Abstract
The cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is a potent enzyme that converts arachidonic acid to prostaglandins (PG), including PGE2, a key mediator of inflammation and angiogenesis. Importantly, COX-2 is activated in response to inflammatory stimuli, where it is also believed to promote the development and progression of head and neck cancers (HNC). COX-2 can mediate its protumorigenic effect through various mechanisms, such as inducing cell proliferation, inhibition of apoptosis, and suppressing the host’s immune response. Furthermore, COX-2 can induce the production of vascular endothelial growth factors, hence, promoting angiogenesis. Indeed, the ability of COX-2 inhibitors to selectively restrict the proliferation of tumor cells and mediating apoptosis provides promising therapeutic targets for cancer patients. Thus, in this comprehensive review, we summarized the reported differential expression patterns of COX-2 in different stages of head and neck carcinogenesis—from potentially premalignant lesions to invasive carcinomas. Furthermore, we examined the available meta-analysis evidence for COX-2 role in the carcinogenesis of HNC. Finally, further understanding of the biological processes of COX-2 and its role in orchestrating cell proliferation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis may give therapeutically beneficial insight to develop the management plan of HNC patients and improve their clinical outcomes.
1. Head and Neck Cancer: An Overview
Head and neck cancers (HNC) represent a heterogeneous group of tumors that arise anywhere in the head and neck region. Approximately 90% of these cancers develop from the squamous cell lining of the oral cavity, oropharynx, hypopharynx, larynx, or nasopharynx [1,2]. In addition, tumors can originate from other tissues, such as the salivary glands, lymphoid tissue, connective tissue, or melanocytes [3]. Epidemiologically, HNC ranks as the sixth most common cancer worldwide, accounting for about 5–10% of all cancers in Europe and North America [4,5].
The risk factors associated with HNC include, e.g., tobacco and alcohol consumption, HPV infection, poor oral hygiene, and improper diet [5]. When consumed together, tobacco and alcohol can produce a synergistic procancerous effect, whereby alcohol increases the body’s exposure to tobacco-derived carcinogens, such as nitrosamines and polycyclic hydrocarbons [4]. Thus, while smoking alone increases the risk of developing oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) by ten times, both smoking and heavy drinking can increase such risk by almost a hundred times [6]. Human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly type 16 and 18, can merge with the host cell DNA and induce a malignant transformation. Interestingly, HPV is mainly associated with oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas (OPSCC), which are commonly diagnosed in younger patients with no clear history of smoking or heavy drinking [2,5]. Despite changes in lifestyle, HPV-driven malignancies have been on the rise over the last decade [2]. Luckily, HPV-driven cancers are more responsive to treatments, and thus, patients have a better survival rate compared to other types of HNC [4].
Unfortunately, despite the advances in cancer diagnosis and treatment, the overall survival (OS) for HNC patients has remained low. The survival outcome, however, varies depending on several crucial prognostic factors. For instance, patients with HPV-positive status show a 3-year OS rate of 82% compared with 57% in those with HPV-negative tumors [4]. Other prognostic factors include tumor site and stage at the time of diagnosis, with the most important factor being whether the patient has metastatic involvement in the lymph nodes [3]. Sadly, HNC are commonly diagnosed at later stages when the disease has already progressed and metastasized. At initial presentation, over 40% of patients have regional nodal involvement, and 10% present with distant metastases [2]. Presentation with distant metastases or a recurrent tumor spells an especially grim prognosis with a median survival of only 6–8 months [7]. In this context, recurrence represents another pressing challenge in HNC. Indeed, approximately one-third of OSCC patients relapse with locoregional recurrence. Second primary tumors are also common, with an annual rate of 4–7% [3]. The occurrence of second primary tumors could, in part, be explained by the field cancerization concept. As such, in tobacco- and/or alcohol-driven carcinogenesis, a considerable area of the mucosal tissue has been exposed to the carcinogens, and hence, may harbor mutations. Consequently, the para-cancerous, tumor-free, epithelium may already be in a premalignant change process, and could develop second primary tumors [6].
2. Cyclooxygenase-2An Overview
The cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme converts arachidonic acid to prostaglandins trough two catalytic steps: First, it adds oxygen to arachidonic acid so that the unstable prostaglandin G2 (PGG2) is formed; second, it reduces PGG2 to the prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), which then can be converted, via specific synthases, to several prostanoids, such as prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), prostaglandin D2, prostacyclin or thromboxane A2 [8]. COX has two isoforms: COX-1 and COX-2. COX-1 is consistently expressed in most cells, where it mediates several physiological functions, such as platelet aggregation and production of protective mucous in the stomach lining [9]. On the other hand, COX-2 is less widely expressed, and it is mainly found in the stomach, kidney, central nervous system, and the female reproductive tract [10]. It can, however, be induced in other cell types by different stimuli, such as growth factors, cytokines, carcinogens and oncogenes, and chronic inflammation [9,11].
An increased expression level of COX-2 has been linked to carcinogenesis [11]. Elevated COX-2 levels have been found in potentially premalignant lesions and malignant tumors, including breast, lung, pancreatic, gastric, esophageal, liver, prostate, and stomach cancers. Supporting these reports, a COX-2 knocked-out mice model of familial adenomatous polyposis reduced the number of polyps, whereas mice that overexpressed COX-2 in mammary glands developed metastatic mammary cancer [11,12]. Furthermore, selectively inhibiting COX-2 in various experimental murine cancer models reduced tumor formation, growth, and metastasis [9].
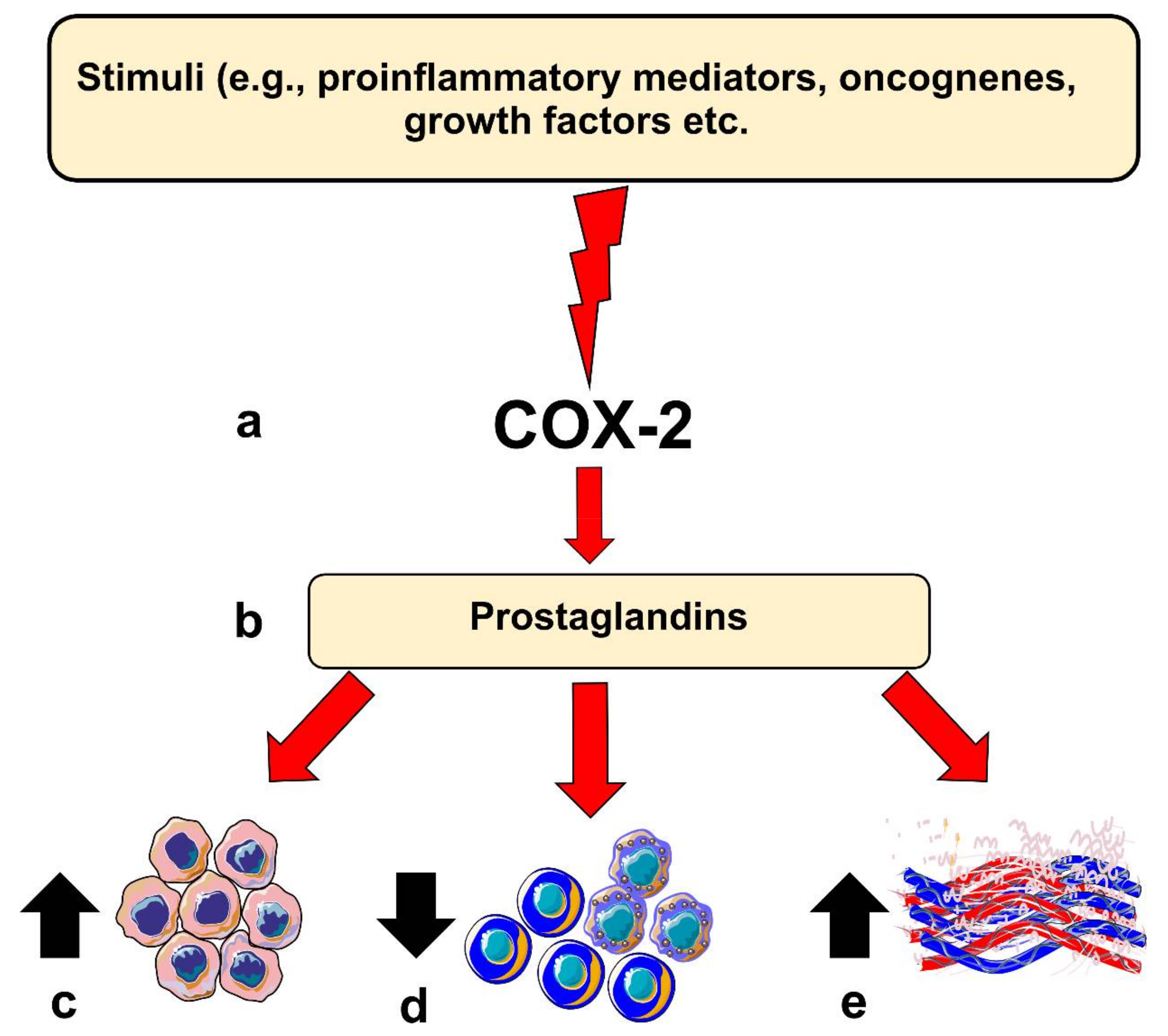
