Infections and Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer: A Bad Relationship?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Bacterial Infections in Lung Cancer
2.1. Antibiotics and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Lung Cancer
2.2. Antibiotics Timing and/or Cumulative Exposure: What Matters?
2.3. Host Microbiome, Immunotherapy, and Antibiotics in Lung Cancer
2.4. Open Issues and Future Perspectives in NSCLC Patients Treated with ICIs and Antibiotics
3. Viral Infections in Lung Cancer
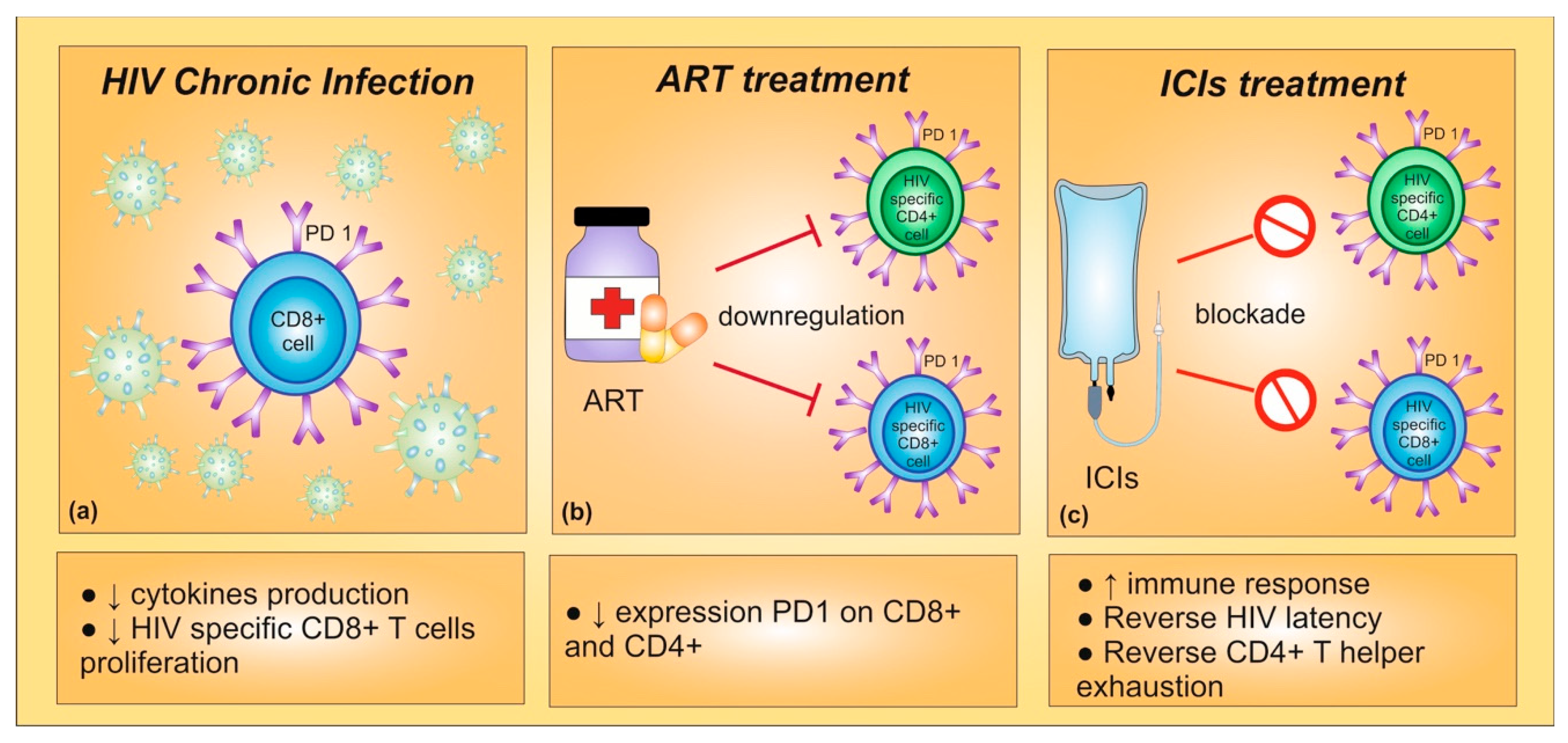
3.1. Human Immune-Deficiency Virus (HIV)
3.1.1. HIV and Risk of Lung Cancer
3.1.2. HIV and Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
3.2. HBV/HCV and Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
3.3. Open Issues and Future Perspectives in HIV, HBV, and HCV Lung Cancer Patients Treated with ICIs
4. Sars-Cov-2 Infection and Lung Cancer
Open Issues and Future Perspectives of Sars-Cov-2 Infection in Lung Cancer Patients
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russo, A.; McCusker, M.G.; Scilla, K.A.; Arensmeyer, K.E.; Mehra, R.; Adamo, V.; Rolfo, C. Immunotherapy in lung cancer: From a minor god to the Olympus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1244, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Tao, M.; Kong, C.; Li, H.; Tong, J.; Zhu, H.; Yan, X. Antibiotic administration shortly before or after immunotherapy initiation is correlated with poor prognosis in solid cancer patients: An up-to-date systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 88, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, G.; Triulzi, T.; Proto, C.; Signorelli, D.; Imbimbo, M.; Poggi, M.; Fuca, G.; Ganzinelli, M.; Vitali, M.; Palmieri, D.; et al. Association between antibiotic-immunotherapy exposure ratio and outcome in metastatic non small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2019, 132, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uldrick, T.S.; Goncalves, P.H.; Abdul-Hay, M.; Claeys, A.J.; Emu, B.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Fling, S.P.; Fong, L.; Kaiser, J.C.; Lacroix, A.M.; et al. Assessment of the safety of pembrolizumab in patients with HIV and advanced cancer—A phase 1 study. JAMA Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertejo-Fernandez, A.; Ricciuti, B.; Hammond, S.P.; Marty, F.M.; Recondo, G.; Rangachari, D.; Costa, D.B.; Awad, M.M. Safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection. Lung Cancer 2020, 145, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 8 November 2020).
- Liang, W.; Guan, W.; Chen, R.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Xu, K.; Li, C.; Ai, Q.; Lu, W.; Liang, H.; et al. Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A nationwide analysis in China. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.; Goel, S.; Kabarriti, R.; Cole, D.; Goldfinger, M.; Acuna-Villaorduna, A.; Pradhan, K.; Thota, R.; Reissman, S.; Sparano, J.A.; et al. Case fatality rate of cancer patients with COVID-19 in a New York hospital system. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, F.; Xie, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Jia, P.; Guan, H.Q.; Peng, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19-infected cancer patients: A retrospective case study in three hospitals within Wuhan, China. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garassino, M.C.; Whisenant, J.G.; Huang, L.-C.; Trama, A.; Torri, V.; Agustoni, F.; Baena, J.; Banna, G.; Berardi, R.; Bettini, A.C.; et al. COVID-19 in patients with thoracic malignancies (TERAVOLT): First results of an international, registry-based, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, K.F.; Watz, H. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinosoglou, K.S.; Karkoulias, K.; Marangos, M. Infectious complications in patients with lung cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perlin, E.; Bang, K.M.; Shah, A.; Hursey, P.D.; Whittingham, W.L.; Hashmi, K.; Campbell, L.; Kassim, O.O. The impact of pulmonary infections on the survival of lung cancer patients. Cancer 1990, 66, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, S.; Koga, H.; Oka, M.; Kadota, J.; Kaku, M.; Soda, H.; Tomono, K.; Hara, K. The pattern of respiratory infection in patients with lung cancer. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1994, 173, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berghmans, T.; Sculier, J.P.; Klastersky, J. A prospective study of infections in lung cancer patients admitted to the hospital. Chest 2003, 124, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assi, H.I.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Moukalled, N.M.; Ramalingam, S.S. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2018, 124, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prelaj, A.; Tay, R.; Ferrara, R.; Chaput, N.; Besse, B.; Califano, R. Predictive biomarkers of response for immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 106, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shui, L.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Yi, C.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, H. Gut microbiome as a potential factor for modulating resistance to cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jernberg, C.; Lofmark, S.; Edlund, C.; Jansson, J.K. Long-term impacts of antibiotic exposure on the human intestinal microbiota. Microbiology 2010, 156, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banna, G.L.; Passiglia, F.; Colonese, F.; Canova, S.; Menis, J.; Addeo, A.; Russo, A.; Cortinovis, D.L. Immune-checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: A tool to improve patients’ selection. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 129, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Z.; Gao, P.; Song, Y.X.; Xu, Y.; Sun, J.X.; Chen, X.W.; Zhao, J.H.; Wang, Z.N. Antibiotic use and the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients: A pooled analysis of 2740 cancer patients. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1665973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, B.E.; Routy, B.; Nagrial, A.; Chin, V.T. The effect of antibiotics on clinical outcomes in immune-checkpoint blockade: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Ge, W.; Cao, D. The association between antibiotics use and outcome of cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 149, 102909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Iaculli, A.; Signorelli, D.; Ghidini, A.; Dottorini, L.; Perego, G.; Ghidini, M.; Zaniboni, A.; Gori, S.; Inno, A. Survival of patients treated with antibiotics and immunotherapy for cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurienne, L.; Cervesi, J.; Duhalde, L.; de Gunzburg, J.; Andremont, A.; Zalcman, G.; Buffet, R.; Bandinelli, P.A. NSCLC Immunotherapy efficacy and antibiotic use: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palleja, A.; Mikkelsen, K.H.; Forslund, S.K.; Kashani, A.; Allin, K.H.; Nielsen, T.; Hansen, T.H.; Liang, S.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, C.; et al. Recovery of gut microbiota of healthy adults following antibiotic exposure. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Pestana, R.C.; Hess, K.; Viola, G.M.; Subbiah, V. Impact of antibiotic use on survival in patients with advanced cancers treated on immune checkpoint inhibitor phase I clinical trials. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2396–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinato, D.J.; Howlett, S.; Ottaviani, D.; Urus, H.; Patel, A.; Mineo, T.; Brock, C.; Power, D.; Hatcher, O.; Falconer, A.; et al. Association of prior antibiotic treatment with survival and response to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1774–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Santamaria, A. Impact of antibiotic use and other concomitant medications on the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmink, B.A.; Khan, M.A.W.; Hermann, A.