NLRC4, ASC and Caspase-1 Are Inflammasome Components That Are Mediated by P2Y2R Activation in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Compared to MDA-MB-231 Cells, RT-R-MDA-MB-231 Cells Exhibited Increased mRNA Levels of NLRP3, NLRC4, ASC, and Cleaved Caspase-1, and NLRC4, ASC, and Cleaved Caspase-1, but Not NLRC3, Were Induced by TNF-α and ATP in Both Breast Cancer Cells
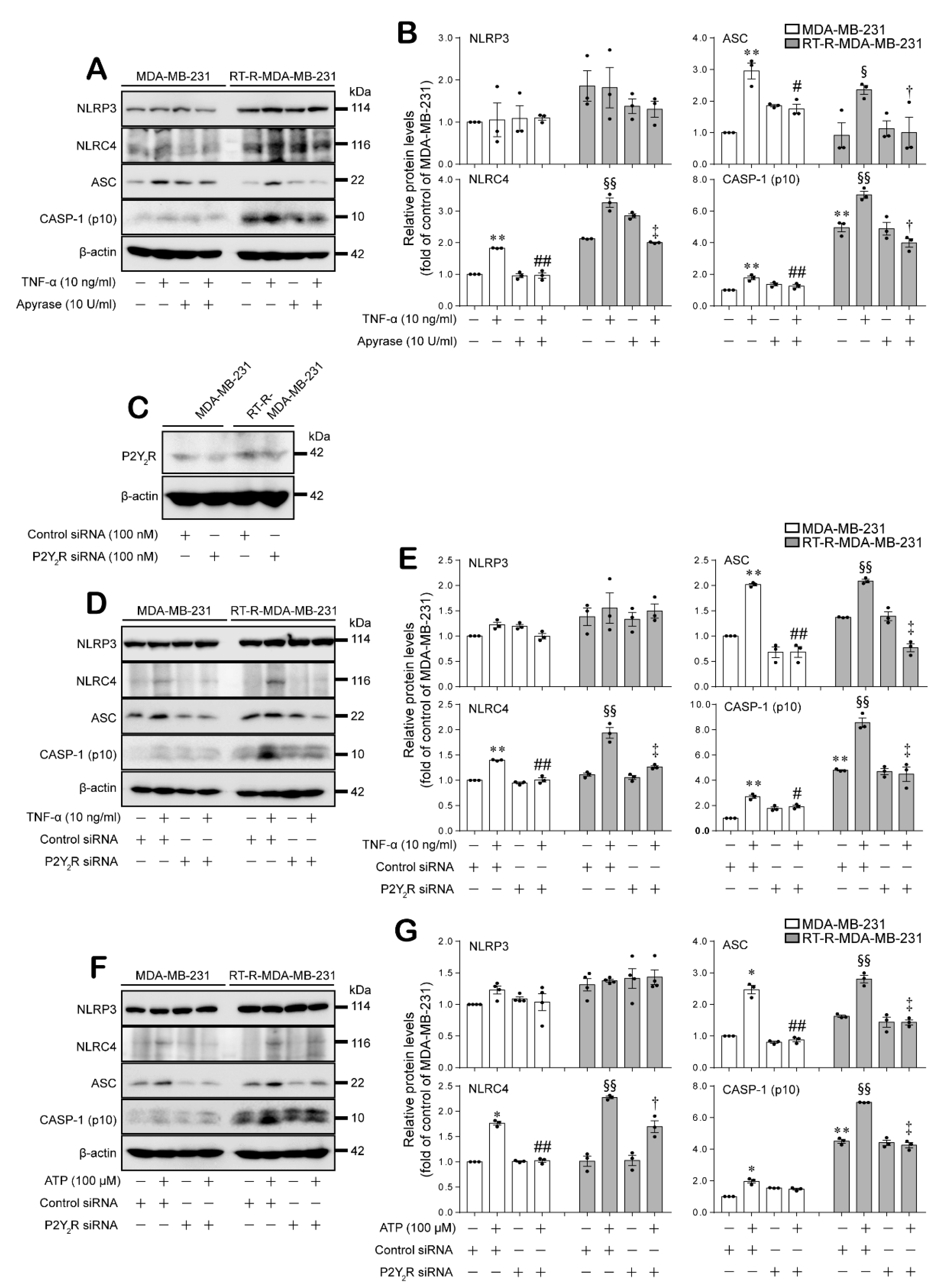
2.2. Expression of the Inflammasome Components NLRC4, ASC, and Cleaved Caspase-1 Were Induced by TNF-α or ATP in a P2Y2R-Dependent Manner in MDA-MB-231 and RT-R-MDA-MB-231 Cells
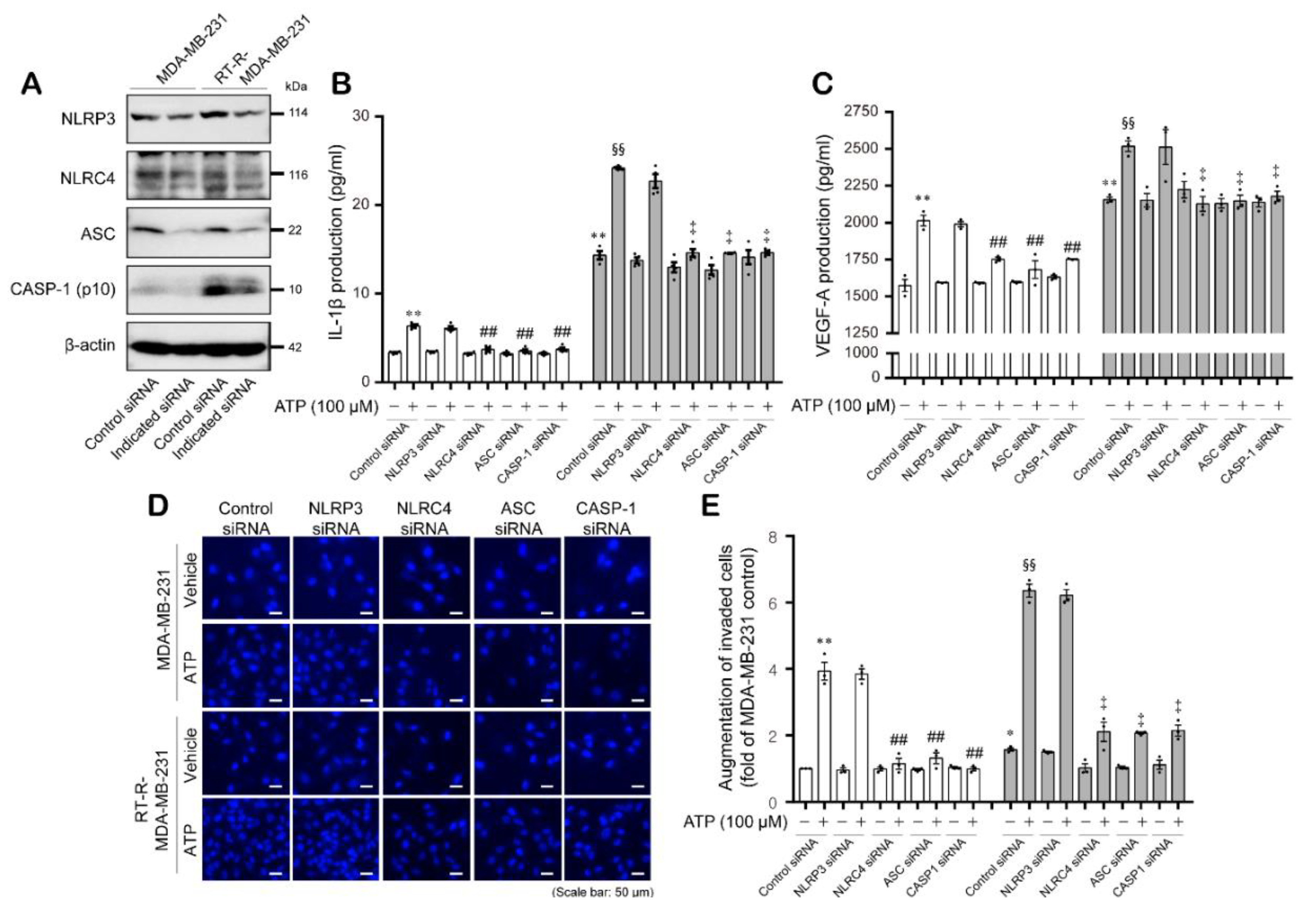
2.3. ATP-Induced Expression of the Inflammasome Components NLRC4, ASC, and Cleaved Caspase-1 Enhanced the Secretion of IL-1β and VEGF-A, as well as Invasion, in MDA-MB-231 and RT-R-MDA-MB-231 Cells in a P2Y2R-Dependent Manner
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Establishment of RT-R-MDA-MB-231 Cells and Cell Culture
4.3. Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
4.4. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
4.5. Gene Silencing with siRNA Transfection
4.6. Quantification of IL-1β and VEGF-A Secretion
4.7. Matrigel Invasion Assay
4.8. Statistical Evaluations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIM2 | Absent in melanoma 2 |
| ASC | Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD complex |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| CARD | Caspase activation and recruitment domain |
| CASP-1 | Caspase-1 |
| CCDN1 | Cyclin D1 |
| DAMP | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| ECL | Enhanced chemiluminescence |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| ERK | Extracellular signal regulated kinase |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| LRR | Leucine-rich repeat |
| MMP | Matrix metallopeptidases |
| NLR | Nucleotide-binding domain-like receptors |
| NLRC4 | NLR Family CARD Domain Containing 4 |
| NLRP1 | NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 1 |
| NLRP3 | NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 |
| NOD | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain |
| NP-40 | Nonylphonoxypolyethoxypthanol-40 |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| P2X7R | P2X purinergic receptor 7 |
| P2Y2R | P2Y purinergic receptor 2 |
| PAMP | Pathogen-associated molecular pattern |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitation assay |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute |
| RT-R | Radiotherapy-resistant |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| TNM | Tumor-node-metastasis |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VEGF-A | Vascular endothelial growth factor-A |
| VEGFR | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor |
References
