Corylifol A from Psoralea corylifolia L. Enhances Myogenesis and Alleviates Muscle Atrophy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
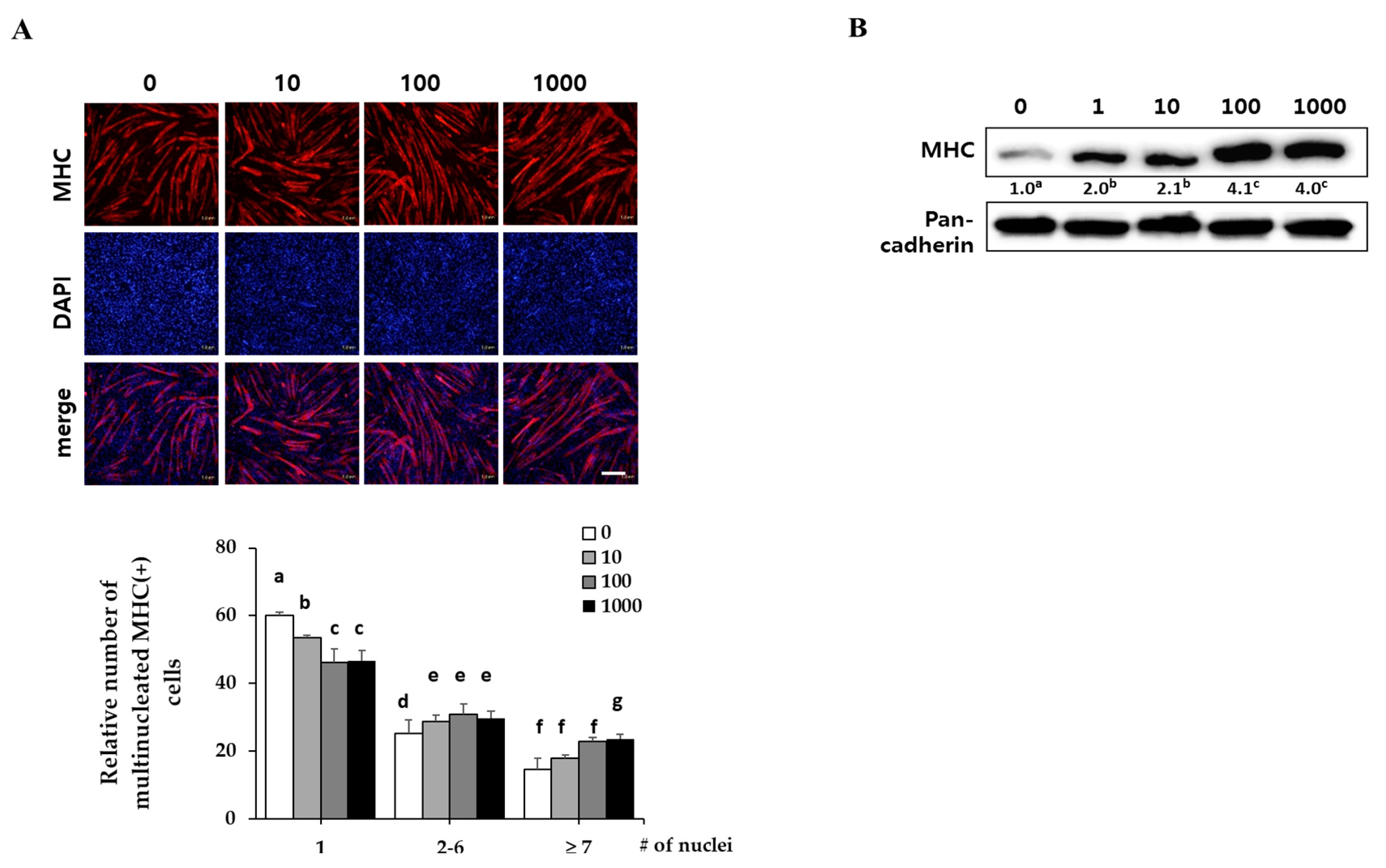
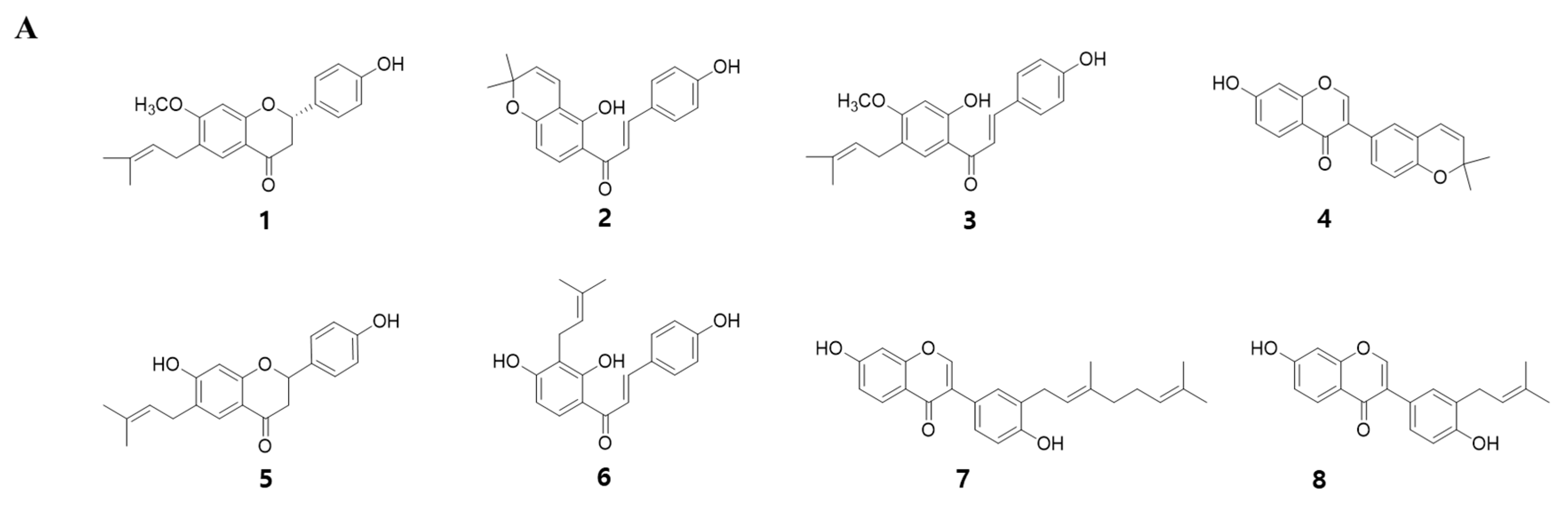
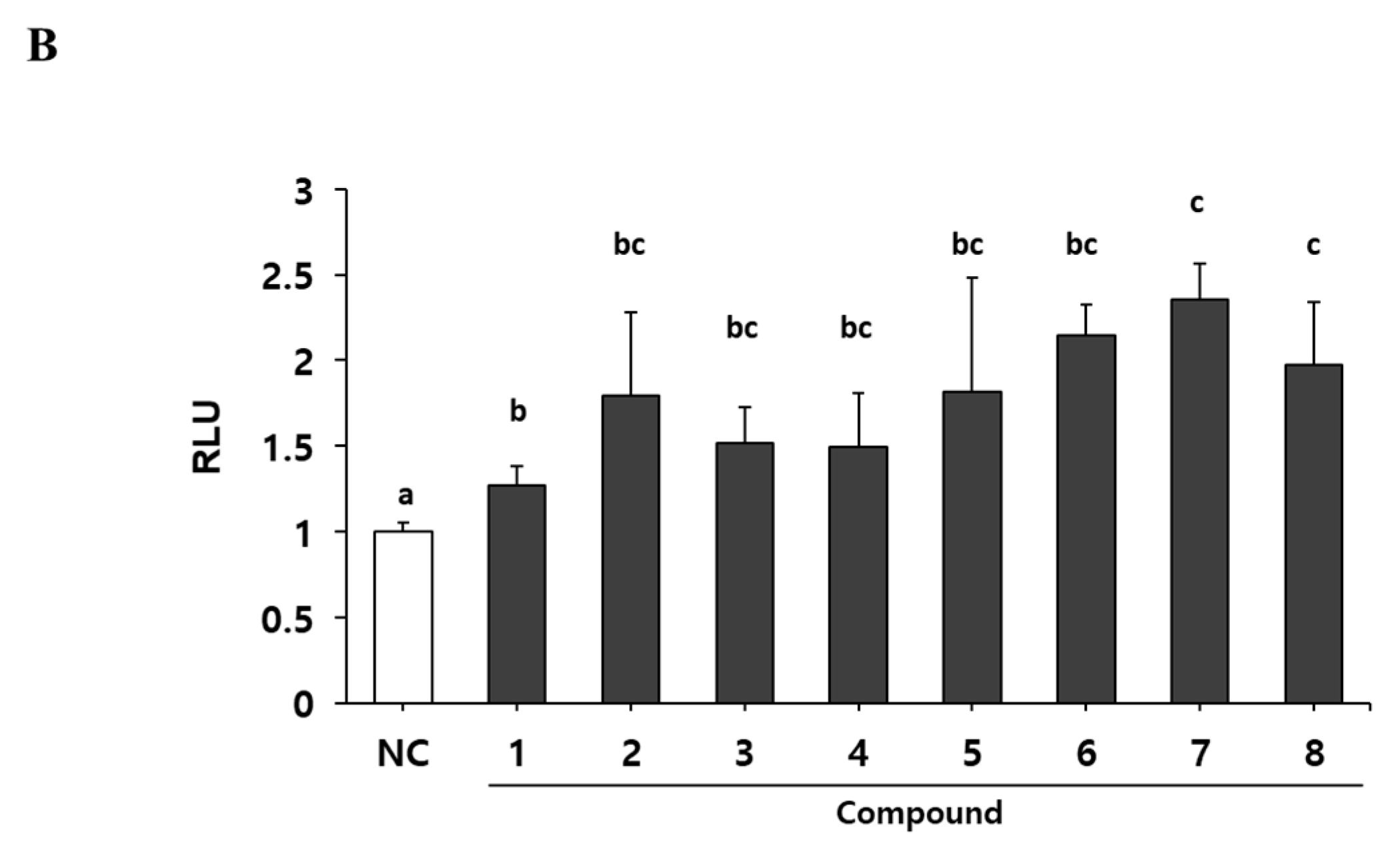
2.1. Extracts of Psoralea Corylifolia Enhance Myogenesis
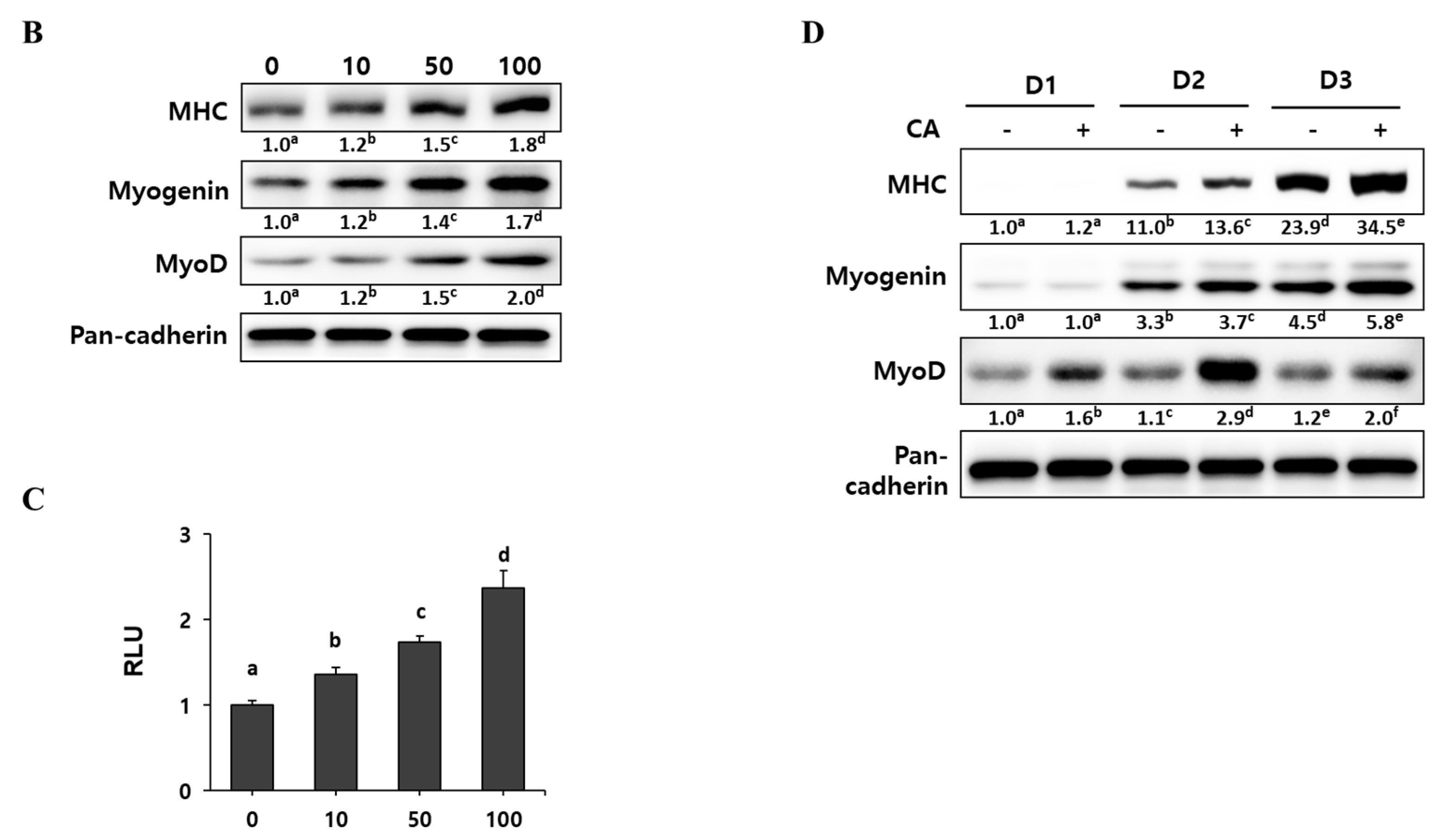
2.2. Corylifol A Promotes Myogenesis
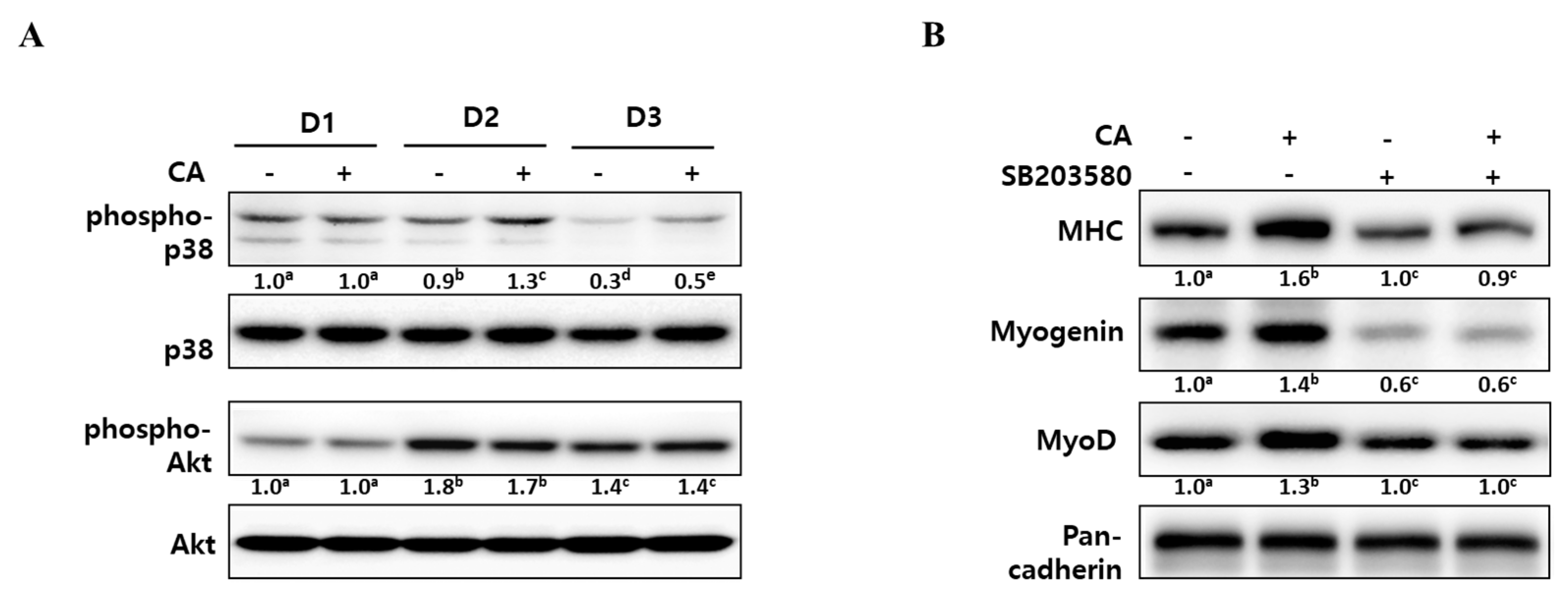
2.3. Corylifol A Promotes Myogenesis via p38 MAPK Activation
2.4. Corylifol A Protects against Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy in Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of the Ethanol Extracts of P. corylifolia L. (PC) and Purification of Flavonoids and Chalcones
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Immunostaining of MHC
4.4. MyoD-Reporter Gene Assay
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalyani, R.R.; Corriere, M.; Ferrucci, L. Age-related and disease-related muscle loss: the effect of diabetes, obesity, and other diseases. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 819–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakuma, K.; Yamaguchi, A. Sarcopenia and age-related endocrine function. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 127362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Welle, S. Cellular and molecular basis of age-related sarcopenia. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 27, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Nathan, J.A.; Goldberg, A.L. Muscle wasting in disease: molecular mechanisms and promising therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, N.A.; Wang, Y.X.; Rudnicki, M.A. Intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms regulating satellite cell function. Dev. (Camb. Engl.) 2015, 142, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutt, V.; Gupta, S.; Dabur, R.; Injeti, E.; Mittal, A. Skeletal muscle atrophy: Potential therapeutic agents and their mechanisms of action. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Dludla, P.V.; Nkambule, B.B.; Obonye, N.; Louw, J. Skeletal muscle as a therapeutic target for natural products to reverse metabolic syndrome. Muscle Cell Tissue: Curr. Status Res. Field 2018, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Heo, J.W.; Kim, A.R.; Kweon, M.; Nam, S.; Lim, J.S.; Sung, M.K.; Kim, S.E.; Ryu, J.H. Z-ajoene from cushed garlic alleviates cancer-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kweon, M.; Lee, H.; Park, C.; Choi, Y.H.; Ryu, J.H. A Chalcone from Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei) stimulates myoblast differentiation and inhibits dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Lee, S.J.; Bae, G.U.; Baek, N.I.; Ryu, J.H. Canadine from Corydalis turtschaninovii stimulates myoblast differentiation and protects against myotube atrophy. Int. J Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.; Lee, S.J.; Yoo, M.; Go, G.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Seo, D.W.; Kang, J.S.; Ryu, J.H.; Bae, G.U. Kazinol-P from Broussonetia kazinoki enhances skeletal muscle differentiation via p38MAPK and MyoD. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 456, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, F.; Khan, G.N.; Asad, M. Psoralea corylifolia L: Ethnobotanical, biological, and chemical aspects: A review. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 597–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.H.; Yon, G.H.; Hong, K.S.; Yoo, D.S.; Choi, C.W.; Park, W.K.; Kong, J.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Ryu, S.Y. In vitro BACE-1 inhibitory phenolic components from the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 1405–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Kuroda, T.; Hatano, T. Constituents of Psoralea corylifolia fruits and their effects on methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2015, 20, 12500–12511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Don, M.J.; Lin, L.C.; Chiou, W.F. Neobavaisoflavone stimulates osteogenesis via p38-mediated up-regulation of transcription factors and osteoid genes expression in MC3T3-E1 cells. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 551–561. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Li, H.; Han, Y.E.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Ryu, J.H. Modulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in LPS-Stimulated BV-2 microglia by prenylated chalcones from Cullen corylifolium (L.) Medik. through inhibition of I-κBα degradation. Molecules 2018, 23, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Ryu, J.H. Prenylflavones from Psoralea corylifolia inhibit nitric oxide synthase expression through the inhibition of I-κB-α degradation in activated microglial cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 2253–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.W.; Yun, B.R.; Kim, M.H.; Park, C.S.; Lee, W.S.; Oh, H.M.; Rho, M.C. Phenolic compounds isolated from Psoralea corylifolia inhibit IL-6-induced STAT3 activation. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, J.; Nam, S.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, H.G.; Ryu, J.H.; Lim, J.S. Antimelanogenic effect of 4-hydroxylonchocarpin through the inhibition of tyrosinase-related proteins and MAPK phosphatase. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, M.H.; Huang, G.S.; Hung, Y.C.; Bin, L.; Liao, L.T.; Lin, L.W. Psoralea corylifolia extract ameliorates experimental osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2007, 35, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Li, H.; Noh, M.; Ryu, J.H. Bavachin from Psoralea corylifolia improves insulin-dependent glucose uptake through insulin signaling and AMPK activation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.K.; Lee, Y.; Chang, E.J.; Lee, M.