Analgesic and Neuroprotective Effects of Electroacupuncture in a Dental Pulp Injury Model—A Basic Research
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
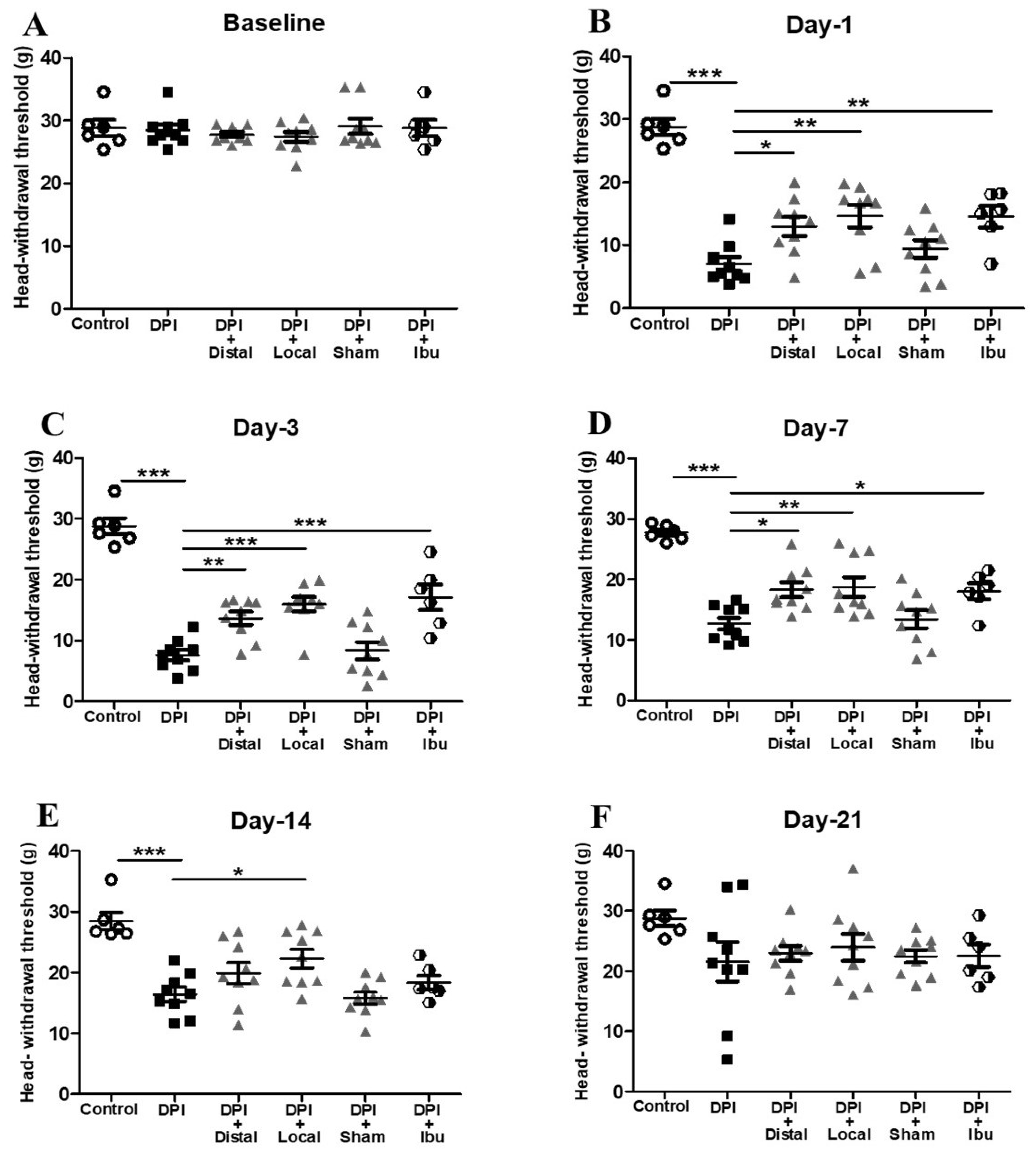
2.1. Analgesic Effect of Electroacupuncture on DPI-Induced Mechanical Allodynia
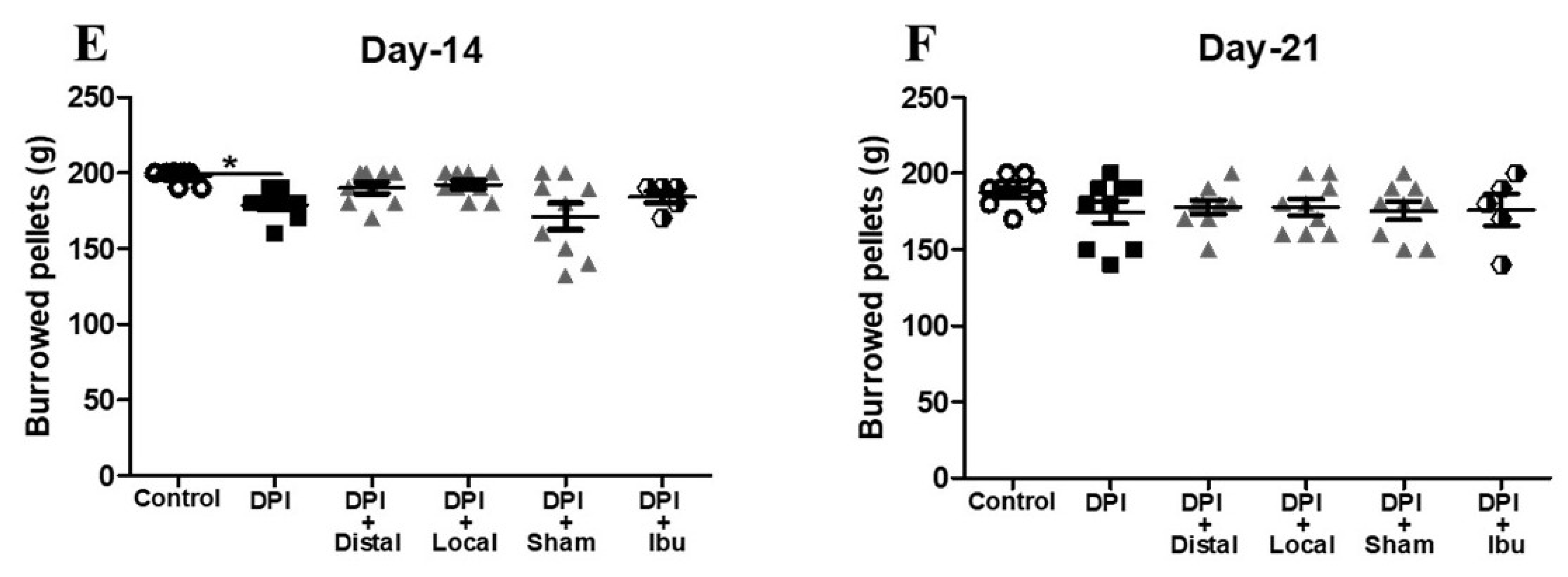
2.2. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Changes in Burrowing Behavior after DPI
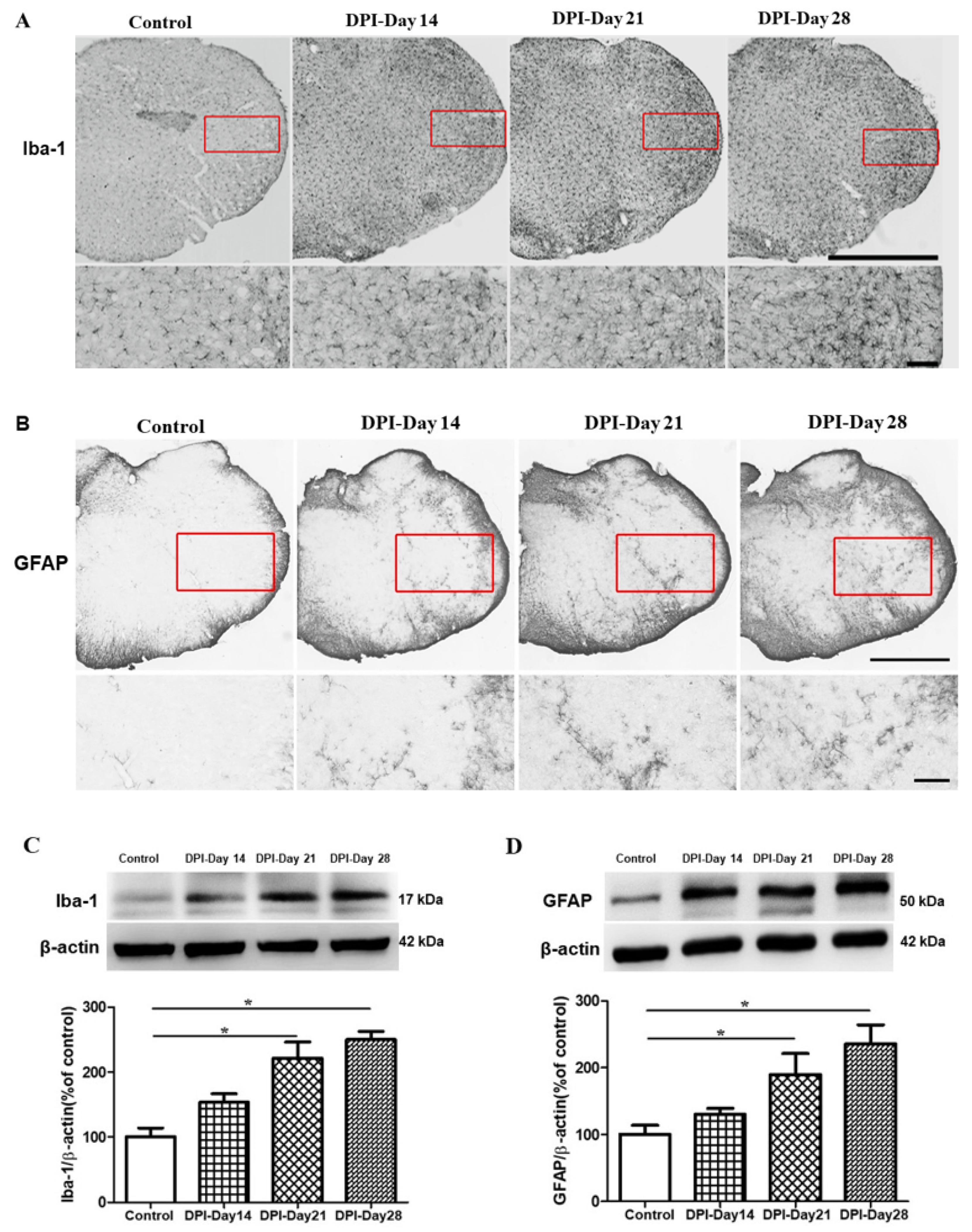
2.3. Microglial and Astrocytes Activation in the Trigeminal Subnucleus Caudalis (Vc) after DPI
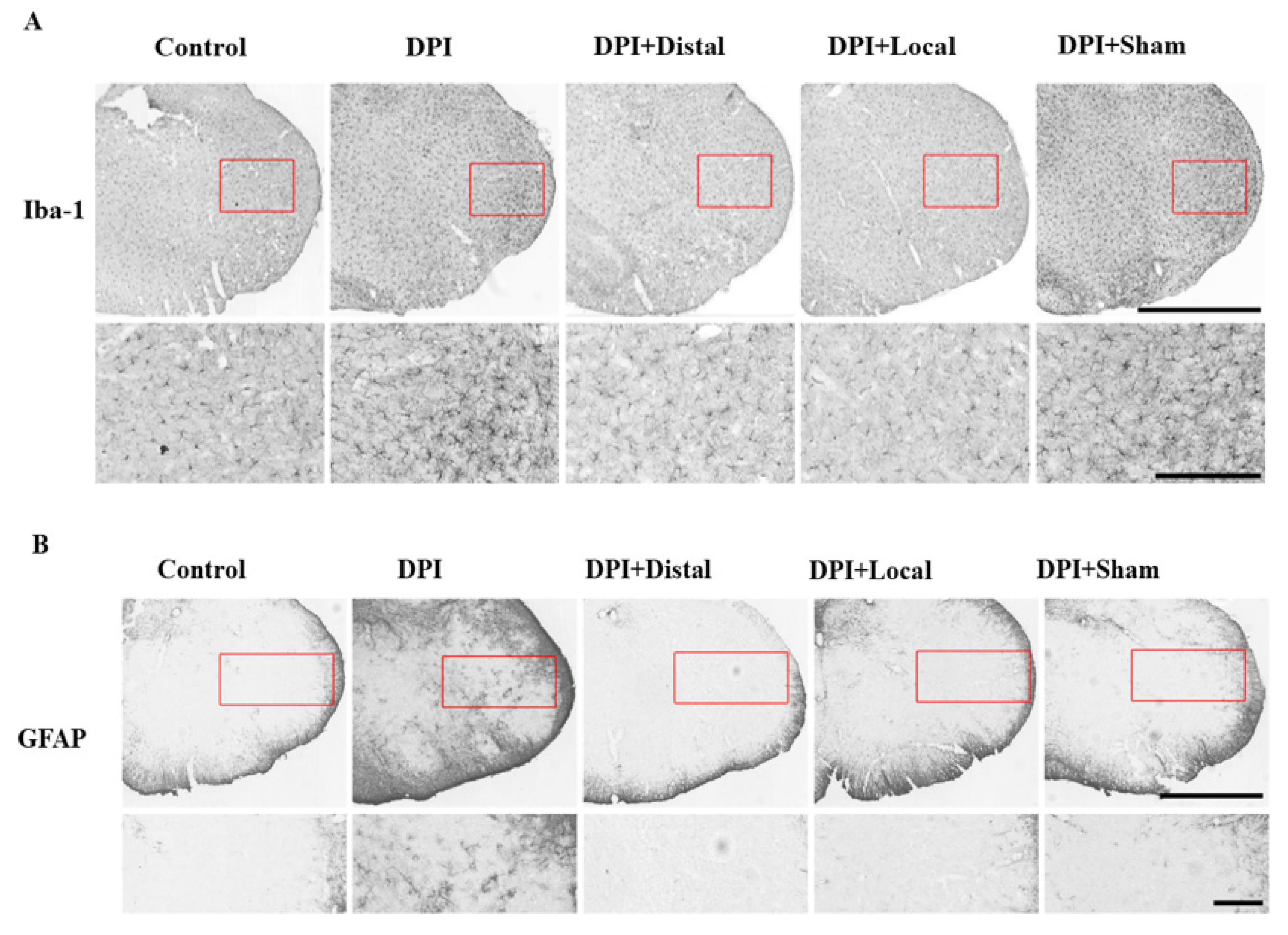
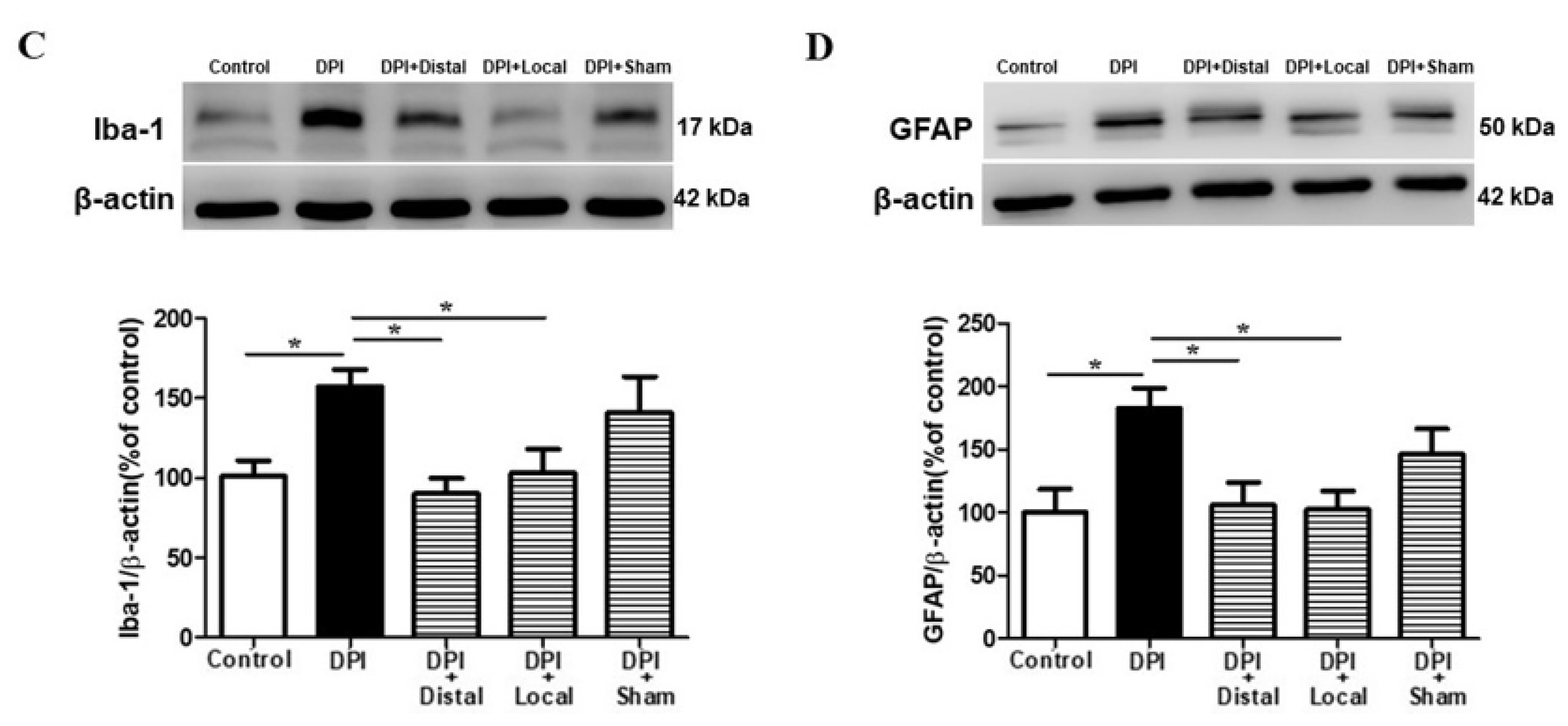
2.4. EA at Verum (Local and Distal) Acupoints Inhibits Microglial and Astrocytes Activation Induced by DPI
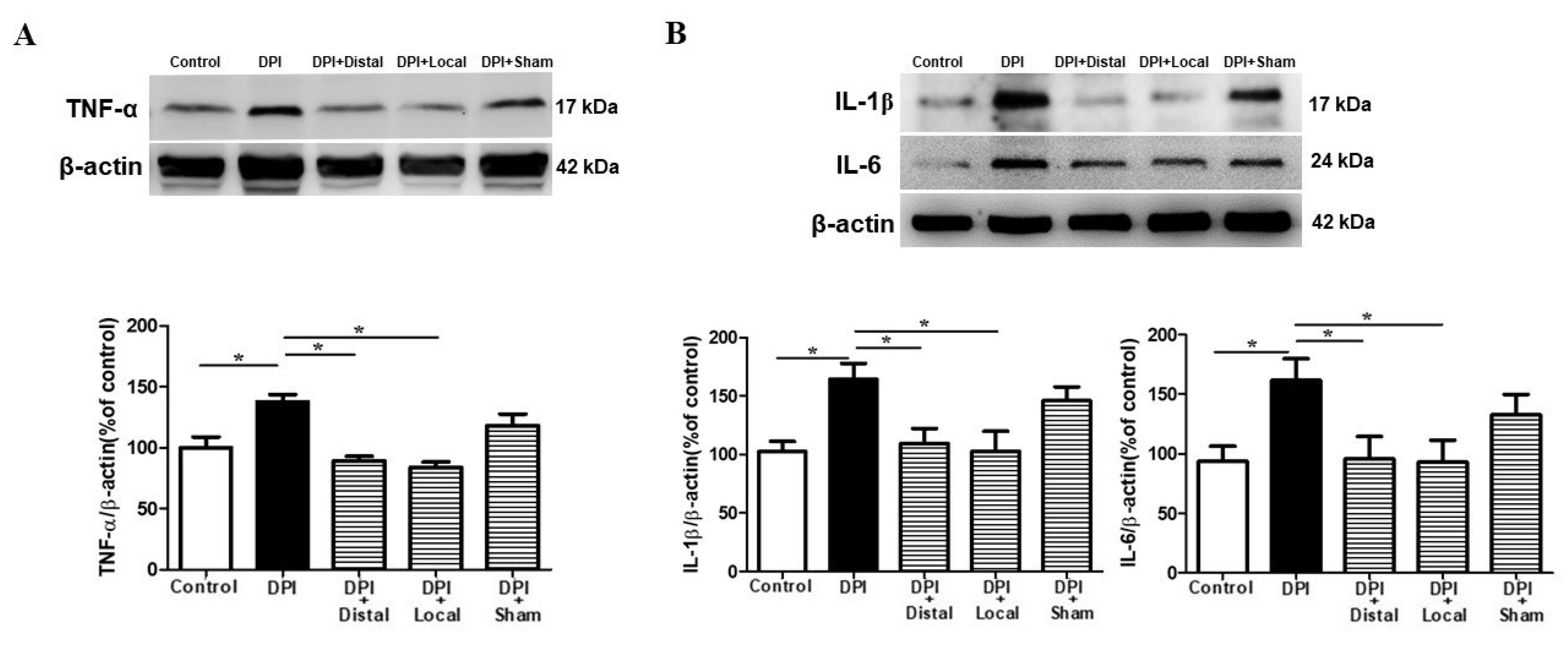
2.5. Verum EA Reduces DPI-Induced Production of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
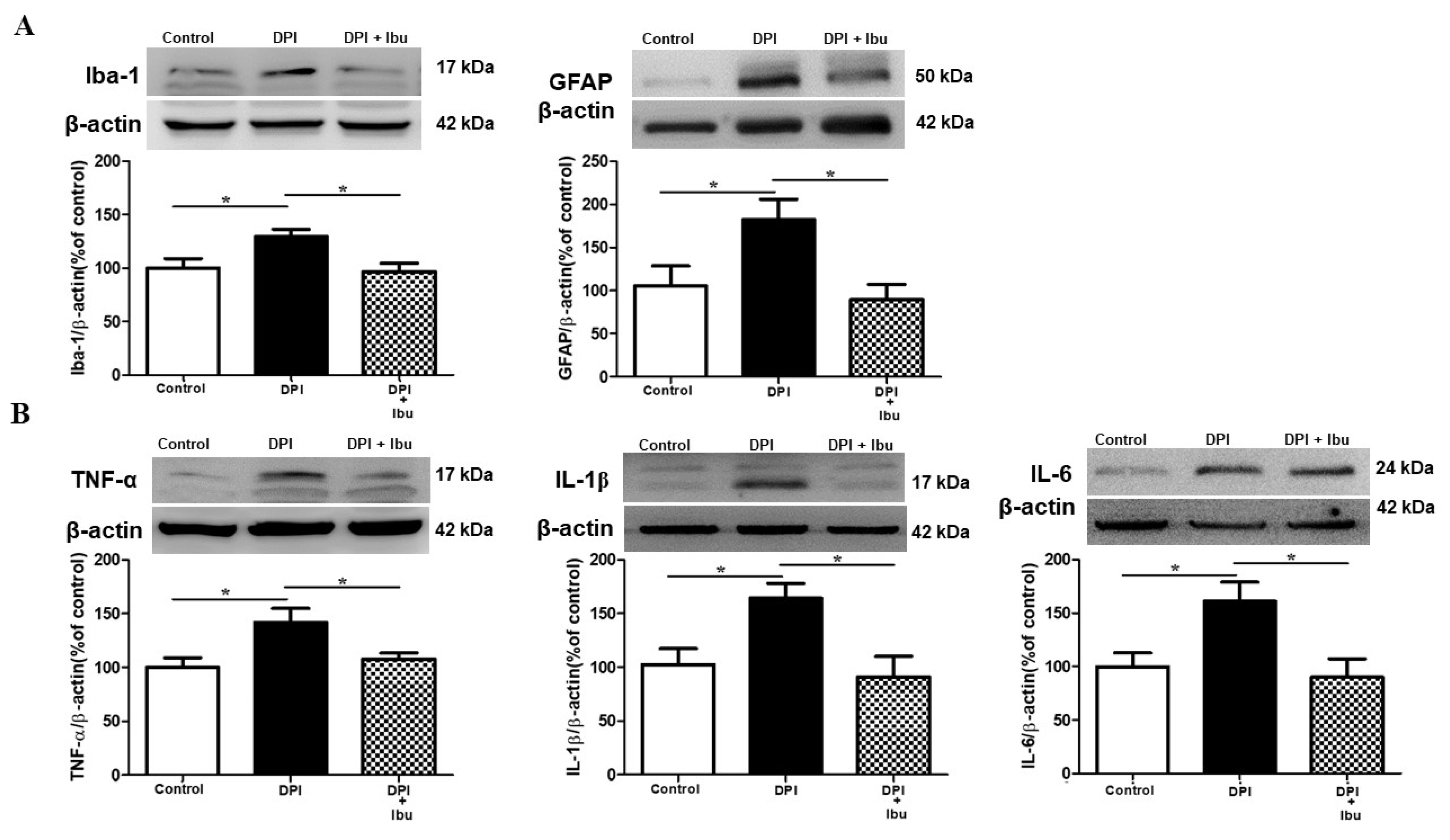
2.6. Ibuprofen Prevents DPI-Induced Changes in Microglial, Astrocyte and Cytokine Expression in the Vc
3. Discussion
3.1. Behavioral Measurements in the DPI Model
3.2. Neuroinflammatory Profile after Pulp Exposure
3.3. Verum EA and Ibuprofen Prevents Neuroinflammation
3.4. Possible Mechanisms of the Analgesic and Neuroprotective Effects of Acupuncture
4. Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Selection of DPI Models
4.3. Electroacupuncture (EA) Procedures
4.4. Verum (Local and Distal) and Sham EA Groups
4.5. Ibuprofen Group
4.6. Von Frey Testing
4.7. Burrowing Behavioral Test
4.8. Immunohistochemistry
4.9. Western Blot
4.10. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, F.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, L.; Fu, D.; Gan, J.; Huang, C. Pannexin3 inhibits TNF-α-induced inflammatory response by suppressing NF-κB signalling pathway in human dental pulp cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frencken, J.E.; Sharma, P.; Stenhouse, L.; Green, D.; Laverty, D.; Dietrich, T. Global epidemiology of dental caries