The Gut Barrier, Intestinal Microbiota, and Liver Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Strategies to Manage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Intestinal Barrier Function and Microbiota
3. Leaky Gut, Gut Microbiota Relationship and Liver Disease
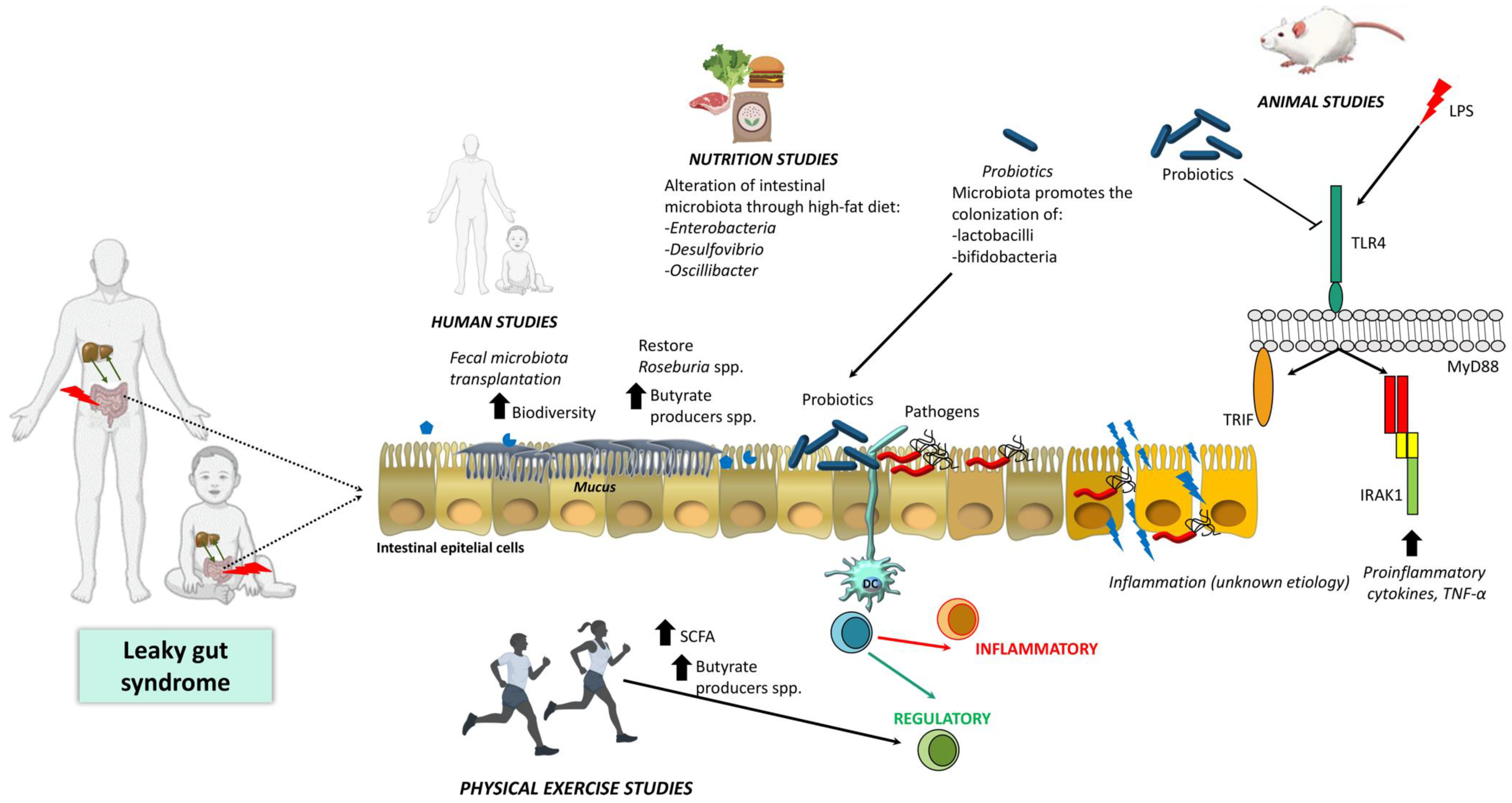
3.1. Animal Studies
3.2. Human Studies
4. Current Main Strategies to Treat Liver Disease
4.1. Drug Therapies
4.2. Diet, Liver Disease and Gut Permeability
4.3. Probiotics Administration As a Strategy for Liver Disease Treatment
4.4. Physical Exercise and Liver Disease
Exercise on Gut Barrier Permeability and Microbiome
5. Further Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tripathi, A.; Debelius, J.; Brenner, D.A.; Karin, M.; Loomba, R.; Schnabl, B.; Knight, R. The gut-liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delzenne, N.M.; Knudsen, C.; Beaumont, M.; Rodriguez, J.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B. Contribution of the gut microbiota to the regulation of host metabolism and energy balance: A focus on the gut-liver axis. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2019, 78, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiest, R.; Albillos, A.; Trauner, M.; Bajaj, J.S.; Jalan, R. Targeting the gut-liver axis in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1084–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albillos, A.; De Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szabo, G.; Bala, S.; Petrasek, J.; Gattu, A. Gut-liver axis and sensing microbes. Dig. Dis. 2010, 28, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milosevic, I.; Vujovic, A.; Barac, A.; Djelic, M.; Korac, M.; Radovanovic Spurnic, A.; Gmizic, I.; Stevanovic, O.; Djordjevic, V.; Lekic, N.; et al. Gut-Liver Axis, Gut Microbiota, and Its Modulation in the Management of Liver Diseases: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baffy, G. Potential mechanisms linking gut microbiota and portal hypertension. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poeta, M.; Pierri, L.; Vajro, P. Gut-Liver Axis Derangement in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Children 2017, 4, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harte, A.L.; Da Silva, N.F.; Creely, S.J.; McGee, K.C.; Billyard, T.; Youssef-Elabd, E.M.; Tripathi, G.; Ashour, E.; Abdalla, M.S.; Sharada, H.M.; et al. Elevated endotoxin levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Inflamm. Lond. 2010, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brun, P.; Castagliuolo, I.; Di Leo, V.; Buda, A.; Pinzani, M.; Palu, G.; Martines, D. Increased intestinal permeability in obese mice: New evidence in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G518–G525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, E.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Bucchi, A.; Krux, F.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D.; et al. Toll-like receptor-induced innate immune responses in non-parenchymal liver cells are cell type-specific. Immunology 2010, 129, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornide-Petronio, M.E.; Alvarez-Mercado, A.I.; Jimenez-Castro, M.B.; Peralta, C. Current Knowledge about the Effect of Nutritional Status, Supplemented Nutrition Diet, and Gut Microbiota on Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion and Regeneration in Liver Surgery. Nutrients 2020, 12, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Mercado, A.I.; Navarro-Oliveros, M.; Robles-Sanchez, C.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Saez-Lara, M.J.; Munoz-Quezada, S.; Fontana, L.; Abadia-Molina, F. Microbial Population Changes and Their Relationship with Human Health and Disease. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trovato, G.M.; Catalano, D.; Martines, G.F.; Pirri, C.; Trovato, F.M. Western dietary pattern and sedentary life: Independent effects of diet and physical exercise intensity on NAFLD. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1932–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meroni, M.; Longo, M.; Dongiovanni, P. Alcohol or Gut Microbiota: Who Is the Guilty? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adolph, T.E.; Grander, C.; Moschen, A.R.; Tilg, H. Liver-Microbiome Axis in Health and Disease. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.C.; Liu, Y.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Wang, C.C.; Wu, Y.J.; Yong, C.C.; Chen, K.D.; Chuah, S.K.; Yao, C.C.; Huang, P.Y.; et al. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Patients with Biopsy-Proven Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in Taiwan. Nutrients 2020, 12, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, C.; Shao, L.; Ye, J.; Shen, Y.; Ren, Y. Role of Bile Acids in Dysbiosis and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 7659509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shama, S.; Liu, W. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Gut Microbiota: A Reciprocal Interaction in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiest, R.; Lawson, M.; Geuking, M. Pathological bacterial translocation in liver cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berg, R.D.; Garlington, A.W. Translocation of certain indigenous bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract to the mesenteric lymph nodes and other organs in a gnotobiotic mouse model. Infect. Immun. 1979, 23, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malaguarnera, G.; Giordano, M.; Nunnari, G.; Bertino, G.; Malaguarnera, M. Gut microbiota in alcoholic liver disease: Pathogenetic role and therapeutic perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16639–16648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez-Brito, M.