Reprogramming and Differentiation of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
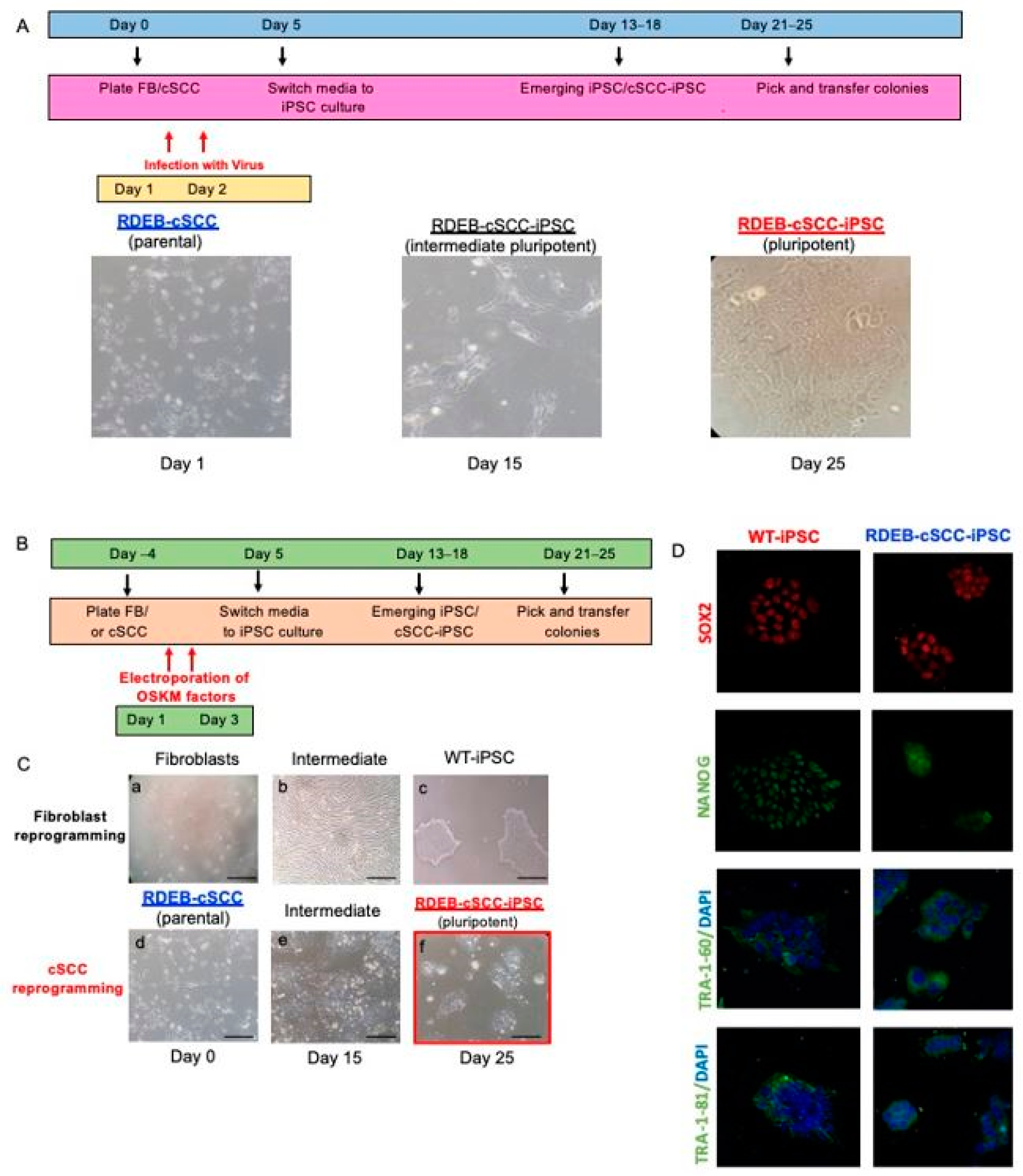
2.1. Reprogramming of RDEB-cSCC into RDEB-cSCC-iPSC
2.2. Re-Differentiation of RDEB-cSCC-iPSCs into RDEB-cSCC-iKCs
2.3. In Vitro Tumorigenicity of Reprogrammed and Re-Differentiated RDEB-cSCC-iKCs
2.4. In Vivo Tumorigenicity of Reprogrammed and Re-Differentiated RDEB-cSCC-iKCs
2.5. RDEB-cSCC and RDEB-cSCC-iKCs are Transcriptionally Different Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Episomal Plasmid-Based Reprogramming Method to Generate RDEB-cSCC-iPSCs
4.3. Human STEMCCa Lentivirus-Based Reprogramming Method to Generate RDEB-cSCC-iPSCs
4.4. Feeder-Free Direct Differentiation of SCC iPSCs to SCC-Keratinocytes (iKC)
4.5. MTS Assay
4.6. Generation of 3D Human Skin Equivalents
4.7. Engraftment of 3D Skin Constructs on Mice
4.8. Bioluminescence Analysis
4.9. Immunostaining and Imaging
4.10. Transcriptomic Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cSCC | Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma |
| DEB | Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa |
| RDEB | Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa |
| iPSC | Induced pluripotent stem cell |
| iKC | Induced keratinocyte |
| C7 | Collagen 7 |
| HSE | Human skin equivalent |
| FB | Fibroblast |
| DAVID | Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery |
References
- Fine, J.-D.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Eady, R.A.J.; Bauer, E.A.; Bauer, J.W.; Has, C.; Heagerty, A.; Hintner, H.; Hovnanian, A.; Jonkman, M.F.; et al. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: Updated recommendations on diagnosis and classification. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 1103–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Has, C.; Bauer, J.; Bodemer, C.; Bolling, M.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Diem, A.; Fine, J.-D.; Heagerty, A.; Hovnanian, A.; Marinkovich, M.; et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epsidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bardhan, A.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Fine, J.-D.; Harper, N.; Has, C.; Magin, T.M.; Marinkovich, M.P.; Marshall, J.F.; McGrath, J.A.; et al. Epidermolysis bullosa. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, R.J.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Breems, N.Y.D.; Atanasova, V.S.; Farshchian, M.; Purdom, E.; Nguyen, T.N.; Coarfa, C.; Rajapakshe, K.; Prisco, M.; et al. APOBEC mutation drives early-onset squamous cell carcinomas in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaas9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knaup, J.; Gruber, C.; Krammer, B.; Ziegler, V.; Bauer, J.; Verwanger, T. TGFβ-signaling in Squamous Cell Carcinoma Occurring in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2011, 34, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.L.; Caley, M.P.; Moore, K.; Szentpetery, Z.; Marsh, S.T.; Murrell, D.F.; Kim, M.H.; Avari, M.; McGrath, J.A.; Cerio, R.; et al. Suppression of TGFβand Angiogenesis by Type VII Collagen in Cutaneous SCC. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittapalli, V.R.; Madl, J.; Löffek, S.; Kiritsi, D.; Kern, J.S.; Römer, W.; Nyström, A.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L. Injury-Driven Stiffening of the Dermis Expedites Skin Carcinoma Progression. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyström, A.; Thriene, K.; Mittapalli, V.R.; Kern, J.S.; Kiritsi, D.; Dengjel, J.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L. Losartan ameliorates dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa and uncovers new disease mechanisms. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitenbach, J.S.; Rinnerthaler, M.; Trost, A.; Weber, M.; Klausegger, A.; Gruber, C.; Bruckner, D.; Reitsamer, H.A.; Bauer, J.W.; Breitenbach, M. Transcriptome and ultrastructural changes in dystrophic Epidermolysis bullosa resemble skin aging. Aging 2015, 7, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chacón-Solano, E.; León, C.; Díaz, F.; García-García, F.; García, M.; Escámez, M.-J.; Guerrero-Aspizua, S.; Conti, C.J.; Mencía, Á.; Martínez-Santamaría, L.; et al. Fibroblast activation and abnormal extracellular matrix remodelling as common hallmarks in three cancer-prone genodermatoses. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichorova, R.N.; Rheinwald, J.G.; Anderson, D.J. Generation of Papillomavirus-Immortalized Cell Lines from Normal Human Ectocervical, Endocervical, and Vaginal Epithelium that Maintain Expression of Tissue-Specific Differentiation Proteins1. Biol. Reprod. 1997, 57, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Vodyanik, M.A.; Smuga-Otto, K.; Antosiewicz-Bourget, J.; Frane, J.L.; Tian, S.; Nie, J.; Jonsdottir, G.A.; Ruotti, V.; Stewart, R.; et al. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Lines Derived from Human Somatic Cells. Science 2007, 318, 1917–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-L.; Chang, D.C.; Lin, C.-H.; Wu, D.T.S.; Chen, D.T.; Ying, S.-Y. Mir-302 reprograms human skin cancer cells into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state. RNA 2008, 14, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Utikal, J.; Maherali, N.; Kulalert, W.; Hochedlinger, K. Sox2 is dispensable for the reprogramming of melanocytes and melanoma cells into induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3502–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyoshi, N.; Ishii, H.; Nagai, K.-I.; Hoshino, H.; Mimori, K.; Tanaka, F.; Nagano, H.; Sekimoto, M.; Doki, Y.; Mori, M. Defined factors induce reprogramming of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carette, J.E.; Pruszak, J.; Varadarajan, M.; Blomen, V.A.; Gokhale, S.; Camargo, F.D.; Wernig, M.; Jaenisch, R.; Brummelkamp, T.R. Generation of iPSCs from cultured human malignant cells. Blood 2010, 115, 4039–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, Y.; Haga, H.; Yamada, Y. Concise review: Dedifferentiation meets cancer development: Proof of concept for epigenetic cancer. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshchehreh, R.; Totonchi, M.; Ramirez, J.C.; Torres, R.; Baharvand, H.; Aicher, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Heeschen, C. Epigenetic reprogramming of primary pancreatic cancer cells counteracts their in vivo tumourigenicity. Oncogene 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pourreyron, C.; Cox, G.; Mao, X.; Volz, A.; Baksh, N.; Wong, T.; Fassihi, H.; Arita, K.; O’Toole, E.A.; Ocampo-Candiani, J.; et al. Patients with Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Develop Squamous-Cell Carcinoma Regardless of Type VII Collagen Expression. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2438–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacków, J.; Guo, Z.; Hansen, C.; Abaci, H.E.; Doucet, Y.S.; Shin, J.U.; Hayashi, R.; DeLorenzo, D.; Kabata, Y.; Shinkuma, S.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-based targeted genome editing for correction of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa using iPS cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 26846–26852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacków, J.; Rami, A.; Hayashi, R.; Hansen, C.; Guo, Z.; DeLorenzo, D.; Pappalardo, A.; Cespedes, D.A.; Kim, A.L.; Perez-Lorenzo, R.; et al. Targeting the Jak/Signal Transducer and Activator Of Transcription 3 Pathway with Ruxolitinib in a Mouse Model of Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa–Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Zhao, R.; Doi, A.; Ng, K.; Unternaehrer, J.; Cahan, P.; Hongguang, H.; Loh, Y.