The Role of NFκB in Healthy and Preeclamptic Placenta: Trophoblasts in the Spotlight
Abstract
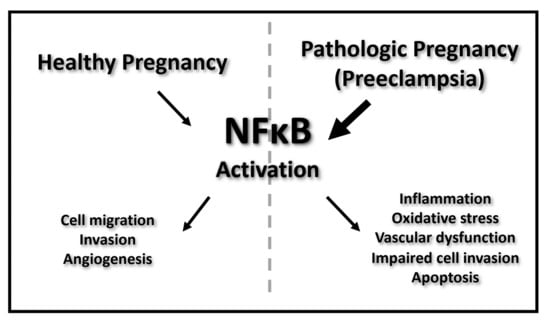
:1. Introduction
2. The NFκB Family of Proteins
2.1. NFκB Activation
2.2. Actions of NFκB
3. NFκB Actions in the Placenta during Normal Pregnancy and Preeclampsia
3.1. NFκB throughout Normal Pregnancy
3.2. Placental Trophoblasts
3.3. EVT Function and NFκB Actions in Normal Pregnancy
3.4. EVT Function and NFκB Actions in Preeclampsia
3.5. VT Function and NFκB Actions in Normal Pregnancies
3.6. VT Function and NFκB Actions in Preeclampsia
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NFκB | Nuclear-Factor Kappa-Light Chain of B Cells |
| PE | Preeclampsia |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| IL-1 | Interleukin-1 |
| TLR | Toll-Like Receptor |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| HIF1 | Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 |
| HIF2 | Hypoxia Inducible Factor 2 |
| DAMPs | Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns |
| PHDs | Prolylhydroxylases |
| FIHs | Factor Inhibiting HIFs |
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| ICP | Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy |
| AP-1 | Activator Protein-1 |
| DMARDs | Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| COX2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| CTB | Cytotrophoblast |
| EVT | Extravillous Cytotrophoblast |
| VT | Villous Cytotrophoblast |
| pCCT | Proliferative Column Cytotrophoblast |
| dCCT | Distal Column Cytotrophoblast |
| EMT | Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 |
| TGFB | Transforming Growth Factor B |
| TLR4 | Toll-Like Receptor 4 |
| PPARG | Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor G |
| GCM1 | Glial Cell Missing 1 |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| PIGF | Placental Growth Factor |
| ENG | Endoglin |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen Peroxide |
| ET-1 | Endothelin-1 |
| sFLT1 | Soluble Fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 1 |
References
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.Y.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappa B signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Tar. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torchinsky, A.; Toder, V. To die or not to die: The function of the transcription factor NF-kappa B in embryos exposed to stress. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2004, 51, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, A.; Scoggin, S.; Gaynor, R.B.; Williams, N.S. Identification of NF-kappa B-regulated genes induced by TNFalpha utilizing expression profiling and RNA interference. Oncogene 2003, 22, 2054–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cummins, E.P.; Comerford, K.M.; Scholz, C.; Bruning, U.; Taylor, C.T. Hypoxic regulation of NF-kappa B signaling. Methods Enzymol. 2007, 435, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.A.; Beug, H.; Wirth, T. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition—NF-kappa B takes center stage. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huber, M.A.; Azoitei, N.; Baumann, B.; Grunert, S.; Sommer, A.; Pehamberger, H.; Kraut, N.; Beug, H.; Wirth, T. NF-kappa B is essential for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in a model of breast cancer progression. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 114, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lingappan, K. NF-kappaB in Oxidative Stress. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.T. Interdependent roles for hypoxia inducible factor and nuclear factor-kappaB in hypoxic inflammation. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 4055–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knofler, M.; Haider, S.; Saleh, L.; Pollheimer, J.; Gamage, T.K.J.B.; James, J. Human placenta and trophoblast development: Key molecular mechanisms and model systems. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3479–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindheimer, M.D.; Roberts, J.M.; Cunningham, F.G. Chesley’s Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Academic Press Inc: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–431. [Google Scholar]
- Mor, G.; Kwon, J.Y. Trophoblast-microbiome interaction: A new paradigm on immune regulation. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 213, S131–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollheimer, J.; Vondra, S.; Baltayeva, J.; Beristain, A.G.; Knofler, M. Regulation of Placental Extravillous Trophoblasts by the Maternal Uterine Environment. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ignazio, L.; Rocha, S. Hypoxia Induced NF-kappaB. Cells 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeyabalan, A. Epidemiology of preeclampsia: Impact of obesity. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, S18–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 202: Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 133, e1–e25.