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, H.H. Bavachalcone inhibits osteoclast differentiation through suppression of NFATc1 induction by RANKL. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Yoo, M.; Go, G.Y.; Kim do, H.; Choi, H.; Leem, Y.E.; Kim, Y.K.; Seo, D.W.; Ryu, J.H.; Kang, J.S.; et al. Bakuchiol augments MyoD activation leading to enhanced myoblast differentiation. Chem. Biol. Int. 2016, 248, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Li, F.; Jiang, Z. Osteoblastic proliferation stimulating activity of Psoralea corylifolia extracts and two of its flavonoids. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 748–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Separation, identification, and quantification of active constituents in Fructus Psoraleae by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV, ion trap mass spectrometry, and electrochemical detection. J. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 2, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pistelli, L.; Spera, K.; Flamini, G.; Mele, S.; Morelli, I. Isoflavonoids and chalcones from Anthyllis hermanniae. Phytochem. 1996, 42, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Fan, C.Q.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Yue, J.M. Antibacterial prenylflavone derivatives from Psoralea corylifolia, and their structure-activity relationship study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 4387–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Cao, G.Q.; Pfefferkorn, J.A. Selenium-based solid-phase synthesis of benzopyrans II: Applications to combinatorial synthesis of medicinally relevant small organic molecules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2000, 39, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentzinger, C.