Genome-Wide Profiling and Phylogenetic Analysis of the SWEET Sugar Transporter Gene Family in Walnut and Their Lack of Responsiveness to Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genome-Wide Identification of SWEET Family Genes in Walnut
2.2. Gene Structure Analysis, Transmembrane Helix, and Motif Recognition of JrSWEETs
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of JrSWEET Proteins
2.4. Expression Profiles of JrSWEETs in Different Tissues and Organs and at Different Developmental Stages
2.5. Expression Analysis of JrSWEET Genes after Xaj417 Infection
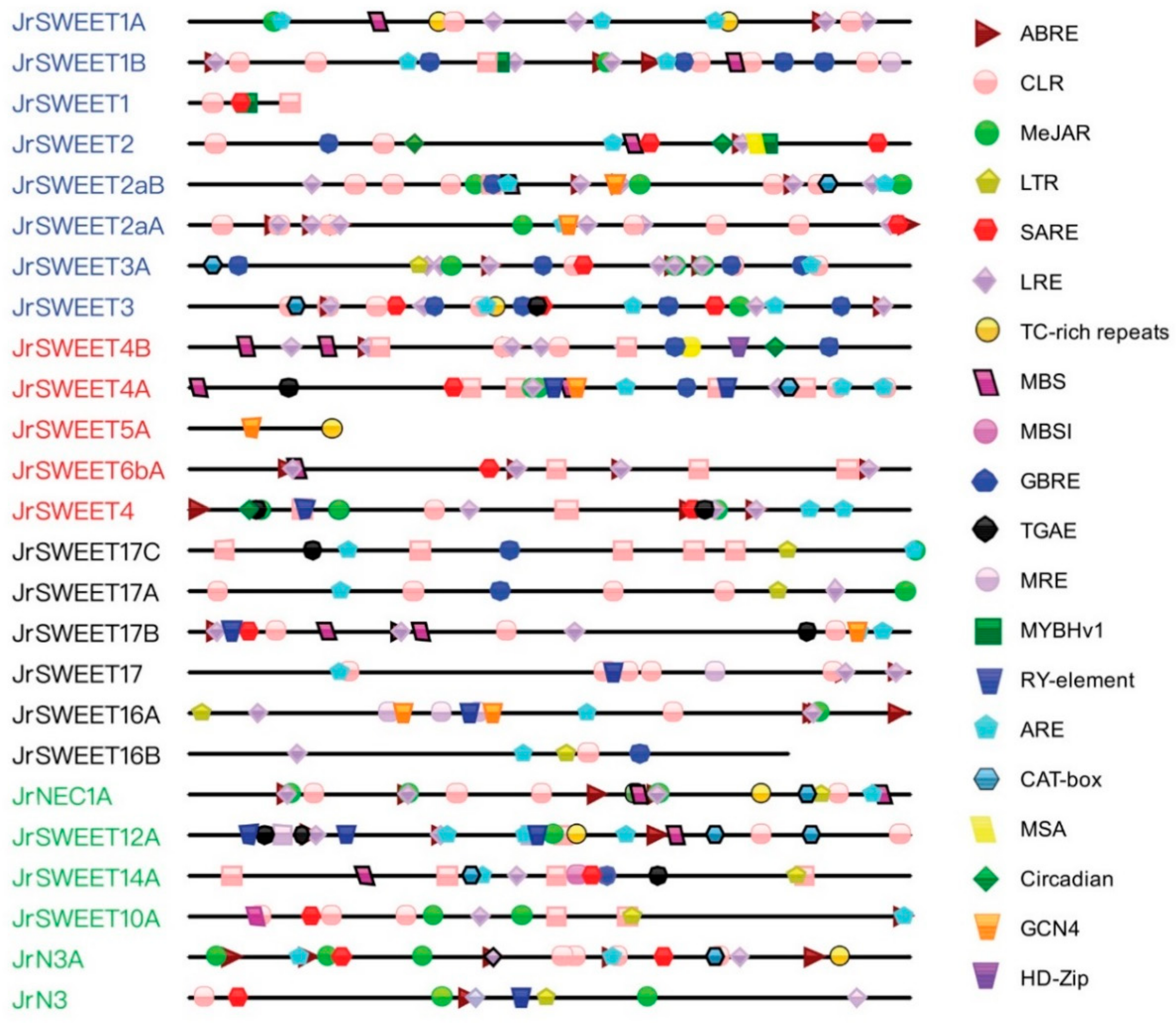
2.6. Prediction and Functional Analysis of Cis-Regulatory Elements in Putative Promoter Regions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genome-Wide Identification of SWEET Family Genes in Walnut
4.2. Gene Structure Analysis, Transmembrane Helix, and Motif Recognition of JrSWEETs
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of JrSWEET Proteins
4.4. Expression Profiles of JrSWEETs in Different Tissues, Organs, and Developmental Stages from RNA-Seq Data
4.5. Expression of JrSWEET Genes after Inoculation with Xaj417
4.6. Total RNA Isolation and Gene Expression by Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.7. Searching for TALEs in Xaj417
4.8. Prediction and Functional Analysis of Cis-Regulatory Elements in Putative Promoter Regions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SWEET | Sugar will eventually be exported transporters |
| Xaj | Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis |
| TALEs | Transcription activator-like effectors |
| SUTs | Sucrose transporters |
| TMDs | Transmembrane domains |
| TMHs | Transmembrane helixes |
| PPO2 | Polyphenol oxidase |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time PCR |
| pI | Isoelectric point |
References
- Chen, L.Q.; Qu, X.Q.; Hou, B.H.; Sosso, D.; Osorio, S.; Fernie, A.R.; Frommer, W.B. Sucrose Efflux Mediated by SWEET Proteins as a Key Step for Phloem Transport. Science 2012, 335, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comtet, J.; Turgeon, R.; Stroock, A.D. Phloem Loading through Plasmodesmata: A Biophysical Analysis. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalonde, S.; Wipf, D.; Frommer, W.B. Transport Mechanisms for Organic Forms of Carbon and Nitrogen between Source and Sink. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 341–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comtet, J.; Jensen, K.H.; Turgeon, R.; Stroock, A.D.; Hosoi, A.E. Passive Phloem Loading and Long Distance Transport in a Synthetic Tree on a chip. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayre, B.G. Membrane-Transport Systems for Sucrose in Relation to Whole-Plant Carbon Partitioning. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Turgeon, R. Mechanisms of Phloem Loading. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 43, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, S.; Frommer, W.B. SUT Sucrose and MST Monosaccharide Transporter Inventory of the Selaginella Genome. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank Baker, R.; Leach, K.A.; Braun, D.M. SWEET as Sugar: New Sucrose Effluxers in Plants. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 766–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doidy, J.; Grace, E.; Kühn, C.; Simon-Plas, F.; Casieri, L.; Wipf, D. Sugar transporters in plants and in their interactions with fungi. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, D. Co-option of developmentally regulated plant SWEET transporters for pathogen nutrition and abiotic stress tolerance: Role of SWEET in Pathogen Nutrition and Srtress Tolerence. