Molecular Characterization of Constipation Disease as Novel Phenotypes in CRISPR-Cas9-Generated Leptin Knockout Mice with Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
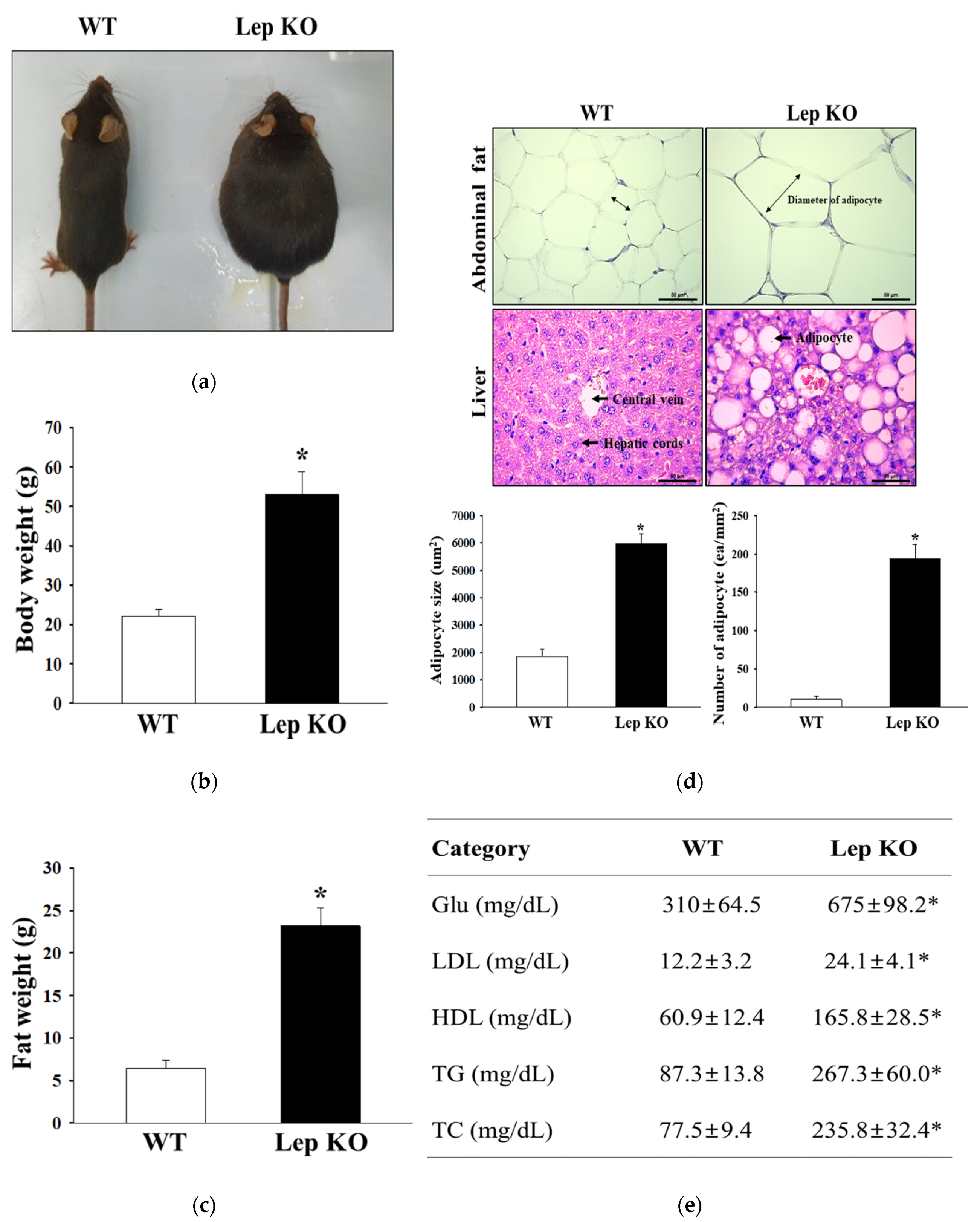
2.1. Confirmation of Obesity Phenotypes in Lep KO Mice
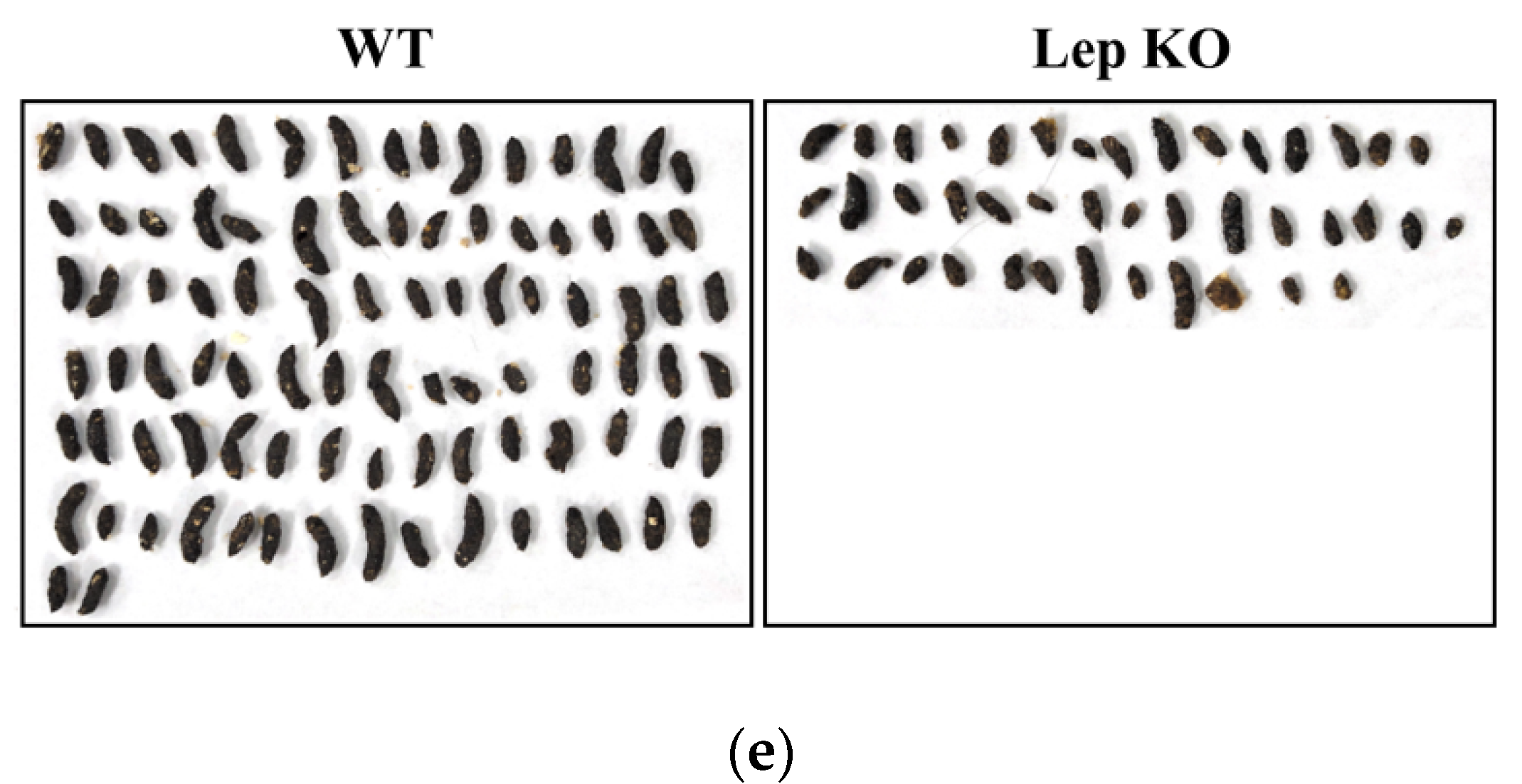
2.2. Alterations on the Feeding Behavior and Stool Parameters of Lep KO Mice
2.3. Alterations on the Gastrointestinal Motility and Intestinal Length of Lep KO Mice
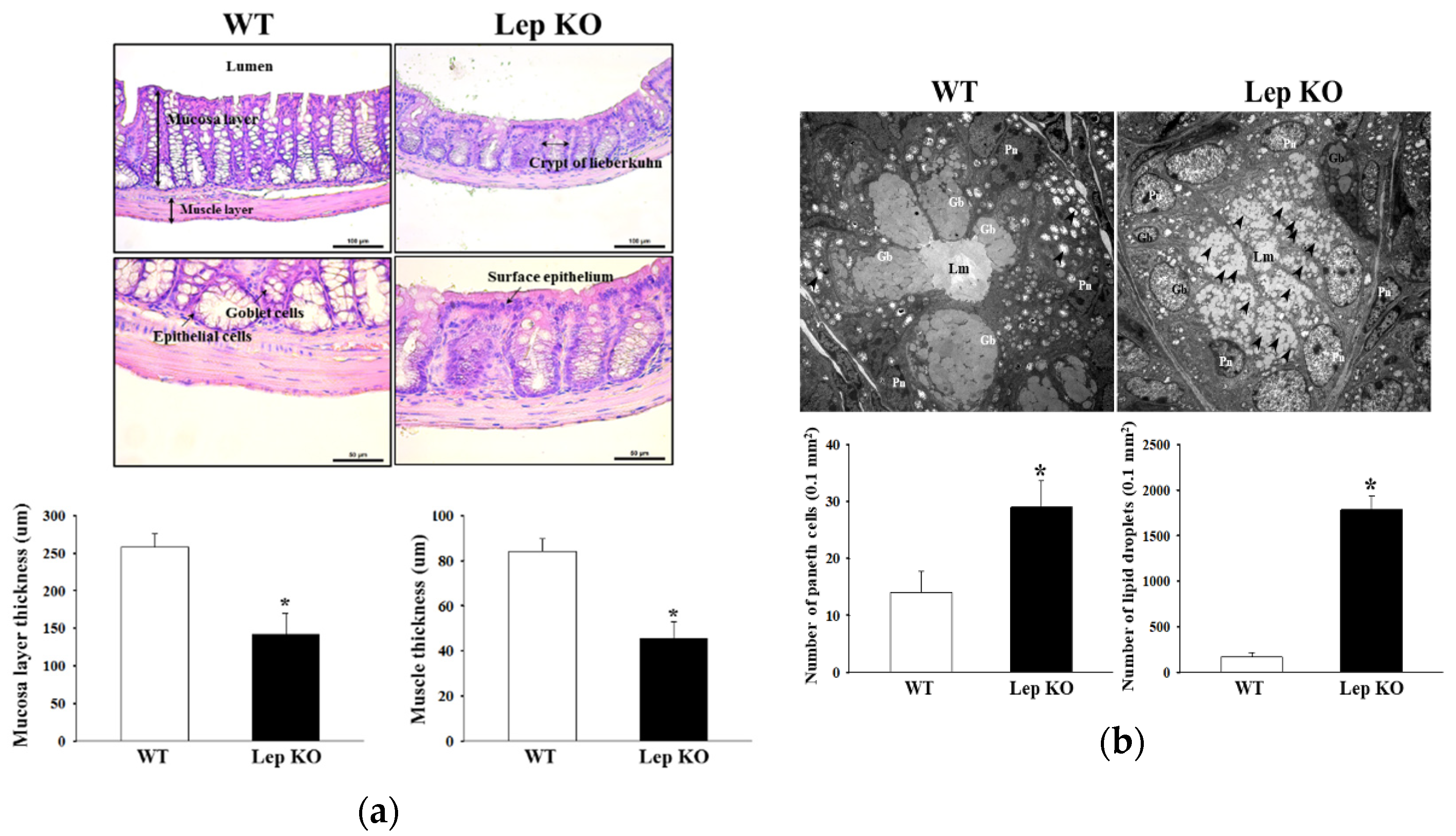
2.4. Alterations in the Histopathological and Cytological Structure in the Transverse Colon of Lep KO Mice
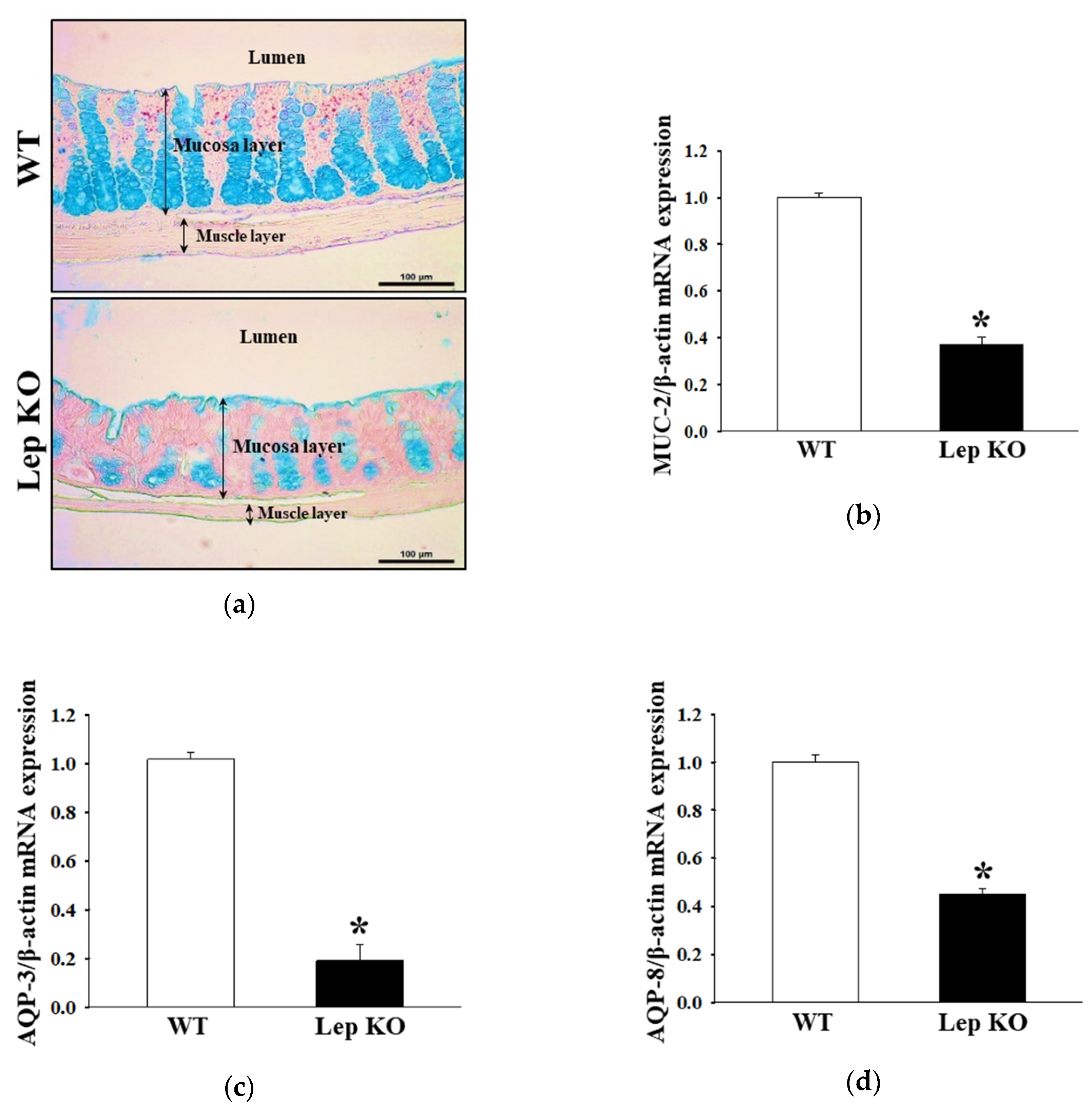
2.5. Alterations on the Mucin Secretion Ability and Membrane Water Channel Expression in the Transverse Colon of Lep KO Mice
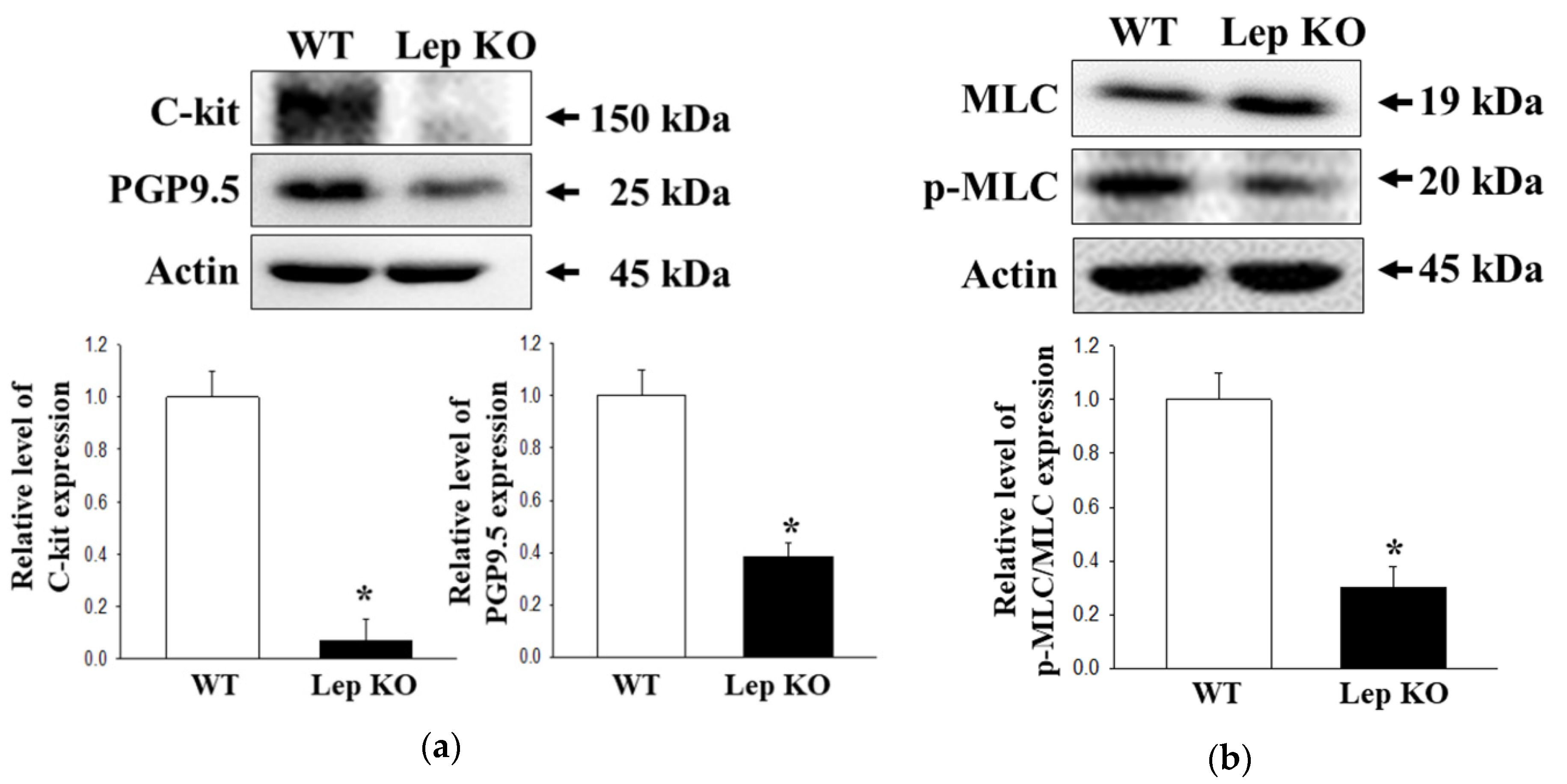
2.6. Alterations on the Loss of Nitrergic Enteric and Myenteric Neurons in the Transverse Colon of Lep KO Mice
2.7. Alterations on the Smooth Muscle Contraction in the Transverse Colon of Lep KO Mice
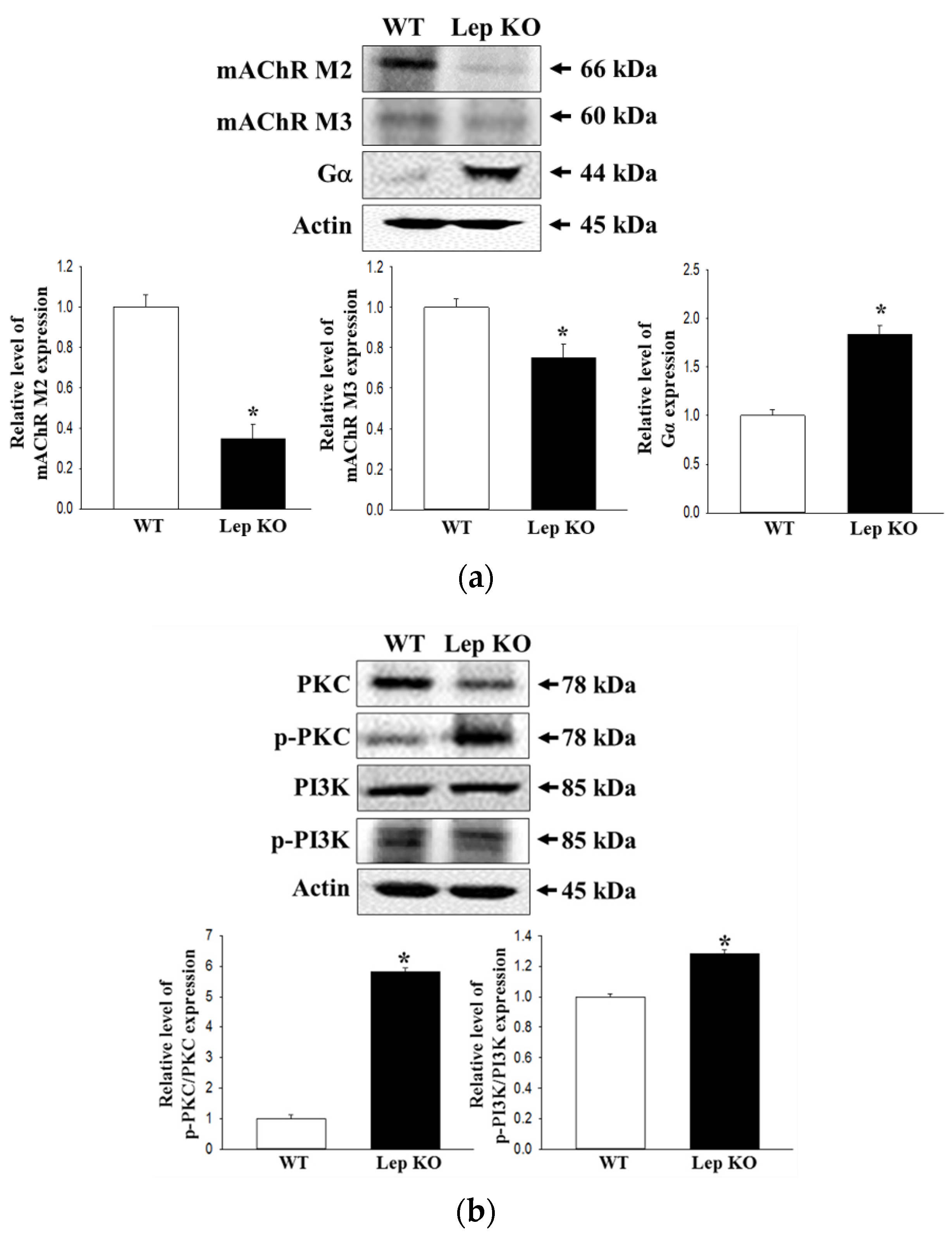
2.8. Alterations on the Downstream Signaling Pathway of mAChRs in the Transverse Colon of Lep KO Mice
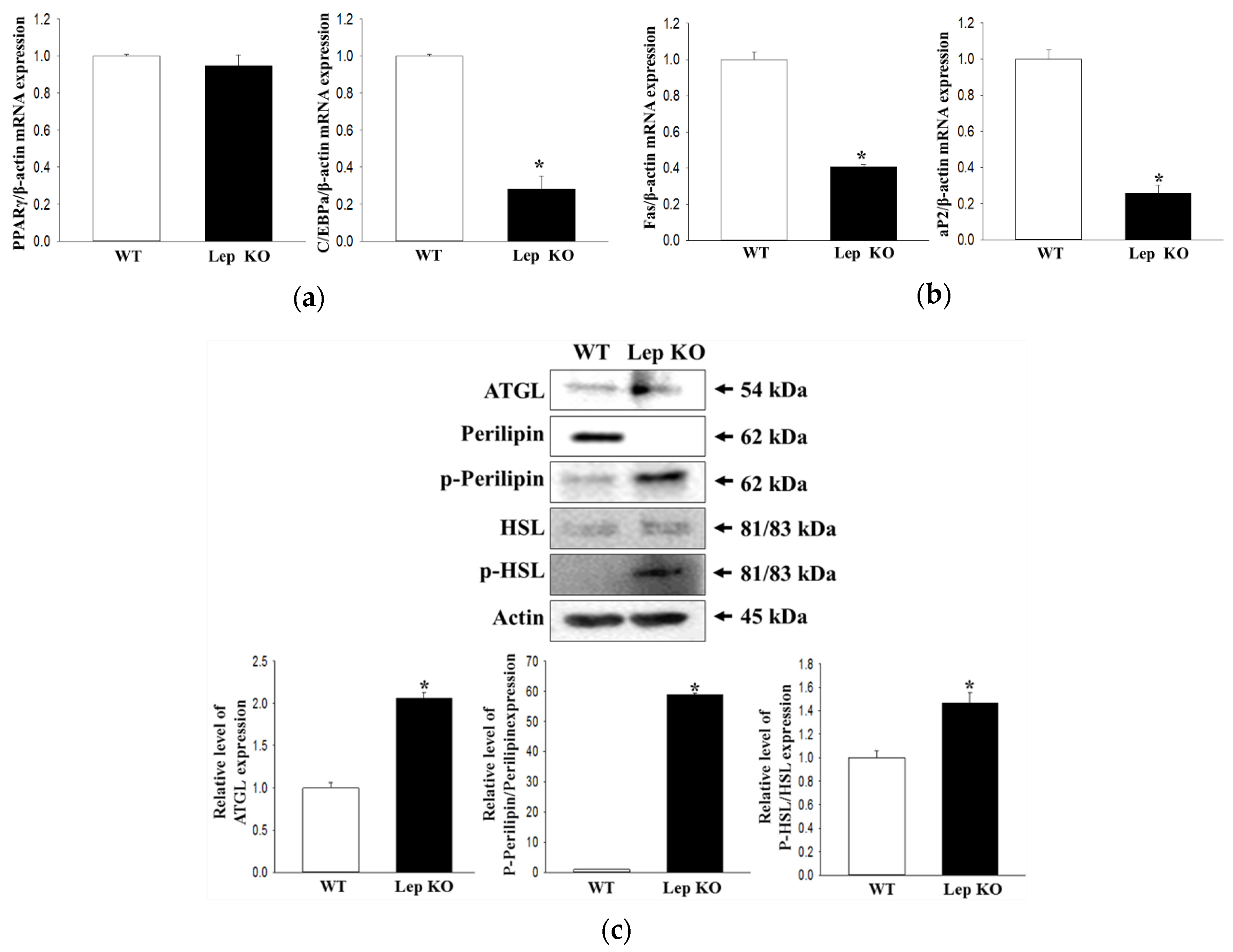
2.9. Alterations on the Adipogenesis and Lipolysis in the Transverse Colon of Lep KO Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Study
4.2. Measurement of Body and Fat Weight
4.3. Measurement of Food Intake and Water Consumption
4.4. Measurement of Stool Parameters
4.5. Measurement of Gastrointestinal Transit Ratio and Intestinal Length
4.6. Histopathological Analysis
4.7. Serum Biochemical Analysis
4.8. TEM Analysis
4.9. Western Blotting Analysis
4.10. Quantitative Real-Time-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) Analysis
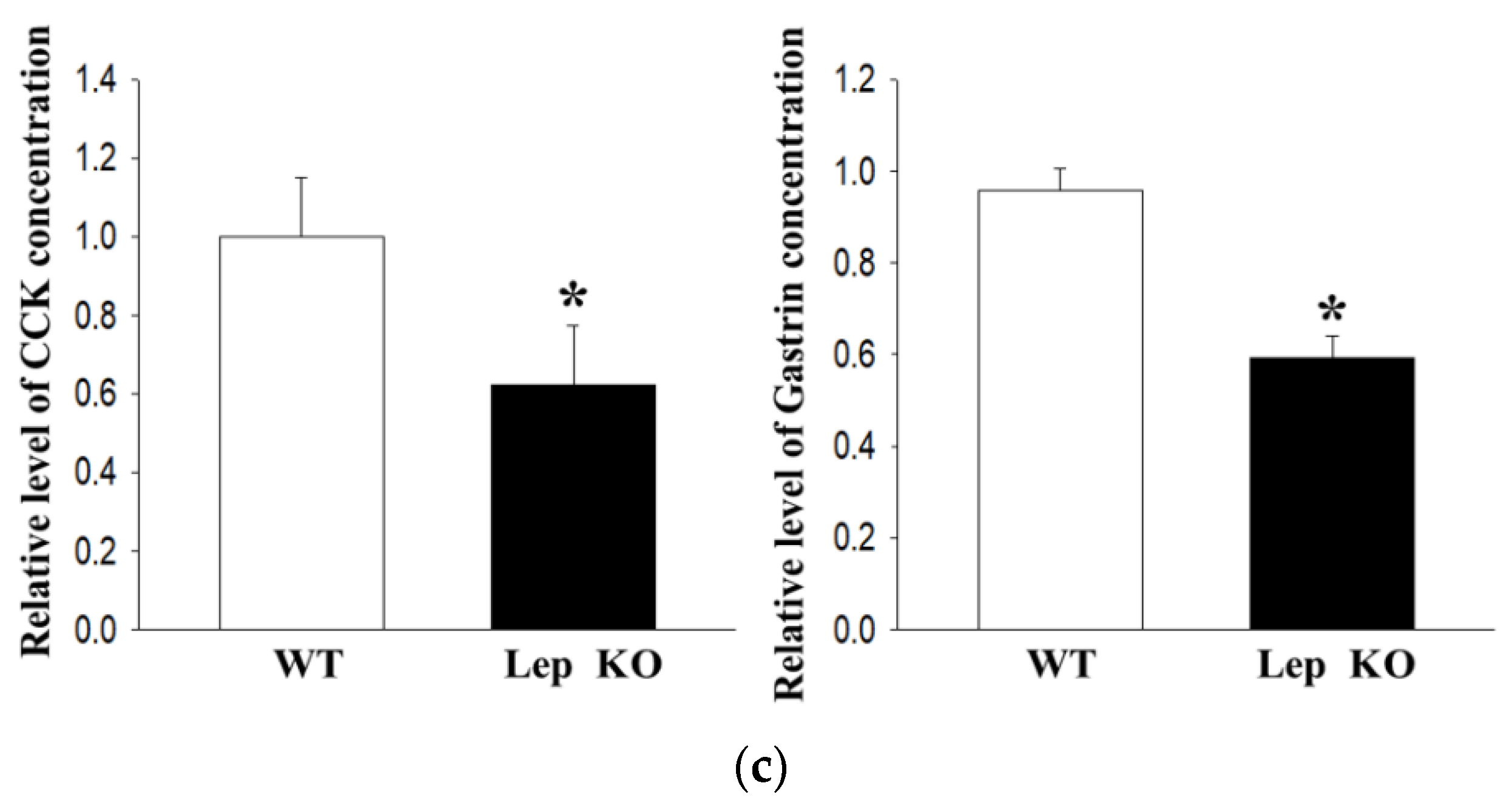
4.11. Measurement of GI Hormone Concentrations
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GEM | genetically engineered mice |
| Lep | leptin |
| KO | knockout |
| ICC | intestinal Cajal cells |
| GI | gastrointestinal |