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Rudnicki, M.A. Building muscle: molecular regulation of myogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012, 4, a008342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassar, A.B. The p38 MAPK family, a pushmi-pullyu of skeletal muscle differentiation. J. Cell. Biol. 2009, 187, 941–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandromme, M.; Rochat, A.; Meier, R.; Carnac, G.; Besser, D.; Hemmings, B.A.; Fernandez, A.; Lamb, N.J. Protein kinase B beta/Akt2 plays a specific role in muscle differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8173–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.W.; Ku, S.K.; Han, M.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, G.Y.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, B.W.; Kim, C.M.; Choi, Y.H. The administration of Fructus Schisandrae attenuates dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menconi, M.; Gonnella, P.; Petkova, V.; Lecker, S.; Hasselgren, P.O. Dexamethasone and corticosterone induce similar, but not identical, muscle wasting responses in cultured L6 and C2C12 myotubes. J. Cell Biochem. 2008, 105, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, N.; Gavin, M.G.; Quinn, W.J., 3rd; Luongo, T.S.; Gelfer, R.G.; Baur, J.A.; Titchenell, P.M. The role of skeletal muscle Akt in the regulation of muscle mass and glucose homeostasis. Mol. Metabol. 2019, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.; Peng, J.; Jiang, S. The epigenetic regulation of embryonic myogenesis and adult muscle regeneration by histone methylation modification. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 6, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saccone, V.; Puri, P.L. Epigenetic regulation of skeletal myogenesis. Organogenesis 2010, 6, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, X.L.; So, K.K.; He, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Yao, M.; Xu, B.; Zhang, S.; Yao, H.; et al. MyoD- and FoxO3-mediated hotspot interaction orchestrates super-enhancer activity during myogenic differentiation. Nucleic acids Res. 2017, 