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Q. SWEET Sugar Transporters for Phloem Transport and Pathogen Nutrition. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, Y.H.; Hu, Y.B.; Chen, L.Q.; Sosso, D.; Ducat, D.C.; Hou, B.-H.; Frommer, W.B. Functional Role of Oligomerization for Bacterial and Plant SWEET Sugar Transporter Family. PNAS 2013, 110, E3685–E3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Cheung, L.S.; Fan, C.; Chen, L.Q.; Xu, S.; Perry, K.; Frommer, W.B.; Feng, L. Structures of Bacterial Homologues of SWEET Transporters in Two Distinct Conformations. Nature 2014, 515, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, D.M. SWEET! The Pathway Is Complete. Science 2012, 335, 173–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Zhao, J.; Huang, R.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. Rice MtN3/saliva/SWEET gene family: Evolution, Expression Profiling, and Sugar Transport. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chardon, F.; Bedu, M.; Calenge, F.; Klemens, P.A.W.; Spinner, L.; Clement, G.; Chietera, G.; Léran, S.; Ferrand, M.; Lacombe, B.; et al. Leaf Fructose Content Is Controlled by the Vacuolar Transporter SWEET17 in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Tian, Z.; Li, J. AtSWEET4, a Hexose Facilitator, Mediates Sugar Transport to Axial Sinks and Affects Plant Development. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Sugio, A.; White, F.F. Os8N3 is a Host Disease-susceptibility Gene for Bacterial Blight of Rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2006, 103, 10503–10508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Peng, Z.; Long, J.; Sosso, D.; Liu, B.; Eom, J.S.; Huang, S.; Liu, S.; Vera Cruz, C.; Frommer, W.B.; et al. Gene targeting by the TAL effector PthXo2 reveals cryptic resistance gene for bacterial blight of rice. Plant J. 2015, 82, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanvillain-Baufumé, S.; Reschke, M.; Solé, M.; Auguy, F.; Doucoure, H.; Szurek, B.; Meynard, D.; Portefaix, M.; Cunnac, S.; Guiderdoni, E.; et al. Targeted Promoter Editing for Rice Resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae reveals differential activities for SWEET14 Inducing TAL effectors. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 306–317. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; Wang, S. Rice MtN3/Saliva/SWEET Family Genes and Their Homologs in Cellular Organisms. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streubel, J.; Pesce, C.; Hutin, M.; Koebnik, R.; Boch, J.; Szurek, B. Five Phylogenetically Close Rice SWEET Genes Confer TAL effector-mediated Susceptibility to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. A Paralog of the MtN3/saliva Family Recessively Confers Race-specific Resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae in Rice: MtN3/saliva-type Gene in Rice Disease Resistance. Plantcell Environ. 2011, 34, 1958–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, K.L.; Meng, F.; Wilkins, K.E.; Li, F.; Wang, P.; Booher, N.J.; Carpenter, S.C.D.; Chen, L.Q.; Zheng, H.; Gao, X.; et al. TAL effector Driven Induction of a SWEET gene Confers Susceptibility to Bacterial Blight of Cotton. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, M.; Bart, R.S.; Shybut, M.; Dahlbeck, D.; Gomez, M.; Morbitzer, R.; Hou, B.H.; Frommer, W.B.; Lahaye, T.; Staskawicz, B.J. Xanthomonas axonopodis Virulence Is Promoted by a Transcription Activator-Like Effector–Mediated Induction of a SWEET Sugar Transporter in Cassava. MPMI 2014, 27, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jia, H.; Sosso, D.; Li, T.; Frommer, W.B.; Yang, B.; White, F.F.; Wang, N.; Jones, J.B. Lateral Organ Boundaries 1 is a Disease Susceptibility Gene for Citrus Bacterial Canker Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E521–E529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boevink, P.C.; McLellan, H.; Gilroy, E.M.; Naqvi, S.; He, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Turnbull, D.; Armstrong, M.R.; Tian, Z.; et al. Oomycetes Seek Help from the Plant: Phytophthora infestans Effectors Target Host Susceptibility Factors. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-Q.; Hou, B.H.; Lalonde, S.; Takanaga, H.; Hartung, M.L.; Qu, X.Q.; Guo, W.J.; Kim, J.-G.; Underwood, W.; Chaudhuri, B.; et al. Sugar transporters for intercellular exchange and nutrition of pathogens. Nature 2010, 468, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Piron, M.C.; Meyer, S.; Merdinoglu, D.; Bertsch, C.; Mestre, P. The SWEET Family of Sugar Transporters in Grapevine: VvSWEET4 is Involved in the Interaction with Botrytis cinerea. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 6589–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamas, P.; de Carvalho Niebel, F.; Lescure, N.; Cullimore, J. Use of a Subtractive Hybridization Approach to Identify New Medicago truncatula Genes Induced During Root Nodule Development. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1996, 9, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.; Lu, K.; Yang, B.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, A.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Qu, C.; Li, J. Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profiling of the SUC and SWEET Gene Families of Sucrose Transporters in Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Kumar, V.; Xu, X.F.; Yuan, D.P.; Zhu, X.F.; Li, T.Y.; Jia, B.; Xuan, Y.H. Genome-wide Identification of the SWEET Gene Family in Wheat. Gene 2018, 642, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Sun, P.; Liu, Q.; Miao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, K.; Hu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Genome-wide Analyses of SWEET Family Proteins Reveal Involvement in Fruit Development and Abiotic/biotic Stress Responses in Banana. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Xuan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wei, Y.; Piao, Z. Genome Wide Identification and Expression Profiling of SWEET Genes Family Reveals Its Role During Plasmodiophora brassicae Induced Formation of Clubroot in Brassica rapa. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schornack, S.; Meyer, A.; Römer, P.; Jordan, T.; Lahaye, T. Gene-for-gene-mediated recognition of nuclear-targeted AvrBs3-like bacterial effector proteins. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 163, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.; Hahn, S.; Marois, E.; Hause, G.; Bonas, U. A Bacterial Effector Acts as a Plant Transcription Factor and Induces a Cell Size Regulator. Science 2007, 318, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadi, F.; Tohidfar, M.; Mohayeji, M.; Dandekar, A.M.; Leslie, C.A.; Kluepfel, D.A.; Butterfield, T.; Vahdati, K. Induction of Polyphenol Oxidase in Walnut and Its Relationship to the Pathogenic Response to Bacterial Blight. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2016, 141, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araji, S.; Grammer, T.A.; Gertzen, R.; Anderson, S.D.; Mikulic-Petkovsek, M.; Veberic, R.; Phu, M.L.; Solar, A.; Leslie, C.A.; Dandekar, A.M.; et al. Novel Roles for the Polyphenol Oxidase Enzyme in Secondary Metabolism and the Regulation of Cell Death in Walnut. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Britton, M.; Wegrzyn, J.; Butterfield, T.; Rao, B.J.; Leslie, C.A.; Aradhaya, M.; Neale, D.; Woeste, K.; Dandekar, A.M. YeATS—A Tool Suite for Analyzing RNA-seq Derived Transcriptome Identifies a Highly Transcribed Putative Extensin in Heartwood/sapwood Transition Zone in Black Walnut. F1000Research 2015, 4, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-García, P.J.; Crepeau, M.W.; Puiu, D.; Gonzalez-Ibeas, D.; Whalen, J.; Stevens, K.A.; Paul, R.; Butterfield, T.S.; Britton, M.T.; Reagan, R.L.; et al. The walnut (Juglans regia) Genome Sequence Reveals Diversity in Genes Coding for the Biosynthesis of Non-structural Polyphenols. Plant J. 2016, 87, 507–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, J.; Reschke, M.; Erkes, A.; Streubel, J.; Morgan, R.D.; Wilson, G.G.; Koebnik, R.; Boch, J. AnnoTALE: Bioinformatics Tools for Identification, Annotation and Momenclature of TALEs from Xanthomonas Genomic Sequences. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M. PlantCARE, a Database of Plant Cis-acting Regulatory Elements and a Portal to Tools for in Silico Analysis of Promoter Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Yao, J.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; LÜ, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. A Genome-wide Analysis of SWEET Gene Family in Cotton and Their Expressions Under Different Stresses. J. Cotton Res. 2018, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qin, M.; Qiao, X.; Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J. A New Insight into the Evolution and Functional Divergence of SWEET Transporters in Chinese White Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). Plant Cell Physiol 2017, 58, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, J.S.; Chen, L.Q.; Sosso, D.; Julius, B.T.; Lin, I.; Qu, X.Q.; Braun, D.M.; Frommer, W.B. SWEETs, transporters for intracellular and intercellular sugar translocation. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 25, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triplett, L.R.; Hamilton, J.P.; Buell, C.R.; Tisserat, N.A.; Verdier, V.; Zink, F.; Leach, J.E. Genomic Analysis of Xanthomonas oryzae Isolates from Rice Grown in the United States Reveals Substantial Divergence from Known X. oryzae Pathovars. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3930–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkes, A.; Reschke, M.; Boch, J.; Grau, J. Evolution of Transcription Activator-Like Effectors in Xanthomonas oryzae. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 1599–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denancé, N.; Szurek, B.; Doyle, E.L.; Lauber, E.; Fontaine-Bodin, L.; Carrère, S.; Guy, E.; Hajri, A.; Cerutti, A.; Boureau, T.; et al. Two ancestral genes shaped the Xanthomonas campestris TAL effector gene repertoire. New Phytol. 2018, 219, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajri, A.; Pothier, J.F.; Fischer-Le Saux, M.; Bonneau, S.; Poussier, S.; Boureau, T.; Duffy, B.; Manceau, C. Type Three Effector Gene Distribution and Sequence Analysis Provide New Insights into the Pathogenicity of Plant-Pathogenic Xanthomonas arboricola. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.Y.; Han, J.X.; Han, X.X.; Jiang, J. Genome-wide Identification, Phylogeny, and Expression Analysis of the SWEET Gene Family in Tomato. Gene 2015, 573, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, S.; Ma, S.; Sui, X.; Zhang, Z. Spatiotemporal Expression and Substrate Specificity Analysis of the Cucumber SWEET Gene Family. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.; Zhu, X.F.; Pu, Z.J.; Duan, Y.X.; Hao, L.J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.Q.; Jeon, C.O.; Xuan, Y.H. Integrative View of the Diversity and Evolution of SWEET and SemiSWEET Sugar Transporters. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liu, J.H. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Polyamine Oxidase Gene Family in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis). Gene 2015, 555, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filyushin, M.A.; Kochieva, E.Z.; Shchennikova, A.V.; Beletsky, A.V.; Mardanov, A.V.; Ravin, N.V.; Skryabin, K.G. SWEET Uniporter Gene Family Expression Profile in the Pitcher Development in the Carnivorous Plant Nepenthes sp. Russ. J. Genet. 2019, 55, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, M.L.; Holmes-Davis, R.; McCormick, S. Green Sperm. Identification of Male Gamete Promoters in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 2124–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.F.; Huang, X.Y.; Zhu, J.; Gao, J.F.; Zhang, H.X.; Yang, Z.N. RUPTURED POLLEN GRAIN1, a Member of the MtN3/saliva Gene Family, Is Crucial for Exine Pattern Formation and Cell Integrity of Microspores in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.-X.; Huang, X.Y.; Yang, J.; Guan, Y.F.; Yang, Z.N. Arabidopsis RPG1 is Important for Primexine Deposition and Functions Redundantly with RPG2 for Plant Fertility at the Late Reproductive Stage. Plant Reprod. 2013, 26, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.J.; Nagy, R.; Chen, H.Y.; Pfrunder, S.; Yu, Y.C.; Santelia, D.; Frommer, W.B.; Martinoia, E. SWEET17, a Facilitative Transporter, Mediates Fructose Transport Across the Tonoplast of Arabidopsis Roots and Leaves. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boch, J.; Bonas, U.; Lahaye, T. TAL effectors pathogen strategies and plant resistance engineering. New Phytol. 2014, 204, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, R.; Ji, C.; Atienza-Grande, G.; Huguet-Tapia, J.C.; Perez-Quintero, A.; Li, T.; Eom, J.S.; Li, C.; Nguyen, H.; Liu, B.; et al. Broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice using genome editing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, J.S.; Luo, D.; Atienza-Grande, G.; Yang, J.; Ji, C.; Thi Luu, V.; Huguet-Tapia, J.C.; Char, S.N.; Liu, B.; Nguyen, H.; et al. Diagnostic kit for rice blight resistance. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De AB Assis, R.; Polloni, L.C.; Patané, J.S.L.; Thakur, S.; Felestrino, É.B.; Diaz-Caballero, J.; Digiampietri, L.A.; Goulart, L.R.; Almeida, N.F.; Nascimento, R.; et al. Identification and analysis of seven effector protein families with different adaptive and evolutionary histories in plant-associated members of the Xanthomonadaceae. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Heger, A.; Hetherington, K.; Holm, L.; Mistry, J.; et al. Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER Web Server: Interactive Sequence Similarity Searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A. CDD: A Database of Conserved Domain Alignments with Links to Domain Three-dimensional Structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. 