The Multifaceted Role of Epoxide Hydrolases in Human Health and Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. EPHX1: Gene, Structure, and Enzymatic Functions
3.1. From Gene to Protein
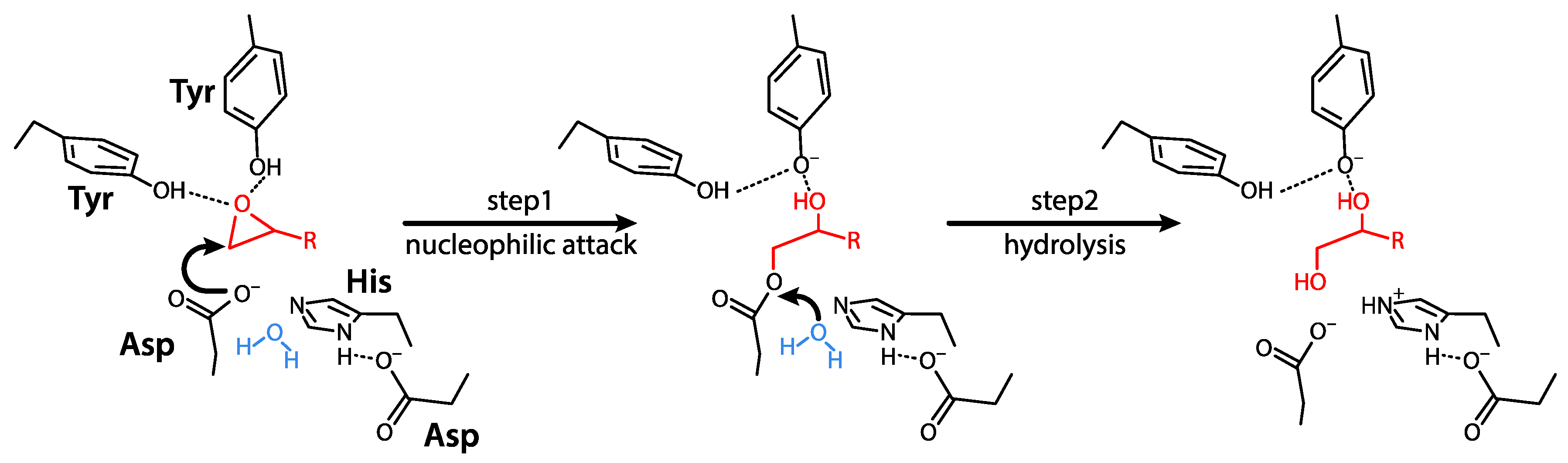
3.2. Mechanisms of Action and Substrates
3.3. Physiological Functions
3.4. EPHX1 Inhibitors
4. EPHX2: Gene, Structure, and Enzyme Function
4.1. From Gene to Protein
4.2. Mechanisms of Action and Substrates
4.3. Physiological Functions
4.4. EPHX2 Inhibitors
5. EPHX3
6. EPHX4 and Other Epoxide Hydrolases
7. Variants of Epoxide Hydrolases in Monogenic Disorders
8. Variants of Epoxide Hydrolases as Susceptibility Factors to Human Diseases
9. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-AG | Endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol |
| AA | Arachidonic acid |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| DiHOME | Dihydroxyoctadecamoic acid |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| DHET | Dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid |
| DiHDPE | Dihydroxydocosapentaenoic acid |
| DiHETE | Dihydroxyeicostetraenoic acid |
| DMBA | 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene |
| DPE | Epoxydocosapentaenoic acid |
| EH | Epoxide hydrolase |
| EPA | Eicosapentanoic acid |
| EpOME | Epoxyoctadecenoic acid |
| ETE | Epoxyeicosatetraenoic acid |
| ETT | Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid |
| LA | Linoleic acid |
| mEH | Microsomal epoxide hydrolase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa B |
| PPAR | Proliferator-activated receptor |
| sEH | Soluble epoxide hydrolase |
References
- Oesch, F.; Jerina, N.M.; Daly, J.W.; Rice, J.M. Induction, activation and inhibition of epoxide hydrase: An anomalous prevention of chlorobenzene-induced hepatotoxicity by an inhibitor of epoxide hydrase. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1973, 6, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesch, F.; Jerina, N.M.; Daly, J.W. Substrate specificity of hepatic epoxide hydrase in microsomes and in a purified preparation: Evidence for homologous enzymes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1971, 144, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebert, D.W.; Dalton, T.P. The role of cytochrome P450 enzymes in endogenous signalling pathways and environmental carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loo, B.; Kingma, J.; Arand, M.; Wubbolts, M.G.; Janssen, D.B. Diversity and Biocatalytic Potential of Epoxide Hydrolases Identified by Genome Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2905–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Decker, M.; Adamska, M.; Cronin, A.; Di Giallonardo, F.; Burgener, J.; Marowsky, A.; Falck, J.R.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Gruzdev, A.; et al. EH3 (ABHD9): The first member of a new epoxide hydrolase family with high activity for fatty acid epoxides. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2038–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fretland, A.J.; Omiecinski, C.J. Epoxide hydrolases: Biochemistry and molecular biology. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2000, 129, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skoda, R.C.; Demierre, A.; McBride, O.W.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Meyer, U.A. Human microsomal xenobiotic epoxide hydrolase. Complementary DNA sequence, complementary DNA-directed expression in COS-1 cells, and chromosomal localization. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Beetham, J.K.; Tian, T.; Hammock, B.D. cDNA Cloning and Expression of a Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase from Human Liver. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1993, 305, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falany, C.N.; McQuiddy, P.; Kasper, C.B. Structure and organization of the microsomal xenobiotic epoxide hydrolase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 5924–5930. [Google Scholar]
