Development of a Modified Three-Day T-maze Protocol for Evaluating Learning and Memory Capacity of Adult Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
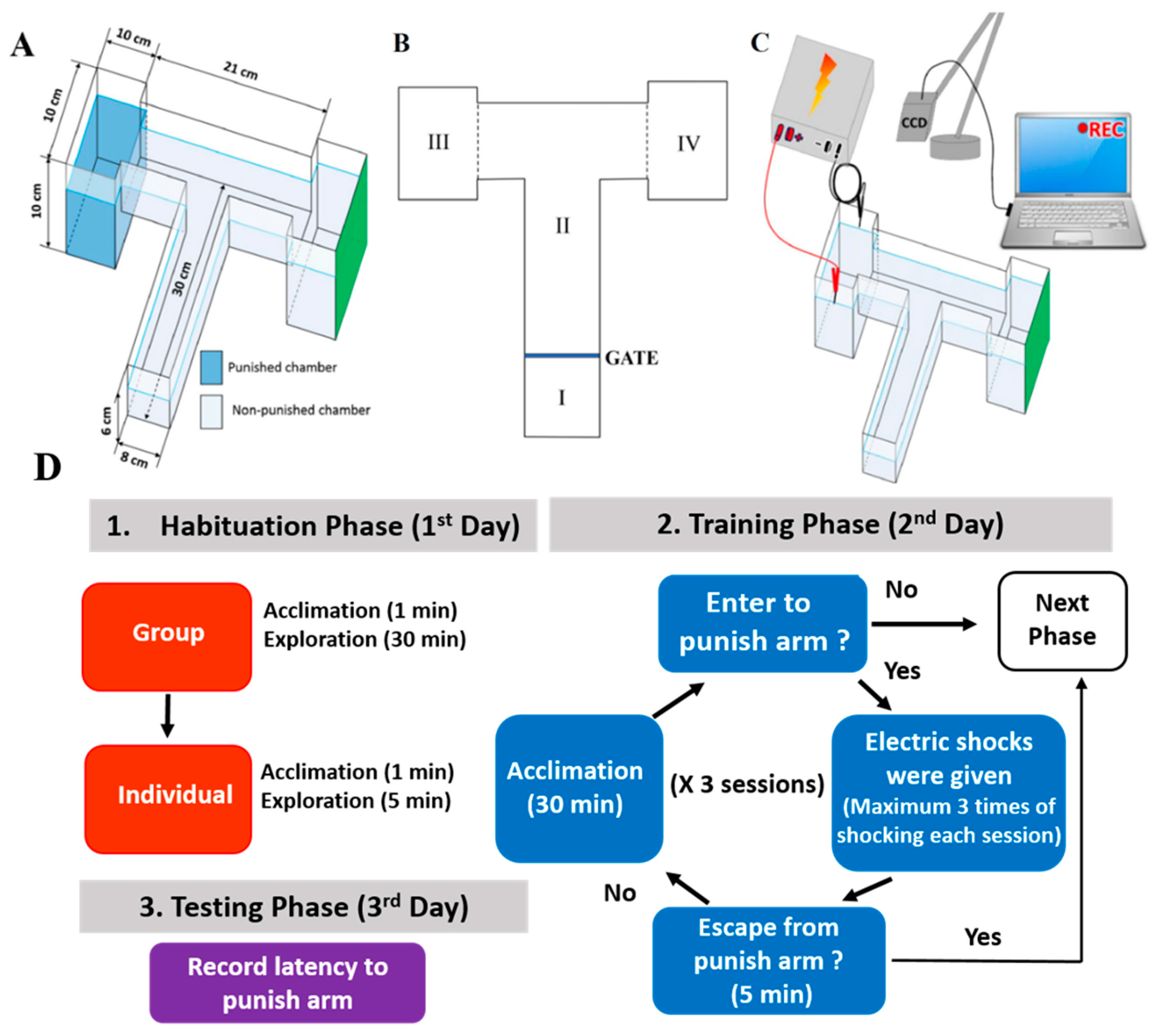
2.1. Overview of the Modified T-Maze to Perform Conditioned Preference Test
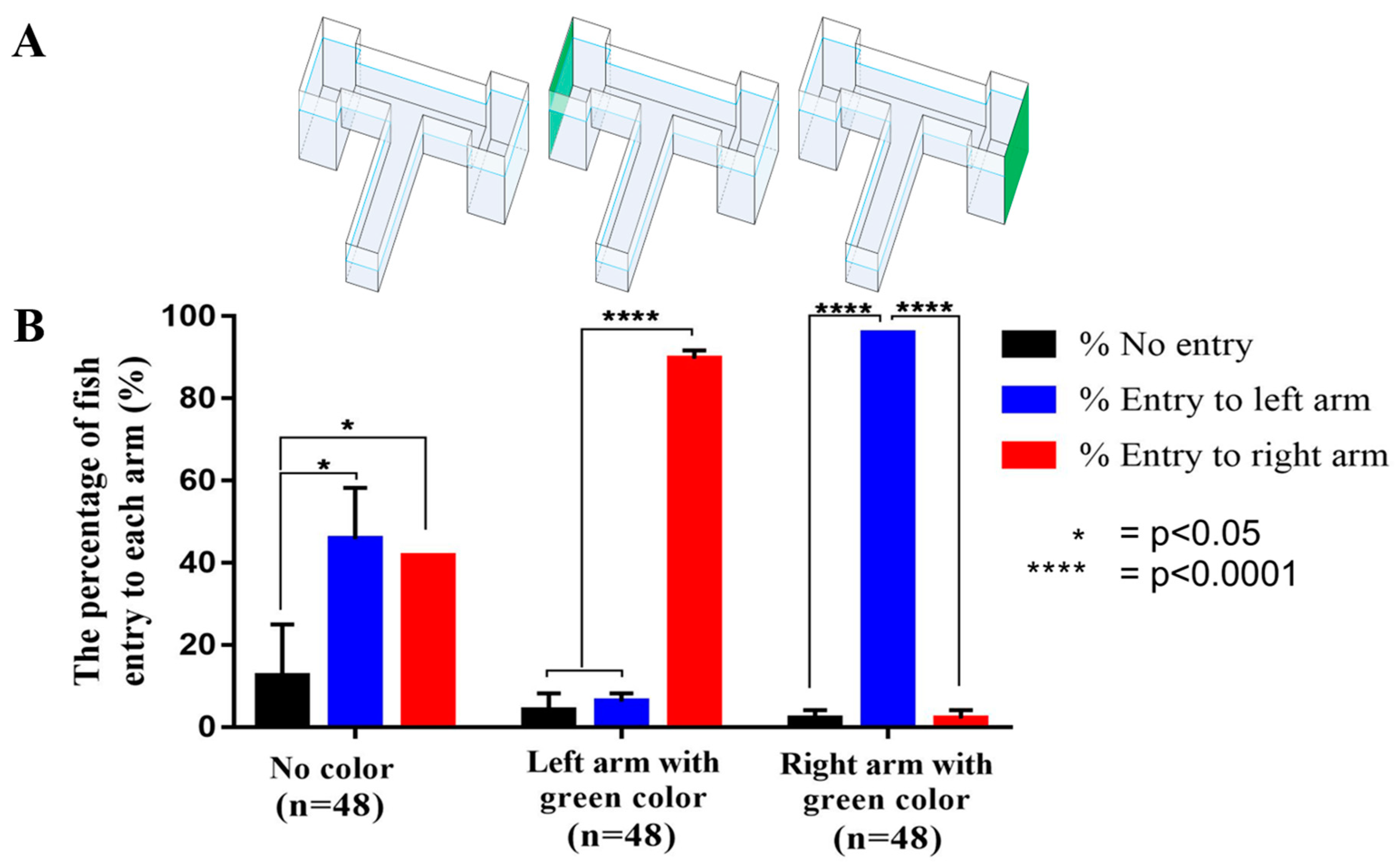
2.2. The T-Maze Paradigm in Enhancing Place Conditioned Preference
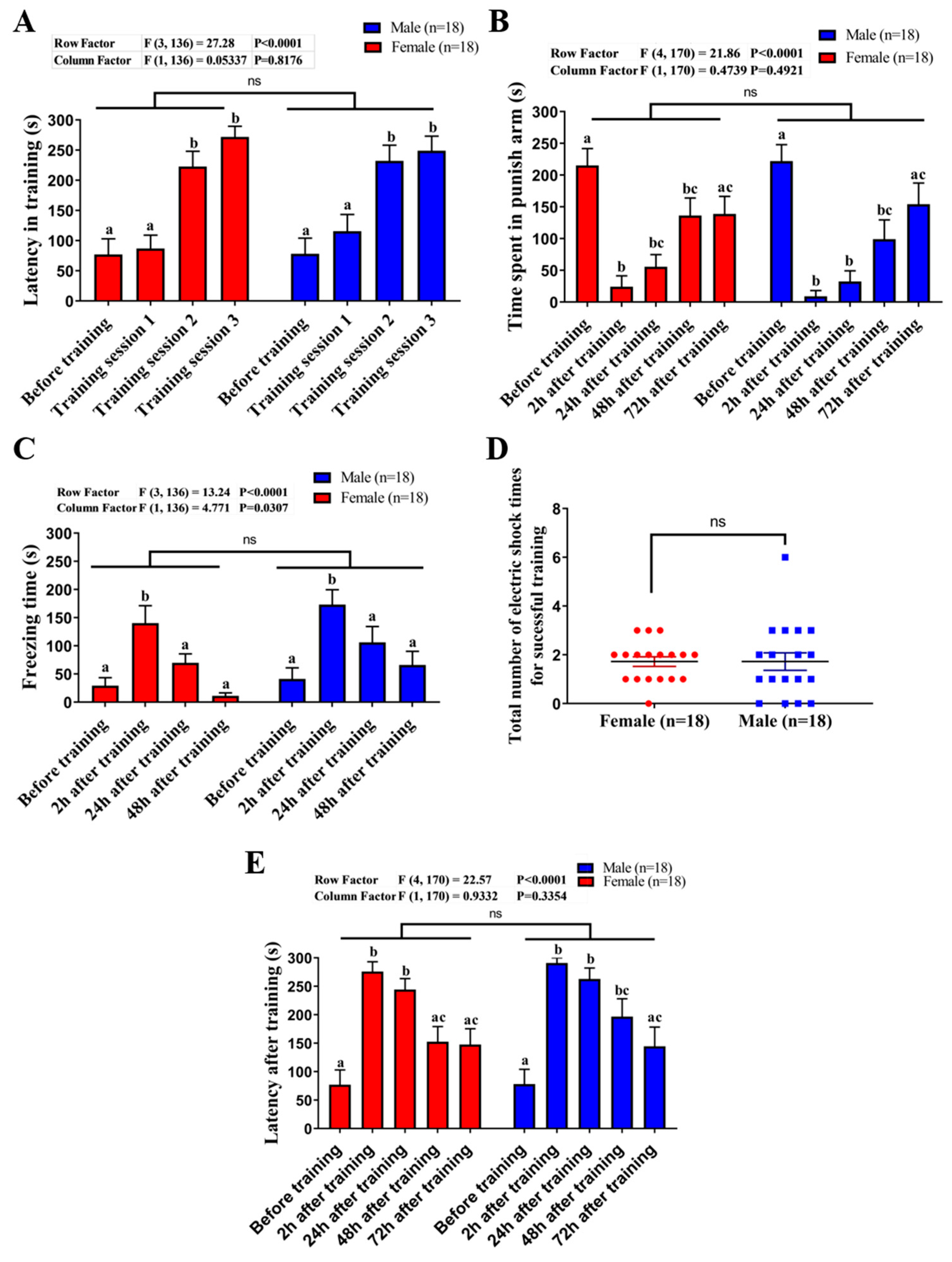
2.3. Comparison of Learning Capacity and Memory Retention Between Male and Female Zebrafish
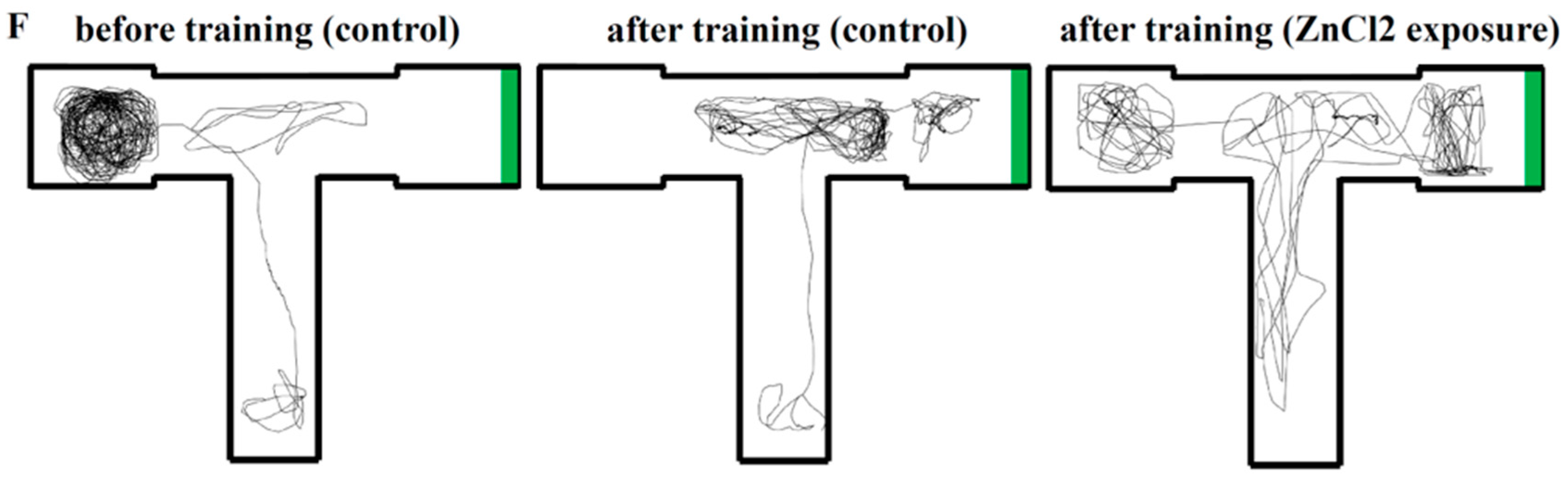
2.4. Comparison of Learning Capacity and Memory Retention Between Control and ZnCl2-Incubated Zebrafish
2.5. Comparison of Learning Capacity and Memory Retention Between the Wild Type and Mutant Zebrafish
3. Discussions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. ZnCl2 Exposure Incubation
4.3. T-Maze Paradigm
4.4. Protocol
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carobrez, A.; Bertoglio, L. Ethological and temporal analyses of anxiety-like behavior: The elevated plus-maze model 20 years on. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, J.N. Behavioral phenotyping of rodents. Comp. Med. 2003, 53, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Pollak, D.D.; Rey, C.E.; Monje, F.J. Rodent models in depression research: Classical strategies and new directions. Ann. Med. 2010, 42, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walf, A.A.; Frye, C.A. The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, C.-M.; Magda, G.; Abel, S. Spatial memory: Theoretical basis and comparative review on experimental methods in rodents. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 203, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, D.L.; Hoefnagels, C.C.; de Kloet, R.E.; Richardson, M.K. Translating rodent behavioral repertoire to zebrafish (danio rerio): Relevance for stress research. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 214, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.; Kadri, F.; DiLeo, J.; Min Chung, K.; Cachat, J.; Goodspeed, J.; Suciu, C.; Roy, S.; Gaikwad, S.; Wong, K. The developing utility of zebrafish in modeling neurobehavioral disorders. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2010, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Stewart, A.M.; Gerlai, R. Zebrafish as an emerging model for studying complex brain disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Mailman, R.B. Strategic neuronal encoding in medial prefrontal cortex of spatial working memory in the t-maze. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 343, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofstad, T.A.; Zuker, C.S.; Reiser, M.B. Visual place learning in drosophila melanogaster. Nature 2011, 474, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darland, T.; Dowling, J.E. Behavioral screening for cocaine sensitivity in mutagenized zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11691–11696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barinaga, M. Zebrafish: Swimming into the development mainstream. Science 1990, 250, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, T.; Alderton, W.; Reynolds, H.; Roach, A.; Berghmans, S. Zebrafish: An emerging technology for in vivo pharmacological assessment to identify potential safety liabilities in early drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 1400–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vascotto, S.G.; Beckham, Y.; Kelly, G.M. The zebrafish’s swim to fame as an experimental model in biology. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 75, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, J.; Nabeshima, T.; Kameyama, T. Utility of an elevated plus-maze for the evaluation of memory in mice: Effects of nootropics, scopolamine and electroconvulsive shock. Psychopharmacology 1990, 101, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudchenko, P.A. An overview of the tasks used to test working memory in rodents. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004, 28, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deacon, R.M.; Rawlins, J.N.P. T-maze alternation in the rodent. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, F.E.; White, D.; Messer, W.S., Jr. A simple spatial alternation task for assessing memory function in zebrafish. Behav. Process. 2002, 58, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Pizarro, K.; Pang, W.G.; Harrison, J.; Ramsdell, J.S. Persisting behavioral consequences of prenatal domoic acid exposure in rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2005, 27, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathangi, D.; Namasivayam, A. Effect of chronic cyanide intoxication on memory in albino rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaugh, J.L.; Roozendaal, B. Drug enhancement of memory consolidation: Historical perspective and neurobiological implications. Psychopharmacology 2009, 202, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, R.N.; Pamplona, F.A.; Fernandes, M.S. The cannabinoid antagonist sr141716a facilitates memory acquisition and consolidation in the mouse elevated t-maze. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 380, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graeff, F.; Viana, M.; Tomaz, C. The elevated t maze, a new experimental model of anxiety and memory: Effect of diazepam. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. Rev. Bras. De Pesqui. Med. E Biol. 1993, 26, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Braida, D.; Ponzoni, L.; Martucci, R.; Sparatore, F.; Gotti, C.; Sala, M. Role of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nachrs) on learning and memory in zebrafish. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 1975–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasamma, S.; Audira, G.; Juniardi, S.; Sampurna, B.; Liang, S.-T.; Hao, E.; Lai, Y.-H.; Hsiao, C.