Revisiting TNF Receptor-Associated Periodic Syndrome (TRAPS): Current Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. TRAPS Genetics
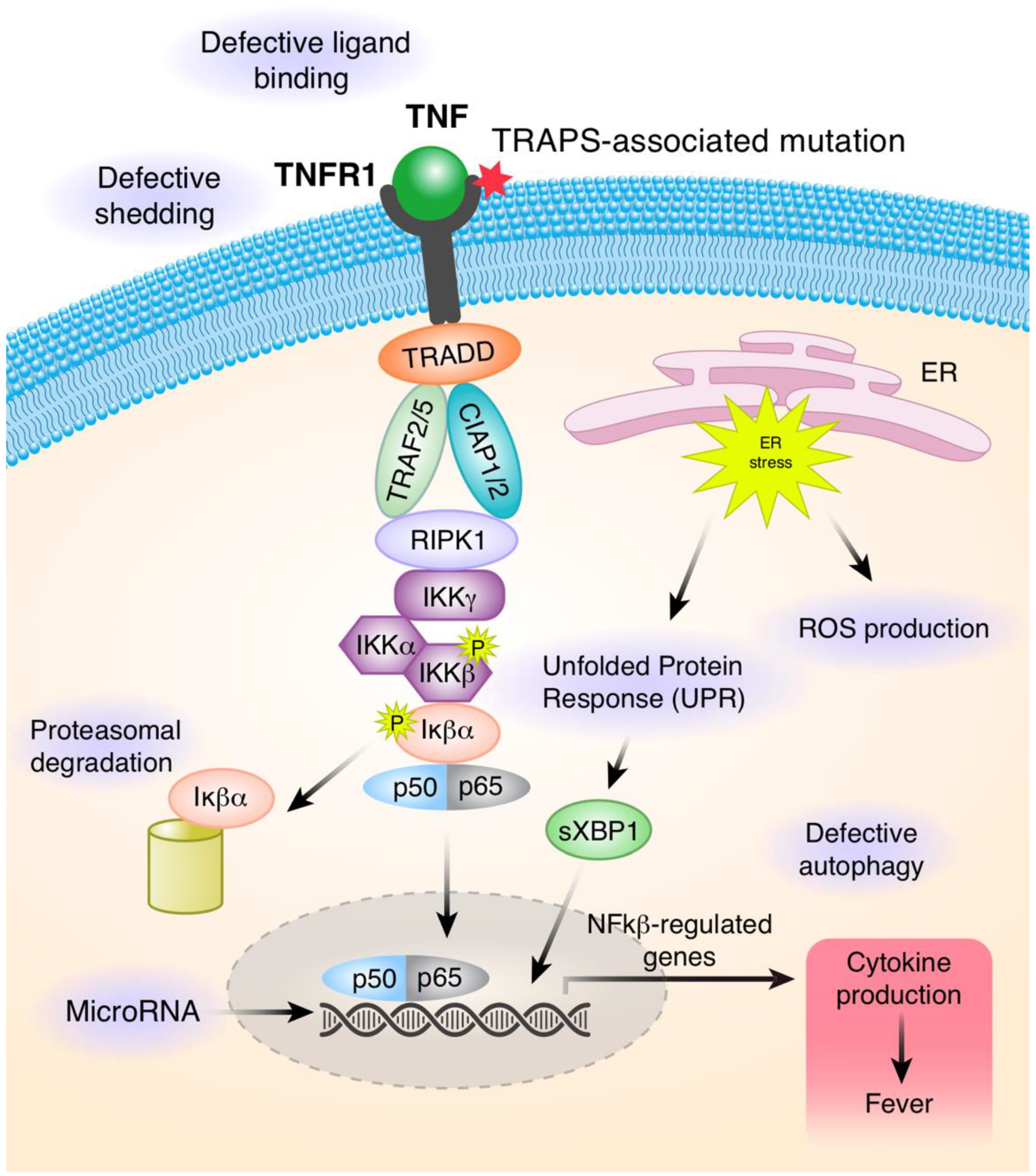
3. Pathophysiology in TRAPS
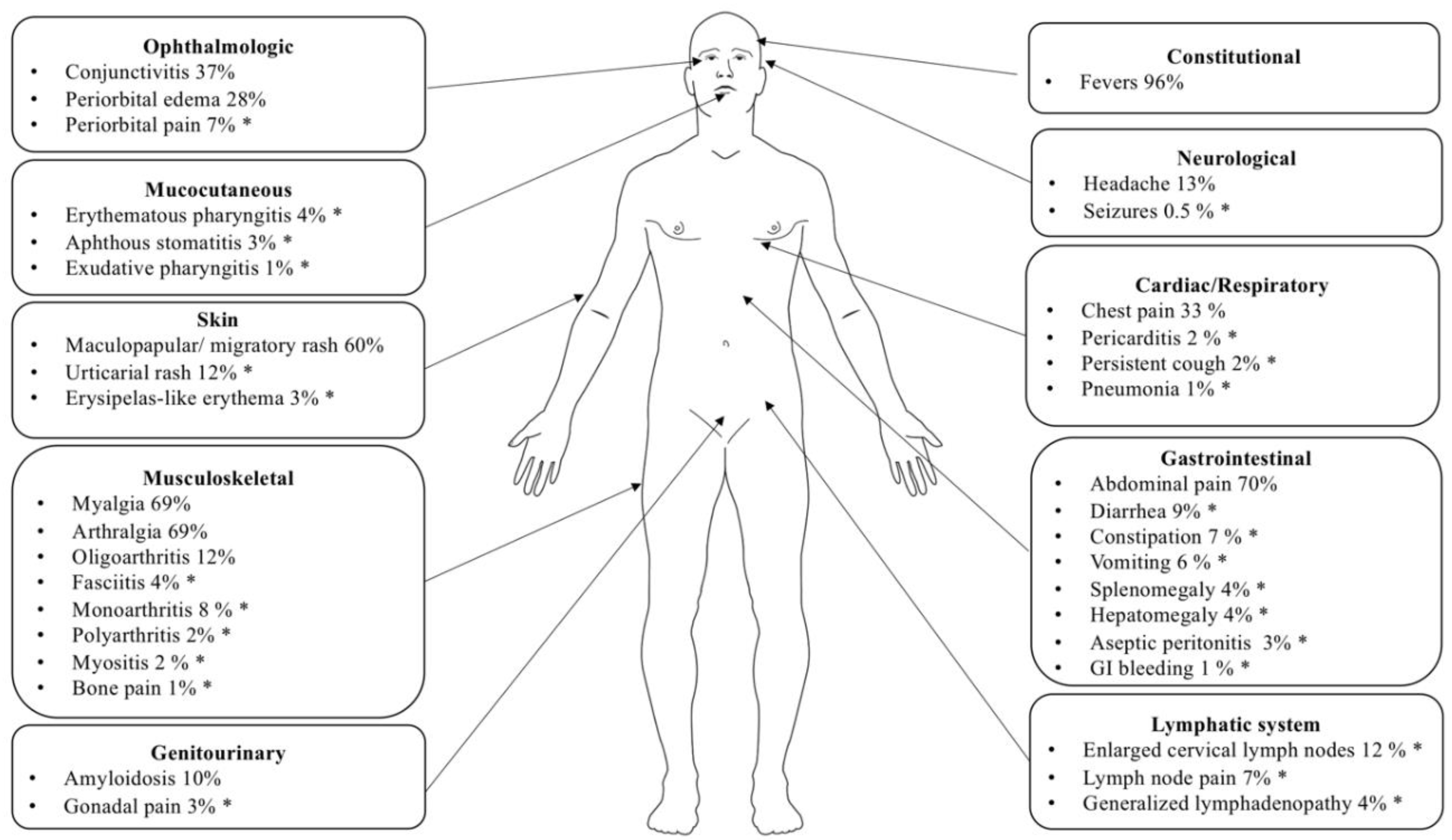
4. Clinical and Laboratory Features in TRAPS Patients
5. TRAPS Diagnosis
6. TRAPS Treatment
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDermott, M.F.; Aksentijevich, I.; Galon, J.; McDermott, E.M.; Ogunkolade, B.W.; Centola, M.; Mansfield, E.; Gadina, M.; Karenko, L.; Pettersson, T.; et al. Germline mutations in the extracellular domains of the 55 kDa TNF receptor, TNFR1, define a family of dominantly inherited autoinflammatory syndromes. Cell 1999, 97, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, D.B.; Aksentijevich, I. Biochemistry of Autoinflammatory Diseases: Catalyzing Monogenic Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savic, S.; Caseley, E.A.; McDermott, M.F. Moving towards a systems-based classification of innate immune-mediated diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manthiram, K.; Zhou, Q.; Aksentijevich, I.; Kastner, D.L. The monogenic autoinflammatory diseases define new pathways in human innate immunity and inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, L.M.; Hull, D.; Mehta, R.; Reeves, W.G.; Robinson, B.H.; Toghill, P.J. Familial Hibernian fever. QJM Int. J. Med. 1982, 51, 469–480. [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann, H.J.; Papa, R.; Gerhold, K.; Obici, L.; Touitou, I.; Cantarini, L.; Frenkel, J.; Anton, J.; Kone-Paut, I.; Cattalini, M.; et al. The phenotype of TNF receptor-associated autoinflammatory syndrome (TRAPS) at presentation: A series of 158 cases from the Eurofever/EUROTRAPS international registry. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 2160–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksentijevich, I.; Galon, J.; Soares, M.; Mansfield, E.; Hull, K.; Oh, H.H.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Dean, J.; Athreya, B.; Reginato, A.J.; et al. The tumor-necrosis-factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome: New mutations in TNFRSF1A, ancestral origins, genotype-phenotype studies, and evidence for further genetic heterogeneity of periodic fevers. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, M.; Siegel, R.M. Beyond TNF: TNF superfamily cytokines as targets for the treatment of rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt, C. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banner, D.W.; D’Arcy, A.; Janes, W.; Gentz, R.; Schoenfeld, H.J.; Broger, C.; Loetscher, H.; Lesslauer, W. Crystal structure of the soluble human 55 kd TNF receptor-human TNF beta complex: Implications for TNF receptor activation. Cell 1993, 73, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Hawari, F.; Alsaaty, S.; Lawrence, M.; Combs, C.A.; Geng, W.; Rouhani, F.N.; Miskinis, D.; Levine, S.J. Identification of ARTS-1 as a novel TNFR1-binding protein that promotes TNFR1 ectodomain shedding. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodmer, J.L.; Schneider, P.; Tschopp, J. The molecular architecture of the TNF superfamily. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrauste de Menthiere, C.; Terriere, S.; Pugnere, D.; Ruiz, M.; Demaille, J.; Touitou, I. INFEVERS: The Registry for FMF and hereditary inflammatory disorders mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gijn, M.E.; Ceccherini, I.; Shinar, Y.; Carbo, E.C.; Slofstra, M.; Arostegui, J.I.; Sarrabay, G.; Rowczenio, D.; Omoyimni, E.; Balci-Peynircioglu, B.; et al. New workflow for classification of genetic variants’ pathogenicity applied to hereditary recurrent fevers by the International Study Group for Systemic Autoinflammatory Diseases (INSAID). J. Med. Genet. 