- McCarthy, F.P.; Drewlo, S.; English, F.A.; Kingdom, J.; Johns, E.J.; Kenny, L.C.; Walsh, S.K. Evidence Implicating Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-gamma in the Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia. Hypertension 2011, 58, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phipps, E.A.; Thadhani, R.; Benzing, T.; Karumanchi, S.A. Pre-eclampsia: Pathogenesis, novel diagnostics and therapies. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, M.; Baczyk, D.; Kingdom, J. Soluable factor versus microparticle—mediated endothelial cell dysfunction in severe pre-eclampsia. Bjog.-Int. J. Obstet. Gy. 2017, 124, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, S.; Lemoine, E.; Granger, J.P.; Karumanchi, S.A. Preeclampsia: Pathophysiology, Challenges, and Perspectives. Circ Res 2019, 124, 1094–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, S.J. Why is placentation abnormal in preeclampsia? Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 213, S115–S122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cartwright, J.E.; Fraser, R.; Leslie, K.; Wallace, A.E.; James, J.L. Remodelling at the maternal-fetal interface: Relevance to human pregnancy disorders. Reproduction 2010, 140, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyall, F.; Robson, S.C.; Bulmer, J.N. Spiral artery remodeling and trophoblast invasion in preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction: Relationship to clinical outcome. Hypertension 2013, 62, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aouache, R.; Biquard, L.; Vaiman, D.; Miralles, F. Oxidative Stress in Preeclampsia and Placental Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Aranguren, L.C.; Prada, C.E.; Riano-Medina, C.E.; Lopez, M. Endothelial dysfunction and preeclampsia: Role of oxidative stress. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiarello, D.I.; Abad, C.; Rojas, D.; Toledo, F.; Vazquez, C.M.; Mate, A.; Sobrevia, L.; Marin, R. Oxidative stress: Normal pregnancy versus preeclampsia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Carmona, A.; Mendieta Zeron, H. NF-kappaBeta and SOD expression in preeclamptic placentas. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 46, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Tian, X.; Sun, Q. Serum NF-kappaBp65, TLR4 as Biomarker for Diagnosis of Preeclampsia. Open Med. 2017, 12, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.E.; Walsh, S.W. Activation of NF-kappaB in placentas of women with preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy 2012, 31, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeland, A.K.; Soncin, F.; Moretto-Zita, M.; Chang, C.W.; Horii, M.; Pizzo, D.; Nelson, K.K.; Laurent, L.C.; Parast, M.M. Hypoxia Directs Human Extravillous Trophoblast Differentiation in a Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-Dependent Manner. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulze-Luehrmann, J.; Ghosh, S. Antigen-receptor signaling to nuclear factor kappa B. Immunity 2006, 25, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrington, F.D.; Carmody, R.J.; Goodyear, C.S. Modulation of NF-kappaB Signaling as a Therapeutic Target in Autoimmunity. J. Biomol. Screen. 2016, 21, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roh, J.S.; Sohn, D.H. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in Inflammatory Diseases. Immune. Netw. 2018, 18, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S. Danger-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs): The Derivatives and Triggers of Inflammation. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018, 18, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrington, M.G.; Fraser, I.D.C. NF-kappaB Signaling in Macrophages: Dynamics, Crosstalk, and Signal Integration. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Regulation of NF-kappaB by TNF family cytokines. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schutze, S.; Wiegmann, K.; Machleidt, T.; Kronke, M. TNF-induced activation of NF-kappa B. Immunobiology 1995, 193, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ietta, F.; Wu, Y.; Winter, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Post, M.; Caniggia, I. Dynamic HIF1A regulation during human placental development. Biol. Reprod. 2006, 75, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, L.; Cui, Y.; Qi, Z.; Huang, X.; Cai, L.; Zhang, T.; Yin, Y.; Lu, Z.; Xiang, J. Roles of PPARgamma/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dong, M.; Xu, F.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. Interaction between NF-kappaB and AP-1 and their intracellular localization at labor in human late pregnant myometrial cells in vivo and in vitro. Medicine 2018, 97, e12494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, I.M. Nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB proteins: Therapeutic targets. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, ii57–ii61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mor, G. Inflammation and pregnancy—The role of toll-like receptors in trophoblast-immune interaction. Ann. Ny. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1127, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakowicz, A. The role of NFB in the three stages of pregnancy—Implantation, maintenance, and labour: A review article. Bjog. Int. J. Obstet. Gy. 2018, 125, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mor, G.; Cardenas, I.; Abrahams, V.; Guller, S. Inflammation and pregnancy: The role of the immune system at the implantation site. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2011, 1221, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaislasuo, J.; Simpson, S.; Petersen, J.F.; Peng, G.; Aldo, P.; Lokkegaard, E.; Paidas, M.; Pal, L.; Guller, S.; Mor, G. IL-10 to TNFalpha ratios throughout early first trimester can discriminate healthy pregnancies from pregnancy losses. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, M.Y.; Moffett, A. Development of the human placenta. Development 2019, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gude, N.M.; Roberts, C.T.; Kalionis, B.; King, R.G. Growth and function of the normal human placenta. Thromb. Res. 2004, 114, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilburgs, T.; Crespo, A.C.; van der Zwan, A.; Rybalov, B.; Raj, T.; Stranger, B.; Gardner, L.; Moffett, A.; Strominger, J.L. Human HLA-G+ extravillous trophoblasts: Immune-activating cells that interact with decidual leukocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7219–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Genbacev, O.; Damsky, C.H.; Fisher, S.J. Oxygen regulates human cytotrophoblast differentiation and invasion: Implications for endovascular invasion in normal pregnancy and in pre-eclampsia. J. Reprod. Immunol. 1998, 39, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Wakeland, A.K.; Parast, M.M. Trophoblast lineage specification, differentiation and their regulation by oxygen tension. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 236, R43–R56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, J.L.; Stone, P.R.; Chamley, L.W. The regulation of trophoblast differentiation by oxygen in the first trimester of pregnancy. Hum. Reprod. Update 2006, 12, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, D.; Tanabe, A.; Sekijima, T.; Soen, H.; Narahara, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Terai, Y.; Kamegai, H.; Ohmichi, M. Role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and AKT cascades in regulating hypoxia-induced angiogenic factors produced by a trophoblast-derived cell line. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 206, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilburn, B.A.; Wang, J.; Duniec-Dmuchowski, Z.M.; Leach, R.E.; Romero, R.; Armant, D.R. Extracellular matrix composition and hypoxia regulate the expression of HLA-G and integrins in a human trophoblast cell line. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 62, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, J.M.; Escudero, C. The placenta in preeclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens 2012, 2, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, J.E.; Pollheimer, J.; Yong, H.E.J.; Kokkinos, M.I.; Kalionis, B.; Knofler, M.; Murthi, P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition during extravillous trophoblast differentiation. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2016, 10, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadam, L.; Kilburn, B.; Baczyk, D.; Kohan-Ghadr, H.R.; Kingdom, J.; Drewlo, S. Rosiglitazone blocks first trimester in-vitro placental injury caused by NF-kappaB-mediated inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaSilva-Arnold, S.C.; Zamudio, S.; Al-Khan, A.; Alvarez-Perez, J.; Mannion, C.; Koenig, C.; Luke, D.; Perez, A.M.; Petroff, M.; Alvarez, M.; et al. Human trophoblast epithelial-mesenchymal transition in abnormally invasive placenta. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 99, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lv, S.S.; Fu, Z.Y.; Hou, L.L. Baicalein Enhances Migration and Invasion of Extravillous Trophoblasts via Activation of the NF-kappaB Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 2983–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabruyn, S.P.; Griffioen, A.W. NF-kappa B: A new player in angiostatic therapy. Angiogenesis 2008, 11, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiden, U.; Eyth, C.P.; Majali-Martinez, A.; Desoye, G.; Tam-Amersdorfer, C.; Huppertz, B.; Ghaffari Tabrizi-Wizsy, N. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 12 is highly specific for non-proliferating invasive trophoblasts in the first trimester and temporally regulated by oxygen-dependent mechanisms including HIF-1A. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 149, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pires, B.R.; Mencalha, A.L.; Ferreira, G.M.; de Souza, W.F.; Morgado-Diaz, J.A.; Maia, A.M.; Correa, S.; Abdelhay, E.S. NF-kappaB Is Involved in the Regulation of EMT Genes in Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, R.; Wang, Q.; He, X.L.; Chu, Y.K.; Lu, J.G.; Ma, Q.J. Role of nuclear factor kappa B and reactive oxygen species in the tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of MCF-7 cells. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2007, 40, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huber, A.V.; Saleh, L.; Bauer, S.; Husslein, P.; Knofler, M. TNFalpha-mediated induction of PAI-1 restricts invasion of HTR-8/SVneo trophoblast cells. Placenta 2006, 27, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.; Pollheimer, J.; Hartmann, J.; Husslein, P.; Aplin, J.D.; Knofler, M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits trophoblast migration through elevation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in first-trimester villous explant cultures. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Widen, S.G.; Yang, J.; Wood, T.G.; Kudlicki, A.; Zhao, Y.; Brasier, A.R. The NFkappaB subunit RELA is a master transcriptional regulator of the committed epithelial-mesenchymal transition in airway epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 16528–16545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coates, M.S.; Alton, E.W.F.W.; Brookes, D.W.; Ito, K.; Davies, J.C. Increased Respiratory Syncytial Virus Burden Leads to More Rapid Cell Death in Phe508del Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Thorax 2016, 71, A44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzman-Genuino, R.M.; Dimova, T.; You, Y.; Aldo, P.; Hayball, J.D.; Mor, G.; Diener, K.R. Trophoblasts promote induction of a regulatory phenotype in B cells that can protect against detrimental T cell-mediated inflammation. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2019, 82, e13187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, L.; Kohan-Ghadr, H.R.; Drewlo, S. The balancing act—PPAR-gamma’s roles at the maternal-fetal interface. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2015, 61, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladunewich, M.; Karumanchi, S.A.; Lafayette, R. Pathophysiology of the clinical manifestations of preeclampsia. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnault, T.R.; Galan, H.L.; Parker, T.A.; Anthony, R.V. Placental development in normal and compromised pregnancies—A review. Placenta 2002, 23, S119–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymanlou, N.; Jurisica, I.; Nevo, O.; Ietta, F.; Zhang, X.; Zamudio, S.; Post, M.; Caniggia, I. Molecular evidence of placental hypoxia in preeclampsia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 4299–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, T.J.; Walsh, S.W. Activation of NF-kappaB and expression of COX-2 in association with neutrophil infiltration in systemic vascular tissue of women with preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 196, e41–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, A.C.; Cornelius, D.C.; Amaral, L.M.; Faulkner, J.L.; Cunningham, M.W., Jr.; Wallace, K.; LaMarca, B. The role of inflammation in the pathology of preeclampsia. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, Y.; Vattai, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Thaler, C.J.; Mahner, S.; Jeschke, U.; von Schonfeldt, V. Role of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Type 1 in Pathologies of Female Reproductive Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbro, D.; D’Elia, A.V.; Spizzo, R.; Driul, L.; Barillari, G.; Di Loreto, C.; Marchesoni, D.; Damante, G. Association between plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 gene polymorphisms and preeclampsia. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest. 2003, 56, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, K.; Mor, G. Toll-like receptors at the maternal-fetal interface in normal pregnancy and pregnancy disorders. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, P.; Zheng, M.; Gong, P.; Lin, C.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Diao, Z.; Yan, G.; Sun, H.; et al. Single administration of ultra-low-dose lipopolysaccharide in rat early pregnancy induces TLR4 activation in the placenta contributing to preeclampsia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Bao, J.; Li, X.; Ye, A.; Zhang, G.; Liu, H. Activation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway by nicotine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced preeclampsia-like symptoms in pregnant rats. Placenta 2017, 49, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Liu, M.; Hong, G.; Li, Y.; Xue, P.; Zheng, M.; Wu, M.; Shen, L.; Yang, M.; Diao, Z.; et al. Curcumin improves LPS-induced preeclampsia-like phenotype in rat by inhibiting the TLR4 signaling pathway. Placenta 2016, 41, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baczyk, D.; Drewlo, S.; Proctor, L.; Dunk, C.; Lye, S.; Kingdom, J. Glial cell missing-1 transcription factor is required for the differentiation of the human trophoblast. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, L.P.; Redmer, D.A. Angiogenesis in the placenta. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 64, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geva, E.; Ginzinger, D.G.; Zaloudek, C.J.; Moore, D.H.; Byrne, A.; Jaffe, R.B. Human placental vascular development: Vasculogenic and angiogenic (branching and nonbranching) transformation is regulated by vascular endothelial growth factor-A, angiopoietin-1, and angiopoietin-2. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 4213–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, H.M.; Seo, K.H.; Han, S.J.; Ahn, K.Y.; Choi, I.H.; Koh, G.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Ra, M.S.; Im, S.Y. Nuclear factor kappaB dependency of platelet-activating factor-induced angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Kofler, S.; Nickel, T.; Weis, M. Role of cytokines in cardiovascular diseases: A focus on endothelial responses to inflammation. Clin. Sci. 2005, 108, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cramer, M.; Nagy, I.; Murphy, B.J.; Gassmann, M.; Hottiger, M.O.; Georgiev, O.; Schaffner, W. NF-kappaB contributes to transcription of placenta growth factor and interacts with metal responsive transcription factor-1 in hypoxic human cells. Biol. Chem. 2005, 386, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.; Pettaway, C.A.; Uehara, H.; Bucana, C.D.; Fidler, I.J. Blockade of NF-kappaB activity in human prostate cancer cells is associated with suppression of angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. Oncogene 2001, 20, 4188–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, Q.; Zheng, L.; Lin, L.; Li, B.; Wang, D.; Huang, C.; Li, D. VEGF is upregulated by hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor via the PI-3K/Akt-NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walton, C.B.; Matter, M.L. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay: Examining the Interaction of NFkB with the VEGF Promoter. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1332, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, S. The discovery of placenta growth factor and its biological activity. Exp. Mol. Med. 2012, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapur, N.K.; Morine, K.J.; Letarte, M. Endoglin: A critical mediator of cardiovascular health. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2013, 9, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregory, A.L.; Xu, G.; Sotov, V.; Letarte, M. Review: The enigmatic role of endoglin in the placenta. Placenta 2014, 35, S93–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.D.; De Long, N.E.; Wang, R.C.; Yazdi, F.T.; Holloway, A.C.; Raha, S. Angiogenesis in the placenta: The role of reactive oxygen species signaling. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 814543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schreck, R.; Rieber, P.; Baeuerle, P.A. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 2247–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajakumar, A.; Powers, R.W.; Hubel, C.A.; Shibata, E.; von Versen-Hoynck, F.; Plymire, D.; Jeyabalan, A. Novel Soluble Flt-1 Isoforms in Plasma and Cultured Placental Explants from Normotensive Pregnant and Preeclamptic Women. Placenta 2009, 30, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirota, K.; Murata, M.; Sachi, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Takeuchi, J.; Mori, K.; Yodoi, J. Distinct roles of thioredoxin in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus. A two-step mechanism of redox regulation of transcription factor NF-kappaB. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 27891–27897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parrish, M.R.; Murphy, S.R.; Rutland, S.; Wallace, K.; Wenzel, K.; Wallukat, G.; Keiser, S.; Ray, L.F.; Dechend, R.; Martin, J.N.; et al. The effect of immune factors, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and agonistic autoantibodies to the angiotensin II type I receptor on soluble fms-like tyrosine-1 and soluble endoglin production in response to hypertension during pregnancy. Am. J. Hypertens. 2010, 23, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eddy, A.; Chapman, H.; Brown, D.T.; George, E. Differential Regulation of sFlt-1 Splicing by U2AF65 and JMJD6 in Placental-Derived and Endothelial Cells. Biosci. Rep. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sankaralingam, S.; Xu, H.; Davidge, S.T. Arginase contributes to endothelial cell oxidative stress in response to plasma from women with preeclampsia. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 85, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Armistead, B.; Kadam, L.; Drewlo, S.; Kohan-Ghadr, H.-R. The Role of NFκB in Healthy and Preeclamptic Placenta: Trophoblasts in the Spotlight. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051775
Armistead B, Kadam L, Drewlo S, Kohan-Ghadr H-R. The Role of NFκB in Healthy and Preeclamptic Placenta: Trophoblasts in the Spotlight. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(5):1775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051775
Chicago/Turabian StyleArmistead, Brooke, Leena Kadam, Sascha Drewlo, and Hamid-Reza Kohan-Ghadr. 2020. "The Role of NFκB in Healthy and Preeclamptic Placenta: Trophoblasts in the Spotlight" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 5: 1775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051775
APA StyleArmistead, B., Kadam, L., Drewlo, S., & Kohan-Ghadr, H.-R. (2020). The Role of NFκB in Healthy and Preeclamptic Placenta: Trophoblasts in the Spotlight. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(5), 1775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051775