Possible Roles of Periostin in the Formation of Hemodialysis Vascular Access Stenosis after Polytetrafluoroethylene Graft Implantation in Dogs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Time-Dependent Intima Formation at 1, 2 and 4 Months after PTFE Graft Implantation
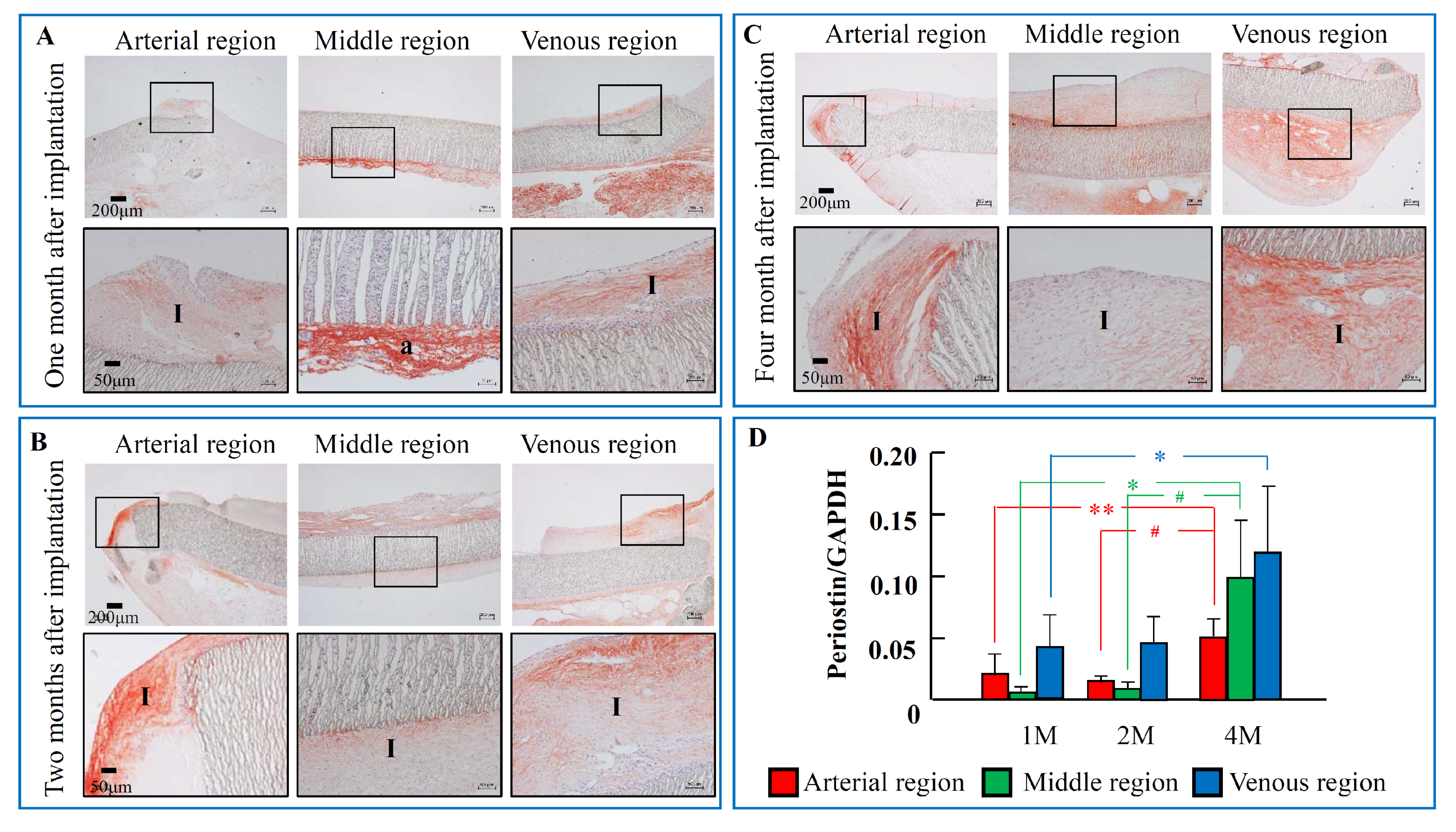
2.2. The Time-Dependent Expression of Periostin 1, 2, and 4 Months after PTFE Graft Implantation
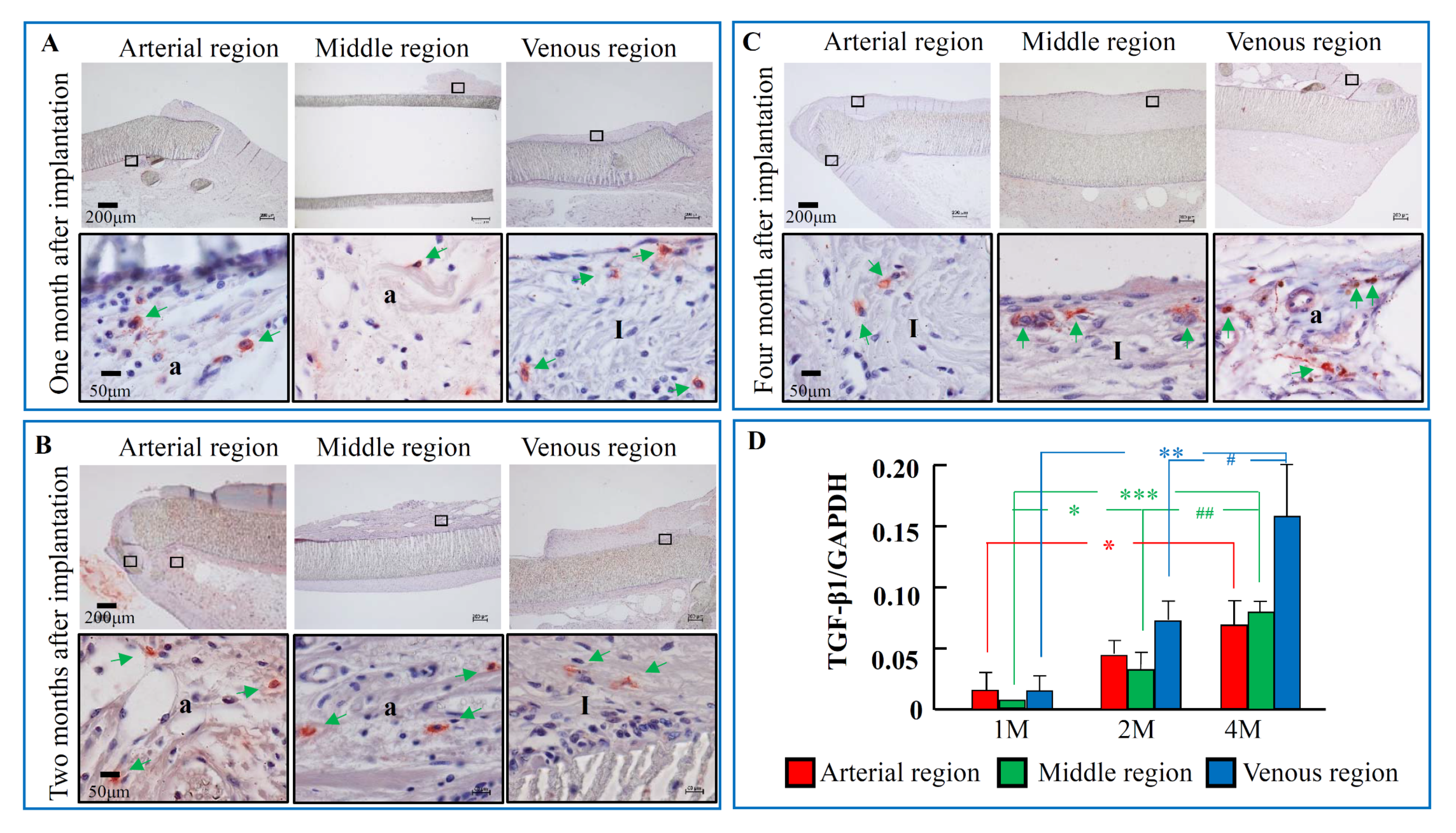
2.3. The Time-Dependent Expression of TGF-β1, 1, 2, and 4 Months after PTFE Graft Implantation
2.4. The Components of the Intima after PTFE Grafts Implantation
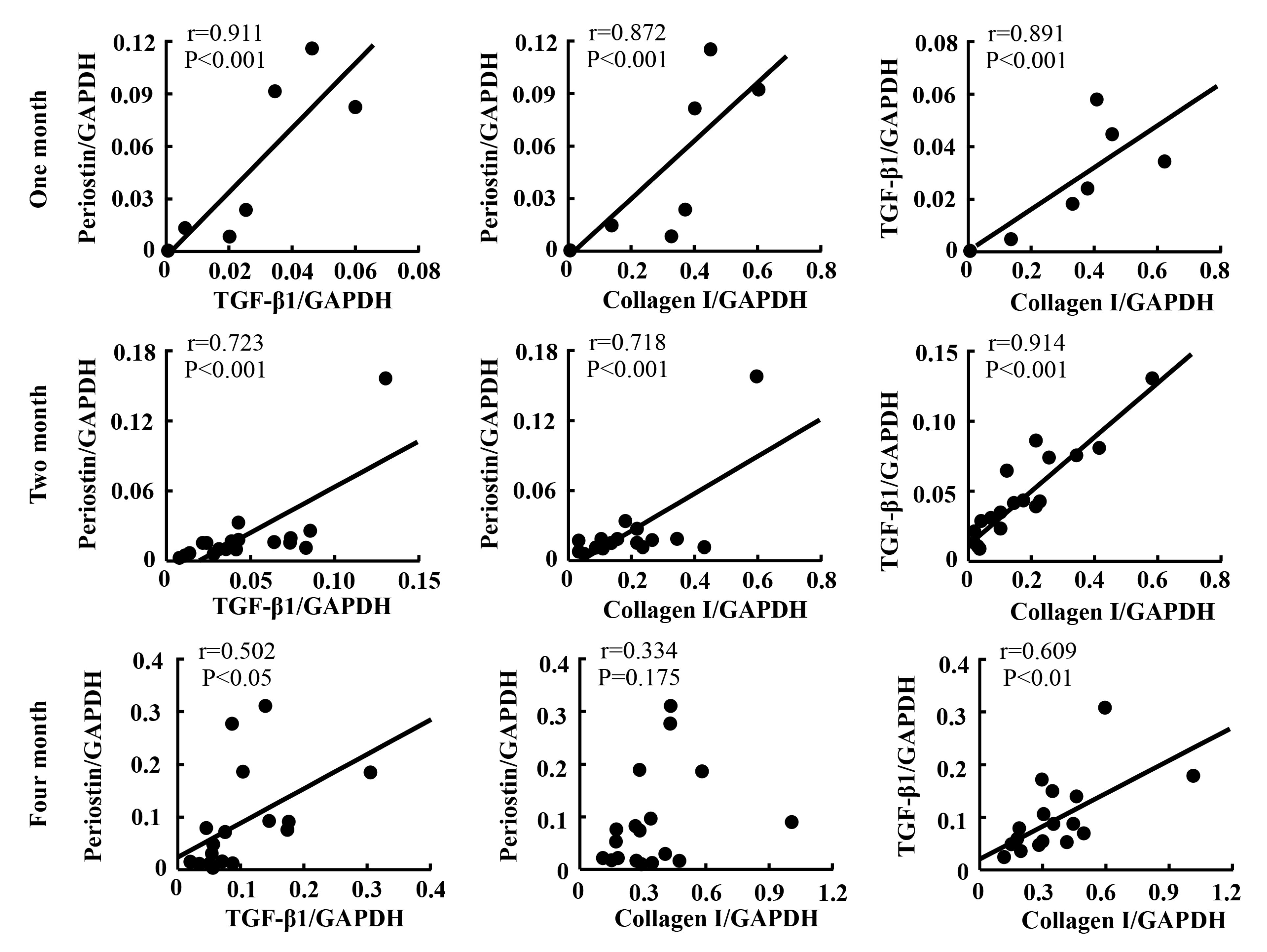
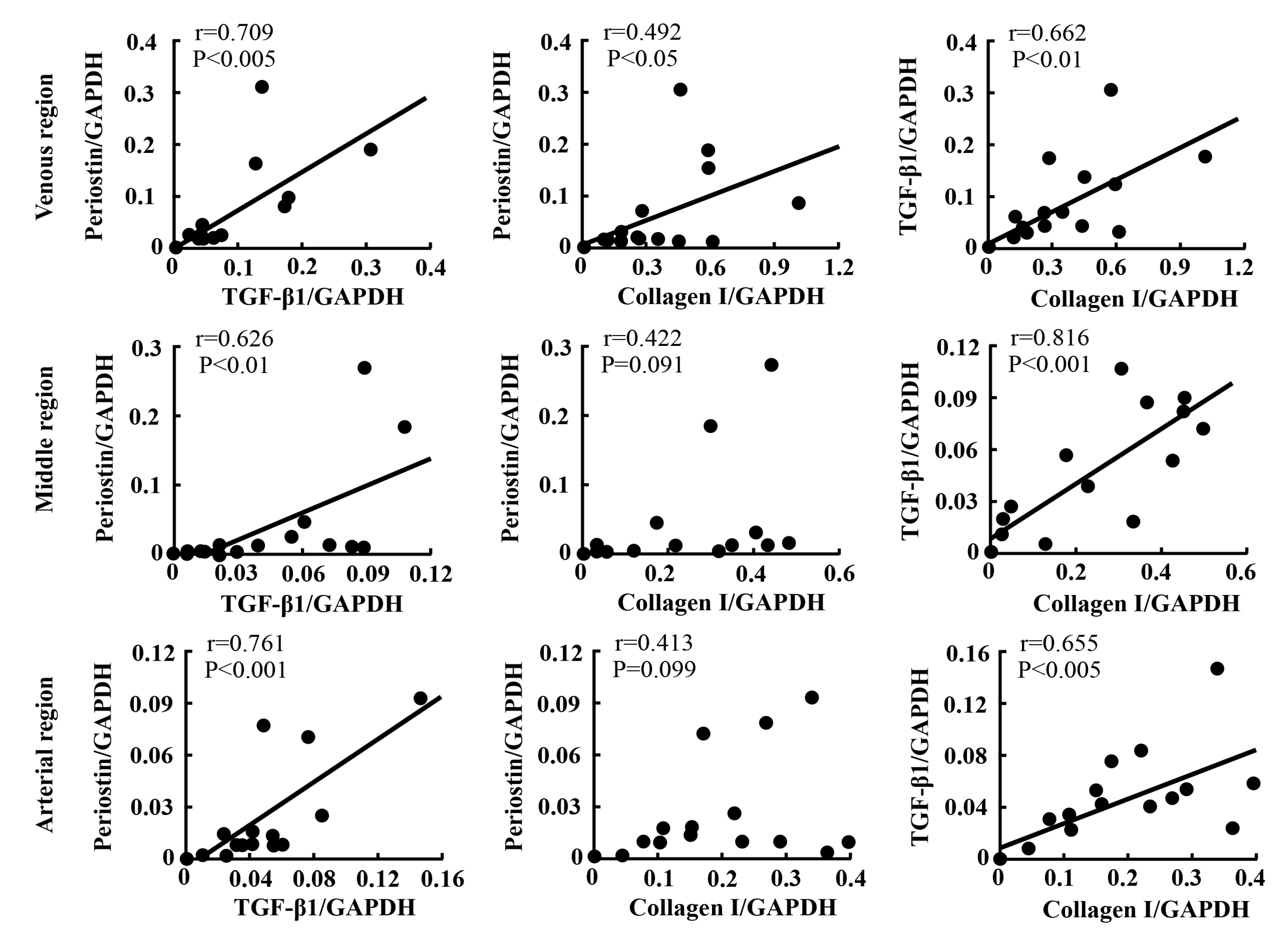
2.5. Linear Regression Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Surgery and Sample Preparation
4.2. Histological Examination
4.3. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.4. Histologic Quantitative Analysis and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hothi, D.K.; Stronach, L.; Harvey, E. Home haemodialysis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2013, 28, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allon, M. Vascular Access for Hemodialysis Patients: New Data Should Guide Decision Making. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, S.J.; Harrington, J.T.; Singh, A.; Roher, R.; Shohaib, S.A.; Perrone, R.D.; Meyer, K.; Beasley, D. Vascular access for hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 1999, 55, 