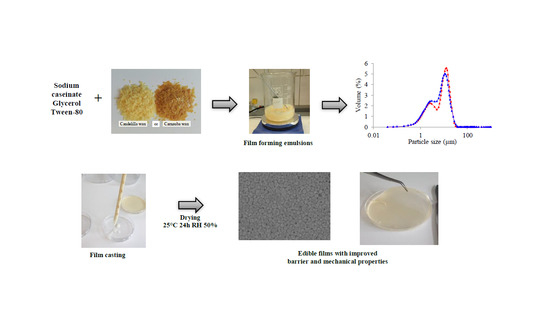
Effects of Candelilla and Carnauba Wax Incorporation on the Functional Properties of Edible Sodium Caseinate Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Particle Size Analysis
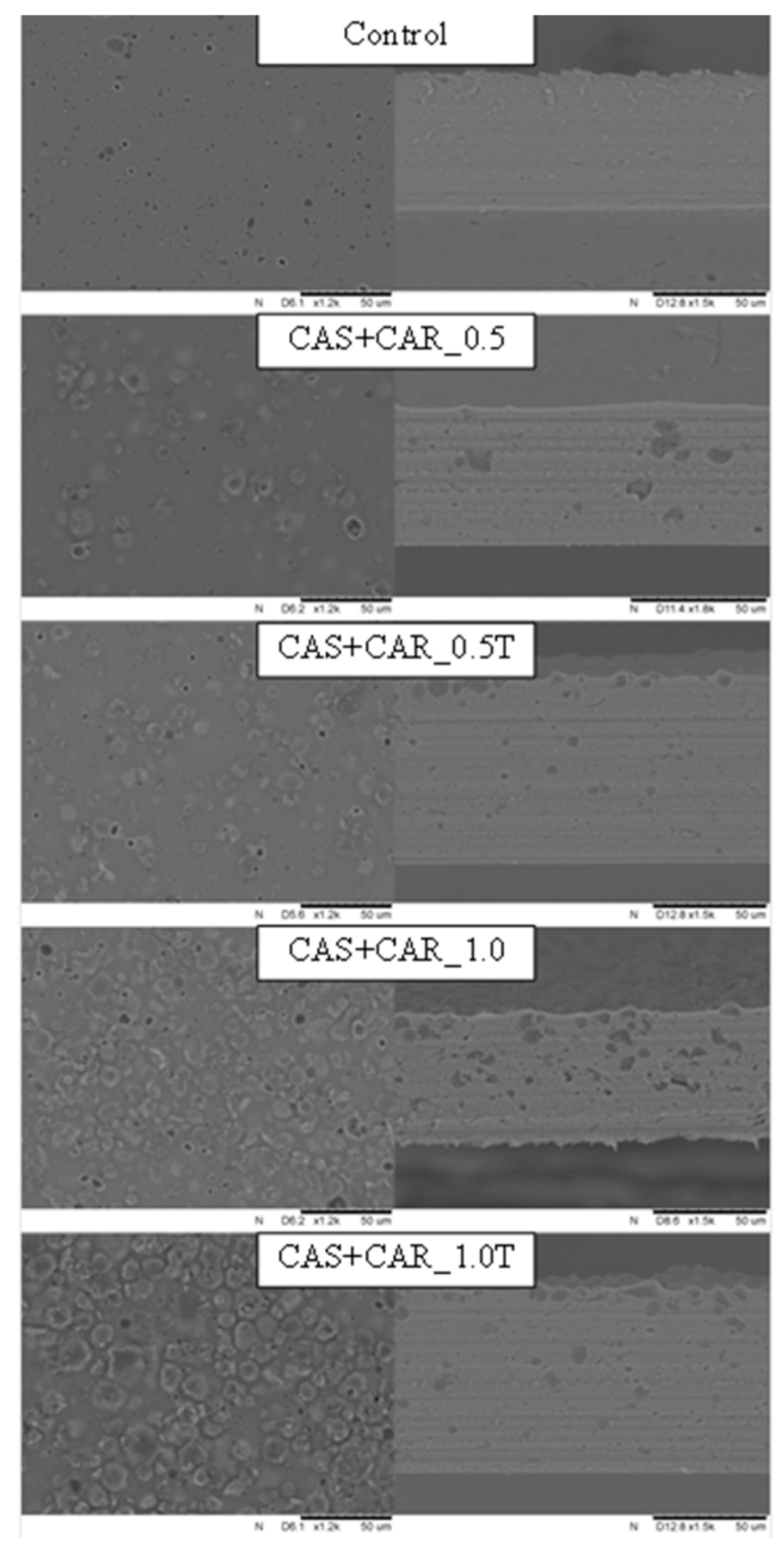
2.2. Film Microstructure
2.3. Water Solubility
2.4. Film Opacity
2.5. Color
2.6. Water Vapor Permeability
2.7. Mechanical Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Film-Forming Emulsions
3.3. Particle Size Analysis
3.4. Film Formation Method
3.5. Film Thickness
3.6. Water Solubility
3.7. Color
3.8. Film Opacity
3.9. Water Vapor Permeability
3.10. Mechanical Properties
3.11. Film Microstructure
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassan, B.; Chatha, S.A.S.; Hussain, A.I.; Zia, K.M.; Akhtar, N. Recent advances on polysaccharides, lipids and protein based edible films and coatings: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maringgal, B.; Hashim, N.; Tawakkal, I.S.M.A.; Mohamed, M.T.M. Recent advance in edible coating and its effect on fresh/fresh-cut fruits quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 96, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, B.; Qadri, O.S.; Srivastava, A.K. Recent developments in shelf-life extension of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables by application of different edible coatings: A review. LWT 2018, 89, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraśniewska, K.; Galus, S.; Gniewosz, M. Biopolymers-based Mmaterials containing silver nanoparticles as active packaging for food applications—A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, R.; Sabbah, M.; Di Pierro, P. Biopolymers as food packaging materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falguera, V.; Quintero, J.P.; Jiménez, A.; Muñoz, J.A.; Ibarz, A. Edible films and coatings: Structures, active functions and trends in their use. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S.; Arik Kibar, E.A.; Gniewosz, M.; Kraśniewska, K. Novel materials in the preparation of edible films and coatings—A review. Coatings 2020, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syahida, S.N.; Fitry, M.R.I.; Ainum, Z.M.A.; Hanani, Z.A.N. Effects of palm wax on the physical, mechanical and water barrier properties of fish gelatin films for food packaging application. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 23, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucedo-Pompa, S.; Rojas-Molina, R.; Aguilera-Carbó, A.F.; Saenz-Galindo, A.; de La Garza, H.; Jasso-Cantú, D.; Aguilar, C.N. Edible film based on candelilla wax to improve the shelf life and quality of avocado. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiumarelli, M.; Hubinger, M.D. Stability, solubility, mechanical and barrier properties of cassava starch—Carnauba wax edible coatings to preserve fresh-cut apples. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, C.A.S.; de Sousa, P.H.M.; Soares, D.J.; da Silva, J.Y.G.; Benjamin, S.R.; Guedes, M.I.F. Carnauba wax uses in food—A review. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huck-Iriart, C.; Álvarez-Cerimedo, M.S.; Candal, R.J.; Herrera, M.L. Structures and stability of lipid emulsions formulated with sodium caseinate. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramescu, S.M.; Butean, C.; Popa, C.V.; Ortan, A.; Moraru, I.; Temocico, G. Edible and functionalized films/coatings-performances and perspectives. Coatings 2020, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, M.J.; Talens, P.; Chiralt, A. Tensile properties and water vapor permeability of sodium caseinate films containing oleic acid–beeswax mixtures. J. Food Eng. 2008, 85, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereda, M.; Aranguren, M.I.; Marcovich, N.E. Caseinate films modified with tung oil. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereda, M.; Marcovich, N.E.; Mosiewicki, M.A. Sodium caseinate films containing linseed oil resin as oily modifier. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsakidou, A.; Tsimidou, M.Z.; Kiosseoglou, V. Storage behavior of caseinate-based films incorporating maize germ oil bodies. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzoska, N.; Muller, M.; Nasui, L.; Schmid, M. Effects of film constituents on packaging-relevant properties of sodium caseinate-based emulsion films. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 114, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, M.J.; Talens, P.; Chiralt, A. Microstructure and optical properties of sodium caseinate films containing oleic acid–beeswax mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, M.J.; Jimenez, A.; Atares, L.; Talens, P.; Chiralt, A. Effect of fatty acids and beeswax addition on properties of sodium caseinate dispersions and films. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, E.; Chaabani, A.; Assezat, G.; Prochazka, F.; Oulahal, N. Casein/wax blend extrusion for production of edible films as carriers of potassium sorbate—A comparative study of waxes and potassium sorbate effect. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2018, 16, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S.; Kadzinska, J. Food applications of emulsion-based edible films and coatings. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Joya, J.A.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Ventura-Sobrevilla, J.; Aguilar-Gonzalez, M.A.; Carbó-Argibay, E.; Castro, L.P.; Aguilar, C.N. Candelilla wax-based coatings and films: Functional and physicochemical characterization. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2019, 12, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Mirabzadeh, S.; Shahvalizadeh, R.; Hamishehkar, H. Development of novel active packaging films based on whey protein isolate incorporated with chitosan nanofiber and nano-formulated cinnamon oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talens, P.; Krochta, J.M. Plasticizing effects of beeswax and carnauba wax on tensile and water vapor permeability properties of whey protein films. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, E239–E243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, M.; Albors, A.; Chiralt, A.; González-Martínez, C. Characterization of chitosan–oleic acid composite films. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Fan, D.D. Exploration of the pore-forming mechanisms of Tween80 and biocompatibility of the hydrogels in vivo. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.Y. Chitosan-whey protein isolate composite films for encapsulation and stabilization of fish oil containing ultra ure omega-3 fatty acids. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C133–C141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodpran, T.; Benjakul, S.; Songtipya, P. Effect of emulsifier on properties and microstructures of surimi protein/palm oil composite film. Res. J. Appl. Sci. 2016, 11, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Lyu, F.; Ding, Y.T.; Zhou, X.X. Effects of oil droplet size and interfacial protein film on the properties of fish myofibrillar protein-oil composite gels. Molecules 2020, 25, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, R.; Chanona, J.; Hernández, P.; Gutiérrez, G.; Chiralt, A. Gloss and transparency of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose films containing surfactants as affected by their microstructure. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.; Fabra, M.J.; Talens, P.; Chiralt, A. Effect of lipid self-association on the microstructure and physical properties of hydroxypropyl-methylcellulose edible films containing fatty acids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscat, D.; Adhikari, R.; McKnight, S.; Guo, Q.P.; Adhikari, B. The physicochemical characteristics and hydrophobicity of high amylose starch-glycerol films in the presence of three natural waxes. J. Food Eng. 2013, 119, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiumarelli, M.; Hubinger, M.D. Evaluation of edible films and coatings formulated with cassava starch, glycerol, carnauba wax and stearic acid. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Simpson, B.K.; Dumont, M.-J. Effect of beeswax and carnauba wax addition on properties of gelatin films: A comparative study. Food Biosci. 2018, 26, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S. Functional properties of soy protein isolate edible films as affected by rapeseed oil concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 85, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Weller, C.L.; Hanna, M.A.; Gennadios, A. heat curing of soy protein films at selected temperatures and pressures. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 35, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soazo, M.; Perez, L.M.; Rubiolo, A.C.; Verdini, R.A. Effect of freezing on physical properties of whey protein emulsion films. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.K.; Silva, K.N.; Xavier, T.D.; Leite, R.H.; Aroucha, E.M. Effect of the addition of carnauba wax on physicochemical properties of chitosan films. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soazo, M.; Rubiolo, A.C.; Verdini, R.A. Effect of drying temperature and beeswax content on physical properties of whey protein emulsion films. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzadi, M.; Jafari, S.M.; Mirzaei, H.; Chegini, F.K.; Maghsoudlou, Y.; Dehnad, D. Physical and mechanical properties in biodegradable films of whey protein concentrate-pullulan by application of beeswax. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 118, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, T.M.; Pinto, A.M.B.; de Oliveira, A.V.; Ribeiro, H.L.; Caceres, C.A.; Ito, E.N.; Azeredo, H.M.C. Physical properties of cassava starch-carnauba wax emulsion films as affected by component proportions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 2045–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S.; Kadzinska, J. Whey protein edible films modified with almond and walnut oils. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Matta, M.D.; Sarmento, S.B.S.; Sarantopoulos, C.I.G.L.; Zocchi, S.S. Barrier properties of films of pea starch associated with xanthan gum and glycerol. Polímeros 2011, 21, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Baraniak, B. Effect of candelilla wax on functional properties of biopolymer emulsion films—A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 41, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Gustaw, W.; Zięba, E.; Lisiecki, S.; Stadnik, J.; Baraniak, B. Microstructure and functional properties of sorbitol-plasticized pea protein isolate emulsion films: Effect of lipid type and concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, M.H.; Wang, Y.; Pang, J. Konjac glucomannan-based composite films fabricated in the presence of carnauba wax emulsion: Hydrophobicity, mechanical and microstructural properties evaluation. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 5138–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajak, P.; Przetaczek-Roznowska, I.; Juszczak, L. Development and physicochemical, thermal and mechanical properties of edible films based on pumpkin, lentil and quinoa starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjarasskul, T.; Rauch, D.J.; McCarthy, K.L.; Krochta, J.M. Barrier and tensile properties of whey protein–candelilla wax film/sheet. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 56, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hassan, A.A.; Norziah, M.H. Starch-gelatin edible films: Water vapor permeability and mechanical properties as affected by plasticizers. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 26, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S.; Lenart, A. Optical, mechanical, and moisture sorption properties of whey protein edible films. J. Food Process. Eng. 2019, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.W.; Gennadios, A.; Weller, C.L.; Cezeirat, C.; Hanna, M.A. Soy protein isolate dialdehyde starch films. Ind. Crops Prod. 1998, 8, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobral, P.J.A.; dos Santos, J.S.; Garcia, F.T. Effect of protein and plasticizer concentrations in film forming solutions on physical properties of edible films based on muscle proteins of a Thai Tilapia. J. Food Eng. 2005, 70, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeaufort, F.; Martinpolo, M.; Voilley, A. Polarity homogeneity and structure affect water-vapor permeability of model edible films. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, C.; Abugoch, L.; Tapia, C. Quinoa protein–chitosan–sunflower oil edible film: Mechanical, barrier and structural properties. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Film | CAS (%) | GLY (%) | CAN (%) | CA (%) | T (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8 | 4 | - | - | - |
| CAS_CAN_0.5 | 8 | 4 | 0.5 | - | - |
| CAS_CAN_0.5T | 8 | 4 | 0.5 | - | 0.09 |
| CAS_CAN_1 | 8 | 4 | 1 | - | - |
| CAS_CAN_1T | 8 | 4 | 1 | - | 0.18 |
| CAS_CAR_0.5 | 8 | 4 | - | 0.5 | - |
| CAS_CAR_0.5T | 8 | 4 | - | 0.5 | 0.09 |
| CAS_CAR_1 | 8 | 4 | - | 1 | - |
| CAS_CAR_1T | 8 | 4 | - | 1 | 0.18 |
| Film | d10 (µm) | d50 (µm) | d90 (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAS_CAN_0.5 | 1.20 ± 0.13 a | 7.74 ± 0.09 d | 16.5 ± 0.05 e |
| CAS_CAN_0.5T | 1.14 ± 0.08 a | 4.31 ± 0.03 b | 11.7 ± 0.06 c |
| CAS_CAN_1 | 1.24 ± 0.12 a | 8.04 ± 0.07 e | 16.7 ± 0.08 e |
| CAS_CAN_1T | 1.14 ± 0.08 a | 4.32 ± 0.01 b | 11.7 ± 0.06 c |
| CAS_CAR_0.5 | 1.16 ± 0.12 a | 6.43 ± 0.10 c | 15.6 ± 0.18 d |
| CAS_CAR_0.5T | 1.08 ± 0.16 a | 3.08 ± 0.06 a | 8.17 ± 0.06 a |
| CAS_CAR_1 | 1.18 ± 0.14 a | 7.97 ± 0.17 e | 16.7 ± 0.08 e |
| CAS_CAR_1T | 1.04 ± 0.11 a | 3.12 ± 0.03 a | 8.56 ± 0.08 b |
| Film | Water Solubility (%) |
|---|---|
| Control | 45.53 ± 0.29 b |