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Munoz-Quezada, S.; Gomez-Llorente, C.; Gil, A. Probiotic mechanisms of action. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopyk, D.M.; Grakoui, A. Contribution of the Intestinal Microbiome and Gut Barrier to Hepatic Disorders. Gastroenterology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farquhar, M.G.; Palade, G.E. Junctional complexes in various epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 17, 375–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Anderson, J.M. Architecture of tight junctions and principles of molecular composition. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2014, 36, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luissint, A.C.; Parkos, C.A.; Nusrat, A. Inflammation and the Intestinal Barrier: Leukocyte-Epithelial Cell Interactions, Cell Junction Remodeling, and Mucosal Repair. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 616–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornick, S.; Tawiah, A.; Chadee, K. Roles and regulation of the mucus barrier in the gut. Tissue Barriers 2015, 3, e982426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, M.E.; Ambort, D.; Pelaseyed, T.; Schutte, A.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Ermund, A.; Subramani, D.B.; Holmen-Larsson, J.M.; Thomsson, K.A.; Bergstrom, J.H.; et al. Composition and functional role of the mucus layers in the intestine. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 3635–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.; Garges, S.; Giovanni, M.; McInnes, P.; Wang, L.; Schloss, J.A.; Bonazzi, V.; McEwen, J.E.; Wetterstrand, K.A.; Deal, C. The NIH human microbiome project. Genome. Res. 2009, 19, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Trinchieri, G. Microbiota: A key orchestrator of cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Rodriguez, E.; Egea-Zorrilla, A.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Aragon-Vela, J.; Munoz-Quezada, S.; Tercedor-Sanchez, L.; Abadia-Molina, F. The Gut Microbiota and Its Implication in the Development of Atherosclerosis and Related Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; FitzGerald, M.G.; Fulton, R.S. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Faith, J.J.; Guruge, J.L.; Charbonneau, M.; Subramanian, S.; Seedorf, H.; Goodman, A.L.; Clemente, J.C.; Knight, R.; Heath, A.C.; Leibel, R.L. The long-term stability of the human gut microbiota. Science 2013, 341, 1237439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Gomez-Fernandez, A.; Chueca, N.; Torre-Aguilar, M.J.; Gil, A.; Perez-Navero, J.L.; Flores-Rojas, K.; Martin-Borreguero, P.; Solis-Urra, P.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; et al. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) with and without Mental Regression is Associated with Changes in the Fecal Microbiota. Nutrients 2019, 11, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, M.F.; Reina-Perez, I.; Astorga, J.M.; Rodriguez-Carrillo, A.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Fontana, L. Breast Cancer and Its Relationship with the Microbiota. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tenorio-Jimenez, C.; Martinez-Ramirez, M.J.; Del Castillo-Codes, I.; Arraiza-Irigoyen, C.; Tercero-Lozano, M.; Camacho, J.; Chueca, N.; Garcia, F.; Olza, J.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; et al. Lactobacillus reuteri V3401 Reduces Inflammatory Biomarkers and Modifies the Gastrointestinal Microbiome in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: The PROSIR Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mouzaki, M.; Comelli, E.M.; Arendt, B.M.; Bonengel, J.; Fung, S.K.; Fischer, S.E.; McGilvray, I.D.; Allard, J.P. Intestinal microbiota in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 58, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, A. Mechanisms of action of probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S49–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granado-Serrano, A.B.; Martín-Garí, M.; Sánchez, V.; Solans, M.R.; Berdun, R.; Ludwig, I.A.; Rubio, L.; Vilaprinyo, E.; Portero-Otín, M.; Serrano, J. Faecal bacterial and short-chain fatty acids signature in hypercholesterolemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkel, P.; Schnabl, B. Bidirectional Communication between Liver and Gut during Alcoholic Liver Disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2016, 36, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Taking Action on Childhood Obesity; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nourian, M.; Askari, G.; Golshiri, P.; Miraghajani, M.; Shokri, S.; Arab, A. Effect of lifestyle modification education based on health belief model in overweight/obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A parallel randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 38, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.C.; Lad, A.; Breidenbach, J.D.; Kleinhenz, A.L.; Modyanov, N.; Malhotra, D.; Haller, S.T.; Kennedy, D.J. Assessment of diagnostic biomarkers of liver injury in the setting of microcystin-LR (MC-LR) hepatotoxicity. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, S.E.; Hackett, D.A.; George, J.; Johnson, N.A. Exercise and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.-S.; Chan, R.S.-M.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Cheung, B.H.-K.; Chu, W.C.-W.; Yeung, D.K.-W.; Chim, A.M.-L.; Lai, J.W.-Y.; Li, L.S.; Sea, M.M.