2018, 55, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, S.L.; Bainbridge, S.E.; Amel-Kashipaz, M.R.; Radford, P.M.; Powell, R.J.; Todd, I.; Tighe, P.J. Modeling of tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 1A mutants associated with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome indicates misfolding consistent with abnormal function. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2674–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchman, S.M.; Church, L.D.; Savic, S.; Coulthard, L.R.; Hayward, B.; Nedjai, B.; Turner, M.D.; Mathews, R.J.; Baguley, E.; Hitman, G.A.; et al. A novel TNFRSF1A splice mutation associated with increased nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) transcription factor activation in patients with tumour necrosis factor receptor associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobito, A.A.; Kimberley, F.C.; Muppidi, J.R.; Komarow, H.; Jackson, A.J.; Hull, K.M.; Kastner, D.L.; Screaton, G.R.; Siegel, R.M. Abnormal disulfide-linked oligomerization results in ER retention and altered signaling by TNFR1 mutants in TNFR1-associated periodic fever syndrome (TRAPS). Blood 2006, 108, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravet, N.; Rouaghe, S.; Dode, C.; Bienvenu, J.; Stirnemann, J.; Levy, P.; Delpech, M.; Grateau, G. Clinical significance of P46L and R92Q substitutions in the tumour necrosis factor superfamily 1A gene. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Park, H.; Maddipati, R.; Lobito, A.A.; Bulua, A.C.; Jackson, A.J.; Chae, J.J.; Ettinger, R.; de Koning, H.D.; Cruz, A.C.; et al. Concerted action of wild-type and mutant TNF receptors enhances inflammation in TNF receptor 1-associated periodic fever syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9801–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelagatti, M.A.; Meini, A.; Caorsi, R.; Cattalini, M.; Federici, S.; Zulian, F.; Calcagno, G.; Tommasini, A.; Bossi, G.; Sormani, M.P.; et al. Long-term clinical profile of children with the low-penetrance R92Q mutation of the TNFRSF1A gene. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ortiz, E.; Iglesias, E.; Soriano, A.; Bujan-Rivas, S.; Espanol-Rego, M.; Castellanos-Moreira, R.; Tome, A.; Yague, J.; Anton, J.; Hernandez-Rodriguez, J. Disease Phenotype and Outcome Depending on the Age at Disease Onset in Patients Carrying the R92Q Low-Penetrance Variant in TNFRSF1A Gene. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, N.; Ida, H.; Washio, M.; Miyahara, H.; Tokunaga, S.; Tanaka, F.; Takahashi, H.; Kusuhara, K.; Ohmura, K.; Nakayama, M.; et al. Clinical and Genetic Features of Patients With TNFRSF1A Variants in Japan: Findings of a Nationwide Survey. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2760–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarini, L.; Rigante, D.; Merlini, G.; Vitale, A.; Caso, F.; Lucherini, O.M.; Sfriso, P.; Frediani, B.; Punzi, L.; Galeazzi, M.; et al. The expanding spectrum of low-penetrance TNFRSF1A gene variants in adults presenting with recurrent inflammatory attacks: Clinical manifestations and long-term follow-up. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 43, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, H.M.; Broderick, L. Editorial: It Just Takes One: Somatic Mosaicism in Autoinflammatory Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowczenio, D.M.; Trojer, H.; Omoyinmi, E.; Arostegui, J.I.; Arakelov, G.; Mensa-Vilaro, A.; Baginska, A.; Silva Pilorz, C.; Wang, G.; Lane, T.; et al. Brief Report: Association of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-Associated Periodic Syndrome With Gonosomal Mosaicism of a Novel 24-Nucleotide TNFRSF1A Deletion. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2044–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontzias, A.; Zarabi, S.K.; Calabrese, C.; Wang, Y.; Judis, L.; Yao, Q.; Cheng, Y.W. Somatic mosaicism in adult-onset TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggins, M.L.; Radford, P.M.; McIntosh, R.S.; Bainbridge, S.E.; Dickinson, P.; Draper-Morgan, K.A.; Tighe, P.J.; Powell, R.J.; Todd, I. Shedding of mutant tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 1A associated with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome: Differences between cell types. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 2651–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, N.; Gould, D.J.; Aganna, E.; Hammond, L.; Mirakian, R.M.; Turner, M.D.; Hitman, G.A.; McDermott, M.F.; Chernajovsky, Y. Tumor necrosis factor receptor I from patients with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome interacts with wild-type tumor necrosis factor receptor I and induces ligand-independent NF-kappaB activation. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2906–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberley, F.C.; Lobito, A.A.; Siegel, R.M.; Screaton, G.R. Falling into TRAPS--receptor misfolding in the TNF receptor 1-associated periodic fever syndrome. Arthritis Res. 2007, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Kim, Y.S.; Lin, Y.; Lewis, J.; Neckers, L.; Liu, Z.G. Tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced activation of the MAP kinase JNK. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, M.; Lepow, T.S.; Billingham, L.K.; Murphy, M.P.; Siegel, R.M. New tricks from an old dog: Mitochondrial redox signaling in cellular inflammation. Semin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulua, A.C.; Simon, A.; Maddipati, R.; Pelletier, M.; Park, H.; Kim, K.Y.; Sack, M.N.; Kastner, D.L.; Siegel, R.M. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species promote production of proinflammatory cytokines and are elevated in TNFR1-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, P.; Ron, D. The unfolded protein response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 2011, 334, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Kaufman, R.J. From acute ER stress to physiological roles of the Unfolded Protein Response. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, R.; Parra, V.; Gatica, D.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Torrealba, N.; Paredes, F.; Wang, Z.V.; Zorzano, A.; Hill, J.A.; Jaimovich, E.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum and the unfolded protein response: Dynamics and metabolic integration. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 301, 215–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickie, L.J.; Aziz, A.M.; Savic, S.; Lucherini, O.M.; Cantarini, L.; Geiler, J.; Wong, C.H.; Coughlan, R.; Lane, T.; Lachmann, H.J.; et al. Involvement of X-box binding protein 1 and reactive oxygen species pathways in the pathogenesis of tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinon, F.; Chen, X.; Lee, A.H.; Glimcher, L.H. TLR activation of the transcription factor XBP1 regulates innate immune responses in macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachetti, T.; Chiesa, S.; Castagnola, P.; Bani, D.; Di Zanni, E.; Omenetti, A.; D’Osualdo, A.; Fraldi, A.; Ballabio, A.; Ravazzolo, R.; et al. Autophagy contributes to inflammation in patients with TNFR-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedjai, B.; Hitman, G.A.; Yousaf, N.; Chernajovsky, Y.; Stjernberg-Salmela, S.; Pettersson, T.; Ranki, A.; Hawkins, P.N.; Arkwright, P.D.; McDermott, M.F.; et al. Abnormal tumor necrosis factor receptor I cell surface expression and NF-kappaB activation in tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, S.; Matsuzaki, H.; Iseki, M.; Nagasu, A.; Hirano, H.; Ishihara, K.; Ueda, N.; Honda, Y.; Horiuchi, T.; Nishikomori, R.; et al. Functional analysis of a novel G87V TNFRSF1A mutation in patients with TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 198, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, O.H.; Singh, S.; Abduljabbar, W.; Hamed, M.R.; Radford, P.; McDermott, E.M.; Drewe, E.; Fairclough, L.; Todd, I.; Tighe, P.J. Patients with tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS) are hypersensitive to Toll-like receptor 9 stimulation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 197, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A.; van der Meer, J.W. Treating inflammation by blocking interleukin-1 in humans. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghini, S.; Ferrera, D.; Prigione, I.; Fiore, M.; Ferraris, C.; Mirisola, V.; Amaro, A.A.; Gueli, I.; Zammataro, L.; Gattorno, M.; et al. Gene expression profile in TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome reveals constitutively enhanced pathways and new players in the underlying inflammation. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, S121–S128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Torene, R.; Nirmala, N.; Obici, L.; Cattalini, M.; Tormey, V.; Caorsi, R.; Starck-Schwertz, S.; Letzkus, M.; Hartmann, N.; Abrams, K.; et al. Canakinumab reverses overexpression of inflammatory response genes in tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroleva, I.A.; Nazarenko, M.S.; Kucher, A.N. Role of microRNA in Development of Instability of Atherosclerotic Plaques. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2017, 82, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, A.; Rani, S. MiRNA Biogenesis and Regulation of Diseases: An Overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1509, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucherini, O.M.; Obici, L.; Ferracin, M.; Fulci, V.; McDermott, M.F.; Merlini, G.; Muscari, I.; Magnotti, F.; Dickie, L.J.; Galeazzi, M.; et al. First report of circulating microRNAs in tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.R.; Scambler, T.; Oubussad, L.; Wong, C.; Wittmann, M.; McDermott, M.F.; Savic, S. Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1-Mediated Downregulation of MicroRNA (miR)-146a and miR-155 in Primary Dermal Fibroblasts across Three TNFRSF1A Mutations Results in Hyperresponsiveness to Lipopolysaccharide. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluher, M. Adipokines—Removing road blocks to obesity and diabetes therapy. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarini, L.; Obici, L.; Simonini, G.; Cimaz, R.; Bacarelli, M.R.; Merlini, G.; Vitale, A.; Lucherini, O.M.; Brizi, M.G.; Galeazzi, M.; et al. Serum leptin, resistin, visfatin and adiponectin levels in tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2012, 30, S108–S114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yang, G.; Shi, S.; Yang, M.; Liu, H.; Boden, G. The adipose triglyceride lipase, adiponectin and visfatin are downregulated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in vivo. Cytokine 2009, 45, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Cava, A.; Matarese, G. The weight of leptin in immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucino, V.; Lucherini, O.M.; Perna, F.; Obici, L.; Merlini, G.; Cattalini, M.; La Torre, F.; Maggio, M.C.; Lepore, M.T.; Magnotti, F.; et al. Differential impact of high and low penetrance TNFRSF1A gene mutations on conventional and regulatory CD4+ T cell functions in TNFR1-associated periodic syndrome. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, I.; Radford, P.M.; Daffa, N.; Bainbridge, S.E.; Powell, R.J.; Tighe, P.J. Mutant tumor necrosis factor receptor associated with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome is altered antigenically and is retained within patients’ leukocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 2765–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aganna, E.; Hammond, L.; Hawkins, P.N.; Aldea, A.; McKee, S.A.; van Amstel, H.K.; Mischung, C.; Kusuhara, K.; Saulsbury, F.T.; Lachmann, H.J.; et al. Heterogeneity among patients with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome phenotypes. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 2632–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, K.M.; Drewe, E.; Aksentijevich, I.; Singh, H.K.; Wong, K.; McDermott, E.M.; Dean, J.; Powell, R.J.; Kastner, D.L. The TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS): Emerging concepts of an autoinflammatory disorder. Medicine 2002, 81, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, H.J. Periodic fever syndromes. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 31, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, T.; Kantonen, J.; Matikainen, S.; Repo, H. Setting up TRAPS. Ann. Med. 2012, 44, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, N. TNF-receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS): An autosomal dominant multisystem disorder. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 25, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezos, A.; Argyropoulou, O.D.; Klinaki, E.; Marketos, N.; Karagianni, P.; Eliopoulos, E.; Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.; Maritsi, D.N.; Tzioufas, A.G. Molecular and clinical spectrum of four pedigrees of TRAPS in Greece: Results from a national referral center. Rheumatology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Luo, Y.; Wu, D.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, R.; Shen, M. Clinical and genetic features of Chinese adult patients with tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic fever syndrome. Rheumatology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesus, A.A.; Fujihira, E.; Watase, M.; Terreri, M.T.; Hilario, M.O.; Carneiro-Sampaio, M.; Len, C.A.; Oliveira, S.K.; Rodrigues, M.C.; Pereira, R.M.; et al. Hereditary autoinflammatory syndromes: A Brazilian multicenter study. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 32, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarini, L.; Lucherini, O.M.; Cimaz, R.; Baldari, C.T.; Bellisai, F.; Rossi Paccani, S.; Laghi Pasini, F.; Capecchi, P.L.; Sebastiani, G.D.; Galeazzi, M. Idiopathic recurrent pericarditis refractory to colchicine treatment can reveal tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharm. 2009, 22, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarini, L.; Lucherini, O.M.; Vitale, A.; Sabadini, L.; Brizi, M.G.; Frediani, B.; Muscari, I.; Galeazzi, M. Expanding spectrum of TNFRSF1A gene mutations among patients with idiopathic recurrent acute pericarditis. Intern. Med. J. 2013, 43, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigante, D.; Cantarini, L.; Imazio, M.; Lucherini, O.M.; Sacco, E.; Galeazzi, M.; Brizi, M.G.; Brucato, A. Autoinflammatory diseases and cardiovascular manifestations. Ann. Med. 2011, 43, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmaltz, R.; Vogt, T.; Reichrath, J. Skin manifestations in tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). Dermato Endocrinol. 2010, 2, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, J.R.; Aksentijevich, I.; Hull, K.; Dean, J.; Kastner, D.L. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome: A novel syndrome with cutaneous manifestations. Arch. Derm. 2000, 136, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigante, D.; Capoluongo, E. The plodding diagnosis of monogenic autoinflammatory diseases in childhood: From the clinical scenery to laboratory investigation. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2011, 49, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piram, M.; Frenkel, J.; Gattorno, M.; Ozen, S.; Lachmann, H.J.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Hentgen, V.; Neven, B.; Stojanovic, K.S.; Simon, A.; et al. A preliminary score for the assessment of disease activity in hereditary recurrent fevers: Results from the AIDAI (Auto-Inflammatory Diseases Activity Index) Consensus Conference. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, S.; Sormani, M.P.; Ozen, S.; Lachmann, H.J.; Amaryan, G.; Woo, P.; Kone-Paut, I.; Dewarrat, N.; Cantarini, L.; Insalaco, A.; et al. Evidence-based provisional clinical classification criteria for autoinflammatory periodic fevers. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattorno, M.; Hofer, M.; Federici, S.; Vanoni, F.; Bovis, F.; Aksentijevich, I.; Anton, J.; Arostegui, J.I.; Barron, K.; Ben-Cherit, E.; et al. Classification criteria for autoinflammatory recurrent fevers. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arostegui, J.I.; Solis, P.; Aldea, A.; Cantero, T.; Rius, J.; Bahillo, P.; Plaza, S.; Vives, J.; Gomez, S.; Yague, J. Etanercept plus colchicine treatment in a child with tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome abolishes auto-inflammatory episodes without normalising the subclinical acute phase response. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2005, 164, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarini, L.; Rigante, D.; Lucherini, O.M.; Cimaz, R.; Laghi Pasini, F.; Baldari, C.T.; Benucci, M.; Simonini, G.; Di Sabatino, V.; Brizi, M.G.; et al. Role of etanercept in the treatment of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome: Personal experience and review of the literature. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharm. 2010, 23, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulua, A.C.; Mogul, D.B.; Aksentijevich, I.; Singh, H.; He, D.Y.; Muenz, L.R.; Ward, M.M.; Yarboro, C.H.; Kastner, D.L.; Siegel, R.M.; et al. Efficacy of etanercept in the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome: A prospective, open-label, dose-escalation study. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewe, E.; McDermott, E.M.; Powell, P.T.; Isaacs, J.D.; Powell, R.J. Prospective study of anti-tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily 1B fusion protein, and case study of anti-tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily 1A fusion protein, in tumour necrosis factor receptor associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS): Clinical and laboratory findings in a series of seven patients. Rheumatology 2003, 42, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, S.; Dejaco, C.; Lohse, P.; Huss, K.; Duftner, C.; Belohradsky, B.H.; Herold, M.; Schirmer, M. Clinical and functional characterisation of a novel TNFRSF1A c.605T>A/V173D cleavage site mutation associated with tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic fever syndrome (TRAPS), cardiovascular complications and excellent response to etanercept treatment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewe, E.; Huggins, M.L.; Morgan, A.G.; Cassidy, M.J.; Powell, R.J. Treatment of renal amyloidosis with etanercept in tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome. Rheumatology 2004, 43, 1405–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ter Haar, N.; Lachmann, H.; Ozen, S.; Woo, P.; Uziel, Y.; Modesto, C.; Kone-Paut, I.; Cantarini, L.; Insalaco, A.; Neven, B.; et al. Treatment of autoinflammatory diseases: Results from the Eurofever Registry and a literature review. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedjai, B.; Hitman, G.A.; Quillinan, N.; Coughlan, R.J.; Church, L.; McDermott, M.F.; Turner, M.D. Proinflammatory action of the antiinflammatory drug infliximab in tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymakcalan, Z.; Sakorafas, P.; Bose, S.; Scesney, S.; Xiong, L.; Hanzatian, D.K.; Salfeld, J.; Sasso, E.H. Comparisons of affinities, avidities, and complement activation of adalimumab, infliximab, and etanercept in binding to soluble and membrane tumor necrosis factor. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 131, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furst, D.E.; Wallis, R.; Broder, M.; Beenhouwer, D.O. Tumor necrosis factor antagonists: Different kinetics and/or mechanisms of action may explain differences in the risk for developing granulomatous infection. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 36, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akasbi, N.; Soyfoo, M.S. Successful treatment of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS) with tocilizumab: A case report. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 2, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoya, T.; Mizoguchi, F.; Hasegawa, H.; Miura, K.; Koike, R.; Kubota, T.; Miyasaka, N.; Kohsaka, H. A Case Presenting with the Clinical Characteristics of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Receptor-associated Periodic Syndrome (TRAPS) without TNFRSF1A Mutations Successfully Treated with Tocilizumab. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 2069–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaitla, P.M.; Radford, P.M.; Tighe, P.J.; Powell, R.J.; McDermott, E.M.; Todd, I.; Drewe, E. Role of interleukin-6 in a patient with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome: Assessment of outcomes following treatment with the anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody tocilizumab. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, F.; Muratore, M.; Vitale, A.; Moramarco, F.; Quarta, L.; Cantarini, L. Canakinumab efficacy and long-term tocilizumab administration in tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, H.J.; Quartier, P.; So, A.; Hawkins, P.N. The emerging role of interleukin-1beta in autoinflammatory diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Bodar, E.J.; van der Hilst, J.C.; van der Meer, J.W.; Fiselier, T.J.; Cuppen, M.P.; Drenth, J.P. Beneficial response to interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in traps. Am. J. Med. 2004, 117, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattorno, M.; Pelagatti, M.A.; Meini, A.; Obici, L.; Barcellona, R.; Federici, S.; Buoncompagni, A.; Plebani, A.; Merlini, G.; Martini, A. Persistent efficacy of anakinra in patients with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentileschi, S.; Rigante, D.; Vitale, A.; Sota, J.; Frediani, B.; Galeazzi, M.; Cantarini, L. Efficacy and safety of anakinra in tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS) complicated by severe renal failure: A report after long-term follow-up and review of the literature. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 1687–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obici, L.; Meini, A.; Cattalini, M.; Chicca, S.; Galliani, M.; Donadei, S.; Plebani, A.; Merlini, G. Favourable and sustained response to anakinra in tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS) with or without AA amyloidosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1511–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimwood, C.; Despert, V.; Jeru, I.; Hentgen, V. On-demand treatment with anakinra: A treatment option for selected TRAPS patients. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1749–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brizi, M.G.; Galeazzi, M.; Lucherini, O.M.; Cantarini, L.; Cimaz, R. Successful treatment of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome with canakinumab. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 156, 907–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopalco, G.; Rigante, D.; Vitale, A.; Frediani, B.; Iannone, F.; Cantarini, L. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome managed with the couple canakinumab-alendronate. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 807–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattorno, M.; Obici, L.; Cattalini, M.; Tormey, V.; Abrams, K.; Davis, N.; Speziale, A.; Bhansali, S.G.; Martini, A.; Lachmann, H.J. Canakinumab treatment for patients with active recurrent or chronic TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS): An open-label, phase II study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Benedetti, F.; Gattorno, M.; Anton, J.; Ben-Chetrit, E.; Frenkel, J.; Hoffman, H.M.; Kone-Paut, I.; Lachmann, H.J.; Ozen, S.; Simon, A.; et al. Canakinumab for the Treatment of Autoinflammatory Recurrent Fever Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1908–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Biological Medication Used | Type of Study | Dose of Medication | Follow-up Period | Number of Patients | Adverse Events | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etanercept | Case report | 0.4 mg/kg 2× week | 12 months | 1 | minor injection site reactions | [73] |
| Open label study | NA | 24 weeks | 7 | NA | [74] | |
| Open label study | 25 mg 2× week | 18 months | 3 | NA | [77] | |
| Open label study | 25 mg 2× week | 24 weeks | 7 | minor injection site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections | [76] | |
| Open label study | 25 mg (adult dose) or 0.4 mg/kg (pediatric dose) 2× week | 6 months | 9 | NA | [57] | |
| Open-label dose escalation study | 25 mg 2× week for 14 weeks, then 25 mg 3× week for 14 weeks | 10 years | 15 | Injection site reactions | [75] | |
| Anakinra | Case report | 100 mg daily | 3 months | 1 | Injection site reactions | [88] |
| Open-label dose | 100 mg daily | On demand | 2 | Injection site reactions | [92] | |
| Open-label dose | 100 mg daily | 12–46 months | 7 | Injection site reactions, respiratory and urinary infections | [91] | |
| Open-label dose | 1.5 mg/kg daily | 15 days | 4 | Injection site reactions | [95] | |
| Canakinumab | Case report | 150 mg every 8 weeks | 18 months | 1 | NA | [93] |
| Case report | 150 mg every 4 weeks | 47 months | 1 | NA | [94] | |
| Case report | 4 mg/kg mg every 8 weeks | 36 months | 1 | NA | [86] | |
| Phase II, open-label study 2b | 150 mg every 4 weeks (2 mg/kg pediatric patients) | 33 months | 20 | Nasopharingitis, abdominal pain, headache | [95] | |
| Phase III, randomized Double-blind, placebo-controlled study | 150 mg every 4 weeks (2 mg/kg if weight less 40 kg) | 4 months | 22 | Nasopharingitis, injection site reactions, upper respiratory tract infection | [96] | |
| Phase III, Randomized, withdrawal period study | 150 mg every 8 weeks (2 mg/kg if weight less 40 kg) | 6 months | 4 | Nasopharingitis, injection site reactions, upper respiratory tract infection | [96] | |
| Tocilizumab | Case report | 8 mg/kg every 4 weeks | 6 months | 1 | NA | [83] |
| Case report | 8 mg/kg every 2 weeks then PRN | >6 months | 1 | NA | [84] | |
| Case report | 8 mg/kg every 4 weeks | 6 months | 1 | Trombocytopenia | [85] | |
| Case report | 8 mg/kg every 4 weeks | 42 months | 1 | NA | [86] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cudrici, C.; Deuitch, N.; Aksentijevich, I. Revisiting TNF Receptor-Associated Periodic Syndrome (TRAPS): Current Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093263
Cudrici C, Deuitch N, Aksentijevich I. Revisiting TNF Receptor-Associated Periodic Syndrome (TRAPS): Current Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(9):3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093263
Chicago/Turabian StyleCudrici, Cornelia, Natalie Deuitch, and Ivona Aksentijevich. 2020. "Revisiting TNF Receptor-Associated Periodic Syndrome (TRAPS): Current Perspectives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 9: 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093263
APA StyleCudrici, C., Deuitch, N., & Aksentijevich, I. (2020). Revisiting TNF Receptor-Associated Periodic Syndrome (TRAPS): Current Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(9), 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093263





