Transposon Insertion Mutagenesis in Mice for Modeling Human Cancers: Critical Insights Gained and New Opportunities
Abstract
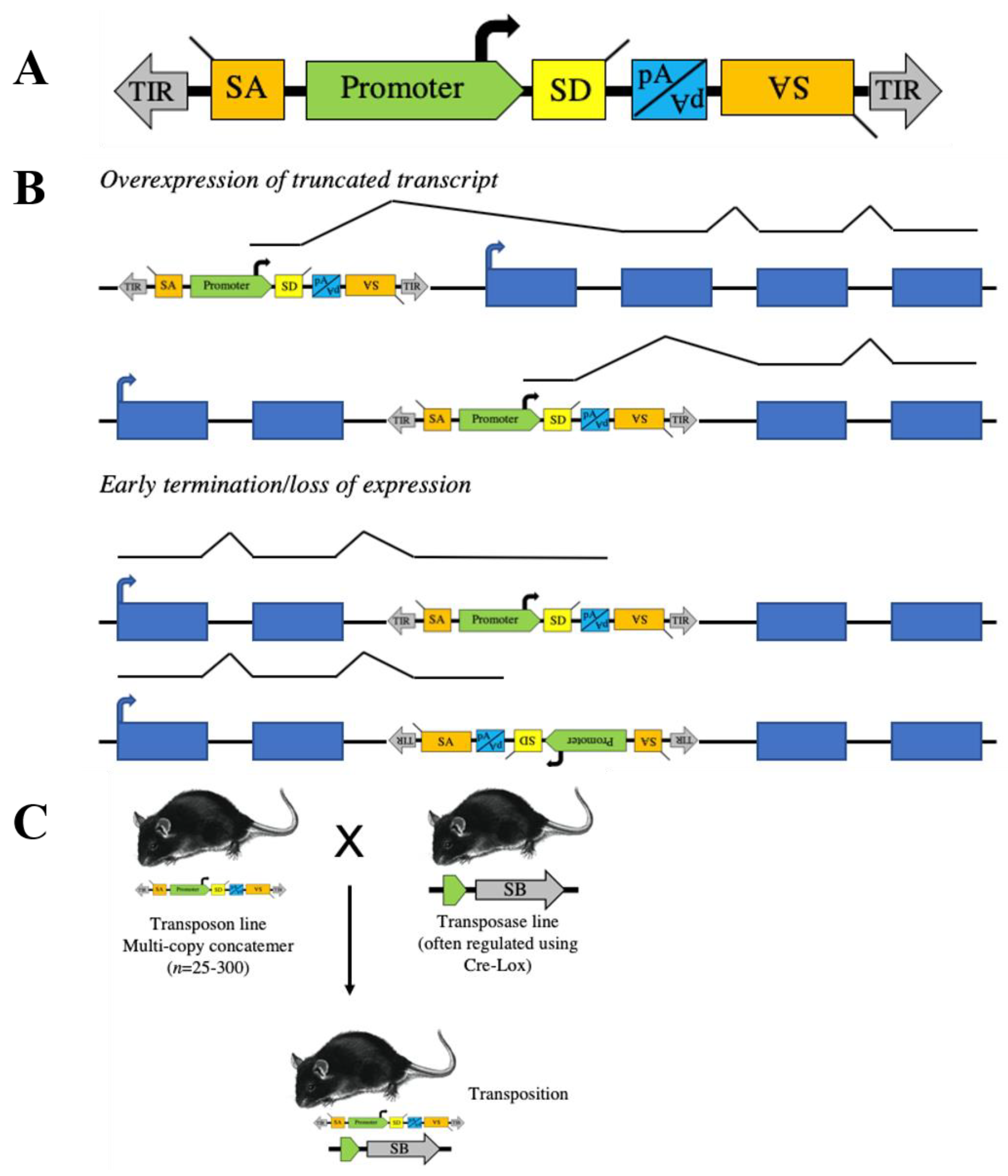
1. Transposon Basics
2. Transposons to Model Human Cancer in Mice
3. Cell of Origin
4. Identification of Rare Events
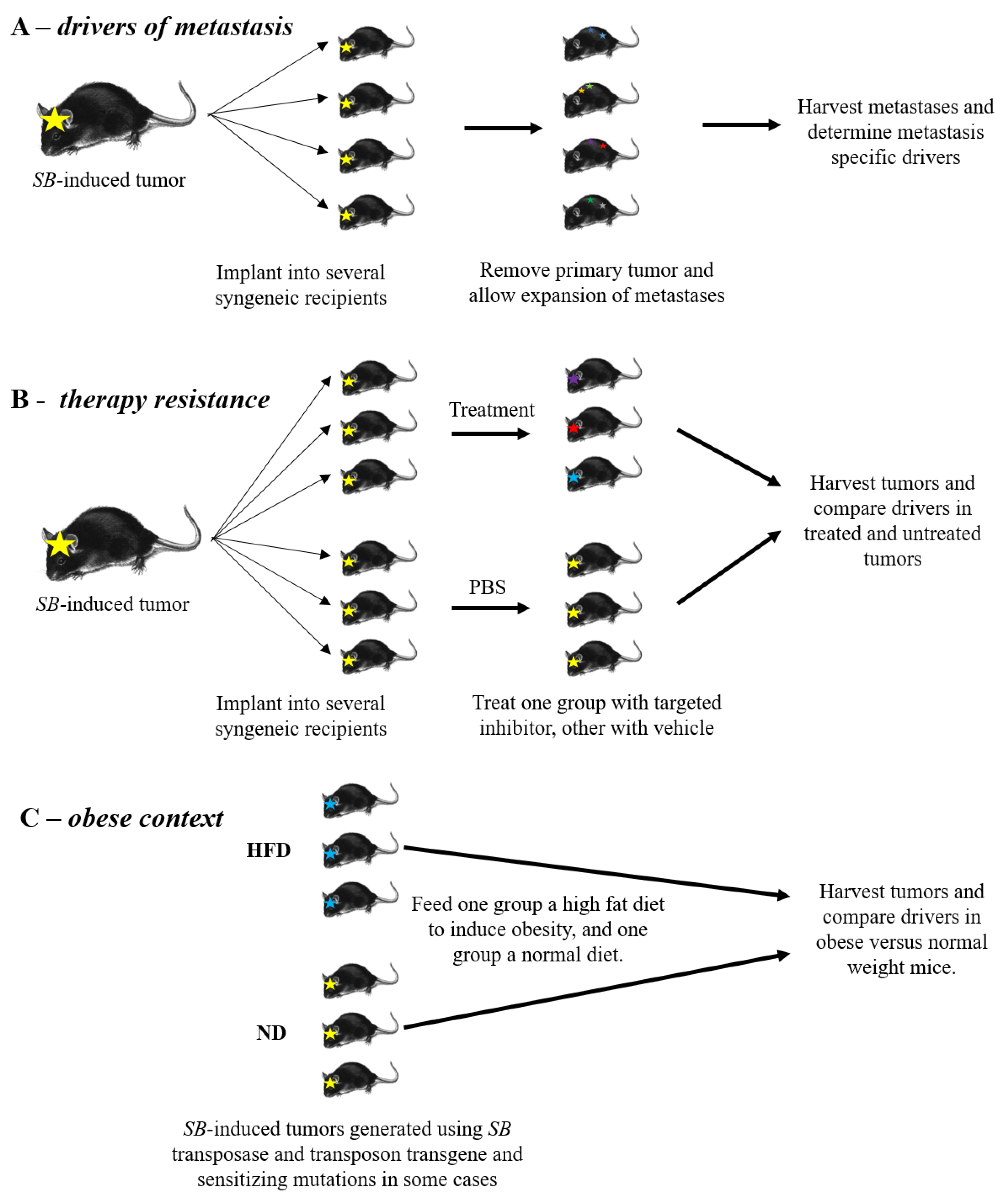
5. Drivers of Metastasis
6. Therapy Resistance
7. Obesity and Tumor Development
8. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mc, C.B. The origin and behavior of mutable loci in maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1950, 36, 344–355. [Google Scholar]
- Paatero, A.O.; Turakainen, H.; Happonen, L.J.; Olsson, C.; Palomaki, T.; Pajunen, M.I.; Meng, X.; Otonkoski, T.; Tuuri, T.; Berry, C.; et al. Bacteriophage Mu integration in yeast and mammalian genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisman, E.; Cardon, G.H.; Fransz, P.; Saedler, H. The behaviour of the autonomous maize transposable element En/Spm in Arabidopsis thaliana allows efficient mutagenesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 37, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoki, H.; Izawa, T.; Kawahara, M.; Komatsu, M.; Koh, S.; Kyozuka, J.; Shimamoto, K. Ac as a tool for the functional genomics of rice. Plant J. 1999, 19, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, R.; Chague, V.; Zhu, Q.; Emmanuel, E.; Elkind, Y.; Levy, A.A. Technical advance: A high throughput system for transposon tagging and promoter trapping in tomato. Plant J. 2000, 22, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuromori, T.; Hirayama, T.; Kiyosue, Y.; Takabe, H.; Mizukado, S.; Sakurai, T.; Akiyama, K.; Kamiya, A.; Ito, T.; Shinozaki, K. A collection of 11 800 single-copy Ds transposon insertion lines in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2004, 37, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, R.; Ouwerkerk, P.B.; Sallaud, C.; Kohli, A.; Colombo, L.; Puigdomenech, P.; Guiderdoni, E.; Christou, P.; Hoge, J.H.; Pereira, A. Transposon insertional mutagenesis in rice. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 1175–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaud, A.F.; Bessereau, J.L. Activation of nicotinic receptors uncouples a developmental timer from the molting timer in C. elegans. Development 2006, 133, 2211–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaud, A.F.; Bessereau, J.L. The P-type ATPase CATP-1 is a novel regulator of C. elegans developmental timing that acts independently of its predicted pump function. Development 2007, 134, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gally, C.; Eimer, S.; Richmond, J.E.; Bessereau, J.L. A transmembrane protein required for acetylcholine receptor clustering in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2004, 431, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yook, K.; Hodgkin, J. Mos1 mutagenesis reveals a diversity of mechanisms affecting response of Caenorhabditis elegans to the bacterial pathogen Microbacterium nematophilum. Genetics 2007, 175, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, T.; Klambt, C. P-element mutagenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 420, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Handler, A.M.; Harrell, R.A., 2nd. Germline transformation of Drosophila melanogaster with the piggyBac transposon vector. Insect Mol. Biol. 1999, 8, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loukeris, T.G.; Arca, B.; Livadaras, I.; Dialektaki, G.; Savakis, C. Introduction of the transposable element Minos into the germ line of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9485–9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urasaki, A.; Mito, T.; Noji, S.; Ueda, R.; Kawakami, K. Transposition of the vertebrate Tol2 transposable element in Drosophila melanogaster. Gene 2008, 425, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Wu, X.; Li, G.; Han, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, T. Efficient transposition of the piggyBac (PB) transposon in mammalian cells and mice. Cell 2005, 122, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabek, D.; Zagoraiou, L.; deWit, T.; Langeveld, A.; Roumpaki, C.; Mamalaki, C.; Savakis, C.; Grosveld, F. Transposition of the Drosophila hydei Minos transposon in the mouse germ line. Genomics 2003, 81, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, K.; Shima, A.; Kawakami, N. Identification of a functional transposase of the Tol2 element, an Ac-like element from the Japanese medaka fish, and its transposition in the zebrafish germ lineage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11403–11408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivics, Z.; Hackett, P.B.; Plasterk, R.H.; Izsvak, Z. Molecular reconstruction of Sleeping Beauty, a Tc1-like transposon from fish, and its transposition in human cells. Cell 1997, 91, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, L.S.; Carlson, C.M.; Ravimohan, S.; Dupuy, A.J.; Largaespada, D.A. Cancer gene discovery in solid tumours using transposon-based somatic mutagenesis in the mouse. Nature 2005, 436, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuy, A.J.; Akagi, K.; Largaespada, D.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A. Mammalian mutagenesis using a highly mobile somatic Sleeping Beauty transposon system. Nature 2005, 436, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, L.S.; Adams, D.J.; Hackett, C.S.; Bendzick, L.E.; Akagi, K.; Davies, M.N.; Diers, M.D.; Rodriguez, F.J.; Bender, A.M.; Tieu, C.; et al. Whole-body sleeping beauty mutagenesis can cause penetrant leukemia/lymphoma and rare high-grade glioma without associated embryonic lethality. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8429–8437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuy, A.J.; Rogers, L.M.; Kim, J.; Nannapaneni, K.; Starr, T.K.; Liu, P.; Largaespada, D.A.; Scheetz, T.E.