Altered synaptic plasticity in a mouse model of fragile X mental retardation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7746–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Hong, S.; Shepardson, N.E.; Walsh, D.M.; Shankar, G.M.; Selkoe, D. Soluble Oligomers of Amyloid β Protein Facilitate Hippocampal Long-Term Depression by Disrupting Neuronal Glutamate Uptake. Neuron 2009, 62, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chévere-Torres, I.; Kaphzan, H.; Bhattacharya, A.; Kang, A.; Maki, J.M.; Gambello, M.J.; Arbiser, J.L.; Santini, E.; Klann, E. Metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression is impaired due to elevated ERK signaling in the ΔRG mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menard, C.; Quirion, R. Successful Cognitive Aging in Rats: A Role for mGluR5 Glutamate Receptors, Homer 1 Proteins and Downstream Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e28666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pignatelli, M.; Piccinin, S.; Molinaro, G.; Di Menna, L.; Riozzi, B.; Cannella, M.; Motolese, M.; Vetere, G.; Catania, M.V.; Battaglia, G.; et al. Changes in mGlu5 Receptor-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity and Coupling to Homer Proteins in the Hippocampus of Ube3A Hemizygous Mice Modeling Angelman Syndrome. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 4558–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, D.; Stoppel, L.J.; Heynen, A.J.; Lindemann, L.; Jaeschke, G.; Mills, A.A.; Bear, M.F. Contribution of mGluR5 to pathophysiology in a mouse model of human chromosome 16p11.2 microdeletion. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Speed, H.E.; Kouser, M.; Xuan, Z.; Reimers, J.M.; Ochoa, C.F.; Gupta, N.; Liu, S.; Powell, C.M. Autism-Associated Insertion Mutation (InsG) of Shank3 Exon 21 Causes Impaired Synaptic Transmission and Behavioral Deficits. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 9648–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhardwaj, S.K.; Ryan, R.T.; Wong, T.P.; Srivastava, L.K. Loss of dysbindin-1, a risk gene for schizophrenia, leads to impaired group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptor function in mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D.; Braunewell, K.-H. Novelty acquisition is associated with induction of hippocampal long-term depression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8739–8744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Popkirov, S.G.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Involvement of the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor mGluR5 in NMDA Receptor-Dependent, Learning-Facilitated Long-Term Depression in CA1 Synapses. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goh, J.J.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Endogenous hippocampal LTD that is enabled by spatial object recognition requires activation of NMDA receptors and the metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGlu5. Hippocampus 2012, 23, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Gong, B.; Li, H.; Bai, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; He, W.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.T. Mechanisms of Hippocampal Long-Term Depression Are Required for Memory Enhancement by Novelty Exploration. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 11980–11990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Prisco, G.V.; Huang, W.; Buffington, S.A.; Hsu, C.-C.; E Bonnen, P.; Placzek, A.N.; Sidrauski, C.; Krnjević, K.; Kaufman, R.J.; Walter, P.; et al. Translational control of mGluR-dependent long-term depression and object-place learning by eIF2α. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonsson, S.; Petursson, H.; Sigurdsson, E.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Bjornsdottir, S.; Sigmundsson, T.; Ghosh, S.; Brynjolfsson, J.; Gunnarsdottir, S.; Ivarsson, O.; et al. Neuregulin 1 and Susceptibility to Schizophrenia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 71, 877–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.Z.; Si, T.M.; Ruan, Y.; Ling, Y.S.; Han, Y.H.; Wang, X.L.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, H.Y.; Kong, Q.M.; Liu, C.; et al. Association study of neuregulin 1 gene with schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2003, 8, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinto, D.; Pagnamenta, A.T.; Klei, L.; Anney, R.; Merico, D.; Regan, R.; Conroy, J.; Magalhaes, T.R.; Correia, C.; Abrahams, B.S.; et al. Functional impact of global rare copy number variation in autism spectrum disorders. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 466, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhury, A.R.; Gerecke, K.M.; Wyss, J.M.; Morgan, D.G.; Gordon, M.N.; Carroll, S.L. Neuregulin-1 and erbB4 immunoreactivity is associated with neuritic plaques in Alzheimer disease brain and in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 62, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Go, R.C.; Perry, R.T.; Wiener, H.; Bassett, S.S.; Blacker, D.; Devlin, B.; Sweet, R.A. Neuregulin-1 polymorphism in late onset Alzheimer’s disease families with psychoses. Am. J. Med Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2005, 139, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, R.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Yu, H.-N.; Song, D.-Y.; Baik, T.-K. Expression of ErbB4 in the apoptotic neurons of Alzheimer’s disease brain. Anat. Cell Biol. 2010, 43, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.-S.; Xu, N.; Wang, L.; Aragon, L.; Ciubuc, R.; Arana, T.; Mao, C.; Petty, L.; Briones, D.; Bin Su, B.; et al. NRG3 gene is associated with the risk and age at onset of Alzheimer disease. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2014, 121, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depboylu, C.; Höllerhage, M.; Schnurrbusch, S.; Brundin, P.; Oertel, W.H.; Schrattenholz, A.; Höglinger, G.U. Neuregulin-1 receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB4 is upregulated in midbrain dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 531, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, I.; Bernstein, H.; Lendeckel, U.; Bukowska, A.; Dobrowolny, H.; Keilhoff, G.; Kanakis, D.; Mawrin, C.; Bielau, H.; Falkai, P.; et al. Immunohistochemical Evidence for Impaired Neuregulin-1 Signaling in the Prefrontal Cortex in Schizophrenia and in Unipolar Depression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1096, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, I.; LaBonte, B.; Yogendran, S.; Isingrini, E.; Perret, L.; Davoli, M.A.; Rachalski, A.; Giros, B.; Turecki, G.; Mechawar, N. Disrupted hippocampal neuregulin-1/ErbB3 signaling and dentate gyrus granule cell alterations in suicide. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikawa, D.; Makinodan, M.; Iwata, K.; Ohgidani, M.; Kato, T.A.; Yamashita, Y.; Yamamuro, K.; Kimoto, S.; Toritsuka, M.; Yamauchi, T.; et al. Microglia-derived neuregulin expression in psychiatric disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 61, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasy, S.; Shahraki, F.; Haghighatfard, A.; Qazvini, M.G.; Rafiei, S.T.; Noshadirad, E.; Farhadi, M.; Asl, H.R.; Shiryazdi, A.A.; Ghamari, R.; et al. Neuregulin1 types mRNA level changes in autism spectrum disorder, and is associated with deficit in executive functions. EBioMedicine 2018, 37, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esnafoglu, E. Levels of peripheral Neuregulin 1 are increased in non-medicated autism spectrum disorder patients. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 57, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.L.; Loukola, A.; Kaprio, J.; Turner, J.R. Role of the Neuregulin Signaling Pathway in Nicotine Dependence and Co-morbid Disorders. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2015, 124, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boxall, A.R.; Lancaster, B. Tyrosine kinases and synaptic transmission. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, U. G-protein-coupled receptors, tyrosine kinases and neurotransmission. Neuropharmacology 2002, 42, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, A.L.; Carew, T.J. Tyrosine kinases, synaptic plasticity and memory: Insights from vertebrates and invertebrates. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.-M.; Geosling, R.; Penman, B.; Wang, J.Q. Local substrates of non-receptor tyrosine kinases at synaptic sites in neurons. Acta Physiol. Sin. 2017, 69, 657–665. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ledonne, A.; Mercuri, N.B. Insights on the Functional Interaction between Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (mGluRI) and ErbB Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217913
Ledonne A, Mercuri NB. Insights on the Functional Interaction between Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (mGluRI) and ErbB Receptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):7913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217913
Chicago/Turabian StyleLedonne, Ada, and Nicola B. Mercuri. 2020. "Insights on the Functional Interaction between Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (mGluRI) and ErbB Receptors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 21: 7913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217913
APA StyleLedonne, A., & Mercuri, N. B. (2020). Insights on the Functional Interaction between Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (mGluRI) and ErbB Receptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 7913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217913




