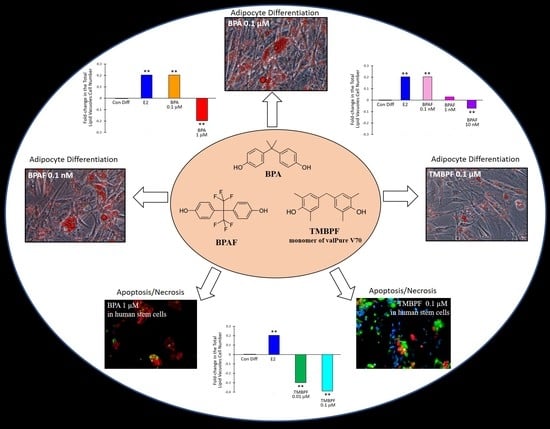
BPA, BPAF and TMBPF Alter Adipogenesis and Fat Accumulation in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells, with Implications for Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cell Viability with Low-Dose BPA, BPAF and TMBPF Exposure
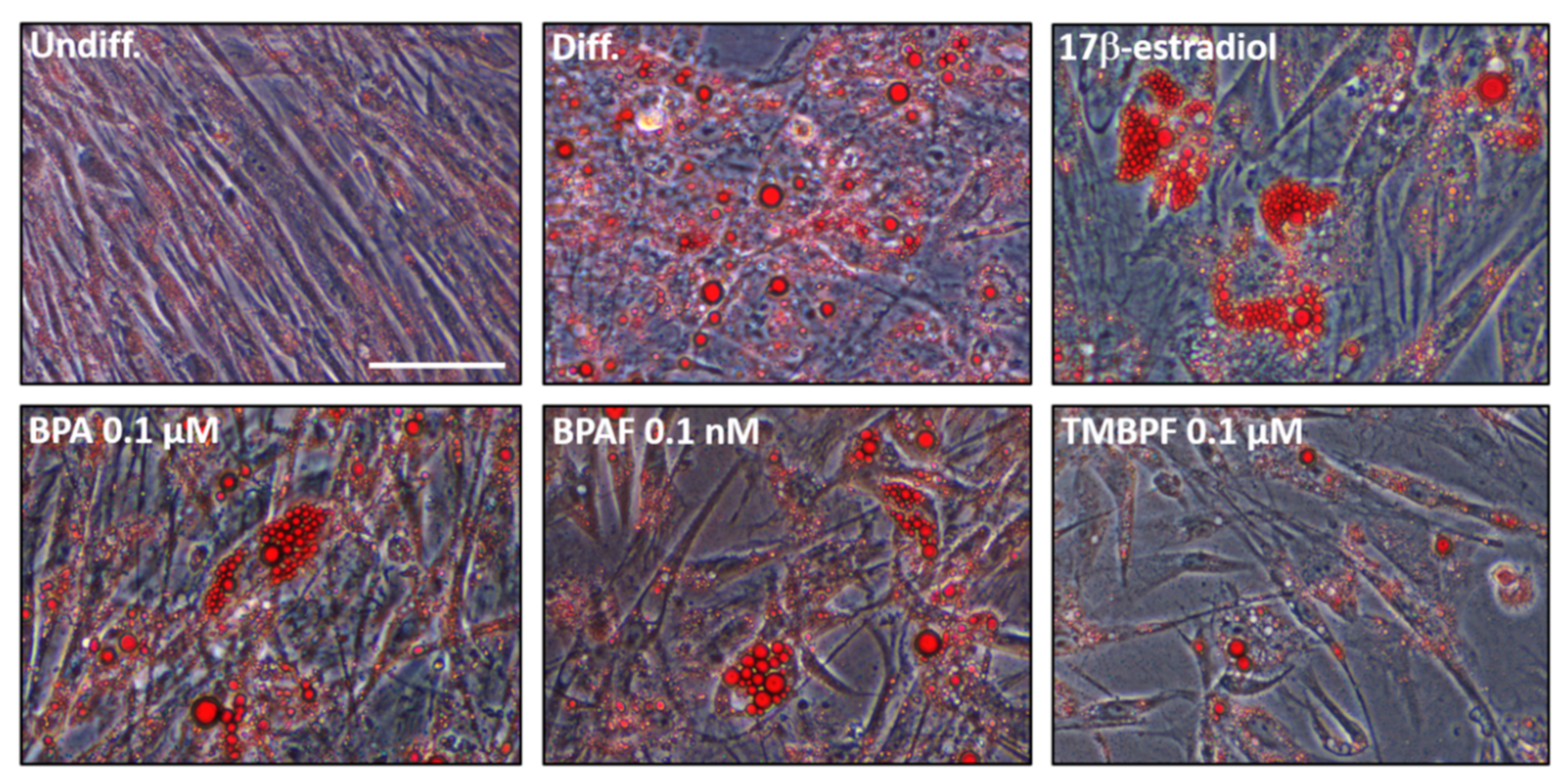
2.2. Differentiation of Human ASCs into Adipocytes
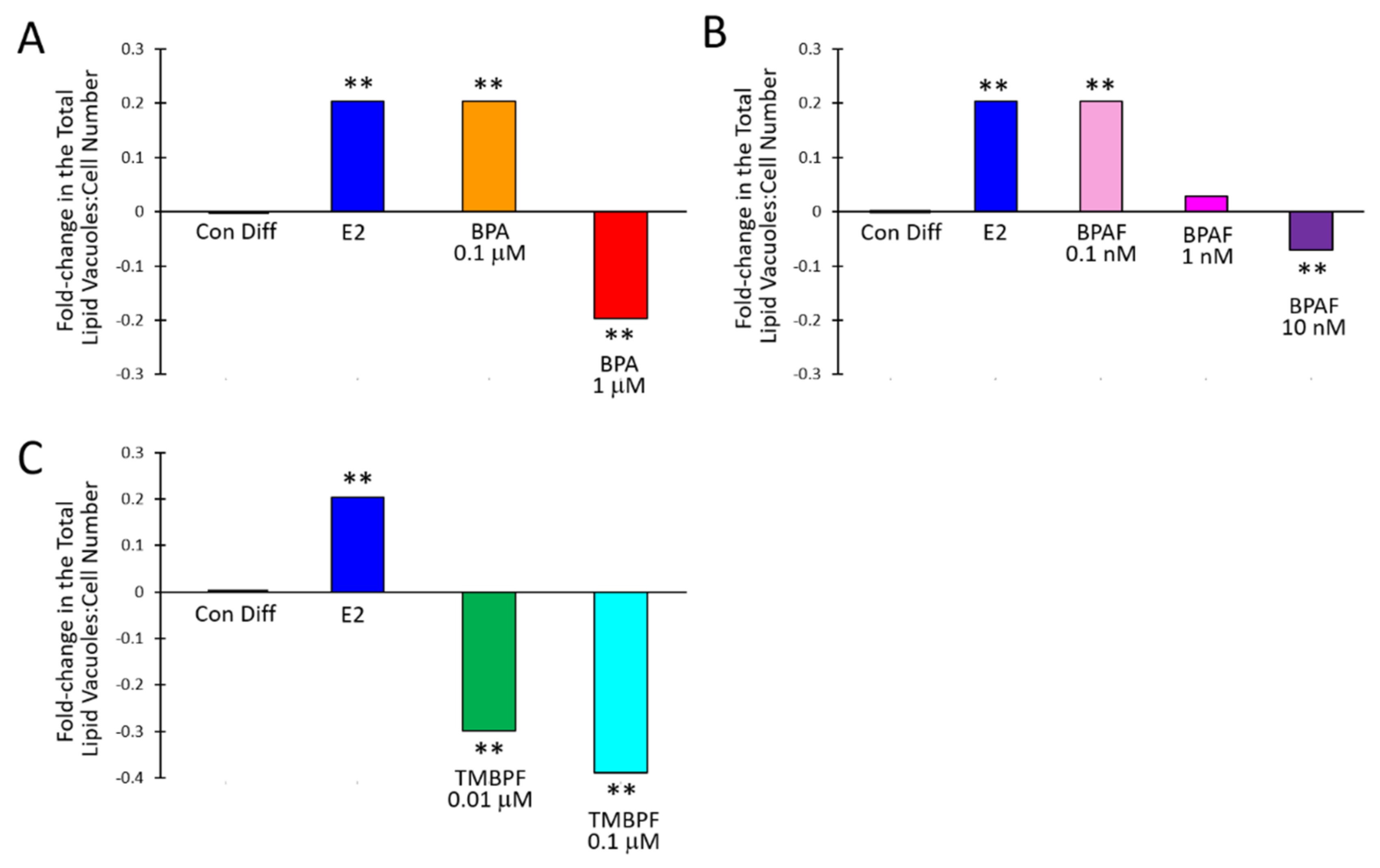
2.3. Low-Dose BPA and BPAF Increase Adipogenesis
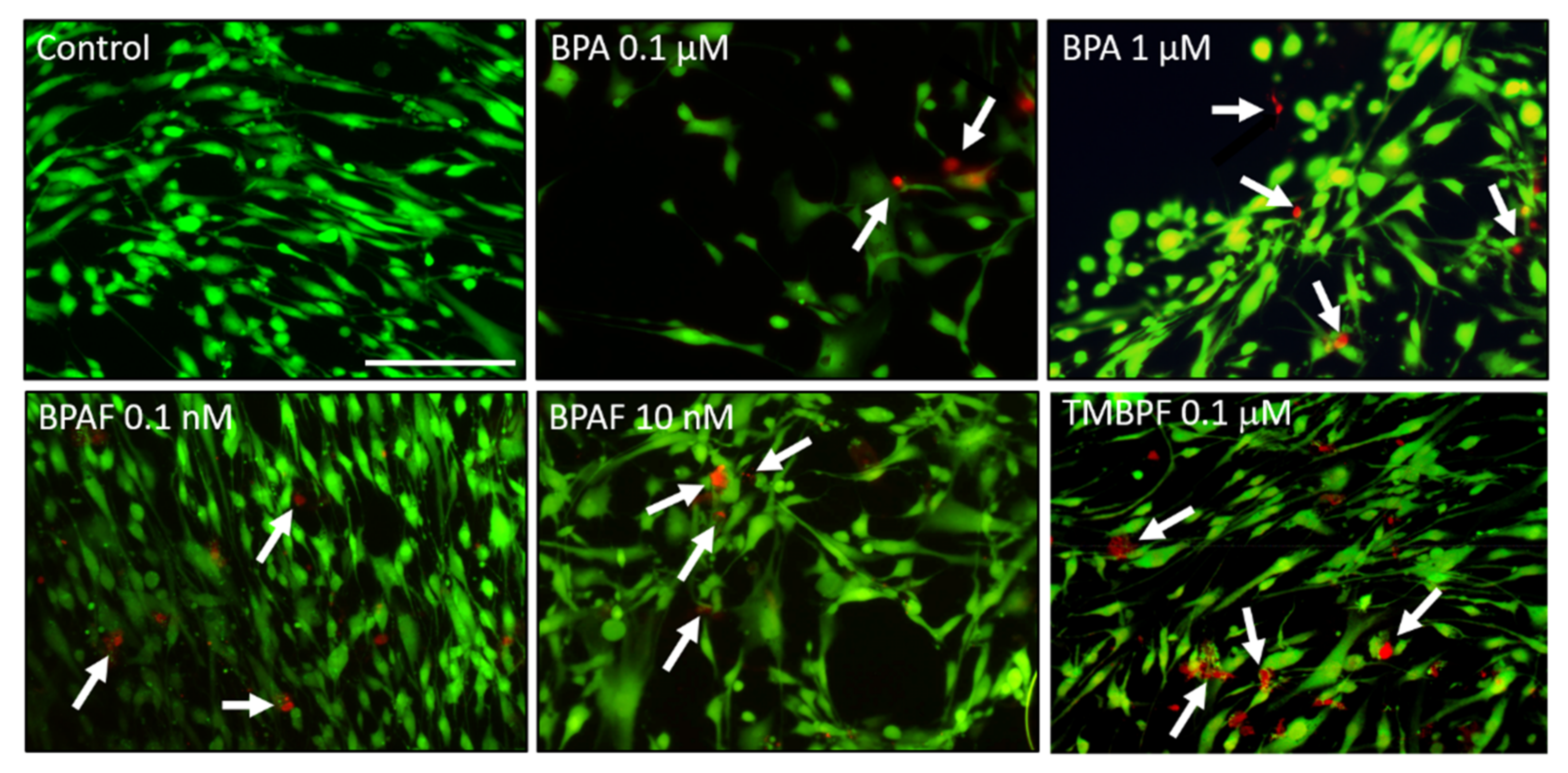
2.4. TMBPF Decreases Adipogenesis and Shows Cytotoxicity in Stem Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Stem Cell Isolation and Cell Culture
4.3. BPA, BPAF and TMBPF Cytotoxicity
4.4. Adipocyte Differentiation of Rat ASCs
4.5. Adipocyte Differentiation of Human ASCs Exposed to BPA Analogs or 17β-Estradiol
4.6. Adipocyte and Lipid Quantification and Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vogel, S.A. The politics of plastics: The making and unmaking of Bisphenol A “Safety”. Am. J. Public Health 2009, 99, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janesick, A.; Bloomberg, B. Obesogens, stem cells, and the developmental programming of obesity. Int. J. Androl. 2012, 35, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.M.; Hauser, R. Bisphenol A and children’s health. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2011, 23, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, S.; Markle, T.; Thompson, S.; Wallace, E. Bisphenol A exposure, effects, and policy: A wildlife perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 104, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onundi, Y.; Drake, B.A.; Malecky, R.T.; DeNardo, M.A.; Mills, M.R.; Kundu, S.; Ryabov, A.D.; Beach, E.S.; Horwitz, C.P.; Simonich, M.T.; et al. A multidisciplinary investigation of the technical and environmental performances of TAML/peroxide elimination of Bisphenol A compounds from water. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 4234–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, R.; Troisi, J.; Richards, S.; Scafuro, M.; Fasano, S.; Guida, M.; Pierantoni, R.; Meccariello, R. Bisphenol A in Reproduction: Epigenetic Effects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 748–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Chahoud, I.; Heindel, J.J.; Padmanabhan, V.; Paumgartten, F.J.R.; Schoenfelder, G. Urinary, Circulating, and Tissue Biomonitoring Studies Indicate Widespread Exposure to Bisphenol A. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, S.; Raposo, A.; Almeida-González, M.; Carrascosa, C. Bisphenol A: Food Exposure and Impact on Human Health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1503–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, B.S.; Schaeberle, C.M.; Soto, A.M. The Case for BPA as an Obesogen: Contributors to the Controversy. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.L.; Perez-Locas, C.; Dufresne, G.; Clement, G.; Popovic, S.; Beraldin, F.; Dabeka, R.W.; Feeley, M. Concentrations of bisphenol A in the composite food samples from the 2008 Canadian total diet study in Quebec City and dietary intake estimates. Food Addit. Contam. 