and severe periodontitis–a comprehensive review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, S94–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wu, Z.; Niu, K.; Xie, Y.; Hu, X.; Fu, J.; Tian, D.; Fu, K.; Zhao, B.; Kong, W. Microbiome of Deep Dentinal Caries from Reversible Pulpitis to Irreversible Pulpitis. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 302–309.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, J.V.; Farman, A.G.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Newton, J.T. A Cochrane systematic review finds no evidence to support the use of antibiotics for pain relief in irreversible pulpitis. J. Endod. 2006, 32, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Hargreaves, K.M. Animal models of orofacial pain. In Analgesia; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Byers, M.; Narhi, M. Dental injury models: Experimental tools for understanding neuroinflammatory interactions and polymodal nociceptor functions. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1999, 10, 4–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, C.; Biber, K.; Michelucci, A. Cellular and molecular characterization of microglia: A unique immune cell population. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanisch, U.K. Microglia as a source and target of cytokines. Glia 2002, 40, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.E.; Hoerner, M.T. Astrocytes modulate macrophage phagocytosis of myelin in vitro. J. Neuroimmunol. 2000, 102, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeber, M.B.; Streit, W.J. Microglia: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Huang, F.; Zhu, X.; Dong, W.; Gao, Z.; Li, D.; He, H. Involvement of microglial activation in the brainstem in experimental dental injury and inflammation. Arch. Oral Biol. 2010, 55, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, A.; Gallelli, L. Pain management for dentists: The role of ibuprofen. Ann. Stomatol. 