-M. Community-based lifestyle modification programme for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Tongson, J.; Kim, K.H.; Park, Y. Piceatannol attenuates fat accumulation and oxidative stress in steatosis-induced HepG2 cells. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2020, 3, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.H.; Yang, E.S.; Cho, H.R.; Lee, S.O.; Ha, K.T.; Kim, K. Herbal formulation MIT ameliorates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Integr. Med. Res. 2020, 9, 100422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, E.M.; Wong, V.W.; Nobili, V.; Day, C.P.; Sookoian, S.; Maher, J.J.; Bugianesi, E.; Sirlin, C.B.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2015, 1, 15080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedossa, P. Pathology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2017, 37 (Suppl 1), 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez, A.; Reyes, D.; Geng, Y.; Arab, J.P.; Cabrera, D.; Sepulveda, R.; Solis, N.; Buist-Homan, M.; Arrese, M.; Moshage, H. Extracellular vesicles derived from fat-laden hepatocytes undergoing chemical hypoxia promote a pro-fibrotic phenotype in hepatic stellate cells. Biochim. Biophys Acta Mol. Basis. Dis. 2020, 1866, 165857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Baker, S.S.; Shahein, A.; Choudhury, S.; Liu, W.; Bhatia, T.; Baker, R.D.; Lee, T. Upregulation of non-canonical Wnt ligands and oxidative glucose metabolism in NASH induced by methionine-choline deficient diet. Trends Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 13, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhu, L.; Baker, S.S.; Baker, R.D.; Lee, T. Secreted phosphoglucose isomerase is a novel biomarker of nonalcoholic fatty liver in mice and humans. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun 2020, 529, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Age-Standardized Death Rates of Liver Cirrhosis. Global Health Observatory. 2014. Available online: http://www/.who.int/gho/alcohol/harms_consequences/deaths_liver_cirrhosis/en/index.html (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Zhao, J.; Nishiumi, S.; Tagawa, R.; Yano, Y.; Inoue, J.; Hoshi, N.; Yoshida, M.; Kodama, Y. Adrenic acid induces oxidative stress in hepatocytes. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawitt, E.L. Autoimmune hepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czaja, A.J. Global Disparities and Their Implications in the Occurrence and Outcome of Autoimmune Hepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 2277–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngu, J.H.; Bechly, K.; Chapman, B.A.; Burt, M.J.; Barclay, M.L.; Gearry, R.B.; Stedman, C.A. Population-based epidemiology study of autoimmune hepatitis: A disease of older women? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boberg, K.M.; Aadland, E.; Jahnsen, J.; Raknerud, N.; Stiris, M.; Bell, H. Incidence and prevalence of primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and autoimmune hepatitis in a Norwegian population. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 33, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Llorente, C.; Hartmann, P.; Yang, A.M.; Chen, P.; Schnabl, B. Methods to determine intestinal permeability and bacterial translocation during liver disease. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 421, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mencin, A.; Kluwe, J.; Schwabe, R.F. Toll-like receptors as targets in chronic liver diseases. Gut 2009, 58, 704–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Gershon, M.D. The bowel and beyond: The enteric nervous system in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meijers, B.; Farré, R.; Dejongh, S.; Vicario, M.; Evenepoel, P. Intestinal barrier function in chronic kidney disease. Toxins 2018, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramezani, A.; Massy, Z.A.; Meijers, B.; Evenepoel, P.; Vanholder, R.; Raj, D.S. Role of the Gut Microbiome in Uremia: A Potential Therapeutic Target. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhiman, R.K. Gut microbiota and hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain. Dis. 2013, 28, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.C.; White, H.; Stoy, S.; Bajaj, J.S.; Shawcross, D.L. Clinical science workshop: Targeting the gut-liver-brain axis. Metab. Brain. Dis. 2016, 31, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tranah, T.H.; Vijay, G.K.; Ryan, J.M.; Shawcross, D.L. Systemic inflammation and ammonia in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain. Dis. 2013, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betrapally, N.S.; Gillevet, P.M.; Bajaj, J.S. Changes in the Intestinal Microbiome and Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Liver Diseases: Causes or Effects? Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1745–1755.e1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bull-Otterson, L.; Feng, W.; Kirpich, I.; Wang, Y.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Gobejishvili, L.