Targeted Mutagenesis of the Rice FW 2.2-Like Gene Family Using the CRISPR/Cas9 System Reveals OsFWL4 as a Regulator of Tiller Number and Plant Yield in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Generation of Rice FWL Gene Mutants Using CRISPR/Cas9
2.2. Segregation of T-DNA in the T1 Generation
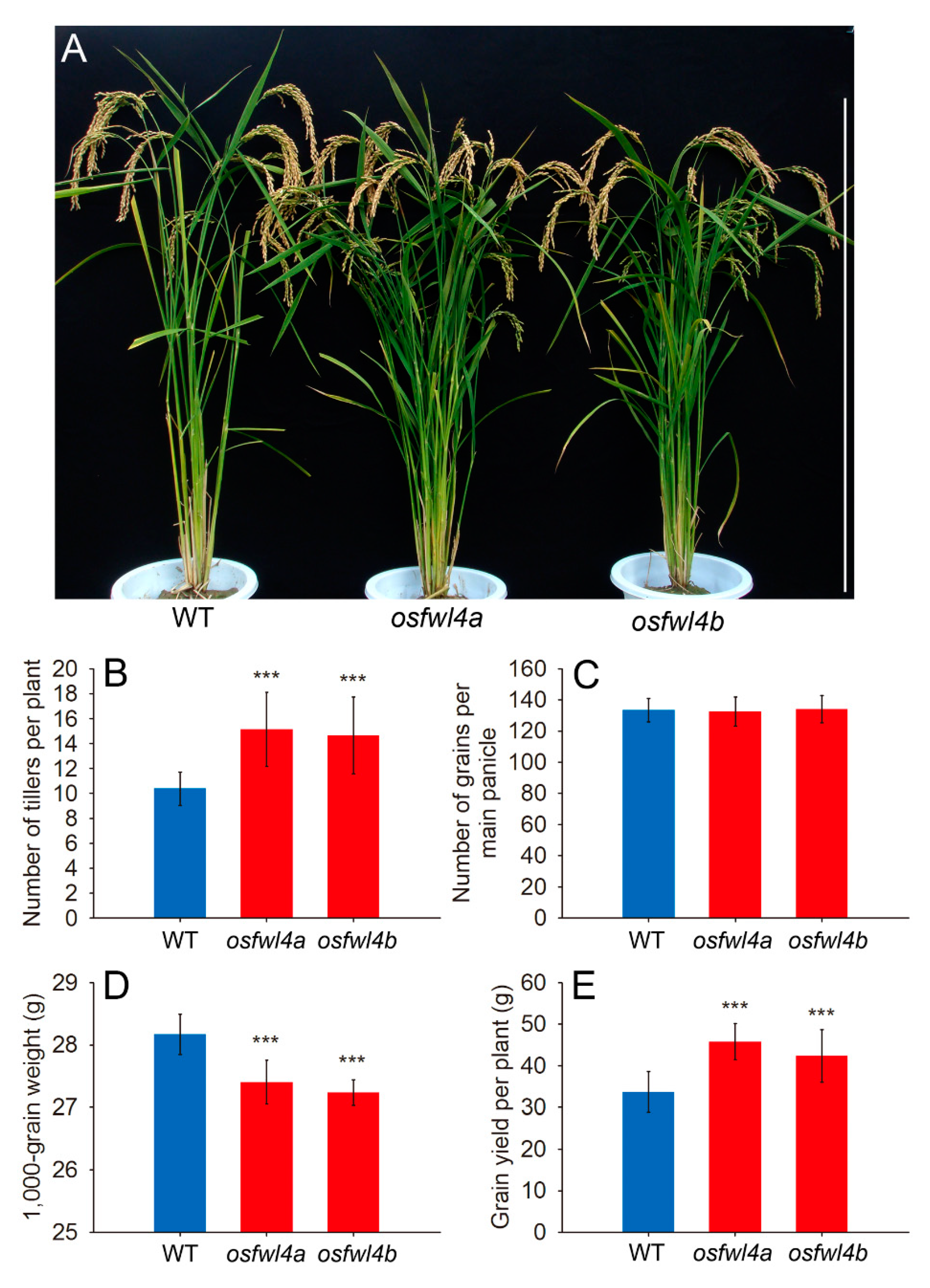
2.3. Phenotypic Analysis of Rice FWL Gene Mutants
2.4. Analysis of Off-Target Effects
2.5. Expression Analysis of Cas9 in Transgenic Plants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Construction of the CRISPR/Cas9 Plasmids
4.3. Detection of On-Target and Off-Target Mutations
4.4. Detection of the T-DNA Fragment
4.5. RNA Isolation and qRT-PCR
4.6. Leaf Epidermal Cell Observation
4.7. Trait Measurement
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cong, B.; Liu, J.P.; Tanksley, S.D. Natural alleles at a tomato fruit size quantitative trait locus differ by heterochronic regulatory mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13606–13611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frary, A.; Nesbitt, T.C.; Grandillo, S.; Knaap, E.; Cong, B.; Liu, J.; Meller, J.; Elber, R.; Alpert, K.B.; Tanksley, S.D. fw2.2: A quantitative trait locus key to the evolution of tomato fruit size. Science 2000, 289, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cong, B.; Tanksley, S.D. Generation and analysis of an artificial gene dosage series in tomato to study the mechanisms by which the cloned quantitative trait locus fw2.2 controls fruit size. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Rupe, M.A.; Dieter, J.A.; Zou, J.; Spielbauer, D.; Duncan, K.E.; Howard, R.J.; Hou, Z.; Simmons, C.R. Cell Number Regulator1 affects plant and organ size in maize: Implications for crop yield enhancement and heterosis. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1057–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libault, M.; Zhang, X.C.; Govindarajulu, M.; Qiu, J.; Ong, Y.T.; Brechenmacher, L.; Berg, R.H.; Hurley-Sommer, A.; Taylor, C.G.; Stacey, G. A member of the highly conserved FWL (tomato FW2.2-like) gene family is essential for soybean nodule organogenesis. Plant J. 2010, 62, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahan, Y.; Rosenfeld, R.; Zadiranov, V.; Irihimovitch, V. A proposed conserved role for an avocado FW2.2-like gene as a negative regulator of fruit cell division. Planta 2010, 232, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Franceschi, P.; Stegmeir, T.; Cabrera, A.; van der Knaap, E.; Rosyara, U.R.; Sebolt, A.M.; Dondini, L.; Dirlewanger, E.; Quero-Garcia, J.; Campoy, J.A.; et al. Cell number regulator genes in Prunus provide candidate genes for the control of fruit size in sweet and sour cherry. Mol. Breeding 2013, 32, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; He, C. Physalis floridana Cell Number Regulator1 encodes a cell membrane-anchored modulator of cell cycle and negatively controls fruit size. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Xiong, W.T.; Cao, B.B.; Yan, T.Z.; Luo, T.; Fan, T.T.; Luo, M.Z. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of “fruit-weight 2.2-like” gene family in rice. Planta 2013, 238, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Brechenmacher, L.; Smith, B.; Strout, G.W.; Mangin, W.; Taylor, C.; Russell, S.D.; Stacey, G.; Libault, M. The GmFWL1 (FW2-2-like) nodulation gene encodes a plasma membrane microdomain-associated protein. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 1442–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, K.; Tian, Y.; Hu, Z.; Chai, T. Wheat Cell Number Regulator CNR10 enhances the tolerance, translocation, and accumulation of heavy metals in plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.Y.; Choi, K.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Geisler, M.; Park, J.; Vincenzetti, V.; Schellenberg, M.; Kim, S.H.; Lim, Y.P.; Noh, E.W.; et al. Arabidopsis PCR2 is a zinc exporter involved in both zinc extrusion and long-distance zinc transport. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2237–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Jin, S.R.; Ko, D.; Martinoia, E.; Lee, Y.; An, G.; Ahn, S.N. Rice PCR1 influences grain weight and Zn accumulation in grains. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 2327–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.Y.; Martinoia, E.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, D.Y.; Vogt, E.; Shim, D.; Choi, K.S.; Hwang, I.; Lee, Y. A novel family of cys-rich membrane proteins mediates cadmium resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.T.; Wang, P.; Yan, T.Z.; Cao, B.B.; Xu, J.; Liu, D.F.; Luo, M.Z. The rice “fruit-weight 2.2-like” gene family member OsFWL4 is involved in the translocation of cadmium from roots to shoots. Planta 2018, 247, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurusu, T.; Nishikawa, D.; Yamazaki, Y.; Gotoh, M.; Nakano, M.; Hamada, H.; Yamanaka, T.; Iida, K.; Nakagawa, Y.; Saji, H.; et al. Plasma membrane protein OsMCA1 is involved in regulation of hypo-osmotic shock-induced Ca2+ influx and modulates generation of reactive oxygen species in cultured rice cells. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Katagiri, T.; Shinozaki, K.; Qi, Z.; Tatsumi, H.; Furuichi, T.; Kishigami, A.; Sokabe, M.; Kojima, I.; Sato, S.; et al. Arabidopsis plasma membrane protein crucial for Ca2+ influx and touch sensing in roots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3639–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.Y.; Choi, K.S.; Alexis de, A.; Martinoia, E.; Lee, Y. Brassica juncea plant cadmium resistance 1 protein (BjPCR1) facilitates the radial transport of calcium in the root. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19808–19813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, T.; Nakagawa, Y.; Mori, K.; Nakano, M.; Imamura, T.; Kataoka, H.; Terashima, A.; Iida, K.; Kojima, I.; Katagiri, T.; et al. MCA1 and MCA2 that mediate Ca2+ uptake have distinct and overlapping roles in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 1284–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tan, H.