Melittin Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity and Kills KM-H2 and L-428 Hodgkin Lymphoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
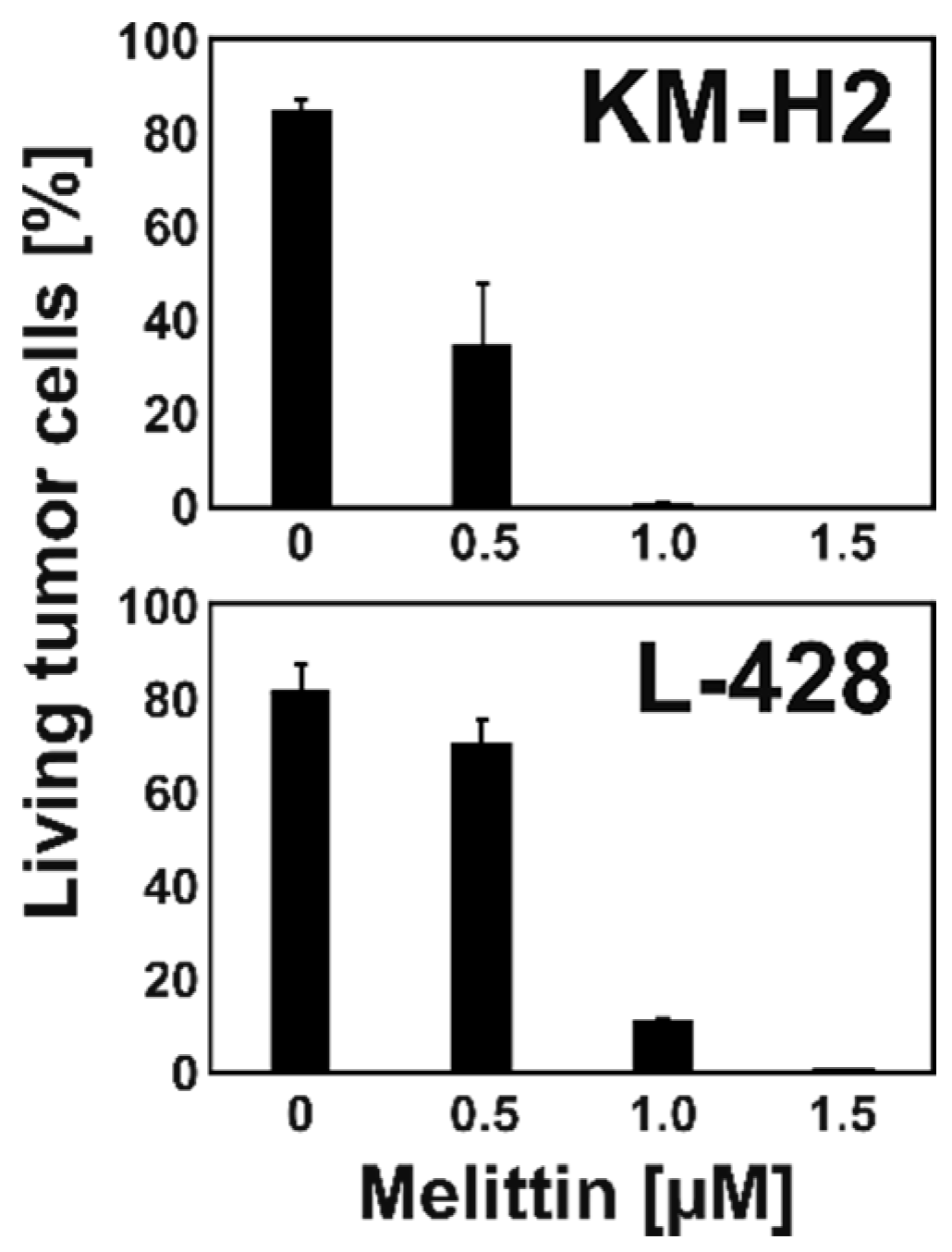
2.1. Melittin is Toxic for KM-H2 and L-428 HL Cells
2.2. Melittin Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity of Chemo-Resistant L-428 Cells
2.3. Melittin Has no Influence on ABC Transporter Activity of KM-H2 and L-428 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Cell Culture
4.2. Rh123 Staining and Flow Cytometry
4.3. Melittin and Cisplatin Treatment
4.4. Co-Culture Experiments
4.5. DNA Microarray Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | ATP binding cassette |
| HL | Hodgkin Lymphoma |
| MEL | Melittin |
| NFKB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B-cells |
| Rh123 | Rhodamin-123 |
References
- Piris, M.A.; Medeiros, L.J.; Chang, K.C. Hodgkin lymphoma: A review of pathological features and recent advances in pathogenesis. Pathology 2020, 52, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bienz, M.; Ramdani, S.; Knecht, H. Molecular pathogenesis of Hodgkin lymphoma: Past, present, future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentsch, J. Zur biologischen Aktivität des Bienengiftes Melittin. Z. Nat. B 1969, 24, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufson, R.A.; Laskin, J.D.; Fisher, P.B.; Weinstein, I.B. Melittin shares certain cellular effects with phorbol ester tumour promoters. Nature 1997, 280, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, P.B.; Dorsch-Häsler, K.; Weinstein, I.B.; Ginsberg, H.S. Interactions between initiating chemical carcinogens, tumor promoters, and adenovirus in cell transformation. Teratog. Carcinog. Mutagen. 1980, 1, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seif, R. Factors which disorganize microtubules or microfilaments increase the frequency of cell transformation by polyoma virus. J. Virol. 1980, 36, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozengurt, E. Stimulation of Na influx, Na-K pump activity and DNA synthesis in quiescent cultured cells. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1980, 19, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallorga, P.; Tallman, J.F.; Henneberry, R.C.; Hirata, F.; Strittmatter, W.T.; Axelrod, J. Mepacrine blocks beta-adrenergic agonist-induced desensitization in astrocytoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vento, R.; D′Alessandro, N.; Giuliano, M.; Lauricella, M.; Carabillò, M.; Tesoriere, G. Induction of apoptosis by arachidonic acid in human retinoblastoma Y79 cells: Involvement of oxidative stress. Exp. Eye Res. 2000, 70, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolf, G.R.; Swetly, P. Tumour-promoting phorbol esters inhibit DNA synthesis and enhance virus-induced interferon production in a human lymphoma cell line. J. Gen. Virol. 1980, 51, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hait, W.N.; Grais, L.; Benz, C.; Cadman, E.C. Inhibition of growth of leukemic cells by inhibitors of calmodulin: Phenothiazines and melittin. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 1985, 14, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazo, J.S.; Hait, W.N.; Kennedy, K.A.; Braun, I.D.; Meandzija, B. Enhanced bleomycin-induced DNA damage and cytotoxicity with calmodulin antagonists. Mol. Pharm. 1985, 27, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.L.; Hai, W.N. Inhibition of growth of C6 astrocytoma cells by inhibitors of calmodulin. Life Sci. 1985, 36, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Miyauchi, M.; Nagata, I. Inhibition of human ovarian cancer cell proliferation by calmodulin inhibitors and the possible mechanism. Gynecol. Oncol. 1989, 35, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, M.S.; Howatt, W.J.; Bloodworth, L.; Anderson, V.A.; Morgan, B.P.; Glennie, M.J. Complement mediated cell death is associated with DNA fragmentation. Cell Death Differ. 2000, 7, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazo, J.S.; Chen, D.L.; Gallicchio, V.S.; Hait, W.N. Increased lethality of calmodulin antagonists and bleomycin to human bone marrow and bleomycin-resistant malignant cells. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 2236–2240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Killion, J.J.; Dunn, J.D. Differential cytolysis of murine spleen, bone-marrow and leukemia cells by melittin reveals differences in membrane topography. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 139, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.G.; Tayeh, I.; Israel, L.; Castagna, M. Different susceptibility of lung cell lines to inhibitors of tumor promotion and inducers of differentiation. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 1991, 5, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Holle, L.; Song, W.; Holle, E.; Wei, Y.; Wagner, T.; Yu, X. A matrix metalloproteinase 2 cleavable melittin/avidin conjugate specifically targets tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 2003, 22, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.D.; Weston, K.M.; Longhurst, T.J.; Lilley, G.; Rivett, D.E.; Hudson, J.; Raison, R.L. Antigen binding and cytotoxic properties of a recombinant immunotoxin incorporating the lytic peptide, melittin. Immunotechnology 1996, 2, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werkmeister, J.A.; Hewish, D.R.; Kirkpatrick, A.; Rivett, D.E. Sequence requirements for the activity of membrane-active peptides. J. Pept. Res. 2002, 60, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, P.J.; Hewish, D.; Carter, T.; Sterling-Levis, K.; Ow, K.; Hattarki, M.; Doughty, L.; Guthrie, R.; Shapira, D.; Molloy, P.L.; et al. Cytotoxic properties of immunoconjugates containing melittin-like peptide 101 against prostate cancer: In vitro and in vivo studies. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2004, 53, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, T.; Sterling-Levis, K.; Ow, K.; Doughty, L.; Hattarki, M.; Shapira, D.; Hewish, D.; Kortt, A.A.; Russell, P.J. Biodistributions of intact monoclonal antibodies and fragments of BLCA-38, a new prostate cancer directed antibody. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2004, 53, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawronska, B.; Leuschner, C.; Enright, F.M.; Hansel, W. Effects of a lytic peptide conjugated to beta HCG on ovarian cancer: Studies in vitro and in vivo. Gynecol. Oncol. 2002, 85, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuschner, C.; Enright, F.M.; Gawronska, B.; Hansel, W. Membrane disrupting lytic peptide conjugates destroy hormone dependent and independent breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2003, 78, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodek, G.; Rahman, N.A.; Zaleska, M.; Soliymani, R.; Lankinen, H.; Hansel, W.; Huhtaniemi, I.; Ziecik, A.J. A novel approach of targeted ablation of mammary carcinoma cells through luteinizing hormone receptors using Hecate-CGbeta conjugate. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2003, 79, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaleska, M.; Bodek, G.; Jana, B.; Hansel, W.; Ziecik, A.J. Targeted destruction of normal and cancer cells through lutropin/choriogonadotropin receptors using Hecate-betaCG conjugate. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2003, 111, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuschner, C.; Enright, F.M.; Gawronska-Kozak, B.; Hansel, W. Human prostate cancer cells and xenografts are targeted and destroyed through luteinizing hormone releasing hormone receptors. Prostate 2003, 56, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaleska, M.; Waclawik, A.; Bodek, G.; Zezula-Szpyra, A.; Li, X.; Janowski, T.; Hansel, W.H.; Rahman, N.A.; Ziecik, A.J. Growth repression in diethylstilbestrol/dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced rat mammary gland tumor using Hecate-CGbeta conjugate. Exp. Biol. Med. 2004, 229, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, C.S.; Leuschner, C.; Doomes, E.E.; Henry, L.; Juban, M.; Hormes, J. Efficacy of lytic peptide-bound magnetite nanoparticles in destroying breast cancer cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2004, 4, 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Bodek, G.; Kowalczyk, A.; Waclawik, A.; Huhtaniemi, I.; Ziecik, A.J. Targeted ablation of prostate carcinoma cells through LH receptor using Hecate-CGbeta conjugate: Functional characteristic and molecular mechanism of cell death pathway. Exp. Biol. Med. 2005, 230, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodek, G.; Vierre, S.; Rivero-Müller, A.; Huhtaniemi, I.; Ziecik, A.J.; Rahman, N.A. A novel targeted therapy of Leydig and granulosa cell tumors through the luteinizing hormone receptor using a hecate-chorionic gonadotropin beta conjugate in transgenic mice. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansel, W.; Enright, F.; Leuschner, C. Destruction of breast cancers and their metastases by lytic peptide conjugates in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 260–262, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.V. Melittin resistance: A counterselection for ras transformation. Oncogene 1992, 7, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.V. Melittin-induced hyperactivation of phospholipase A2 activity and calcium influx in ras-transformed cells. Oncogene 1993, 8, 939–947. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, S.T.; Cheng, H.H.; Huang, C.J.; Chang, H.C.; Chi, C.C.; Su, H.H.; Hsu, S.S.; Wang, J.L.; Chen, I.S.; Liu, S.I.; et al. Phospholipase A2-independent Ca2+ entry and subsequent apoptosis induced by melittin in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, Y.; Ciobotariu, A.; Jones, J.; Morgan, B.P.; Fishelson, Z. Complement membrane attack complex, perforin, and bacterial exotoxins induce in K562 cells calcium-dependent cross-protection from lysis. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar]
- Winder, D.; Günzburg, W.H.; Erfle, V.; Salmons, B. Expression of antimicrobial peptides has an antitumour effect in human cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 26, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.Q.; Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, D.Z.; Huang, X.Q.; Gu, W.; Li, S.X. Inhibitory effect of recombinant adenovirus carrying melittin gene on hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gu, W.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.Q.; Han, K.Q.; Ling, C.Q. Growth arrest and apoptosis of the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line BEL-7402 induced by melittin. Onkologie 2006, 29, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Jiang, X.R.; Newland, A.C.; Kelsey, S.M. Failure to activate cytosolic phospholipase A2 causes TNF resistance in human leukemic cells. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 5929–5935. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saini, S.S.; Chopra, A.K.; Peterson, J.W. Melittin activates endogenous phospholipase D during cytolysis of human monocytic leukemia cells. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1605–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Park, H.S.; Lee, S.J.; Choi, M.U. Melittin exerts multiple effects on the release of free fatty acids from L1210 cells: Lack of selective activation of phospholipase A2 by melittin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 389, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, D.O.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, N.D.; Lee, C.; Kim, G.Y. Melittin induces Bcl-2 and caspase-3-dependent apoptosis through downregulation of Akt phosphorylation in human leukemic U937 cells. Toxicon 2008, 51, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yu, M.; He, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wang, F.; Song, C.; Sun, S.; Ling, C.; Xu, Z. Melittin prevents liver cancer cell metastasis through inhibition of the Rac1-dependent pathway. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, N.; Yang, M.; Li, B.; Lü, X.; Cao, X.; Ling, C. Melittin, a major component of bee venom, sensitizes human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis by activating CaMKII-TAK1-JNK/p38 and inhibiting IkappaBalpha kinase-NFkappaB. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3804–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, H.J.; Jeong, Y.J.; Park, K.K.; Park, Y.Y.; Chung, I.K.; Lee, K.G.; Yeo, J.H.; Han, S.M.; Bae, Y.S.; Chang, Y.C. Bee venom suppresses PMA-mediated MMP-9 gene activation via JNK/p38 and NF-kappaB-dependent mechanisms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Jeong, Y.J.; Park, K.K.; Cho, H.J.; Chung, I.K.; Min, K.S.; Kim, M.; Lee, K.G.; Yeo, J.H.; Park, K.K.; et al. Melittin suppresses PMA-induced tumor cell invasion by inhibiting NF-kappaB and AP-1-dependent MMP-9 expression. Mol. Cells 2010, 29, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, M.