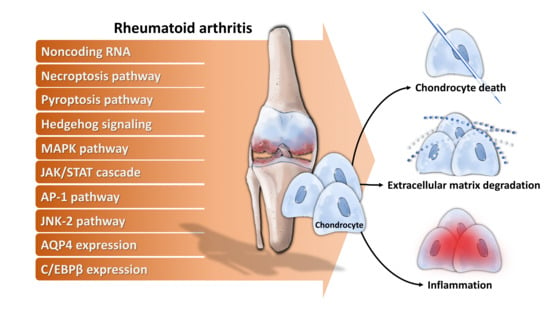
Dual Role of Chondrocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Chicken and the Egg
Abstract
Share and Cite
Tseng, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chang, W.-A.; Tsai, W.-C.; Ou, T.-T.; Wu, C.-C.; Sung, W.-Y.; Yen, J.-H.; Kuo, P.-L. Dual Role of Chondrocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Chicken and the Egg. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031071
Tseng C-C, Chen Y-J, Chang W-A, Tsai W-C, Ou T-T, Wu C-C, Sung W-Y, Yen J-H, Kuo P-L. Dual Role of Chondrocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Chicken and the Egg. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031071
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseng, Chia-Chun, Yi-Jen Chen, Wei-An Chang, Wen-Chan Tsai, Tsan-Teng Ou, Cheng-Chin Wu, Wan-Yu Sung, Jeng-Hsien Yen, and Po-Lin Kuo. 2020. "Dual Role of Chondrocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Chicken and the Egg" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031071
APA StyleTseng, C.-C., Chen, Y.-J., Chang, W.-A., Tsai, W.-C., Ou, T.-T., Wu, C.-C., Sung, W.-Y., Yen, J.-H., & Kuo, P.-L. (2020). Dual Role of Chondrocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Chicken and the Egg. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031071