| mAChRs | muscarinic acetylcholine receptors |
| PTHS | Pitt-Hopkins syndrome |
| A2BAR | adenosine 2B receptor |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| TZDs | thiazolidinediones |
| WT | wild type |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| Glu | glucose |
| LDL-C | low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol |
| HDL-C | high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol |
| TG | triglyceride |
| TC | total cholesterol |
| TEM | tansmission electron microscopy |
| MUC2 | mucin 2 |
| AQP | aquaporin |
| nNOS | neuronal nitric oxide synthase |
| NSE | neuron-specific enolase |
| AChE | acetylcholinesterase |
| C-kit | Receptor tyrosine kinase |
| PGP9.5 | protein gene product 9.5 |
| MLC | Myosin light chain |
| CCK | cholecystokinin |
| PKC | protein kinase C |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinases |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| C/EBP | CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein |
| aP2 | fatty acid-binding protein |
| FAS | fatty acid synthase |
| ATGL | adipose triglyceride lipase |
| HSL | hormone-sensitive lipase |
| ENU | N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea |
| HPA | hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal |
| VLDL | very-low-density lipoprotein |
| ICR | institute of cancer research |
| SD | Sprague Dawley |
| TRPV1 | transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| cDNA | complementary DNA |
References
- Walia, R.; Mahajan, L.; Steffen, R. Recent advances in chronic constipation. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2009, 21, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, I.J.D.; Ong, S.; Mercer-Jones, M. Chronic constipation in adults. BMJ 2009, 338, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, A.V.; Tack, J.; Quigley, E.M.; Talley, N.J. Pharmacological management of constipation. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2009, 21, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, H.; Zhao, X.; Qian, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Xie, J.; Li, J. Therapeutic effect of activated carbon-induced constipation mice with Lactobacillus fermentum Suo on treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 21875–21895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Lee, M.R.; Park, J.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Song, B.R.; Son, H.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Kim, K.M.; Hong, J.T.; Hwang, D.Y. Quercetin promotes gastrointestinal motility and mucin secretion in loperamide-induced constipation of SD rats through regulation of the mAChRs downstream signal. Pharm. Biol. 2018, 56, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Yu, Y.; Wang, P.; Dong, Y.; Wang, T.; Zuo, X.; Li, Y. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor accelerates gut motility in slow-transit constipation. Acta Physiol. 2014, 212, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Park, J.J.; Lee, M.R.; Choi, J.Y.; Song, B.R.; Park, J.W.; Kang, M.J.; Son, H.J.; Hong, J.T.; Hwang, D.Y. Constipation in Tg2576 mice model for Alzheimer’s disease associated with dysregulation of mechanism involving the mAChR signaling pathway and ER stress response. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubišić, V.; Kennedy, A.J.; Sweatt, J.D.; Parpura, V. Pitt-Hopkins mouse model has altered particular gastrointestinal transits in vivo. Autism Res. 2015, 8, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaji, M.; Mahmoud, M.; Evans, I.M.; Zachary, I.C. Neuropilin 1 is essential for gastrointestinal smooth muscle contractility and motility in aged mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekharan, B.P.; Kolachala, V.L.; Dalmasso, G.; Merlin, D.; Ravid, K.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Srinivasan, S. Adenosine 2B receptors (A(2B)AR) on enteric neurons regulate murine distal colonic motility. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2727–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktar, R.; Peiris, M.; Fikree, A.; Cibert-Goton, V.; Walmsley, M.; Tough, I.R.; Watanabe, P.; Araujo, E.J.A.; Mohammed, S.D.; Delalande, J.M.; et al. The extracellular matrix glycoprotein tenascin-X regulates peripheral sensory and motor neurones. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 4237–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, R.; Handa, O.; Naito, Y.; Takayama, S.; Suyama, Y.; Ushiroda, C.; Majima, A.; Hirai, Y.; Mizushima, K.; Okayama, T.; et al. High-fat diet causes constipation in mice via decreasing colonic mucus. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.; Spiegel, B.M.R. The Relationship between obesity and functional gastrointestinal disorders: Causation, association, or neither? Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 2008, 4, 572–578. [Google Scholar]
- Ingalls, A.M.; Dickie, M.M.; Snell, G.D. Obese, a new mutation in the house mouse. J. Hered 1950, 41, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaas, J.L.; Gajiwala, K.S.; Maffei, M.; Cohen, S.L.; Chait, B.T.; Rabinowitz, D.; Lallone, R.L.; Burley, S.K.; Friedman, J.M. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science 1995, 269, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.L. Obese and diabetes: two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia 1978, 14, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarges, R.; Hank, R.F.; Blake, J.F.; Bordner, J.; Bussolotti, D.L.; Hargrove, D.M.; Treadway, J.L.; Gibbs, E.M. Glucose transport enhancing and hypoglycemic activity of 2-methyl-2phenoxy-3-phenylpropanoic acids. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 4783–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, P.W.; Cawthorne, M.A.; Coyle, P.J.; Holder, J.C.; Holman, G.D.; Kozka, I.J.; Kirkham, D.M.; Lister, C.A.; Smith, S.A. Repeat treatment of obese mice with BRL 49653, a new potent insulin sensitizer, enhances insulin action in white adipocytes. Association with increased insulin binding and cell-surface GLUT4 as measured by photoaffinity labeling. Diabetes 1995, 44, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nanteuil, G.; Herve, Y.; Duhault, J.; Espinal, J.; Boulanger, M.; Ravel, D. Euglycemic and biological activities of novel thiazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives. Arzneimittel-forschung 1995, 45, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, J.I.; Lee, J.H.; Park, S.U.; Kang, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, A.R.; Choi, D.J.; Cha, J.Y.; Lee, H.W. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated generation of obese and diabetic mouse models. Exp. Anim. 2018, 67, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecora, P.; Suraci, C.; Antonelli, M.; De Maria, S.; Marrocco, W. Constipation and obesity: a statistical analysis. Boll Soc. Ital. Biol. Sper. 1981, 57, 2384–2388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.R.; Xu, X.J.; Yao, S.K. Increased intestinal mycosal leptin levels in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qarawi, A.A.; Ali, B.H.; Al-Mougy, S.A.; Mousa, H.M. Gastrointestinal transit in mice treated with various extracts. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J. Aging decreases the density of colonic interstitial cells of Cajal associated with constipation in rats. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiskur, B.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B. The aging colon: The role of enteric neurodegeneration in constipation. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 12, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, K.M.; Koh, S.D.; Ro, S.; War, S.M. Regulation of gastrointestinal motility—insights from smooth muscle biology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttichau, H.R.; Van Solinge, W.W.; Nielsen, F.C.; Rehfeld, J.F. Developmental expression of the gastrin and cholecystokinin genes in rat colon. Gastroenterology 1993, 104, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargeas, M.J.; Bassotti, G.; Fioramonti, J.; Bueno, L. Involvement of different mechanisms in the stimulatory effects of cholecystokinin octapeptide on gastrointestinal and colonic motility in dogs. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1989, 67, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedell, M.A.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G. Mouse models of human disease. Part I: Techniques and resources for genetic analysis in mice. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardouin, S.N.; Nagy, A. Mouse models for human disease. Clin. Genet 2000, 57, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, L.J.; Silha, J.V. Unexpected and unexplained phenotypes in transgenic models. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2000, 10, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbaric, I.; Miller, G.; Dear, T.N. Appearances can be deceiving: phenotypes of knockout mice. Brief Funct Genomics 2007, 6, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.J.; Ellacott, K.L.J.; King, V.L.; Hasty, A.H. Mouse models of the metabolic syndrome. Dis. Model Mech. 2010, 3, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malendowicz, L.K.; Rucinski, M.; Belloni, A.S.; Ziolkowska, A.; Nussdorfer, G.G. Leptin and the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2007, 263, 63–102. [Google Scholar]
- Genuth, S.M.; Przybylski, R.J.; Rosenberg, D.M. Insulin resistance in genetically obese, hyperglycemic mice. Endocrinology 1971, 88, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.L.; Hummel, K.P. The influence of genetic background on the expression of the obese (ob) gene in the mouse. Diabetologia 1973, 9, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishina, P.M.; Lowe, S.; Wang, J.; Paigen, B. Characterization of plasma lipids in genetically obese mice: the mutants obese, diabetes, fat, tubby, and lethal yellow. Metabolism 1994, 43, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shboul, O.A. The importance of interstitial cells of cajal in the gastrointestinal tract. Saudi. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedel, T.; Spiegler, J.; Soellner, S.; Roblick, U.J.; Schiedeck, T.H.; Bruch, H.P.; Krammer, H.J. Enteric nerves and interstitial cells of cajal are altered in patients with slow-transit constipation and megacolon. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.L.; Burgart, L.; Wang, L.; Pemberton, J.; Young-Fadok, T.; Szurszewski, J.; Farrugia, G. Decreased interstitial cell of cajal volume in patients with slow-transit constipation. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Kim, N.; Jo, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Nam, R.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, D.H. Comparison of changes in the interstitial cells of cajal and neuronal nitric oxide synthase-positive neuronal cells with aging between the ascending and descending colon of F344 rats. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 23, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Park, J.W.; Kang, M.J.; Choi, H.J.; Bae, S.J.; Choi, Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, S.; Hong, J.T.; Hwang, D.Y. Laxative effect of spicatoside A by cholinergic regulation of enteric nerve in loperamide-induced constipation: ICR mice model. Molecules 2019, 24, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yan, Z.; Yin, H.; Wu, D.; Su, Q. Naringenin induces laxative effects by upregulating the expression levels of c-Kit and SCF, as well as those of aquaporin 3 in mice with loperamide-induced constipation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagger, Finlayson, Kumar. Interstitial cells of Cajal in slow transit constipation and megabowel. Colorectal Dis. 2000, 2, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beraldi, E.J.; Soares, A.; Borges, S.C.; da Silva de Souza, A.C.; Natali, M.R.M.; Bazotte, R.B.; Buttow, N.C. High-fat diet promotes neuronal loss in the myenteric plexus of the large intestine in mice. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, F.; Baudry, C.; Gruber, L.; Mazzuoli, G.; Moriez, R.; Scherling, C.; Kollmann, P.; Daniel, H.; Kisling, S.; Haller, D.; et al. Properties of myenteric neurons and mucosal functions in the distal colon of diet-induced obese mice. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 5125–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, R.L.; Senadheera, S.; Tanoto, A.; Tan, K.L.; Howitt, L.; Chen, H.; Murphy, T.V.; Sandow, S.L.; Liu, L.; Bertrand, P.P. Serotonin availability in rat colon is reduced during a Western diet model of obesity. Am J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G424–G434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Kim, J.W.; Cho, H.R.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, J.K.; Sohn, J.H.; Ku, S.K. Laxative effects of fermented rice extract in rats with loperamide-induced constipation. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.E.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, S.J.; Gong, J.E.; Lim, Y.; Hong, J.T.; Hwang, D.Y. Molecular Characterization of Constipation Disease as Novel Phenotypes in CRISPR-Cas9-Generated Leptin Knockout Mice with Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249464
Kim JE, Choi YJ, Lee SJ, Gong JE, Lim Y, Hong JT, Hwang DY. Molecular Characterization of Constipation Disease as Novel Phenotypes in CRISPR-Cas9-Generated Leptin Knockout Mice with Obesity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(24):9464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249464
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ji Eun, Yun Ju Choi, Su Jin Lee, Jeong Eun Gong, Yong Lim, Jin Tae Hong, and Dae Youn Hwang. 2020. "Molecular Characterization of Constipation Disease as Novel Phenotypes in CRISPR-Cas9-Generated Leptin Knockout Mice with Obesity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 24: 9464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249464
APA StyleKim, J. E., Choi, Y. J., Lee, S. J., Gong, J. E., Lim, Y., Hong, J. T., & Hwang, D. Y. (2020). Molecular Characterization of Constipation Disease as Novel Phenotypes in CRISPR-Cas9-Generated Leptin Knockout Mice with Obesity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(24), 9464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249464