45, 8785–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, A.M.; Tonks, N.K. Regulation of distinct stages of skeletal muscle differentiation by mitogen-activated protein kinases. Science 1997, 278, 1288–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcales, S.V.; Albini, S.; Giordani, L.; Malecova, B.; Cignolo, L.; Chernov, A.; Coutinho, P.; Saccone, V.; Consalvi, S.; Williams, R.; et al. Signal-dependent incorporation of MyoD-BAF60c into Brg1-based SWI/SNF chromatin-remodelling complex. Embo J. 2012, 31, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogaars, W.M.H.; Jaspers, R.T. Past, Present, and future perspective of targeting myostatin and related signaling pathways to counteract muscle atrophy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1088, 153–206. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Y.J.; Son, H.J.; Choi, Y.M.; Ahn, J.; Jung, C.H.; Ha, T.Y. Apigenin enhances skeletal muscle hypertrophy and myoblast differentiation by regulating Prmt7. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 78300–78311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirasaka, K.; Maeda, T.; Ikeda, C.; Haruna, M.; Kohno, S.; Abe, T.; Ochi, A.; Mukai, R.; Oarada, M.; Eshima-Kondo, S.; et al. Isoflavones derived from soy beans prevent MuRF1-mediated muscle atrophy in C2C12 myotubes through SIRT1 activation. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2013, 59, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murillo Ortiz, B.O.; Fuentes Preciado, A.R.; Ramirez Emiliano, J.; Martinez Garza, S.; Ramos Rodriguez, E.; de Alba Macias, L.A. Recovery of bone and muscle mass in patients with chronic kidney disease and iron overload on hemodialysis and taking combined supplementation with curcumin and resveratrol. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, D.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Su, Y.F.; Fan, G.W.