Activation Effects of Carnosine- and Histidine-Containing Dipeptides on Human Carbonic Anhydrases: A Comprehensive Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Biological Activity
2.2. Computational Study for the Binding of CAAs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of d-Carnosinamide
4.3. Biological Assays
4.4. Molecular Modelling
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CA | Carbonic Anhydrase |
| ER | Eudismic Ratio |
| RCS | Reactive Carbonyl Species |
| SAR | Structure-Activity Relationships |
References
- Boldyrev, A.A.; Aldini, G.; Derave, W. Physiology and pathophysiology of carnosine. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1803–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowski, S.; Kiersztan, A.; Drozak, J. Biosynthesis of Carnosine and Related Dipeptides in Vertebrates. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 771–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vistoli, G.; Carini, M.; Aldini, G. Transforming dietary peptides in promising lead compounds: The case of bioavailable carnosine analogs. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cararo, J.H.; Streck, E.L.; Schuck, P.F.; Ferreira Gda, C. Carnosine and Related Peptides: Therapeutic Potential in Age-Related Disorders. Aging Dis. 2015, 6, 369–379. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Kumar, N. A review on “imidazoles”: Their chemistry and pharmacological potentials. Int. J. Pharmtech. Res. 2011, 3, 268–282. [Google Scholar]
- Aldini, G.; Vistoli, G.; Stefek, M.; Chondrogianni, N.; Grune, T.; Sereikaite, J.; Sadowska-Bartosz, I.; Bartosz, G. Molecular strategies to prevent, inhibit, and degrade advanced glycoxidation and advanced lipoxidation end products. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 93–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, J.J.; Artioli, G.G.; Turner, M.D.; Sale, C. The Physiological Roles of Carnosine and β-Alanine in Exercising Human Skeletal Muscle. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 2098–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briganti, F.; Mangani, S.; Orioli, P.; Scozzafava, A.; Vernaglione, G.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase activators: X-ray crystallographic and spectroscopic investigations for the interaction of isozymes I and II with histamine. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 10384–10392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan-Jones, R.D.; Spitzer, K.W.; Swietach, P. Spatial aspects of intracellular pH regulation in heart muscle. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2006, 90, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdag, M.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Vullo, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Carta, F. State of the Art on Carbonic Anhydrase Modulators for Biomedical Purposes. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 2558–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Structure and function of carbonic anhydrases. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase activators. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases: Novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase activators: High affinity isozymes I, II, and IV activators, incorporating a beta-alanyl-histidine scaffold. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saada, M.C.; Vullo, D.; Montero, J.L.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Winum, J.Y. Mono- and di-halogenated histamine, histidine and carnosine derivatives are potent carbonic anhydrase I, II, VII, XII and XIV activators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 4752–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldini, G.; Orioli, M.; Rossoni, G.; Savi, F.; Braidotti, P.; Vistoli, G.; Yeum, K.J.; Negrisoli, G.; Carini, M. The carbonyl scavenger carnosine ameliorates dyslipidaemia and renal function in Zucker obese rats. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1339–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Yuan, Z.; Zhu, X.; Chen, B.; Chen, X. Tripeptide GGH as the Inhibitor of Copper-Amyloid-β-Mediated Redox Reaction and Toxicity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.J.; Vistoli, G.; Katunga, L.A.; Funai, K.; Regazzoni, L.; Monroe, T.B.; Gilardoni, E.; Cannizzaro, L.; Colzani, M.; De Maddis, D.; et al. A carnosine analog mitigates metabolic disorders of obesity by reducing carbonyl stress. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 5280–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temperini, C.; Scozzafava, A.; Puccetti, L.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase activators: X-ray crystal structure of the adduct of human isozyme II with L-histidine as a platform for the design of stronger activators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 5136–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootsma, A.N.; Wheeler, S.E. Stacking Interactions of Heterocyclic Drug Fragments with Protein Amide Backbones. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hipkiss, A.R. Carnosine and its possible roles in nutrition and health. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2009, 57, 87–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prokopieva, V.D.; Yarygina, E.G.; Bokhan, N.A.; Ivanova, S.A. Use of Carnosine for Oxidative Stress Reduction in Different Pathologies. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hipkiss, A.R.; Baye, E.; de Courten, B. Carnosine and the processes of ageing. Maturitas 2016, 93, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandurangan, M.; Mistry, B.; Enkhataivan, G.; Kim, D.H. Efficacy of carnosine on activation of caspase 3 and human renal carcinoma cell inhibition. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, E.; Saunders, B.; Harris, R.C.; Bicudo, J.E.P.W.; Bishop, D.J.; Sale, C.; Gualano, B. Comparative physiology investigations support a role for histidine-containing dipeptides in intracellular acid-base regulation of skeletal muscle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2019, 234, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhipinti, R.; Boron, W.F. Role of Carbonic Anhydrases and Inhibitors in Acid-Base Physiology: Insights from Mathematical Modeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellia, F.; Vecchio, G.; Rizzarelli, E. Carnosinases, their substrates and diseases. Molecules 2014, 19, 2299–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hisatsune, T.; Kaneko, J.; Kurashige, H.; Cao, Y.; Satsu, H.; Totsuka, M.; Katakura, Y.; Imabayashi, E.; Matsuda, H. Effect of Anserine/Carnosine Supplementation on Verbal Episodic Memory in Elderly People. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 50, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masuoka, N.; Yoshimine, C.; Hori, M.; Tanaka, M.; Asada, T.; Abe, K.; Hisatsune, T. Effects of Anserine/Carnosine Supplementation on Mild Cognitive Impairment with APOE4. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schön, M.; Mousa, A.; Berk, M.; Chia, W.L.; Ukropec, J.; Majid, A.; Ukropcová, B.; de Courten, B. The Potential of Carnosine in Brain-Related Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Current Evidence. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Posa, D.K.; Kumar, V.; Hoetker, D.; Kumar, A.; Ganesan, S.; Riggs, D.W.; Bhatnagar, A.; Wempe, M.F.; Baba, S.P. Carnosine protects cardiac myocytes against lipid peroxidation products. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifah, R.G. The carbon dioxide hydration activity of carbonic anhydrase. I. Stop-flow kinetic studies on the native human isoenzymes B and C. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Temperini, C.; Scozzafava, A.; Vullo, D.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase activators. Activation of isoforms I, II, IV, VA, VII, and XIV with L- and D-phenylalanine and crystallographic analysis of their adducts with isozyme II: Stereospecific recognition within the active site of an enzyme and its consequences for the drug design. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3019–3027. [Google Scholar]