- Decker, M.; Arand, M.; Cronin, A. Mammalian epoxide hydrolases in xenobiotic metabolism and signalling. Arch. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, J.; Hällberg, B.M.; Bergfors, T.; Oesch, F.; Arand, M.; Mowbray, S.L.; Jones, T.A. Structure of Aspergillus niger epoxide hydrolase at 1.8 Å resolution: Implications for the structure and function of the mammalian microsomal class of epoxide hydrolases. Structure 2000, 8, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coller, J.K.; Fritz, P.; Zanger, U.M.; Siegle, I.; Eichelbaum, M.; Kroemer, H.K.; Mürdter, T.E. Distribution of microsomal epoxide hydrolase in humans: An immunohistochemical study in normal tissues, and benign and malignant tumours. Histol. J. 2001, 33, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaedigk, A.; Leeder, J.S.; Grant, D.M. Tissue-Specific Expression and Alternative Splicing of Human Microsomal Epoxide Hydrolase. DNA Cell Biol. 1997, 16, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.-H.; Hassett, C.; Omiecinski, C.J. Alternative Promoters Determine Tissue-Specific Expression Profiles of the Human Microsomal Epoxide Hydrolase Gene (EPHX1). Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.K.; Woodcroft, K.J.; Novak, R.F.; Kim, S.G. Insulin and glucagon signaling in regulation of microsomal epoxide hydrolase expression in primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, S.L.; Abele, I.S.; Buck, M.B.; Stope, M.B.; Blok, L.J.; Hanifi-Moghaddam, P.; Burger, C.W.; Fritz, P.; Knabbe, C. Microsomal epoxide hydrolase expression in the endometrial uterine corpus is regulated by progesterone during the menstrual cycle. J. Mol. Histol. 2010, 41, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aström, A.; Maner, S.; DePIERRE, J.W. Induction of liver microsomal epoxide hydrolase, UDP-glucuronyl transferase and cytosolic glutathione transferase in different rodent species by 2-acetylaminofluorene or 3-methylcholanthrene. Xenobiotica 1987, 17, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.-K.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Sutter, T.R.; Kensler, T.W. Role of Transcription Factor Nrf2 in the Induction of Hepatic Phase 2 and Antioxidative Enzymes in vivo by the Cancer Chemoprotective Agent, 3H-1, 2-Dithiole-3-thione. Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.-S.; Qian, B.; Levy, D. Regulation of human microsomal epoxide hydrolase gene (EPHX1) expression by the transcription factor GATA-4. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gene Struct. Expr. 2004, 1676, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedberg, T.; Löllmann, B.; Becker, R.; Holler, R.; Oesch, F. The microsomal epoxide hydrolase has a single membrane signal anchor sequence which is dispensable for the catalytic activity of this protein. Biochem. J. 1994, 303, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, D.F.; Lake, B.G.; Bird, M.G. Molecular modelling of human microsomal epoxide hydrolase (EH) by homology with a fungal (Aspergillus niger) EH crystal structure of 1.8 Å resolution: Structure–activity relationships in epoxides inhibiting EH activity. Toxicol. In Vitro 2005, 19, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthanarayanan, M.; Von Dippe, P.; Levy, D. Identification of the hepatocyte Na+-dependent bile acid transport protein using monoclonal antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 8338–8343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oesch, F.; Herrero, M.E.; Hengstler, J.G.; Lohmann, M.; Arand, M. Metabolic Detoxification: Implications for Thresholds. Toxicol. Pathol. 2000, 28, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Sherbeni, A.A.; El-Kadi, A.O.S. The role of epoxide hydrolases in health and disease. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 2013–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. EPOXIDE HYDROLASES: Mechanisms, Inhibitor Designs, and Biological Roles. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 45, 311–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edin, M.L.; Hamedani, B.G.; Gruzdev, A.; Graves, J.P.; Lih, F.B.; Arbes, S.J., 3rd; Singh, R.; Leon, A.C.O.; Bradbury, J.A. Epoxide hydrolase 1 (EPHX1) hydrolyzes epoxyeicosanoids and impairs cardiac recovery after ischemia. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 3281–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marowsky, A.; Meyer, I.; Erismann-Ebner, K.; Pellegrini, G.; Mule, N.; Arand, M. Beyond detoxification: A role for mouse mEH in the hepatic metabolism of endogenous lipids. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 3571–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snider, N.T.; Kornilov, A.M.; Kent, U.M.; Hollenberg, P.F. Anandamide Metabolism by Human Liver and Kidney Microsomal Cytochrome P450 Enzymes to Form Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic and Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid Ethanolamides. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 321, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imig, J.D. Epoxides and Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase in Cardiovascular Physiology. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 101–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogel-Bindel, U.; Bentley, P.; Oesch, F. Endogenous role of microsomal epoxide hydrolase. Ontogenesis, induction inhibition, tissue distribution, immunological behaviour and purification of microsomal epoxide hydrolase with 16 alpha, 17 alpha-epoxyandrostene-3-one as substrate. Eur. J. Biochem. 1982, 126, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, T.; Kanehira, S. Solubilization of Epoxide Hydrolase from Liver Microsomes. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1970, 18, 1295–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oesch, F. Purification and specificity of a human microsomal epoxide hydratase. Biochem. J. 1974, 139, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Václavíková, R.; Hughes, D.J.; Souček, P. Microsomal epoxide hydrolase 1 (EPHX1): Gene, structure, function, and role in human disease. Gene 2015, 571, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fandrich, F.; Degiuli, B.; Vogel-Bindel, U.; Arand, M.; Oesch, F. Induction of rat liver microsomal epoxide hydrolase by its endogenous substrate 16α, 17α-epoxyestra-1,3,5-trien-3-ol. Xenobiotica 1995, 25, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, N.; Fujiwara, H.; Maeda, M.; Fujii, S.; Ueda, M. Epoxide hydrolase affects estrogen production in the human ovary. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 3353–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Dippe, P.; Amoui, M.; Alves, C.; Levy, D. Na(+)-dependent bile acid transport by hepatocytes is mediated by a protein similar to microsomal epoxide hydrolase. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 264, G528–G534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Von Dippe, P.; Amoui, M.; Levy, D. Bile acid transport into hepatocyte smooth endoplasmic reticulum vesicles is mediated by microsomal epoxide hydrolase, a membrane protein exhibiting two distinct topological orientations. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 20148–20155. [Google Scholar]
- Guenthner, T.M.; Cai, D.; Wallin, R. Co-purification of microsomal epoxide hydrolase with the warfarin-sensitive vitamin K1 oxide reductase of the vitamin K cycle. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 55, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithipatikom, K.; Endsley, M.P.; Pfeiffer, A.W.; Falck, J.R.; Campbell, W.B. A novel activity of microsomal epoxide hydrolase: Metabolism of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosetti, F. Arachidonic acid metabolism in brain physiology and pathology: Lessons from genetically altered mouse models. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hohmann, A.G.; Suplita, R.L.; Bolton, N.M.; Neely, M.H.; Fegley, D.; Mangieri, R.; Krey, J.F.; Walker, J.M.; Holmes, P.V.; Crystal, J.D.; et al. An endocannabinoid mechanism for stress-induced analgesia. Nature 2005, 435, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Jaimes, L.J.; Palmer, J.A. The role of endocannabinoids in pain modulation and the therapeutic potential of inhibiting their enzymatic degradation. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 1644–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, M.; Kudo, G.; Lee, Y.H.; Yang, T.J.; Gelboin, H.V.; Fernandez-Salguero, P.; Kimura, S.; Gonzalez, F.J. Targeted disruption of the microsomal epoxide hydrolase gene. Microsomal epoxide hydrolase is required for the carcinogenic activity of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 23963–23968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marowsky, A.; Haenel, K.; Bockamp, E.; Heck, R.; Rutishauser, S.; Mule, N.; Kindler, D.; Rudin, M.; Arand, M. Genetic enhancement of microsomal epoxide hydrolase improves metabolic detoxification but impairs cerebral blood flow regulation. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 3017–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Lauer, F.T.; Mitchell, L.A.; Burchiel, S.W. Microsomal Expoxide Hydrolase Is Required for 7,12-Dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA)-Induced Immunotoxicity in Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 98, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Gelboin, H.V. Stereoselective epoxidation and hydration at the K-region of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by cDNA-expressed cytochromes P450 1A1, 1A2, and epoxide hydrolase. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 15807–15813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Huang, C.; Tang, G.; Qiu, H.; Gao, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, L. Emerging role of EPHX1 in chemoresistance of acute myeloid leukemia by regurlating drug-metabolizing enzymes and apoptotic signaling. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, G.I.; Weaver, R.J.; Paterson, P.J.; Ewen, S.W.B.; Melvin, W.T.; Danny, M.B. Expression of xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in breast cancer. J. Pathol. 1993, 169, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, P.; Mürdter, T.E.; Eichelbaum, M.; Siegle, I.; Weissert, M.; Zanger, U.M. Microsomal Epoxide Hydrolase Expression as a Predictor of Tamoxifen Response in Primary Breast Cancer: A Retrospective Exploratory Study with Long-Term Follow-Up. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, P.; Behrle, E.; Zanger, U.M.; Murdter, T.; Schwarzmann, P.; Kroemer, H. Immunohistochemical assessment of human microsomal epoxide hydrolase in primary and secondary liver neoplasm: A quantitative approach. Xenobiotica 1996, 26, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, G.M.; Rane, A. Epoxide Hydrolase in Human Fetal Liver. Pharmacology 1983, 26, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, J.W.; Binnie, C.D.; Debets, R.M.; van Parys, J.A.; de Beer-Pawlikowski, N.K. Possible hazard of valpromide-carbamazepine combination therapy in epilepsy. Lancet 1984, 323, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisseau, C.; Newman, J.W.; Dowdy, D.L.; Goodrow, M.H.; Hammock, B.D. Inhibition of microsomal epoxide hydrolases by ureas, amides, and amines. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisseau, C.; Newman, J.W.; Wheelock, C.E.; Hill, T.; Morin, D.; Buckpitt, A.R.; Hammock, B.D. Development of Metabolically Stable Inhibitors of Mammalian Microsomal Epoxide Hydrolase. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, M.; Ioki, Y.; Nagata, C. Dose-dependent effect of trichloropropene oxide on benzo[a]pyrene carcinogenesis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1980, 98, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Hammock, B.D. Distribution and properties of a mammalian soluble epoxide hydrase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1980, 29, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Hammock, B.D.; Kong, W.; Zhu, Y. Homocysteine Upregulates Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase in Vascular Endothelium In Vitro and In Vivo. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ai, D.; Pang, W.; Li, N.; Xu, M.; Jones, P.D.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chiamvimonvat, N.; Shyy, J.Y.-J.; Hammock, B.D.; et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase plays an essential role in angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, C.; Stark, A.; Sandberg, M.; Ek, B.; Rask, L.; Meijer, J. Tissue specific basal expression of soluble murine epoxide hydrolase and effects of clofibrate on the mRNA levels in extrahepatic tissues and liver. Arch. Toxicol. 1995, 70, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EnayetAllah, A.E.; French, R.A.; Barber, M.; Grant, D.F. Cell-specific Subcellular Localization of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase in Human Tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2006, 54, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, G.A.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Christianson, D.W. Structure of Human Epoxide Hydrolase Reveals Mechanistic Inferences on Bifunctional Catalysis in Epoxide and Phosphate Ester Hydrolysis. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 4716–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.W.