Bulked Segregant Analysis Coupled with Whole-Genome Sequencing (BSA-Seq) Mapping Identifies a Novel pi21 Haplotype Conferring Basal Resistance to Rice Blast Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
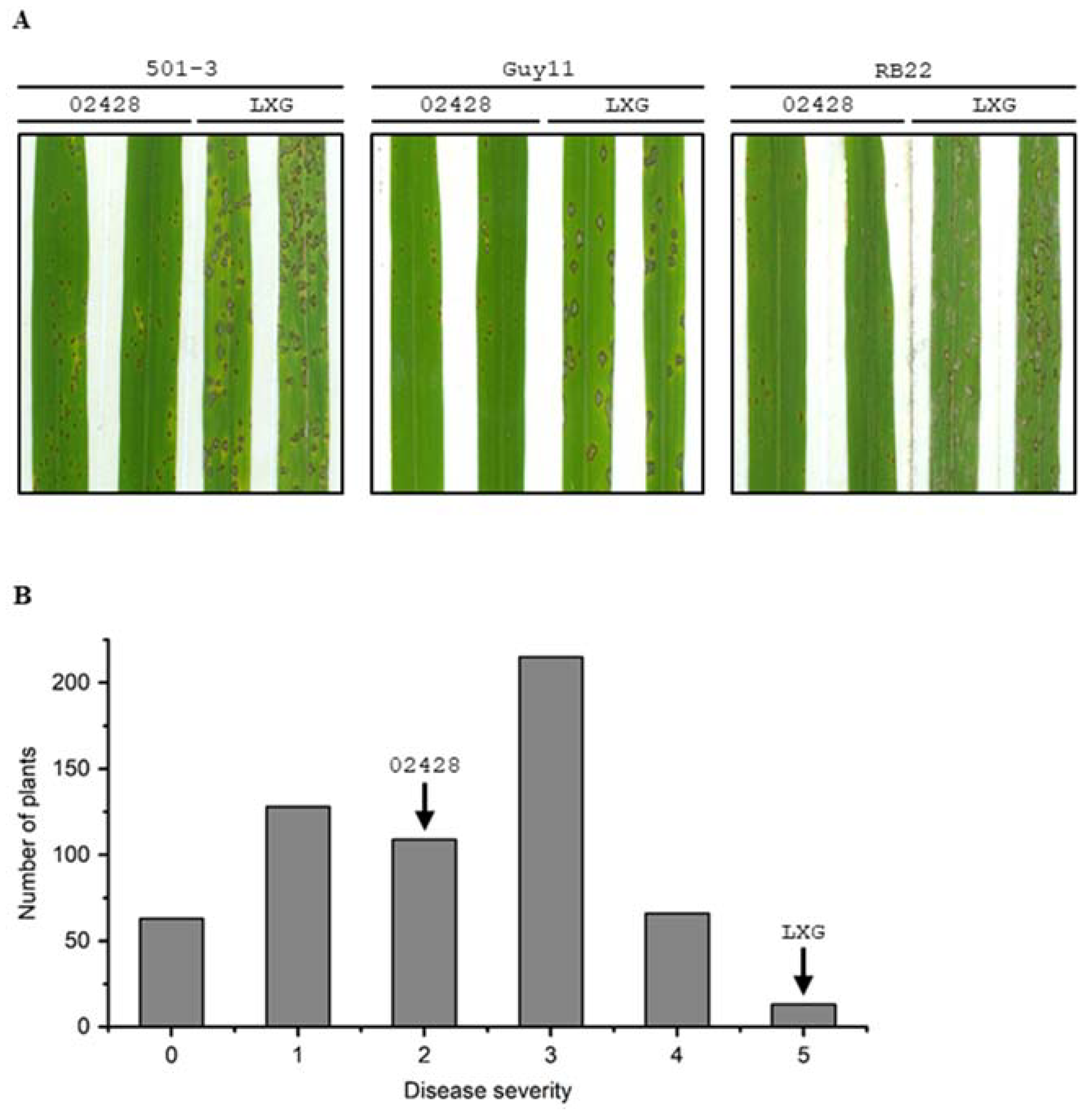
2.1. Evaluation of 02428 and LXG in Basal Resistance to Rice Blast Disease
2.2. SNP and Short InDel Polymorphism Profiling
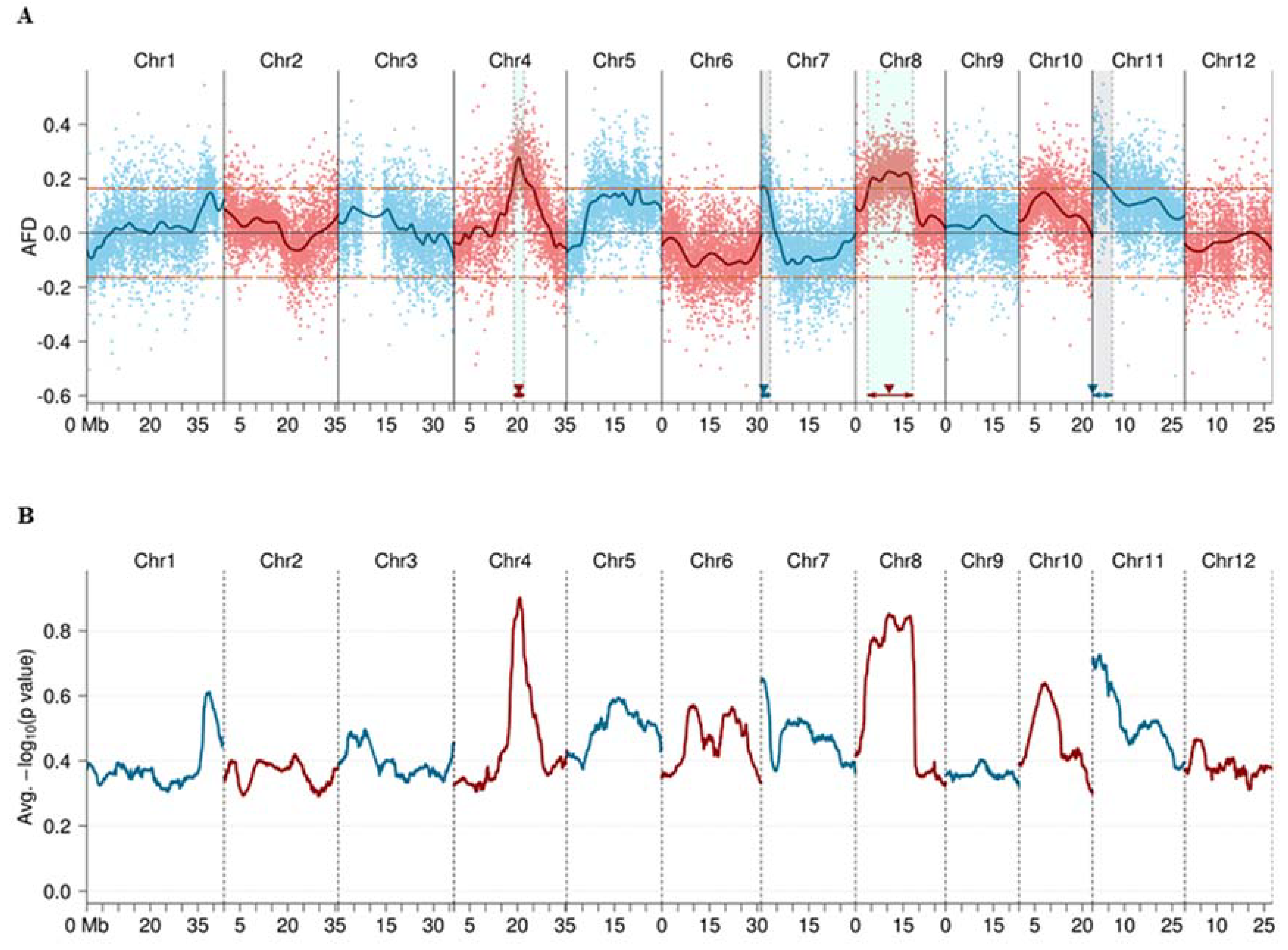
2.3. QTL Mapping and Heritability Estimation
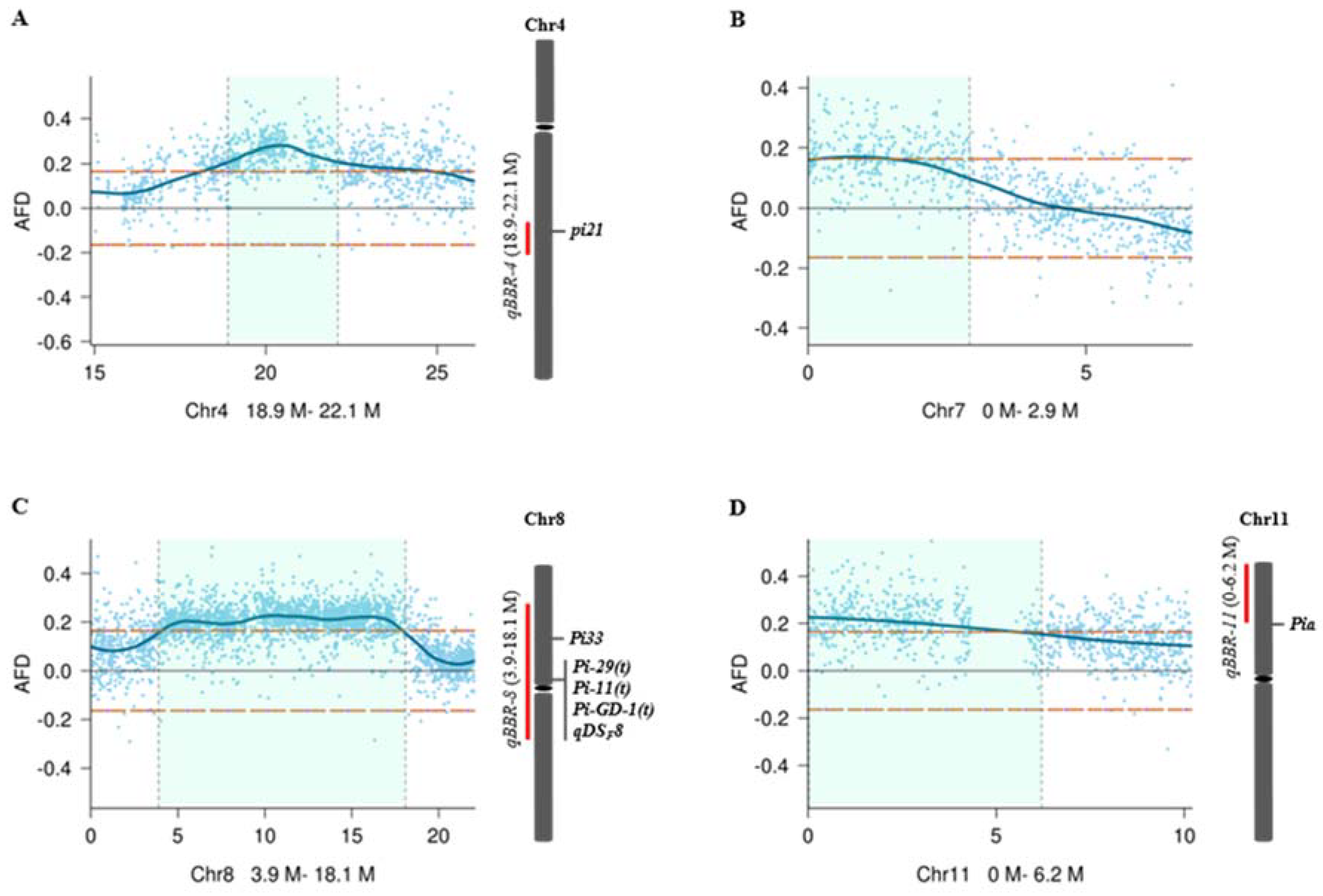
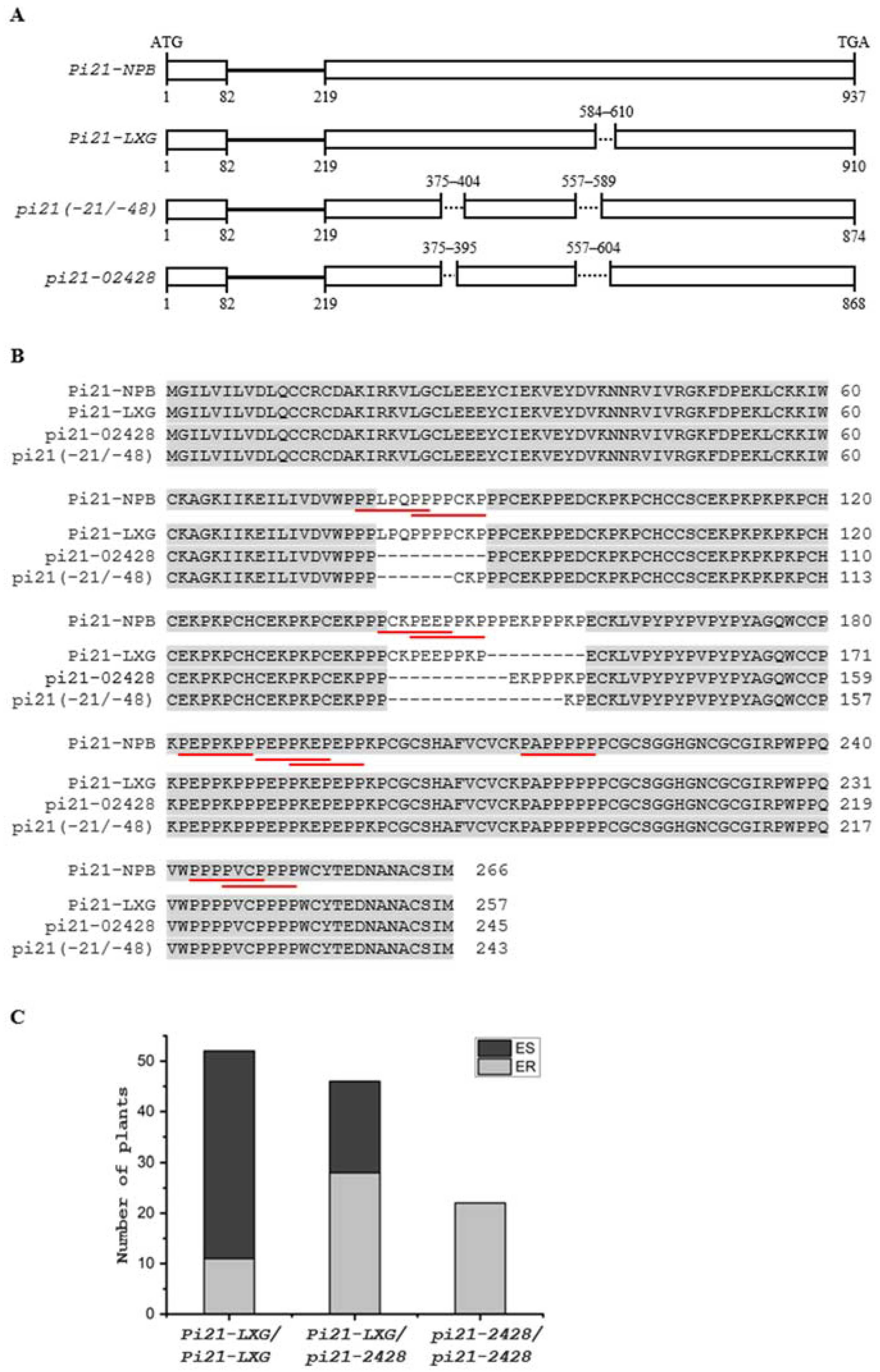
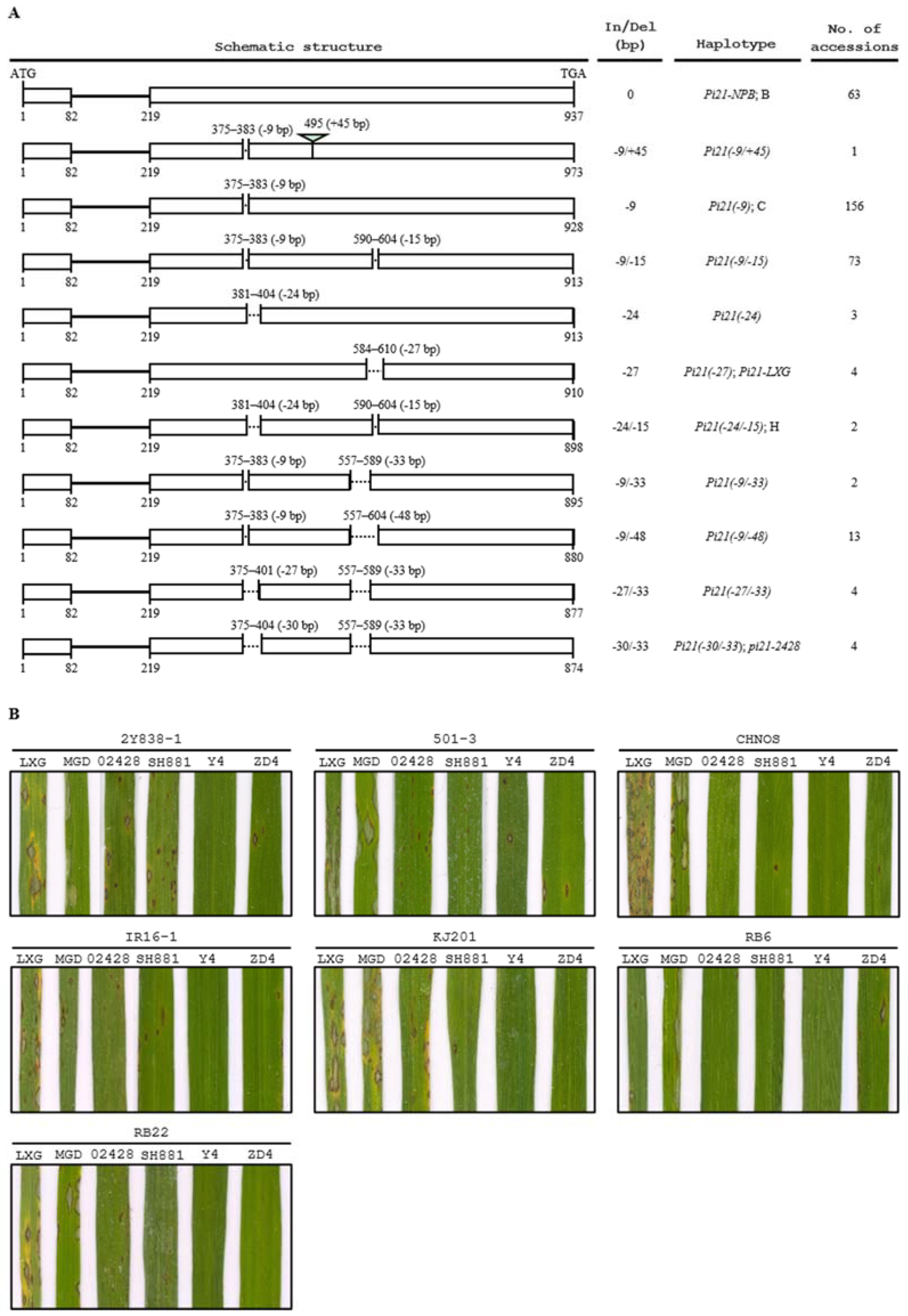
2.4. Identification of a New Haplotype of pi21 as a Candidate Gene of qBBR-4
2.5. Assessment of the pi21-2428 Haplotype in 325 Rice Accessions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Blast Isolates
4.2. Rice Blast Inoculations
4.3. Bulking, DNA Extraction, and Whole-Genome Resequencing
4.4. Analysis of Reads and Variants
4.5. QTL Analysis
4.6. Detection of Haplotypes of Pi21
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khush, G.S. What it will take to feed 5.0 billion rice consumers in 2030. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 59, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbot, N.J. On the trail of a cereal killer: Exploring the biology of Magnaporthe grisea. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 57, 177–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wang, S.; Dai, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, Z.; Pan, S.; Wang, D.; et al. Molecular mapping of the blast resistance gene Pi49 in the durably resistant rice cultivar Mowanggu. Euphytica 2013, 192, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, J.A.; Balint-Kurti, P.J.; Wisser, R.J.; Pratt, R.C.; Nelson, R.J. Shades of gray: The world of quantitative disease resistance. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Wang, S. Broad-spectrum and durability: Understanding of quantitative disease resistance. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, S.T.; Coaker, G.; Day, B.; Staskawicz, B.J. Host-microbe interactions: Shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 2006, 124, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, J.D.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, N.C.; Thordal-Christensen, H.; Lipka, V.; Bau, S.; Kombrink, E.; Qiu, J.L.; Hückelhoven, R.; Stein, M.; Freialdenhoven, A.; Somerville, S.C.; et al. SNARE-protein-mediated disease resistance at the plant cell wall. Nature 2003, 425, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghnoum, R.; Marcel, T.C.; Johrde, A.; Pecchioni, N.; Schweizer, P.; Niks, R.E. Basal host resistance of barley to powdery mildew: Connecting quantitative trait Loci and candidate genes. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact 2010, 23, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasuda, N.; Mitsunaga, T.; Hayashi, K.; Koizumi, S.; Fujita, Y. Effects of pyramiding quantitative resistance genes Pi21, Pi34, and Pi35 on rice leaf blast disease. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, D.; Yang, L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Lou, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, S. Proteomic analysis of the defense response to Magnaporthe oryzae in rice harboring the blast resistance gene Piz-t. Rice 2018, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, D.; Peng, S.; Chen, Y.; Su, P.; Chen, J.; Zheng, L.; Tan, X.; Liu, J.