The Bark Beetle Dendroctonus rhizophagus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) Has Digestive Capacity to Degrade Complex Substrates: Functional Characterization and Heterologous Expression of an ?-Amylase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
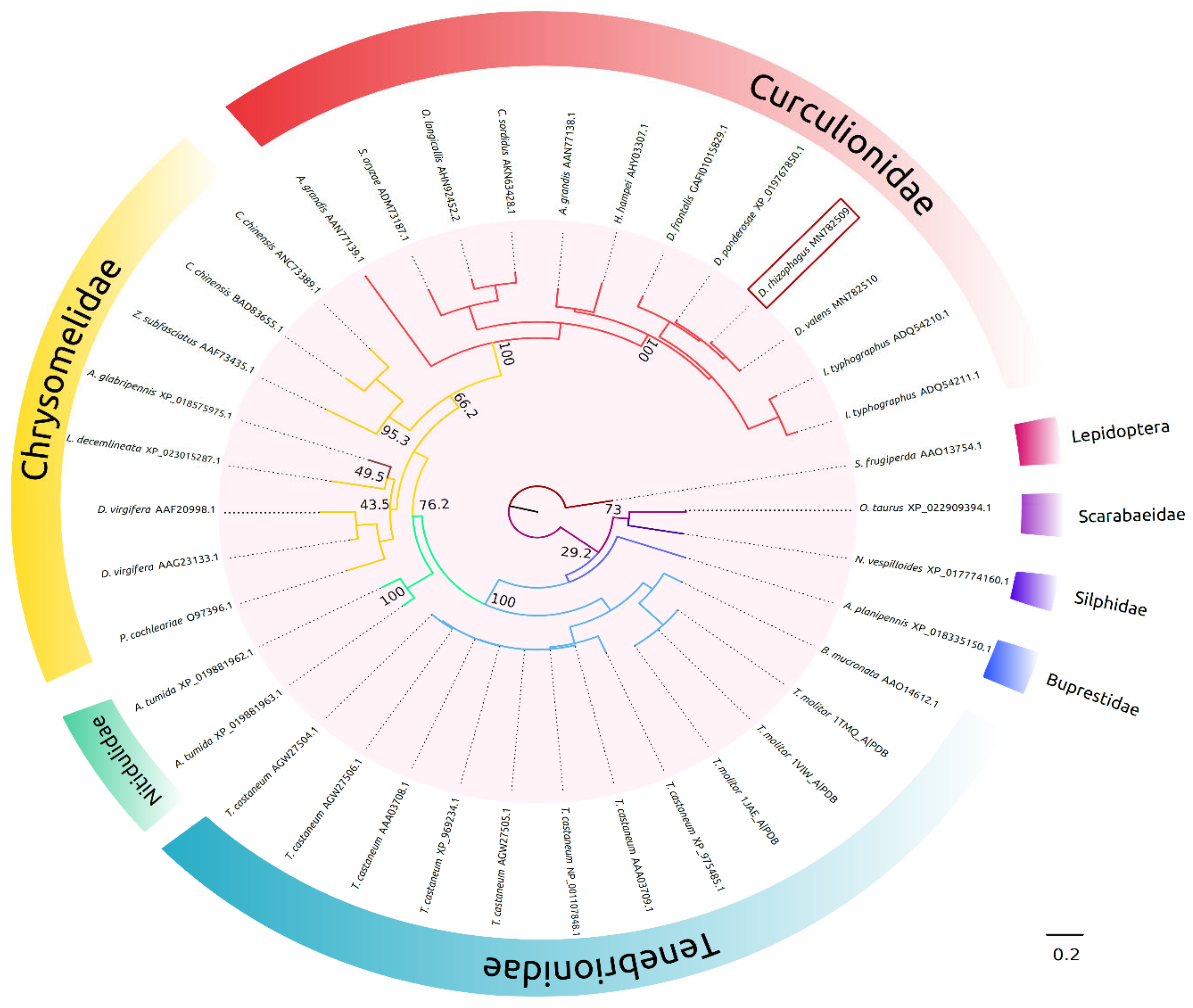
2.1. In Silico Molecular Characterization
2.2. Assays of Functional Activity
2.3. RT-qPCR Expression of AmyDr
2.4. Expression of AmyDr Recombinant Enzyme
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insects
4.2. DNA Cloning, Sequencing, and Full-Length Sequence Analyses
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.4. Molecular Modelling and Docking
4.5. Amylolytic Activity and Peptide Identification
4.6. RT-qPCR
4.7. Statistical Analysis
4.8. Expression of Recombinant AmyDr
4.9. Preparation of Amylase Crude Extract
4.10. Protein Electrophoresis
4.11. Enzyme Assay
4.12. Effect of Metal and Non-Metal Anions on Enzyme Activity
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| L5 | Fifth-instar larvae |
| PU | Pupa |
| PI | Pre-imago |
| AD RT-qPCR GAPDH AIC BIC PMSF PIC DTT SDS-PAGE TMA TFA NTCs | Pre-emergent adult Quantitative real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Akaike information criteria Bayesian information criteria Phenyl-methyl-sulfonyl-fluoride Protease inhibitor cocktail Dithiothreitol Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Tenebrio molitor amylase Trifluoroacetic acid Unintended amplification products |
References
- Raffa, K.F.; Gregoire, J.C.; Lindgren, B.S. Natural history and ecology of bark beetles. In Bark Beetles Biology and Ecology of Native and Invasive Species; Vega, F.E., Hofstetter, R.W., Eds.; Elsevier/Academic Press: London, UK, 2015; pp. 1–40. ISBN 9780124171565/9780124171732. [Google Scholar]
- Raffa, K.F.; Aukema, B.H.; Bentz, B.J.; Carroll, A.L.; Hicke, J.A.; Turner, M.G.; Romme, H.W. Cross-scale drivers of natural disturbances prone to anthropogenic amplification: The dynamics of bark beetle eruptions. Bioscience 2008, 58, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bentz, B.J.; Régnière, J.; Fettig, C.J.; Hansen, E.M.; Hayes, J.L.; Hicke, J.A.; Kelsey, R.G.; Negrón, J.F.; Seybold, S.J. Climate change and bark beetles of the western United States and Canada: Direct and indirect effects. BioScience 2010, 60, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Moreno, Y.; Vargas, C.F.; Zúñga, G.; Víctor, J.; Ager, A.; Hayes, J.L. Atlas de distribución geográfica de los descortezadores del género Dendroctonus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) en México/Atlas of the Geographic Distribution of Bark Beetles of the Genus Dendroctonus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) in Mexico; Instituto Politécnico Nacional-Comisión Nacional Forestal México: Mexico City, Mexico, 2010; pp. 1–90.
