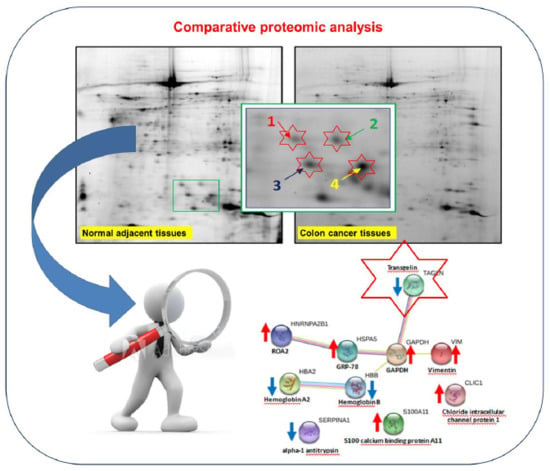
Proteomic Profiling of Colon Cancer Tissues: Discovery of New Candidate Biomarkers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
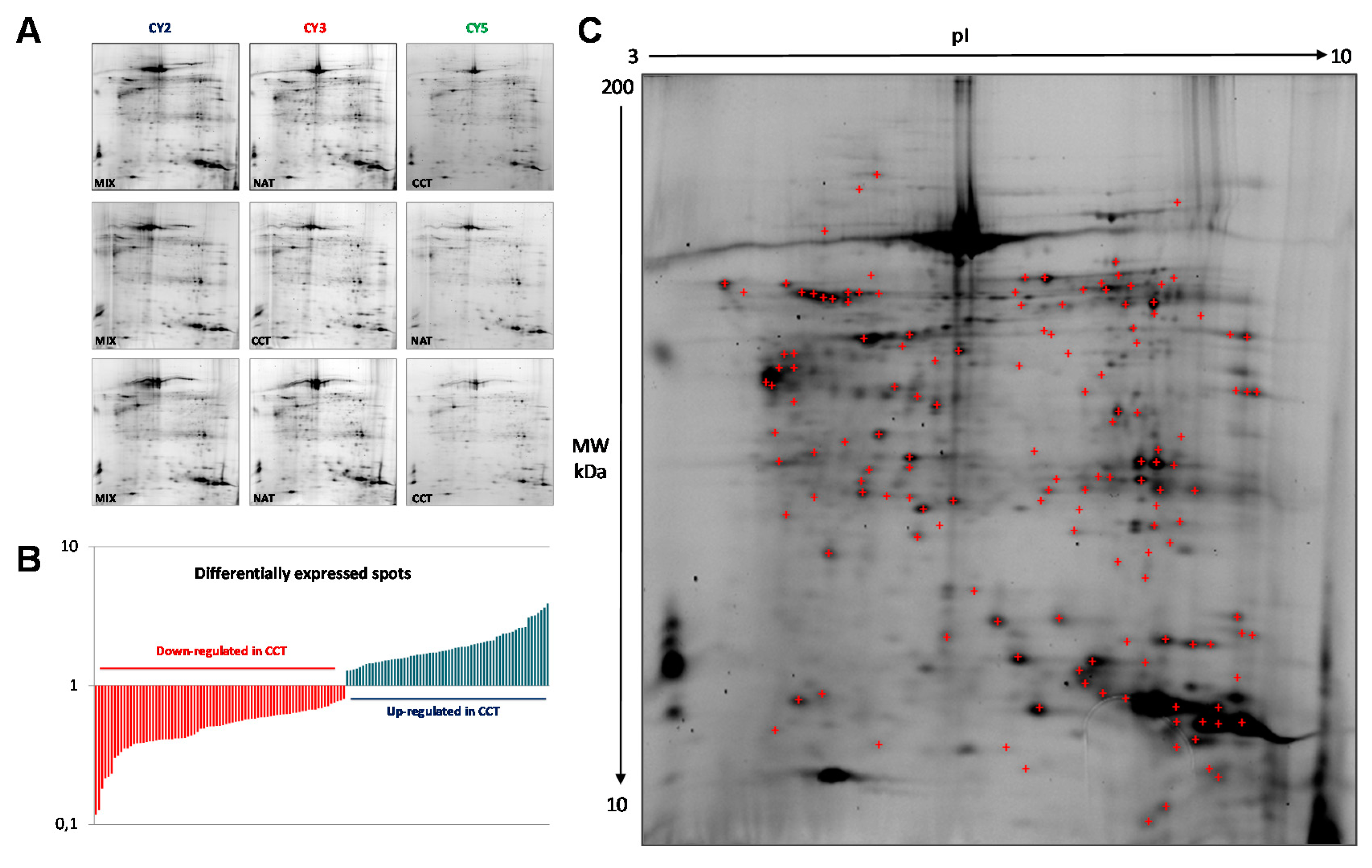
2.1. Pooling of Samples for Proteomics Experiments
2.2. Differential Proteomic Profile in Colon Cancer Versus Normal Adjacent Tissue
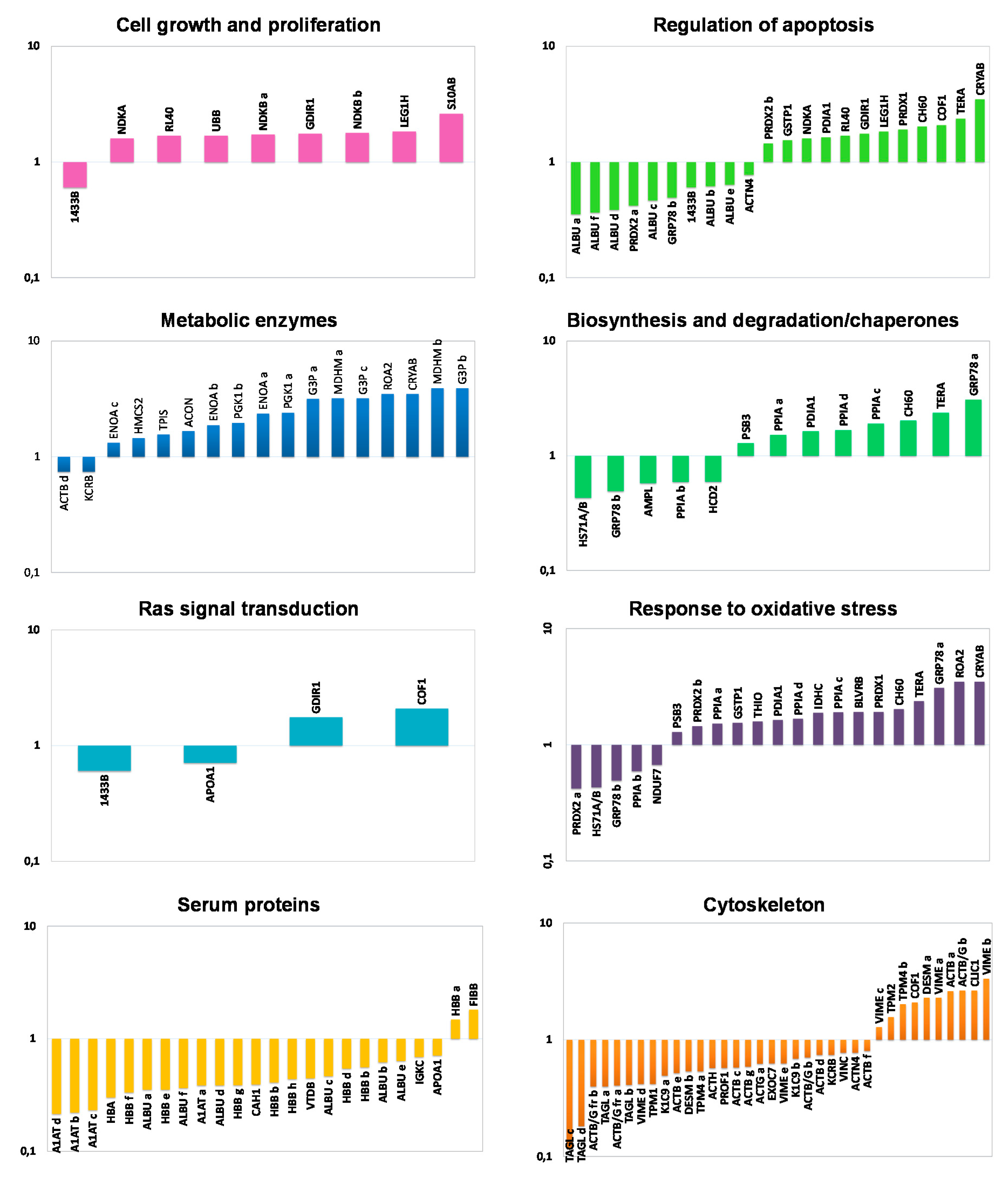
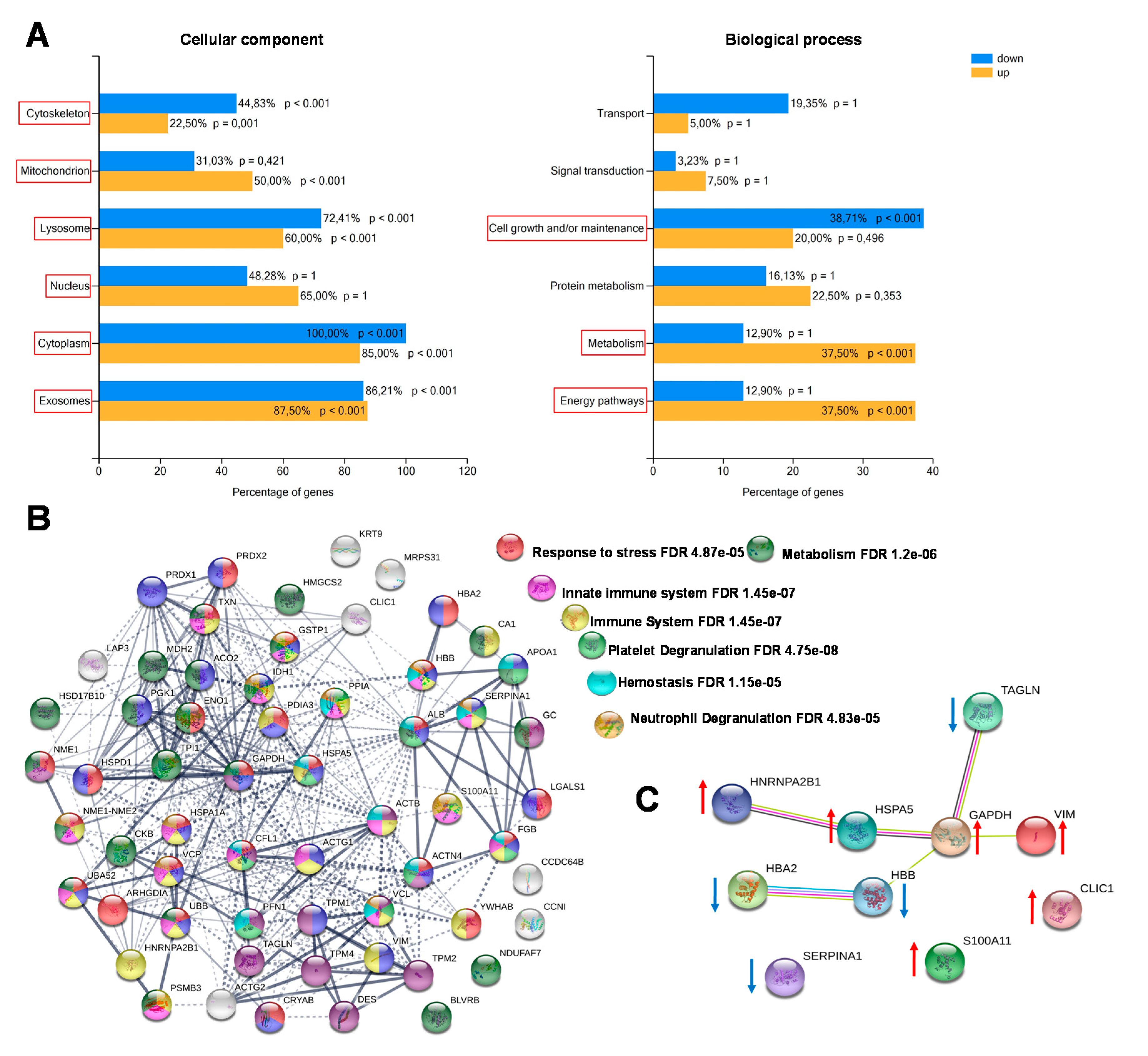
2.3. Functional Classification and Biological Network Analysis
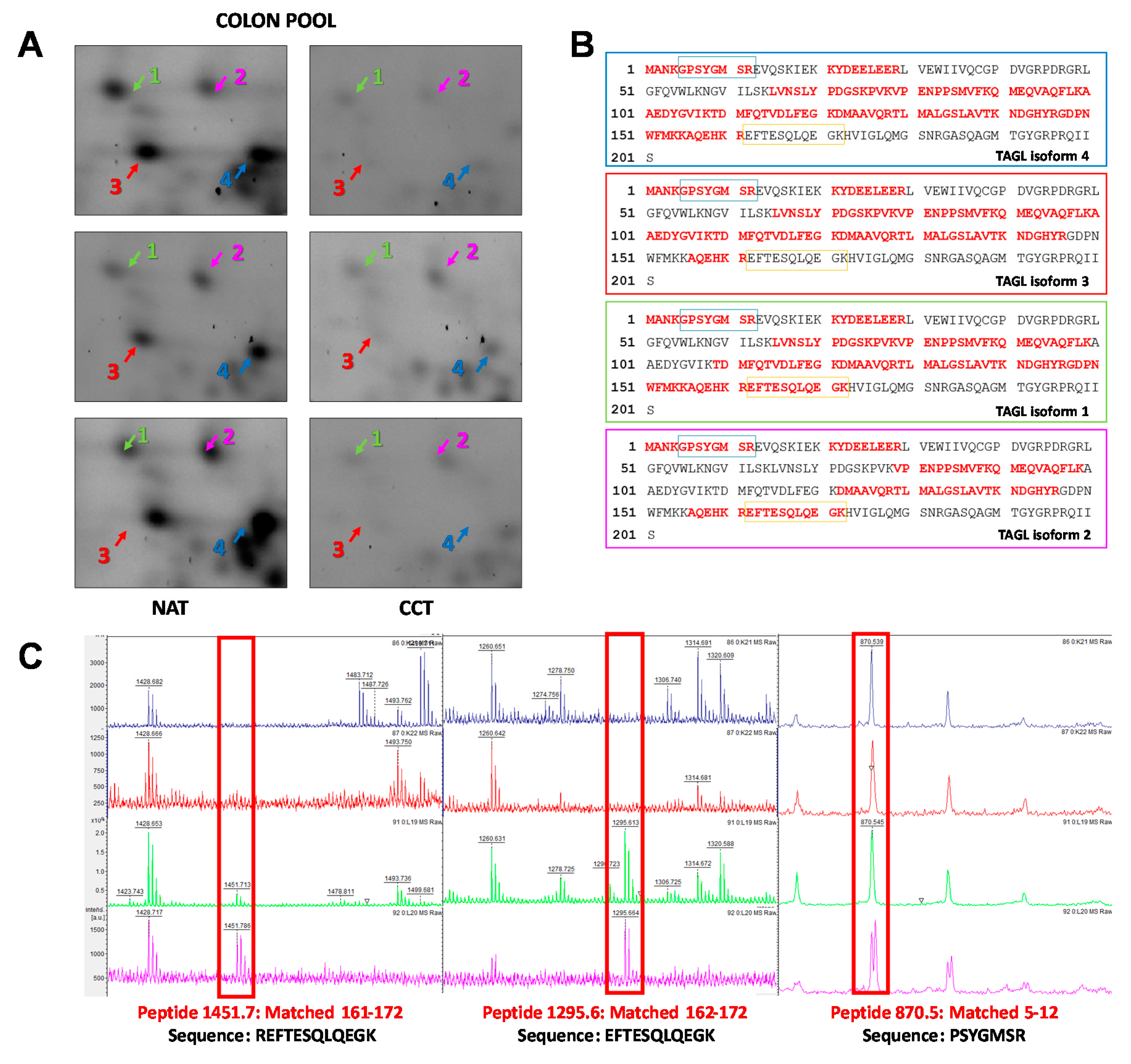
2.4. TAGL as Possible Biomarker in Colon Cancer
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Tissue Samples
4.2. Tissues Processing and Pooling Samples
4.3. Electrophoresis SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.4. 2-D-Differential-In-Gel-Electrophoresis (2D-DIGE)
4.5. Protein Identification by MALDI-TOF MS
4.6. Functional Classification and Pathway Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henley, S.J.; Ward, E.M.; Scott, S.; Ma, J.; Anderson, R.N.; Firth, A.U.; Thomas, C.C.; Islami, F.; Weir, H.K.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, part I: National cancer statistics. Cancer 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Hua, X.; Win, A.K.; MacInnis, R.J.; Gallinger, S.; Marchand, L.L.; Lindor, N.M.; Baron, J.A.; Hopper, J.L.; Dowty, J.G.; et al. A New Comprehensive Colorectal Cancer Risk Prediction Model Incorporating Family History, Personal Characteristics, and Environmental Factors. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Chapelle, A. Genetic predisposition to colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, H.T.; de la Chapelle, A. Hereditary colorectal cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.W. Colon Cancer: The Road Traveled. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 27, xv–xviii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, K.; Bekaii-Saab, T. Clinical Trials and Progress in Metastatic Colon Cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 27, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, S.R.; Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Asadi, F.; Vahedi, M.; Pasha, S.; Alizadeh, L.; Zali, M.R. Recurrence and Five -Year Survival in Colorectal Cancer Patients After Surgery. Iran. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 8, e3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maguire, A.; Sheahan, K. Controversies in the pathological assessment of colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9850–9861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.; Atkin, W.; Lenz, H.J.; Lynch, H.T.; Minsky, B.; Nordlinger, B.; Starling, N. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2010, 375, 1030–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnekamp, J.F.; Wang, X.; Medema, J.P.; Vermeulen, L. Colorectal cancer heterogeneity and targeted therapy: A case for molecular disease subtypes. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boja, E.S.; Rodriguez, H. Proteogenomic convergence for understanding cancer pathways and networks. Clin. Proteom. 2014, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saleem, S.; Tariq, S.; Aleem, I.; Sadr-Ul, S.; Tahseen, M.; Atiq, A.; Hassan, S.; Abu Bakar, M.; Khattak, S.; Syed, A.A.; et al. Proteomics analysis of colon cancer progression. Clin. Proteom. 2019, 16, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diz, A.P.; Truebano, M.; Skibinski, D.O. The consequences of sample pooling in proteomics: An empirical study. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 2967–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karp, N.A.; Lilley, K.S. Investigating sample pooling strategies for DIGE experiments to address biological variability. Proteomics 2009, 9, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucci-Minafra, I.; Fontana, S.; Cancemi, P.; Basirico, L.; Caricato, S.; Minafra, S. A contribution to breast cancer cell proteomics: Detection of new sequences. Proteomics 2002, 2, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci-Minafra, I.; Fontana, S.; Cancemi, P.; Alaimo, G.; Minafra, S. Proteomic patterns of cultured breast cancer cells and epithelial mammary cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 963, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pucci-Minafra, I.; Cancemi, P.; Di Cara, G.; Minafra, L.; Feo, S.; Forlino, A.; Tira, M.E.; Tenni, R.; Martini, D.; Ruggeri, A.; et al. Decorin transfection induces proteomic and phenotypic modulation in breast cancer cells 8701-BC. Connect. Tissue Res. 2008, 49, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Cara, G.; Marengo, G.; Albanese, N.N.; Marabeti, M.R.; Musso, R.; Cancemi, P.; Pucci-Minafra, I. Proteomic profiling of Trastuzumab (Herceptin(R))-sensitive and -resistant SKBR-3 breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 489–503. [Google Scholar]