2011, 2, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Poveda Roda, R.; Bagán, J.V.; Jiménez Soriano, Y.; Gallud Romero, L. Use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in dental practice: A review. Med. OralPatol. Oral Y Cirugía Bucal 2007, 12, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.M.; Tang, J.L.; Lin, X.P.; Lau, J.T.; Leung, P.C.; Woo, J.; Li, Y. Acupuncture for stroke rehabilitation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Murugesan, H.; Venkatappan, S.; Renganathan, S.K.; Narasimhan, S.; Sekar, M. Comparison of acupuncture with ibuprofen for pain management in patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis: A randomized double-blind clinical trial. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2017, 10, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.B. Acupuncture in dentistry: Its possible role and application. Proc. Singap. Healthc. 2012, 21, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Xu, T.-L.; Li, F.; Su, J.; Li, W.-G. Temporal dynamics of anxiety phenotypes in a dental pulp injury model. Mol. Pain 2015, 11, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, N.; Chen, M.; Fujita, T.; Xu, Q.; Peng, W.; Liu, W.; Jensen, T.K.; Pei, Y.; Wang, F.; Han, X. Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Matos, N.M.; Pach, D.; Xing, J.J.; Barth, J.; Beyer, L.E.; Shi, X.; Kern, A.; Lukic, N.; Ettlin, D.A.; Brügger, M. Evaluating the Effects of Acupuncture Using a Dental Pain Model in Healthy Subjects–A Randomized, Cross-Over Trial. J. Pain 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, C.-M.; Chiang, C.; Yu, X.-M.; Sessle, B. Involvement of trigeminal subnucleus caudalis (medullary dorsal horn) in craniofacial nociceptive reflex activity. Pain 1999, 81, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, K.; Katagiri, A.; Shinoda, M. Neuron-glia interaction is a key mechanism underlying persistent orofacial pain. J. Oral Sci. 2017, 59, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.