COX-2 is believed to contribute to carcinogenesis in different ways. For instance, COX-2 overexpression leads to a B-cell lymphoma 2-driven anti-apoptotic effect in epithelial cells. Moreover, elevated COX-2 in these cells leads to increased production of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) and the formation of networks resembling capillaries. COX-2 knocked-out mice models showed less intratumoral vascular density compared with the wild-type group [5,9]. However, COX-2 expression level per se may not directly reflect such carcinogenic potential, which could in part be mediated by its downstream pro-inflammatory products, such as PGE2 [12]. COX-2-derived PGE2 has been found to be one of the most important in carcinogenesis. Noteworthy, PGE2 levels were significantly induced in various cancer types, including OSCC [5]. PGE2 can bind to several receptors (EP1 to EP4) and acts in both autocrine and paracrine fashions, which could enhance protumorigenic processes in OSCC [5,12]. Importantly, PGE2 can suppress the immune system by inhibiting T- and B-cell proliferation and natural killer cell function; suppress the production of tumor necrosis factor-α; induce the production of interleukin-10; and stimulate regulatory T cells [8,9]. Additionally, PGE2 can also mediate chronic inflammation by promoting vasodilation and angiogenesis. Altogether, these activities, when dysregulated, may contribute to carcinogenesis (Figure 1).
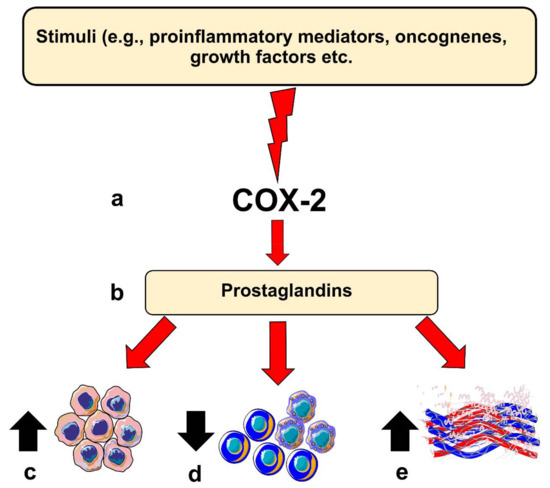
Figure 1.
Role of Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in head and neck carcinogenesis. (a) Inflammatory stimuli, oncogenes or other factors can induce COX-2 expression in epithelial cells; (b) this results in the production of prostaglandins which can influence various protumorigenic processes, such as (c) enhancing anti-apoptotic response, (d) suppression of immune cell response, or (e) inducing angiogenesis in the host tissue.
3. COX-2 Expression in Head and Neck Cancers
The expression of COX-2 has been examined at both gene and protein levels in different types of HNC. The main findings are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of COX-2 expression in different types of head and neck cancers.
3.1. COX-2 Expression in Head and Neck Tumorigenesis
In general, normal oral mucosa has a very low expression of, or completely lacks, COX-2 [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. However, certain tissues of the oral cavity, such as the ductal epithelial cells of salivary glands, normally express COX-2 [29,30,31,32,33]. COX-2 expression in oral mucosa is induced by exposure to tobacco and other carcinogens [25,26,27,28]. Interestingly, normal oral mucosa of smokers exhibits 4-fold more COX-2 mRNA than non-smokers, and oral cancer tissues express 50 times more than para-cancer areas [22,26]. Likewise, COX-2 is typically induced in oral potentially malignant lesions. Hay et al. found that patients with oral lichen planus (OLP) showed significantly higher levels of PGE2 compared with the control group [34].
Furthermore, patients with an erosive type of OLP had significantly higher PGE2 than the atrophic type group [34]. In agreement, Prado et al. found that the COX-2 mRNA levels were induced in oral leukoplakia compared to a normal-appearing mucosa from the same patient, as well as to healthy controls [27]. Other studies have found that COX-2 expression is gradually increased along with the transition from normal oral mucosa to cancer, where it is highest in severe dysplasia/carcinoma in situ samples [28,35].
In HNC, a large body of evidence has demonstrated the upregulation of COX-2 in malignant tumors when compared to normal oral mucosa [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. For instance, one study found that COX-2 mRNA was 11-fold higher in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) compared to paired normal tissue from the same patient [36]. Chan et al. found that when comparing the levels of COX-2 mRNA in HNSCC tissue, it was around 50 times higher than in the adjacent normal epithelium from the same patients and around 150 times higher when compared to normal oral mucosa from healthy controls [22]. However, some studies did not find a statistically significant difference in COX-2 levels between normal oral mucosa and tumors [38,39]. Additionally, similar amounts of COX-2 have been found in both normal oral mucosa and leukoplakia compared to OSCC samples [43]. Wenghoefer et al. found that irritation fibromas expressed less COX-2 in comparison to the healthy gingiva samples, the leukoplakia, and the OSCC samples [44]. Altogether, these reports highlight the potential involvement of COX-2 in oral carcinogenesis.
3.2. COX-2 Expression in Other Head and Neck Tumors
Several studies have assessed the expression of COX-2 in benign and malignant salivary gland tumors. Interestingly, Sakurai et al. found that the expression of COX-2 was group-dependent and increased from the normal salivary glands, to the salivary gland adenomas, with the highest expression detected in the salivary gland carcinoma group [31]. Furthermore, two studies found that the level of COX-2 in mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) was strongly increased, whereas most of the pleomorphic adenomas and adenoid cystic carcinomas (AdCC) were COX-2-negative [46,47]. In melanomas, Nascimento et al. found that oral melanomas were consistently COX-2-positive compared with the benign oral nevi, which were completely COX-2-negative [48]. However, in another study on odontogenic tumors, both the benign and the malignant tumors expressed COX-2, however, the malignant amelocarcinoma specimens exhibited higher levels of COX-2 compared with the benign ameloblastoma samples. On the contrary, the benign ameloblastic fibromas showed higher COX-2 than the malignant ameloblastic fibrosarcomas [49]. Nevertheless, fibrous hyperplasia was found to express a very low level of COX-2 compared with other premalignant and malignant lesions of the oral cavity [50].
3.3. COX-2 Expression in Tumor Microenvironment
Indeed, the tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a crucial role in tumor development and metastasis [5,6]. The expression of COX-2 seems to be particularly strong at the tumor invasive-front area of the HNSCC [17,18,51]. For instance, Gallo et al. has shown that the median PGE2 protein level was 2.36 μg/mg in the tumoral core compared with 3.85 μg/mg in the invasive-front area of HNSCC [52]. In this study, the cohort included 52 surgical specimens from laryngeal, oral cavity, and oropharyngeal SCC. Positive expression of COX-2 has also been found in the tumoral surrounding stroma of HNSCC, most notably in the inflammatory cells, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells [17,19,41,49,51,53,54,55,56]. Höing et al. compared the expression of various markers, including COX-2, between stroma and tumor nests in 110 laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) patients [57]. Interestingly, and in contrast to the other markers, COX-2 was expressed more in the tumor nest (53%) than in the stroma (39%) of the LSCC patients. Furthermore, this study revealed that tumoral, but not stromal, COX-2 expression correlated with lymph node metastasis and reduced patients’ survival. Hence, since COX-2 can influence immune cell recruitment, the authors proposed that COX-2 could play an important role in establishing tumor-stromal cell crosstalk [57].