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Wargo, J.A. The microbiome, cancer, and cancer therapy. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, S.; Inno, A.; Belluomini, L.; Bocus, P.; Bisoffi, Z.; Russo, A.; Arcaro, G. Gut microbiota and cancer: How gut microbiota modulates activity, efficacy and toxicity of antitumoral therapy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 143, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Deng, Y.; Chu, Q.; Zhang, P. Gut microbiome and cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2019, 447, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivan, A.; Corrales, L.; Hubert, N.; Williams, J.B.; Aquino-Michaels, K.; Earley, Z.M.; Benyamin, F.W.; Lei, Y.M.; Jabri, B.; Alegre, M.L.; et al. Commensal Bifidobacterium promotes antitumor immunity and facilitates anti-PD-L1 efficacy. Science 2015, 350, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vetizou, M.; Pitt, J.M.; Daillere, R.; Lepage, P.; Waldschmitt, N.; Flament, C.; Rusakiewicz, S.; Routy, B.; Roberti, M.P.; Duong, C.P.; et al. Anticancer immunotherapy by CTLA-4 blockade relies on the gut microbiota. Science 2015, 350, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Routy, B.; le Chatelier, E.; Derosa, L.; Duong, C.P.M.; Alou, M.T.; Daillere, R.; Fluckiger, A.; Messaoudene, M.; Rauber, C.; Roberti, M.P.; et al. Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1-based immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Science 2018, 359, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.; Dong, H.; Xia, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, H.; Yao, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S. The Diversity of gut microbiome is associated with favorable responses to anti-programmed death 1 immunotherapy in chinese patients with NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosa, L.; Routy, B.; Kroemer, G.; Zitvogel, L. The intestinal microbiota determines the clinical efficacy of immune checkpoint blockers targeting PD-1/PD-L1. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1434468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krief, J.O.; de Tauriers, P.H.; Dumenil, C.; Neveux, N.; Dumoulin, J.; Giraud, V.; Labrune, S.; Tisserand, J.; Julie, C.; Emile, J.-F.; et al. Role of antibiotic use, plasma citrulline and blood microbiome in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with nivolumab. J. Immuno Ther. Cancer 2019, 7, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagasaka, M.; Sexton, R.; Alhasan, R.; Rahman, S.; Azmi, A.S.; Sukari, A. Gut microbiome and response to checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer—A review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 145, 102841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, M.T.; Peek, R.M., Jr. Gastrointestinal malignancy and the microbiome. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1534–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Gail, M.H.; Consonni, D.; Carugno, M.; Humphrys, M.; Pesatori, A.C.; Caporaso, N.E.; Goedert, J.J.; Ravel, J.; Landi, M.T. Characterizing human lung tissue microbiota and its relationship to epidemiological and clinical features. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickson, R.P.; Erb-Downward, J.R.; Huffnagle, G.B. Towards an ecology of the lung: New conceptual models of pulmonary microbiology and pneumonia pathogenesis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, J.; Gan, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Deng, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yang, S.; et al. Diminishing microbiome richness and distinction in the lower respiratory tract of lung cancer patients: A multiple comparative study design with independent validation. Lung Cancer 2019, 136, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroumagne, S.; Salinas-Pineda, A.; Hermant, C.; Murris, M.; Gourraud, P.A.; Do, C.; Segonds, C.; Didier, A.; Mazieres, J. Incidence and characteristics of bronchial colonisation in patient with lung cancer: A retrospective study of 388 cases. Rev. Mal. Respir. 