-Y.; Namgung, U. Electroacupuncture therapy in inflammation regulation: Current perspectives. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibbs, J.L.; Urban, R.; Basbaum, A.I. Paradoxical surrogate markers of dental injury-induced pain in the mouse. Pain® 2013, 154, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, H.L.; See, L.P.; Foster, W.; Pitake, S.; Gibbs, J.; Schmidt, B.; Mitchell, C.H.; Abdus-Saboor, I. Evoked and spontaneous pain assessment during tooth pulp injury. bioRxiv 2019, 742049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deseure, K.; Hans, G. Orofacial neuropathic pain reduces spontaneous burrowing behavior in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 191, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, T.; Arai, Y.-C.P.; Shiro, Y.; Shimo, K.; Nishihara, M.; Sato, J.; Ushida, T. Comparative effects of acupressure at local and distal acupuncture points on pain conditions and autonomic function in females with chronic neck pain. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.M.; Jiang, F.; Longhurst, J.C. Point specificity in acupuncture. Chin. Med. 2012, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, C.-E.; Lee, I.-S.; Jung, W.-M.; Kim, H.-G.; Jang, H.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, H.; Park, H.-J.; Chae, Y. Network analysis of acupuncture points used in the treatment of low back pain. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, Z.G.; Cho, I.-H.; Park, C.K.; Hong, J.P.; Choi, S.-Y.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, S.; Park, K.; Kim, J.S.; Oh, S.B. Activation of glia and microglial p38 MAPK in medullary dorsal horn contributes to tactile hypersensitivity following trigeminal sensory nerve injury. Pain 2006, 121, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, L.; Gu, W.; Liu, Q.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Z.; He, H.; Huang, F.; Fan, W. Activation of satellite glial cells in trigeminal ganglion following dental injury and inflammation. J. Mol. Histol. 