Apigenin, a Partial Antagonist of the Estrogen Receptor (ER), Inhibits ER-Positive Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation through Akt/FOXM1 Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
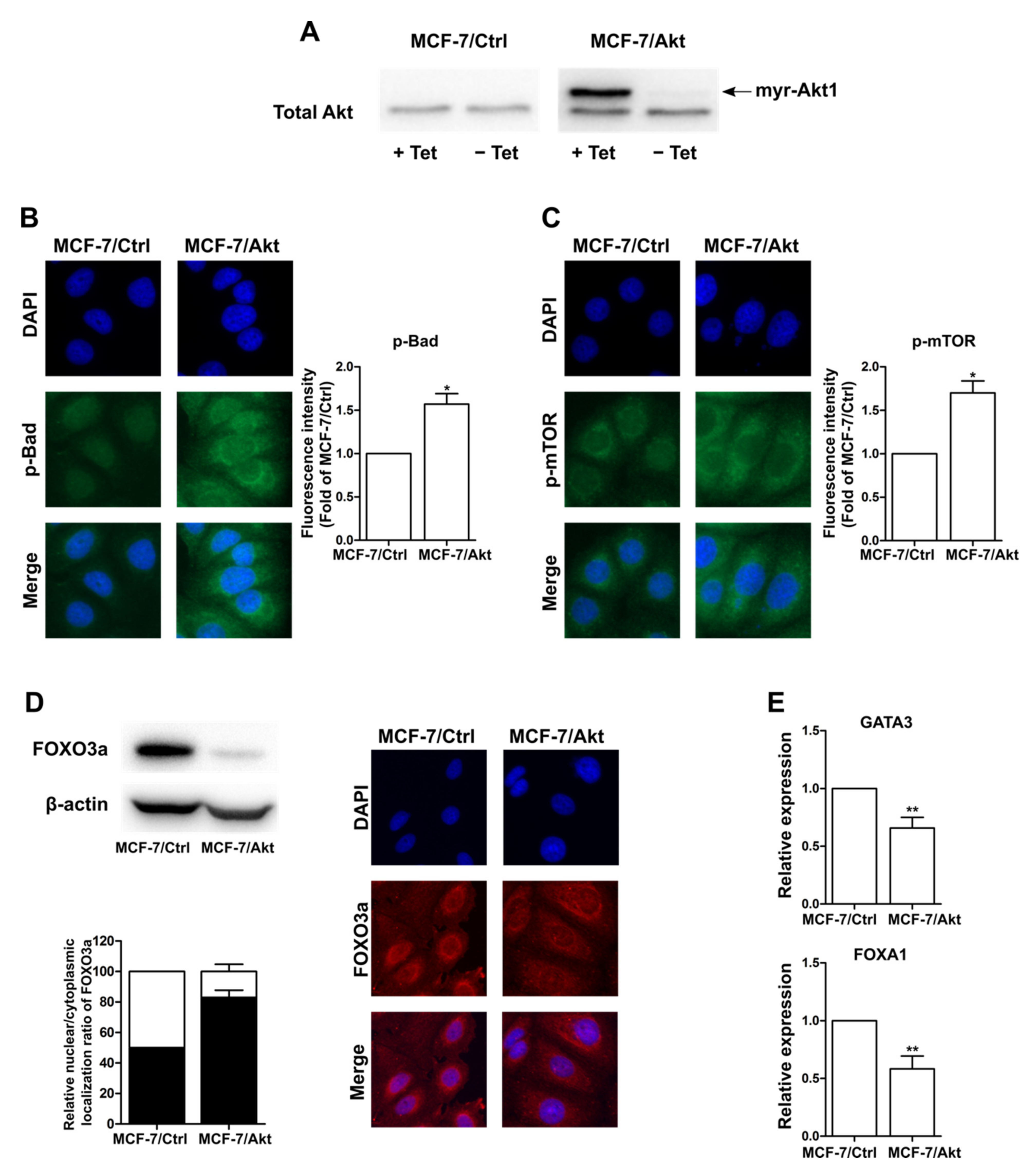
2.1. Construction and Characterization of Akt-Activated MCF-7 (MCF-7/Akt) Cells and MCF-7/Ctrl Cells
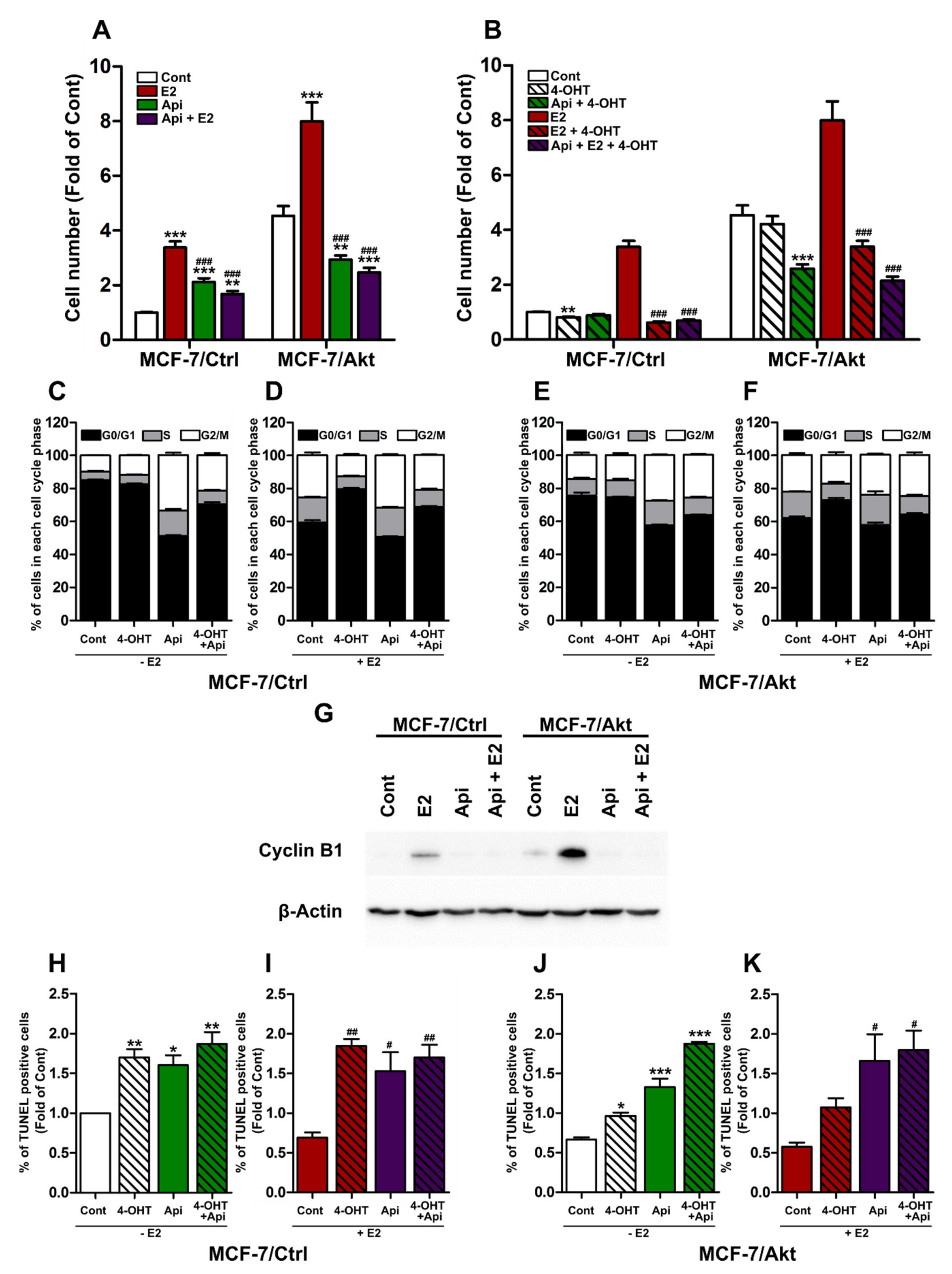
2.2. Effects of Api on the Proliferation of MCF-7/Ctrl Cells and MCF-7/Akt Cells
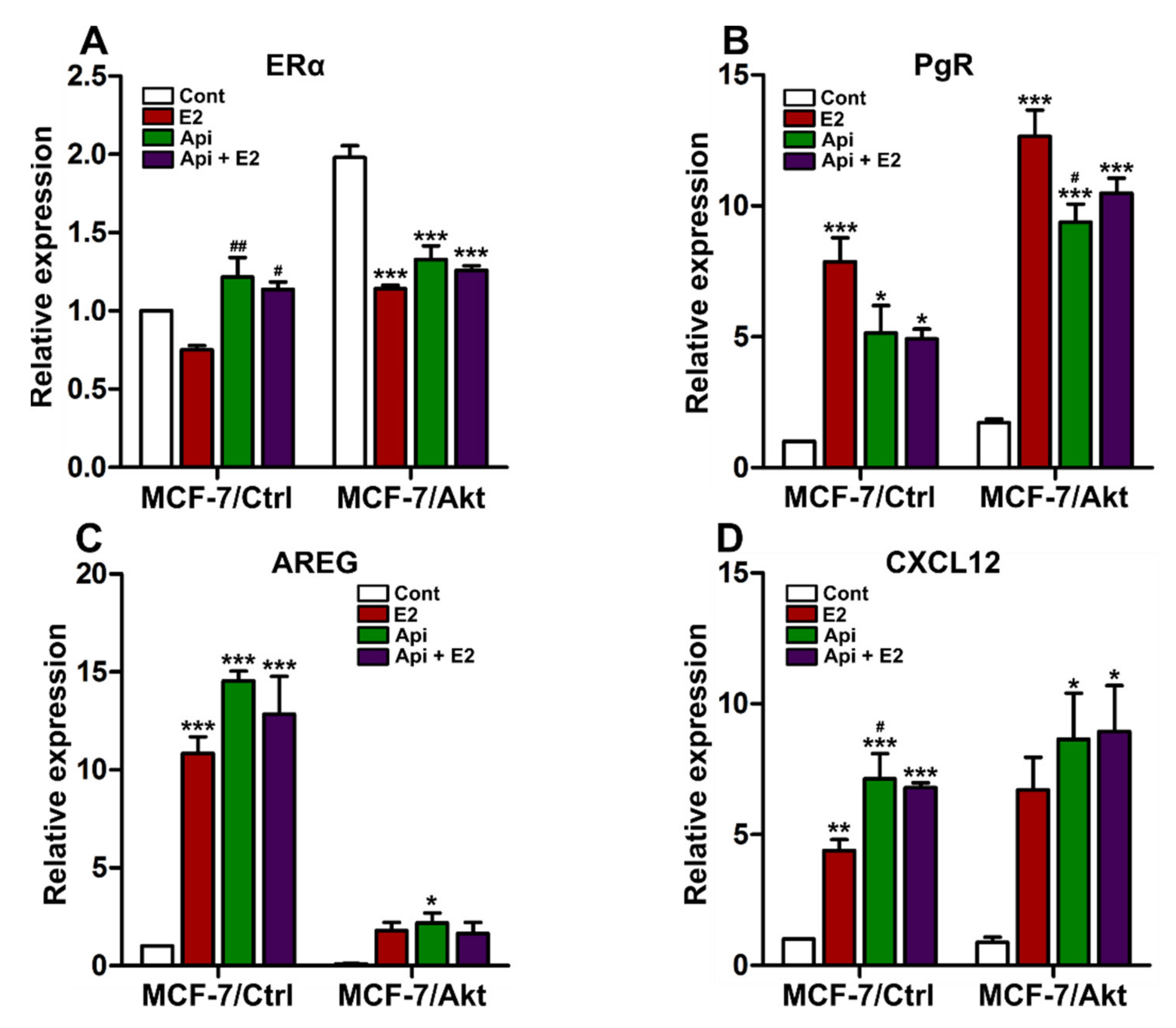
2.3. Effects of Apigenin on ER Genomic Activity
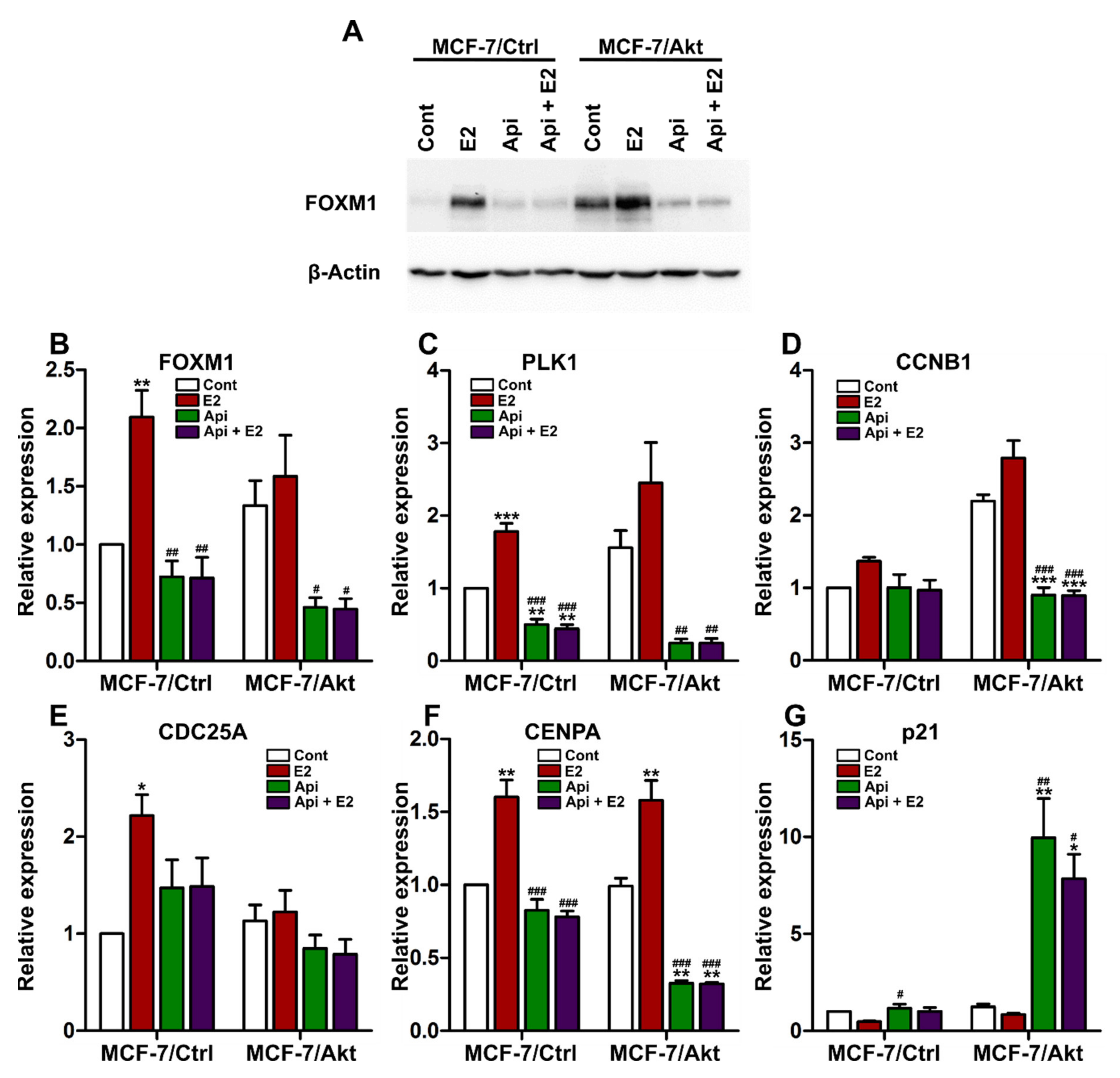
2.4. Effects of Apigenin on the Expression of FOXM1 and FOXM1-Related Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Clone Establishment and Maintenance
4.3. Proliferation Assay
4.4. Cell Cycle Analysis by Flow Cytometry (FACS)
4.5. Apoptosis Analysis
4.6. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
4.7. Luciferase Assay
4.8. Immunofluorescence
4.9. Nuclear/Cytoplasmic Ratio Quantification from Immunofluorescence Images
4.10. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
4.11. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4-OHT | 4-Hydroxytamoxifen |
| Api | Apigenin |
| BC | Breast cancer |
| E2 | Estradiol |
| FOXM1 | Forkhead box protein M1 |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harbeck, N.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Cortes, J.; Gnant, M.; Houssami, N.; Poortmans, P.; Ruddy, K.; Tsang, J.; Cardoso, F. Breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2019, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anurag, M.; Ellis, M.J.; Haricharan, S. DNA damage repair defects as a new class of endocrine treatment resistance driver. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 36252–36253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, M.H. The LncRNA HOTAIRM1 Promotes Tamoxifen Resistance by Mediating HOXA1 Expression in ER+ Breast Cancer Cells. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 3416–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Zotano, A.; Mayer, I.A.; Arteaga, C.L. PI3K/AKT/mTOR: Role in breast cancer progression, drug resistance, and treatment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.A.; Fraile-Martínez, O.; Asúnsolo, Á.; Buján, J.; García-Honduvilla, N.; Coca, S. Signal Transduction Pathways in Breast Cancer: The Important Role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 9258396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Tenorio, G.; Stål, O. Southeast Sweden Breast Cancer Group Activation of AKT/PKB in breast cancer predicts a worse outcome among endocrine treated patients. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokunaga, E.; Kimura, Y.; Mashino, K.; Oki, E.; Kataoka, A.; Ohno, S.; Morita, M.; Kakeji, Y.; Baba, H.; Maehara, Y. Activation of PI3K/Akt signaling and hormone resistance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2006, 13, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.L.; Lien, E.C.; Toker, A. Oncogenic AKT1(E17K) mutation induces mammary hyperplasia but prevents HER2-driven tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 17301–17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Regan, R.M.; Nahta, R. Targeting forkhead box M1 transcription factor in breast cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 154, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.-B.; Li, X.-Z.; Zeng, S.; Liu, C.; Yang, S.-M.; Yang, L.; Hu, C.-J.; Bai, J.-Y. Regulation of the master regulator FOXM1 in cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergamaschi, A.; Madak-Erdogan, Z.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, Y.-L.; Lu, H.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. The forkhead transcription factor FOXM1 promotes endocrine resistance and invasiveness in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by expansion of stem-like cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomes, A.R.; Zhao, F.; Lam, E.W.F. Role and regulation of the forkhead transcription factors FOXO3a and FOXM1 in carcinogenesis and drug resistance. Chin. J. Cancer 2013, 32, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, S.; Fan, L.Y.-N.; Lam, E.W.-F. The FOXO3-FOXM1 axis: A key cancer drug target and a modulator of cancer drug resistance. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 50, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellami, M.; Bragazzi, N.L. Nutrigenomics and Breast Cancer: State-of-Art, Future Perspectives and Insights for Prevention. Nutrients 2020, 12, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patterson, R.E.; Cadmus, L.A.; Emond, J.A.; Pierce, J.P. Physical activity, diet, adiposity and female breast cancer prognosis: A review of the epidemiologic literature. Maturitas 2010, 66, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Spezia, M.; Huang, S.; Yuan, C.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ji, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, B.; Luo, W.; et al. Breast cancer development and progression: Risk factors, cancer stem cells, signaling pathways, genomics, and molecular pathogenesis. Genes Dis. 2018, 5, 77–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosetti, C.; Spertini, L.; Parpinel, M.; Gnagnarella, P.; Lagiou, P.; Negri, E.; Franceschi, S.; Montella, M.; Peterson, J.; Dwyer, J.; et al. Flavonoids and breast cancer risk in Italy. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2005, 14, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fink, B.N.; Steck, S.E.; Wolff, M.S.; Britton, J.A.; Kabat, G.C.; Schroeder, J.C.; Teitelbaum, S.L.; Neugut, A.I.; Gammon, M.D. Dietary flavonoid intake and breast cancer risk among women on Long Island. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 165, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hui, C.; Qi, X.; Qianyong, Z.; Xiaoli, P.; Jundong, Z.; Mantian, M. Flavonoids, flavonoid subclasses and breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sak, K. Intake of Individual Flavonoids and Risk of Carcinogenesis: Overview of Epidemiological Evidence. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 1119–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostetler, G.L.; Ralston, R.A.; Schwartz, S.J. Flavones: Food Sources, Bioavailability, Metabolism, and Bioactivity. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Qi, M.; Li, P.; Zhan, Y.; Shao, H. Apigenin in cancer therapy: Anti-cancer effects and mechanisms of action. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Rajabi, H.; Kufe, D. Mucin 1 C-Terminal Subunit Oncoprotein Is a Target for Small-Molecule Inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 79, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mafuvadze, B.; Liang, Y.; Besch-Williford, C.; Zhang, X.; Hyder, S.M. Apigenin induces apoptosis and blocks growth of medroxyprogesterone acetate-dependent BT-474 xenograft tumors. Horm. Cancer 2012, 3, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, H.