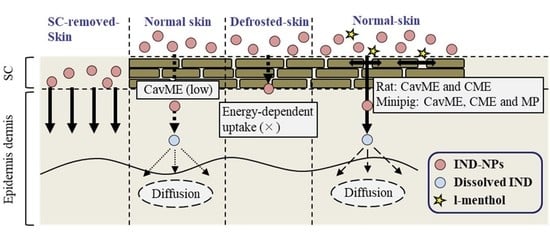
Energy-Dependent Endocytosis Is Responsible for Skin Penetration of Formulations Based on a Combination of Indomethacin Nanoparticles and l-Menthol in Rat and Göttingen Minipig
Abstract
Share and Cite
Otake, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Ogata, F.; Deguchi, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Sasaki, H.; Kawasaki, N.; Nagai, N. Energy-Dependent Endocytosis Is Responsible for Skin Penetration of Formulations Based on a Combination of Indomethacin Nanoparticles and l-Menthol in Rat and Göttingen Minipig. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105137
Otake H, Yamaguchi M, Ogata F, Deguchi S, Yamamoto N, Sasaki H, Kawasaki N, Nagai N. Energy-Dependent Endocytosis Is Responsible for Skin Penetration of Formulations Based on a Combination of Indomethacin Nanoparticles and l-Menthol in Rat and Göttingen Minipig. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(10):5137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105137
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtake, Hiroko, Mizuki Yamaguchi, Fumihiko Ogata, Saori Deguchi, Naoki Yamamoto, Hiroshi Sasaki, Naohito Kawasaki, and Noriaki Nagai. 2021. "Energy-Dependent Endocytosis Is Responsible for Skin Penetration of Formulations Based on a Combination of Indomethacin Nanoparticles and l-Menthol in Rat and Göttingen Minipig" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 10: 5137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105137
APA StyleOtake, H., Yamaguchi, M., Ogata, F., Deguchi, S., Yamamoto, N., Sasaki, H., Kawasaki, N., & Nagai, N. (2021). Energy-Dependent Endocytosis Is Responsible for Skin Penetration of Formulations Based on a Combination of Indomethacin Nanoparticles and l-Menthol in Rat and Göttingen Minipig. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(10), 5137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105137