Evaluation of Calyculin A Effect on γH2AX/53BP1 Focus Formation and Apoptosis in Human Umbilical Cord Blood Lymphocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Overall, Assessment of Data at 2 h Post-Irradiation
2.2. Overall, Assessment of Apoptosis Measured at 2, 20 and 44 h Post-Irradiation
2.3. DNA Damage Response in UCBL Induced by Cal A 2 h Post-Irradiation
2.3.1. DNA Repair Foci
Gamma-Radiation
Effect of DMSO
Effect of Cal A
2.3.2. Apoptotic Response in UCBL
γH2AX Pan-Staining Assay
Annexin V-FITC/PI Assay
2.4. Apoptosis in UCBL Induced by Radiation and Cal A 20 and 44 h Post-Irradiation
2.4.1. Gamma-Radiation
2.4.2. Effect of DMSO
2.4.3. Effect of Cal A
2.5. Correlation Analysis of Apoptotic Response and DNA Repair Focus Formation 2 h Post-Irradiation
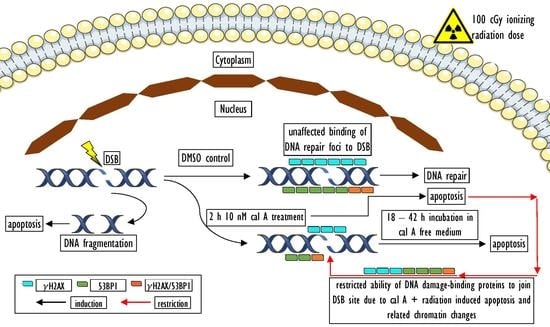
3. Discussion
3.1. Gamma-Radiation
3.2. Effect of DMSO
3.3. Effect of Cal A
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Umbilical Cord Blood Cells
4.3. Cell Treatment
4.4. Irradiation
4.5. Immunofluorescence and Image Acquisition
4.6. Flow Cytometry
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BM | Basal medium |
| cal A | Calyculin A |
| CFA | Colony formation assay |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DNA DSB | DNA double-strand breaks |
| EA cells | Early apoptotic cells |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| HBSS | Hanks’ balanced salt solution medium |
| HEPES | 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethane-sulfonic acid |
| IRIF | Ionizing radiation-induced foci |
| LAN cells | Late apoptotic/necrotic cells |
| PAB | Pre-apoptotic bodies |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium |
| RT | Room temperature |
| Spearman ROC | Spearman rank-order correlations test |
| UCB MNC | Umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells |
| UCBL | Umbilical cord blood lymphocytes |
References
- O’Driscoll, M.; Jeggo, P.A. The role of double-strand break repair—Insights from human genetics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogakou, E.P.; Pilch, D.R.; Orr, A.H.; Ivanova, V.S.; Bonner, W.M. DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 5858–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothkamm, K.; Lobrich, M. Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low x-ray doses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5057–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, S.; Barnard, S.; Rothkamm, K. Gamma-H2AX-based dose estimation for whole and partial body radiation exposure. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojewodzka, M.; Sommer, S.; Kruszewski, M.; Sikorska, K.; Lewicki, M.; Lisowska, H.; Wegierek-Ciuk, A.; Kowalska, M.; Lankoff, A. Defining Blood Processing Parameters for Optimal Detection of gamma-H2AX Foci: A Small Blood Volume Method. Radiat. Res. 2015, 184, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, P.; Aly, A.; Escandell, J.M.; Pieterse, M.; Bartkova, J.; van der Gulden, H.; Hiddingh, S.; Thanasoula, M.; Kulkarni, A.; Yang, Q.; et al. 53BP1 loss rescues BRCA1 deficiency and is associated with triple-negative and BRCA-mutated breast cancers. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, S.F.; Callen, E.; Wong, N.; Chen, H.T.; Polato, F.; Gunn, A.; Bothmer, A.; Feldhahn, N.; Fernandez-Capetillo, O.; Cao, L.; et al. 53BP1 inhibits homologous recombination in Brca1-deficient cells by blocking resection of DNA breaks. Cell 2010, 141, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, J.R.; Sossick, A.J.; Boulton, S.J.; Jackson, S.P. BRCA1-associated exclusion of 53BP1 from DNA damage sites underlies temporal control of DNA repair. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 3529–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobrich, M.; Rief, N.; Kuhne, M.; Heckmann, M.; Fleckenstein, J.; Rube, C.; Uder, M. In vivo formation and repair of DNA double-strand breaks after computed tomography examinations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8984–8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothkamm, K.; Balroop, S.; Shekhdar, J.; Fernie, P.; Goh, V. Leukocyte DNA damage after multi-detector row CT: A quantitative biomarker of low-level radiation exposure. Radiology 2007, 242, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisel, D.; Heverhagen, J.T.; Kalinowski, M.; Wagner, H.J. DNA double-strand breaks after percutaneous transluminal angioplasty. Radiology 2008, 248, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuefner, M.A.; Grudzenski, S.; Hamann, J.; Achenbach, S.; Lell, M.; Anders, K.; Schwab, S.A.; Haberle, L.; Lobrich, M.; Uder, M. Effect of CT scan protocols on x-ray-induced DNA double-strand breaks in blood lymphocytes of patients undergoing coronary CT angiography. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 2917–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuefner, M.A.; Grudzenski, S.; Schwab, S.A.; Wiederseiner, M.; Heckmann, M.; Bautz, W.; Lobrich, M.; Uder, M. DNA double-strand breaks and their repair in blood lymphocytes of patients undergoing angiographic procedures. Investig. Radiol. 2009, 44, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuefner, M.A.; Hinkmann, F.M.; Alibek, S.; Azoulay, S.; Anders, K.; Kalender, W.A.; Achenbach, S.; Grudzenski, S.; Lobrich, M.; Uder, M. Reduction of X-ray induced DNA double-strand breaks in blood lymphocytes during coronary CT angiography using high-pitch spiral data acquisition with prospective ECG-triggering. Investig. Radiol. 2010, 45, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.J.; Hall, E.J. Computed tomography--an increasing source of radiation exposure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2277–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, M.S.; Salotti, J.A.; Little, M.P.; McHugh, K.; Lee, C.; Kim, K.P.; Howe, N.L.; Ronckers, C.M.; Rajaraman, P.; Sir Craft, A.W.; et al. Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumours: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2012, 380, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.D.; Forsythe, A.V.; Brady, Z.; Butler, M.W.; Goergen, S.K.; Byrnes, G.B.; Giles, G.G.; Wallace, A.B.; Anderson, P.R.; Guiver, T.A.; et al. Cancer risk in 680,000 people exposed to computed tomography scans in childhood or adolescence: Data linkage study of 11 million Australians. BMJ 2013, 346, f2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.Y.; Muo, C.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Jen, Y.M.; Yang, M.H.; Lin, J.C.; Sung, F.C.; Kao, C.H. Paediatric head CT scan and subsequent risk of malignancy and benign brain tumour: A nation-wide population-based cohort study. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2354–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaev, I.Y. Radiation-induced DNA repair foci: Spatio-temporal aspects of formation, application for assessment of radiosensitivity and biological dosimetry. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2010, 704, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuefner, M.A.; Brand, M.; Engert, C.; Kappey, H.; Uder, M.; Distel, L.V. The effect of calyculin A on the dephosphorylation of the histone gamma-H2AX after formation of X-ray-induced DNA double-strand breaks in human blood lymphocytes. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2013, 89, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, I.B.; Smirnova, A.N.; Krutilina, R.I.; Svetlova, M.P.; Solovjeva, L.V.; Nikiforov, A.A.; Oei, S.L.; Zalenskaya, I.A.; Yau, P.M.; Bradbury, E.M.; et al. Dephosphorylation of histone gamma-H2AX during repair of DNA double-strand breaks in mammalian cells and its inhibition by calyculin A. Radiat. Res. 2003, 160, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2Antonelli, F.; Belli, M.; Cuttone, G.; Dini, V.; Esposito, G.; Simone, G.; Sorrentino, E.; Tabocchini, M.A. Induction and repair of DNA double-strand breaks in human cells: Dephosphorylation of histone H2AX and its inhibition by calyculin A. Radiat. Res. 2005, 164, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakl, L.; Lobachevsky, P.; Vokalova, L.; Durdik, M.; Markova, E.; Belyaev, I. Validation of JCountPro software for efficient assessment of ionizing radiation-induced foci in human lymphocytes. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2016, 92, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roch-Lefevre, S.; Mandina, T.; Voisin, P.; Gaetan, G.; Gonzalez Mesa, J.E.; Valente, M.; Bonnesoeur, P.; Garcia, O.; Voisin, P.; Roy, L. Quantification of gamma-H2AX Foci in Human Lymphocytes: A Method for Biological Dosimetry after Ionizing Radiation Exposure. Radiat. Res. 2010, 174, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilyev, S.A.; Kubes, M.; Markova, E.; Belyaev, I. DNA damage response in CD133+stem/progenitor cells from umbilical cord blood: Low level of endogenous foci and high recruitment of 53BP1. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2013, 89, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durdik, M.; Kosik, P.; Gursky, J.; Vokalova, L.; Markova, E.; Belyaev, I. Imaging flow cytometry as a sensitive tool to detect low-dose-induced DNA damage by analyzing 53BP1 and gammaH2AX foci in human lymphocytes. Cytom. Part A J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2015, 87, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solier, S.; Pommier, Y. The apoptotic ring: A novel entity with phosphorylated histones H2AX and H2B, and activated DNA damage response kinases. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anglada, T.; Terradas, M.; Hernandez, L.; Genesca, A.; Martin, M. Analysis of Residual DSBs in Ataxia-Telangiectasia Lymphoblast Cells Initiating Apoptosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8279560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Yin, L.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, H. Induction and inhibition of the pan-nuclear gamma-H2AX response in resting human peripheral blood lymphocytes after X-ray irradiation. Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2, 16011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaev, I.Y.; Czene, S.; Harms-Ringdahl, M. Changes in chromatin conformation during radiation-induced apoptosis in human lymphocytes. Radiat. Res. 2001, 156, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torudd, J.; Protopopova, M.; Sarimov, R.; Nygren, J.; Eriksson, S.; Markova, E.; Chovanec, M.; Selivanova, G.; Belyaev, I.Y. Dose-response for radiation-induced apoptosis, residual 53BP1 foci and DNA-loop relaxation in human lymphocytes. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2005, 81, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durdik, M.; Kosik, P.; Kruzliakova, J.; Jakl, L.; Markova, E.; Belyaev, I.; Durdik, M.; Kosik, P.; Kruzliakova, J.; Jakl, L.; et al. Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells are less prone to undergo apoptosis than lymphocytes despite similar DNA damage response. Oncotarget 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 3Kosik, P.; Durdik, M.; Jakl, L.; Skorvaga, M.; Markova, E.; Vesela, G.; Vokalova, L.; Kolarikova, L.; Horvathova, E.; Kozics, K.; et al. DNA damage response and preleukemic fusion genes induced by ionizing radiation in umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogakou, E.P.; Boon, C.; Redon, C.; Bonner, W.M. Megabase chromatin domains involved in DNA double-strand breaks in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 146, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, L.B.; Chehab, N.H.; Malikzay, A.; Halazonetis, T.D. p53 binding protein 1 (53BP1) is an early participant in the cellular response to DNA double-strand breaks. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 151, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakl, L.; Markova, E.; Kolarikova, L.; Belyaev, I. Biodosimetry of Low Dose Ionizing Radiation Using DNA Repair Foci in Human Lymphocytes. Genes 2020, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rube, C.E.; Fricke, A.; Widmann, T.A.; Furst, T.; Madry, H.; Pfreundschuh, M.; Rube, C. Accumulation of DNA damage in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells during human aging. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkevich, A.N.; Martin, O.A.; Smith, A.J.; Redon, C.E.; Bonner, W.M.; Martin, R.F.; Lobachevsky, P.N. gammaH2AX foci as a measure of DNA damage: A computational approach to automatic analysis. Mutat. Res. 2011, 711, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuefner, M.A.; Brand, M.; Ehrlich, J.; Braga, L.; Uder, M.; Semelka, R.C. Effect of antioxidants on X-ray-induced gamma-H2AX foci in human blood lymphocytes: Preliminary observations. Radiology 2012, 264, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zastko, L.; Petrovicova, P.; Rackova, A.; Jakl, L.; Jakusova, V.; Markova, E.; Belyaev, I. DNA damage response and apoptosis induced by hyperthermia in human umbilical cord blood lymphocytes. Toxicol. In Vitro 2021, 73, 105127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicker, F.; Hauswald, H.; Debus, J.; Huber, P.E.; Weber, K.J. Impact of dimethyl sulfoxide on irradiation-related DNA double-strand-break induction, -repair and cell survival. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2019, 58, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashino, G.; Liu, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Masunaga, S.; Kinashi, Y.; Ono, K.; Tano, K.; Watanabe, M. An alternative mechanism for radioprotection by dimethyl sulfoxide; possible facilitation of DNA double-strand break repair. J. Radiat. Res. 2010, 51, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joza, N.; Kroemer, G.; Penninger, J.M. Genetic analysis of the mammalian cell death machinery. Trends Genet. 2002, 18, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Antoku, S. Enhancement of X-ray cell killing in cultured mammalian cells by the protein phosphatase inhibitor calyculin A. Cancer research 1994, 54, 2088–2090. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]