-D. Zinc chloride exposure inhibits brain acetylcholine levels, produces neurotoxic signatures, and diminishes memory and motor activities in adult zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audira, G.; Sarasamma, S.; Chen, J.-R.; Juniardi, S.; Sampurna, B.; Liang, S.-T.; Lai, Y.-H.; Lin, G.-M.; Hsieh, M.-C.; Hsiao, C.-D. Zebrafish mutants carrying leptin a (lepa) gene deficiency display obesity, anxiety, less aggression and fear, and circadian rhythm and color preference dysregulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustino, A.I.; Tacão-Monteiro, A.; Oliveira, R.F. Mechanisms of social buffering of fear in zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; de Brito, T.M.; da Silva Batista, A.W.; Herculano, A.M.; Morato, S.; Gouveia, A. Measuring anxiety in zebrafish: A critical review. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 214, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Tucci, V.; Kishi, S.; Zhdanova, I.V. Cognitive aging in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwill, R.M.; Raymond, M.P.; Ferreira, L.; Escudero, H. Visual discrimination learning in zebrafish (danio rerio). Behav. Process. 2005, 70, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, R.; Tsuboi, T.; Okamoto, H. Y-maze avoidance: An automated and rapid associative learning paradigm in zebrafish. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 91, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, P.M.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Karnik, R.; Langer, R. Microfluidic technologies for accelerating the clinical translation of nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroock, A.D. Microfluidics. In Optical Biosensors; Elsevier: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 659–681. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, F.B.; Lee, L.P. Innovations in optical microfluidic technologies for point-of-care diagnostics. Lab. A Chip 2008, 8, 2015–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, K.P.; Neuhauss, S.C. Automated visual choice discrimination learning in zebrafish (danio rerio). J. Integr. Neurosci. 