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, C. A novel family of PLAC8 motif-containing/PCR genes mediates Cd tolerance and Cd accumulation in rice. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, R.; Panday, A.; Elango, R.; Willis, N.A. DNA double-strand break repair-pathway choice in somatic mammalian cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.L.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.W.; Gao, C.X. CRISPR/Cas genome editing and precision plant breeding in agriculture. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 667–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, S.H.; Redding, S.; Jinek, M.; Greene, E.C.; Doudna, J.A. DNA interrogation by the CRISPR RNA-guided endonuclease Cas9. Nature 2014, 507, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Su, H.D.; Bai, H.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.L.; Guo, X.R.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, J.; Birchler, J.A.; et al. High-efficiency genome editing using a dmc1 promoter-controlled CRISPR/Cas9 system in maize. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.P.; Xing, H.L.; Dong, L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Han, C.Y.; Wang, X.C.; Chen, Q.J. Egg cell-specific promoter-controlled CRISPR/Cas9 efficiently generates homozygous mutants for multiple target genes in Arabidopsis in a single generation. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wei, P.; Zhang, B.; Gou, F.; Feng, Z.; Mao, Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, N.; Zhu, J.K. The CRISPR/Cas9 system produces specific and homozygous targeted gene editing in rice in one generation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, B.; Weeks, D.P.; Spalding, M.H.; Yang, B. Large chromosomal deletions and heritable small genetic changes induced by CRISPR/Cas9 in rice. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 10903–10914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, R.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.; et al. A robust CRISPR/Cas9 system for convenient, high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, R.; Yeo, N.C.; Chavez, A.; Church, G.M. sgRNA Scorer 2.0: A species-independent model to predict CRISPR/Cas9 activity. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017, 6, 902–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Botella, J.R.; Zhu, J.K. Heritability of targeted gene modifications induced by plant-optimized CRISPR systems. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 1075–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.F.; Li, H.; Qin, R.Y.; Li, J.; Qiu, C.H.; Yang, Y.C.; Ma, H.; Li, L.; Wei, P.C.; Yang, J.B. Generation of inheritable and “transgene clean” targeted genome-modified rice in later generations using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruz, T.; Laule, O.; Szabo, G.; Wessendorp, F.; Bleuler, S.; Oertle, L.; Widmayer, P.; Gruissem, W.; Zimmermann, P. Genevestigator v3: A reference expression database for the meta-analysis of transcriptomes. Adv. Bioinform. 