Preparation of Peptide and Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator Conjugated Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) (PLGA) Magnetic Nanoparticles for Dual Targeted Thrombolytic Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation of Peptide and rtPA Conjugated PLGA Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.2. Characterization of Physico-Chemical Properties
2.3. In Vitro Biocompatibility
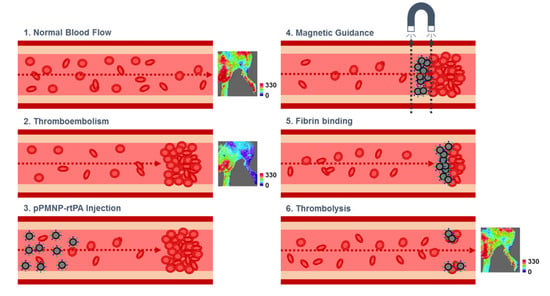
2.4. Targeting Effects
2.5. In Vitro Thrombolysis
2.6. In Vivo Thrombolysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.3. Determination of rtPA and Peptide Conjugation
3.4. Charactrization of Physico-Chemical Properties
3.5. Fibrin Binding Efficiency and Fibrinolysis Asaasy
3.6. Determination of Thrombolysis Using Rotational Thromboelastometry
3.7. In Vitro Biocompatibility and Hemocompatibility
3.8. In Vitro Blood Clot Lysis
3.9. In Vivo Thrombolysis Using Rat Embolic Model
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shiber, J.R.; Fontane, E.; Adewale, A. Stroke registry: Hemorrhagic vs ischemic strokes. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 28, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivin, J.A. Acute stroke therapy with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) since it was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurman, P.; Miranda, O.R.; Nathan, A.; Washington, C.; Rosen, Y.; Elman, N.M. Recombinant tissue plasminogen activators (rtPA): A review. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 97, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, F.E.; Bray, N.; Denes, A.; Allan, S.M.; Schiessl, I. Delayed reperfusion deficits after experimental stroke account for increased pathophysiology. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metabol. 2015, 35, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gravanis, I.; Tsirka, S.E. Tissue-type plasminogen activator as a therapeutic target in stroke. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zamanlu, M.; Farhoudi, M.; Eskandani, M.; Mahmoudi, J.; Barar, J.; Rafi, M.; Omidi, Y. Recent advances in targeted delivery of tissue plasminogen activator for enhanced thrombolysis in ischaemic stroke. J. Drug Target 2018, 26, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, T.L.; Burda, C. The unique role of nanoparticles in nanomedicine: Imaging, drug delivery and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2885–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnard, T.; Gauberti, M.; Martinez de Lizarrondo, S.; Campos, F.; Vivien, D. Recent advances in nanomedicine for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Shao, Y.; Peng, J.; Dai, X.; Li, H.; Wu, Q.; Shi, D. Near-infrared laser light mediated cancer therapy by photothermal effect of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4078–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Park, J.S.; Byun, Y.; Kim, C.K. The use of PEGylated liposomes to prolong circulation lifetimes of tissue plasminogen activator. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5751–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.K.; Park, J.; Jon, S. Targeting strategies for multifunctional nanoparticles in cancer imaging and therapy. Theranostics 2012, 2, 3–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.-H.; Liu, C.-H.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.-P.; Wu, T. Targeted delivery of plasminogen activators for thrombolytic therapy: An integrative evaluation. Molecules 2019, 24, 3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.-H.; Wu, S.-Y.; Wu, T.; Chang, Y.-J.; Hua, M.-Y.; Chen, J.-P. Magnetically targeted thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator bound to polyacrylic acid-coated nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3343–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-P.; Yang, P.-C.; Ma, Y.-H.; Wu, T. Characterization of chitosan magnetic nanoparticles for in situ delivery of tissue plasminogen activator. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Yang, P.-C.; Ma, Y.-H.; Tu, S.-J.; Lu, Y.-J. Targeted delivery of tissue plasminogen activator by binding to silica-coated magnetic nanoparticle. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5137–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, H.-L.; Chen, J.-P. Preparation of thermosensitive magnetic liposome encapsulated recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for targeted thrombolysis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 427, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Hsu, H.-L.; Chen, J.-P.; Wu, T.; Ma, Y.-H. Thrombolysis induced by intravenous administration of plasminogen activator in magnetoliposomes: Dual targeting by magnetic and thermal manipulation. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 20, 101992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.R.; Sazonova, I.Y.; Erdem, S.S.; Hara, T.; Thompson, B.D.; Patel, P.; Botnaru, I.; Lin, C.P.; Reed, G.L.; Weissleder, R.; et al. Multifunctional nanoagent for thrombus-targeted fibrinolytic therapy. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 7, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yurko, Y.; Maximov, V.; Andreozzi, E.; Thompson, G.L.; Vertegel, A.A. Design of biomedical nanodevices for dissolution of blood clots. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, P.; He, Y.; Tan, K.; Chen, Q.; Gao, Y.; Gao, Y. In vivo thrombolysis with targeted microbubbles loading tissue plasminogen activator in a rabbit femoral artery thrombus model. J. Thromb. Thromb. 2014, 38, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Guo, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Ran, H.; Wang, Z. Construction and evaluation of Fe3O4-based plga nanoparticles carrying rtpa used in the detection of thrombosis and in targeted thrombolysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5566–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Absar, S.; Kwon, Y.M.; Ahsan, F. Bio-responsive delivery of tissue plasminogen activator for localized thrombolysis. J. Control. Release 2014, 177, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juenet, M.; Aid-Launais, R.; Li, B.; Berger, A.; Aerts, J.; Ollivier, V.; Nicoletti, A.; Letourneur, D.; Chauvierre, C. Thrombolytic therapy based on fucoidan-functionalized polymer nanoparticles targeting P-selectin. Biomaterials 2018, 156, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Li, N.; Gao, J. Recent strategies on targeted delivery of thrombolytics. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruva, M.R.; Daviau, J.; Sharma, S.S.; Thakur, M.L. Imaging thromboembolism with fibrin-avid 99mTc-peptide: Evaluation in swine. J. Nuclear Med. 2006, 47, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, M.L.; Pallela, V.R.; Consigny, P.M.; Rao, P.S.; Vessileva-Belnikolovska, D.; Shi, R. Imaging vascular thrombosis with 99mTc-labeled fibrin alpha-chain peptide. J. Nuclear Med. 2000, 41, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lv, W.; Wang, Z.; Lv, L.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Sun, W.; et al. Dual targeted nanocarrier for brain ischemic stroke treatment. J. Control. Release 2016, 233, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Hu, B. Dual and multi-targeted nanoparticles for site-specific brain drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 317, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, Z.-L.; Wu, M.; Ren, J.-G.; Xia, H.-F.; Sa, G.-L.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Pang, D.-W.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Chen, G. Magnetic and folate functionalization enables rapid isolation and enhanced tumor-targeting of cell-derived microvesicles. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, F.; Jin, H.; Xu, Q.; Huang, Y. Dual-targeting magnetic plga nanoparticles for codelivery of paclitaxel and curcumin for brain tumor therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32159–32169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengruengrit, C.; Ritprajak, P.; Wanichwecharungruang, S.; Sharma, A.; Salvan, G.; Zahn, D.R.T.; Insin, N. The combined magnetic field and iron oxide-PLGA composite particles: Effective protein antigen delivery and immune stimulation in dendritic cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 520, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, C.; Priyanto, P.; Davis, T.P.; Pissuwan, D.; Bulmus, V.; Kavallaris, M.; Teoh, W.Y.; Amal, R.; Carroll, M.; Woodward, R.; et al. Anti-fouling magnetic nanoparticles for siRNA delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livnah, O.; Bayer, E.A.; Wilchek, M.; Sussman, J.L. Three-dimensional structures of avidin and the avidin-biotin complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5076–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Northrop, B.H.; Frayne, S.H.; Choudhary, U. Thiol-maleimide “click” chemistry: Evaluating the influence of solvent, initiator, and thiol on the reaction mechanism, kinetics, and selectivity. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 3415–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravasco, J.M.J.M.; Faustino, H.; Trindade, A.; Gois, P.M.P. Bioconjugation with Maleimides: A Useful Tool for Chemical Biology. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-L.; Jiang, H.; Hancock, W.S.; Karger, B.L. Identification of the unpaired cysteine status and complete mapping of the 17 disulfides of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator using LC-MS with electron transfer dissociation/collision induced dissociation. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5296–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Absar, S.; Nahar, K.; Kwon, Y.M.; Ahsan, F. Thrombus-targeted nanocarrier attenuates bleeding complications associated with conventional thrombolytic therapy. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Liu, C.-H.; Hsu, H.-L.; Wu, T.; Lu, Y.-J.; Ma, Y.-H. Magnetically controlled release of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator from chitosan nanocomposites for targeted thrombolysis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2578–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Xu, L.; Yu, S.; Hong, W.; Huang, M.; Xu, P. Therapeutics targeting the fibrinolytic system. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Gong, H.; Luan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Brash, J.L.; Chen, H. A t-PA/nanoparticle conjugate with fully retained enzymatic activity and prolonged circulation time. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalatonne, Y.; Richardi, J.; Pileni, M.P. Van der Waals versus dipolar forces controlling mesoscopic organizations of magnetic nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Ulbrich, P.; Prokopec, V.; Svoboda, P.; Šantavá, E.; Štěpánek, F. Effect of hydrophobic coating on the magnetic anisotropy and radiofrequency heating of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 339, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hermanson, G.T. Chapter 11—(Strept)avidin-Biotin Systems. In Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd ed.; Hermanson, G.T., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 465–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruntu, D.; Caruntu, G.; O’Connor, C.J. Magnetic properties of variable-sized Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized from non-aqueous homogeneous solutions of polyols. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 5801–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahajuddin Arora, S. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Magnetic nanoplatforms as drug carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3445–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torno, M.D.; Kaminski, M.D.; Xie, Y.; Meyers, R.E.; Mertz, C.J.; Liu, X.; O’Brien, W.D., Jr.; Rosengart, A.J. Improvement of in vitro thrombolysis employing magnetically-guided microspheres. Thromb. Res. 2008, 121, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, P.; Chiono, V.; Carmagnola, I.; Hatton, P.V. An overview of poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA)-based biomaterials for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 3640–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.R.; Patel, P.; Botnaru, I.; Haghayeghi, P.; Weissleder, R.; Jaffer, F.A. Multimodal nanoagents for the detection of intravascular thrombi. Bioconjug Chem. 2009, 20, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Runge, M.S.; Quertermous, T.; Zavodny, P.J.; Love, T.W.; Bode, C.; Freitag, M.; Shaw, S.Y.; Huang, P.L.; Chou, C.C.; Mullins, D.; et al. A recombinant chimeric plasminogen activator with high affinity for fibrin has increased thrombolytic potency in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10337–10341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapurina, Y.E.; Drozdov, A.S.; Popov, I.; Vinogradov, V.V.; Dudanov, I.P.; Vinogradov, V.V. Streptokinase@alumina nanoparticles as a promising thrombolytic colloid with prolonged action. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 5921–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Feng, X.; Jin, R.; Li, G. Tissue plasminogen activator-based nanothrombolysis for ischemic stroke. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whiting, D.; Dinardo, J. TEG and ROTEM: Technology and clinical applications. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]













| Sample 1 | Average Diameter 2 (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | Crystal Size 3 (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNP | 230.7 ± 17.1 | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 12.1 ± 2.9 | 10.2 |
| OMNP | 229.3 ± 18.5 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | −17.6 ± 0.9 | 10.5 |
| PMNP | 252.7 ± 13.4 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | −30.0 ± 1.3 | 10.3 |
| PMNP-avidin | 278.8 ± 19.1 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | −25.8 ± 0.4 | 11.7 |
| PMNP-rtPA | 291.2 ± 27.3 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | −24.4 ± 1.1 | 10.7 |
| pPMNP-rtPA | 321.1 ± 26.9 | 0.22 ± 0.05 | −22.1 ± 2.0 | 10.9 |
| Sample 1 | Residual Weight from TGA (%) | Fe3O4 from ICP-OES (%) | Fe3O4 from SQUID (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MNP | 97.9 | 97.8 ± 1.6 | 100.0 ± 0.05 |
| OMNP | 87.7 | 87.1 ± 2.1 | 90.9 ± 0.11 |
| PMNP | 14.0 | 13.5 ± 0.3 | 15.5 ± 0.06 |
| PMNP-avidin | 13.4 | 12.3 ± 0.8 | 14.4± 0.11 |
| PMNP-rtPA | 17.1 | 10.5 ± 0.3 | 13.3 ± 0.07 |
| pPMNP-rtPA | 16.9 | 10.1 ± 0.4 | 13.5 ± 0.07 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.-A.; Ma, Y.-H.; Hsu, T.-Y.; Chen, J.-P. Preparation of Peptide and Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator Conjugated Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) (PLGA) Magnetic Nanoparticles for Dual Targeted Thrombolytic Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082690
Chen H-A, Ma Y-H, Hsu T-Y, Chen J-P. Preparation of Peptide and Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator Conjugated Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) (PLGA) Magnetic Nanoparticles for Dual Targeted Thrombolytic Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(8):2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082690
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Huai-An, Yunn-Hwa Ma, Tzu-Yuan Hsu, and Jyh-Ping Chen. 2020. "Preparation of Peptide and Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator Conjugated Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) (PLGA) Magnetic Nanoparticles for Dual Targeted Thrombolytic Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 8: 2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082690
APA StyleChen, H.-A., Ma, Y.-H., Hsu, T.-Y., & Chen, J.-P. (2020). Preparation of Peptide and Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator Conjugated Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) (PLGA) Magnetic Nanoparticles for Dual Targeted Thrombolytic Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(8), 2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082690