Novel Symmetrical Cage Compounds as Inhibitors of the Symmetrical MRP4-Efflux Pump for Anticancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
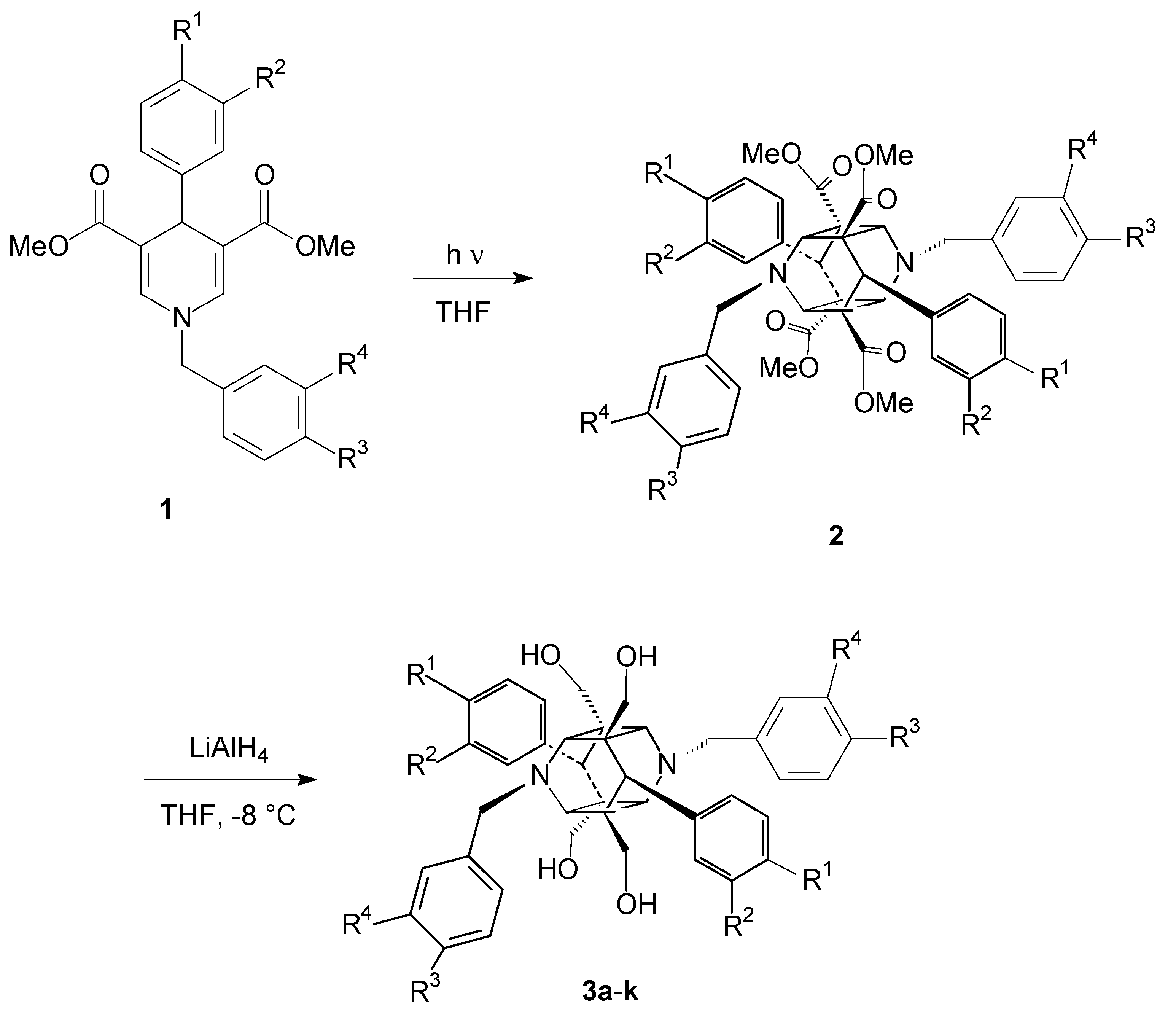
2.1. Formation of the 1,4-Dihydropyridine Cage Dimer Formation
2.2. MRP4 Efflux Pump Inhibition with the 1,4-Dihydropyridines
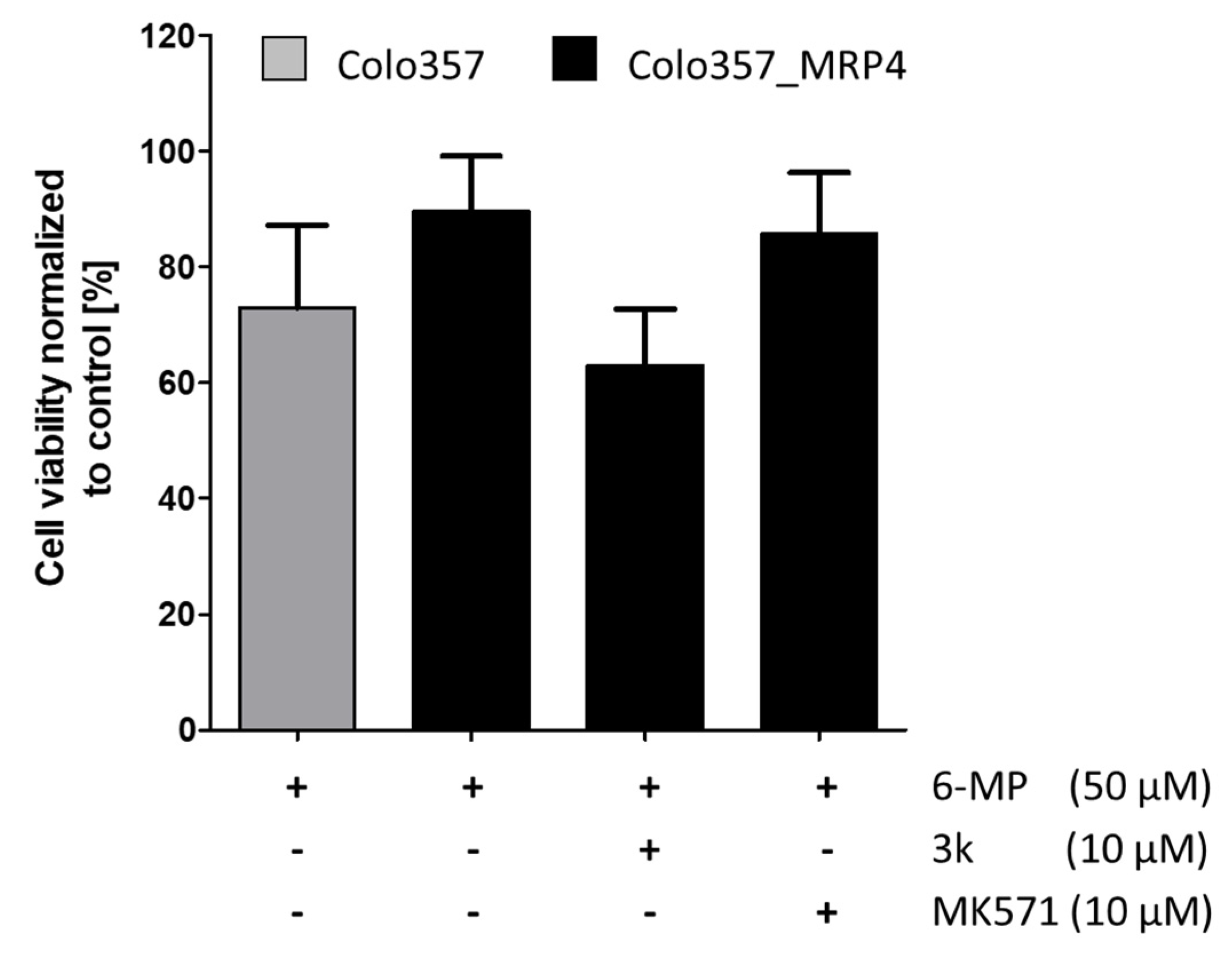
2.3. In Vitro MRP Resistance Studies of Drug Reversal
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Chemical Reagents and Instruments
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 1
3.3. General Procedure for the Cage Dimer Formation of Compounds 2
3.4. General Procedure for the Ester Group Reduction in the Cage Dimers to Form the Target Compounds 3a–k
3.4.1. 3,9-dibenzyl-1,5,7,11-tetrakishydroxymethyl-6,12-diphenyl-3,9-diazhexacyclo-[6.4.0.02.7.04.11.05.10]dodecane 3a
3.4.2. 3,9-bis(4-methoxybenzyl)-1,5,7,11-tetrakishydroxymethyl-6,12-diphenyl-3,9-diazhexa-cyclo[6.4.0.02.7.04.11.05.10]dodecane 3b
3.4.3. 3,9-bis(4-methoxybenzyl)-1,5,7,11-tetrakishydroxymethyl-6,12-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-3,9-diazhexacyclo[6.4.0.02.7.04.11.05.10]dodecane 3c
3.4.4. 3,9-bis(3-methoxybenzyl)-1,5,7,11-tetrakishydroxymethyl-6,12-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-3,9-diazhexacyclo[6.4.0.02.7.04.11.05.10]dodecane 3d
3.4.5. 3,9-bis(3-methoxybenzyl)-1,5,7,11-tetrakishydroxymethyl-6,12-bis(3-methoxyphenyl)-3,9-diazhexacyclo[6.4.0.02.7.04.11.05.10]dodecane 3e
3.4.6. 3,9-bis(4-methoxybenzyl)-1,5,7,11-tetrakishydroxymethyl-6,12-bis(3-methoxyphenyl)-3,9-diazhexacyclo[6.4.0.02.7.04.11.05.10]dodecane 3f
3.4.7. 3,9-bis(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-1,5,7,11-tetrakishydroxymethyl-6,12-bis(3-methoxyphenyl)-3,9-diazhexacyclo[6.4.0.02.7.04.11.05.10]dodecane 3g
3.4.8. 3,9-bis(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-1,5,7,11-tetrakishydroxymethyl-6,12-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-3,9-diazhexacyclo[6.4.0.02.7.04.11.05.10]dodecane 3h
3.4.9. 3,9-bis(3-dimethoxybenzyl)-1,5,7,11-tetrakishydroxymethyl-6,12-bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3,9-diazhexacyclo[6.4.0.02.7.04.11.05.10]dodecane 3i
3.4.10. 3,9-bis(4-methoxybenzyl)-1,5,7,11-tetrakishydroxymethyl-6,12-bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3,9-diazhexacyclo[6.4.0.02.7.04.11.05.10]dodecane 3j
3.4.11. 3,9-bis(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-1,5,7,11-tetrakishydroxymethyl-6,12-bis(3,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3,9-diazhexacyclo[6.4.0.02.7.04.11.05.10]dodecane 3k
3.5. MRP4 Inhibition Assay