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Genome-wide association mapping of resistance against rice blast strains in South China and identification of a new Pik allele. Rice 2019, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Shang, J.; Chen, D.; Lei, C.; Zou, Y.; Zhai, W.; Liu, G.; Xu, J.; Ling, Z.; Cao, G.; et al. A B-lectin receptor kinase gene conferring rice blast resistance. Plant J. 2006, 46, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Minkenberg, B.; Wheatley, M.; Fan, J.; Jia, M.H.; Famoso, A.; Edwards, J.D.; Wamishe, Y.; et al. The rice blast resistance gene Ptr encodes an atypical protein required for broad-spectrum disease resistance. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Kang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, G.L. A genome-wide association study of field resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae in rice. Rice 2016, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuoka, S.; Saka, N.; Koga, H.; Ono, K.; Shimizu, T.; Ebana, K.; Hayashi, N.; Takahashi, A.; Hirochika, H.; Okuno, K.; et al. Loss of function of a proline-containing protein confers durable disease resistance in rice. Science 2009, 325, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Inoue, H.; Kato, T.; Funao, T.; Shirota, M.; Shimizu, T.; Kanamori, H.; Yamane, H.; Hayano-Saito, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; et al. Durable panicle blast-resistance gene Pb1 encodes an atypical CC-NBS-LRR protein and was generated by acquiring a promoter through local genome duplication. Plant J. 2010, 64, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, S.; Yamamoto, S.I.; Mizobuchi, R.; Yamanouchi, U.; Ono, K.; Kitazawa, N.; Yasuda, N.; Fujita, Y.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Koizumi, S.; et al. Multiple functional polymorphisms in a single disease resistance gene in rice enhance durable resistance to blast. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hayashi, N.; Wang, C.T.; Fukuoka, S.; Kawasaki, S.; Takatsuji, H.; Jiang, C.J. Rice blast resistance gene Pikahei-1(t), a member of a resistance gene cluster on chromosome 4, encodes a nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeat protein. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, Z.; Chern, M.; Yin, J.; Yang, C.; Ran, L.; Cheng, M.; He, M.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; et al. A natural allele of a transcription factor in rice confers broad-spectrum blast resistance. Cell 2017, 170, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abe, A.; Kosugi, S.; Yoshida, K.; Natsume, S.; Takagi, H.; Kanzaki, H.; Matsumura, H.; Yoshida, K.; Mitsuoka, C.; Tamiru, M.; et al. Genome sequencing reveals agronomically important loci in rice using MutMap. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takagi, H.; Abe, A.; Yoshida, K.; Kosugi, S.; Natsume, S.; Mitsuoka, C.; Uemura, A.; Utsushi, H.; Tamiru, M.; Takuno, S.; et al. QTL-seq: Rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. Plant J. 2013, 74, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Pan, Q.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhong, W.; Li, M.; Han, L.; Li, J.; et al. QTG-Seq accelerates QTL fine mapping through QTL partitioning and whole-genome sequencing of bulked segregant samples. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Lu, X. Genetic mapping and molecular marker development for Pi65 (t), a novel broad-spectrum resistance gene to rice blast using next-generation sequencing. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Qiu, J.; Gao, Q. QTL-BSA: A bulked segregant analysis and visualization pipeline for QTL-seq. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, Y.; Kanzaki, H.; Abe, A.; Yoshida, K.; Tamiru, M.; Saitoh, H.; Fujibe, T.; Matsumura, H.; Shenton, M.; Galam, D.C.; et al. A multifaceted genomics approach allows the isolation of the rice Pia-blast resistance gene consisting of two adjacent NBS-LRR protein genes. Plant J. 2011, 66, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Cai, H.; Ling, Z. Construction of a molecular map of rice and gene mapping using a double-haploid population of a cross between indica and japonica varieties. Rice Genet. Newsl. 1993, 10, 132–134. [Google Scholar]
- Sallaud, C.; Lorieux, M.; Roumen, E.; Tharreau, D.; Berruyer, R.; Svestasrani, P.; Garsmeur, O.; Ghesquiere, A.; Notteghem, J.L. Identification of five new blast resistance genes in the highly blast-resistant rice variety IR64 using a QTL mapping strategy. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berruyer, R.; Adreit, H.; Milazzo, J.; Gaillard, S.; Berger, A.; Dioh, W.; Lebrun, M.H.; Tharreau, D. Identification and fine mapping of Pi33, the rice resistance gene corresponding to the Magnaporthe grisea avirulence gene ACE1. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Q.; Wu, S.; Mei, M.; Mauleon, R.; Leach, J.; Mew, T.; Leung, H. Candidate defense genes as predictors of quantitative blast resistance in rice. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact 2004, 17, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Dai, G.; Zhou, W.; Liang, H.; Huang, J.; Qing, D.; Chen, W.; Wu, H.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; et al. Mapping and identifying a candidate gene Plr4, a recessive gene regulating purple leaf in rice, by using bulked segregant and transcriptome analysis with next-generation sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawson, T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature 1995, 373, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, L.J.; Kuhne, R.; Schneider-Mergener, J.; Oschkinat, H. Recognition of proline-rich motifs by protein-protein-interaction domains. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2005, 44, 2852–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, S.; Okuno, K. Strategies for breeding durable resistance to rice blast using pi21. Crop Breed. Genet. Genom. 2019, 1, e190013. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuoka, S.; Saka, N.; Mizukami, Y.; Koga, H.; Yamanouchi, U.; Yoshioka, Y.; Hayashi, N.; Ebana, K.; Mizobuchi, R.; Yano, M. Gene pyramiding enhances durable blast disease resistance in rice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, D.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Chen, S. Allele-specific marker-based assessment revealed that the rice blast resistance genes Pi2 and Pi9 have not been widely deployed in Chinese indica rice cultivars. Rice 2016, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackill, D.J.; Bonman, J.M. Inheritance of blast resistance in near-isogenic lines of rice. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, Y.; de la Bastide, M.; Hamilton, J.P.; Kanamori, H.; McCombie, W.R.; Ouyang, S.; Schwartz, D.C.; Tanaka, T.; Wu, J.; Zhou, S.; et al. Improvement of the Oryza sativa Nipponbare reference genome using next generation sequence and optical map data. Rice 2013, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows—Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrison, E.; Marth, G. Haplotype-based variant detection from short-read sequencing. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1207.3907. [Google Scholar]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Tang, W.; Bu, S.; Wu, W. BRM: A statistical method for QTL mapping based on bulked segregant analysis by deep sequencing. Bioinformatics 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenreich, I.M.; Torabi, N.; Jia, Y.; Kent, J.; Martis, S.; Shapiro, J.A.; Gresham, D.; Caudy, A.A.; Kruglyak, L. Dissection of genetically complex traits with extremely large pools of yeast segregants. Nature 2010, 464, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.; Huang, L.; Bu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W. Estimation of QTL heritability based on pooled sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Chr. | Length | SNP | Short InDel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Density (per kb) | Number | Density (per kb) | ||
| Chr1 | 43,270,923 | 48,669 | 1.12 | 7735 | 0.18 |
| Chr2 | 35,937,250 | 67,302 | 1.87 | 9069 | 0.25 |
| Chr3 | 36,413,819 | 20,399 | 0.56 | 3336 | 0.09 |
| Chr4 | 35,502,694 | 42,156 | 1.19 | 5558 | 0.16 |
| Chr5 | 29,958,434 | 67,386 | 2.25 | 9189 | 0.31 |
| Chr6 | 31,248,787 | 34,848 | 1.12 | 5309 | 0.17 |
| Chr7 | 29,697,621 | 25,681 | 0.86 | 4040 | 0.14 |
| Chr8 | 28,443,022 | 56,474 | 1.99 | 7152 | 0.25 |
| Chr9 | 23,012,720 | 23,331 | 1.01 | 2965 | 0.13 |
| Chr10 | 23,207,287 | 36,435 | 1.57 | 4062 | 0.18 |
| Chr11 | 29,021,106 | 31,309 | 1.08 | 4680 | 0.16 |
| Chr12 | 27,531,856 | 15,522 | 0.56 | 2671 | 0.10 |
| Total | 373,245,519 | 469,512 | 1.26 | 65,766 | 0.18 |
| QTL | Chr. | AFD value a | Pos. (Mb) b | Interval (Mp) c | Max. NLP d | (%) e | (%) f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qBBR-4 | 4 | 0.278 | 20.46 | 18.90–22.10 | 0.90 | 2.09 | 7.82 |
| qBBR-7 | 7 | 0.172 | 0.86 | 0–2.91 | 0.65 | 0.89 | 0.26 |
| qBBR-8 | 8 | 0.227 | 10.63 | 3.89–18.09 | 0.85 | 1.56 | 0.01 |