- Morales-Jiménez, J.; Zúñiga, G.; Villa-Tanaca, L.; Hernández-Rodríguez, C. Bacterial community and nitrogen fixation in the red turpentine beetle, Dendroctonus valens LeConte (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Microb. Ecol. 2009, 58, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Jiménez, J.; Zúñiga, G.; Ramírez-Saad, H.C.; Hernández-Rodríguez, C. Gut-associated bacteria throughout the life cycle of the bark beetle Dendroctonus rhizphagous Thomas and Bright (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) and their cellulytic activities. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Jiménez, J.; Vera-Ponce de León, A.; García-Domínguez, A.; Martínez-Romero, E.; Zúñiga, G.; Hernández-Rodríguez, C. Nitrogen-fixing and uricolytic bacteria associated with the gut of Dendroctonus rhizophagus and Dendroctonus valens (Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones-Roblero, C.I.; Hernández-García, J.A.; González-Escobedo, R.; Soto-Robles, L.V.; Rivera-Orduña, F.N.; Zúñiga, G. Structure and dynamics of the gut bacterial microbiota of the bark beetle, Dendroctonus rhizophagus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) across their life stages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, A.A.; Bergeron, A.; Constant, P.; Buffet, J.P.; Déziel, E.; Guertin, C. Surveying the endomicrobiome and ectomicrobiome of bark beetles: The case of Dendroctonus simplex. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-García, J.A.; Gonzalez-Escobedo, R.; Briones-Roblero, C.I.; Cano-Ramírez, C.; Rivera-Orduña, F.N.; Zúñiga, G. Gut bacterial communities of Dendroctonus valens and D. mexicanus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae): A metagenomic analysis across different geographical locations in Mexico. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Six, D.L.; Bracewell, R. Dendroctonus. In Bark Beetles; Vega, F.E., Hofstetter, R.W., Eds.; Elsevier/Academic Press: London, UK, 2015; pp. 305–350. ISBN 9780124171565/9780124171732. [Google Scholar]
- Briones-Roblero, C.I.; Rodríguez-Díaz, R.; Santiago-Cruz, J.A.; Zúñiga, G.; Rivera-Orduña, F.N. Degradation capacities of bacteria and yeasts isolated from the gut of Dendroctonus rhizophagus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Folia Microbiol. 2017, 62, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Ramírez, C.; Santiago-Hernández, A.; Rivera-Orduña, F.N.; García-Huante, Y.; Zúñiga, G.; Hidalgo-Lara, M.E. Expression, purification and characterization of an endoglucanase from Serratia proteamaculans CDBB-1961, isolated from the gut of Dendroctonus adjunctus (Coleoptera: Scolytinae). AMB Express 2016, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boone, C.K.; Keefover-Ring, K.; Mapes, A.C.; Adams, A.S.; Bohlmann, J.; Kenneth, F.R. Bacteria associated with a tree-killing insect reduce concentrations of plant defense compounds. J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 9, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Lou, Q.; Cheng, C.; Lu, M.; Sun, J. Gut-associated bacteria of Dendroctonus valens and their involvement in verbenone production. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.T.; Lu, M.; Sun, J.H. Invasive bark beetle-associated microbes degrade a host defensive monoterpene. Insect Sci. 2016, 23, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noronha, H.; Silva, A.; Dai, Z.; Gallusci, P.; Rombolà, A.D.; Delrot, S.; Gerós, H. A molecular perspective on starch metabolism in woody tissues. Planta 2018, 248, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gott, B.; Barton, H.; Samuel, D.; Torrence, R. Biology of starch. In Ancient Starch Research; Torrence, R., Barton, H., Eds.; Left Coast Press Inc.: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2006; pp. 