2012, 11, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Escudero, A.; Vicente-Page, J.; Hinz, R.C.; Arganda, S.; De Polavieja, G.G. Idtracker: Tracking individuals in a group by automatic identification of unmarked animals. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ngoc Hieu, B.T.; Ngoc Anh, N.T.; Audira, G.; Juniardi, S.; Liman, R.A.D.; Villaflores, O.B.; Lai, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-R.; Liang, S.-T.; Huang, J.-C.; et al. Development of a Modified Three-Day T-maze Protocol for Evaluating Learning and Memory Capacity of Adult Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041464
Ngoc Hieu BT, Ngoc Anh NT, Audira G, Juniardi S, Liman RAD, Villaflores OB, Lai Y-H, Chen J-R, Liang S-T, Huang J-C, et al. Development of a Modified Three-Day T-maze Protocol for Evaluating Learning and Memory Capacity of Adult Zebrafish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(4):1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041464
Chicago/Turabian StyleNgoc Hieu, Bui Thi, Nguyen Thi Ngoc Anh, Gilbert Audira, Stevhen Juniardi, Rhenz Alfred D. Liman, Oliver B. Villaflores, Yu-Heng Lai, Jung-Ren Chen, Sung-Tzu Liang, Jong-Chin Huang, and et al. 2020. "Development of a Modified Three-Day T-maze Protocol for Evaluating Learning and Memory Capacity of Adult Zebrafish" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 4: 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041464
APA StyleNgoc Hieu, B. T., Ngoc Anh, N. T., Audira, G., Juniardi, S., Liman, R. A. D., Villaflores, O. B., Lai, Y.-H., Chen, J.-R., Liang, S.-T., Huang, J.-C., & Hsiao, C.-D. (2020). Development of a Modified Three-Day T-maze Protocol for Evaluating Learning and Memory Capacity of Adult Zebrafish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(4), 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041464







