Periodic Membrane Potential and Ca2+ Oscillations in T Cells Forming an Immune Synapse
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 Ion Channels Expressed in D10 T Cells and Formation of an Immune Synapse with CH12 B Cells
2.2. The Membrane Potential Oscillates More Frequently in Conjugated T Cells Than in Lone T Cells
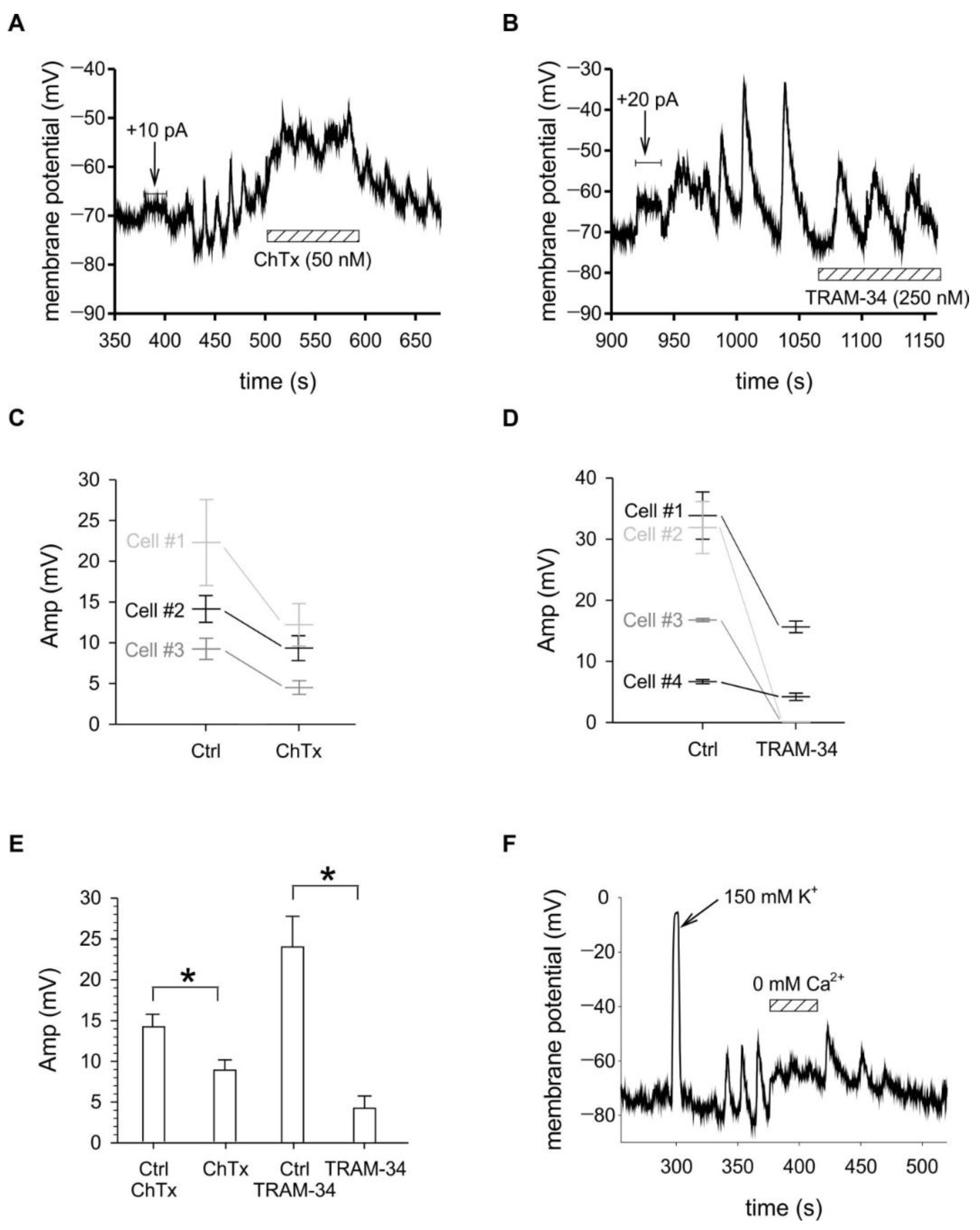
2.3. Membrane Potential Oscillations Are Sensitive to Potassium Channel Blockers and to Extracellular Calcium
2.4. Oscillation of the Intracellular Calcium Concentration in Conjugated and in Lone T Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells
4.2. Electrophysiology
4.3. Intracellular Calcium Measurements
4.4. Labeling of Kv1.3 Channels
4.5. Confocal Microscopy
4.6. Determination of the presence of MPO
4.7. Analysis of the MPO amplitudes
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TCR | T-cell receptor |
| CD3 | Cluster of differentiation 3 |
| CRAC | Ca2+-release activated Ca2+ |
| MP | Membrane potential |
| MPO | Membrane potential oscillation |
| ICaO | Intracellular calcium oscillation |
| Kv | Voltage gated K+ ion channels |
| KCa | Calcium activated K+ ion channels |
| STIM1 | Stromal interaction molecule 1 |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| IS | Immunological synapse |
| APC | Antigen-presenting cell |
| ChTx | Charybdotoxin |
| MgTx | Margatoxin |
| GFP | Green fluorescein protein |
Appendix A




References
- DeCoursey, T.E.; Chandy, K.G.; Gupta, S.; Cahalan, M.D. Voltage-dependent ion channels in T-lymphocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 1985, 10, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandy, K.G.; Decoursey, T.E.; Cahalan, M.D.; McLaughlin, C.; Gupta, S. Voltage-gated potassium channels are required for human T lymphocyte activation. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 160, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Decoursey, T.E.; Chandy, K.G.; Gupta, S.; Cahalan, M.D. Voltage-gated K + channels in human T lymphocytes: A role in mitogenesis? Nature 1984, 307, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelfand, E.W.; Cheung, R.K.; Grinstein, S. Role of membrane potential in the regulation of lectin-induced calcium uptake. J. Cell. Physiol. 1984, 121, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnadieu, E.; Bismuth, G.; Trautmann, A. Calcium fluxes in T lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 25864–25872. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, S.D.; Oortgiesen, M.; Cahalan, M.D. Calcium oscillations in human T and natural killer cells depend upon membrane potential and calcium influx. J. Immunol. 1993, 150, 2620–2633. [Google Scholar]
- Maltsev, V.A. A negative resistance region underlies the triggering property of membrane potential in human T-lymphocytes. Cell Signal. 1992, 4, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheugen, J.A.; Vijverberg, H.P. Intracellular Ca2+ oscillations and membrane potential fluctuations in intact human T lymphocytes: Role of K+ channels in Ca2+ signaling. Cell Calcium 1995, 17, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheugen, J.A.; Vijverberg, H.P.; Oortgiesen, M.; Cahalan, M.D. Voltage-gated and Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in intact human T lymphocytes. Noninvasive measurements of membrane currents, membrane potential, and intracellular calcium. J. Gen. Physiol. 1995, 105, 765–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cahalan, M.D.; Chandy, K.G. The functional network of ion channels in T lymphocytes. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 231, 59–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beeton, C.; Wulff, H.; Standifer, N.E.; Azam, P.; Mullen, K.M.; Pennington, M.W.; Kolski-Andreaco, A.; Wei, E.; Grino, A.; Counts, D.R.; et al. Kv1.3 channels are a therapeutic target for T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17414–17419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicolaou, S.A.; Szigligeti, P.; Neumeier, L.; Lee, S.M.; Duncan, H.J.; Kant, S.K.; Mongey, A.B.; Filipovich, A.H.; Conforti, L. Altered dynamics of Kv1.3 channel compartmentalization in the immunological synapse in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panyi, G.; Bagdany, M.; Bodnar, A.; Vamosi, G.; Szentesi, G.; Jenei, A.; Matyus, L.; Varga, S.; Waldmann, T.A.; Gaspar, R.; et al. Colocalization and nonrandom distribution of Kv1.3 potassium channels and CD3 molecules in the plasma membrane of human T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2592–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panyi, G.; Vamosi, G.; Bacso, Z.; Bagdany, M.; Bodnar, A.; Varga, Z.; Gaspar, R.; Matyus, L.; Damjanovich, S. Kv1.3 potassium channels are localized in the immunological synapse formed between cytotoxic and target cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolaou, S.A.; Neumeier, L.; Peng, Y.; Devor, D.C.; Conforti, L. The Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel KCa3.1 compartmentalizes in the immunological synapse of human T lymphocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C1431–C1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, X.; Pedi, L.; Diver, M.M.; Long, S.B. Crystal structure of the calcium release-activated calcium channel Orai. Science 2012, 338, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.L.; Yu, Y.; Roos, J.; Kozak, J.A.; Deerinck, T.J.; Ellisman, M.H.; Stauderman, K.A.; Cahalan, M.D. STIM1 is a Ca2+ sensor that activates CRAC channels and migrates from the Ca2+ store to the plasma membrane. Nature 2005, 437, 902–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.S.; Cahalan, M.D. Mitogen-induced oscillations of cytosolic Ca2+ and transmembrane Ca2+ current in human leukemic T cells. Cell Regul. 1989, 1, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zweifach, A.; Lewis, R.S. Mitogen-regulated Ca2+ current of T lymphocytes is activated by depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6295–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eichinger, P.; Herrmann, A.M.; Ruck, T.; Herty, M.; Gola, L.; Kovac, S.; Budde, T.; Meuth, S.G.; Hundehege, P. Human T cells in silico: Modelling dynamic intracellular calcium and its influence on cellular electrophysiology. J. Immunol. Methods 2018, 461, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupfer, A.; Kupfer, H. Imaging immune cell interactions and functions: SMACs and the Immunological Synapse. Semin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monks, C.R.; Freiberg, B.A.; Kupfer, H.; Sciaky, N.; Kupfer, A. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature 1998, 395, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, D.M. Assembly of the immunological synapse for T cells and NK cells. Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioudyno, M.I.; Kozak, J.A.; Penna, A.; Safrina, O.; Zhang, S.L.; Sen, D.; Roos, J.; Stauderman, K.A.; Cahalan, M.D. Orai1 and STIM1 move to the immunological synapse and are up-regulated during T cell activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quintana, A.; Pasche, M.; Junker, C.; Al-Ansary, D.; Rieger, H.; Kummerow, C.; Nunez, L.; Villalobos, C.; Meraner, P.; Becherer, U.; et al. Calcium microdomains at the immunological synapse: How ORAI channels, mitochondria and calcium pumps generate local calcium signals for efficient T-cell activation. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3895–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartzell, C.A.; Jankowska, K.I.; Burkhardt, J.K.; Lewis, R.S. Calcium influx through CRAC channels controls actin organization and dynamics at the immune synapse. Elife 2016, 5, e14850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandy, K.G.; Wulff, H.; Beeton, C.; Pennington, M.; Gutman, G.A.; Cahalan, M.D. K+ channels as targets for specific immunomodulation. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2004, 25, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panyi, G.; Vamosi, G.; Bodnar, A.; Gaspar, R.; Damjanovich, S. Looking through ion channels: Recharged concepts in T-cell signaling. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.V.; Yun, Y.; Conforti, L. Modulation of T cell activation by localized K(+) accumulation at the immunological synapse--a mathematical model. J. Biol. 2012, 300, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matteson, D.R.; Deutsch, C. K channels in T lymphocytes: A patch clamp study using monoclonal antibody adhesion. Nature 1984, 307, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Calvo, M.; Leonard, R.J.; Novick, J.; Stevens, S.P.; Schmalhofer, W.; Kaczorowski, G.J.; Garcia, M.L. Purification, characterization, and biosynthesis of margatoxin, a component of Centruroides margaritatus venom that selectively inhibits voltage-dependent potassium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 18866–18874. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grissmer, S.; Nguyen, A.N.; Cahalan, M.D. Calcium-activated potassium channels in resting and activated human T lymphocytes. Expression levels, calcium dependence, ion selectivity, and pharmacology. J. Gen. Physiol. 1993, 102, 601–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulff, H.; Miller, M.J.; Hansel, W.; Grissmer, S.; Cahalan, M.D.; Chandy, K.G. Design of a potent and selective inhibitor of the intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel, IKCa1: A potential immunosuppressant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8151–8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schaefer, B.C.; Kappler, J.W.; Kupfer, A.; Marrack, P. Complex and dynamic redistribution of NF-kappaB signaling intermediates in response to T cell receptor stimulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horn, R.; Korn, S.J. Prevention of rundown in electrophysiological recording. Methods Enzym. 1992, 207, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.S. Calcium signaling mechanisms in T lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 497–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.D.; Gutman, G.A.; Aldrich, R.; Chandy, K.G.; Grissmer, S.; Wulff, H. International Union of Pharmacology. LII. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of calcium-activated potassium channels. Pharm. Rev. 2005, 57, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, C.; Moczydlowski, E.; Latorre, R.; Phillips, M. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature 1985, 313, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, H.; Calabresi, P.A.; Allie, R.; Yun, S.; Pennington, M.; Beeton, C.; Chandy, K.G. The voltage-gated Kv1.3 K + channel in effector memory T cells as new target for MS. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monks, C.R.; Kupfer, H.; Tamir, I.; Barlow, A.; Kupfer, A. Selective modulation of protein kinase C-theta during T-cell activation. Nature 1997, 385, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, S.A.; Neumeier, L.; Steckly, A.; Kucher, V.; Takimoto, K.; Conforti, L. Localization of Kv1.3 channels in the immunological synapse modulates the calcium response to antigen stimulation in T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6296–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicolaou, S.A.; Neumeier, L.; Takimoto, K.; Lee, S.M.; Duncan, H.J.; Kant, S.K.; Mongey, A.B.; Filipovich, A.H.; Conforti, L. Differential calcium signaling and Kv1.3 trafficking to the immunological synapse in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Calcium 2010, 47, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, S.C.; Beatty, J.A.; Wilson, C.J. The ionic mechanism of membrane potential oscillations and membrane resonance in striatal LTS interneurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2016, 116, 1752–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobelli, J.; Andres, P.G.; Boisvert, J.; Krummel, M.F. New views of the immunological synapse: Variations in assembly and function. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivas, O.; Moreno, C.M.; Santana, L.F.; Hille, B. Proximal clustering between BK and CaV1.3 channels promotes functional coupling and BK channel activation at low voltage. Elife 2017, 6, e28029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, W.M. Localization of calcium signals by a mobile calcium buffer in frog saccular hair cells. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 3246–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simon, S.M.; Llinas, R.R. Compartmentalization of the submembrane calcium activity during calcium influx and its significance in transmitter release. Biophys. J. 1985, 48, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diercks, B.P.; Werner, R.; Weidemuller, P.; Czarniak, F.; Hernandez, L.; Lehmann, C.; Rosche, A.; Kruger, A.; Kaufmann, U.; Vaeth, M.; et al. ORAI1, STIM1/2, and RYR1 shape subsecond Ca(2+) microdomains upon T cell activation. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cahalan, M.D.; Chandy, K.G.; Decoursey, T.E.; Gupta, S. A voltage-gated potassium channel in human T lymphocytes. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 1985, 358, 197–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zweifach, A.; Lewis, R.S. Rapid inactivation of depletion-activated calcium current (ICRAC) due to local calcium feedback. J. Gen. Physiol. 1995, 105, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zweifach, A.; Lewis, R.S. Slow calcium-dependent inactivation of depletion-activated calcium current. Store-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 14445–14451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuras, Z.; Yun, Y.H.; Chimote, A.A.; Neumeier, L.; Conforti, L. KCa3.1 and TRPM7 channels at the uropod regulate migration of activated human T cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubovszky, B.; Hajdu, P.; Krasznai, Z.; Gaspar, R., Jr.; Waldmann, T.A.; Damjanovich, S.; Bene, L. Detection of channel proximity by nanoparticle-assisted delaying of toxin binding; a combined patch-clamp and flow cytometric energy transfer study. Eur. Biophys. J. 2005, 34, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdany, M.; Batista, C.V.; Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; Somodi, S.; Rodriguez de la Vega, R.C.; Licea, A.F.; Varga, Z.; Gaspar, R.; Possani, L.D.; Panyi, G. Anuroctoxin, a new scorpion toxin of the alpha-KTx 6 subfamily, is highly selective for Kv1.3 over IKCa1 ion channels of human T lymphocytes. Mol. Pharm. 2005, 67, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizvári, B.; Bacsi, Z. Technological Development and the stability of technology in crop porduction. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2002, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.; Ripley, B. Modern Applied Statistics with S; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papp, F.; Hajdu, P.; Tajti, G.; Toth, A.; Nagy, E.; Fazekas, Z.; Kovacs, S.; Vámosi, G.; Varga, Z.; Panyi, G. Periodic Membrane Potential and Ca2+ Oscillations in T Cells Forming an Immune Synapse. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051568
Papp F, Hajdu P, Tajti G, Toth A, Nagy E, Fazekas Z, Kovacs S, Vámosi G, Varga Z, Panyi G. Periodic Membrane Potential and Ca2+ Oscillations in T Cells Forming an Immune Synapse. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(5):1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051568
Chicago/Turabian StylePapp, Ferenc, Peter Hajdu, Gabor Tajti, Agnes Toth, Eva Nagy, Zsolt Fazekas, Sandor Kovacs, György Vámosi, Zoltan Varga, and Gyorgy Panyi. 2020. "Periodic Membrane Potential and Ca2+ Oscillations in T Cells Forming an Immune Synapse" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 5: 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051568
APA StylePapp, F., Hajdu, P., Tajti, G., Toth, A., Nagy, E., Fazekas, Z., Kovacs, S., Vámosi, G., Varga, Z., & Panyi, G. (2020). Periodic Membrane Potential and Ca2+ Oscillations in T Cells Forming an Immune Synapse. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(5), 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051568