| qBBR-11 | 11 | 0.226 | 0.02 | 0–6.21 | 0.73 | 1.54 | 3.50 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, T.; Chi, W.; Huang, L.; Qu, M.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.-Q.; Chen, Z.-J.; Tian, D.; Gui, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Bulked Segregant Analysis Coupled with Whole-Genome Sequencing (BSA-Seq) Mapping Identifies a Novel pi21 Haplotype Conferring Basal Resistance to Rice Blast Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062162
Liang T, Chi W, Huang L, Qu M, Zhang S, Chen Z-Q, Chen Z-J, Tian D, Gui Y, Chen X, et al. Bulked Segregant Analysis Coupled with Whole-Genome Sequencing (BSA-Seq) Mapping Identifies a Novel pi21 Haplotype Conferring Basal Resistance to Rice Blast Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(6):2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062162
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Tingmin, Wenchao Chi, Likun Huang, Mengyu Qu, Shubiao Zhang, Zi-Qiang Chen, Zai-Jie Chen, Dagang Tian, Yijie Gui, Xiaofeng Chen, and et al. 2020. "Bulked Segregant Analysis Coupled with Whole-Genome Sequencing (BSA-Seq) Mapping Identifies a Novel pi21 Haplotype Conferring Basal Resistance to Rice Blast Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 6: 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062162
APA StyleLiang, T., Chi, W., Huang, L., Qu, M., Zhang, S., Chen, Z.-Q., Chen, Z.-J., Tian, D., Gui, Y., Chen, X., Wang, Z., Tang, W., & Chen, S. (2020). Bulked Segregant Analysis Coupled with Whole-Genome Sequencing (BSA-Seq) Mapping Identifies a Novel pi21 Haplotype Conferring Basal Resistance to Rice Blast Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(6), 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062162