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G. A modified sleeping beauty transposon system that can be used to model a wide variety of human cancers in mice. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8150–8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Mancera, P.A.; Rust, A.G.; van der Weyden, L.; Kristiansen, G.; Li, A.; Sarver, A.L.; Silverstein, K.A.; Grutzmann, R.; Aust, D.; Rummele, P.; et al. The deubiquitinase USP9X suppresses pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nature 2012, 486, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, R.M.; Dupuy, A.J.; Bravo, A.; Casanova, M.L.; Alameda, J.P.; Page, A.; Sanchez-Viera, M.; Ramirez, A.; Navarro, M. A transposon-based analysis of gene mutations related to skin cancer development. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyazunova, I.; Maklakova, V.I.; Berman, S.; De, I.; Steffen, M.D.; Hong, W.; Lincoln, H.; Morrissy, A.S.; Taylor, M.D.; Akagi, K.; et al. Sleeping Beauty mouse models identify candidate genes involved in gliomagenesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tschida, B.R.; Temiz, N.A.; Kuka, T.P.; Lee, L.A.; Riordan, J.D.; Tierrablanca, C.A.; Hullsiek, R.; Wagner, S.; Hudson, W.A.; Linden, M.A.; et al. Sleeping Beauty Insertional Mutagenesis in Mice Identifies Drivers of Steatosis-Associated Hepatic Tumors. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6576–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, P.J.; Larson, J.D.; Larsson, A.T.; Ostergaard, J.P.; Wagner, S.; Rahrmann, E.P.; Shamsan, G.A.; Otto, G.M.; Williams, R.L.; Wang, J.; et al. Sleeping Beauty Insertional Mutagenesis Reveals Important Genetic Drivers of Central Nervous System Embryonal Tumors. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahrmann, E.P.; Watson, A.L.; Keng, V.W.; Choi, K.; Moriarity, B.S.; Beckmann, D.A.; Wolf, N.K.; Sarver, A.; Collins, M.H.; Moertel, C.L.; et al. Forward genetic screen for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor formation identifies new genes and pathways driving tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, K.; Ishishita, S.; Tosaka, K.; Takahashi, R.; Ueda, M.; Keng, V.W.; Horie, K.; Takeda, J. Transposon-tagged mutagenesis in the rat. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasevicius, A.; Ekker, S.C. Effective targeted gene ‘knockdown’ in zebrafish. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinzelle, L.; Vallin, J.; Coen, L.; Chesneau, A.; Du Pasquier, D.; Pollet, N.; Demeneix, B.; Mazabraud, A. Generation of trangenic Xenopus laevis using the Sleeping Beauty transposon system. Transgenic Res. 2006, 15, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izsvak, Z.; Ivics, Z.; Plasterk, R.H. Sleeping Beauty, a wide host-range transposon vector for genetic transformation in vertebrates. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 302, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geurts, A.M.; Yang, Y.; Clark, K.J.; Liu, G.; Cui, Z.; Dupuy, A.J.; Bell, J.B.; Largaespada, D.A.; Hackett, P.B. Gene transfer into genomes of human cells by the sleeping beauty transposon system. Mol. Ther. 2003, 8, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsi, A.; Moav, B.; Hackett, P.; Liu, Z. Effects of insert size on transposition efficiency of the sleeping beauty transposon in mouse cells. Mar. Biotechnol. 2001, 3, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostovskaya, M.; Fu, J.; Obst, M.; Baer, I.; Weidlich, S.; Wang, H.; Smith, A.J.; Anastassiadis, K.; Stewart, A.F. Transposon-mediated BAC transgenesis in human ES cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, H.; Izsvak, Z.; Walisko, O.; Ivics, Z. Development of hyperactive sleeping beauty transposon vectors by mutational analysis. Mol. Ther. 2004, 9, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balciunas, D.; Wangensteen, K.J.; Wilber, A.; Bell, J.; Geurts, A.; Sivasubbu, S.; Wang, X.; Hackett, P.B.; Largaespada, D.A.; McIvor, R.S.; et al. Harnessing a high cargo-capacity transposon for genetic applications in vertebrates. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lin, C.; Lu, D.; Ning, Z.; Cox, T.; Melvin, D.; Wang, X.; Bradley, A.; Liu, P. Chromosomal transposition of PiggyBac in mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9290–9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yant, S.R.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Garrison, B.; Burgess, S.M.; Kay, M.A. High-resolution genome-wide mapping of transposon integration in mammals. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Geurts, A.M.; Yae, K.; Srinivasan, A.R.; Fahrenkrug, S.C.; Largaespada, D.A.; Takeda, J.; Horie, K.; Olson, W.K.; Hackett, P.B. Target-site preferences of Sleeping Beauty transposons. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 346, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.E.; Wienholds, E.; Plasterk, R.H. Regulated transposition of a fish transposon in the mouse germ line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6759–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.; Ollinger, R.; Friedrich, M.; Ehmer, U.; Barenboim, M.; Steiger, K.; Heid, I.; Mueller, S.; Maresch, R.; Engleitner, T.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9 somatic multiplex-mutagenesis for high-throughput functional cancer genomics in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13982–13987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Qi, X.; Du, X.; Zou, H.; Gao, F.; Feng, T.; Lu, H.; Li, S.; An, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. piggyBac mediates efficient in vivo CRISPR library screening for tumorigenesis in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, J.; Berns, A. High-throughput insertional mutagenesis screens in mice to identify oncogenic networks. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, V.; Kimm, M.A.; Boer, M.; Wessels, L.; Theelen, W.; Jonkers, J.; Hilkens, J. MMTV insertional mutagenesis identifies genes, gene families and pathways involved in mammary cancer. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laboratory, T.J. Characterized Cre Lines. Available online: https://www.jax.org/research-and-faculty/resources/cre-repository/characterized-cre-lines-jax-cre-resource# (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- Moriarity, B.S.; Otto, G.M.; Rahrmann, E.P.; Rathe, S.K.; Wolf, N.K.; Weg, M.T.; Manlove, L.A.; LaRue, R.S.; Temiz, N.A.; Molyneux, S.D.; et al. A Sleeping Beauty forward genetic screen identifies new genes and pathways driving osteosarcoma development and metastasis. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Keng, V.W.; Patmore, D.M.; Kendall, J.J.; Patel, A.V.; Jousma, E.; Jessen, W.J.; Choi, K.; Tschida, B.R.; Silverstein, K.A.; et al. Insertional Mutagenesis Identifies a STAT3/Arid1b/beta-catenin Pathway Driving Neurofibroma Initiation. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Been, R.A.; Linden, M.A.; Hager, C.J.; DeCoursin, K.J.; Abrahante, J.E.; Landman, S.R.; Steinbach, M.; Sarver, A.L.; Largaespada, D.A.; Starr, T.K. Genetic signature of histiocytic sarcoma revealed by a sleeping beauty transposon genetic screen in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Cabrera, C.; Quintana, R.M.; Bravo, A.; Casanova, M.L.; Page, A.; Alameda, J.P.; Paramio, J.M.; Maroto, A.; Salamanca, J.; Dupuy, A.J.; et al. A Transposon-based Analysis Reveals RASA1 Is Involved in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jenjaroenpun, P.; Pillai, A.M.; Ivshina, A.V.; Ow, G.S.; Efthimios, M.; Zhiqun, T.; Tan, T.Z.; Lee, S.C.; Rogers, K.; et al. Transposon insertional mutagenesis in mice identifies human breast cancer susceptibility genes and signatures for stratification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2215–E2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kas, S.M.; de Ruiter, J.R.; Schipper, K.; Annunziato, S.; Schut, E.; Klarenbeek, S.; Drenth, A.P.; van der Burg, E.; Klijn, C.; Ten Hoeve, J.J.; et al. Insertional mutagenesis identifies drivers of a novel oncogenic pathway in invasive lobular breast carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kas, S.M.; de Ruiter, J.R.; Schipper, K.; Schut, E.; Bombardelli, L.; Wientjens, E.; Drenth, A.P.; de Korte-Grimmerink, R.; Mahakena, S.; Phillips, C.; et al. Transcriptomics and Transposon Mutagenesis Identify Multiple Mechanisms of Resistance to the FGFR Inhibitor AZD4547. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5668–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel, R.; Lee, S.C.; Hon-Kim Ban, K.; Guzman-Rojas, L.; Mann, M.B.; Newberg, J.Y.; Kodama, T.; McNoe, L.A.; Selvanesan, L.; Ward, J.M.; et al. Transposon mutagenesis identifies genes that cooperate with mutant Pten in breast cancer progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7749–E7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, K.M.; Ward, J.M.; Yew, C.C.; Kovochich, A.; Dawson, D.W.; Black, M.A.; Brett, B.T.; Sheetz, T.E.; Dupuy, A.J.; Chang, D.K.; et al. Sleeping Beauty mutagenesis reveals cooperating mutations and pathways in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5934–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, R.; Rad, L.; Wang, W.; Strong, A.; Ponstingl, H.; Bronner, I.F.; Mayho, M.; Steiger, K.; Weber, J.; Hieber, M.; et al. A conditional piggyBac transposition system for genetic screening in mice identifies oncogenic networks in pancreatic cancer. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Rust, A.G.; Ward, J.M.; Yew, C.C.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G. Sleeping Beauty transposon mutagenesis identifies genes that cooperate with mutant Smad4 in gastric cancer development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2057–E2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Wei, Z.; Koso, H.; Rust, A.G.; Yew, C.C.; Mann, M.B.; Ward, J.M.; Adams, D.J.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A. Transposon mutagenesis identifies genes and evolutionary forces driving gastrointestinal tract tumor progression. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, T.K.; Allaei, R.; Silverstein, K.A.; Staggs, R.A.; Sarver, A.L.; Bergemann, T.L.; Gupta, M.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Matise, I.; Dupuy, A.J.; et al. A transposon-based genetic screen in mice identifies genes altered in colorectal cancer. Science 2009, 323, 1747–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, T.K.; Scott, P.M.; Marsh, B.M.; Zhao, L.; Than, B.L.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Sarver, A.L.; Dupuy, A.J.; Largaespada, D.A.; Cormier, R.T. A Sleeping Beauty transposon-mediated screen identifies murine susceptibility genes for adenomatous polyposis coli (Apc)-dependent intestinal tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5765–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, H.N.; Rust, A.G.; Wright, N.A.; ten Hoeve, J.; de Ridder, J.; Eldridge, M.; van der Weyden, L.; Berns, A.; Gadiot, J.; Uren, A.; et al. Insertional mutagenesis identifies multiple networks of cooperating genes driving intestinal tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, S.M.; Davison, J.; Carter, K.T.; O’Leary, R.M.; Trobridge, P.; Knoblaugh, S.E.; Myeroff, L.L.; Markowitz, S.D.; Brett, B.T.; Scheetz, T.E.; et al. Transposon mutagenesis identifies candidate genes that cooperate with loss of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in mouse intestinal neoplasms. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bard-Chapeau, E.A.; Nguyen, A.T.; Rust, A.G.; Sayadi, A.; Lee, P.; Chua, B.Q.; New, L.S.; de Jong, J.; Ward, J.M.; Chin, C.K.; et al. Transposon mutagenesis identifies genes driving hepatocellular carcinoma in a chronic hepatitis B mouse model. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keng, V.W.; Villanueva, A.; Chiang, D.Y.; Dupuy, A.J.; Ryan, B.J.; Matise, I.; Silverstein, K.A.; Sarver, A.; Starr, T.K.; Akagi, K.; et al. A conditional transposon-based insertional mutagenesis screen for genes associated with mouse hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keng, V.W.; Sia, D.; Sarver, A.L.; Tschida, B.R.; Fan, D.; Alsinet, C.; Sole, M.; Lee, W.L.; Kuka, T.P.; Moriarity, B.S.; et al. Sex bias occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in Poly7 molecular subclass is associated with EGFR. Hepatology 2013, 57, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.A.; Keng, V.W.; York, B.; Reineke, E.L.; Seo, D.; Fan, D.; Silverstein, K.A.; Schrum, C.T.; Xie, W.R.; Mularoni, L.; et al. A Sleeping Beauty mutagenesis screen reveals a tumor suppressor role for Ncoa2/Src-2 in liver cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1377–E1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, T.; Yi, J.; Newberg, J.Y.; Tien, J.C.; Wu, H.; Finegold, M.J.; Kodama, M.; Wei, Z.; Tamura, T.; Takehara, T.; et al. Molecular profiling of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma using SB transposon mutagenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E10417–E10426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Bazai, S.K.; Daian, F.; Arechederra, M.; Richelme, S.; Temiz, N.A.; Yim, A.; Habermann, B.H.; Dono, R.; Largaespada, D.A.; et al. Evaluating the landscape of gene cooperativity with receptor tyrosine kinases in liver tumorigenesis using transposon-mediated mutagenesis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, C.; Janik, C.; Weg, M.; Been, R.A.; Bader, J.; Kang, R.; Ng, B.; Foran, L.; Landman, S.R.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; et al. Transposon Mutagenesis Screen Identifies Potential Lung Cancer Drivers and CUL3 as a Tumor Suppressor. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahrmann, E.P.; Collier, L.S.; Knutson, T.P.; Doyal, M.E.; Kuslak, S.L.; Green, L.E.; Malinowski, R.L.; Roethe, L.; Akagi, K.; Waknitz, M.; et al. Identification of PDE4D as a proliferation promoting factor in prostate cancer using a Sleeping Beauty transposon-based somatic mutagenesis screen. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4388–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Mui, E.; Galbraith, L.; Patel, R.; Tan, E.H.; Salji, M.; Rust, A.G.; Repiscak, P.; Hedley, A.; Markert, E.; et al. Sleeping Beauty screen reveals Pparg activation in metastatic prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8290–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Conde, C.; Leandro-Garcia, L.J.; Chen, X.; Oler, G.; Ruiz-Llorente, S.; Ryder, M.; Landa, I.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; La, K.; Ghossein, R.A.; et al. Transposon mutagenesis identifies chromatin modifiers cooperating with Ras in thyroid tumorigenesis and detects ATXN7 as a cancer gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4951–E4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, D.; Karreth, F.A.; Rust, A.G.; Perez-Mancera, P.A.; Rashid, M.; Iorio, F.; Alifrangis, C.; Arends, M.J.; Bosenberg, M.W.; Bollag, G.; et al. BRAF inhibitor resistance mediated by the AKT pathway in an oncogenic BRAF mouse melanoma model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E536–E545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, M.B.; Black, M.A.; Jones, D.J.; Ward, J.M.; Yew, C.C.; Newberg, J.Y.; Dupuy, A.J.; Rust, A.G.; Bosenberg, M.W.; McMahon, M.; et al. Transposon mutagenesis identifies genetic drivers of Braf melanoma. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karreth, F.A.; Tay, Y.; Perna, D.; Ala, U.; Tan, S.M.; Rust, A.G.; DeNicola, G.; Webster, K.A.; Weiss, D.; Perez-Mancera, P.A.; et al. In vivo identification of tumor- suppressive PTEN ceRNAs in an oncogenic BRAF-induced mouse model of melanoma. Cell 2011, 147, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, T.K.; Landrette, S.F.; Bjornson, R.D.; Bosenberg, M.W.; Xu, T. Low-copy piggyBac transposon mutagenesis in mice identifies genes driving melanoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3640–E3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berquam-Vrieze, K.E.; Nannapaneni, K.; Brett, B.T.; Holmfeldt, L.; Ma, J.; Zagorodna, O.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Knudson, C.M.; et al. Cell of origin strongly influences genetic selection in a mouse model of T-ALL. Blood 2011, 118, 4646–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Weyden, L.; Rust, A.G.; McIntyre, R.E.; Robles-Espinoza, C.D.; del Castillo Velasco-Herrera, M.; Strogantsev, R.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C.; McCarthy, S.; Keane, T.M.; Arends, M.J.; et al. Jdp2 downregulates Trp53 transcription to promote leukaemogenesis in the context of Trp53 heterozygosity. Oncogene 2013, 32, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wartewig, T.; Kurgyis, Z.; Keppler, S.; Pechloff, K.; Hameister, E.; Ollinger, R.; Maresch, R.; Buch, T.; Steiger, K.; Winter, C.; et al. PD-1 is a haploinsufficient suppressor of T cell lymphomagenesis. Nature 2017, 552, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heltemes-Harris, L.M.; Larson, J.D.; Starr, T.K.; Hubbard, G.K.; Sarver, A.L.; Largaespada, D.A.; Farrar, M.A. Sleeping Beauty transposon screen identifies signaling modules that cooperate with STAT5 activation to induce B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncogene 2015, 35, 3454–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van der Weyden, L.; Giotopoulos, G.; Rust, A.G.; Matheson, L.S.; van Delft, F.W.; Kong, J.; Corcoran, A.E.; Greaves, M.F.; Mullighan, C.G.; Huntly, B.J.; et al. Modeling the evolution of ETV6-RUNX1-induced B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia in mice. Blood 2011, 118, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanesi, N.; Balatti, V.; Riordan, J.; Burch, A.; Rizzotto, L.; Palamarchuk, A.; Cascione, L.; Lagana, A.; Dupuy, A.J.; Croce, C.M.; et al. A Sleeping Beauty screen reveals NF-kB activation in CLL mouse model. Blood 2013, 121, 4355–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Weyden, L.; Giotopoulos, G.; Wong, K.; Rust, A.G.; Robles-Espinoza, C.D.; Osaki, H.; Huntly, B.J.; Adams, D.J. Somatic drivers of B-ALL in a model of ETV6-RUNX1; Pax5(+/-) leukemia. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahrmann, E.P.; Wolf, N.K.; Otto, G.M.; Heltemes-Harris, L.; Ramsey, L.B.; Shu, J.; LaRue, R.S.; Linden, M.A.; Rathe, S.K.; Starr, T.K.; et al. Sleeping Beauty Screen Identifies RREB1 and Other Genetic Drivers in Human B-cell Lymphoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.; de la Rosa, J.; Grove, C.S.; Schick, M.; Rad, L.; Baranov, O.; Strong, A.; Pfaus, A.; Friedrich, M.J.; Engleitner, T.; et al. PiggyBac transposon tools for recessive screening identify B-cell lymphoma drivers in mice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, K.M.; Newberg, J.Y.; Black, M.A.; Jones, D.J.; Amaya-Manzanares, F.; Guzman-Rojas, L.; Kodama, T.; Ward, J.M.; Rust, A.G.; van der Weyden, L.; et al. Analyzing tumor heterogeneity and driver genes in single myeloid leukemia cells with SBCapSeq. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.Z.; Carmichael, C.L.; Shi, W.; Metcalf, D.; Ng, A.P.; Hyland, C.D.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Howell, V.M.; Zhao, Z.J.; et al. Transposon mutagenesis reveals cooperation of ETS family transcription factors with signaling pathways in erythro-megakaryocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6091–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliou, G.S.; Cooper, J.L.; Rad, R.; Li, J.; Rice, S.; Uren, A.; Rad, L.; Ellis, P.; Andrews, R.; Banerjee, R.; et al. Mutant nucleophosmin and cooperating pathways drive leukemia initiation and progression in mice. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giotopoulos, G.; van der Weyden, L.; Osaki, H.; Rust, A.G.; Gallipoli, P.; Meduri, E.; Horton, S.J.; Chan, W.I.; Foster, D.; Prinjha, R.K.; et al. A novel mouse model identifies cooperating mutations and therapeutic targets critical for chronic myeloid leukemia progression. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1551–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Weyden, L.; Papaspyropoulos, A.; Poulogiannis, G.; Rust, A.G.; Rashid, M.; Adams, D.J.; Arends, M.J.; O’Neill, E. Loss of RASSF1A synergizes with deregulated RUNX2 signaling in tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3817–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Weyden, L.; Arends, M.J.; Rust, A.G.; Poulogiannis, G.; McIntyre, R.E.; Adams, D.J. Increased tumorigenesis associated with loss of the tumor suppressor gene Cadm1. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeb, K.R.; Hughes, B.T.; Fissel, B.M.; Osteen, N.J.; Knoblaugh, S.E.; Grim, J.E.; Drury, L.J.; Sarver, A.; Dupuy, A.J.; Clurman, B.E. Insertional mutagenesis using the Sleeping Beauty transposon system identifies drivers of erythroleukemia in mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziyad, S.; Riordan, J.D.; Cavanaugh, A.M.; Su, T.; Hernandez, G.E.; Hilfenhaus, G.; Morselli, M.; Huynh, K.; Wang, K.; Chen, J.N.; et al. A Forward Genetic Screen Targeting the Endothelium Reveals a Regulatory Role for the Lipid Kinase Pi4ka in Myelo- and Erythropoiesis. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovesi, L.A.; Ng, C.G.; Davis, M.J.; Remke, M.; Taylor, M.D.; Adams, D.J.; Rust, A.G.; Ward, J.M.; Ban, K.H.; Jenkins, N.A.; et al. Sleeping Beauty mutagenesis in a mouse medulloblastoma model defines networks that discriminate between human molecular subgroups. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E4325–E4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koso, H.; Tsuhako, A.; Lyons, E.; Ward, J.M.; Rust, A.G.; Adams, D.J.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Watanabe, S. Identification of FoxR2 as an oncogene in medulloblastoma. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2351–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastowska, M.; Al-Afghani, H.; Al-Balool, H.H.; Sheth, H.; Mercer, E.; Coxhead, J.M.; Redfern, C.P.; Peters, H.; Burt, A.D.; Santibanez-Koref, M.; et al. Identification of a neuronal transcription factor network involved in medulloblastoma development. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2013, 1, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, K.C.; Faria, C.C.; Skowron, P.; Luck, A.; Garzia, L.; Wu, X.; Agnihotri, S.; Smith, C.A.; Taylor, M.D.; Mack, S.C.; et al. A functional genomics approach to identify pathways of drug resistance in medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Northcott, P.A.; Dubuc, A.; Dupuy, A.J.; Shih, D.J.; Witt, H.; Croul, S.; Bouffet, E.; Fults, D.W.; Eberhart, C.G.; et al. Clonal selection drives genetic divergence of metastatic medulloblastoma. Nature 2012, 482, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koso, H.; Takeda, H.; Yew, C.C.; Ward, J.M.; Nariai, N.; Ueno, K.; Nagasaki, M.; Watanabe, S.; Rust, A.G.; Adams, D.J.; et al. Transposon mutagenesis identifies genes that transform neural stem cells into glioma-initiating cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2998–E3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, A.M.; Collier, L.S.; Rodriguez, F.J.; Tieu, C.; Larson, J.D.; Halder, C.; Mahlum, E.; Kollmeyer, T.M.; Akagi, K.; Sarkar, G.; et al. Sleeping beauty-mediated somatic mutagenesis implicates CSF1 in the formation of high-grade astrocytomas. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3557–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.M.; Olivier, A.K.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Dupuy, A.J. Adaptive immunity does not strongly suppress spontaneous tumors in a Sleeping Beauty model of cancer. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4393–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, R.; Rad, L.; Wang, W.; Cadinanos, J.; Vassiliou, G.; Rice, S.; Campos, L.S.; Yusa, K.; Banerjee, R.; Li, M.A.; et al. PiggyBac transposon mutagenesis: A tool for cancer gene discovery in mice. Science 2010, 330, 1104–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Rosa, J.; Weber, J.; Friedrich, M.J.; Li, Y.; Rad, L.; Ponstingl, H.; Liang, Q.; de Quiros, S.B.; Noorani, I.; Metzakopian, E.; et al. A single-copy Sleeping Beauty transposon mutagenesis screen identifies new PTEN-cooperating tumor suppressor genes. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapeau, E.A.; Gembarska, A.; Durand, E.Y.; Mandon, E.; Estadieu, C.; Romanet, V.; Wiesmann, M.; Tiedt, R.; Lehar, J.; de Weck, A.; et al. Resistance mechanisms to TP53-MDM2 inhibition identified by in vivo piggyBac transposon mutagenesis screen in an Arf-/- mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3151–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedel, R.H.; Friedel, C.C.; Bonfert, T.; Shi, R.; Rad, R.; Soriano, P. Clonal expansion analysis of transposon insertions by high-throughput sequencing identifies candidate cancer genes in a PiggyBac mutagenesis screen. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, N.; Ridgway, R.A.; van Es, J.H.; van de Wetering, M.; Begthel, H.; van den Born, M.; Danenberg, E.; Clarke, A.R.; Sansom, O.J.; Clevers, H. Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of intestinal cancer. Nature 2009, 457, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Ellis, T.; Markant, S.L.; Read, T.A.; Kessler, J.D.; Bourboulas, M.; Schuller, U.; Machold, R.; Fishell, G.; Rowitch, D.H.; et al. Medulloblastoma can be initiated by deletion of Patched in lineage-restricted progenitors or stem cells. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiserson, M.D.; Vandin, F.; Wu, H.T.; Dobson, J.R.; Eldridge, J.V.; Thomas, J.L.; Papoutsaki, A.; Kim, Y.; Niu, B.; McLellan, M.; et al. Pan-cancer network analysis identifies combinations of rare somatic mutations across pathways and protein complexes. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, D.; Orr, B.A.; Toprak, U.H.; Hovestadt, V.; Jones, D.T.W.; Capper, D.; Sill, M.; Buchhalter, I.; Northcott, P.A.; Leis, I.; et al. New Brain Tumor Entities Emerge from Molecular Classification of CNS-PNETs. Cell 2016, 164, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; He, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, T. High expression of FOXR2 in breast cancer correlates with poor prognosis. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 5991–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, B.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y. FOXR2 contributes to cell proliferation and malignancy in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 10459–10467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Chang, J.; Liu, G.; Du, X.; Li, X. Knockdown of FOXR2 suppresses the tumorigenesis, growth and metastasis of prostate cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, K.L.; Nyre, E.T.; Abrahante, J.; Ho, Y.Y.; Isaksson Vogel, R.; Starr, T.K. The Candidate Cancer Gene Database: A database of cancer driver genes from forward genetic screens in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D844–D848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.L.; Wang, L.; Luo, J.; Zhu, H.W.; Cai, Z.W. Ambra1 modulates the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to epirubicin by regulating autophagy via ATG12. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 3129–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Yu, L.; Wei, W.; Lin, X.; Hou, X.; Tian, Y. shRNA-mediated AMBRA1 knockdown reduces the cisplatin-induced autophagy and sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 41, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.L. Ambra1 in autophagy and apoptosis: Implications for cell survival and chemotherapy resistance. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondy-Chorney, E.; Baldwin, R.M.; Didillon, A.; Chabot, B.; Jasmin, B.J.; Cote, J. RNA binding protein RALY promotes Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 1 alternatively spliced isoform v2 relative expression and metastatic potential in breast cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 91, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Tang, Y.; Sun, C.; Ju, W.; He, X. Overexpression of RALY promotes migration and predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 5559–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsofack, S.P.; Garand, C.; Sereduk, C.; Chow, D.; Aziz, M.; Guay, D.; Yin, H.H.; Lebel, M. NONO and RALY proteins are required for YB-1 oxaliplatin induced resistance in colon adenocarcinoma cell lines. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.P.; Powell, D.J.; Cunnane, M.; Greco, A.; Portella, G.; Santoro, M.; Fusco, A.; Rothstein, J.L. The TRK-T1 fusion protein induces neoplastic transformation of thyroid epithelium. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5729–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognon, C.; Knezevich, S.R.; Huntsman, D.; Roskelley, C.D.; Melnyk, N.; Mathers, J.A.; Becker, L.; Carneiro, F.; MacPherson, N.; Horsman, D.; et al. Expression of the ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion as a primary event in human secretory breast carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2002, 2, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnavi, A.; Capelletti, M.; Le, A.T.; Kako, S.; Butaney, M.; Ercan, D.; Mahale, S.; Davies, K.D.; Aisner, D.L.; Pilling, A.B.; et al. Oncogenic and drug-sensitive NTRK1 rearrangements in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesner, T.; He, J.; Yelensky, R.; Esteve-Puig, R.; Botton, T.; Yeh, I.; Lipson, D.; Otto, G.; Brennan, K.; Murali, R.; et al. Kinase fusions are frequent in Spitz tumours and spitzoid melanomas. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishnavi, A.; Le, A.T.; Doebele, R.C. TRKing down an old oncogene in a new era of targeted therapy. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stransky, N.; Cerami, E.; Schalm, S.; Kim, J.L.; Lengauer, C. The landscape of kinase fusions in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Kummar, S.; DuBois, S.G.; Lassen, U.N.; Demetri, G.D.; Nathenson, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Farago, A.F.; Pappo, A.S.; et al. Efficacy of Larotrectinib in TRK Fusion-Positive Cancers in Adults and Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhu, X.; Bao, H.; Wh Shek, T.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Chang, Z.; Wu, S.; et al. Genetic and clonal dissection of osteosarcoma progression and lung metastasis. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascierto, P.A.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Grob, J.J.; Simeone, E.; Grimaldi, A.M.; Maio, M.; Palmieri, G.; Testori, A.; Marincola, F.M.; Mozzillo, N. The role of BRAF V600 mutation in melanoma. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarian, R.; Shi, H.; Wang, Q.; Kong, X.; Koya, R.C.; Lee, H.; Chen, Z.; Lee, M.K.; Attar, N.; Sazegar, H.; et al. Melanomas acquire resistance to B-RAF(V600E) inhibition by RTK or N-RAS upregulation. Nature 2010, 468, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babina, I.S.; Turner, N.C. Advances and challenges in targeting FGFR signalling in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, R.; Borea, R.; Coelho, A.; Khan, S.; Araujo, A.; Reclusa, P.; Franchina, T.; Van Der Steen, N.; Van Dam, P.; Ferri, J.; et al. FGFR a promising druggable target in cancer: Molecular biology and new drugs. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 113, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.K.; Ranganath, K.; Hammerman, P.S.; Vaklavas, C.; Mohindra, N.; Kalyan, A.; Matsangou, M.; Costa, R.; Carneiro, B.; Villaflor, V.M.; et al. Inhibition of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) pathway: The current landscape and barriers to clinical application. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 16052–16074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Pak, E.; Ornell, K.J.; Pazyra-Murphy, M.F.; MacKenzie, E.L.; Chadwick, E.J.; Ponomaryov, T.; Kelleher, J.F.; Segal, R.A. A Transposon Screen Identifies Loss of Primary Cilia as a Mechanism of Resistance to SMO Inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1436–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feddersen, C.R.; Schillo, J.L.; Varzavand, A.; Vaughn, H.R.; Wadsworth, L.S.; Voigt, A.P.; Zhu, E.Y.; Jennings, B.M.; Mullen, S.A.; Bobera, J.; et al. Src-Dependent DBL Family Members Drive Resistance to Vemurafenib in Human Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5074–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- Unger, R.H.; Scherer, P.E. Gluttony, sloth and the metabolic syndrome: A roadmap to lipotoxicity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, N.; Chandran, U.; Bandera, E.V. Obesity in cancer survival. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2012, 32, 311–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Euhus, D.M.; Scherer, P.E. Paracrine and endocrine effects of adipose tissue on cancer development and progression. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 550–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, K.; Douglas, I.; Forbes, H.; dos-Santos-Silva, I.; Leon, D.A.; Smeeth, L. Body-mass index and risk of 22 specific cancers: A population-based cohort study of 5.24 million UK adults. Lancet 2014, 384, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Pandeya, N.; Byrnes, G.; Renehan, P.A.G.; Stevens, G.A.; Ezzati, P.M.; Ferlay, J.; Miranda, J.J.; Romieu, I.; Dikshit, R.; et al. Global burden of cancer attributable to high body-mass index in 2012: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.T.; Newton, C.C.; Dehal, A.N.; Jacobs, E.J.; Patel, A.V.; Gapstur, S.M. Impact of body mass index on survival after colorectal cancer diagnosis: The Cancer Prevention Study-II Nutrition Cohort. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastarrachea, J.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Smith, T.L.; Kau, S.W.; Buzdar, A.U. Obesity as an adverse prognostic factor for patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 120, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyerhardt, J.A.; Tepper, J.E.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Hollis, D.R.; McCollum, A.D.; Brady, D.; O’Connell, M.J.; Mayer, R.J.; Cummings, B.; Willett, C.; et al. Impact of body mass index on outcomes and treatment-related toxicity in patients with stage II and III rectal cancer: Findings from Intergroup Trial 0114. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlow, W.E.; White, E.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Vacek, P.M.; Titus-Ernstoff, L.; Carney, P.A.; Tice, J.A.; Buist, D.S.; Geller, B.M.; Rosenberg, R.; et al. Prospective breast cancer risk prediction model for women undergoing screening mammography. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle, E.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Walker-Thurmond, K.; Thun, M.J. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenkovich, C.F. Insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.H.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, K.M.; Kenny, H.A.; Penicka, C.V.; Ladanyi, A.; Buell-Gutbrod, R.; Zillhardt, M.R.; Romero, I.L.; Carey, M.S.; Mills, G.B.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; et al. Adipocytes promote ovarian cancer metastasis and provide energy for rapid tumor growth. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessitore, L.; Vizio, B.; Pesola, D.; Cecchini, F.; Mussa, A.; Argiles, J.M.; Benedetto, C. Adipocyte expression and circulating levels of leptin increase in both gynaecological and breast cancer patients. Int. J. Oncol. 