2018, 49, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taves, S.; Berta, T.; Chen, G.; Ji, R.-R. Microglia and spinal cord synaptic plasticity in persistent pain. Neural Plast. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Torres, R. Role of interleukin-1β during pain and inflammation. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 60, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, Q.; Liu, S.; Shu, H.; Tang, Y.; George, S.; Dong, T.; Schmidt, B.L.; Tao, F. TNFα in the Trigeminal Nociceptive System Is Critical for Temporomandibular Joint Pain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latrémolière, A.; Mauborgne, A.; Masson, J.; Bourgoin, S.; Kayser, V.; Hamon, M.; Pohl, M. Differential implication of proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 in the development of cephalic versus extracephalic neuropathic pain in rats. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 8489–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia, R.I.; Henshaw, M.M.; Krall, E.A. Relationship between periodontal disease and systemic health. Periodontology 2000 2001, 25, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbayya, K.; Puthanakar, N.Y.; Naduwinmani, S.; Chidambar, Y. Association between periodontitis and Alzheimer’s disease. North Am. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 7, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berta, T.; Qadri, Y.; Chen, G.; Ji, R. Microglial signaling in chronic pain with a special focus on caspase 6, p38 MAP kinase, and sex dependence. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, D.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Moon, Y.J.; Kim, S.W.; Oh, T.H.; Yune, T.Y. Acupuncture-mediated inhibition of inflammation facilitates significant functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 39, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.; Zarruk, J.G.; Ghasemlou, N. Inflammatory pathways in spinal cord injury. In International Review of Neurobiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 106, pp. 127–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.; De La Pena, I.; Lin, L.; Zhou, S.