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Z.; Lv, Y.; Wu, R. MEL-pep, an analog of melittin, disrupts cell membranes and reverses 5-fluorouracil resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 101, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staege, M.S.; Banning-Eichenseer, U.; Weissflog, G.; Volkmer, I.; Burdach, S.; Richter, G.; Mauz-Körholz, C.; Föll, J.; Körholz, D. Gene expression profiles of Hodgkin’s lymphoma cell lines with different sensitivity to cytotoxic drugs. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, W.G.; de Brito, J.C.M.; Cardoso, V.N.; Fernandes, S.O.A. In-depth characterization of antibacterial activity of melittin against Staphylococcus aureus and use in a model of non-surgical MRSA-infected skin wounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 156, 105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memariani, H.; Memariani, M.; Moravvej, H.; Shahidi-Dadras, M. Melittin: A venom-derived peptide with promising anti-viral properties. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarneri, C.; Bevelacqua, V.; Polesel, J.; Falzone, L.; Cannavò, P.S.; Spandidos, D.A.; Malaponte, G.; Libra, M. NF κB inhibition is associated with OPN/MMP 9 downregulation in cutaneous melanoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karin, M. NF-kappaB as a critical link between inflammation and cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000141. [Google Scholar]
- An, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, W.H.; Gwon, M.G.; Gu, H.M.; Jeon, M.J.; Han, S.M.; Pak, S.C.; Lee, C.K.; Park, I.S.; et al. Therapeutic effects of bee venom and its major component, melittin, on atopic dermatitis in vivo and in vitro. Br. J. Pharm. 2018, 175, 4310–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmedy, O.A.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Salem, H.H.; Kandil, E.A. Antiulcerogenic effect of melittin via mitigating TLR4/TRAF6 mediated NF-kappaB and p38MAPK pathways in acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 331, 109276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, M.; Niu, H.; Liu, J.; Ruilian, M.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, J.; Dong, Y.; et al. Astragalus polysaccharide from Astragalus Melittin ameliorates inflammation via suppressing the activation of TLR-4/NF-kappaB p65 signal pathway and protects mice from CVB3-induced virus myocarditis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Ahmadi, F.; Parivar, K.; Nabiuni, M.; Haghighi, S.; Imani, S.; Afrouzi, H. Effect of honey bee venom on lewis rats with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, a model for multiple sclerosis. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 11, 671–678. [Google Scholar]
- Bogacki, M.; Enright, F.M.; Todd, W.J.; Hansel, W. Immune response to lytic peptides conjugated to a betaCG fragment in treated BALB/C mice. Reprod. Biol. 2008, 8, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepstra, A.; van Imhoff, G.W.; Karim-Kos, H.E.; van den Berg, A.; te Meerman, G.J.; Niens, M.; Nolte, I.M.; Bastiaannet, E.; Schaapveld, M.; Vellenga, E.; et al. HLA class II expression by Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells is an independent prognostic factor in classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 3101–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.R.; Monti, S.; Rodig, S.J.; Juszczynski, P.; Currie, T.; O’Donnell, E.; Chapuy, B.; Takeyama, K.; Neuberg, D.; Golub, T.R.; et al. Integrative analysis reveals selective 9p24.1 amplification, increased PD-1 ligand expression, and further induction via JAK2 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2010, 116, 3268–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.; Diefenbach, C.S. Advances in therapy for relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staege, M.S. A multi-component model of Hodgkin’s lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, L.; Dreyer, J.H.; Hartmann, D.; Barros, M.H.M.; Büttner-Herold, M.; Grittner, U.; Niedobitek, G. Tumor-associated