- Norling, L.V.; Serhan, C.N. Profiling in resolving inflammatory exudates identifies novel anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving mediators and signals for termination. J. Intern. Med. 2010, 268, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Clevers, H. Reparative inflammation takes charge of tissue regeneration. Nature 2016, 529, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virchov, R. Cellular Pathology as Based Upon Physiological and Pathological Histology; J. B. Lippincott: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1863; p. 529. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, H.; Akaike, T. Nitric oxide and oxygen radicals in infection, inflammation, and cancer. Biochemistry C/C Biokhimiia 1998, 63, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shaked, H.; Hofseth, L.J.; Chumanevich, A.; Chumanevich, A.A.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Taniguchi, K.; Guma, M.; Shenouda, S.; Clevers, H.; et al. Chronic epithelial NF-kappaB activation accelerates APC loss and intestinal tumor initiation through iNOS up-regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14007–14012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Ouyang, W.; Huang, C. Inflammation, a key event in cancer development. Mol. Cancer Res. 2006, 4, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Jiang, Y.C.; Sun, C.K.; Chen, Q.M. Role of the tumor microenvironment in tumor progression and the clinical applications (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2499–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoric, J.; Antonucci, L.; Karin, M. Targeting Inflammation in Cancer Prevention and Therapy. Cancer Prev. Res. 2016, 9, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, B.P. Inflammation: A driving force speeds cancer metastasis. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3267–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Yuan, R.Q.; Fuchs, A.; Yao, Y.; Joseph, A.; Schwall, R.; Schnitt, S.J.; Guida, A.; Hastings, H.M.; Andres, J.; et al. Expression of interleukin-1beta in human breast carcinoma. Cancer 1997, 80, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.J.; Kurtzman, S.H.; Anderson, K.; Wang, Y.; Stankus, M.; Renna, M.; Lindquist, R.; Barrows, G.; Kreutzer, D.L. Interleukin-1 family expression in human breast cancer: Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Cancer Investig. 2000, 18, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsunaga, S.; Ikeda, M.; Shimizu, S.; Ohno, I.; Furuse, J.; Inagaki, M.; Higashi, S.; Kato, H.; Terao, K.; Ochiai, A. Serum levels of IL-6 and IL-1β can predict the efficacy of gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 20632069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzler, M.; Kurzrock, R.; Estrov, Z.; Kantarjian, H.; Gisslinger, H.; Underbrink, M.; Talpaz, M. Altered levels of interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in chronic myelogenous leukemia: Clinical and prognostic correlates. Blood 1994, 84, 3142–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elaraj, D.M.; Weinreich, D.M.; Varghese, S.; Puhlmann, M.; Hewitt, S.M.; Carroll, N.M.; Feldman, E.D.; Turner, E.M.; Alexander, H.R. The role of interleukin 1 in growth and metastasis of human cancer xenografts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel-Velazquez, M.; Ostoa-Saloma, P.; Palacios-Arreola, M.I.; Nava-Castro, K.E.; Castro, J.I.; Morales-Montor, J. The role of cytokines in breast cancer development and progression. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015, 35, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voronov, E.; Shouval, D.S.; Krelin, Y.; Cagnano, E.; Benharroch, D.; Iwakura, Y.; Dinarello, C.A.; Apte, R.N. IL-1 is required for tumor invasiveness and angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2645–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Bae, S.Y.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, S.K.; Kil, W.H.; Kim, S.W.; Nam, S.J.; et al. Zerumbone suppresses IL-1β-induced cell migration and invasion by inhibiting IL-8 and MMP-3 expression in human triple-negative breast cancer cells. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, G.; Ofri-Shahak, M.; Haas, I.; Yaal-Hahoshen, N.; Leider-Trejo, L.; Leibovich-Rivkin, T.; Weitzenfeld, P.; Meshel, T.; Shabtai, E.; Gutman, M.; et al. Inflammatory mediators in breast cancer: Coordinated expression of TNFα & IL-1β with CCL2 & CCL5 and effects on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamkanfi, M. Emerging inflammasome effector mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Huang, H.; Qiu, Z.; Li, H.; Tan, J.; Ren, G.; Wang, X. NLRP1 Overexpression Is Correlated with the Tumorigenesis and Proliferation of Human Breast Tumor. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4938473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, R.; Phan, L.; Borcherding, N.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, F.; Janowski, A.M.; Xie, Q.; Markan, K.R.; Li, W.; Potthoff, M.J.; et al. Obesity-associated NLRC4 inflammasome activation drives breast cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Zhao, F.; Guo, F.; Wang, C.; Fu, Z. Polymeric Nanoparticles Induce NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Promote Breast Cancer Metastasis. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.F.; Ou-Yang, F.; Hung, J.Y.; Liu, J.C.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.C.; Hou, M.F.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Hung, M.C. AIM2 suppresses human breast cancer cell proliferation in vitro and mammary tumor growth in a mouse model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodin, P.; Burnstock, G. Purinergic signalling: ATP release. Neurochem. Res. 2001, 26, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.S.; Pulskens, W.P.; Sadler, J.J.; Butter, L.M.; Teske, G.J.; Ulland, T.K.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Florquin, S.; Flavell, R.A.; Leemans, J.C.; et al. Necrotic cells trigger a sterile inflammatory response through the Nlrp3 inflammasome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20388–20393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Dal Ben, D.; Sarti, A.C.; Giuliani, A.L.; Falzoni, S. The P2X7 Receptor in Infection and Inflammation. Immunity 2017, 47, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vénéreau, E.; Ceriotti, C.; Bianchi, M.E. DAMPs from cell death to new life. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegatti, P.; Raffaghello, L.; Bianchi, G.; Piccardi, F.; Pistoia, V.; Di Virgilio, F. Increased level of extracellular ATP at tumor sites: In vivo imaging with plasma membrane luciferase. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, G.; Kang, H.C.; Cho, Y.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.Y. Inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome in tumor microenvironment leads to suppression of metastatic potential of cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Ko, Y.S.; Kim, H.J. P2Y2R-mediated inflammasome activation is involved in tumor progression in breast cancer cells and in radiotherapy-resistant breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.S.; Jin, H.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.W.; Chang, K.C.; Kang, K.M.; Jeong, B.K.; Kim, H.J. Radioresistant breast cancer cells exhibit increased resistance to chemotherapy and enhanced invasive properties due to cancer stem cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3752–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karan, D. Inflammasomes: Emerging Central Players in Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Barajon, I.; Garlanda, C. IL-1 and IL-1 regulatory pathways in cancer progression and therapy. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Yi, J.; Liu, F.E. The molecular mechanism of breast cancer cell apoptosis induction by absent in melanoma (AIM2). Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 14750–14758. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiringhelli, F.; Apetoh, L.; Tesniere, A.; Aymeric, L.; Ma, Y.; Ortiz, C.; Vermaelen, K.; Panaretakis, T.; Mignot, G.; Ullrich, E.; et al. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in dendritic cells induces IL-1beta-dependent adaptive immunity against tumors. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Yepez, E.A.; Ayala-Sumuano, J.T.; Lezama, R.; Meza, I. A novel beta-catenin signaling pathway activated by IL-1β leads to the onset of epithelial mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2014, 354, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Lan, F.; Zheng, Z.; Xie, F.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Han, J.; Zheng, F.; Xie, Y.; Huang, Q. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and interleukin (IL)-1β synergistically promote ERK1/2-mediated invasive breast ductal cancer cell migration and invasion. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Awad, B.; Kreft, B.; Wolber, E.M.; Hellwig-Bürgel, T.; Metzen, E.; Fandrey, J.; Jelkmann, W. Hypoxia and interleukin-1beta stimulate vascular endothelial growth factor production in human proximal tubular cells. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.D.; Liu, W.; Reinmuth, N.; Ahmad, S.A.; Fan, F.; Gallick, G.E.; Ellis, L.