2011, 28, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; O’Brien, J.L.; Ajami, N.J.; Scheurer, M.E.; Amirian, E.S.; Armstrong, G.; Tsavachidis, S.; Thrift, A.P.; Jiao, L.; Wong, M.C.; et al. Lung tissue microbial profile in lung cancer is distinct from emphysema. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 1775–1787. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.H.; Mirabolfathinejad, S.G.; Katta, H.; Cumpian, A.M.; Gong, L.; Caetano, M.S.; Moghaddam, S.J.; Dong, C. T helper 17 cells play a critical pathogenic role in lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5664–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickson, R.P.; Martinez, F.J.; Huffnagle, G.B. The role of the microbiome in exacerbations of chronic lung diseases. Lancet 2014, 384, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jungnickel, C.; Schmidt, L.H.; Bittigkoffer, L.; Wolf, L.; Wolf, A.; Ritzmann, F.; Kamyschnikow, A.; Herr, C.; Menger, M.D.; Spieker, T.; et al. IL-17C mediates the recruitment of tumor-associated neutrophils and lung tumor growth. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4182–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursi, B.; Mamtani, R.; Haynes, K.; Yang, Y.X. Recurrent antibiotic exposure may promote cancer formation—Another step in understanding the role of the human microbiota? Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2655–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbone, C.; Piro, G.; di Noia, V.; D’Argento, E.; Vita, E.; Ferrara, M.G.; Pilotto, S.; Milella, M.; Cammarota, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Lung and gut microbiota as potential hidden driver of immunotherapy efficacy in lung cancer. Mediators Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 7652014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaderbhai, C.; Richard, C.; Fumet, J.D.; Aarnink, A.; Foucher, P.; Coudert, B.; Favier, L.; Lagrange, A.; Limagne, E.; Boidot, R.; et al. Antibiotic Use Does Not Appear to Influence Response to Nivolumab. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 3195–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemer, F.; Rinnerthaler, G.; Lang, D.; Hackl, H.; Lamprecht, B.; Greil, R. Association between antibiotics use and outcome in patients with NSCLC treated with immunotherapeutics. Ann. Oncol 2019, 30, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metges, J.-P.; Michaud, E.; Lagadec, D.D.; Marhuenda, F.; Chaslerie, A.; Grude, F. Impact of anti-infectious and corticosteroids on immunotherapy: Nivolumab and pembrozilumab follow-up in a French study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 15157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Pezzuto, A.; Sini, C.; Tuzi, A.; Citarella, F.; McCusker, M.G.; Nigro, O.; Tanda, E.; Russo, A. Concomitant medications during immune checkpoint blockage in cancer patients: Novel insights in this emerging clinical scenario. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 142, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalabi, M.; Cardona, A.; Nagarkar, D.R.; Scala, A.D.; Gandara, D.R.; Rittmeyer, A.; Albert, M.L.; Powles, T.; Kok, M.; Herrera, F.G.; et al. Efficacy of chemotherapy and atezolizumab in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer receiving antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors: Pooled post hoc analyses of the OAK and POPLAR trials. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielgo-Rubio, X.; Chara, L.; Sotelo-Lezama, M.; Castro, R.L.; Rubio-Martínez, J.; Velastegui, A.; Olier-Garate, C.; Falagan, S.; Gómez-Barreda, I.; Bautista-Sanz, P.; et al. MA10.01 antibiotic use and PD-1 inhibitors: Shorter survival in lung cancer, especially when given intravenously. Type of infection also matters. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahajan, R.; Xing, J.; Liu, S.J.; Ly, K.N.; Moorman, A.C.; Rupp, L.; Xu, F.; Holmberg, S.D. Chronic hepatitis cohort study, I. Mortality among persons in care with hepatitis C virus infection: The chronic hepatitis cohort study (CHeCS), 2006–2010. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yarchoan, R.; Uldrick, T.S. HIV-associated cancers and related diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakova, L.; Pavlik, J.; Chrenkova, L.; Martinec, O.; Cerveny, L. Current antiviral drugs and their analysis in biological materials—Part II: Antivirals against hepatitis and HIV viruses. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 378–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNAIDS. Global HIV & AIDS Statistics—2020 Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Grulich, A.E.; van Leeuwen, M.T.; Falster, M.O.; Vajdic, C.M. Incidence of cancers in people with HIV/AIDS compared with immunosuppressed transplant recipients: A meta-analysis. Lancet 2007, 370, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, M.S.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Gail, M.H.; Hall, H.I.; Li, J.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Bhatia, K.; Uldrick, T.S.; Yarchoan, R.; Goedert, J.J.; et al. Cancer burden in the HIV-infected population in the United States. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenhende, M.A.; Roussillon, C.; Henard, S.; Morlat, P.; Oksenhendler, E.; Aumaitre, H.; Georget, A.; May, T.; Rosenthal, E.; Salmon, D.; et al. Cancer-related causes of death among HIV-infected patients in France in 2010: Evolution since 2000. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mdodo, R.; Frazier, E.L.; Dube, S.R.; Mattson, C.L.; Sutton, M.Y.; Brooks, J.T.; Skarbinski, J. Cigarette smoking prevalence among adults with HIV compared with the general adult population in the United States: Cross-sectional surveys. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrao, R.; Pinero, C.; Velez, J.; Coutinho, D.; Maltez, F.; Lino, S.; Sarmento, E.C.R.; Tavares, A.P.; Pacheco, P.; Lopes, M.J.; et al. Non-AIDS-related comorbidities in people living with HIV-1 aged 50 years and older: The AGING POSITIVE study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 79, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sigel, K.; Wisnivesky, J.; Gordon, K.; Dubrow, R.; Justice, A.; Brown, S.T.; Goulet, J.; Butt, A.A.; Crystal, S.; Rimland, D.; et al. HIV as an independent risk factor for incident lung cancer. AIDS 2012, 26, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, K.P.; Kong, C.Y.; Hyle, E.P.; Baggett, T.P.; Huang, M.; Parker, R.A.; Paltiel, A.D.; Losina, E.; Weinstein, M.C.; Freedberg, K.A.; et al. Lung cancer mortality associated with smoking and smoking cessation among people living with HIV in the United States. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uldrick, T.S.; Ison, G.; Rudek, M.A.; Noy, A.; Schwartz, K.; Bruinooge, S.; Schenkel, C.; Miller, B.; Dunleavy, K.; Wang, J.; et al. Modernizing clinical trial eligibility criteria: Recommendations of the American Society of clinical oncology-friends of cancer research HIV working group. J. Clin. Oncol 2017, 35, 3774–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velu, V.; Shetty, R.D.; Larsson, M.; Shankar, E.M. Role of PD-1 co-inhibitory pathway in HIV infection and potential therapeutic options. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabmeier-Pfistershammer, K.; Steinberger, P.; Rieger, A.; Leitner, J.; Kohrgruber, N. Identification of PD-1 as a unique marker for failing immune reconstitution in HIV-1-infected patients on treatment. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2011, 56, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porichis, F.; Hart, M.G.; Massa, A.; Everett, H.L.; Morou, A.; Richard, J.; Brassard, N.; Veillette, M.; Hassan, M.; Ly, N.L.; et al. Immune checkpoint blockade restores HIV-specific CD4 T cell help for NK cells. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuma, Y.; Hishima, T.; Kashima, J.; Homma, S. High PD-L1 expression indicates poor prognosis of HIV-infected patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guihot, A.; Marcelin, A.G.; Massiani, M.A.; Samri, A.; Soulie, C.; Autran, B.; Spano, J.P. Drastic decrease of the HIV reservoir in a patient treated with nivolumab for lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 517–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCullar, B.; Alloway, T.; Martin, M. Durable complete response to nivolumab in a patient with HIV and metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 540–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ostios-Garcia, L.; Faig, J.; Leonardi, G.C.; Adeni, A.E.; Subegdjo, S.J.; Lydon, C.A.; Rangachari, D.; Huberman, M.S.; Sehgal, K.; Shea, M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors among HIV-positive patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lavole, A.; Guihot, A.; Veyri, M.; Lambotte, O.; Autran, B.; Cloarec, N.; le Garff, G.; Flament, T.; Cadranel, J.; Spano, J.P. PD-1 blockade in HIV-infected patients with lung cancer: A new challenge or already a strategy? Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samri, A.; Lavolé, A.; Even, S.; Lambert-Niclot, S.; le Garff, G.; Cadranel, J.; Spano, J.-P.; Autran, B.; Marcelin, A.-G.; Guihot, A. Immunovirological evolution in HIV-infected patients treated with anti-PD1 therapy. In Proceedings of the 9th IAS Conference on HIV Science (IAS 2017), Paris, France, 23–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Spano, J.P.; Veyri, M.; Gobert, A.; Guihot, A.; Perre, P.; Kerjouan, M.; Brosseau, S.; Cloarec, N.; Montaudie, H.; Helissey, C.; et al. Immunotherapy for cancer in people living with HIV: Safety with an efficacy signal from the series in real life experience. AIDS 2019, 33, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlesi, F.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Felip, E.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Jao, K.; Rijavec, E.; Urban, L.; Aucoin, J.S.; Zannori, C.; Vermaelen, K.; et al. Nivolumab plus low-dose IPILIMUMAB as first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC: Overall survival analysis of checkmate 817. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Cao, M.; Moran, T.; Dalmau, J.; Garcia-Corbacho, J.; Bracht, J.W.P.; Bernabe, R.; Juan, O.; de Castro, J.; Blanco, R.; Drozdowskyj, A.; et al. Assessment of the feasibility and safety of durvalumab for treatment of solid tumors in patients with HIV-1 infection: The phase 2 DURVAST study. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajdev, L.; Lensing, S.; Ramos, J.C.; Baiocchi, R.; Wang, C.C.J.; Ratner, L.; Rubinstein, P.G.; Ambinder, R.; Henry, D.; Streicher, H.; et al. 1023MO AMC 095: A report of nivolumab (nivo) in advanced HIV associated solid tumours (ST). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavole, A.; Mazieres, J.; Schneider, S.; Brosseau, S.; Kiakouama, L.M.; Greillier, L.; Guihot, A.; Abbar, B.; Baron, M.; Makinson, A.; et al. 1389P IFCT-1602 CHIVA2 phase II trial: Nivolumab in previously treated HIV-patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.; Kilickap, S.; Gümüş, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Gogishvili, M.; Turk, H.M.; Çiçin, İ.; Bentsion, D.; Gladkov, O.; et al. LBA52 EMPOWER-Lung 1: Phase III first-line (1L) cemiplimab monotherapy vs. platinum-doublet chemotherapy (chemo) in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) ≥ 50%. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1182–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.J.; Al-Shbool, G.; Blackburn, M.; Cook, M.; Belouali, A.; Liu, S.V.; Madhavan, S.; He, A.R.; Atkins, M.B.; Gibney, G.T.; et al. Safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in cancer patients with HIV, hepatitis B, or hepatitis C viral infection. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, M.R.; Kim, C. Safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with HIV infection and advanced-stage cancer: A systematic review. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothapalli, A.; Khattak, M.A. Safety and efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy for metastatic melanoma and non-small-cell lung cancer in patients with viral hepatitis: A case series. Melanoma Res. 2018, 28, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tio, M.; Rai, R.; Ezeoke, O.M.; McQuade, J.L.; Zimmer, L.; Khoo, C.; Park, J.J.; Spain, L.; Turajlic, S.; Ardolino, L.; et al. Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy in patients with solid organ transplant, HIV or hepatitis B/C infection. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 104, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanina, N.; Goodman, A.M.; Cohen, P.R.; Frampton, G.M.; Kurzrock, R. Successful treatment of HIV-associated kaposi sarcoma with immune checkpoint blockade. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahin, I.H.; Kane, S.R.; Brutcher, E.; Guadagno, J.; Smith, K.E.; Wu, C.; Lesinski, G.B.; Gunthel, C.J.; El-Rayes, B.F. Safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with cancer living with HIV: A perspective on recent progress and future needs. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2020, 16, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuderer, N.M.; Choueiri, T.K.; Shah, D.P.; Shyr, Y.; Rubinstein, S.M.; Rivera, D.R.; Shete, S.; Hsu, C.Y.; Desai, A.; Lopes, G.D.L., Jr.; et al. Clinical impact of COVID-19 on patients with cancer (CCC19): A cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinar, J.B.; Torri, V.; Whisenant, J.; Hirsch, F.R.; Rogado, J.; de Castro Carpeño, J.; Halmos, B.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Rueda, A.G.; Tiseo, M.; et al. LBA75 Defining COVID-19 outcomes in thoracic cancer patients: TERAVOLT (Thoracic cancERs international coVid 19 cOLlaboraTion). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1204–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Noia, V.; D’Aveni, A.; Squadroni, M.; Beretta, G.D.; Ceresoli, G.L. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in SARS-CoV-2 infected cancer patients: The spark that ignites the fire? Lung Cancer 2020, 145, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Rizvi, H.; Egger, J.V.; Preeshagul, I.R.; Wolchok, J.D.; Hellmann, M.D. Impact of PD-1 blockade on severity of COVID-19 in patients with lung cancers. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise-Draper, T.M.; Desai, A.; Elkrief, A.; Rini, B.I.; Flora, D.B.; Bowles, D.W.; Shah, D.; Rivera, D.; Johnson, D.B.; Lopes, G.; et al. LBA71 Systemic cancer treatment-related outcomes in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: A CCC19 registry analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1201–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Boyer, M.; Lee, J.H.; Kao, S.C. COVID-19: The use of immunotherapy in metastatic lung cancer. Immunotherapy 2020, 12, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, A.; Addeo, A.; von Garnier, C.; Blackhall, F.; Planchard, D.; Felip, E.; Dziadziuszko, R.; de Marinis, F.; Reck, M.; Bouchaab, H.; et al. ESMO Management and treatment adapted recommendations in the COVID-19 era: Lung cancer. ESMO Open 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Meta-Analysis. | N. of Included Studies | Pooled HR PFS [95% CI] p-Value | Pooled HR OS [95% CI] p-Value | NSCLC–HR PFS [95% CI] p-Value | NSCLC–HR OS [95% CI] p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [21] | 19 | 1.84 [1.49–2.26] p < 0.001 | 2.37 [2.05–2.75] p < 0.001 | 1.79 [1.29–2.49] p < 0.001 | 2.68 [2.19–3.28] p < 0.001 |