2004, 24, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Scherer, P.E. Adipocyte-derived endotrophin promotes malignant tumor progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4243–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elinav, E.; Nowarski, R.; Thaiss, C.A.; Hu, B.; Jin, C.; Flavell, R.A. Inflammation-induced cancer: Crosstalk between tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, K.E.; Reynolds, J.V.; O’Hanlon, C.; O’Sullivan, J.N.; Lysaght, J. Could signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 be a therapeutic target in obesity-related gastrointestinal malignancy? J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2014, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, Y.; Scuoppo, C.; Wang, X.; Fang, X.; Balgley, B.; Bolden, J.E.; Premsrirut, P.; Luo, W.; Chicas, A.; Lee, C.S.; et al. Control of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype by NF-kappaB promotes senescence and enhances chemosensitivity. Genes. Dev. 2011, 25, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exley, M.A.; Hand, L.; O’Shea, D.; Lynch, L. Interplay between the immune system and adipose tissue in obesity. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 223, R41–R418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mutagenesis System | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| CRISPR/Cas9 |
|
|
| Transposon |
|
|
| Retroviruses |
|
|
| Tumor Type | Transposase | Transposon | Cre | Sensitizing Mutations | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sarcomas | |||||
| Fibrosarcoma | CGS-SB10 | T2/Onc | - | p19arf | [20] |
| Osteosarcoma | R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc | Osx-Cre | Trp53 | [48] |
| Peripheral nerve sheath tumor | R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc, T2/Onc15 | Cnp-Cre, Dhh-Cre | Trp53, EGFR Nf1 | [29,49] |
| Histiocytic sarcoma | R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc, T2/Onc2 | Lyz2-Cre | - | [50] |
| Carcinomas | |||||
| Skin | K5-SB11 | T2/Onc2 | - | Hras | [25] |
| Mammary | K5-SB11, R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc2, T2/Onc3 | K5-Cre, Wap-Cre | Trp53, β-catenin, Cdh1, FGFR, Pten | [51,52,53,54,55] |
| Pancreatic | R26-lsl-SB11, R26-lsl-SB13, R26-lsl-PB | T2/Onc, T2/Onc2, T2Onc3, ATP1 | Pdx1-Cre | Kras | [24,56,57] |
| Gastric adenoma | R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc3 | β-actin-Cre | Smad4 | [58] |
| Intestinal tract | R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc, T2/Onc2 | Vil-CreERT2, Vil-Cre, Ah-Cre | Apc, Kras, Smad4, Trp53, Tgfbr2 | [59,60,61,62,63] |
| Liver | R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc, T2/Onc2, T2/Onc3 | Alb-Cre | HBsAg, Trp53, Myc, Steatosis, Pten, Sav1, Met | [27,64,65,66,67,68,69] |
| Lung | R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc | Spc-Cre | Trp53, p19arf, Pten | [70] |
| Prostate | CGS-SB10, R26-SB11, R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc, T2/Onc3 | PB-Cre | p19arf, Pten | [71,72] |
| Thyroid | R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc2 | Tpo-Cre | Hras | [73] |
| Melanoma | R26-lsl-SB11, R26-lsl-SB13, Act-PBase | T2/Onc, T2/Onc2, T2/Onc3 Luc-PB[mut]7 | Tyr-Cre-ERT2 | Braf | [74,75,76,77] |
| Hematopoietic | |||||
| T cell leukemia | R26-lsl-SB11, R26-SB11 | T2/Onc2 | Vav-iCre, Lck-Cre, CD4-Cre | - | [21,78] |
| T cell lymphoma | R26-SB11, R26-lsl-PB | T2/Onc, ATP2 | CD4-Cre | Trp53, ITK-SYK, Pdc1 | [79,80] |
| B cell leukemia | R26-lsl-SB11, Etv6-RUNX1-HSB5 | T2/Onc | Cd79a-Cre | Stat5b, Etv6-RUNX1 fusion | [81,82] |
| B cell lymphoma | R26-lsl-SB11, Etv6-RUNX1-HSB5, R26-PB | T2/Onc, T2/Onc2, T2/Onc15, ITP1, ITP2 | Aid-Cre, CD19-Cre, Cnp-Cre | Eμ-TCL1, Pax5, Etv6-RUNX1 fusion, Trp53, Pten, Blm | [23,83,84,85,86] |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc2, GrOnc | β-actin-Cre, Vav-Cre, Mx1-Cre | Trp53, Jak2, Npm1c, BCR-ABL | [87,88,89,90] |
| Mixture of T cell and B cell lymphoma, myeloid leukemia | R26-SB11 | T2/Onc | - | Rassf1a, Cadm1 | [91,92] |
| Erythroleukemia | R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc2 | Mx1-Cre | Cyclin E | [93] |
| Myeloid and lymphoid malignancies, thymus, spleen | R26-lsl-SB11 | T2/Onc2 | Vec-Cre | - | [94] |
| Brain tumors | |||||
| Medulloblastoma/CNS-ET * | R26-lsl-SB11, R26-SB11, Math1-SB11 | T2/Onc, T2/Onc2, T2/Onc3 | β-actin-Cre, Nestin-Cre | Ptch1, Trp53, Pten | [28,95,96,97,98,99] |
| Glioma | R26-lsl-SB11, R26-SB11 | T2/Onc, T2/Onc2, T2/Onc3, T2OncATG | Nestin-Cre | Trp53, p19Arf, Blm, Csf1 | [26,100,101] |
| Multiple tumor types | |||||
| Skin, brain, airway, liver, leukemia, lymphoma, intestine | R26-SB11 | T2/Onc3 | - | Rag2 | [102] |
| Leukemia, medulloblastoma, glioma | CGS-SB10, R26-SB11 | T2/Onc | - | p19Arf | [22] |
| Skin, liver, lung, brain, lymphoma, sarcoma, mammary, colon, etc. | R26-SB11 | T2/Onc3 | - | - | [23] |
| T cell and B cell leukemia, lymphoma, skin, sarcoma, intestinal tract, lung, liver, etc. | R26-PB | ATP1, ATP2, ATP3 | - | - | [103] |
| Prostate, mammary and skin carcinomas | R26-SB11 | ITP2m | - | Pten, Blm | [104] |
| Sarcoma, carcinoma, leukemia, resistance to MDM2 inhibition | R26-PB | ATP2 | - | p19Arf | [105] |
| Liver, lung carcinoma, skin carcinoma, lymphoma | R26-PB | ATP1 | - | - | [106] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beckmann, P.J.; Largaespada, D.A. Transposon Insertion Mutagenesis in Mice for Modeling Human Cancers: Critical Insights Gained and New Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031172
Beckmann PJ, Largaespada DA. Transposon Insertion Mutagenesis in Mice for Modeling Human Cancers: Critical Insights Gained and New Opportunities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031172
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeckmann, Pauline J., and David A. Largaespada. 2020. "Transposon Insertion Mutagenesis in Mice for Modeling Human Cancers: Critical Insights Gained and New Opportunities" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031172
APA StyleBeckmann, P. J., & Largaespada, D. A. (2020). Transposon Insertion Mutagenesis in Mice for Modeling Human Cancers: Critical Insights Gained and New Opportunities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031172