-S.; Choi, H.-S.; Kim, S.-R.; Choi, Y.K.; Woo, S.-M.; Shin, I.; Woo, J.-K.; Park, S.-Y.; Shin, Y.C.; Ko, S.-G.; et al. Apigenin induces apoptosis via extrinsic pathway, inducing p53 and inhibiting STAT3 and NFκB signaling in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 366, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, B.; Cao, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, H.; Meng, R.; Zhang, L.; Niu, R.; Hao, X.; et al. Autophagy inhibition enhances apigenin-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Chin. J. Cancer Res. Chung-Kuo Yen Cheng Yen Chiu 2013, 25, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Landis-Piwowar, K.R.; Chen, M.S.; Dou, Q.P. Inhibition of proteasome activity by the dietary flavonoid apigenin is associated with growth inhibition in cultured breast cancer cells and xenografts. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2007, 9, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.-J.; Chen, W.-K.; Wang, C.-J.; Lin, W.-L.; Tseng, T.-H. Apigenin inhibits HGF-promoted invasive growth and metastasis involving blocking PI3K/Akt pathway and β4 integrin function in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 226, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-W.; Xu, J.; Zhu, G.-Y.; Huang, Z.-J.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.-Q.; Wang, N.; Zhang, F.-X. Apigenin suppresses the stem cell-like properties of triple-negative breast cancer cells by inhibiting YAP/TAZ activity. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Jung, J.; Moon, A.; Kang, H.; Cho, H. Antitumor and Anti-Invasive Effect of Apigenin on Human Breast Carcinoma through Suppression of IL-6 Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Ji, P.; Liu, B.; Qiao, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Deng, T.; Ba, Y. Apigenin enhances the cisplatin cytotoxic effect through p53-modulated apoptosis. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seo, H.-S.; Ku, J.M.; Choi, H.S.; Woo, J.-K.; Lee, B.H.; Kim, D.S.; Song, H.J.; Jang, B.-H.; Shin, Y.C.; Ko, S.