3.6. MTT-Based Viability Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cancer (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Sun, J.; Wei, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Xu, H. A systematic analysis of FDA-approved anticancer drugs. BMC Syst. Biol. 2017, 11 (Suppl. 5), 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buolamwini, J.K.; Assefa, H. Overview of Novel Anticancer Drug Targets. In Novel Anticancer Drug Protocols; Buolamwini, J.K., Adjei, A.A., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Medicine; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2003; p. 85. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, C.; Ng, J.; Wigmore, T. The side effects of chemotherapeutic agents. Curr. Anaest. Crit. Care 2008, 19, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug Resistance in Cancer: An Overview. Cancers 2014, 6, 1769–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhullar, K.S.; Largarón, N.O.; McGowan, E.M.; Parmar, I.; Jha, A.; Hubbard, B.P.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Kinase-targeted cancer therapies: Progress, challenges and future directions. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.M.; Allison, J.P.; Wolchok, J.D. Monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy. Cancer Immun. 2012, 12, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barouche-Bentov, R. Mechanisms of Drug-Resistance in Kinases. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2011, 20, 153–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San-Juan-Rodriguez, A.; Newman, T.V.; Hernandez, I. Pricing of Monoclonal Antibodies in the United States. Glob. J. Qual. Saf. Healthc. 2018, 1, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lowrence, R.C.; Subramaniapillai, S.G.; Ulaganthan, V.; Nagarajan, S. Tackling drug resistance with efflux pump inhibitors: From bacteria to cancerous cells. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 45, 334–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robey, R.W.; Pluchino, K.M.; Hall, M.D.; Fojo, A.T.; Bates, S.E.; Gottesman, M.M. Revisiting the role of efflux pumps in multidrug-resistant cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S.E. Multidrug resistance in cancer: Role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, G.D.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S.E. The role of ABC transporters in clinical practice. Oncologist 2003, 8, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkhatlan, Z.; Lavasanifar, A. P-glycoprotein inhibition as a therapeutic approach for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer: Current status and future perspectives. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 326–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leeuwen, F.W.; Buckle, T.; Kersbergen, A.; Rottenberg, S.; Gilhuijs, K.G. Noninvasiv functional imaging of P-glycoprotein-mediated doxorubicin resistance in a mouse model of hereditary breast cancer to predict response and assign P-gp inhibitory sensitivity. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 36, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajic, M. Moderate increase in Mdr1a/b expression causes in vivo resistance to doxorubicin in a mouse model for hereditary cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6396–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russel, F.G.; Koenderink, J.B.; Masereeuw, R. Multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4): A versatile efflux transporter for drugs and signalling molecules. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 29, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, X.; Xiao, Z.; Jin, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z. Discovery of novel multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4) inhibitors as active agents reducing resistance to anticancer drug 6-Mercaptopurin (6-MP) by structure and ligand-based virtual screening. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205175. [Google Scholar]
- Deeley, R.G.; Westlake, C.; Cole, S.P. Transmembrane transport of endo- and xenobiotics by mammalian ATP-binding cassette multidrug resistance proteins. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 849–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Bera, N.; Ghosh, S. [2+2] Photochemical Cycloaddition in Organic Synthesis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 1310–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, P.; Jorgensen, M.J. Photodimer Cage Compounds. I. The Structure of the Photodimer of 2,3-Dimethyl-4-pyrone. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 2956–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolowa, R.D.; Vayssilov, G.N.; Rodios, N.; Bojilova, A. Regio- and Stereoselective [2+2] Photodimerization of 3-Substituted 2-Alkoxy-2-oxo-2H-1,2-benzoxaphosphorines. Molecules 2002, 7, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr-Esfahani, M.; Montazerozohori, M.; Raeatikia, R. An efficient Hantzsch synthesis of 1,4-dihydropyridines using p-toluensulfonic acid under solvent-free condition. Maejo Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Berson, J.A.; Brown, E.J. Studies on Dihydropyridines. II. The Photochemical Disproportionation of 4-(2′-Nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridines. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.J.; Haber, M.; Porro, A.; Munoz, M.A.; Iraci, N.; Xue, C. ABC multidrug transporters in childhood neuroblastoma: Clinical and biological effects independent of cytotoxic drug efflux. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1236–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Omwanche, J.; Hsieh, C.L.; Shemshedini, L. Androgen induces expression of the multidrug resistance protein gene MRP4 in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2007, 10, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimerl, S.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Langmann, T.; Ecker, J.; Schmitz, G. Mapping ATP-binding cassette transporter gene expression profiles in melanocytes and melanoma cells. Melanoma Res. 2007, 17, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copsel, S.; Garcia, C.; Diez, F.; Vermeulen, M.; Baldi, A.; Bianciotti, L.G. Multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4) regulates cAMP cellular levels and controls human leukemia cell proliferation and differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 6979–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochel, T.J.; Reader, J.C.; Ma, X.; Kindu, N.; Fulton, A.M. Multiple drug-resistance-associated protein (MRP4) exports prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and contributes to metastasis in basal/triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 6540–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carozzo, A.; Yaneff, A.; Gómez, N.; Di Siervi, N.; Sahores, A.; Attorresi, A.; Rodríguez-González, À.; Monczor, F.; Abba, M.; Shayo, C.; et al. Identification of MRP4/ABCC4 as Target for Reducing the Proliferation of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells by Modulating the cAMP Efflux. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 96, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzic, D.; Noel, P.; Merien, F.; Liu, D.-X.; Lu, J.; Han, H.; McKeage, M.J.; Li, Y. The Effects of Synthetically Modified Natural Compounds on ABC Transporters. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Rich, T.C.; Scheitrum, C.; Conti, M.; Richter, W. Inactivation of multidrug resistance protein disrupts both cellular extrusion and intracellular degradation of cAMP. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawan, A.; Wagner, E.; Roidl, A. Consecutive salinomycin treatment reduv’ces doxorubicin resistance of breast tumor cells by diminishing drug efflux pump expression and activity. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhwa, B.; Paddar, M.; Khan, S.; Mir, S.; Clarke, P.A.; Grabowska, A.M.; Vijay, D.G.; Malik, F. AKT isoforms have discrete expression in triple negative breast cancers and roles in cisplatin sensitivity. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 4178–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Fang, D.; Ding, H.-F.; Dong, Z.; Jing, Q.; Su, S.-B.; Huang, S. Tripel negative breat cancer development can be selectively suppressed by sustaining level of cellular cyclic AMP through simultaneously blocking its efflux and decomposition. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 87232–87245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rius, M.; Nies, A.T.; Hummel-Eisenbeiss, J.; Jedlitschky, G.; Keppler, D. Cotransport of reduced glutathione with bile salts by MRP4 (ABCC4) localized to the basolateral hepatocyte membrane. Hepatology 2003, 38, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cpd. | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | FAR Value a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3a | H | H | H | H | 1.15 |
| 3b | H | H | OMe | H | 1.15 |
| 3c | OMe | H | OMe | H | 1.34 |
| 3d | OMe | H | H | OMe | 1.56 |
| 3e | H | OMe | H | OMe | 1.52 |
| 3f | H | OMe | OMe | H | 1.70 |
| 3g | H | OMe | OMe | OMe | 1.55 |
| 3h | OMe | H | OMe | OMe | 1.36 |
| 3i | OMe | OMe | H | OMe | 1.25 |
| 3j | OMe | OMe | OMe | H | 1.41 |
| 3k | OMe | OMe | OMe | OMe | 1.74 |
| MK571 | 0.82 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kreutzer, D.; Döring, H.; Werner, P.; Ritter, C.A.; Hilgeroth, A. Novel Symmetrical Cage Compounds as Inhibitors of the Symmetrical MRP4-Efflux Pump for Anticancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105098
Kreutzer D, Döring H, Werner P, Ritter CA, Hilgeroth A. Novel Symmetrical Cage Compounds as Inhibitors of the Symmetrical MRP4-Efflux Pump for Anticancer Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(10):5098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105098
Chicago/Turabian StyleKreutzer, David, Henry Döring, Peter Werner, Christoph A. Ritter, and Andreas Hilgeroth. 2021. "Novel Symmetrical Cage Compounds as Inhibitors of the Symmetrical MRP4-Efflux Pump for Anticancer Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 10: 5098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105098
APA StyleKreutzer, D., Döring, H., Werner, P., Ritter, C. A., & Hilgeroth, A. (2021). Novel Symmetrical Cage Compounds as Inhibitors of the Symmetrical MRP4-Efflux Pump for Anticancer Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(10), 5098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105098