-F.; Borlongan, C.; Cao, C. The neuroprotective role of acupuncture and activation of the BDNF signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-H.; Nam, D.-H.; Kim, K.-T.; Lee, J.-H. Acupuncture with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) versus acupuncture or NSAIDs alone for the treatment of chronic neck pain: An assessor-blinded randomised controlled pilot study. Acupunct. Med. 2014, 32, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corder, G.; Castro, D.C.; Bruchas, M.R.; Scherrer, G. Endogenous and exogenous opioids in pain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Castro, E.; Navarro, X. Chronic ibuprofen administration reduces neuropathic pain but does not exert neuroprotection after spinal cord injury in adult rats. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 252, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Budel, S.; Baughman, K.; Gould, G.; Song, K.-H.; Strittmatter, S.M. Ibuprofen enhances recovery from spinal cord injury by limiting tissue loss and stimulating axonal growth. J. Neurotrauma 2009, 26, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Hue, J.; Li, S. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs promote axon regeneration via RhoA inhibition. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 4154–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.-Q. Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 85, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-S. Acupuncture: Neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, M.T.; Wu, Y.-T.; Lee, Y.-H.; Hwang, L.-L.; Hung, M.-S.; Zimmer, A.; Mackie, K.; Chiou, L.-C. Median nerve stimulation induces analgesia via orexin-initiated endocannabinoid disinhibition in the periaqueductal gray. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E10720–E10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Lao, L.; Ren, K.; Berman, B.M. Mechanisms of acupuncture–electroacupuncture on persistent pain. Anesthesiol. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2014, 120, 482–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.-T.; Hung, S.-Y.; Hsu, S.-F.; MacDonald, I.; Lin, J.-G.; Luo, S.-T.; Lin, P.-L.; Chen, Y.-H. Inhibiting the LPS-induced enhancement of mEPSC frequency in superficial dorsal horn neurons may serve as an electrophysiological model for alleviating pain. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, T.; Beggs, S.; Salter, M.W. ATP receptors gate microglia signaling in neuropathic pain. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 234, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, C.S.; Jeong, H.-S.; Park, H.-J.; Baik, Y.; Yoon, M.-H.; Choi, C.-B.; Koh, H.G. A proposed transpositional acupoint system in a mouse and rat model. Res. Vet. Sci. 2008, 84, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaertner, D.J. Anesthesia and analgesia for laboratory rodents. Anesth. Analg. Lab. Anim. 2008, 240–297. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.-J.; Du, Y.; Cai, W.-K.; Kuang, R.; Chang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.-X.; Sun, C.; Li, Z.-Y.; Kuang, F. Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in neurons of trigeminal ganglion contributes to nociception induced by acute pulpitis in rats. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.-J.; Li, Q.; Wu, A.-Z. Psychological stress induces temporary masticatory muscle mechanical sensitivity in rats. Biomed. Res. Int. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirkof, P. Burrowing and nest building behavior as indicators of well-being in mice. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 234, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.-G.; Lee, Y.-C.; Tseng, C.-H.; Chen, D.-Y.; Shih, C.