-H.; Aryee, M.J.; Lensch, M.W.; et al. Donor cell type can influence the epigenome and differentiation potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oshima, N.; Yamada, Y.; Nagayama, S.; Kawada, K.; Hasegawa, S.; Okabe, H.; Sakai, Y.; Aoi, T. Induction of Cancer Stem Cell Properties in Colon Cancer Cells by Defined Factors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.-F.; Suk, K.H.; Kim, H.S.; Chang, B.; Papatsenko, D.; Zhao, R.; Yuan, Y.; Gingold, J.; Xia, W.; Darr, H.; et al. Modeling Familial Cancer with Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell 2015, 161, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramos-Mejia, V.; Fraga, M.F.; Menéndez, P. iPSCs from cancer cells: Challenges and opportunities. Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.-Y.; Shi, Y.; Chin, Y.E. Reprogramming cancer cells: Back to the future. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2247–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, M.; Kiuru, M.; Cairo, M.S.; Christiano, A.M. Generation of keratinocytes from normal and recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa-induced pluripotent stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8797–8802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, A.L.; Rubin, A.J.; Thrane, K.; Jiang, S.; Reynolds, D.L.; Meyers, R.M.; Guo, M.G.; George, B.M.; Mollbrink, A.; Bergenstråhle, J.; et al. Multimodal Analysis of Composition and Spatial Architecture in Human Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell 2020, 182, 1661–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condorelli, A.G.; Dellambra, E.; Logli, E.; Zambruno, G.; Castiglia, D. Epidermolysis Bullosa-Associated Squamous Cell Carcinoma: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atlasi, Y.; Megchelenbrink, W.; Peng, T.; Habibi, E.; Joshi, O.; Wang, S.-Y.; Wang, C.; Logie, C.; Poser, I.; Marks, H.; et al. Epigenetic modulation of a hardwired 3D chromatin landscape in two naive states of pluripotency. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrico, P.M.; Melendez, J.A. Manganese Superoxide Dismutase (Sod2) and Redox-Control of Signaling Events That Drive Metastasis. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Dai, H.; Zhou, M.; Li, M.; Singh, P.; Qiu, J.; Tsark, W.; Huang, Q.; Kernstine, K.; Zhang, X.; et al. Fen1 mutations result in autoimmunity, chronic inflammation and cancers. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abaci, H.E.; Guo, Z.; Coffman, A.; Gillette, B.; Lee, W.-H.; Sia, S.K.; Christiano, A.M. Human Skin Constructs with Spatially Controlled Vasculature Using Primary and iPSC-Derived Endothelial Cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rami, A.; Łaczmański, Ł.; Jacków-Nowicka, J.; Jacków, J. Reprogramming and Differentiation of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010245
Rami A, Łaczmański Ł, Jacków-Nowicka J, Jacków J. Reprogramming and Differentiation of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(1):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010245
Chicago/Turabian StyleRami, Avina, Łukasz Łaczmański, Jagoda Jacków-Nowicka, and Joanna Jacków. 2021. "Reprogramming and Differentiation of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 1: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010245
APA StyleRami, A., Łaczmański, Ł., Jacków-Nowicka, J., & Jacków, J. (2021). Reprogramming and Differentiation of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010245