-G. Apigenin overcomes drug resistance by blocking the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling in breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, X.; Bai, J.; Zhao, S.; Hu, M.; Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; Ji, M.; Jin, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; et al. Evaluation of inhibitory effects of flavonoids on breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP): From library screening to biological evaluation to structure-activity relationship. Toxicol. In Vitro Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2019, 61, 104642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakaran, M.; Parra, M.R.; Stoub, H.; Gallo, K.A.; Doseff, A.I. Apigenin by targeting hnRNPA2 sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer spheroids to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis and regulates expression of ABCC4 and ABCG2 drug efflux transporters. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 114259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozwik, K.M.; Carroll, J.S. Pioneer factors in hormone-dependent cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Wang, S.; Jiang, N.; Li, J.J. Cyclin B1/CDK1-regulated mitochondrial bioenergetics in cell cycle progression and tumor resistance. Cancer Lett. 2019, 443, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.D.; Brooks, L.; Zhang, X.; Mahoney, J.M.; Martyanov, V.; Wood, T.A.; Sherlock, G.; Cheng, C.; Whitfield, M.L. Identification of cell cycle–regulated genes periodically expressed in U2OS cells and their regulation by FOXM1 and E2F transcription factors. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 3634–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, C.J.; Zhang, W.; Hillman, J.; Stablewski, A.B.; Higgins, M.J.; Vanderhyden, B.C.; Odunsi, K.; Karpf, A.R. Genetic determinants of FOXM1 overexpression in epithelial ovarian cancer and functional contribution to cell cycle progression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27613–27627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shariati, M.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Targeting AKT for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Gondal, T.A.; Atif, M.; Shahbaz, M.; Qaisarani, T.B.; Mughal, M.H.; Salehi, B.; Martorell, M.