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Ayvaz, T.; Petrosino, J. Metagenomic analyses of alcohol induced pathogenic alterations in the intestinal microbiome and the effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Duan, Y.; Yang, L.; Schnabl, B. Small metabolites, possible big changes: A microbiota-centered view of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2019, 68, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopis, M.; Cassard, A.M.; Wrzosek, L.; Boschat, L.; Bruneau, A.; Ferrere, G.; Puchois, V.; Martin, J.C.; Lepage, P.; Le Roy, T.; et al. Intestinal microbiota contributes to individual susceptibility to alcoholic liver disease. Gut 2016, 65, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benten, D.; Wiest, R. Gut microbiome and intestinal barrier failure-The "Achilles heel" in hepatology? J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1221–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Minicis, S.; Rychlicki, C.; Agostinelli, L.; Saccomanno, S.; Candelaresi, C.; Trozzi, L.; Mingarelli, E.; Facinelli, B.; Magi, G.; Palmieri, C. Dysbiosis contributes to fibrogenesis in the course of chronic liver injury in mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1738–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Stärkel, P.; Turner, J.R.; Ho, S.B.; Schnabl, B. Dysbiosis-induced intestinal inflammation activates tumor necrosis factor receptor I and mediates alcoholic liver disease in mice. Hepatology 2015, 61, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Teitelbaum, D.H. Tumour necrosis factor--induced loss of intestinal barrier function requires TNFR1 and TNFR2 signalling in a mouse model of total parenteral nutrition. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 3709–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, B.; Jeon, K.; Moon, S.; Lee, K.; Kim, W.K.; Jeong, H.; Cha, K.H.; Lim, M.Y.; Kang, W.; Kweon, M.N.; et al. Roseburia spp. Abundance Associates with Alcohol Consumption in Humans and Its Administration Ameliorates Alcoholic Fatty Liver in Mice. Cell Host Microb. 2020, 27, 25–40.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierantonelli, I.; Rychlicki, C.; Agostinelli, L.; Giordano, D.M.; Gaggini, M.; Fraumene, C.; Saponaro, C.; Manghina, V.; Sartini, L.; Mingarelli, E.; et al. Lack of NLRP3-inflammasome leads to gut-liver axis derangement, gut dysbiosis and a worsened phenotype in a mouse model of NAFLD. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teltschik, Z.; Wiest, R.; Beisner, J.; Nuding, S.; Hofmann, C.; Schoelmerich, J.; Bevins, C.L.; Stange, E.F.; Wehkamp, J. Intestinal bacterial translocation in rats with cirrhosis is related to compromised Paneth cell antimicrobial host defense. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.J.; Betrapally, N.S.; Ghosh, S.A.; Sartor, R.B.; Hylemon, P.B.; Gillevet, P.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Heuman, D.M.; Carl, D.; Zhou, H.; et al. Gut microbiota drive the development of neuroinflammatory response in cirrhosis in mice. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1232–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrasek, J.; Iracheta-Vellve, A.; Csak, T.; Satishchandran, A.; Kodys, K.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Szabo, G. STING-IRF3 pathway links endoplasmic reticulum stress with hepatocyte apoptosis in early alcoholic liver disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16544–16549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koop, D.R.; Klopfenstein, B.; Iimuro, Y.; Thurman, R.G. Gadolinium chloride blocks alcohol-dependent liver toxicity in rats treated chronically with intragastric alcohol despite the induction of CYP2E1. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 51, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douhara, A.; Moriya, K.; Yoshiji, H.; Noguchi, R.; Namisaki, T.; Kitade, M.; Kaji, K.; Aihara, Y.; Nishimura, N.; Takeda, K.; et al. Reduction of endotoxin attenuates liver fibrosis through suppression of hepatic stellate cell activation and remission of intestinal permeability in a rat non-alcoholic steatohepatitis model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tedesco, D.; Thapa, M.; Chin, C.Y.; Ge, Y.; Gong, M.; Li, J.; Gumber, S.; Speck, P.; Elrod, E.J.; Burd, E.M.; et al. Alterations in Intestinal Microbiota Lead to Production of Interleukin 17 by Intrahepatic gammadelta T-Cell Receptor-Positive Cells and Pathogenesis of Cholestatic Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 2178–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soderborg, T.K.; Clark, S.E.; Mulligan, C.E.; Janssen, R.C.; Babcock, L.; Ir, D.; Young, B.; Krebs, N.; Lemas, D.J.; Johnson, L.K.; et al. The gut microbiota in infants of obese mothers increases inflammation and susceptibility to NAFLD. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rainer, F.; Horvath, A.; Sandahl, T.; Leber, B.; Schmerboeck, B.; Blesl, A.; Groselj-Strele, A.; Stauber, R.; Fickert, P.; Stiegler, P. Soluble CD 163 and soluble mannose receptor predict survival and decompensation in patients with liver cirrhosis, and correlate with gut permeability and bacterial translocation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Kakiyama, G.; Zhao, D.; Takei, H.; Fagan, A.; Hylemon, P.; Zhou, H.; Pandak, W.M.; Nittono, H.; Fiehn, O. Continued alcohol misuse in human cirrhosis is associated with an impaired gut–liver axis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, C.; Parlesak, A.; Schütt, C.; Christian Bode, J.; Bode, C. Concentrations of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein, soluble CD14 and plasma lipids in relation to endotoxaemia in patients with alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Alcohol. 2002, 37, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.; Baker, S.S.; Liu, W.; Alkhouri, R.; Baker, R.D.; Xie, J.; Ji, G.; Zhu, L. Endotoxemia unrequired in the pathogenesis of pediatric nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luther, J.; Garber, J.J.; Khalili, H.; Dave, M.; Bale, S.S.; Jindal, R.; Motola, D.L.; Luther, S.; Bohr, S.; Jeoung, S.W. Hepatic injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis contributes to altered intestinal permeability. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 222–232 .e222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miele, L.; Marrone, G.; Lauritano, C.; Cefalo, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Day, C.; Grieco, A. Gut-liver axis and microbiota in NAFLD: Insight pathophysiology for novel therapeutic target. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 5314–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Baker, S.S.; Gill, C.; Liu, W.; Alkhouri, R.; Baker, R.D.; Gill, S.R. Characterization of gut microbiomes in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients: A connection between endogenous alcohol and NASH. Hepatology 2013, 57, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, A.; Patel, V.; Kurioka, A.; Jeffery, H.C.; Wright, G.; Tarff, S.; Shawcross, D.; Ryan, J.M.; Evans, A.; Azarian, S.; et al. Mucosa-associated invariant T cells link intestinal immunity with antibacterial immune defects in alcoholic liver disease. Gut 2018, 67, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B. Abnormal intestinal permeability and microbiota in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 5153. [Google Scholar]
- Maccioni, L.; Gao, B.; Leclercq, S.; Pirlot, B.; Horsmans, Y.; De Timary, P.; Leclercq, I.; Fouts, D.; Schnabl, B.; Starkel, P. Intestinal permeability, microbial translocation, changes in duodenal and fecal microbiota, and their associations with alcoholic liver disease progression in humans. Gut Microb. 2020, 12, 1782157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Shen, J.; Bo, T.; Peng, L.; Xu, H.; Nasser, M.I.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhao, M. Cutting edge: Probiotics and fecal microbiota transplantation in immunomodulation. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 16, 1603758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Craven, L.; Rahman, A.; Nair Parvathy, S.; Beaton, M.; Silverman, J.; Qumosani, K.; Hramiak, I.; Hegele, R.; Joy, T.; Meddings, J.; et al. Allogenic Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Improves Abnormal Small Intestinal Permeability: A Randomized Control Trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.S.; Shanahan, E.R.; Tran, C.D.; Bhat, P.; Fletcher, L.M.; Vesey, D.A.; Morrison, M.; Holtmann, G.; Macdonald, G.A. Dysbiosis of the Duodenal Mucosal Microbiota Is Associated With Increased Small Intestinal Permeability in Chronic Liver Disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, L.; Sun, C.; Miao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Lian, M.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.; et al. Alterations of gut microbiome in autoimmune hepatitis. Gut 2020, 69, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeser, F.; Munch, P.; Lesker, T.R.; Lutz, P.L.; Kramer, B.; Kaczmarek, D.J.; Finnemann, C.; Nischalke, H.D.; Geffers, R.; Parcina, M.; et al. Neither black nor white: Do altered intestinal microbiota reflect chronic liver disease severity? Gut 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ji, F.; Guo, J.; Shi, D.; Fang, D.; Li, L. Dysbiosis of small intestinal microbiota in liver cirrhosis and its association with etiology. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Lu, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, L. Changes of fecal Bifidobacterium species in adult patients with hepatitis B virus-induced chronic liver disease. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidrich, B.; Vital, M.; Plumeier, I.; Doscher, N.; Kahl, S.; Kirschner, J.; Ziegert, S.; Solbach, P.; Lenzen, H.; Potthoff, A.; et al. Intestinal microbiota in patients with chronic hepatitis C with and without cirrhosis compared with healthy controls. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nier, A.; Engstler, A.J.; Maier, I.B.; Bergheim, I. Markers of intestinal permeability are already altered in early stages of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Studies in children. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwimmer, J.B.; Johnson, J.S.; Angeles, J.E.; Behling, C.; Belt, P.H.; Borecki, I.; Bross, C.; Durelle, J.; Goyal, N.P.; Hamilton, G.; et al. Microbiome Signatures Associated with Steatohepatitis and Moderate to Severe Fibrosis in Children With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giorgio, V.; Miele, L.; Principessa, L.; Ferretti, F.; Villa, M.P.; Negro, V.; Grieco, A.; Alisi, A.; Nobili, V. Intestinal permeability is increased in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and correlates with liver disease severity. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colakoglu, M.; Xue, J.; Trajkovski, M. Bacteriophage Prevents Alcoholic Liver Disease. Cell 2020, 180, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Llorente, C.; Lang, S.; Brandl, K.; Chu, H.; Jiang, L.; White, R.C.; Clarke, T.H.; Nguyen, K.; Torralba, M.; et al. Bacteriophage targeting of gut bacterium attenuates alcoholic liver disease. Nature 2019, 575, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, S.; Matamoros, S.; Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Jamar, F.; Starkel, P.; Windey, K.; Tremaroli, V.; Backhed, F.; Verbeke, K.; et al. Intestinal permeability, gut-bacterial dysbiosis, and behavioral markers of alcohol-dependence severity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4485–E4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, S.; Duan, Y.; Liu, J.; Torralba, M.G.; Kuelbs, C.; Ventura-Cots, M.; Abraldes, J.G.; Bosques-Padilla, F.; Verna, E.C.