4. COX-2 Expression and Cancer Staging
The TNM Classification is a system used for classifying solid tumors and can be employed to assist in prognostic cancer staging [58]. The T stands for tumor size; N stands for nodes, and it describes the regional lymph node involvement of the tumor; and M stands for metastasis, and it informs whether the tumor has metastasized to distant tissues. Cancer stages are usually divided into stages (0 to IV), with stage 0 having the score Tis (i.e., carcinoma in situ), with the numbers increasing gradually (T1-T4, N1-N3, and M1) with the most advanced stage being IV [58].
Importantly, many prognostic studies indicated a significant relationship between the level of COX-2 and the T-stage in patients with HNC. Among these, three studies concluded that induced immunoexpression of COX-2 was significantly associated with the T-stage in OSCC patients [41,59,60]. Similarly, Loong et al. found that advanced T-stage tumors of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinomas (NPC) showed stronger COX-2 expression compared with the lower T-stage tumors [61]. In LSCC patients, COX-2 expression was, likewise, more prevalent in the T3 and T4 tumors than in the lower T1 and T2 tumors [62,63]. Furthermore, Yang et al. reported a similar observation that COX-2 expression was significantly correlated with advanced T-stage in hypopharyngeal SCC (HPSCC) patients [64]. Xu et al. [65] found a significant relationship between COX-2 expression and T stage when looking at NPC samples. However, a correlation between COX-2 immunoexpression and T-stage was not found to be statistically significant in some studies about OSCC [25,51,55,66,67] LSCC [16,68,69], HPSCC [24], MEC [70], NPC [71,72,73], HNSCC [74,75], and tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC) [76]. Nonetheless, some of these studies found a significant correlation with at least one other prognostic parameter, such as the N-stage [24,51,70,71].
Specifically, the N-stage was significantly correlated with COX-2 immunoexpression in OSCC [45,51,59,77,78], LSCC [62], HPSCC [24,64], MEC [70], NPC [65,71,79], TSCC [37], OPSCC [80], and HNSCC [52,81]. Like with T-stage studies, some studies revealed a statistically non-significant relationship between the N-stage and COX-2 expression. These studies included samples from patients with OSCC [20,41,55,60,66,67,82,83], LSCC [16,68], NPC [61,72,73,84], HNSCC [28,74,75,85], and TSCC [76,86]. Almost all the included studies have not assessed the M-stage separately, instead, it was included in the cancer stage. In this regard, a possible link between tumor stage (I-IV) and COX-2 expression has been evaluated in different HNC. On one hand, COX-2 immunoexpression was significantly correlated with the cancer stage in OSCC [20,23,59,60,87], LSCC [62,63], MEC [70], HNSCC [52,81], and TSCC [40,88]. On the other hand, such a link between cancer stage and COX-2 immunoexpression was not statistically significant in some studies that examined patient samples from OSCC [39,41,51,55,66,67,78], TSCC [37,76], LSCC [69], HNSCC [74,75], NPC [52,70,71,82], and glottic cancer [89].
In a meta-analysis study conducted by Yang et al., COX-2 immunoexpression levels were significantly associated with N-stage and cancer stage, but not with T-stage. However, the subgroup analysis revealed that such a significant correlation between N-stage and COX-2 was only seen in patients with OSCC, but not in other HNSCC [90]. For the cancer stage, the correlation was significant in OSCC patients, as well as in no site-specific HNC patients, but not in patients with LSCC or NPC [90].
5. COX-2 Expression and Cancer Grading
Cancer grading is a delineation of the microscopic features of the tumoral cells and tissue. Low-grade, well-differentiated tumors exhibit histological structures that relatively well mimic the normal tissue. On the contrary, higher-grade tumors (i.e., poorly differentiated or undifferentiated tumors) have more abnormal appearing structures, and they tend to be more aggressive and have a worse prognosis [58]. Unlike TNM-staging, most studies did not find any significant correlations between cancer grade and immunoexpression of COX-2, including studies on OSCC [25,39,51,54,55,60,67,78,91], HPSCC [24,64], LSCC [16], MEC [70], TSCC [37,88], HNSCC [52,74,81,85], NPC [72,73], and glottic cancer [89]. Interestingly, the significant correlation was only seen in a few studies, including OSCC [23,41,45] and LSCC [62,63].
6. COX-2 Expression and Survival Outcomes
6.1. COX-2 Expression and Overall Survival
Itoh et al. found that OSCC patients with COX-2 overexpression had worse OS in the univariate analysis, however, COX-2 was not an independent prognostic factor in the multivariate analysis [51]. In a univariate analysis of an LSCC cohort, patients with elevated cytoplasmic expression of COX-2 had shorter OS [63]. Pan et al. showed that Cox-2 was overexpressed in 75.7% of NPCs, and this was associated with the worse OS on both univariate and multivariate analyses [92]. In the same manner, several other studies found a significant association between higher COX-2 level and reduced OS both in univariate and multivariate analyses, including studies on OPSCC [93], OSCC [94], LSCC [62], HNSCC [28,52], NPC [65,84], HPSCC [64], and glottic cancer [89]. Interestingly, Kyzas et al. found that co-expression of COX-2 and VEGF-C meant a significantly shorter OS, which was also an independent prognostic factor in the multivariate analysis [81]. Furthermore, Gallo et al. showed that HNSCC patients with higher PGE2 tumor levels had significantly shorter OS estimates in Kaplan–Meier analysis [52].
On the contrary, Ranelletti et al. reported that LSCC patients with COX-2 positive tumors had a longer OS compared to patients with COX-2 negative tumors. In this study, the 5-year OS rate for patients with COX-2-positive tumors was 100%, whereas it was 34% for those with COX-2-negative tumors [69]. In the multivariate analysis, COX-2 retained its significance as an independent prognostic marker. The authors concluded that COX-2 is overexpressed in less aggressive, low-grade laryngeal SCCs, whereas its expression is lost as the tumors progress to a more malignant phenotype [69]. Other studies found no relationship between COX-2 expression and OS, including studies on NPC [71,72,73], TSCC [67,76], OSCC [39,60,66,82,95,96], HNSCC [85], OPSCC [80], and AdCC [32].
6.2. COX-2 Expression and Disease-Specific Survival
In two OSCC studies, patients with higher COX-2 expression had a significantly shorter 5-year disease-specific survival (DSS) [59,60]. In contrast, Loong et al. found that DSS was shorter in patients with low COX-2 expression compared to patients with moderate or strong expression scores [61]. However, this study had a small sample size, and hence, a multivariate analysis could not be performed. Four other studies found no correlation between COX-2 expression and DSS, including patients with LSCC [68], TSCC [97], tonsils, and base of tongue SCC [98].