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Apigenin as an anticancer agent. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1812–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecomte, S.; Demay, F.; Pham, T.H.; Moulis, S.; Efstathiou, T.; Chalmel, F.; Pakdel, F. Deciphering the Molecular Mechanisms Sustaining the Estrogenic Activity of the Two Major Dietary Compounds Zearalenone and Apigenin in ER-Positive Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Nutrients 2019, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, Y.; Laws, M.J.; Sanabria Guillen, V.; Kim, S.H.; Dey, P.; Smith, B.P.; Gong, P.; Bindman, N.; Zhao, Y.; Carlson, K.; et al. Suppression of FOXM1 activities and breast cancer growth in vitro and in vivo by a new class of compounds. NPJ Breast Cancer 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shendge, A.K.; Chaudhuri, D.; Basu, T.; Mandal, N. A natural flavonoid, apigenin isolated from Clerodendrum viscosum leaves, induces G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in MCF-7 cells through the regulation of p53 and caspase-cascade pathway. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Ding, Z.; Yao, Y.; Ren, F.; Yin, M.; Yang, S.; Chen, A. Apigenin induces apoptosis and counteracts cisplatin-induced chemoresistance via Mcl-1 in ovarian cancer cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Wu, T.H.Y.; Leung, S.S.Y.; To, K.K.W. Flavonoids potentiated anticancer activity of cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro by inhibiting histone deacetylases. Life Sci. 2020, 258, 118211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Sim, J.; Abdul, R.; Chung, M.S.; Paik, S.S.; Oh, Y.-H.; Park, C.K.; Jang, K. Increased Expression of Forkhead Box M1 Is Associated with Aggressive Phenotype and Poor Prognosis in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name and Symbol | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3) | GCCGTTGAGGGTTTCAGAGA | TCCGAGCACAACCACCTTAG |
| Forkhead box A1 (FOXA1) | CCCCTTTGTCCTCTCTACCC | CTGCAAAGCAAGAAGCAGAGT |
| Estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1/ERα) | TTTATGGGAAAAGGCTCAAA | GACAAAACCGAGTCACATCA |
| Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12 (CXCL12) | CACCATTGAGAGGTCGGAAG | AATGAGACCCGTCTTTGCAG |