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Robyt, J.F. Starch: Structure, Properties, Chemistry, and Enzymology. In Glycoscience: Chemistry and Chemical Biology; Fraser-Reid, B.O., Tatsuta, K., Thiem, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 1437–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Gigras, P.; Mohapatra, H.; Goswami, V.K.; Chauhan, B. Microbial α-amylases: A biotechnological perspective. Process Biochem. 2003, 38, 1599–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaei, A.; Ghanbarzadeh, M.; Monsef, F. Biochemical features and kinetic properties of α-amylases from marine organisms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 83, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Chakravarty, S. Amylases. In Enzymes in Human and Animal Nutrition: Principles and Perspectives; Nunes, C.S., Kumar, V., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 163–180. ISBN 0128054190. [Google Scholar]
- Da Lage, J.L. The amylases of insects. Int. J. Insect Sci. 2018, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, Ch.; Leitinger, R.; Simsek, Z.; Schreiber, J.D.; Führer, E. Allozyme variation among nine Austrian Ips typographus L. (Col. Scolytidae) populations. J. Appl. Ent. 1992, 114, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viktorinova, I.; Kucerova, L.; Bohmova, M.; Henry, I.; Jindra, M.; Dolezal, P.; Zurovcova, M.; Zurovec, M. Characterization of two closely related α-amylase paralogs in the bark beetle, Ips typographus (L.). Arch. Insect Biochem. 2011, 77, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martínez, G.; Wagner, M.R. Host preference and attack pattern of Dendroctonus rhizophagus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae): A bark beetle specialist on pine regeneration. Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salinas-Moreno, Y.; Ager, A.; Vargas, C.F.; Hayes, J.L.; Zúñiga, G. Determining the vulnerability of Mexican pine forests to bark beetles of the genus Dendroctonus Erichson (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Forest Ecol. Manag. 2010, 260, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Neto, O.B.; Batista, J.A.; Rigden, D.J.; Franco, O.L.; Falcão, R.; Fragoso, R.R.; Mello, L.V.; dos Santos, R.C.; Grossi-de-Sá, M.F. Molecular cloning of α-amylases from cotton boll weevil, Anthonomus grandis and structural relations to plant inhibitors: An approach to insect resistance. J. Protein Chem. 2003, 22, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darvishzadeh, A.; Bandani, A.R.; Karimi, J.; Gholamhossein, T. Biochemical characterisation of digestive α-amylase of Red Palm Weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Oliver, 1790) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Arch. Phytopathol. Pflanzenschutz 2012, 45, 2132–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Banda, V.; Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Ciudad de México, Ciudad de México, México. Personal communication, 2019.