20 Years of the SMART Protein Domain Annotation Resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E. ExPASy: The Proteomics Server for in-depth Protein Knowledge and Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujita, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.J.; Nakai, K. WoLF PSORT: Protein Localization Predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuelsson, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. Locating Proteins in the Cell using TargetP, SignalP and Related Tools. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, L.; You, F.M.; Rodriguez, J.C.; Deal, K.R.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Chakraborty, S.; Balan, B.; Jiang, C.Z.; et al. Sequencing a Juglans regia × J. microcarpa hybrid yields high-quality genome assemblies of parental species. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L. Predicting Transmembrane Protein Topology with a Hidden Markov Model: Application to Complete Genomes11Edited by F. Cohen. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An Upgraded Gene Feature Visualization Server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Xia, R.; Chen, H.; He, Y. TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists Integrating Various HTS-Data Handling Tools with a User-friendly Interface. BioRxiv 2018, 289660. [Google Scholar]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v3: an Online Tool for the Display and Annotation of Phylogenetic and Other Trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W242–W245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Britton, M.; Martínez-García, P.J.; Dandekar, A.M. Deep RNA-Seq Profile Reveals Biodiversity, Plant–microbe Interactions and a Large Family of NBS-LRR Resistance genes in walnut (Juglans regia) Tissues. Amb Express 2016, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, U.P.; Gouran, H.; Nascimento, R.; Adaskaveg, J.E.; Goulart, L.R.; Dandekar, A.M. Complete Genome Sequence of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis 417, a Copper-Resistant Strain Isolated from Juglans regia L. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e01126–e01215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, M.L. GraphPad Prism, Data Analysis, and Scientific Graphing. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1997, 37, 411–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, Y.; Ma, J.; Luo, X.; Nie, P.; Zuo, Z.; Lahrmann, U.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. IBS: An Illustrator for the Presentation and Visualization of Biological Sequences: Fig. 1. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3359–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Clade | Gene Name | Locus | Size (aa) a | Mw (kDa) | pI | Genomic Location | MtN3/Saliva (PQ-Loop Repeat) Domain Position | Loc b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | JrSWEET1 | 108999697 | 254 | 28.22 | 9.43 | NW_017444989.1:303-3465 | 7–94, 131–213 | PM |
| I | JrSWEET1A | 109004166 | 258 | 28.22 | 6.3 | NW_017388835.1:280022-280798 | 6–95, 129–215 | PM |
| I | JrSWEET1B | 109004173 | 261 | 29.01 | 9.35 | NW_017388835.1:318614-319399 | 7–96, 130–216 | PM |
| I | JrSWEET2 | 108985341 | 235 | 26.11 | 9.27 | NW_017442681.1:95892-99748 | 18–102, 139–222 | PM |
| I | JrSWEET2aA | 108987476 | 235 | 25.72 | 8.84 | NW_017442906.1:10127-13031 | 18–102, 138–219 | PM |
| I | JrSWEET2aB | 108998082 | 235 | 26.01 | 9.34 | NW_017443613.1:377035-380456 | 18–102, 138–220 | VM |
| I | JrSWEET3 | 108985064 | 246 | 27.72 | 9.15 | NW_017442611.1:20354-22484 | 9–95, 133–216 | PM |
