Genome Sequence and QTL Analyses Using Backcross Recombinant Inbred Lines (BILs) and BILF1 Lines Uncover Multiple Heterosis-related Loci
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
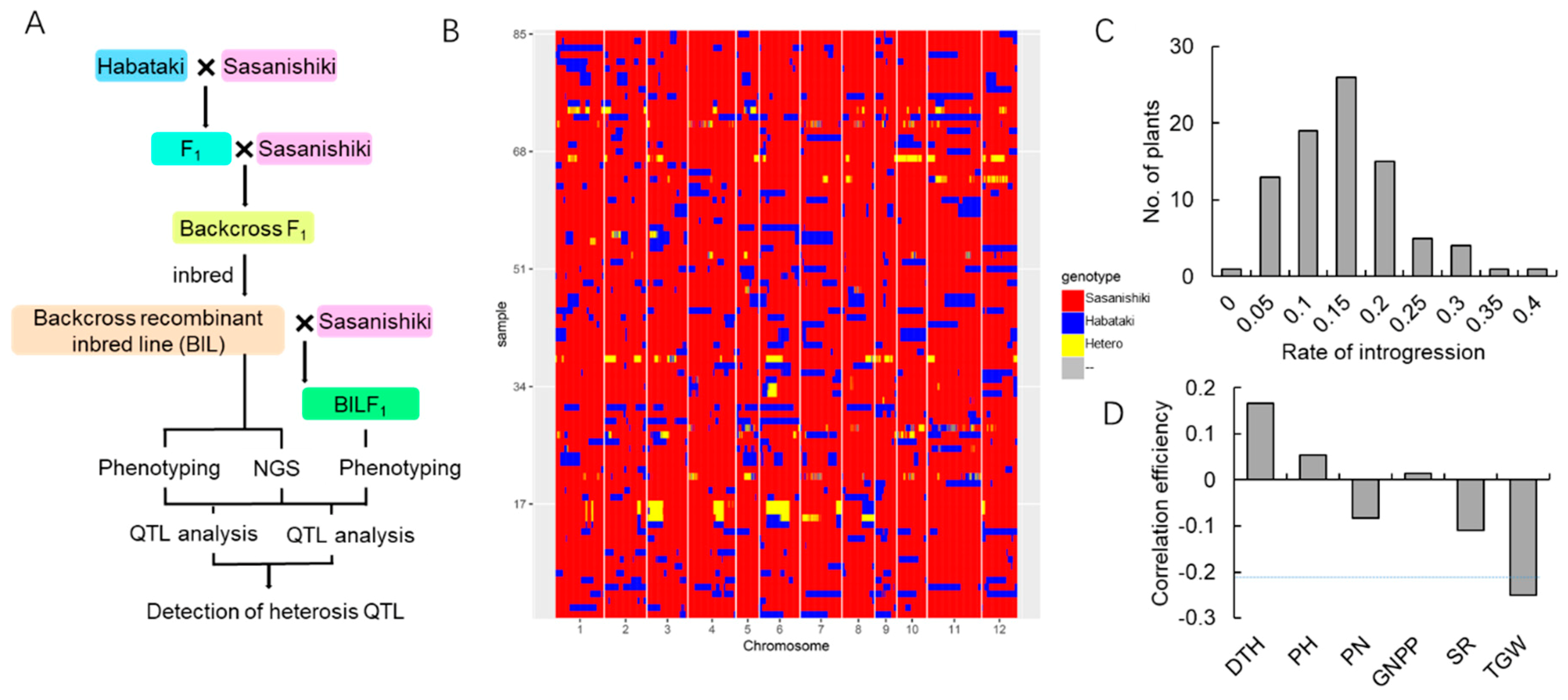
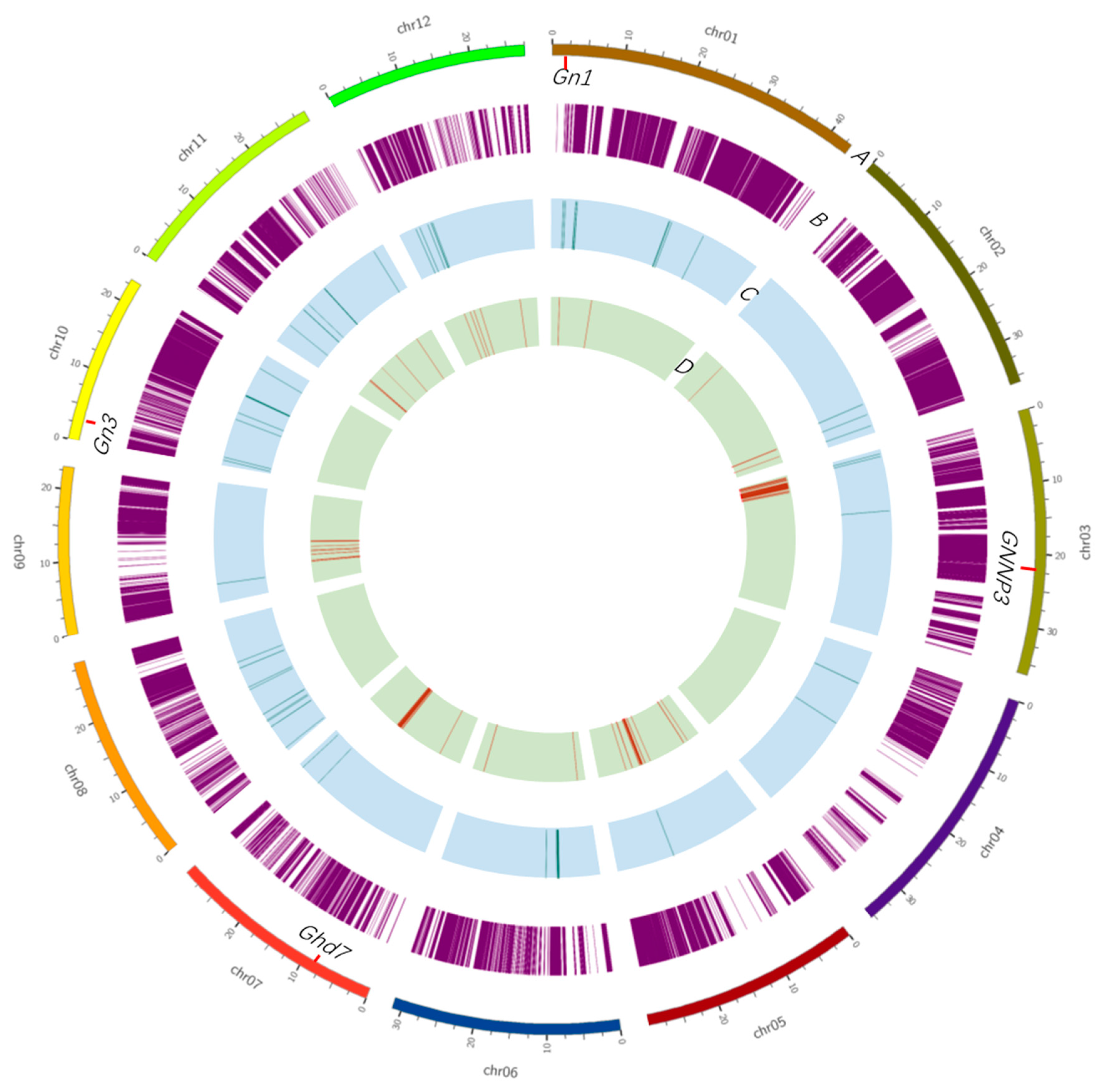
2.1. Population Sequencing and Linkage Map Construction
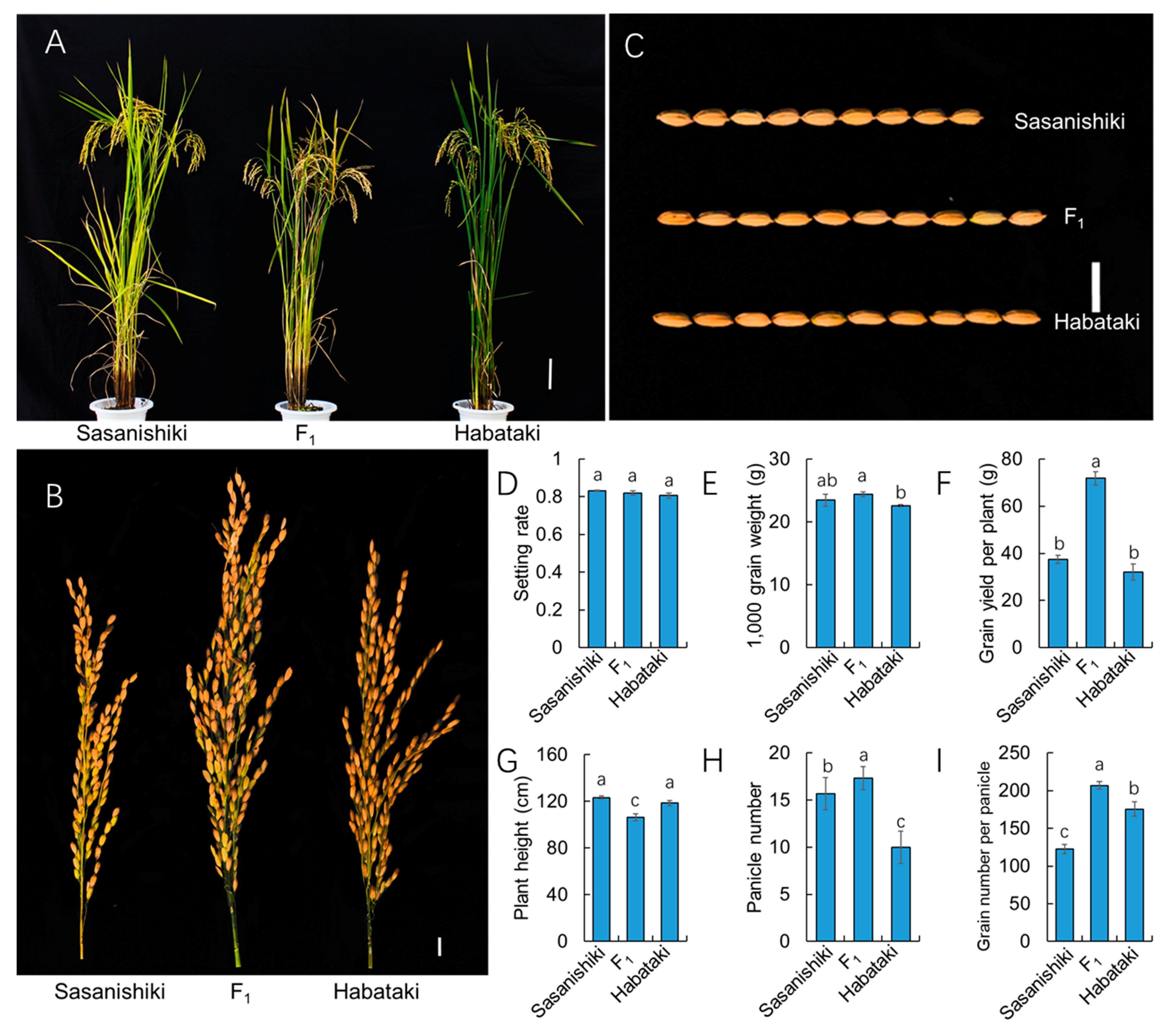
2.2. Grain Yield Heterosis is the Result of Hybrid Vigor in Grain Number Per Panicle
2.3. Yield Components and Other Important Agronomic Traits of BILs and BILF1s
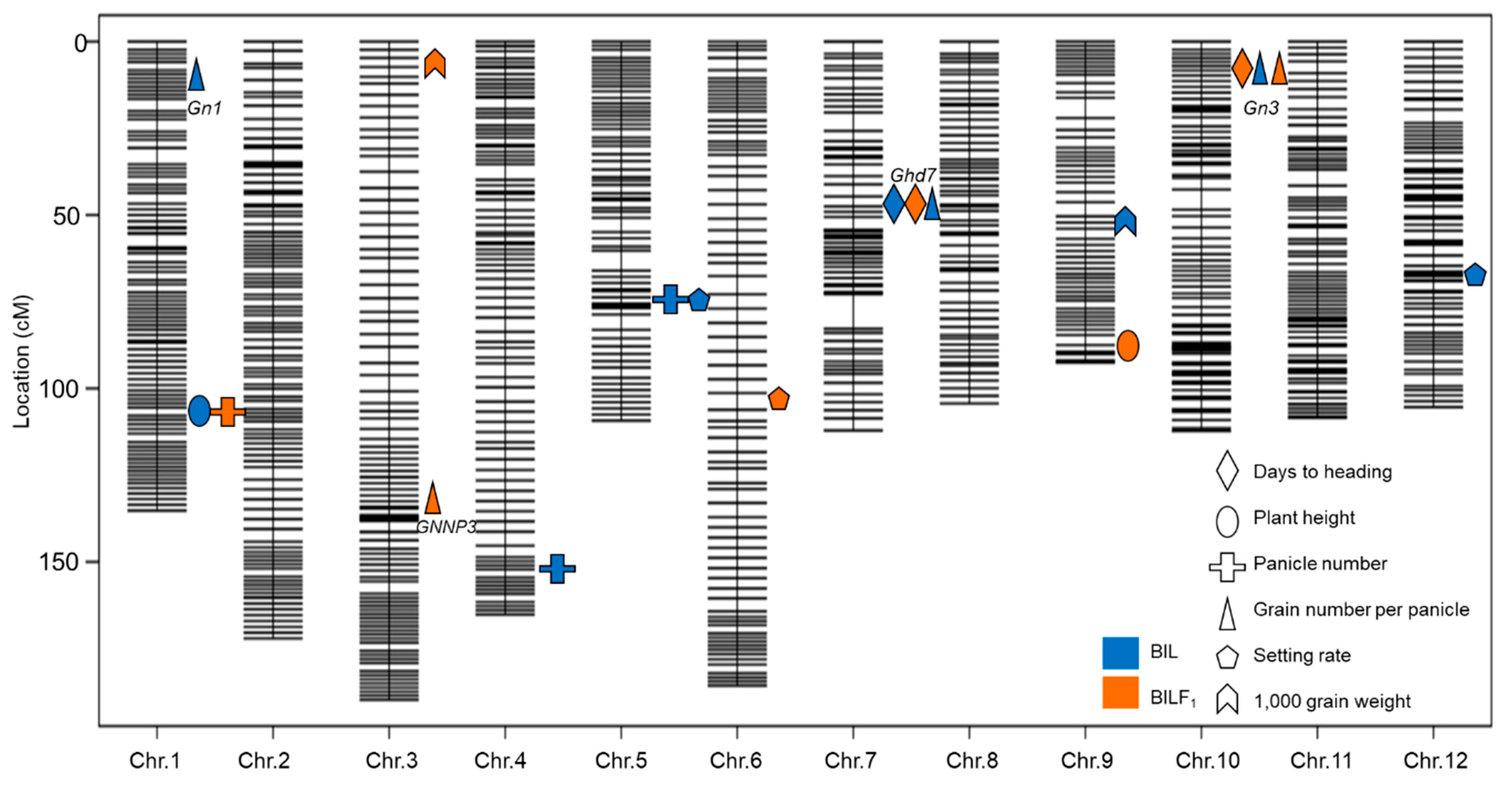
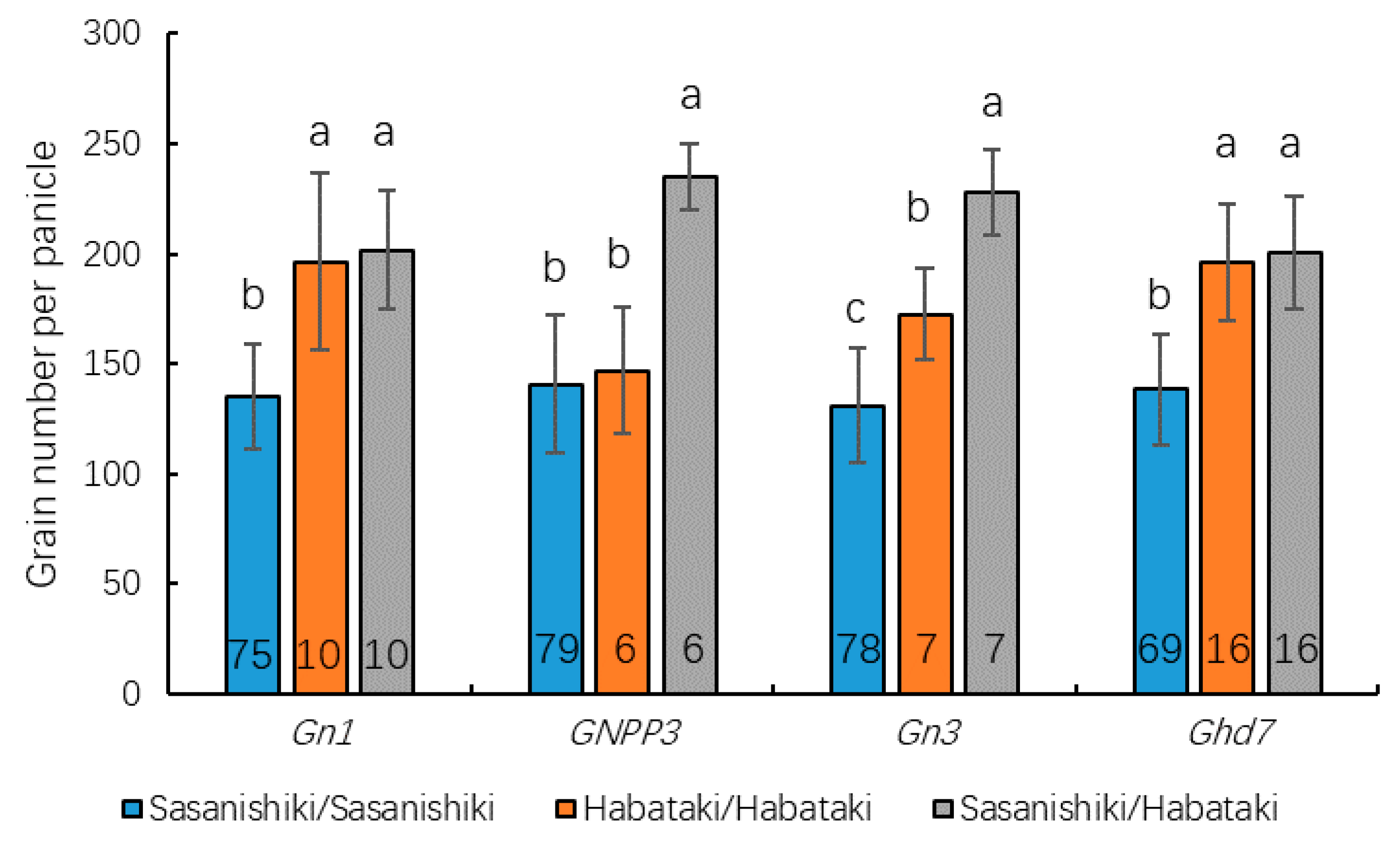
2.4. QTL Detection and Analysis Using the BILs and BILF1 Population
2.5. The Indica/Japonica Pedigree Analysis of Sasanishiki and Habataki
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. DNA Extraction and QTL Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
References
- Fiévet, J.B.; Thibault, N.; Christine, D.; de Dominique, V. Heterosis Is a Systemic Property Emerging From Non-linear Genotype-Phenotype Relationships: Evidence From in Vitro Genetics and Computer Simulations. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, B.A. The Mendelian Theory of Heredity and the Augmentation of Vigor. Science 1910, 32, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.F. Dominance of Linked Factors as a Means of Accounting for Heterosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1917, 3, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shull, G.H. The Genotypes of Maize. Am. Nat. 1911, 45, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- East, E.M. Heterosis. Genetics 1936, 21, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Minvielle, F. Dominance is not necessary for heterosis: A two-locus model. Genet. Res. 1987, 49, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. Developing Marker-Assisted Selection Strategies for Breeding Hybrid Rice; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Huang, Z.; Song, S.; Xin, Y.; Mao, D.; Lv, Q.; Zhou, M.; Tian, D.; Tang, M.; Wu, Q. Integrated analysis of phenome, genome, and transcriptome of hybrid rice uncovered multiple heterosis-related loci for yield increase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6026–E6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yang, S.; Gong, J.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhan, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Cheng, B.; Xia, J. Genomic architecture of heterosis for yield traits in rice. Nature 2016, 537, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, Y.; Bastide, M.D.L.; Hamilton, J.P.; Kanamori, H.; Mccombie, W.R.; Shu, O.; Schwartz, D.C.; Tanaka, T.; Wu, J.; Zhou, S. Improvement of the Oryza sativa Nipponbare reference genome using next generation sequence and optical map data. Rice 2013, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Lam, T.W.; Yiu, S.M.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP2: An improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1966–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.; Fang, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SNP detection for massively parallel whole-genome resequencing. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wei, X.; Sang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, C.; Lu, T.; Zhang, Z. Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, C.; Wang, A.; Zhao, Q.