| Variables | Multifactorial ANOVA | Categorical Factors | p-Values Adjusted by FDR | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| γH2AX * | 53BP1 * | γH2AX/ 53BP1 * | Viable (%) | EA (%) | LAN (%) | Pan-st. (%) | Multivariate | Univariate | Dose | Treatment | Dose | Treatment |
| + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | 0.00000 | 0.36717 |
| - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | 0.95145 | 0.00032 |
| - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | 0.91988 | 0.00241 |
| - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | + | + | 0.98870 | 0.00359 |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | 0.56980 | 0.00004 |
| Variables | Multifactorial ANOVA | Categorical Factors | p-Values Adjusted by FDR | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viable (%) | EA (%) | LAN (%) | Multivariate | Univariate | Time | Dose | Treatment | Time | Dose | Treatment |
| + | + | + | + | - | all | + | + | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| + | - | - | - | + | all | + | + | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| - | + | - | - | + | all | + | + | 0.00000 | 0.51274 | 0.00000 |
| - | - | + | - | + | all | + | + | 0.00000 | 0.02060 | 0.00000 |
| + | + | + | + | - | 2 h | + | + | - | 0.82175 | 0.00485 |
| + | - | - | - | + | 2 h | + | + | - | 0.95145 | 0.00039 |
| - | + | - | - | + | 2 h | + | + | - | 0.91988 | 0.00241 |
| - | - | + | - | + | 2 h | + | + | - | 0.98870 | 0.00359 |
| + | + | + | + | - | 20 h | + | + | - | 0.77601 | 0.00025 |
| + | - | - | - | + | 20 h | + | + | - | 0.92268 | 0.00000 |
| - | + | - | - | + | 20 h | + | + | - | 0.99875 | 0.00002 |
| - | - | + | - | + | 20 h | + | + | - | 0.84090 | 0.09587 |
| + | + | + | + | - | 44 h | + | + | - | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| + | - | - | - | + | 44 h | + | + | - | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| - | + | - | - | + | 44 h | + | + | - | 0.77013 | 0.00000 |
| - | - | + | - | + | 44 h | + | + | - | 0.04194 | 0.00000 |
| Author | Cell Type | Solvent of Cal A | Concentration of Cal A (nM) | Cell Treatmet with Cal A Prior-/Post-Irradiation | Dose of Irradiation (Gy) | Effect on γH2AX Foci | Analysis of Apoptosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nazarov et al. (2003) | Chinese hamster V79 | unknown | 10 | post-; for 0.5 h | 20 | stabilization identified at 6 h | NO |
| Antonelli et al. (2005) | Primary human lung fibroblasts (MRC-5) | unknown | 2.5 | post-; continual cal A treatment | 1 | stabilization identified at 2 h | NO |
| Roch-Lefevre et al. (2010) | Human peripheral blood lymphocytes | unknown | 5 | prior-; whole blood irr.; continual cal A treatment | 0.05–5 | no stabilization identified at 2 h | YES |
| Kuefner et al. (2013) | Human peripheral blood lymphocytes | ethanol | 1; 10 | prior-; continual cal A treatment | 0.001–0.01 | stabilization identified at 2 h | colony formation assay (but not using lymphocytes) |
| Jakl et al. (2016) | Human umbilical cord blood lymphocytes | DMSO | 1; 10 | immediately prior-/post; continual for 2 h | 0.001–0.01 | no stabilization identified at 2 h | NO |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zastko, L.; Račková, A.; Petrovičová, P.; Durdík, M.; Míšek, J.; Marková, E.; Belyaev, I. Evaluation of Calyculin A Effect on γH2AX/53BP1 Focus Formation and Apoptosis in Human Umbilical Cord Blood Lymphocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115470
Zastko L, Račková A, Petrovičová P, Durdík M, Míšek J, Marková E, Belyaev I. Evaluation of Calyculin A Effect on γH2AX/53BP1 Focus Formation and Apoptosis in Human Umbilical Cord Blood Lymphocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(11):5470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115470
Chicago/Turabian StyleZastko, Lucián, Anna Račková, Petra Petrovičová, Matúš Durdík, Jakub Míšek, Eva Marková, and Igor Belyaev. 2021. "Evaluation of Calyculin A Effect on γH2AX/53BP1 Focus Formation and Apoptosis in Human Umbilical Cord Blood Lymphocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 11: 5470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115470
APA StyleZastko, L., Račková, A., Petrovičová, P., Durdík, M., Míšek, J., Marková, E., & Belyaev, I. (2021). Evaluation of Calyculin A Effect on γH2AX/53BP1 Focus Formation and Apoptosis in Human Umbilical Cord Blood Lymphocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(11), 5470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115470