- Da Lage, J.L.; Van Wormhoudt, A.; Cariou, M.L. Diversity and evolution of the alpha-amylase genes in Animals. Biologia (Bratisl) 2002, 57, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Da Lage, J.L.; Danchin, E.G.J.; Casane, D. Where do animal α-amylases come from? An interkingdom trip. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 3927–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.M.; Wang, M.H.; Rhee, H.I. A novel α-glucosidase inhibitor from pine bark. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstenberg-Hägg, J.; Zagrobelny, M.; Bak, S. Plant defence against insect herbivores. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10242–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aghajari, N.; Haser, R.; Feller, G.; Gerday, C. Crystal structures of the psychrophilic α-amylase from Alteromonas haloplanctis in its native form and complexed with an inhibitor. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aghajari, N.; Feller, G.; Gerday, C.; Haser, R. Structural basis of alpha-amylase activation by chloride. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, N. The regulation of sodium, potassium and chloride in an aphid subjected to ionic stress. J. Exp. Biol. 1980, 87, 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, M.P.; Wilkens, R.T.; Ruel, J.J.; Lombardero, M.J.; Vallery, E. Nitrogen budgets of phloem-feeding bark beetles with and without symbiotic fungi. Ecology 2000, 81, 2198–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.P.; Terra, W.R.; Xavier-Filho, J.; Grossi de Sá, M.F.; Lopes, A.R.; Pontes, E.G. Digestion in larvae of Callosobruchus maculatus and Zabrotes subfasciatus (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) with emphasis on α-amylases and oligosaccharidases. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 29, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, E.; Cisneros, R.; Zúñiga, G.; Uria-Galicia, E. Comparative anatomical and histological study of the alimentary canal of Dendroctonus parallelocollis, D. rhizophagus and D. valens (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1998, 91, 479–487. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, E.; Cisneros, R.; Zúñiga, G. Comparative anatomical and histological study of the alimentary canal of the Dendroctonus frontalis (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) complex. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2000, 93, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, E.; Cisneros, R.; Arciniega, O.; Sánchez, L.; Zúñiga, G. Comparative anatomical and histological study of the alimentary canal of the Dendroctonus terebrans, D. micans, D. rufipennis, D. pseudotsugae pseudotsugae and D. ponderosae (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2003, 96, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, O.L.; Rigden, D.J.; Melo, F.R.; Grossi-de-Sá, M.F. Plant α-amylase inhibitors and their interaction with insect α-amylases. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichersky, E.; Raguso, R.A. Why do plants produce so many terpenoid compounds? New Phytol. 2018, 220, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, T.T. Carbohydrate sources and sinks in woody plants. Bot. Rev. 1992, 58, 107–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibrián-Tovar, D.; Méndez-Montiel, J.T.; Campos-Bolaños, R.; Yates, H.O., III; Flores-Lara, J. Insectos Forestales de México/Forests Insects of México COFAN/NAFC; Universidad Autónoma Chapingo: Texcoco, Mexico, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.D.; Watanabe, C.K. GMAP: A genomic mapping and alignment program for mRNA and EST sequences. Bioinformatic 2005, 21, 1859–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 35, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, S.Q.; Gascuel, O. An improved general amino acid replacement matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eswar, N.; Webb, B.; Marti-Renom, M.A.; Madhusudhan, M.S.; Eramian, D.; Shen, M.Y.; Pipeper, U.; Sali, A. Comparative protein structure modeling using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics 2006, 50, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strobl, S.; Gomis-Rüth, F.X.; Maskos, K.; Frank, G.; Huber, R.; Glockshuber, R. The α-amylase from the yellow meal worm: Complete primary structure, crystallization, and preliminary X-ray analysis. FEBS Lett. 1998, 409, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenberg, D.; Lüthy, R.; Bowie, J.U. VERIFY3D: Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Methods Enzymol. 1997, 277, 396–404. [Google Scholar]
- Colovos, C.; Yeates, T.O. Verification of protein structures: Patterns of nonbonded atomic interactions. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooft, R.W.W.; Sander, C.; Vriend, G. Verification of protein structures: Side-chain planarity. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1996, 29, 714–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, C.; Ramachandran, G.N. Stereochemical criteria for polypeptide and protein chain conformations. II. Allowed conformations for a pair of peptide units. Biophys. J. 1965, 5, 909–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gouet, P.; Robert, X.; Courcelle, E. ESPript/ENDscript: Extracting and rendering sequence and 3D information from atomic structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3320–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger, L.L.C. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.0.; Schrödinger Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision B.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Autodock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 16, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goodford, P.J. A computational procedure for determining energetically favorable binding sites on biologically important macromolecules. J. Med. Chem. 1985, 28, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havli, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soto-Robles, L.V.; López, M.F.; Torres-Banda, V.; Cano-Ramírez, C.; Obregón-Molina, G.; Zúñiga, G. The Bark Beetle Dendroctonus rhizophagus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) Has Digestive Capacity to Degrade Complex Substrates: Functional Characterization and Heterologous Expression of an ?-Amylase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010036
Soto-Robles LV, López MF, Torres-Banda V, Cano-Ramírez C, Obregón-Molina G, Zúñiga G. The Bark Beetle Dendroctonus rhizophagus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) Has Digestive Capacity to Degrade Complex Substrates: Functional Characterization and Heterologous Expression of an ?-Amylase. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoto-Robles, L. Viridiana, María Fernanda López, Verónica Torres-Banda, Claudia Cano-Ramírez, Gabriel Obregón-Molina, and Gerardo Zúñiga. 2021. "The Bark Beetle Dendroctonus rhizophagus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) Has Digestive Capacity to Degrade Complex Substrates: Functional Characterization and Heterologous Expression of an ?-Amylase" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010036
APA StyleSoto-Robles, L. V., López, M. F., Torres-Banda, V., Cano-Ramírez, C., Obregón-Molina, G., & Zúñiga, G. (2021). The Bark Beetle Dendroctonus rhizophagus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) Has Digestive Capacity to Degrade Complex Substrates: Functional Characterization and Heterologous Expression of an ?-Amylase. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010036