| CAS_CAN_0.5 | 43.79 ± 0.16 a |
| CAS_CAN_0.5T | 43.92 ± 0.28 ac |
| CAS_CAN_1 | 43.41 ± 0.27 a |
| CAS_CAN_1T | 43.61 ± 0.36 a |
| CAS_CAR_0.5 | 45.38 ± 0.31 be |
| CAS_CAR_0.5T | 45.42 ± 0.12 b |
| CAS_CAR_1 | 44.46 ± 0.53 cd |
| CAS_CAR_1T | 44.76 ± 0.20 de |
| Film | L* | a* | b* | ΔE | Opacity (A·mm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 98.9 ± 0.03 f | −0.85 ± 0.01 g | 3.50 ± 0.03 f | 1.73 ± 0.03 f | 2.28 ± 0.50 d |
| CAS_CAN_0.5 | 97.2 ± 0.63 e | −2.21 ± 0.16 e | 4.84 ± 0.74 e | 2.75 ± 0.82 e | 6.40 ± 1.29 a |
| CAS_CAN_0.5T | 96.1 ± 0.84 a | −2.53 ± 0.23 be | 7.04 ± 1.56 ab | 5.24 ± 1.78 ab | 4.62 ± 0.70 b |
| CAS_CAN_1 | 96.6 ± 0.37 ae | −2.37 ± 0.10 be | 6.73 ± 0.64 a | 4.75 ± 0.72 a | 7.03 ± 0.92 a |
| CAS_CAN_1T | 95.9 ± 0.49 a | −2.82 ± 0.12 cd | 7.48 ± 0.87 abc | 5.74 ± 0.99 abc | 5.45 ± 0.92 ab |
| CAS_CAR_0.5 | 95.9 ± 0.63 ab | −2.56 ± 0.14 be | 8.90 ± 0.01 c | 7.04 ± 1.35 c | 6.85 ± 0.96 a |
| CAS_CAR_0.5T | 95.9 ± 0.48 ab | −2.62 ± 0.17 ad | 8.43 ± 0.74 bc | 6.60 ± 0.86 bc | 5.71 ± 0.45 ab |
| CAS_CAR_1 | 95.1 ± 0.45 bd | −2.95 ± 0.16 c | 12.7 ± 0.97 d | 10.9 ± 1.06 d | 10.55 ± 1.64 c |
| CAS_CAR_1T | 94.1 ± 0.87 c | −3.22 ± 0.16 f | 13.8 ± 1.49 d | 12.3 ± 1.69 d | 10.05 ± 1.77 c |
| Film | WVP (×10−10 g·m−1·Pa−1·s−1) |
|---|---|
| Control | 4.75 ± 0.10 e |
| CAS_CAN_0.5 | 3.52 ± 0.07 cd |
| CAS_CAN_0.5T | 2.83 ± 0.04 a |
| CAS_CAN_1 | 3.06 ± 0.14 abc |
| CAS_CAN_1T | 2.66 ± 0.27 a |
| CAS_CAR_0.5 | 3.90 ± 0.11 d |
| CAS_CAR_0.5T | 3.66 ±0.12 d |
| CAS_CAR_1 | 3.45 ± 0.25 bcd |
| CAS_CAR_1T | 3.05 ± 0.18 ab |
| Film | TS (MPa) | E (%) | YM (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.65 ± 0.42 a | 142. 0 ± 31.3 ef | 0.26 ± 0.06 a |
| CAS_CAN_0.5 | 2.30 ± 0.49 a | 120.1 ± 25.9 de | 0.64 ± 0.18 abc |
| CAS_CAN_0.5T | 4.78 ± 1.11 b | 159.9 ± 22.4 f | 1.66 ± 0.50 d |
| CAS_CAN_1 | 2.60 ± 0.7 a | 68.9 ± 17.1 ab | 0.62 ± 0.10 abc |
| CAS_CAN_1T | 4.73 ± 1.51 b | 102.4 ± 16.5 bcd | 1.78 ± 0.55 d |
| CAS_CAR_0.5 | 1.91 ± 0.34 a | 76.6 ± 24.2 abc | 0.48 ± 0.15 ab |
| CAS_CAR_0.5T | 2.50 ± 0.43 a | 114.5 ± 29.9 cde | 0.68 ± 0.15 abc |
| CAS_CAR_1 | 2.28 ± 0.72 a | 63.7 ± 19.5 a | 0.71 ± 0.15 bc |
| CAS_CAR_1T | 2.84 ± 0.65 a | 93.4 ± 21.1 abcd | 0.96 ± 0.12 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galus, S.; Gaouditz, M.; Kowalska, H.; Debeaufort, F. Effects of Candelilla and Carnauba Wax Incorporation on the Functional Properties of Edible Sodium Caseinate Films. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249349
Galus S, Gaouditz M, Kowalska H, Debeaufort F. Effects of Candelilla and Carnauba Wax Incorporation on the Functional Properties of Edible Sodium Caseinate Films. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(24):9349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249349
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalus, Sabina, Margaux Gaouditz, Hanna Kowalska, and Frédéric Debeaufort. 2020. "Effects of Candelilla and Carnauba Wax Incorporation on the Functional Properties of Edible Sodium Caseinate Films" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 24: 9349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249349
APA StyleGalus, S., Gaouditz, M., Kowalska, H., & Debeaufort, F. (2020). Effects of Candelilla and Carnauba Wax Incorporation on the Functional Properties of Edible Sodium Caseinate Films. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(24), 9349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249349