| [22] | 18 | 1.65 [1.3–2.1] p < 0.0001 | 1.92 [1.37–2.68] p < 0.001 | 1.64 [1.07–2.52] p = 0.0023 | 2.00 [1.23–3.24] p = 0.0052 |
| [23] | 20 | 1.53 [1.30–1.79] p < 0.01 | 1.90 [1.55–2.34] p < 0.01 | 1.39 [1.16–1.67] p = 0.0004 | 1.73 [1.26–2.38] p = 0.0007 |
| [24] | 15 | 1.53 [1.22–1.93] p < 0.01 | 2.07 [1.51–2.84] p < 0.01 | N.A. | N.A. |
| [25] * | 23 | N.A. | N.A. | 1.47 [1.13–1.90] p < 0.01 | 1.69 [1.25–2.29] p < 0.01 |
| [2] | 33 | 1.76 [1.47–2.12] p < 0.00001 | 1.76 [1.41–2.19] p < 0.00001 | 1.70 [1.21–2.27] p = 0.0004 | 1.80 [1.28–2.55] p = 0.0008 |
| Trial | Phase | Type of Cancer | N. of Patients | Type of ICIs | Primary Endpoints | Secondary Endpoints | Main Findings | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [4] [NCT02595866] | 1 | Advanced or metastatic solid and hematological cancers | 60 HIV-positive * | Pembrolizumab | Safety | ORR, PFS, DoR, OS | Results on 30 patients:
| Recruiting |
| [79] [NCT02869789] | 3b/4 | Advanced or metastatic NSCLC | 1036 [4 HIV-positive in cohort 1A] § | Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab | Safety | PFS, ORR, DoR, FACT-L, OS |
| Active, not recruiting |
| [80] [NCT03094286] | 2 | Advanced or metastatic solid and hematological cancers | 20 HIV-positive [14 NSCLC, 2 melanoma, 1 SCLC, 2 anal carcinoma, 1 bladder carcinoma] § | Durvalumab | Feasibility (ability to receive at least a median number of 4 cycles) | ORR, PFS, OS |
| Active, not recruiting |
| [81] [NCT02408861] | 1 | Advanced or metastatic solid and hematological cancers | 96 HIV-positive * | Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab | MTD | ORR, immune function, change in immune status, change in HIV viral load | Results on 37 patients:
| Recruiting |
| [82] [NCT03304093] | 2 | Advanced or metastatic NSCLC | 16 HIV-positive § | Nivolumab | DCR | PFS, OS, tolerance, impact on HIV control, DoR |
| Active, not recruiting |
| [83] [NCT03088540] | 3 | Advanced or metastatic NSCLC | 712 [not yet specify the number of HIV-positive patients] § | Cemiplimab vs. SOC | OS, PFS | ORR, DOR, BOR | Not yet available data on HIV population | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT04514484 | 1 | Advanced or metastatic solid cancers | 18 HIV-positive * | Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib | Safety and feasibility (ability to receive at least a median number of 4 cycles) | DOR, PFS, OS, analysis on HIV reservoir | NA | Recruiting |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belluomini, L.; Caldart, A.; Avancini, A.; Dodi, A.; Trestini, I.; Kadrija, D.; Sposito, M.; Tregnago, D.; Casali, M.; Riva, S.T.; et al. Infections and Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer: A Bad Relationship? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010042
Belluomini L, Caldart A, Avancini A, Dodi A, Trestini I, Kadrija D, Sposito M, Tregnago D, Casali M, Riva ST, et al. Infections and Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer: A Bad Relationship? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(1):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010042
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelluomini, Lorenzo, Alberto Caldart, Alice Avancini, Alessandra Dodi, Ilaria Trestini, Dzenete Kadrija, Marco Sposito, Daniela Tregnago, Miriam Casali, Silvia Teresa Riva, and et al. 2021. "Infections and Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer: A Bad Relationship?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 1: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010042
APA StyleBelluomini, L., Caldart, A., Avancini, A., Dodi, A., Trestini, I., Kadrija, D., Sposito, M., Tregnago, D., Casali, M., Riva, S. T., Sartori, G., Menis, J., Milella, M., & Pilotto, S. (2021). Infections and Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer: A Bad Relationship? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010042