- Pucci-Minafra, I.; Cancemi, P.; Fontana, S.; Minafra, L.; Feo, S.; Becchi, M.; Freyria, A.M.; Minafra, S. Expanding the protein catalogue in the proteome reference map of human breast cancer cells. Proteomics 2006, 6, 2609–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci-Minafra, I.; Di Cara, G.; Musso, R.; Cancemi, P.; Albanese, N.N.; Roz, E.; Minafra, S. Retrospective Proteomic Screening of 100 Breast Cancer Tissues. Proteomes 2017, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cancemi, P.; Buttacavoli, M.; Roz, E.; Feo, S. Expression of Alpha-Enolase (ENO1), Myc Promoter-Binding Protein-1 (MBP-1) and Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) Reflect the Nature and Aggressiveness of Breast Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancemi, P.; Di Cara, G.; Albanese, N.N.; Costantini, F.; Marabeti, M.R.; Musso, R.; Riili, I.; Lupo, C.; Roz, E.; Pucci-Minafra, I. Differential occurrence of S100A7 in breast cancer tissues: A proteomic-based investigation. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2012, 6, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pucci-Minafra, I.; Cancemi, P.; Albanese, N.N.; Di Cara, G.; Marabeti, M.R.; Marrazzo, A.; Minafra, S. New protein clustering of breast cancer tissue proteomics using actin content as a cellularity indicator. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cancemi, P.; Di Cara, G.; Albanese, N.N.; Costantini, F.; Marabeti, M.R.; Musso, R.; Lupo, C.; Roz, E.; Pucci-Minafra, I. Large-scale proteomic identification of S100 proteins in breast cancer tissues. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pucci-Minafra, I.; Cancemi, P.; Marabeti, M.R.; Albanese, N.N.; Di Cara, G.; Taormina, P.; Marrazzo, A. Proteomic profiling of 13 paired ductal infiltrating breast carcinomas and non-tumoral adjacent counterparts. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2007, 1, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Cara, G.; Marabeti, M.R.; Musso, R.; Riili, I.; Cancemi, P.; Pucci Minafra, I. New Insights into the Occurrence of Matrix Metalloproteases -2 and -9 in a Cohort of Breast Cancer Patients and Proteomic Correlations. Cells 2018, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cancemi, P.; Buttacavoli, M.; Di Cara, G.; Albanese, N.N.; Bivona, S.; Pucci-Minafra, I.; Feo, S. A