2008, 2008, 420747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gingerich, D.J.; Hanada, K.; Shiu, S.H.; Vierstra, R.D. Large-scale, lineage-specific expansion of a bric-a-brac/tramtrack/broad complex ubiquitin-ligase gene family in rice. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2329–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, R.; Lin, J. Organization and dynamics of functional plant membrane microdomains. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheysen, G.; Herman, L.; Breyne, P.; Gielen, J.; Van Montagu, M.; Depicker, A. Cloning and sequence analysis of truncated T-DNA inserts from Nicotiana tabacum. Gene 1990, 94, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, L.; Jacobs, A.; Van Montagu, M.; Depicker, A. Plant chromosome/marker gene fusion assay for study of normal and truncated T-DNA integration events. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1990, 224, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheysen, G.; Villarroel, R.; Van Montagu, M. Illegitimate recombination in plants: A model for T-DNA integration. Genes Dev. 1991, 5, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Lee, J.; Jun, S.H.; Park, S.; Kang, H.G.; Kwon, S.; An, G. Transgene structures in T-DNA-inserted rice plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 52, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, G.L. Evidence of multiple complex patterns of T-DNA integration into the rice genome. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 100, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Mao, Y.; Xu, N.; Zhang, B.; Wei, P.; Yang, D.L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, R.; Yang, L.; et al. Multigeneration analysis reveals the inheritance, specificity, and patterns of CRISPR/Cas-induced gene modifications in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4632–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Liu, G.Q.; Zhou, J.P.; Ren, Q.R.; You, Q.; Tian, L.; Xin, X.H.; Zhong, Z.H.; Liu, B.L.; Zheng, X.L.; et al. A large-scale whole-genome sequencing analysis reveals highly specific genome editing by both Cas9 and Cpf1 (Cas12a) nucleases in rice. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, M.; Mikami, M.; Toki, S. Multigene knockout utilizing off-target mutations of the CRISPR/Cas9 system in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrenson, T.; Shorinola, O.; Stacey, N.; Li, C.; Ostergaard, L.; Patron, N.; Uauy, C.; Harwood, W. Induction of targeted, heritable mutations in barley and Brassica oleracea using RNA-guided Cas9 nuclease. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.R.; Li, X.X.; Zhou, Z.J.; Wu, P.Z.; Fang, M.C.; Pan, X.P.; Lin, Q.P.; Luo, W.B.; Wu, G.J.; Li, H.Q. Reassessment of the four yield-related genes Gn1a, DEP1, GS3, and IPA1 in rice using a CRISPR/Cas9 system. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xing, H.L.; Wang, Z.P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.C.; Chen, Q.J. Potential high-frequency off-target mutagenesis induced by CRISPR/Cas9 in Arabidopsis and its prevention. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 96, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doench, J.G.; Fusi, N.; Sullender, M.; Hegde, M.; Vaimberg, E.W.; Donovan, K.F.; Smith, I.; Tothova, Z.; Wilen, C.; Orchard, R.; et al. Optimized sgRNA design to maximize activity and minimize off-target effects of CRISPR-Cas9. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.D.; Scott, D.A.; Weinstein, J.A.; Ran, F.A.; Konermann, S.; Agarwala, V.; Li, Y.; Fine, E.J.; Wu, X.; Shalem, O.; et al. DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Ran, F.A.; Cox, D.; Lin, S.; Barretto, R.; Habib, N.; Hsu, P.D.; Wu, X.; Jiang, W.; Marraffini, L.A.; et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 2013, 339, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Ding, W.; Liu, X.; Yang, D.L.; Wei, P.; Cao, F.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, F.; Mao, Y.; et al. Efficient genome editing in plants using a CRISPR/Cas system. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 1229–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Aichi, I.; Matsuoka, M. A protocol for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in rice. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2796–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Ma, X.; Zhu, Q.; Zeng, D.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.G. CRISPR-GE: A convenient software toolkit for CRISPR-based genome editing. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1246–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Xie, X.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.G. DSDecode: A web-based tool for decoding of sequencing chromatograms for genotyping of targeted mutations. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1431–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.S.; Xu, S.H.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wang, L.L.; Yang, Z.F.; Zhao, X.X. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the RIO atypical kinase family in plants. Genes Genom. 2018, 40, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Eiguchi, M.; Hibara, K.; Ito, J.; Nagato, Y. Rice slender leaf 1 gene encodes cellulose synthase-like D4 and is specifically expressed in M-phase cells to regulate cell proliferation. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Gene | Locus | Target Name | Target Sequence (5′–3′) 1 | GC Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsFWL1 | LOC_Os02g52550 | Osfwl1a | CTGAAGGACTTACAGTTTCC GGG | 45 |
| Osfwl1b | TGGGCAGGTCGCTGACATCG TGG | 65 | ||
| OsFWL2 | LOC_Os02g36940 | Osfwl2a | GCGCTGGTGATGCTCCTCAC GGG | 65 |
| Osfwl2b | CATCTTGGCGCGGTAGAAGC AGG | 60 | ||
| OsFWL3 | LOC_Os02g36950 | Osfwl3a | ATCGCGGAGATCGTCGACCG GGG | 65 |
| Osfwl3b | GTGGACGAGGCAGTCGGGGC AGG | 75 | ||
| OsFWL4 | LOC_Os03g61440 | Osfwl4a | ATTGAAGCAGGCGAAGAGTC CGG | 50 |
| Osfwl4b | CGCAGCATGGGTCCTCGGGG AGG | 75 | ||
| OsFWL5 | LOC_Os10g02300 | Osfwl5a | ATCGCAGAAATCGTCGACAG GGG | 50 |
| Osfwl5b | CTCACGGTGCATCTGTGCGA TGG | 60 | ||
| OsFWL6 | LOC_Os03g61470 | Osfwl6a | TCGACGTCGTGCGGCACCGG CGG | 75 |
| Osfwl6b | GGCAAGATGCGCACTCAGTA CGG | 55 | ||
| OsFWL7 | LOC_Os03g61500 | Osfwl7a | CCCGTGCATCACGTTCGGGC GGG | 70 |