6.3. COX-2 Expression and Disease-Free Survival
COX-2 expression was found to correlate with disease-free survival (DFS) in HNSCC patients. For instance, Chen et al. found a higher recurrence rate in LSCC patients expressing high COX-2 levels compared with those with low COX-2 expression [62]. In a univariate analysis, Pan et al. found that NPC patients exhibited a significant correlation between COX-2 expression and DFS [92]. In the multivariate analysis, multiple variables, including COX-2, were combined into a principal component (Z), which was an independent prognostic factor in NPC. However, COX-2 expression was not assessed separately [92]. In HNSCC patients, the 5-year relapse-free survival rate in the univariate analysis was worse in patients who had elevated expression of COX-2, however, this was not statistically significant in the multivariate analysis [75,80]. Pannone et al. examined a cohort of OSCC patients and found that COX-2 overexpression was correlated with reduced DFS in the univariate analysis, however, multivariate analysis was not performed [39]. Similarly, Kourelis et al. reported a lower recurrence rate in LSCC patients with higher levels of COX-2 immunostaining, although the multivariate analysis was not performed [68]. Interestingly, higher COX-2 levels were associated with a poor outcome in chemotherapy-naïve OSCC patients compared to those who had received chemotherapy [99]. In the multivariate analysis, Itoh et al. reported that COX-2 overexpression was an independent prognostic factor for shorter DFS in OSCC patients [51]. In agreement with this study, Gallo et al. delineated that HNSCC patients with low or absent COX-2 expression had better DFS than patients with overexpressed COX-2 status, which was also true in the multivariate analysis [52]. However, and despite the aforementioned evidence, several studies found no correlation between COX-2 and DFS, including studies on NPC [71,72,73,84], OSCC [41,45], HNSCC [81,85], TSCC [67,88], glottic cancer [89], and LSCC [100].
6.4. Meta-Analyses of COX-2 Expression and Survival
Two meta-analysis studies examined the prognostic value of COX-2 expression. Wang et al. performed a meta-analysis of 12 studies encompassing 979 OSCC patients. They found that patients with positive COX-2 status had a poor OS rate (hazard ratio (HR) = 2.23) compared with the COX-2-negative group [101]. An analysis conducted by Yang et al. included 29 studies with a total of 2430 patients with HNSCC [91]. They found that positive COX-2 expression was associated with poor outcomes in OS, relapse-free survival, and DFS (HR = 1.93; 2.02; 5.14, respectively). When the authors conducted a subgroup meta-analysis, COX-2 expression predicted reduced, statistically non-significant, survival time [91].
7. COX-2 Polymorphisms and Risk of Cancers
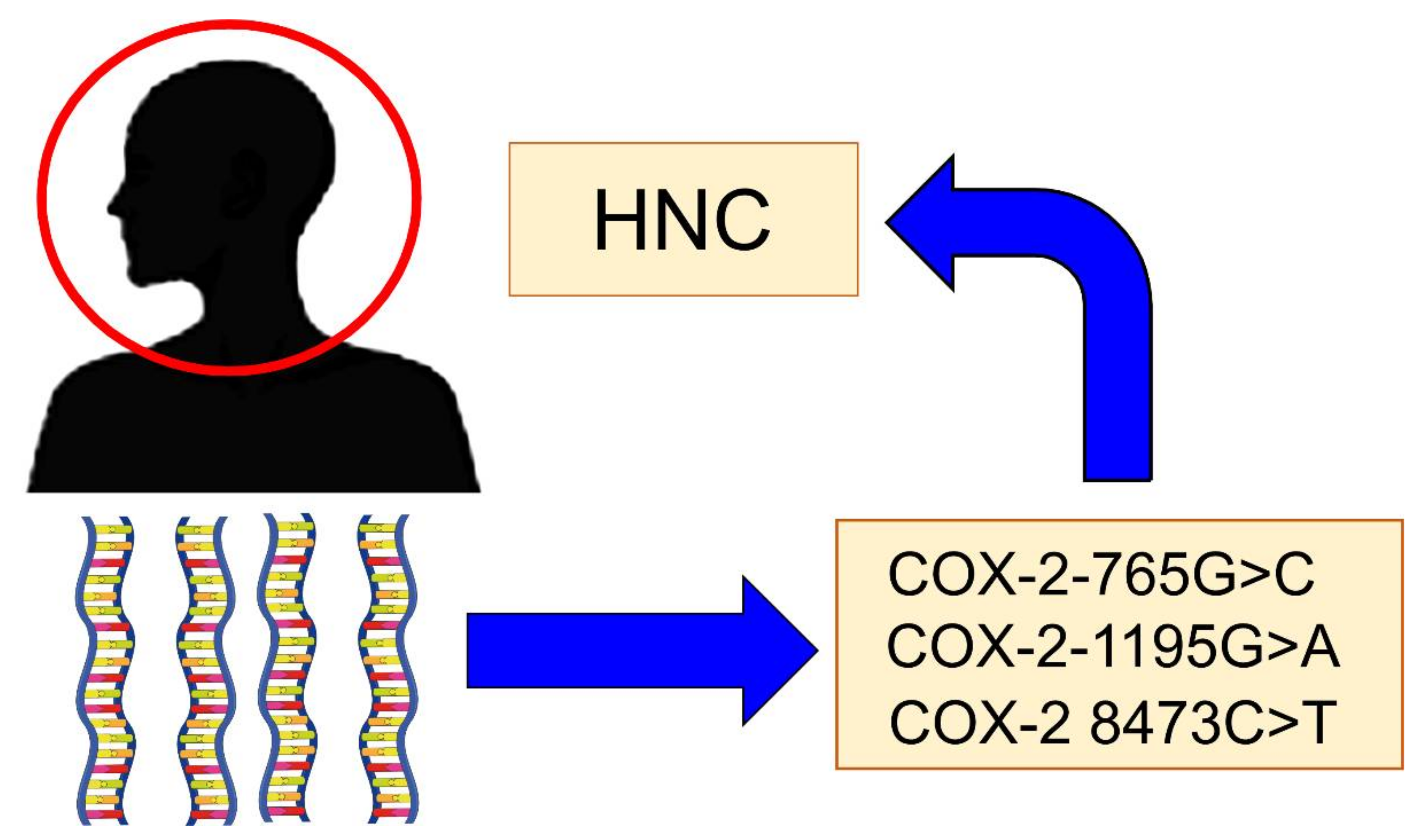
There are some genetic polymorphisms of COX-2 that have been implicated in the risk of developing HNC (Figure 2). The main polymorphisms are:
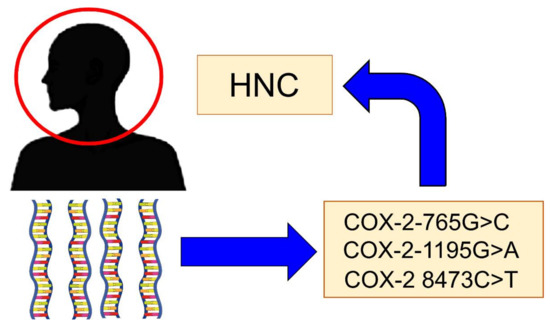
Figure 2.
The main Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) polymorphisms are implicated in the risk of head and neck cancer (HNC).
7.1. COX-2-765G>C
The COX-2-765G>C is a functional polymorphism that disrupts the binding site of stimulatory protein 1 (Sp1), but creates a binding site for E2 promoter binding factor 1 (E2F1), leading to stimulated transcription activity, which could enhance the cancer risk [102,103]. Lin et al. found that the GC and CC genotype was protective against OSCC when compared to the GG genotype in a study that included 297 OSCC patients and 280 healthy controls [102]. In another study on OSCC, Mittal et al. analyzed a single locus and found no significant difference between 193 OSCC patients and 137 controls in the 765 G>C allele frequency [104]. However, in the multivariate logistic regression analysis, the −765 G>C genotype appeared to be protective with an odds ratio of 0.71. Thus, they concluded that the −765 G>C and CC variant might be protective against OSCC compared to the GG variant [104]. However, this was in contrast to another study, in which the GG genotype was more frequent in controls than in OSCC patients (94.66% vs. 73.3%), and thus, could be protective against OSCC. Moreover, the study found that both the GC and the CC genotypes were associated with a significantly increased risk of OSCC [105]. Nonetheless, another two studies found no evidence for the role of −765G>C polymorphisms in the risk of developing OSCC [106,107].
7.2. COX-2-1195G>A
The COX-2-1195G>A polymorphism has also been suggested to influence the risk of oral cancer. The −1195A allele displays an increased transcriptional activity of the COX-2 gene compared to the −1195G allele [108]. Mittal et al. found that −1195GA genotype was relatively higher in OSCC patients compared to the controls, which seemed to confer an increased risk of tobacco-related oral carcinogenesis [104]. Chiang et al. found that the AA genotype was significantly associated with OSCC when compared to the GG genotype and had a 1.55-fold increased risk of OSCC [107]. However, two studies found no association between different COX-2-1195G>A polymorphisms and head and neck cancer risk [106,109].