- Angeli, A.; Donald, W.A.; Parkkila, S.; Supuran, C.T. Activation studies with amines and amino acids of the β-carbonic anhydrase from the pathogenic protozoan Leishmania donovani chagasi. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 78, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rami, M.; Winum, J.Y.; Supuran, C.T.; Melnyk, P.; Yous, S. (Hetero)aryl substituted thiazol-2,4-yl scaffold as human carbonic anhydrase I, II, VII and XIV activators. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angeli, A.; Alasmary, F.A.S.; Del Prete, S.; Osman, S.M.; AlOthman, Z.; Donald, W.A.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. The first activation study of a δ-carbonic anhydrase: TweCAδ from the diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii is effectively activated by amines and amino acids. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vistoli, G.; Colzani, M.; Mazzolari, A.; Maddis, D.D.; Grazioso, G.; Pedretti, A.; Carini, M.; Aldini, G. Computational approaches in the rational design of improved carbonyl quenchers: Focus on histidine containing dipeptides. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 1721–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korb, O.; Stützle, T.; Exner, T.E. Empirical scoring functions for advanced protein-ligand docking with PLANTS. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
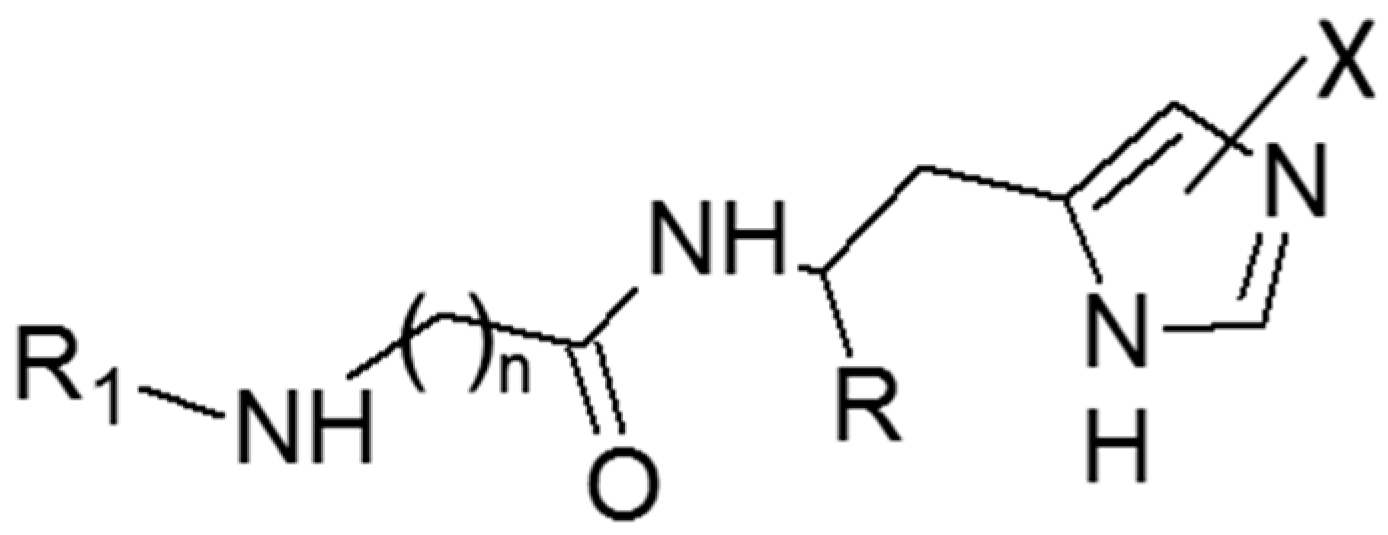


| No. | Compound | R | R1 | X | n | KA (µM) * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hCA I | hCA II | hCA VA | hCA IX | ||||||
| 1 | l-carnosine | COOH | H | H | 2 | 92.1 | 83.4 | 17.2 | 46.3 |
| 2 | d-carnosine | COOH | H | H | 2 | 54.3 | 76.6 | 8.93 | 10.1 |
| 3 | l-carnosinamide | CONH2 | H | H | 2 | 45.2 | 91.5 | 18.5 | 4.71 |
| 4 | d-carnosinamide | CONH2 | H | H | 2 | 16.6 | >100 | 16.1 | 45.5 |
| 5 | l-homocarnosine | COOH | H | H | 3 | 77.0 | 88.9 | 51.3 | 7.35 |
| 6 | l-anserine | COOH | H | 1-Me | 2 | 80.4 | 93.7 | 17.4 | 1.14 |
| 7 | l-balenine | COOH | H | 3-Me | 2 | 20.7 | >100 | 47.2 | 50.2 |
| 8 | carcinine | H | H | H | 2 | 16.6 | >100 | 6.4 | 38.0 |
| 7 | Gly-l-His | COOH | H | H | 1 | 31.9 | 90.1 | 9.83 | 11.5 |
| 8 | Gly-Gly-l-His | COOH | Gly | H | 1 | 74.3 | >100 | 52.8 | 19.4 |
| 9 | N-acetyl-X-carnosine | COOH | Acetyl | H | 2 | 79.6 | 102 | 47.1 | 32.6 |
| 10 | l-carnosinol | CH2OH | H | H | 2 | 28.3 | >100 | 12.2 | 20.5 |
| 11 | histamine | - | - | - | - | 2.1 | 125 | 0.010 | 35.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vistoli, G.; Aldini, G.; Fumagalli, L.; Dallanoce, C.; Angeli, A.; Supuran, C.T. Activation Effects of Carnosine- and Histidine-Containing Dipeptides on Human Carbonic Anhydrases: A Comprehensive Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051761
Vistoli G, Aldini G, Fumagalli L, Dallanoce C, Angeli A, Supuran CT. Activation Effects of Carnosine- and Histidine-Containing Dipeptides on Human Carbonic Anhydrases: A Comprehensive Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(5):1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051761
Chicago/Turabian StyleVistoli, Giulio, Giancarlo Aldini, Laura Fumagalli, Clelia Dallanoce, Andrea Angeli, and Claudiu T. Supuran. 2020. "Activation Effects of Carnosine- and Histidine-Containing Dipeptides on Human Carbonic Anhydrases: A Comprehensive Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 5: 1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051761
APA StyleVistoli, G., Aldini, G., Fumagalli, L., Dallanoce, C., Angeli, A., & Supuran, C. T. (2020). Activation Effects of Carnosine- and Histidine-Containing Dipeptides on Human Carbonic Anhydrases: A Comprehensive Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(5), 1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051761