| Osfwl7b | CATCTTGCCCCGGTAGACGC AGG | 65 | ||
| OsFWL8 | LOC_Os03g61480 | Osfwl8a | GGGTCGACGTCGTTCGGCAC CGG | 70 |
| Osfwl8b | GTTGAGGTGCCATCCGAGCT TGG | 60 |
| Target | No. of T0 Plants Obtained | No. of Plants with Mutations | Zygosity | Combined Percentage of Homozygous and Bi-Allelic Mutants (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homozygous | Bi-Allelic | Heterozygous | Chimeric | ||||
| Osfwl1a | 15 | 7 (46.7%) | – | 7 (46.7%) | – | – | 46.7 |
| Osfwl1b | 14 | 14 (100.0%) | 9 (64.3%) | 5 (35.7%) | – | – | 100.0 |
| Osfwl2a | 16 | 15 (93.8%) | 1 (6.3%) | 14 (87.5%) | – | – | 93.8 |
| Osfwl2b | 14 | 11 (78.6%) | 3 (21.4%) | 8 (57.1%) | – | – | 78.6 |
| Osfwl3a | 7 | 6 (85.7%) | – | 4 (57.1%) | – | 2 (28.6%) | 57.1 |
| Osfwl3b | 25 | 22 (88.0%) | 2 (8.0%) | 13 (52.0%) | 1 (4.0%) | 6 (24.0%) | 60.0 |
| Osfwl4a | 15 | 11 (73.3%) | 3 (20.0%) | 8 (53.3%) | – | – | 73.3 |
| Osfwl4b | 15 | 10 (66.7%) | 1 (6.7%) | 8 (53.3%) | – | 1 (6.7%) | 60.0 |
| Osfwl5a | 14 | 14 (100.0%) | 2 (14.3%) | 12 (85.7%) | – | – | 100.0 |
| Osfwl5b | 14 | 14 (100.0%) | 7 (50.0%) | 7 (50.0%) | – | – | 100.0 |
| Osfwl6a | 15 | 4 (26.7%) | 1 (6.7%) | 3 (20.0%) | – | – | 26.7 |
| Osfwl6b | 16 | 15 (93.8%) | 5 (31.3%) | 10 (62.5%) | – | – | 93.8 |
| Osfwl7a | 14 | 13 (92.9%) | 2 (14.3%) | 10 (71.4%) | 1 (7.1%) | – | 85.7 |
| Osfwl7b | 15 | 12 (80.0%) | 5 (33.3%) | 6 (40.0%) | 1 (6.7%) | – | 73.3 |
| Osfwl8b | 14 | 14 (100.0%) | 3 (21.4%) | 11 (78.6%) | – | – | 100.0 |
| Total | 223 | 182 (81.6%) | 44 (19.7%) | 126 (56.5%) | 3 (1.3%) | 9 (4.0%) | 76.2 |
| Name of Putative Off-Target Site | Locus | Sequence of Putative Off-Target Site 1 | Region | No. of Mismatching Bases | No. of Plants Tested | No. of Plants with Mutations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osfwl1aOFF-1 | Chr2: 11000661–11000683 | CTGAATGACTGACTGTCTCC TGG | LOC_Os02g18850 intron | 4 | 32 | 0 |
| Osfwl1aOFF-2 | Chr2: 1853752–1853774 | CTGAAGGACTTGCACATTTC AGG | LOC_Os02g04230 intron | 4 | 32 | 0 |
| Osfwl1bOFF-1 | Chr6: 17267236–17267258 | CGGGCAGGACGCCGACATCG CGG | LOC_Os06g29994 CDS | 3 | 32 | 2 |
| Osfwl1bOFF-2 | Chr8: 15832268–15832290 | TGTGCAGGTCGATGACATCA TGG | Intergenic | 3 | 32 | 0 |
| Osfwl2aOFF-1 | Chr1: 14111612–14111634 | GCGATGGTGATGCTCCTCGC CGG | Intergenic | 2 | 32 | 4 |
| Osfwl2aOFF-2 | Chr6: 463763–463785 | ACGCAGGTGAAGCTCCTAAC TGG | LOC_Os06g01800 intron | 4 | 32 | 7 |
| Osfwl2bOFF-1 | Chr4: 24327403–24327425 | CATCTTGGGGAGGTAGAAGA AGG | LOC_Os04g40990 CDS | 3 | 30 | 0 |
| Osfwl2bOFF-2 | Chr2: 22320818–22320840 | CAGCTTGGAGCGGTAGATGC AGG | LOC_Os02g36950 CDS | 3 | 30 | 0 |
| Osfwl3aOFF-1 | Chr4: 23060613–23060635 | ATCGCGGAGATCGTCGACCA GGG | LOC_Os04g38790 CDS | 1 | 27 | 26 |
| Osfwl3aOFF-2 | Chr2: 22312627–22312649 | ATCGCGGAGATCATCGACCG GGG | LOC_Os02g36940 CDS | 1 | 27 | 26 |
| Osfwl3bOFF-1 | Chr2: 22312479–22312501 | GTGGACGGGGCAGTCGGCGC AGG | LOC_Os02g36940 CDS | 2 | 41 | 7 |
| Osfwl3bOFF-2 | Chr2: 4426323–4426345 | GTGGAAGAAGAAGTCGAGGC AGG | LOC_Os02g08330 CDS | 4 | 41 | 0 |
| Osfwl4aOFF-1 | Chr7: 3799011–3799033 | TTTGAAGCAGGTGAAGAGTC CGG | LOC_Os07g07580 intron | 2 | 28 | 23 |