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Epoxide hydrolases: Their roles and interactions with lipid metabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 2005, 44, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imig, J.D.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase as a therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morisseau, C. Role of epoxide hydrolases in lipid metabolism. Biochimie 2013, 95, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Impact of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase and Epoxyeicosanoids on Human Health. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulu, A.; Harris, T.R.; Morisseau, C.; Miyabe, C.; Inoue, H.; Schuster, G.; Dong, H.; Iosif, A.-M.; Liu, J.-Y.; Weiss, R.H.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors in angiotensin-II-dependent hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 62, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulu, A.; Lee, K.S.S.; Miyabe, C.; Yang, J.; Hammock, B.D.; Dong, H. An Omega-3 Epoxide of Docosahexaenoic Acid Lowers Blood Pressure in Angiotensin-II–Dependent Hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 64, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, A.I.; Reutzel, M.; Hartung, N.; Franke, N.; Kutzner, L.; Schoenfeld, K.; Weylandt, K.-H.; Eckert, G.P.; Schebb, N.H. A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids enhances expression of soluble epoxide hydrolase in murine brain. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017, 133, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vicario, C.; Alcaraz-Quiles, J.; García-Alonso, V.; Rius, B.; Hwang, S.H.; Titos, E.; Lopategi, A.; Hammock, B.D.; Arroyo, V.; Clària, J. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase modulates inflammation and autophagy in obese adipose tissue and liver: Role for omega-3 epoxides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanna, V.S.; Hafez, E.A.A. Synopsis of arachidonic acid metabolism: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 11, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.R.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase: Gene structure, expression and deletion. Gene 2013, 526, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hildreth, K.; Kodani, S.D.; Hammock, B.D.; Zhao, L. Cytochrome P450-derived linoleic acid metabolites EpOMEs and DiHOMEs: A review of recent studies. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 86, 108484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Plopper, C.G.; Lakritz, J.; Storms, D.H.; Hammock, B.D. Leukotoxin-diol: A putative toxic mediator involved in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2001, 25, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghaddam, M.F.; Grant, D.F.; Cheek, J.M.; Greene, J.F.; Williamson, K.C.; Hammock, B.D. Bioactivation of leukotoxins to their toxic diols by epoxide hydrolase. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisseau, C.; Du, G.; Newman, J.W.; Hammock, B.D. Mechanism of Mammalian Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibition by Chalcone Oxide Derivatives. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 356, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisseau, C.; Goodrow, M.H.; Dowdy, D.; Zheng, J.; Greene, J.F.; Sanborn, J.R.; Hammock, B.D. Potent urea and carbamate inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8849–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Napimoga, M.H.; Rocha, E.P.; Trindade-Da-Silva, C.A.; Demasi, A.P.D.; Martinez, E.F.; Macedo, C.G.; Abdalla, H.B.; Bettaieb, A.; Haj, F.G.; Clemente-Napimoga, J.T.; et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor promotes immunomodulation to inhibit bone resorption. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade-Da-Silva, C.A.; Clemente-Napimoga, J.T.; Abdalla, H.B.; Rosa, S.M.; Ueira-Vieira, C.; Morisseau, C.; Verri, W.A.; Montalli, V.A.M.; Hammock, B.D.; Napimoga, M.H. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, TPPU, increases regulatory T cells pathway in an arthritis model. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 9074–9086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisdorf, W.C.; Xie, Q.; Zeng, X.; Xie, W.; Rajpal, N.; Hoang, B.; Burgert, M.E.; Kumar, V.; Hurle, M.R.; Rajpal, D.K.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of EPHX2 inhibition as a novel treatment for inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inceoglu, B.; Jinks, S.L.; Schmelzer, K.R.; Waite, T.; Kim, I.H.; Hammock, B.D. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase reduces LPS-induced thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in a rat model of inflammatory pain. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klocke, J.; Ulu, A.; Wu, K.; Rudolph, B.; Dragun, D.; Gollasch, M.; Schunck, W.-H.; Hammock, B.D.; Riemekasten, G.; Enghard, P. Prophylactic inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase delays onset of nephritis and ameliorates kidney damage in NZB/W F1 mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Lee, P.; Yan, C.; Gao, N.; Wang, J.-M.; Fan, X.; Yu, F.-S.X. Inhibition of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase 2 Ameliorates Diabetic Keratopathy and Impaired Wound Healing in Mouse Corneas. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elmarakby, A.A.; Faulkner, J.; Al-Shabrawey, M.; Wang, M.-H.; Maddipati, K.R.; Imig, J.D. Deletion of soluble epoxide hydrolase gene improves renal endothelial function and reduces renal inflammation and injury in streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 301, R1307–R1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhiani, M.; Quigley, J.E.; Knight, S.F.; Tasoobshirazi, S.; Moore, T.; Brands, M.W.; Hammock, B.D.; Imig, J.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase gene deletion attenuates renal injury and inflammation with DOCA-salt hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2009, 297, F740–F748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simpkins, A.N.; Rudic, R.D.; Roy, S.; Tsai, H.J.; Hammock, B.D.; Imig, J.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition modulates vascular remodeling. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 298, H795–H806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomson, S.J.; Askari, A.; Bishop-Bailey, D. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acids. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2012, 2012, 605101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinal, C.J.; Miyata, M.; Tohkin, M.; Nagata, K.; Bend, J.R.; Gonzalez, F.J. Targeted Disruption of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Reveals a Role in Blood Pressure Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 40504–40510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Yu, G.; Yuan, S.; Tan, C.; Lian, P.; Fu, L.; Hou, Q.; Xu, B.; Wang, H. Cigarette Smoke-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation and Autophagy Are Attenuated in Ephx2-Deficient Mice. Inflammation 2017, 40, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Uyeminami, D.; Dong, H.; Hammock, B.D.; Pinkerton, K.E. Use of a Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor in Smoke-Induced Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, K.R.; Pinkerton, K.E.; Watanabe, T.; Pedersen, T.L.; Ma, S.J.; Hammock, B.D. Attenuation of tobacco smoke-induced lung inflammation by treatment with a soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2186–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zarriello, S.; Tuazon, J.P.; Corey, S.; Schimmel, S.; Rajani, M.; Gorsky, A.; Incontri, D.; Hammock, B.D.; Borlongan, C.V. Humble beginnings with big goals: Small molecule soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors for treating CNS disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 172, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoopes, S.L.; Gruzdev, A.; Edin, M.L.; Graves, J.P.; Bradbury, J.A.; Flake, G.P.; Lih, F.B.; DeGraff, L.M.; Zeldin, D.C. Generation and characterization of epoxide hydrolase 3 (EPHX3)-deficient mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanashi, H.; Boeglin, W.E.; Morisseau, C.; Davis, R.W.; Sulikowski, G.A.; Hammock, B.D.; Brash, A.R. Catalytic activities of mammalian epoxide hydrolases with cis and trans fatty acid epoxides relevant to skin barrier function. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.-S.; Xing, W.; Qian, B.; Von Dippe, P.; Shneider, B.L.; Fox, V.L.; Levy, D. Inhibition of human m-epoxide hydrolase gene expression in a case of hypercholanemia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2003, 1638, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, M.I.; Abecasis, G.R.; Cardon, L.R.; Goldstein, D.B.; Little, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Hirschhorn, J.N. Genome-wide association studies for complex traits: Consensus, uncertainty and challenges. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolio, T.A.; Collins, F.S.; Cox, N.J.; Goldstein, D.B.; Hindorff, L.A.; Hunter, D.J.; McCarthy, M.I.; Ramos, E.M.; Cardon, L.R.; Chakravarti, A.; et al. Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 2009, 461, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sang, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Feng, R.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X.; Xing, Q.; et al. Quantitative Methylation Level of the EPHX1 Promoter in Peripheral Blood DNA Is Associated with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, M.; Hassett, C.; Adman, E.T.; Meijer, J.; Omiecinski, C.J. Identification and Functional Characterization of Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Genetic Polymorphisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28873–28881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przybyla-Zawislak, B.D.; Srivastava, P.K.; Vázquez-Matías, J.; Mohrenweiser, H.W.; Maxwell, J.E.; Hammock, B.D.; Bradbury, J.A.; EnayetAllah, A.E.; Zeldin, D.C.; Grant, D.F. Polymorphisms in Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, K.; Emi, M.; Ezura, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Takada, D.; Ishigami, T.; Umemura, S.; Xin, Y.; Wu, L.L.; Larrinaga-Shum, S.; et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase variant (Glu287Arg) modifies plasma total cholesterol and triglyceride phenotype in familial hypercholesterolemia: Intrafamilial association study in an eight-generation hyperlipidemic kindred. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 49, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fornage, M.; Boerwinkle, E.; Doris, P.A.; Jacobs, D.; Liu, K.; Wong, N.D. Polymorphism of the soluble epoxide hydrolase is associated with coronary artery calcification in African-American subjects: The Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) study. Circulation 2004, 109, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burdon, K.P.; Lehtinen, A.B.; Langefeld, C.D.; Carr, J.J.; Rich, S.S.; Freedman, B.I.; Herrington, D.; Bowden, D.W. Genetic analysis of the soluble epoxide hydrolase gene, EPHX2, in subclinical cardiovascular disease in the Diabetes Heart Study. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2008, 5, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohtoshi, K.; Kaneto, H.; Node, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Shiraiwa, T.; Matsuhisa, M.; Yamasaki, Y. Association of soluble epoxide hydrolase gene polymorphism with insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.R.; North, K.E.; Bray, M.S.; Fornage, M.; Seubert, J.M.; Newman, J.W.; Hammock, B.D.; Couper, D.J.; Heiss, G.; Zeldin, D.C. Genetic variation in soluble epoxide hydrolase (EPHX2) and risk of coronary heart disease: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 1640–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, I.P.; Jacks, R.; DeBarber, A.E.; Koop, D.; Mao, P.; Grant, D.F.; Alkayed, N.J. Polymorphisms in the Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Gene EPHX2 Linked to Neuronal Survival after Ischemic Injury. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 4642–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taura, K.; Yamada, H.; Naito, E.; Ariyoshi, N.; Mori Ma, M.A.; Oguri, K. Activation of microsomal epoxide hydrolase by interaction with cytochromes P450: Kinetic analysis of the association and substrate-specific activation of epoxide hydrolase function. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 402, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gautheron, J.; Jéru, I. The Multifaceted Role of Epoxide Hydrolases in Human Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010013
Gautheron J, Jéru I. The Multifaceted Role of Epoxide Hydrolases in Human Health and Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleGautheron, Jérémie, and Isabelle Jéru. 2021. "The Multifaceted Role of Epoxide Hydrolases in Human Health and Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010013
APA StyleGautheron, J., & Jéru, I. (2021). The Multifaceted Role of Epoxide Hydrolases in Human Health and Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010013