| I | JrSWEET3A | 108982726 | 292 | 33.24 | 9.32 | NW_017441679.1:10593-14236 | 9–95, 121–201 | PM |
| II | JrSWEET4 | 108997137 | 241 | 26.75 | 9.01 | NW_017388976.1:192220-194338 | 10–97, 136–217 | PM |
| II | JrSWEET4A | 109002076 | 265 | 29.06 | 9.13 | NW_017443554.1:481695-483478 | 10–97, 133–217 | PM |
| II | JrSWEET4B | 108993759 | 301 | 33.19 | 9.23 | NW_017443600.1:567007-569556 | 49–136, 172–256 | PM |
| II | JrSWEET5A | 108999161 | 231 | 26.37 | 8.9 | NW_017443629.1:533788-536495 | 10–95, 133–216 | PM |
| II | JrSWEET6bA | 108992796 | 225 | 24.89 | 9.3 | NW_017443540.1:669544-671368 | 9–98, 134–220 | PM |
| III | JrN3 | 108984368 | 295 | 33.08 | 7.63 | NW_017442395.1:48585-51197 | 12–96, 132–217 | PM |
| III | JrN3A | 109004781 | 294 | 32.77 | 8.29 | NW_017389221.1:55377-57616 | 13–97, 133–219 | PM |
| III | JrNEC1A | 108992134 | 294 | 32.72 | 6.99 | NW_017443525.1:147356-149392 | 14–97, 136–219 | PM |
| III | JrSWEET10A | 108990746 | 281 | 31.88 | 9.06 | NW_017443364.1:192481-194495 | 10–95, 131–215 | PM |
| III | JrSWEET12A | 108990744 | 298 | 32.84 | 8.27 | NW_017443364.1:211540-213673 | 13–98, 134–218 | PM |
| III | JrSWEET14A | 108998489 | 272 | 30.98 | 9 | NW_017388807.1:776356-778642 | 10–96, 132–216 | PM |
| IV | JrSWEET16A | 109006766 | 154 | 16.63 | 9.72 | NW_017389361.1:1228957-1230806 | 6–93 | PM |
| IV | JrSWEET16B | 108979882 | 277 | 30.37 | 9.52 | NW_017439469.1:3236-6113 | 7–90, 128–211 | PM |
| IV | JrSWEET17 | 108994709 | 247 | 27.37 | 5.87 | NW_017443571.1:1587292-1596052 | 6–95, 133–214 | VM |
| IV | JrSWEET17A | 108987463 | 259 | 28.83 | 6.59 | NW_017442898.1:55816-57539 | 16–97, 136–218 | CL |
| IV | JrSWEET17B | 108987468 | 247 | 27.03 | 7.73 | NW_017442898.1:62119-64578 | 7–90, 128–212 | PM |
| IV | JrSWEET17C | 109012696 | 253 | 28.11 | 5.85 | NW_017389857.1:1048384-1050148 | 9–90, 129–211 | PM |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Balan, B.; Assis, R.d.A.B.; Sagawa, C.H.D.; Wan, X.; Han, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zaini, P.A.; Walawage, S.L.; et al. Genome-Wide Profiling and Phylogenetic Analysis of the SWEET Sugar Transporter Gene Family in Walnut and Their Lack of Responsiveness to Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041251
Jiang S, Balan B, Assis RdAB, Sagawa CHD, Wan X, Han S, Wang L, Zhang L, Zaini PA, Walawage SL, et al. Genome-Wide Profiling and Phylogenetic Analysis of the SWEET Sugar Transporter Gene Family in Walnut and Their Lack of Responsiveness to Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(4):1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041251
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shijiao, Bipin Balan, Renata de A. B. Assis, Cintia H. D. Sagawa, Xueqin Wan, Shan Han, Le Wang, Lanlan Zhang, Paulo A. Zaini, Sriema L. Walawage, and et al. 2020. "Genome-Wide Profiling and Phylogenetic Analysis of the SWEET Sugar Transporter Gene Family in Walnut and Their Lack of Responsiveness to Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 4: 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041251
APA StyleJiang, S., Balan, B., Assis, R. d. A. B., Sagawa, C. H. D., Wan, X., Han, S., Wang, L., Zhang, L., Zaini, P. A., Walawage, S. L., Jacobson, A., Lee, S. H., Moreira, L. M., Leslie, C. A., & Dandekar, A. M. (2020). Genome-Wide Profiling and Phylogenetic Analysis of the SWEET Sugar Transporter Gene Family in Walnut and Their Lack of Responsiveness to Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(4), 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041251