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhu, C. Genome-wide association study of flowering time and grain yield traits in a worldwide collection of rice germplasm. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.W.; Qiang, H.E.; Zhang, W.H.; Shu, F.; Xing, J.J.; Sun, P.Y.; Deng, H.F.; University, H.A. Reflection of Rice Development in Yangtze River Basin under the New Situation. Hybrid Rice 2015, 30, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Chen, Y.; Yao, W.; Zhang, C.; Xie, W.; Hua, J.; Xing, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q. Genetic composition of yield heterosis in an elite rice hybrid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 15847–15852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.-Y.; Ma, D.-R.; Tang, L.; Gao, H.; Xu, Z.-J.; Chen, W.-F. The contribution of intersubspecific hybridization to the breeding of super-high-yielding japonica rice in northeast China. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.-Y.; Zhao, S.-C.; He, W.-M.; Guo, L.-B.; Peng, Y.-L.; Wang, J.-J.; Guo, X.-S.; Zhang, X.-M.; Rao, Y.-C.; Zhang, C. Dissecting yield-associated loci in super hybrid rice by resequencing recombinant inbred lines and improving parental genome sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14492–14497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashikari, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Lin, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Takashi, T.; Nishimura, A.; Angeles, E.R.; Qian, Q.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. Cytokinin oxidase regulates rice grain production. Science 2005, 309, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Ma, C.; Hong, W.; Huang, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Zeng, H.; Deng, D.; Xin, H.; Song, J. Construction and Analysis of High-Density Linkage Map Using High-Throughput Sequencing Data. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Xia, X.; Geng, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Q. Genome sequencing of rice subspecies and genetic analysis of recombinant lines reveals regional yield- and quality-associated loci. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, N.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Sui, G. Genome Sequence and QTL Analyses Using Backcross Recombinant Inbred Lines (BILs) and BILF1 Lines Uncover Multiple Heterosis-related Loci. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030780
Yu Y, Zhu M, Cui Y, Liu Y, Li Z, Jiang N, Xu Z, Xu Q, Sui G. Genome Sequence and QTL Analyses Using Backcross Recombinant Inbred Lines (BILs) and BILF1 Lines Uncover Multiple Heterosis-related Loci. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030780
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yahui, Mengmeng Zhu, Yue Cui, Yu Liu, Zhenyu Li, Nan Jiang, Zhengjin Xu, Quan Xu, and Guomin Sui. 2020. "Genome Sequence and QTL Analyses Using Backcross Recombinant Inbred Lines (BILs) and BILF1 Lines Uncover Multiple Heterosis-related Loci" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030780
APA StyleYu, Y., Zhu, M., Cui, Y., Liu, Y., Li, Z., Jiang, N., Xu, Z., Xu, Q., & Sui, G. (2020). Genome Sequence and QTL Analyses Using Backcross Recombinant Inbred Lines (BILs) and BILF1 Lines Uncover Multiple Heterosis-related Loci. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030780