| Osfwl4aOFF-2 | Chr9: 2298486–2298508 | CATGAGGAAGGCGAGGAGTC CGG | LOC_Os09g04339 CDS | 5 | 28 | 0 |
| Osfwl4bOFF-1 | Chr1: 31161078–31161100 | CGCTGCATCTGTCCTCGGGA AGG | Intergenic | 4 | 31 | 0 |
| Osfwl4bOFF-2 | Chr2: 5315090–5315112 | AGCAGAAAGGATCCTGGGGG AGG | Intergenic | 5 | 31 | 0 |
| Osfwl5aOFF-1 | Chr6: 7393721–7393743 | ATCTCAGAAATAATCGACAG CGG | Intergenic | 3 | 31 | 0 |
| Osfwl5aOFF-2 | Chr4: 19176717–19176739 | GTCCCAGGACTCGTCGACAG AGG | LOC_Os04g32020 5′ UTR | 4 | 31 | 0 |
| Osfwl5bOFF-1 | Chr4: 34131133–34131155 | CGCCCGGTGCATCTGCGCGA TGG | LOC_Os04g57330 5′ UTR | 3 | 32 | 3 |
| Osfwl5bOFF-2 | Chr6: 22532424–22532446 | ATCACGGTGAGCATGTGCGA TGG | LOC_Os06g38090 intron | 5 | 32 | 0 |
| Osfwl6aOFF-1 | Chr3: 34884082–34884104 | TCGACGTCGTGCGGCACCAG CGG | LOC_Os03g61500 CDS | 1 | 33 | 21 |
| Osfwl6aOFF-2 | Chr3: 16449514–16449536 | AAGACGTCGAGCGGCACCGG CGG | LOC_Os03g28980 CDS | 3 | 33 | 21 |
| Osfwl6bOFF-1 | Chr3: 34878541–34878563 | GGCAAGATGCGCGCACAGTA CGG | LOC_Os03g61490 CDS | 2 | 31 | 0 |
| Osfwl6bOFF-2 | Chr1: 29494129–29494151 | AGCTAGACGTGCAATCAGTA CGG | Intergenic | 5 | 31 | 0 |
| Osfwl7aOFF-1 | Chr3: 34870990–34871012 | CCCGTGCATCACGTTCGGGA GGG | LOC_Os03g61470 CDS | 1 | 31 | 17 |
| Osfwl7aOFF-2 | Chr10: 21731587–21731609 | CCCATGCATCACGTTAGGTC CGG | LOC_Os10g40580 5′ UTR | 3 | 31 | 0 |
| Osfwl7bOFF-1 | Chr11: 6506399–6506421 | GATCTTGCTCCGGTCGACGC CGG | Intergenic | 3 | 32 | 0 |
| Osfwl7bOFF-2 | Chr2: 22312530–22312552 | CATCTTGGCGCGGTAGAAGC AGG | LOC_Os02g36940 CDS | 3 | 32 | 0 |
| Osfwl8bOFF-1 | Chr3: 34883868–34883890 | GTTGAGGTCCCATCCGAGCT TGG | LOC_Os03g61500 CDS | 1 | 30 | 30 |
| Osfwl8bOFF-2 | Chr3: 34857174–34857196 | GTTGAGGTGCCACCCAAGCT TGG | LOC_Os03g61430 CDS | 2 | 30 | 13 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Q.; Li, G.; Sun, H.; Xu, M.; Wang, H.; Ji, J.; Wang, D.; Yuan, C.; Zhao, X. Targeted Mutagenesis of the Rice FW 2.2-Like Gene Family Using the CRISPR/Cas9 System Reveals OsFWL4 as a Regulator of Tiller Number and Plant Yield in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030809
Gao Q, Li G, Sun H, Xu M, Wang H, Ji J, Wang D, Yuan C, Zhao X. Targeted Mutagenesis of the Rice FW 2.2-Like Gene Family Using the CRISPR/Cas9 System Reveals OsFWL4 as a Regulator of Tiller Number and Plant Yield in Rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030809
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Qingsong, Gang Li, Hui Sun, Ming Xu, Huanhuan Wang, Jianhui Ji, Di Wang, Caiyong Yuan, and Xiangxiang Zhao. 2020. "Targeted Mutagenesis of the Rice FW 2.2-Like Gene Family Using the CRISPR/Cas9 System Reveals OsFWL4 as a Regulator of Tiller Number and Plant Yield in Rice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030809
APA StyleGao, Q., Li, G., Sun, H., Xu, M., Wang, H., Ji, J., Wang, D., Yuan, C., & Zhao, X. (2020). Targeted Mutagenesis of the Rice FW 2.2-Like Gene Family Using the CRISPR/Cas9 System Reveals OsFWL4 as a Regulator of Tiller Number and Plant Yield in Rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030809