-Y.; MacDonald, I.; Hung, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H. Electroacupuncture inhibits pruritogen-induced spinal microglial activation in mice. Brain Res. 2016, 1649, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, S.; Dun, N.J.; Cowan, A. Inhibitory effect of lidocaine on pain and itch using formalin-induced nociception and 5′-guanidinonaltrindole-induced scratching models in mice: Behavioral and neuroanatomical evidence. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 616, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, S.-Y.; Huang, W.-P.; Liou, H.-C.; Fu, W.-M. LC3 overexpression reduces Aβ neurotoxicity through increasing α7nAchR expression and autophagic activity in neurons and mice. Neuropharmacology 2015, 93, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ballon Romero, S.S.; Lee, Y.-C.; Fuh, L.-J.; Chung, H.-Y.; Hung, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H. Analgesic and Neuroprotective Effects of Electroacupuncture in a Dental Pulp Injury Model—A Basic Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072628
Ballon Romero SS, Lee Y-C, Fuh L-J, Chung H-Y, Hung S-Y, Chen Y-H. Analgesic and Neuroprotective Effects of Electroacupuncture in a Dental Pulp Injury Model—A Basic Research. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(7):2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072628
Chicago/Turabian StyleBallon Romero, Sharmely Sharon, Yu-Chen Lee, Lih-Jyh Fuh, Hsin-Yi Chung, Shih-Ya Hung, and Yi-Hung Chen. 2020. "Analgesic and Neuroprotective Effects of Electroacupuncture in a Dental Pulp Injury Model—A Basic Research" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 7: 2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072628
APA StyleBallon Romero, S. S., Lee, Y.-C., Fuh, L.-J., Chung, H.-Y., Hung, S.-Y., & Chen, Y.-H. (2020). Analgesic and Neuroprotective Effects of Electroacupuncture in a Dental Pulp Injury Model—A Basic Research. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(7), 2628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072628