multiomics analysis of S100 protein family in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 29064–29081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sole, X.; Crous-Bou, M.; Cordero, D.; Olivares, D.; Guino, E.; Sanz-Pamplona, R.; Rodriguez-Moranta, F.; Sanjuan, X.; de Oca, J.; Salazar, R.; et al. Discovery and validation of new potential biomarkers for early detection of colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernald, K.; Kurokawa, M. Evading apoptosis in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2013, 23, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, C.; He, Z.; Hou, N.; Ni, Y.; Xiong, L.; Chen, P. Alpha B-crystallin correlates with poor survival in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 6056–6063. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Understanding the Intersections between Metabolism and Cancer Biology. Cell 2017, 168, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liberti, M.V.; Locasale, J.W. The Warburg Effect: How Does it Benefit Cancer Cells? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xi, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Cui, F.; Wang, X. Suppression of GRP78 sensitizes human colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin by downregulation of CD24. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9861–9867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, R.; Yang, P.; Wu, H.L.; Li, Z.W.; Li, Z.Y. GRP78 secreted by colon cancer cells facilitates cell proliferation via PI3K/Akt signaling. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 7245–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, X.; Cui, L.; Zeng, Y.; Song, W.; Gaur, U.; Yang, M. 14-3-3 Proteins Are on the Crossroads of Cancer, Aging, and Age-Related Neurodegenerative Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, H.; Xu, Q.; Bu, Y.; Lei, Y. Redox Imbalance in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahani-Sherafat, S.; Alebouyeh, M.; Moghim, S.; Ahmadi Amoli, H.; Ghasemian-Safaei, H. Role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer; a review article. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2018, 11, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- De Almeida, C.V.; de Camargo, M.R.; Russo, E.; Amedei, A. Role of diet and gut microbiota on colorectal cancer immunomodulation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Querol, E.; Rosales, C. Neutrophils in Cancer: Two Sides of the Same Coin. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 983698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollinedo, F. Neutrophil Degranulation, Plasticity, and Cancer Metastasis. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werther, K.; Christensen, I.J.; Nielsen, H.J.; Danish, R.C.C.S.G. Prognostic impact of matched preoperative plasma and serum VEGF in patients with primary colorectal carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, J.L.; Palumbo, J.S. Hemostatic factors, innate immunity and malignancy. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129 (Suppl. S1), S1–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knekt, P.; Hakulinen, T.; Leino, A.; Heliovaara, M.; Reunanen, A.; Stevens, R. Serum albumin and colorectal cancer risk. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 54, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, M.; Joenväärä, S.; Saraswat, M.T.; Tohmola, T.I.; Ristimäki, A.; Renkonen, R.; Haglund, C. Differences and overlap in plasma protein expression during colorectal cancer progression. Transl. Med. Commun. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Azab, A.K. The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia 2015, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toiyama, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Saigusa, S.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Goel, A.; Kusunoki, M. Increased expression of Slug and Vimentin as novel predictive biomarkers for lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2548–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Littler, D.R.; Harrop, S.J.; Goodchild, S.C.; Phang, J.M.; Mynott, A.V.; Jiang, L.; Valenzuela, S.M.; Mazzanti, M.; Brown, L.J.; Breit, S.N.; et al. The enigma of the CLIC proteins: Ion channels, redox proteins, enzymes, scaffolding proteins? FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, C.; Yu, P.; Tang, B.; Liu, T.; Cui, H.; Xu, J. Regulation of colon cancer cell migration and invasion by CLIC1-mediated RVD. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 365, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, C.; Yu, P.W.; Hao, Y.X.; Luo, H.X.; Liu, G. Chloride intracellular channel 1 regulates colon cancer cell migration and invasion through ROS/ERK pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 2071–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, D.T.; Asif, A.R.; Armstrong, V.W.; Dimova, I.; Toshev, S.; Yaramov, N.; Oellerich, M.; Toncheva, D. Expression of chloride intracellular channel protein 1 (CLIC1) and tumor protein D52 (TPD52) as potential biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 41, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorakova, M.; Nenutil, R.; Bouchal, P. Transgelins, cytoskeletal proteins implicated in different aspects of cancer development. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2014, 11, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos Hidalgo, G.; Meola, J.; Rosa, E.S.J.C.; Paro de Paz, C.C.; Ferriani, R.A. TAGLN expression is deregulated in endometriosis and may be involved in cell invasion, migration, and differentiation. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 96, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, O.; Moghraby, J.S.; Ayscough, K.R.; Winder, S.J. Depletion of the actin bundling protein SM22/transgelin increases actin dynamics and enhances the tumourigenic phenotypes of cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsui, K.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Chang, K.S.; Hou, C.P.; Chen, P.J.; Feng, T.H.; Juang, H.H. Transgelin, a p53 and PTEN-Upregulated Gene, Inhibits the Cell Proliferation and Invasion of Human Bladder Carcinoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Hong, Q.; Xu, S.G.; Kuang, X.Y.; Di, G.H.; Liu, G.Y.; Wu, J.; Shao, Z.M.; Yu, S.J. Downregulation of transgelin 2 promotes breast cancer metastasis by activating the reactive oxygen species/nuclear factorkappaB signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 4045–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.R.; Solway, J.; Boyd, D.D. Expression cloning identifies transgelin (SM22) as a novel repressor of 92-kDa type IV collagenase (MMP-9) expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26424–26436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shields, J.M.; Rogers-Graham, K.; Der, C.J. Loss of transgelin in breast and colon tumors and in RIE-1 cells by Ras deregulation of gene expression through Raf-independent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9790–9799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayar, N.; Karahan, G.; Konu, O.; Bozkurt, B.; Bozdogan, O.; Yulug, I.G. Transgelin gene is frequently downregulated by promoter DNA hypermethylation in breast cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2015, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Deng, Y.J.