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor is upregulated by interleukin-1 beta in human vascular smooth muscle cells via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Angiogenesis 2001, 4, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: Basic science and clinical progress. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 581–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A. The Yin-Yang of tumor-associated macrophages in neoplastic progression and immune surveillance. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 222, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson-Welsh, L.; Welsh, M. VEGFA and tumour angiogenesis. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 273, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Chida, K.; Shibuya, M. A single autophosphorylation site on KDR/Flk-1 is essential for VEGF-A-dependent activation of PLC-gamma and DNA synthesis in vascular endothelial cells. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.H.; Liu, L.Z. PI3K/PTEN signaling in angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. Adv. Cancer Res. 2009, 102, 19–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Size (bp) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLRP1 | Forward | CCTGGTGGCTCAGTATGGGG | 60 | 334 |
| Reverse | CTCATGGTCTGGGGAGCTTG | |||
| NLRP3 | Forward | GCACGTGTTTCGAATCCCAC | 60 | 250 |
| Reverse | CCTGCTGGCTCCGGTGCTCC | |||
| NLRP6 | Forward | GGACGGACGCAGCATCCCGT | 65 | 470 |
| Reverse | GGCCCTGCAGCACCACGGTC | |||
| NLRC4 | Forward | CAGAACCTGTCCTGTGGAGG | 60 | 317 |
| Reverse | CCGCAGCTTCAGCAGCATGG | |||
| AIM2 | Forward | ACTCTTGCTAACAGGCCTGG | 55 | 283 |
| Reverse | ACTTAGTGGCTTTGGTTTTG | |||
| ASC | Forward | GCGCTGGAGAACCTGACCGC | 65 | 210 |
| Reverse | CTCCTGCAGGCCCATGTCGC | |||
| Caspase-1 (p10) | Forward | GAAAGCCCACATAGAGAAGG | 55 | 218 |
| Reverse | CTCTTTCAGTGGTGGGCATC | |||
| GAPDH | Forward | TCAACAGCGACACCCACTCC | 60 | 126 |
| Reverse | TGAGGTCCACCACCCTGTTG | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, H.; Kim, H.J. NLRC4, ASC and Caspase-1 Are Inflammasome Components That Are Mediated by P2Y2R Activation in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093337
Jin H, Kim HJ. NLRC4, ASC and Caspase-1 Are Inflammasome Components That Are Mediated by P2Y2R Activation in Breast Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(9):3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093337
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Hana, and Hye Jung Kim. 2020. "NLRC4, ASC and Caspase-1 Are Inflammasome Components That Are Mediated by P2Y2R Activation in Breast Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 9: 3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093337
APA StyleJin, H., & Kim, H. J. (2020). NLRC4, ASC and Caspase-1 Are Inflammasome Components That Are Mediated by P2Y2R Activation in Breast Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(9), 3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093337