2078–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Englesbe, M.J.; Hawkins, S.M.; Hsieh, P.C.; Daum, G.; Kenagy, R.D.; Clowes, A.W. Concomitant blockade of platelet-derived growth factor receptors alpha and beta induces intimal atrophy in baboon PTFE grafts. J. Vasc. Surg. 2004, 39, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Um, J.W.; Kim, J.M.; Min, B.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Son, G.S.; Lee, J.B.; Jung, S.I.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Koo, B.H.; et al. Transforming growth factor-beta1 expression and the role of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor on perianastomotic intimal hyperplasia in polytetrafluoroethylene. Kurume Med. J. 2004, 51, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.Q. Focal expression of angiotensin II type 1 receptor and smooth muscle cell proliferation in the neointima of experimental vein grafts: Relation to eddy blood flow. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 2630–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindner, V.; Wang, Q.; Conley, B.A.; Friesel, R.E.; Vary, C.P. Vascular injury induces expression of periostin: Implications for vascular cell differentiation and migration. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwanekamp, J.A.; Lorts, A.; Vagnozzi, R.J.; Vanhoutte, D.; Molkentin, J.D. Deletion of Periostin Protects Against Atherosclerosis in Mice by Altering Inflammation and Extracellular Matrix Remodeling. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litvin, J.; Chen, X.; Keleman, S.; Zhu, S.; Autieri, M. Expression and function of periostin-like factor in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C1672–C1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, W.; Chau, E.; Jackson-Boeters, L.; Elliott, C.; Daley, T.D.; Hamilton, D.W. TGF-ß1 and FAK regulate periostin expression in PDL fibroblasts. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 1439–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, D.; Kubo, T.; Kiya, K.; Kawai, K.; Matsuzaki, S.; Kobayashi, D.; Fujiwara, T.; Katayama, T.; Hosokawa, K. Periostin is induced by IL-4/IL-13 in dermal fibroblasts and promotes RhoA/ROCK pathway-mediated TGF-β1 secretion in abnormal scar formation. J. Plast. Surg. Hand. Surg. 2019, 53, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.; Hollenbeck, S.T.; Ryer, E.J.; Edlin, R.; Yamanouchi, D.; Kundi, R.; Wang, C.; Liu, B.; Kent, K.C. TGF-beta through Smad3 signaling stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal formation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H509–H540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Jeon, E.J.; Leem, J.; Park, K.K. Melatonin Prevents Transforming Growth Factor-β1-Stimulated Transdifferentiation of Renal Interstitial Fibroblasts to Myofibroblasts by Suppressing Reactive Oxygen Species-Dependent Mechanisms. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, D.; Ueda, H.; Takai, S.; Muramatsu, M.; Furubayashi, K.; Ibaraki, T.; Kishi, K.; Katsuoka, Y.; Miyazaki, M. Roles of chymase in stenosis occurring after polytetrafluoroethylene graft implantations. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Stamenovic, D. Mechanics of vimentin intermediate filaments. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2002, 23, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasek, J.J.; McRae, J.; Owens, G.K.; Haaksma, C.J. Regulation of alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts is dependent on the intronic CArG element and the transforming growth factor-beta1 control element. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Takai, S.; Li, Z.; Sakonjo, H.; Otsuki, Y.; Shibayama, Y.; Miyazaki, M. Outside fibroblasts play a key role in the development of inner neointima after the implantation of polytetrafluoroethylene grafts. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 119, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, D.; Ueda, H.; Takai, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Muramatsu, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Shibahara, N.; Katsuoka, Y.; Miyazaki, M. Effect of chymase inhibition on the arteriovenous fistula stenosis in dogs. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Jin, R.; Norris, R.A.; Zhang, L.; Yu, S.; Wu, F.; Markwald, R.R.; Nanda, A.; Conway, S.J.; Smyth, S.S.; et al. Periostin mediates vascular smooth muscle cell migration through the integrins alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta5 and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) pathway. Atherosclerosis 2010, 208, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; O’Brien, J.E., Jr.; Fard, A.; Zalewski, A. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 expression and myofibroblast formation during arterial repair. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1996, 16, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Liu, J.; Luo, F.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhuang, S.; Zhang, H. miR-29 mediates TGFβ1-induced extracellular matrix synthesis through activation of PI3K-AKT pathway in human lung fibroblasts. J. Cell Biochem. 2013, 114, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, K.; Amizuka, N.; Takeshita, S.; Takamatsu, H.; Katsuura, M.; Ozawa, H.; Toyama, Y.; Bonewald, L.F.; Kudo, A. Identification and characterization of a novel protein, periostin, with restricted expression to periosteum and periodontal ligament and increased expression by transforming growth factor beta. J. Bone Miner Res. 1999, 14, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaoka, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Komitsu, N.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A.; Ogawa, M.; Arima, K.; Izuhara, K.; Aihara, M. Pro-fibrotic phenotype of human skin fibroblasts induced by periostin via modulating TGF-β signaling. J. Dermatol Sci. 2018, 90, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nanri, Y.; Nunomura, S.; Terasaki, Y.; Yoshihara, T.; Hirano, Y.; Yokosaki, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.; Ajito, K.; Murakami, S.; et al. Cross-Talk between Transforming Growth Factor-β and Periostin Can Be Targeted for Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 62, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watase, K.; Jin, D.; Terai, K.; Kanemiya, T.; Nakakura, H.; Shibahara, N.; Arima, S.; Takai, S. Possible Roles of Periostin in the Formation of Hemodialysis Vascular Access Stenosis after Polytetrafluoroethylene Graft Implantation in Dogs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093251
Watase K, Jin D, Terai K, Kanemiya T, Nakakura H, Shibahara N, Arima S, Takai S. Possible Roles of Periostin in the Formation of Hemodialysis Vascular Access Stenosis after Polytetrafluoroethylene Graft Implantation in Dogs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(9):3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093251
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatase, Kenji, Denan Jin, Kentaro Terai, Taketoshi Kanemiya, Hyogo Nakakura, Nobuhisa Shibahara, Shuji Arima, and Shinji Takai. 2020. "Possible Roles of Periostin in the Formation of Hemodialysis Vascular Access Stenosis after Polytetrafluoroethylene Graft Implantation in Dogs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 9: 3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093251
APA StyleWatase, K., Jin, D., Terai, K., Kanemiya, T., Nakakura, H., Shibahara, N., Arima, S., & Takai, S. (2020). Possible Roles of Periostin in the Formation of Hemodialysis Vascular Access Stenosis after Polytetrafluoroethylene Graft Implantation in Dogs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(9), 3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093251