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, X.M. Phytoestrogens from Psoralea corylifolia reveal estrogen receptor-subtype selectivity. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Yang, X.Z.; Yuan, J.Q. Cytotoxic constituents from Psoralea corylifolia. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 15, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Lv, X.; Li, S.Y.; Hou, J.; Ning, J.; Wang, J.Y.; Cao, Y.F.; Ge, G.B.; Guo, B.; Yang, L. Identification and characterization of naturally occurring inhibitors against UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 in Fructus Psoraleae (Bu-gu-zhi). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 289, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurgan, N.; Whitley, K.C.; Maddalena, L.A.; Moradi, F.; Stoikos, J.; Hamstra, S.I.; Rubie, E.A.; Kumar, M.; Roy, B.D.; Woodgett, J.R.; et al. A low-therapeutic dose of lithium inhibits GSK3 and enhances myoblast fusion in C2C12 cells. Cells 2019, 8, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Lee, H.; Li, H.; Ryu, J.-H. Corylifol A from Psoralea corylifolia L. Enhances Myogenesis and Alleviates Muscle Atrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051571
Han Y, Lee H, Li H, Ryu J-H. Corylifol A from Psoralea corylifolia L. Enhances Myogenesis and Alleviates Muscle Atrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(5):1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051571
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yeongeun, Hyejin Lee, Hua Li, and Jae-Ha Ryu. 2020. "Corylifol A from Psoralea corylifolia L. Enhances Myogenesis and Alleviates Muscle Atrophy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 5: 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051571
APA StyleHan, Y., Lee, H., Li, H., & Ryu, J.-H. (2020). Corylifol A from Psoralea corylifolia L. Enhances Myogenesis and Alleviates Muscle Atrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(5), 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051571