| Progesterone receptor (PgR) | CCCGCCGTCGTAACTTTGG | GTGCCTATCCTGCCTCTCAATC |
| Amphiregulin (AREG) | GTATTTTCACTTTCCGTCTTGTTTTG | CCTGGCTATATTGTCGATTCA |
| Forkhead box M1 (FOXM1) | AGTGCCAACCGCTACTTGAC | CACCGGGAACTGGATAGGTA |
| Cell division cycle 25A (CDC25A) | CAAGGGTGCAGTGAACTTGC | ACAACAATGACACGCTTGCC |
| Cyclin B1 (CCNB1) | TCTGGATAATGGTGAATGGACA | CGATGTGGCATACTTGTTCTTG |
| Centromere protein A (CENPA) | ACATGCAGGCCGAGTTACTC | AGAGTCCCCGGTATCATCCC |
| Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) | CTCAACACGCCTCATCCTC | GTGCTCGCTCATGTAATTGC |
| Cyclin-Dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (CDKN1A/p21) | CTGTCTTGTACCCTTGTGCC | GGTAGAAATCTGTCATGCTGG |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) | TGCACCACCAACTGCTTAGC | GGCATGGACTGTGGTCATGAG |
| TATA box-binding protein (TBP) | TGCACAGGAGCCAAGAGTGAA | CACATCACAGCTCCCCACCA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pham, T.H.; Page, Y.L.; Percevault, F.; Ferrière, F.; Flouriot, G.; Pakdel, F. Apigenin, a Partial Antagonist of the Estrogen Receptor (ER), Inhibits ER-Positive Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation through Akt/FOXM1 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010470
Pham TH, Page YL, Percevault F, Ferrière F, Flouriot G, Pakdel F. Apigenin, a Partial Antagonist of the Estrogen Receptor (ER), Inhibits ER-Positive Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation through Akt/FOXM1 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(1):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010470
Chicago/Turabian StylePham, Thu Ha, Yann Le Page, Frédéric Percevault, François Ferrière, Gilles Flouriot, and Farzad Pakdel. 2021. "Apigenin, a Partial Antagonist of the Estrogen Receptor (ER), Inhibits ER-Positive Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation through Akt/FOXM1 Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 1: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010470
APA StylePham, T. H., Page, Y. L., Percevault, F., Ferrière, F., Flouriot, G., & Pakdel, F. (2021). Apigenin, a Partial Antagonist of the Estrogen Receptor (ER), Inhibits ER-Positive Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation through Akt/FOXM1 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010470