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; et al. Intestinal Fungal Dysbiosis and Systemic Immune Response to Fungi in Patients With Alcoholic Hepatitis. Hepatology 2020, 71, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Ratziu, V.; Loomba, R.; Rinella, M.; Anstee, Q.M.; Goodman, Z.; Bedossa, P.; Geier, A.; Beckebaum, S.; Newsome, P.N. Obeticholic acid for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Interim analysis from a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 2184–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staels, B.; Rubenstrunk, A.; Noel, B.; Rigou, G.; Delataille, P.; Millatt, L.J.; Baron, M.; Lucas, A.; Tailleux, A.; Hum, D.W.; et al. Hepatoprotective effects of the dual peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/delta agonist, GFT505, in rodent models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, G.; Cassader, M.; Gambino, R. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Emerging molecular targets and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 249–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratziu, V.; Ladron-De-Guevara, L.; Safadi, R.; Poordad, F.; Fuster, F.; Flores-Figueroa, J.; Harrison, S.A.; Arrese, M.; Fargion, S.; Ben-Bashat, D. One-year results of the global phase 2b randomized placebo-controlled arrest trial of aramchol, a stearoyl CoA desaturase inhibitor, in patients with NASH. Proc. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1448A–1449A. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, J.S.; Cho, S.Y.; Rou, W.S.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, S.H.; Lee, E.S.; Moon, H.S.; Kim, S.H.; Sung, J.K.; Kwon, I.S.; et al. TEAD2 as a novel prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 1785–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, A.P.; Jain, S.; Pocock, S.; Thomas, H.C.; Sherlock, S. Late results of the Royal Free Hospital prospective controlled trial of prednisolone therapy in hepatitis B surface antigen negative chronic active hepatitis. Gut 1980, 21, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soloway, R.D.; Summerskill, W.; Baggenstoss, A.H.; Geall, M.G.; Gitnick, G.L.; Elveback, L.R.; Schoenfield, L.J. Clinical, biochemical, and histological remission of severe chronic active liver disease: A controlled study of treatments and early prognosis. Gastroenterology 1972, 63, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerskill, W.H.; Korman, M.G.; Ammon, H.V.; Baggenstoss, A.H. Prednisone for chronic active liver disease: Dose titration, standard dose, and combination with azathioprine compared. Gut 1975, 16, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, A.; Kaido, T.; Uemoto, S. Perioperative nutritional therapy in liver transplantation. Surg. Today 2015, 45, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, Z.; Monnoye, M.; Abuja, P.M.; Mariadassou, M.; Kashofer, K.; Gerard, P.; Zatloukal, K. Steatosis and gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by high-fat diet are reversed by 1-week chow diet administration. Nutr. Res. 2019, 71, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, J.B.; Pimentel-Nunes, P.; Roncon-Albuquerque, R.; Leite-Moreira, A. The role of lipopolysaccharide/toll-like receptor 4 signaling in chronic liver diseases. Hepatol. Int. 2010, 4, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.S.; Zeng, X.F.; Liu, Z.N.; Zhao, Q.H.; Tan, Y.T.; Gao, J.; Li, H.L.; Xiang, Y.B. Diet and liver cancer risk: A narrative review of epidemiological evidence. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 124, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, L.; Jena, P.K.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H.X.; Nagar, N.; Kalanetra, K.M.; French, S.W.; French, S.W.; Mills, D.A.; Wan, Y.Y. Hepatic inflammation caused by dysregulated bile acid synthesis is reversible by butyrate supplementation. J. Pathol. 2017, 243, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.; Yeoh, B.S.; Chassaing, B.; Xiao, X.; Saha, P.; Aguilera Olvera, R.; Lapek, J.D., Jr.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.B.; Hao, S.; et al. Dysregulated Microbial Fermentation of Soluble Fiber Induces Cholestatic Liver Cancer. Cell 2018, 175, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keshavarzian, A.; Choudhary, S.; Holmes, E.W.; Yong, S.; Banan, A.; Jakate, S.; Fields, J.Z. Preventing gut leakiness by oats supplementation ameliorates alcohol-induced liver damage in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 299, 442–448. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.E.; Kim, D.K.; Seo, W.; Gao, B.; Yoo, S.H.; Song, B.J. Fructose Promotes Leaky Gut, Endotoxemia, and Liver Fibrosis Through Ethanol-Inducible Cytochrome P450-2E1-Mediated Oxidative and Nitrative Stress. Hepatology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munukka, E.; Pekkala, S.; Wiklund, P.; Rasool, O.; Borra, R.; Kong, L.; Ojanen, X.; Cheng, S.M.; Roos, C.; Tuomela, S. Gut-adipose tissue axis in hepatic fat accumulation in humans. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferolla, S.M.; Couto, C.A.; Costa-Silva, L.; Armiliato, G.N.; Pereira, C.A.; Martins, F.S.; Ferrari Mde, L.; Vilela, E.G.; Torres, H.O.; Cunha, A.S.; et al. Beneficial Effect of Synbiotic Supplementation on Hepatic Steatosis and Anthropometric Parameters, But Not on Gut Permeability in a Population with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horvath, A.; Leber, B.; Schmerboeck, B.; Tawdrous, M.; Zettel, G.; Hartl, A.; Madl, T.; Stryeck, S.; Fuchs, D.; Lemesch, S.