7.3. COX-2 8473C>T
The 8473 C>T polymorphism is located in the 3′ UTR region of the COX-2 gene, and the T to C change may affect the stability and the secondary structure of the mRNA of COX-2 [110]. COX-2 8473 C>T polymorphisms have also been assessed in patients with HNSCC. Although there was no significant difference between healthy controls and OSCC patients in the single-locus analysis, the CT genotype was less frequent in patients than controls [104]. Campa et al. investigated the SNPs, including the 8473 C>T polymorphism in 811 patients with upper aerodigestive tract cancers, including OSCC, LSCC, and OPSCC [110]. The authors indicated a possible association between esophageal cancer and the 8473C>T polymorphism.
7.4. Meta-Analyses of COX-2 Gene Polymorphisms and Risk of Cancer
Three meta-analyses assessed the potential association between COX-2 gene polymorphisms and the risk of HNC. Deng et al. reported a significantly increased risk of HNSCC in three genetic models of COX-2 polymorphisms. However, the odd ratios were small, and not all models showed an association with HNSCC, which could result from sample size that was too small [111]. Li et al. investigated the polymorphisms: +837T>C, −765G>C, and −1195A>G among seven clinical studies, including a total of 2296 oral cancer patients. Interestingly, the authors found that the +837T>C and the −765G>C polymorphisms are related to the susceptibility of oral cancer and that the gene frequencies in the case group compared to the control group were significantly different both in the allele model and the dominant model [112]. On the other hand, a meta-analysis by Leng et al. included eight case control studies and found no association with either the 8473T>C or the −765G>C polymorphism in the risk of HNSCC. However, they found an association between the −1195G>A polymorphism and HNSCC risk in the pooled result from the crude data in certain models (AA vs. GG, AA vs. GA, and AA vs. GG + GA) [113].
8. COX-2 and Cancer Biomarkers
Several studies investigated the potential correlation between COX-2 and other biomarkers in HNC. However, no significant correlation was found between COX-2 and p53 [19,67,91], Ki67 [19,54], CD68 [54], epidermal growth factor receptor [72,73,84], E-cadherin [37], C-erbB2 [84], p-ERK1/2 [25] or mast cell density [95]. Nevertheless, a positive correlation has been found in a limited number of studies between COX-2 and HGF [33], EP300 [62], matrix metalloproteinase 2 [63], prostate-specific membrane antigen [94], DNA topoisomerase II α [18,77], NF-κB [41], H-Ras [23], cytoplasmic, but not nuclear HuR expression [16,47,60], CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3+ regulatory T cells [75], tumor-associated tissue eosinophilia [87] or platelet-lymphocyte ratio [66].
Importantly, a significant correlation between COX-2 and VEGF was reported in HNSCC [52,59,81,95]. The VEGF family plays a crucial role in tumor-associated angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Cancer cells can secrete VEGF-C and VEGF-D to induce intratumoral and peritumoral lymphangiogenesis, as well as tumor neovascularization [52,59]. COX-2 is believed to stimulate VEGF expression (e.g., VEGF-A and C), and hence, both are associated with lymph node metastasis and tumor angiogenesis [52,59,81]. Co-expression of both factors may also negatively impact the survival of HNSCC patients [76,81].
9. Conclusions
To summarize, there is enormously growing evidence supporting the involvement of COX-2 in tumor-initiating and tumor-promoting events for several solid tumors, including HNC. Furthermore, elevated COX-2 levels were also documented in potentially premalignant lesions of the oral cavity. It is also acknowledged that COX-2 plays vital role in regulating tumorigenesis-related processes, such as apoptosis, angiogenesis, and immunomodulation [5,8,9]. Therefore, there is considerable potential for COX2-based therapeutics, such as COX-2 inhibitors, to serve as either adjuvant therapeutics increasing the overall response rate, or as targeted therapeutics for HNC patients. Recently, Janakiraman et al. determined that inhibition of COX-2 via celecoxib promoted apoptosis in paclitaxel-resistant oral cancer cells, both in vitro and in vivo. Thus, the authors recommended the use of the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib, in combination with paclitaxel, for the management of paclitaxel-resistant oral cancer cells [114]. However, as aforementioned in this review, some studies showed no significant association between COX-2 and HNC, which, therefore, necessitates more studies with larger sample sizes across different populations. In conclusion, further in vitro and in vivo model studies of COX-2 role in cancer, paralleled with clinical trials, could provide promising therapeutic targets in HNC, and improve the patients’ clinical outcome.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.F., T.S. and A.S.; methodology, E.F., T.S. and A.S.; software, E.F., T.S. and A.S.; formal analysis, E.F., T.S. and A.S.; resources, T.S.; data curation, E.F., T.S. and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, E.F.; writing—review and editing, T.S. and A.S.; visualization, A.S.; supervision, T.S. and A.S.; project administration, T.S. and A.S.; funding acquisition, T.S. and A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Emil Aaltonen Foundation; Minerva Foundation Institute for Medical Research; Cancer Society of Finland; Sigrid Jusélius Foundation; Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation; Helsinki University Central Hospital Research Funds.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| COX | cyclooxygenase |
| HNC | head and neck cancers |
| OSCC | oral squamous cell carcinoma |
| HPV | human papillomavirus |
| OPSCC | oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma |
| PG | prostaglandin |
| NPC | nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| EP | prostanoid receptors |
| PGE2 | prostaglandin E2 |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factors |
| HNSCC | head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| AdCC | adenoid cystic carcinomas |
| MEC | mucoepidermoid carcinoma |
| TSCC | tongue squamous cell carcinoma |
| LSCC | laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma |
| OTSCC | oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma |
| HPSCC | hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma |
References
- Sanderson, R.J.; Ironside, J.A. Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Head and Neck. BMJ 2002, 325, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marur, S.; Forastiere, A.A. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Update on Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, P.H.; Patel, S.G. Cancer of the Oral Cavity. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 24, 491–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfouzan, A.F. Head and Neck Cancer Pathology: Old World versus New World Disease. Niger J. Clin. Pract. 2019, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasry, W.H.; Rodriguez-Lecompte, J.C.; Martin, C.K. Role of COX-2/PGE2 Mediated Inflammation in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2018, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippman, S.M.; Sudbø, J.; Hong, W.K. Oral Cancer Prevention and the Evolution of Molecular-Targeted Drug Development. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, J.C.; Khuri, F.R.; Shin, D.M. Advances in Chemoprevention of Head and Neck Cancer. Oncologist 2004, 9, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.A.; Carvalho, J.C.; van der Waal, I. An Overview on the Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Tumors of the Head and Neck. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.T.; Subbaramaiah, K.; Shah, J.P.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Boyle, J.O. Cyclooxygenase-2: A Novel Molecular Target for the Prevention and Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer. Head Neck 2002, 24, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goradel, N.M.; Najafi, M.; Salehi, E.; Farhood, B.; Mortezaee, K. Cyclooxygenase-2 in Cancer: A Review. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 5683–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamakawa, H.; Nakashiro, K.; Sumida, T.; Shintani, S.; Myers, J.N.; Takes, R.P.; Rinaldo, A.; Ferlito, A. Basic Evidence of Molecular Targeted Therapy for Oral Cancer and Salivary Gland Cancer. Head Neck 2008, 30, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chang, K. Eicosanoids and HB-EGF/EGFR in Cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedmajidi, M.; Shafaee, S.; Siadati, S.; Khorasani, M.; Bijani, A.; Ghasemi, N. Cyclo-oxygenase-2 Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Can. Res. Ther. 2014, 10, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, N.; Krishnapillai, R.; Bindhu, P.; Thomas, P. Immunohistochemical Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2019, 30, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhi, W.S.; Sebastian, P.; Varghese, B.T.; Prakash, O.; Pillai, M.R. NF-κB and COX-2 During Oral Tumorigenesis and in Assessment of Minimal Residual Disease in Surgical Margins. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2006, 81, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.; Han, H.; Soh, Y.; Lee, K.; Son, H. Cytoplasmic HuR Over-expression is Associated with Increased Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Pathology 2007, 39, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatsuka, H.; Siar, C.H.; Tsujigiwa, H.; Naomoto, Y.; Han, P.P.; Gunduz, M.; Sugahara, T.; Sasaki, A.; Nakajima, M. Heparanase and Cyclooxygenase-2 Gene and Protein Expressions During Progression of Oral Epithelial Dysplasia to Carcinoma. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 16, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, E.; Sakurai, K.; Kishimoto, H.; Takaoka, K.; Noguchi, K.; Hashitani, S.; Hirota, S.; Urade, M. Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 and DNA Topoisomerase II α in Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions of the Oral Mucosa. Oral Oncol. 2008, 44, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Kodani, I.; Osaki, M.; Araki, K.; Adachi, H.; Ryoke, K.; Ito, H. Cyclo-oxygenase-1 and -2 Expression in Human Oral Mucosa, Dysplasias and Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Their Pathological Significance. Oral Oncol. 2005, 41, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Cui, J. COX-2, MMP-7 Expression in Oral Lichen Planus and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2013, 6, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, A.; Lipari, L.; Leone, A.; Tortorici, S.; Burruano, F.; Provenzano, S.; Gerbino, A.; Buscemi, M. Expression of Cyclooxygenase-1 and Cyclooxygenase-2 in Normal and Pathological Human Oral Mucosa. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2010, 48, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.; Boyle, J.O.; Yang, E.K.; Zhang, F.; Sacks, P.G.; Shah, J.P.; Edelstein, D.; Soslow, R.A.; Koki, A.T.; Woerner, B.M.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression Is Up-Regulated in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moazeni-Roodi, A.; Allameh, A.; Harirchi, I.; Motiee-Langroudi, M.; Garajei, A. Studies on the Contribution of Cox-2 Expression in the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and H-Ras Activation. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2017, 23, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Su, C.; Chang, H.; Chai, C.; Hung, W. Overexpression of Cyclo-oxygenase 2 in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Hypopharynx. Hum. Pathol. 2002, 33, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søland, T.M.; Husvik, C.; Koppang, H.S.; Boysen, M.; Sandvik, L.; Clausen, O.P.; Christoffersen, T.; Bryne, M. A Study of Phosphorylated ERK1/2 and COX-2 in Early Stage (T1–T2) Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2008, 37, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraitis, D.; Du, B.; de Lorenzo, M.S.; Boyle, J.O.; Weksler, B.B.; Cohen, E.G.; Carew, J.F.; Altorki, N.K.; Kopelovich, L.; Subbaramaiah, K.; et al. Levels of Cyclooxygenase-2 Are Increased in the Oral Mucosa of Smokers: Evidence for the Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Its Ligands. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 664–670. [Google Scholar]
- Prado, S.M.; Cedrún, J.L.; Rey, R.L.; Villaamil, V.M.; García, A.Á.; Ayerbes, M.V.; Aparicio, L.A. Evaluation of COX-2, EGFR, and p53 as Biomarkers of Non-Dysplastic Oral Leukoplakias. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2010, 89, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saba, N.F.; Choi, M.; Muller, S.; Shin, H.J.; Tighiouart, M.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Khuri, F.R.; Chen, Z.; Shin, D.M. Role of COX-2 in Tumor Progression and Survival of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, K.F.; Ribeiro, A.L.; de Mendonça, R.P.; de Jesus Viana Pinheiro, J.; da Silva Kataoka, M.S.; Arnaud, M.V.; de Melo Alves Junior, S. Abnormal Activation of the Akt Signaling Pathway in Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 275, 3039–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipari, L.; Mauro, A.; Gallina, S.; Tortorici, S.; Buscemi, M.; Tete, S.; Gerbino, A. Expression of Gelatinases (MMP-2, MMP-9) and Cyclooxygenases (COX-1, COX-2) in Some Benign Salivary Gland Tumors. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2012, 25, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, K.; Urade, M.; Noguchi, K.; Kishimoto, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Yasoshima, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Kubota, A. Increased Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Human Salivary Gland Tumors. Pathol. Int. 2001, 51, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, D.; Roberts, D.; Karpowicz, M.; Hanna, E.Y.; Weber, R.S.; El-Naggar, A.K. Clinical Significance of Myb Protein and Downstream Target Genes in Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Tsukinoki, K.; Kurabayashi, H.; Sasaki, M.; Yasuda, M.; Ota, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Kaneko, A. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Expression Correlates with Cyclooxygenase-2 Pathway in Human Salivary Gland Tumors. Oral Oncol. 2006, 42, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Hay, R.M.; Fawzy, M.M.; Metwally, D.; Kadry, D.; Ezzat, M.; Rashwan, W.; Rashed, L.A. DNA Polymorphisms and Tissue Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Oral Lichen Planus: A Case-Control Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, Y.; Kozaki, K.; Nakagawa, A.; Saito, T.; Ito, S.; Tamada, Y.; Fujiwara, S.; Nishikawa, N.; Uchida, K.; Yoshikawa, K.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 is a Possible Target of Treatment Approach in Conjunction with Photodynamic Therapy for Various Disorders in Skin and Oral Cavity. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 151, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celenk, F.; Bayramoglu, I.; Yilmaz, A.; Menevse, A.; Bayazit, Y. Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2, 12-Lipoxygenase, and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2013, 24, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, R.; Imanishi, Y.; Shibata, K.; Sakai, N.; Sakamoto, K.; Shigetomi, S.; Habu, N.; Otsuka, K.; Sato, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; et al. Restoration of E-cadherin Expression by Selective Cox-2 Inhibition and the Clinical Relevance of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasry, W.H.; Wang, H.; Jones, K.; Tesch, M.; Rodriguez-Lecompte, J.C.; Martin, C.K. Cyclooxygenase and CD147 Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patient Samples and Cell Lines. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2019, 128, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, G.; Sanguedolce, F.; de Maria, S.; Farina, E.; Muzio, L.L.; Serpico, R.; Emanuelli, M.; Rubini, C.; de Rosa, G.; Staibano, S.; et al. Cyclooxygenase Isozymes in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Real-Time RT-PCR Study with Clinic Pathological Correlations. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2007, 20, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renkonen, J.; Wolff, H.; Paavonen, T. Expression of Cyclo-oxygenase-2 in Human Tongue Carcinoma and its Precursor Lesions. Virchows Arch. 2002, 440, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawhney, M.; Rohatgi, N.; Kaur, J.; Shishodia, S.; Sethi, G.; Gupta, S.D.; Suryanaryana, V.S.; Shukla, N.K.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Ralhan, R. Expression of NF-κB Parallels COX-2 Expression in Oral Precancer and Cancer: Association with Smokeless Tobacco. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 2545–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.; Putti, T.C. Cyclooxygenase 2 Expression in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Immunohistochemical Findings and Potential Implications. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirchaghmaghi, M.; Mohtasham, N.; Mozaffari, P.M. Comparison of COX2 Expression between Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Leukoplakia and Normal Mucosa. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2012, 13, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenghoefer, M.; Pantelis, A.; Dommisch, H.; Reich, R.; Martini, M.; Allam, J.P.; Novak, N.; Bergé, S.; Jepsen, S.; Winter, J. Decreased Gene Expression of Human β-defensin-1 in the Development of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 37, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byatnal, A.A.; Byatnal, A.; Sen, S.; Guddattu, V.; Solomon, M.C. Cyclooxygenase-2–An Imperative Prognostic Biomarker in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma- An Immunohistochemical Study. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2015, 21, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Rocha Tenório, J.; da Silva, L.P.; de Aguiar Xavier, M.G.; Santana, T.; do Nascimento, G.J.; Sobral, A.P. Differential Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 and Cyclin D1 in Salivary Gland Tumors. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 275, 2341–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.; Han, H.; Soh, Y.; Son, H. Overexpression of Cyclooxygenase-2 Correlates with Cytoplasmic HuR Expression in Salivary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma but Not in Pleomorphic Adenoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2007, 36, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza do Nascimento, J.; Carlos, R.; Delgado-Azañero, W.; Mosqueda-Taylor, A.; de Almeida, O.P.; Romañach, M.J.; de Andrade, B.A. Immunohistochemical Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in Oral Nevi and Melanoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Romero, C.; Mosqueda-Taylor, A.; Delgado-Azañero, W.; de Almedia, O.P.; Bologna-Molina, R. Comparison of Fatty Acid Synthase and Cyclooxygenase-2 Immunoexpression in Embryonal, Benign, and Malignant Odontogenic Tissues. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2019, 127, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, H.A.; Pontes, F.S.; Fonseca, F.P.; de Carvalho, P.L.; Pereira, É.M.; de Abreu, M.C.; de Freitas Silva, B.S.; dos Santos Pinto, D., Jr. Nuclear Factor κ B and Cyclooxygenase-2 Immunoexpression in Oral Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 17, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, S.; Matsui, K.; Furuta, I.; Takano, Y. Immunohistochemical Study on Overexpression of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity: Its Importance as a Prognostic Predictor. Oral Oncol. 2003, 39, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, O.; Masini, E.; Bianchi, B.; Bruschini, L.; Paglierani, M.; Franchi, A. Prognostic Significance of Cyclooxygenase-2 Pathway and Angiogenesis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2002, 33, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.G.; Gopalakrishnan, V.K.; Bhattacharya, I.; Vishwanatha, J.K. Deregulated Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Oral Premalignant Tissues. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bôas, D.S.; Takiya, C.M.; Coelho-Sampaio, T.L.; Monção-Ribeiro, L.C.; Ramos, E.A.; Cabral, M.G.; dos Santos, J.N. Immunohistochemical Detection of Ki-67 is not Associated with Tumor-Infiltrating Macrophages and Cyclooxygenase-2 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2010, 39, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannone, G.; Bufo, P.; Caiaffa, M.F.; Serpico, R.; Lanza, A.; Muzio, L.L.; Rubini, C.; Staibano, S.; Petruzzi, M.; de Benedictis, M.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2004, 17, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltanova, B.; Raudenska, M.; Masarik, M. Effect of Tumor Microenvironment on Pathogenesis of the Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höing, B.; Kanaan, O.; Altenhoff, P.; Petri, R.; Thangavelu, K.; Schlüter, A.; Lang, S.; Bankfalvi, A.; Brandau, S. Stromal Versus Tumoral Inflammation Differentially Contribute to Metastasis and Poor Survival in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 8415–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, R.D.; Sapra, A. TNM Classification. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553187/ (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Kono, M.; Watanabe, M.; Abukawa, H.; Hasegawa, O.; Satomi, T.; Chikazu, D. Cyclo-Oxygenase–2 Expression is Associated with Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C Expression and Lymph Node Metastasis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 71, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.; Li, S.; Cha, I. Association between Expression of Embryonic Lethal Abnormal Vision-like Protein HuR and Cyclooxygenase-2 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Head Neck 2011, 33, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loong, S.L.; Hwang, J.S.; Li, H.H.; Wee, J.T.; Yap, S.P.; Chua, M.L.; Fong, K.W.; Tan, T.W. Weak Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 is Associated with Poorer Outcome in Endemic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Analysis of Data from Randomized Trial between Radiation Alone Versus Concurrent Chemo-radiation (SQNP-01). Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, R.; Li, Y.; Cui, B.; Song, M.; Yang, A.; Chen, W. High Expression Levels of COX-2 and P300 Are Associated with Unfavorable Survival in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 270, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, P.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.; Lu, G. Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 in Patients with Primary Laryngeal Carcinoma: A Tissue Microarray Study. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2007, 121, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, D.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Duan, M. Expression of COX-2, CD44v6 and CD147 and Relationship with Invasion and Lymph Node Metastasis in Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xie, G.; Li, J.; Shi, L.; Fan, S. Aberrant Expression of β -catenin and E-cadherin is Correlated with Poor Prognosis of Nasopharyngeal Cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, Y.; Kogashiwa, Y.; Araki, R.; Enoki, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Yoda, T.; Nakahira, M.; Sugasawa, M. Correlation of Inflammatory Markers, Survival, and COX2 Expression in Oral Cancer and Implications for Prognosis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 158, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atula, T.; Hedström, J.; Ristimäki, A.; Finne, P.; Leivo, I.; Markkanen-Leppänen, M.; Haglund, C. Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity and Pharynx: Association to p53 and Clinical Outcome. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 16, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kourelis, K.; Vandoros, G.; Kourelis, T.; Papadas, T.; Goumas, P.; Sotiropoulou-Bonikou, G. Low COX2 in Tumor and Upregulation in Stroma Mark Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranelletti, F.O.; Almadori, G.; Rocca, B.; Ferrandina, G.; Ciabattoni, G.; Habib, A.; Galli, J.; Maggiano, N.; Gessi, M.; Lauriola, L. Prognostic Significance of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 95, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyada, M.M.; Grawish, M.E.; Elsabaa, H.M. Predictive Value of Cyclooxygenase 2 and Bcl-2 for Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma. Ann. Diagn Pathol. 2009, 13, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.M.; Ma, B.B.; Hui, E.P.; Wong, S.C.; Mo, F.K.; Leung, S.F.; Kam, M.K.; Chan, A.T. Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma—A Prognostic Evaluation and Correlation with Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1α and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Oral Oncol. 2007, 43, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Li, C.; Chien, C.; Rau, K.; Huang, H. Immunohistochemical Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Cyclooxygenase-2 in Pediatric Nasopharyngeal Carcinomas: No Significant Correlations with Clinicopathological Variables and Treatment Outcomes. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 71, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Li, C.; Huang, H.; Fang, F. Correlations between Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR), Phosphorylated EGFR, Cyclooxygenase-2 and Clinicopathological Variables and Treatment Outcomes in Nasopharyngeal Carcinomas. Chang. Gung. Med. J. 2010, 33, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bron, L.; Jandus, C.; Andrejevic-Blant, S.; Speiser, D.E.; Monnier, P.; Romero, P.; Rivals, J. Prognostic Value of Arginase-II Expression and Regulatory T-cell Infiltration in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, E85–E93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhao, M.; Xia, M.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y. The Correlation between Tumor-Infiltrating Foxp3+ regulatory T cells and Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression and Their Association with Recurrence in Resected Head and Neck Cancers. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, Y.; Morita, N.; Hata, K.; Nakanishi, M.; Kimoto, N.; Omata, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Yoneda, T. Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression is Associated with Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-C and Lymph Node Metastasis in Human Oral Tongue Cancer. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2014, 117, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, K.; Urade, M.; Noguchi, K.; Hashitani, S.; Takaoka, K.; Segawa, E.; Kishimoto, H. Prognostic Significance of Cyclooxygenase-2 and DNA topoisomerase IIα Expression in Oral Carcinoma. Head Neck 2007, 29, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sappayatosok, K.; Maneerat, Y.; Swasdison, S.; Viriyavejakul, P.; Dhanuthai, K.; Zwang, J.; Chaisri, U. Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Protein, iNOS, VEGF and COX-2 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC), Relationship with Angiogenesis and Their Clinico-Pathological Correlation. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2009, 14, E319–E324. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; McBride, W.H.; Chen, S.; Lee, K.; Hwang, T.; Jung, S.; Shau, H.; Liao, S.; Hong, J.; Chen, M. Prediction of Poor Survival by Cyclooxygenase-2 in Patients with T4 Nasopharyngeal Cancer Treated by Radiation Therapy: Clinical and in vitro Studies. Head Neck 2005, 27, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekimizu, M.; Ozawa, H.; Saito, S.; Ikari, Y.; Nakahara, N.; Nakamura, S.; Yoshihama, K.; Ito, F.; Watanabe, Y.; Imanishi, Y.; et al. Cyclo-oxygenase-2 Expression is Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis in Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Under the New TNM Classification. Anticancer. Res. 2019, 39, 5623–5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, P.A.; Stefanou, D.; Agnantis, N.J. COX-2 Expression Correlates with VEGF-C and Lymph Node Metastases in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2005, 18, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Li, S.; Cha, J.; Zhang, X.; Cha, I. Significance of Molecular Markers in Survival Prediction of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Head Neck 2012, 34, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Cha, I. A Novel Algorithm for Lymph Node Status Prediction of Oral Cancer before Surgery. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Lee, Y.S.; Kang, J.; Kim, Y.; Kang, C.S. Prognostic Significance of Expression of VEGF and Cox-2 in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and its Association with Expression of C-erbB2 and EGFR. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 103, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erovic, B.M.; Pelzmann, M.; Turhani, D.; Pammer, J.; Niederberger, V.; Neuchrist, C.; Grasl, M.C.; Thurner, D. Differential Expression Pattern of Cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Acta OtoLaryngol. 2003, 123, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Zhang, S.; Ishii, G.; Endoh, Y.; Kodama, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Hayashi, R.; Ebihara, S.; Cho, J.; Ochiai, A. Predictive Markers for Late Cervical Metastasis in Stage I and II Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Tongue. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, N.; Iyengar, A.; Majumdar, K.; Vidya, G.S.; Kumar, S.S. Quantitative Evaluation of Tumour-Associated Tissue Eosinophilia and Cyclo-oxegenase-2 Gene in Oral Cancer Patients with Assessment of Long Term Outcomes. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2016, 22, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryott, M.; Marklund, L.; Wangsa, D.; Elmberger, G.; Munck-Wikland, E. Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackett, M.K.; Bairati, I.; Meyer, F.; Jobin, E.; Lussier, S.; Fortin, A.; Gélinas, M.; Nabid, A.; Brochet, F.; Têtu, B. Prognostic Significance of Cyclooxygenase-2 Overexpression in Glottic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jia, L.; Guo, Q.; Ren, H.; Hu, Y.; Xie, T. Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Head and Neck Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 47265–47277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, J.A.; Nonaka, C.F.; da Costa Miguel, M.C.; de Almeida Freitas, R.; Galvão, H.C. Immunoexpression of Cyclooxygenase-2 and p53 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2009, 30, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Tang, T.; Xu, L.; Lu, J.J.; Lin, S.; Qiu, S.; Chen, G.; Tham, I.W. Prognostic Significance of Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor, and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Head Neck 2013, 35, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.W.; Kim, D.H.; Kowalski, D.P.; Burleson, J.A.; Son, Y.H.; Wilson, L.D.; Haffty, B.G. Prognostic Significance of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, M.C.; Laimer, J.; Chaux, A.; Schäfer, G.; Obrist, P.; Brunner, A.; Kronberger, I.E.; Laimer, K.; Gurel, B.; Koller, J.; et al. High Expression of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen in the Tumor-Associated Neo-Vasculature is Associated with Worse Prognosis in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baghban, A.A.; Taghavi, N.; Shahla, M. Combined Analysis of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression with Cyclooxygenase-2 and Mast Cell Density in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Pathobiology 2017, 84, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, S.; Fujiwara, M.; Matsuura, M.; Fujita, S.; Ikeda, H.; Asahina, I.; Ikeda, T. Prediction of Outcome of Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using Vascular Invasion and the Strongly Positive Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwa, J.S.; Kwon, O.J.; Park, J.J.; Woo, S.H.; Kim, J.P.; Ko, G.H.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, R.B. The Prognostic Value of Immunohistochemical Markers for Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 272, 2953–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindquist, D.; Ahrlund-Richter, A.; Tarján, M.; Tot, T.; Dalianis, T. Intense CD44 Expression is a Negative Prognostic Factor in Tonsillar and Base of Tongue Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2012, 32, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kekatpure, V.D.; Singh, M.; Selvam, S.; Shetkar, G.; Hedne, N.C.; Trivedi, N.P.; Siddappa, G.; Govindan, S.V.; Suresh, A.; Rangarajan, B.; et al. Factors Predicting Outcome After Salvage Treatment for Stage IV Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Evidence of the Potential Importance of the Cyclooxygenase-2–Prostaglandin E2 Pathway. Head Neck 2015, 37, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildeman, M.A.; Gibcus, J.H.; Hauptmann, M.; Begg, A.C.; van Velthuysen, M.L.; Hoebers, F.J.; Mastik, M.F.; Schuuring, E.; van der Wal, J.E.; van den Brekel, M.W. Radiotherapy in Laryngeal Carcinoma: Can a Panel of 13 Markers Predict Response? Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D. Abnormal COX2 Protein Expression May Be Correlated with Poor Prognosis in Oral Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 364207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, L.; Tsai, C.; Lung, O.; Dai, C.; Yu, M.; Ho, C.; Chen, C. Polymorphisms of COX-2 -765G > C and p53 Codon 72 and Risks of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Taiwan Population. Oral Oncol. 2008, 44, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, X.; Lippman, S.M.; Yang, H.; Lee, J.J.; Wu, X. Cyclooxygenase-2 Gene Polymorphisms Reduce the Risk of Oral Premalignant Lesions. Cancer 2009, 115, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, M.; Kapoor, V.; Mohanti, B.K.; Das, S.N. Functional Variants of COX-2 and Risk of Tobacco-Related Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in High-Risk Asian Indians. Oral Oncol. 2010, 46, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmi, A.; Muralidhar, S.; Kumar, C.K.; Kumar, A.P.; Chakravarthy, P.K.; Anjaneyulu, V.; Kaiser, J. Cyclooxygenase-2−765G>C Functional Promoter Polymorphism and Its Association with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2012, 3, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, W.H.; Lacko, M.; te Morsche, R.H.; Voogd, A.C.; Ophuis, M.B.; Manni, J.J. COX-2 Polymorphisms and the Risk for Head and Neck cancer in White Patients. Head Neck 2009, 31, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.; Chen, P.; Lee, C.; Ko, A.M.; Lee, K.; Lin, Y.; Ho, P.; Tu, H.; Wu, D.; Shieh, T.; et al. Up-regulation of Inflammatory Signalings by Areca Nut Extract and Role of Cyclooxygenase-2 -1195G>A Polymorphism Reveal Risk of Oral Cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8489–8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wei, B.; Shan, X.; Liu, P. -765G>C and 8473T>C Polymorphisms of COX-2 and Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis Based on 33 Case–Control Studies. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.T.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, K.C.; Wong, T.Y.; Ou, C.Y.; Tsai, S.T.; Yen, C.J.; Fang, S.Y.; Lo, H.I.; Wu, Y.H.; et al. Genetic Polymorphisms in the Prostaglandin Pathway Genes and Risk of Head and Neck Cancer. Oral Dis. 2015, 21, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, D.; Hashibe, M.; Zaridze, D.; Szeszenia-Dabrowska, N.; Mates, I.N.; Janout, V.; Holcatova, I.; Fabiánová, E.; Gaborieau, V.; Hung, R.J.; et al. Association of Common Polymorphisms in Inflammatory Genes with Risk of Developing Cancers of the Upper Aerodigestive Tract. Cancer Causes Control. 2007, 18, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Xia, L.; He, B.; Guo, J.; Huang, C.; Zeng, X. Cyclooxygenase-2-1195G>A Polymorphism and Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Susceptibility: A Meta-Analysis of 1564 Cases and 2346 Controls. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 3514–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Hao, S.; Sun, Y.; Hu, C.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Functional Polymorphisms in COX-2 Gene Are Correlated with the Risk of Oral Cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 580652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, W.; Wen, X.; Kwong, J.S.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Zeng, X. COX-2 rs689466, rs5275, and rs20417 Polymorphisms and Risk of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of Adjusted and Unadjusted data. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janakiraman, H.; House, R.P.; Talwar, S.; Courtney, S.M.; Hazard, E.S.; Hardiman, G.; Mehrotra, S.; Howe, P.H.; Gangaraju, V.; Palanisamy, V. Repression of caspase-3 and RNA-binding protein HuR cleavage by cyclooxygenase-2 promotes drug resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3137–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).