macrophages in classical Hodgkin lymphoma: Hormetic relationship to outcome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, M.J.; Krasovskis, E.; Sutton, V.R.; Johnstone, R.W. The drug efflux protein, P-glycoprotein, additionally protects drug-resistant tumor cells from multiple forms of caspase-dependent apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7024–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibalová, L.; Sereš, M.; Rusnák, A.; Ditte, P.; Labudová, M.; Uhrík, B.; Pastorek, J.; Sedlák, J.; Breier, A.; Sulová, Z. P-glycoprotein depresses cisplatin sensitivity in L1210 cells by inhibiting cisplatin-induced caspase-3 activation. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 435–444. [Google Scholar]
- Schlaifer, D.; Brousset, P.; Attal, M.; Voigt, J.J.; Laurent, G.; Delsol, G. Immunohistochemical detection of multidrug resistance associated P-glycoprotein in stromal cells of malignant lymphomas. Nouv. Rev. Fr. Hematol. 1990, 32, 365–367. [Google Scholar]
- Mhaidat, N.M.; Alshogran, O.Y.; Khabour, O.F.; Alzoubi, K.H.; Matalka, I.I.; Haddadin, W.J.; Mahasneh, I.O.; Aldaher, A.N. Multi-drug resistance 1 genetic polymorphism and prediction of chemotherapy response in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stuhlmeier, K.M. Apis mellifera venom and melittin block neither NF-kappa B-p50-DNA interactions nor the activation of NF-kappa B, instead they activate the transcription of proinflammatory genes and the release of reactive oxygen intermediates. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonezi, S.; Tusiimire, J.; Wallace, J.; Dufton, M.J.; Parkinson, J.A.; Young, L.C.; Clements, C.J.; Park, J.K.; Jeon, J.W.; Ferro, V.A.; et al. Metabolomic profiling of the synergistic effects of melittin in combination with cisplatin on ovarian cancer cells. Metabolites 2017, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perry, J.M.; Tao, F.; Roy, A.; Lin, T.; He, X.C.; Chen, S.; Lu, X.; Nemechek, J.; Ruan, L.; Yu, X.; et al. Overcoming Wnt-β-catenin dependent anticancer therapy resistance in leukaemia stem cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffrey, P.B.; Frenkel, G.D.; McAndrew, K.L.; Marks, K. A model of the development of cisplatin resistance in human small cell lung cancer xenografts. Vivo 2016, 30, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fonatsch, C.; Diehl, V.; Schaadt, M.; Burrichter, H.; Kirchner, H.H. Cytogenetic investigations in Hodgkin’s disease: I. Involvement of specific chromosomes in marker formation. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1986, 20, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamesaki, H.; Fukuhara, S.; Tatsumi, E.; Uchino, H.; Yamabe, H.; Miwa, H.; Shirakawa, S.; Hatanaka, M.; Honjo, T. Cytochemical, immunologic, chromosomal, and molecular genetic analysis of a novel cell line derived from Hodgkin’s disease. Blood 1986, 68, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foell, J.L.; Volkmer, I.; Giersberg, C.; Kornhuber, M.; Horneff, G.; Staege, M.S. Loss of detectability of Charcot-Leyden crystal protein transcripts in blood cells after treatment with dimethyl sulfoxide. J. Immunol. Methods 2008, 339, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kreinest, T.; Volkmer, I.; Staege, M.S. Melittin Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity and Kills KM-H2 and L-428 Hodgkin Lymphoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010343
Kreinest T, Volkmer I, Staege MS. Melittin Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity and Kills KM-H2 and L-428 Hodgkin Lymphoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(1):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010343
Chicago/Turabian StyleKreinest, Teresa, Ines Volkmer, and Martin S. Staege. 2021. "Melittin Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity and Kills KM-H2 and L-428 Hodgkin Lymphoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 1: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010343
APA StyleKreinest, T., Volkmer, I., & Staege, M. S. (2021). Melittin Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity and Kills KM-H2 and L-428 Hodgkin Lymphoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010343