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: The effects of a multispecies probiotic vs. placebo on innate immune function, bacterial translocation and gut permeability in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nier, A.; Brandt, A.; Rajcic, D.; Bruns, T.; Bergheim, I. Short-Term Isocaloric Intake of a Fructose- but not Glucose-Rich Diet Affects Bacterial Endotoxin Concentrations and Markers of Metabolic Health in Normal Weight Healthy Subjects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolato, M.; Manca, F.; Marrone, G.; Cefalo, C.; Racco, S.; Miggiano, G.A.; Valenza, V.; Gasbarrini, A.; Miele, L.; Grieco, A. Intestinal permeability after Mediterranean diet and low-fat diet in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol 2019, 25, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damms-Machado, A.; Louis, S.; Schnitzer, A.; Volynets, V.; Rings, A.; Basrai, M.; Bischoff, S.C. Gut permeability is related to body weight, fatty liver disease, and insulin resistance in obese individuals undergoing weight reduction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Hui, S.; Lang, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, C.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yi, L.; Mi, M. SIRT3 Deficiency Promotes High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Correlation with Impaired Intestinal Permeability through Gut Microbial Dysbiosis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, E.D.; Chen, D.Z.; Wu, J.L.; Lu, F.B.; Chen, L.; Zheng, M.H.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Jin, X.Y.; et al. High fiber dietary and sodium butyrate attenuate experimental autoimmune hepatitis through regulation of immune regulatory cells and intestinal barrier. Cell Immunol. 2018, 328, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.T.; Fukumori, C.; Ferreira, C.M. New insights into therapeutic strategies for gut microbiota modulation in inflammatory diseases. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2016, 5, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, M.C.S.; Paulino, D.S.; Brambilla, S.R.; Camargo, J.A.; Persinoti, G.F.; Carvalheira, J.B.C. Microbiota modification by probiotic supplementation reduces colitis associated colon cancer in mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Farhadi, A.; Jakate, S.M.; Tang, Y.; Shaikh, M.; Keshavarzian, A. Lactobacillus GG treatment ameliorates alcohol-induced intestinal oxidative stress, gut leakiness, and liver injury in a rat model of alcoholic steatohepatitis. Alcohol 2009, 43, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Qi, S.; Zhang, W.; Mao, J.; Tang, R.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Luo, X.M.; Wang, H. Lactobacillus reuteri ZJ617 culture supernatant attenuates acute liver injury induced in mice by lipopolysaccharide. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ritze, Y.; Bardos, G.; Claus, A.; Ehrmann, V.; Bergheim, I.; Schwiertz, A.; Bischoff, S.C. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e80169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwak, D.S.; Jun, D.W.; Seo, J.G.; Chung, W.S.; Park, S.E.; Lee, K.N.; Khalid-Saeed, W.; Lee, H.L.; Lee, O.Y.; Yoon, B.C.; et al. Short-term probiotic therapy alleviates small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, but does not improve intestinal permeability in chronic liver disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 26, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencarelli, A.; Cipriani, S.; Renga, B.; Bruno, A.; D’Amore, C.; Distrutti, E.; Fiorucci, S. VSL#3 resets insulin signaling and protects against NASH and atherosclerosis in a model of genetic dyslipidemia and intestinal inflammation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Zhu, L.; Xie, A.; Yuan, J. Oral administration of Saccharomyces boulardii ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats via reducing intestinal permeability and modulating gut microbial composition. Inflammation 2015, 38, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorletti, E.; Afolabi, P.R.; Miles, E.A.; Smith, D.E.; Almehmadi, A.; Alshathry, A.; Childs, C.E.; Del Fabbro, S.; Bilson, J.; Moyses, H.E.; et al. Synbiotics Alter Fecal Microbiomes, But Not Liver Fat or Fibrosis, in a Randomized Trial of Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1597–1610 e1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Saltin, B. Exercise as medicine-evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26 different chronic diseases. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25 (Suppl. 3), 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, B.; Torres, D.M.; Harrison, S.A. Physical activity: An essential component of lifestyle modification in NAFLD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the, L.; European Association for the Study of, D.; European Association for the Study of, O. EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Obes. Facts 2016, 9, 65–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thyfault, J.P.; Rector, R.S. Exercise Combats Hepatic Steatosis: Potential Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Diabetes 2020, 69, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ni, Y.; Cheung, C.K.Y.; Lam, K.S.L.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Z.; Ye, D.; Guo, J.; Tse, M.A.; et al. Gut Microbiome Fermentation Determines the Efficacy of Exercise for Diabetes Prevention. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 77–91.e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantartzis, K.; Thamer, C.; Peter, A.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Schraml, C.; Konigsrainer, A.; Konigsrainer, I.; Krober, S.; Niess, A.; et al. High cardiorespiratory fitness is an independent predictor of the reduction in liver fat during a lifestyle intervention in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2009, 58, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailing, L.J.; Allen, J.M.; Buford, T.W.; Fields, C.J.; Woods, J.A. Exercise and the Gut Microbiome: A Review of the Evidence, Potential Mechanisms, and Implications for Human Health. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2019, 47, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirns, B.H.; Koemel, N.A.; Sciarrillo, C.M.; Anderson, K.L.; Emerson, S.R. Exercise and Intestinal Permeability: Another Form of Exercise-Induced Hormesis? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, J.A. Microbiota and muscle highway-two way traffic. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Mach, N. Exercise-induced stress behavior, gut-microbiota-brain axis and diet: A systematic review for athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2016, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mach, N.; Fuster-Botella, D. Endurance exercise and gut microbiota: A review. J. Sport Health Sci. 2017, 6, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oseini, A.M.; Sanyal, A.J. Therapies in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Liver Int. 2017, 37 (Suppl. 1), 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Hong, S.W.; Rhee, E.J.; Lee, W.Y. GLP-1 Receptor Agonist and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Diabetes. Metab. J. 2012, 36, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietrich, P.; Hellerbrand, C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Review, T.; LaBrecque, D.R.; Abbas, Z.; Anania, F.; Ferenci, P.; Khan, A.G.; Goh, K.L.; Hamid, S.S.; Isakov, V.; Lizarzabal, M.; et al. World Gastroenterology Organisation global guidelines: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Lavine, J.E.; Van Natta, M.L.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Chalasani, N.; Dasarathy, S.; Diehl, A.M.; Hameed, B.; et al. Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adorini, L.; Pruzanski, M.; Shapiro, D. Farnesoid X receptor targeting to treat nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.K.; Hu, B. Brain-gut axis after stroke. Brain. Circ. 2018, 4, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, C.A.; Maes, M.; Slyepchenko, A.; Berk, M.; Solmi, M.; Lanctot, K.L.; Carvalho, A.F. The Gut-Brain Axis, Including the Microbiome, Leaky Gut and Bacterial Translocation: Mechanisms and Pathophysiological Role in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 6152–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikantha, P.; Mohajeri, M.H. The Possible Role of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain-Axis in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutta, S.K.; Verma, S.; Jain, V.; Surapaneni, B.K.; Vinayek, R.; Phillips, L.; Nair, P.P. Parkinson’s Disease: The Emerging Role of Gut Dysbiosis, Antibiotics, Probiotics, and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slyepchenko, A.; Maes, M.; Jacka, F.N.; Kohler, C.A.; Barichello, T.; McIntyre, R.S.; Berk, M.; Grande, I.; Foster, J.A.; Vieta, E.; et al. Gut Microbiota, Bacterial Translocation, and Interactions with Diet: Pathophysiological Links between Major Depressive Disorder and Non-Communicable Medical Comorbidities. Psychother. Psychosom. 2017, 86, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, J.R.; Kennedy, P.J.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G.; Hyland, N.P. Breaking down the barriers: The gut microbiome, intestinal permeability and stress-related psychiatric disorders. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karakula-Juchnowicz, H.; Dzikowski, M.; Pelczarska, A.; Dzikowska, I.; Juchnowicz, D. The brain-gut axis dysfunctions and hypersensitivity to food antigens in the etiopathogenesis of schizophrenia. Psychiatr. Pol. 2016, 50, 747–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Seitz, J.; Baines, J. Food matters: How the microbiome and gut-brain interaction might impact the development and course of anorexia nervosa. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, D.H.; Yimlamai, D. The intestinal microbiome and paediatric liver disease. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plaza-Díaz, J.; Solís-Urra, P.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, F.; Olivares-Arancibia, J.; Navarro-Oliveros, M.; Abadía-Molina, F.; Álvarez-Mercado, A.I. The Gut Barrier, Intestinal Microbiota, and Liver Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Strategies to Manage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218351
Plaza-Díaz J, Solís-Urra P, Rodríguez-Rodríguez F, Olivares-Arancibia J, Navarro-Oliveros M, Abadía-Molina F, Álvarez-Mercado AI. The Gut Barrier, Intestinal Microbiota, and Liver Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Strategies to Manage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):8351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218351
Chicago/Turabian StylePlaza-Díaz, Julio, Patricio Solís-Urra, Fernando Rodríguez-Rodríguez, Jorge Olivares-Arancibia, Miguel Navarro-Oliveros, Francisco Abadía-Molina, and Ana I. Álvarez-Mercado. 2020. "The Gut Barrier, Intestinal Microbiota, and Liver Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Strategies to Manage" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 21: 8351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218351
APA StylePlaza-Díaz, J., Solís-Urra, P., Rodríguez-Rodríguez, F., Olivares-Arancibia, J., Navarro-Oliveros, M., Abadía-Molina, F., & Álvarez-Mercado, A. I. (2020). The Gut Barrier, Intestinal Microbiota, and Liver Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Strategies to Manage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 8351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218351