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Jin, H.; Ding, Y.Q. Transgelin as a suppressor is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal carcinoma patients. Mod. Pathol. 2009, 22, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Xie, W.; Li, L.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; He, X. Elevated transgelin/TNS1 expression is a potential biomarker in human colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Shen, D.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, H.; Sun, W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, F.; Cui, Z.; Wang, S. Identification of transgelin-2 as a biomarker of colorectal cancer by laser capture microdissection and quantitative proteome analysis. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Yao, W.; Zhao, A.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y. Upregulation of transgelin is an independent factor predictive of poor prognosis in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danninger, C.; Gimona, M. Live dynamics of GFP-calponin: Isoform-specific modulation of the actin cytoskeleton and autoregulation by C-terminal sequences. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 21, 3725–3736. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, H.W.; Forsythe, S.M.; Kogut, P.; McConville, J.F.; Halayko, A.J.; Camoretti-Mercado, B.; Solway, J. Mutagenesis analysis of human SM22: Characterization of actin binding. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minafra, L.; Di Cara, G.; Albanese, N.N.; Cancemi, P. Proteomic differentiation pattern in the U937 cell line. Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancemi, P.; Albanese, N.N.; DiCara, G.; Marabeti, M.R.; Costantini, F.; Minafra, S.; Pucci-Minafra, I. Multiple changes induced by fibroblasts on breast cancer cells. Connect. Tissue Res. 2010, 51, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coppola, A.; Tomasello, L.; Pizzolanti, G.; Pucci-Minafra, I.; Albanese, N.; Di Cara, G.; Cancemi, P.; Pitrone, M.; Bommarito, A.; Carissimi, E.; et al. In vitro phenotypic, genomic and proteomic characterization of a cytokine-resistant murine beta-TC3 cell line. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schiera, G.; Di Liegro, C.M.; Puleo, V.; Colletta, O.; Fricano, A.; Cancemi, P.; Di Cara, G.; Di Liegro, I. Extracellular vesicles shed by melanoma cells contain a modified form of H1.0 linker histone and H1.0 mRNA-binding proteins. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buttacavoli, M.; Albanese, N.N.; Di Cara, G.; Alduina, R.; Faleri, C.; Gallo, M.; Pizzolanti, G.; Gallo, G.; Feo, S.; Baldi, F.; et al. Anticancer activity of biogenerated silver nanoparticles: An integrated proteomic investigation. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 9685–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Tan, Q.; Kir, J.; Liu, D.; Bryant, D.; Guo, Y.; Stephens, R.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; et al. DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: Expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W169–W175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pathan, M.; Keerthikumar, S.; Ang, C.S.; Gangoda, L.; Quek, C.Y.; Williamson, N.A.; Mouradov, D.; Sieber, O.M.; Simpson, R.J.; Salim, A.; et al. FunRich: An open access standalone functional enrichment and interaction network analysis tool. Proteomics 2015, 15, 2597–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buttacavoli, M.; Albanese, N.N.; Roz, E.; Pucci-Minafra, I.; Feo, S.; Cancemi, P. Proteomic Profiling of Colon Cancer Tissues: Discovery of New Candidate Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093096
Buttacavoli M, Albanese NN, Roz E, Pucci-Minafra I, Feo S, Cancemi P. Proteomic Profiling of Colon Cancer Tissues: Discovery of New Candidate Biomarkers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(9):3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093096
Chicago/Turabian StyleButtacavoli, Miriam, Nadia Ninfa Albanese, Elena Roz, Ida Pucci-Minafra, Salvatore Feo, and Patrizia Cancemi. 2020. "Proteomic Profiling of Colon Cancer Tissues: Discovery of New Candidate Biomarkers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 9: 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093096
APA StyleButtacavoli, M., Albanese, N. N., Roz, E., Pucci-Minafra, I., Feo, S., & Cancemi, P. (2020). Proteomic Profiling of Colon Cancer Tissues: Discovery of New Candidate Biomarkers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(9), 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093096