2011, 28, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Kannan, K. Concentrations and Profiles of Bisphenol A and Other Bisphenol Analogues in Foodstuffs from the United States and Their Implications for Human Exposure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4655–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geens, T.; Aerts, D.; Berthot, C.; Bourguignon, J.-P.; Goeyens, L.; Lecomte, P.; Maghuin-Rogister, G.; Pironnet, A.-M.; Pussemier, L.; Scippo, M.-L.; et al. A review of dietary and non-dietary exposure to bisphenol-A. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3725–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanaoka, T.; Kawamura, N.; Hara, K.; Tsugane, S. Urinary bisphenol A and plasma hormone concentrations in male workers exposed to bisphenol A diglycidyl ether and mixed organic solvents. Occup. Environ. Med. 2002, 59, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, A.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Fujita, T.; Kuroda, K.; Endo, G. Chemical analysis and genotoxicological safety assessment of paper and paperboard used for food packaging. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrales, J.; Kristofco, L.A.; Steele, W.B.; Yates, B.S.; Breed, C.S.; Williams, E.S.; Brooks, B.W. Global assessment of bisphenol A in the environment: Review and analysis of its occurrence and bioaccumulation. Dose Response 2015, 13, 1559325815598308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Liu, F.; Moon, H.-B.; Yamashita, N.; Yun, S.; Kannan, K. Bisphenol Analogues in Sediments from Industrialized Areas in the United States, Japan, and Korea: Spatial and Temporal Distributions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11558–11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Zhu, L. Occurrence and partitioning of bisphenol analogues in water and sediment from Liaohe River Basin and Taihu Lake, China. Water Res. 2016, 103, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, H.; Küchler, T.; Otto, T.; Pilz, K.; Müller, J.; Wenzel, A. Occurrence of phthalates and bisphenol A and F in the environment. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-B.; Peart, T.E. Bisphenol A Contamination in Canadian Municipal and Industrial Wastewater and Sludge Samples. Water Qual. Res. J. 2000, 35, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hauser, R.; Marcus, M.; Olea, N.; Welshons, W.V. Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Lam, J.; Lam, P.K.; Moon, H.-B.; Jeong, Y.; Kannan, P.; Achyuthan, H.; Munuswamy, N.; et al. Bisphenol A and other bisphenol analogues including BPS and BPF in surface water samples from Japan, China, Korea and India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu-Denoncourt, J.; Wallace, S.J.; De Solla, S.R.; Langlois, V.S. Influence of Lipophilicity on the Toxicity of Bisphenol A and Phthalates to Aquatic Organisms. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernier, M.R.; Vandenberg, L.N. Handling of thermal paper: Implications for dermal exposure to bisphenol A and its alternatives. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toner, F.; Allan, G.; Dimond, S.S.; Waechter, J.M.; Beyer, D. In Vitro percutaneous absorption and metabolism of Bisphenol A (BPA) through fresh human skin. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 47, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Alomirah, H.; Cho, H.-S.; Li, Y.-F.; Liao, C.; Minh, T.B.; Mohd, M.A.; Nakata, H.; Ren, N.; Kannan, K. Urinary Bisphenol A Concentrations and Their Implications for Human Exposure in Several Asian Countries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7044–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Wu, Q.; Sakthivel, S.; Pavithran, P.V.; Vasukutty, J.R.; Kannan, K. Urinary levels of endocrine-disrupting chemicals, including bisphenols, bisphenol A diglycidyl ethers, benzophenones, parabens, and triclosan in obese and non-obese Indian children. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, M.; Arbuckle, T.E.; MacPherson, S.; Braun, J.M.; Feeley, M.; Gaudreau, É. Phthalate and BPA Exposure in Women and Newborns through Personal Care Product Use and Food Packaging. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10813–10826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, L.E.; Ferguson, K.K.; Meeker, J.D. Relationships Between Urinary Phthalate Metabolite and Bisphenol A Concentrations and Vitamin D Levels in U.S. Adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 2005–2010. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 4062–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, H.M.; Kolossa-Gehring, M.; Schröter-Kermani, C.; Angerer, J.; Brüning, T. Bisphenol A in 24 h urine and plasma samples of the German Environmental Specimen Bank from 1995 to 2009: A retrospective exposure evaluation. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longnecker, M.; Harbak, K.; Kissling, G.; Hoppin, J.; Eggesbo, M.; Jusko, T.; Eide, J.; Koch, H. The concentration of bisphenol A in urine is affected by specimen collection, a preservative, and handling. Environ. Res. 2013, 126, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmler, H.J.; Liu, B.; Gadogbe, M.; Bao, W. Exposure to bisphenol A, bisphenol F, and bisphenol S in U. S. adults and children: The national health and nutrition examination survey 2013–2014. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6523–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlstein, J.F.; Strong, A.L.; McLachlan, J.A.; Gimble, J.M.; Burow, M.E.; Bunnell, B.A. Bisphenol A enhances adipogenic differentiation of human adipose stromal/stem cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 53, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, J.C.; Leonard, L.S.; Maness, S.C.; Wagner, B.L.; Conner, K.; Zacharewski, T.; Safe, S.; McDonell, D.P.; Gaido, K.W. Bisphenol A interacts with the estrogen receptor alpha in a distinct manner from estradiol. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1998, 142, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouzand, F.; Thierry-Mieg, M.; Burga, K.; Vérines-Jouin, L.; Fiore, K.; Beausoleil, C.; Michel, C.; Rousselle, C.; Pasquier, E. Concerns related to ED-Mediated effects of Bisphenol A and their regulatory consideration. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 475, 30055–30058. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, B.S. Bisphenol A: An endocrine disruptor with widespread exposure and multiple effects. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 127, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karwacka, A.; Zamkowksa, D.; Radwan, M.; Jurewicz, J. Exposure to modern, widespread environmental endocrine disrupting chemicals and their effect on the reproductive potential of women: An overview of current epidemiological research. Hum. Fertil. 2019, 22, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moklin, E.; Ehrlich, S.; Williams, P.L.; Petrozza, J.C.; Wright, D.L.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Hauser, R. Urinary bisphenol A concentrations and ovarian response among women undergoing IVF. Int. J. Androl. 2010, 33, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiola, J.; Jørgensen, N.; Andersson, A.-M.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Redmon, J.B.; Drobnis, E.Z.; Wang, C.; Sparks, A.; Thurston, S.W.; et al. Are Environmental Levels of Bisphenol A Associated with Reproductive Function in Fertile Men? Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbucka-Kretowska, M.; Zbucki, R.; Parfieniuk, E.; Maslyk, M.; Lazarek, U.; Miltyk, W.; Czerniecki, J.; Wolczynski, S.; Kretowski, A.; Ciborowski, M. Evaluation of Bisphenol A influence on endocannabinoid system in pregnant women. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, S.; Suzuki, T.; Sanoh, S.; Kohta, R.; Jinno, N.; Sugihara, K.; Yoshihara, S.; Fujimoto, N.; Watanabe, H.; Ohta, S. Comparative Study of the Endocrine-Disrupting Activity of Bisphenol A and 19 Related Compounds. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 84, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardas, F.; Bayram, A.K.; Demirci, E.; Akin, L.; Ozmen, S.; Kendirci, M.; Canpolat, M.; Oztop, D.B.; Narin, F.; Gumus, H.; et al. Increased Serum Phthalates (MEHP, DEHP) and Bisphenol A Concentrations in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: The Role of Endocrine Disruptors in Autism Etiopathogenesis. J. Child Neurol. 2016, 31, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongkorn, S.; Kanlayaprasit, S.; Jindatip, D.; Tencomnao, T.; Hu, V.W.; Sarachana, T. Sex Differences in the Effects of Prenatal Bisphenol A Exposure on Genes Associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder in the Hippocampus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, S.; Raghuraman, N.; Eltoum, I.; Carpenter, M.; Russo, J.; Lamartiniere, C.A. Oral Exposure to Bisphenol A Increases Dimethylbenzanthracene-Induced Mammary Cancer in Rats. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafei, A.; Ramzy, M.M.; Hegazy, A.I.; Husseny, A.K.; El-Hadary, U.G.; Taha, M.M.; Mosa, A.A. The molecular mechanisms of action of the endocrine disrupting chemical bisphenol A in the development of cancer. Gene 2018, 647, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.S.; Chen, H.Q.; Chen, Y.S.; Qiu, K.F.; Zheng, X.B.; Li, G.C.; Yang, H.D.; Wen, C.J. Bisphenol A stimulates human lung cancer cell migration via upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases by GPER/EGFR/ERK1/2 signal pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2014, 68, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obesity and Overweight Factsheets. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Jacobson, M.H.; Woodward, M.; Bao, W.; Liu, B.; Trasande, L. Urinary Bisphenols and Obesity Prevalence among U.S. Children and Adolescents. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafat, A.; Ye, X.; Wong, L.Y.; Reidy, J.A.; Needham, L.L. Exposure of the U.S. Population to bisphenol a and 4-Tert-Octylphenol: 2003–2004. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Lee, E.; Kim, Y. The Association between Bisphenol A Exposure and Obesity in Children—A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, R.; Xiao, J.; Shankar, A. Urinary Bisphenol A and Obesity in US Children. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Woerden, I.; Bruening, M.; Montresor-López, J.; Payne-Sturges, D.C. Trends and disparities in urinary BPA concentrations among U.S. emerging adults. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagobian, T.; Smouse, A.; Streeter, M.; Wurst, C.; Schaffner, A.; Phelan, S. Randomized Intervention Trial to Decrease Bisphenol A Urine Concentrations in Women: Pilot Study. J. Women Health 2017, 26, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, M.T.; Chang, V.C.; Mendez, M.A.; De Groh, M. Urinary bisphenol A and obesity in adults: Results from the Canadian Health Measures Survey. Health Promot. Chronic Dis. Prev. Can. 2017, 37, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, J.; Salhotra, S.; Goswami, P.; Akhter, J.; Jahan, S.; Gupta, S.; Sharma, S.; Banerjee, B.D.; Parvez, S.; Gupta, S.; et al. Bisphenol A triggers axonal injury and myelin degeneration with concomitant neurobehavioral toxicity in C57BL/6J male mic. Toxicology 2019, 428, 152299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, M.; Iwano, H.; Yanagisawa, R.; Koike, N.; Inoue, H.; Yokota, H. Placental Transfer of Conjugated Bisphenol A and Subsequent Reactivation in the Rat Fetus. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1196–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aris, A. Estimation of bisphenol A (BPA) concentrations in pregnant women, fetuses and nonpregnant women in Eastern Townships of Canada. Reprod. Toxicol. 2014, 45, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Choi, K.; Park, J.; Moon, H.-B.; Choi, G.; Lee, J.J.; Suh, E.; Kim, H.-J.; Eun, S.-H.; Kim, G.-H.; et al. Bisphenol A distribution in serum, urine, placenta, breast milk, and umbilical cord serum in a birth panel of mother–neonate pairs. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoli, S.; Leone, A.; Battezzati, A. Human Bisphenol A exposure and the “Diabetes Phenotype”. Dose Response 2015, 13, 1559325815599173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.F.; Arrebola, J.; Taoufiki, J.; Navalón, A.; Ballesteros, O.; Pulgar, R.; Vilchez, J.; Olea, N. Bisphenol-A and chlorinated derivatives in adipose tissue of women. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, E.; Shoemaker, R.; Larian, N.; Cassis, L. Adipose Tissue as a Site of Toxin Accumulation. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 7, 1085–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Kannan, K. Accumulation of 19 environmental phenolic and xenobiotic heterocyclic aromatic compounds in human adipose tissue. Environ. Int. 2015, 78, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariemma, F.; D’Esposito, V.; Liguoro, D.; Oriente, F.; Cabaro, S.; Liotti, A.; Cimmino, I.; Longo, M.; Beguinot, F.; Formisano, P.; et al. Low-Dose Bisphenol-A Impairs Adipogenesis and Generates Dysfunctional 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Ferrini, M.G.; Jellyman, J.K.; Han, G.; Ross, M.G. In Vivo and In Vitro bisphenol A exposure effects on adiposity. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2018, 9, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ValPure V70 Series Next Generation Coatings. Available online: https://www.valsparpackaging.com/assets/files/valpure_v70_bulletin_2017_v4.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Soto, A.M.; Schaeberle, C.; Maier, M.S.; Sonnenschein, C.; Maffini, M.V. Evidence of Absence: Estrogenicity Assessment of a New Food-Contact Coating and the Bisphenol Used in Its Synthesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffini, M.V.; Canatsey, R.D. An expanded toxicological profile of tetramethyl bisphenol F (TMBPF), a precursor for a new food-contact metal packaging coating. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 135, 110889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Na, H.; Zhang, Z. Synthesis and characterization of a novel resin monomer with low viscosity. J. Dent. 2017, 59, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreman, J.; Lee, O.; Trznadel, M.; David, A.; Kudoh, T.; Tyler, C.R. Acute Toxicity, Teratogenic, and Estrogenic Effects of Bisphenol A and Its Alternative Replacements Bisphenol S, Bisphenol F, and Bisphenol AF in Zebrafish Embryo-Larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12796–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancio, A.L.; Cole, K.D.; Dominguez, A.R.; Cohenour., E.R.; Kadie, J.; Maloney, W.C.; Schuh, S.M. Bisphenol A, Bisphenol AF, di-n-butyl phthalate, and 17β-Estradiol have shared and unique dose-Dependent effects on early embryo cleavage divisions and development in Xenopus laevis. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 84, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancio, A.L.; Cole, K.D.; Dominguez, A.R.; Cohenour., E.R.; Kadie, J.; Maloney, W.C.; Schuh, S.M. Data demonstrating distinct embryonic developmental defects induced by bisphenol A alternatives. Data Brief 2019, 25, 104091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnett, K.G.; Chin, A.; Schuh, S.M. BPA and BPA alternatives BPS, BPAF, and TMBPF, induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis in rat and human stem cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenmai, A.K.; Dybdahl, M.; Pederson, M.; van Vugt-Lussenburg, B.M.A.; Wedebye, E.B.; Taxvig, C.; Vinggaard, A.M. Are structural analogues to bisphenol A safe alternatives? Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 139, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hunt, P.A.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine disruptors and the future of toxicology testing—Lessons from CLARITY–BPA. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, P.A.; Koehler, K.E.; Susiarjo, M.; Hodges, C.A.; Ilagan, A.; Voigt, R.C.; Thomas, S.; Thomas, B.F.; Hassold, T.J. Bisphenol a exposure causes meiotic aneuploidy in the female mouse. Curr. Biol. 2003, 1, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Takeuchi, S.; Sanoh, S.; Okuda, K.; Kitamura, S.; Uramaru, N.; Sugihara, K.; Yoshinari, K. Profiling of bisphenol A and eight of its analogues on transcriptional activity via human nuclear receptors. Toxicology 2019, 413, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Yin, L.; Yu, K.S.; Hofmann, M.-C.; Yu, X. High-Content Analysis Provides Mechanistic Insights into the Testicular Toxicity of Bisphenol A and Selected Analogues in Mouse Spermatogonial Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 155, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michałowicz, J.; Mokra, K.; Bąk, A. Bisphenol A and its analogs induce morphological and biochemical alterations in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (In Vitro study). Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 29, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, T.; Deng, Z.; Lian, J.; Jia, D.; Li, R.; Zheng, T.; Ding, X.; et al. Low concentration of BPA induces mice spermatocytes apoptosis via GPR30. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 49005–49015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Pan, C.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, L.; Lei, P.; Yang, M. Bioconcentration pattern and induced apoptosis of bisphenol A in zebrafish embryos at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 6611–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, J.G.; Ahmed, S.; Atlas, E. Bisphenol S Induces Adipogenesis in Primary Human Preadipocytes from Female Donors. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelch, K.; Wignall, J.A.; Goldstone, A.E.; Ross, P.K.; Blain, R.B.; Shapiro, A.J.; Holmgren, S.D.; Hsieh, J.-H.; Svoboda, D.; Auerbach, S.S.; et al. A scoping review of the health and toxicological activity of bisphenol A (BPA) structural analogues and functional alternatives. Toxicology 2019, 424, 152235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, H.Y.; Guo, Z.Y.; Xu, F.; Xiao, B.; Jiang, W.L.; Guo, W.M.; Meng, H.Y.; Lu, S.B.; et al. Differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells into Schwann cell-like cells through intermittent induction: Potential advantage of cellular transient memory function. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshdary, V.; Styles, G.; Gagné, R.; Yauk, C.L.; Sorisky, A.; Atlas, E. Depot-Specific Analysis of Human Adipose Cells and Their Responses to Bisphenol S. Endocrinology 2020, 161, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargis, R.M.; Johnson, D.N.; Choudhury, R.A.; Brady, M.J. Environmental Endocrine Disruptors Promote Adipogenesis in the 3T3-L1 Cell Line through Glucocorticoid Receptor Activation. Obesity 2010, 18, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, E.; Li, T.; Rosen, E.D. Exposure of adipocytes to bisphenol-A in vitro interferes with insulin action without enhancing adipogenesis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shao, B. Simultaneous determination of seven bisphenols in environmental water and solid samples by liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1328, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Ruan, T.; Wang, T.; Liu, R.; Jiang, G. Distribution and Preliminary Exposure Assessment of Bisphenol AF (BPAF) in Various Environmental Matrices around a Manufacturing Plant in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 13136–13143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernis, N.; Masschelin, P.; Cox, A.R.; Hartig, S.M. Bisphenol AF promotes inflammation in human white adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C63–C72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skledar, D.G.; Carino, A.; Trontelj, J.; Troberg, J.; Distrutti, E.; Marchianò, S.; Tomašič, T.; Zega, A.; Finel, M.; Fiorucci, S.; et al. Endocrine activities and adipogenic effects of bisphenol AF and its main metabolite. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwall, W. To replace controversial plastic additive BPA, a chemical company teams up with unlikely allies. Science 2020, 367, 6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafran, A.T.; Stossi, F.; Mancini, M.G.; Walker, C.L.; Mancini, M.A. Characterizing properties of non-estrogenic substituted bisphenol analogs using high throughput microscopy and image analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cohen, I.C.; Cohenour, E.R.; Harnett, K.G.; Schuh, S.M. BPA, BPAF and TMBPF Alter Adipogenesis and Fat Accumulation in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells, with Implications for Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105363
Cohen IC, Cohenour ER, Harnett KG, Schuh SM. BPA, BPAF and TMBPF Alter Adipogenesis and Fat Accumulation in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells, with Implications for Obesity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(10):5363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105363
Chicago/Turabian StyleCohen, Isabel C., Emry R. Cohenour, Kristen G. Harnett, and Sonya M. Schuh. 2021. "BPA, BPAF and TMBPF Alter Adipogenesis and Fat Accumulation in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells, with Implications for Obesity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 10: 5363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105363
APA StyleCohen, I. C., Cohenour, E. R., Harnett, K. G., & Schuh, S. M. (2021). BPA, BPAF and TMBPF Alter Adipogenesis and Fat Accumulation in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells, with Implications for Obesity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(10), 5363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105363