SRPassing Co-translational Targeting: The Role of the Signal Recognition Particle in Protein Targeting and mRNA Protection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Protein Targeting Signals
3. Evolution of SRP
4. SRP Biogenesis in Mammalian Cells
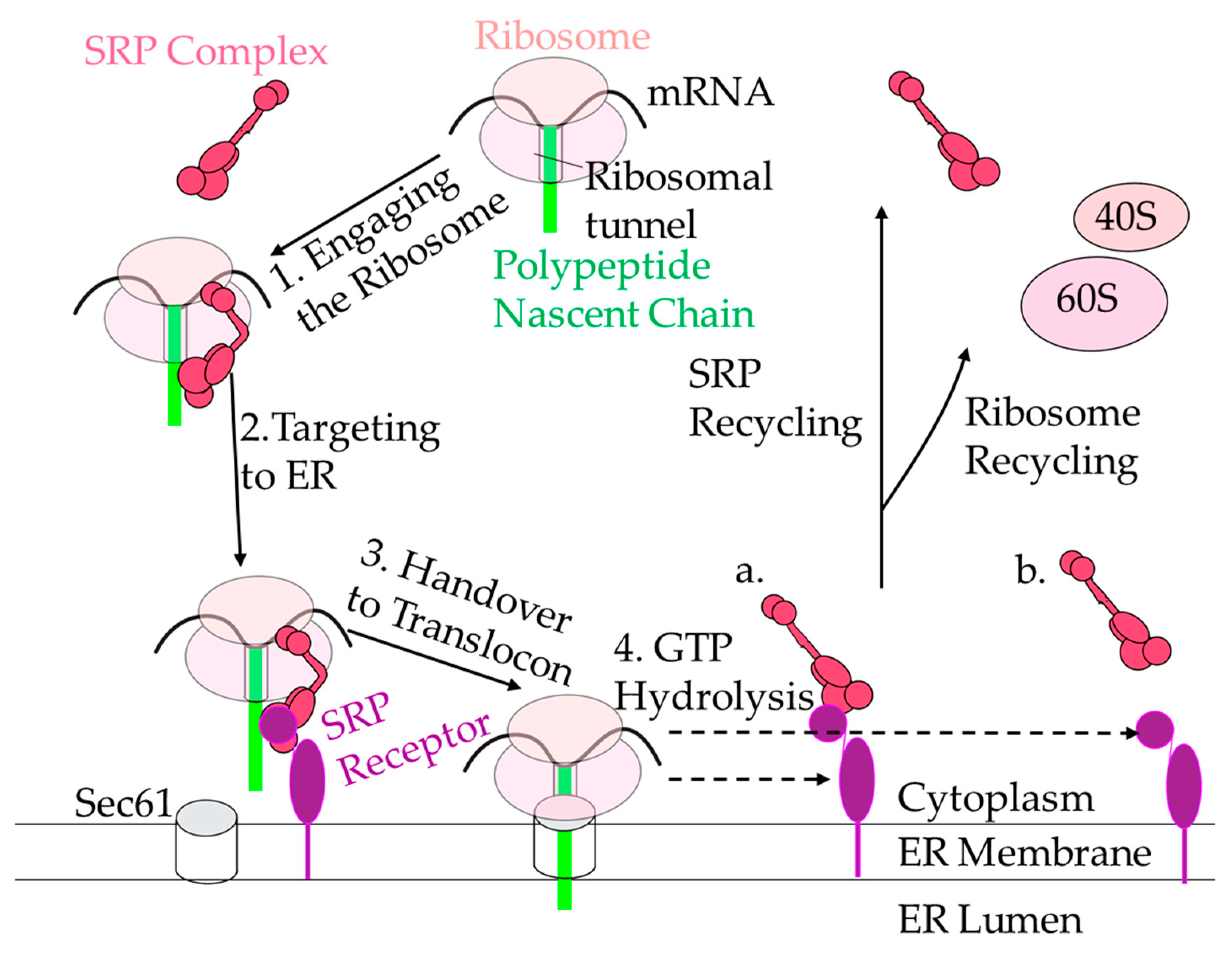
5. The SRP Cycle
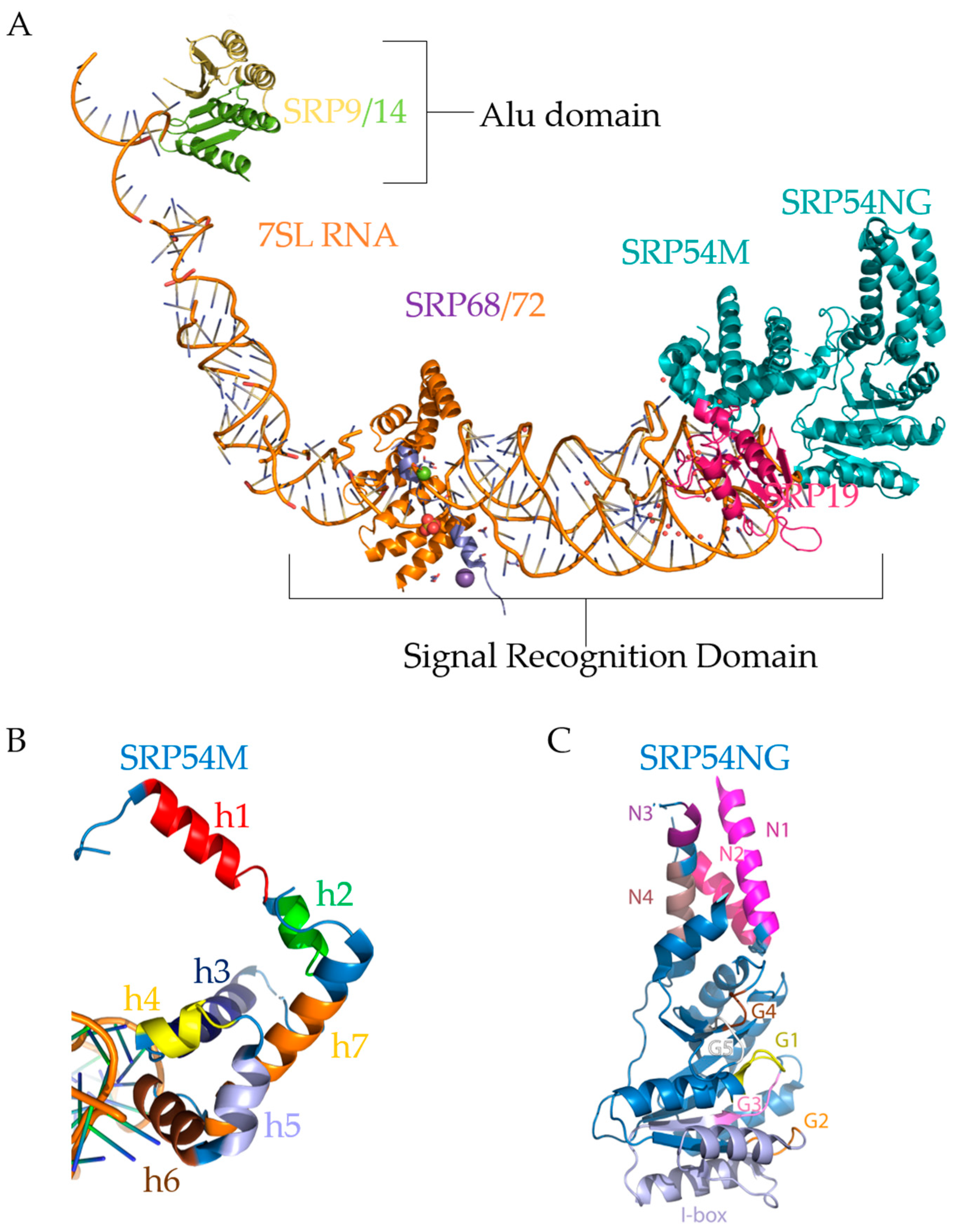
6. Structure and Function
7. RAPP and SRP
8. SRPassing Co-Translational Targeting
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milo, R. What Is the Total Number of Protein Molecules per Cell Volume? A Call to Rethink Some Published Values. Bioessays 2013, 35, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karamyshev, A.L.; Tikhonova, E.B.; Karamysheva, Z.N. Translational Control of Secretory Proteins in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunze, M.; Berger, J. The Similarity between N-terminal Targeting Signals for Protein Import into Different Organelles and Its Evolutionary Relevance. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, T.; Song, J.; Pfanner, N. Versatility of Preprotein Transfer from the Cytosol to Mitochondria. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ast, T.; Schuldiner, M. All Roads Lead to Rome (but Some May Be Harder to Travel): SRP-Independent Translocation into the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, A.; Mills, R.E.; Lange, C.J.; Stewart, M.; Devine, S.E.; Corbett, A.H. Classical Nuclear Localization Signals: Definition, Function, and Interaction with Importin α. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5101–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akopian, D.; Shen, K.; Zhang, X.; Shan, S. Signal Recognition Particle: An Essential Protein-Targeting Machine. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 693–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gould, S.G.; Keller, G.A.; Subramani, S. Identification of a Peroxisomal Targeting Signal at the Carboxy Terminus of Firefly Luciferase. J. Cell Biol. 1987, 105, 2923–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiel, J.A.; Emmrich, K.; Meyer, H.E.; Kunau, W. Ubiquitination of the Peroxisomal Targeting Signal Type 1 Receptor, PEX5p, Suggests the Presence of a Quality Control Mechanism during Peroxisomal Matrix Protein Transport. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunze, M.; Malkani, N.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Wiesinger, C.; Schmid, J.A.; Berger, J. Mechanistic Insights into PTS2-Mediated Peroxisomal Protein Import the co-receptor PEX5L drastically increases the interaction strength between the cargo protein and the receptor PEX7. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 4928–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dingwall, C.; Robbins, J.; Dilworth, S.M.; Roberts, B.; Richardson, W.D. The Nucleoplasmin Nuclear Location Sequence Is Larger and More Complex than That of SV-40 Large T Antigen. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 107, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Cour, T.; Kiemer, L.; Mølgaard, A.; Gupta, R.; Skriver, K.; Brunak, S. Analysis and Prediction of Leucine-Rich Nuclear Export Signals. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2004, 17, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, X.F.S. Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Localization Sequences for Mammalian Target of Rapamycin. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kjer-Nielsen, L.; van Vliet, C.; Erlich, R.; Toh, B.-H.; Gleeson, P.A. The Golgi-targeting sequence of the peripheral membrane protein p230. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, N.R.; Schekman, R.W. The Role of Coat Proteins in the Biosynthesis of Secretory Proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1995, 7, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braulke, T.; Bonifacino, J.S. Sorting of Lysosomal Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2009, 1793, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Von Heijne, G. Mitochondrial Targeting Sequences May Form Amphiphilic Helices. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roise, D.; Horvath, S.J.; Tomich, J.M.; Richards, J.H.; Schatz, G. A Chemically Synthesized Pre-Sequence of an Imported Mitochondrial Protein Can Form an Amphiphilic Helix and Perturb Natural and Artificial Phospholipid Bilayers. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, S.R.; Kasinadhuni, N.R.P.; Chan, C.K.; Grant, W.N. Evidence of Evolutionary Constraints That Influences the Sequence Composition and Diversity of Mitochondrial Matrix Targeting Signals. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, S.; Hegde, R.S. A Calmodulin-Dependent Translocation Pathway for Small Secretory Proteins. Cell 2011, 147, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, H.; Shu, H.; Zhu, R.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Madley, R.; et al. Positive Charge in the N-Region of the Signal Peptide Contributes to Efficient Post-Translational Translocation of Small Secretory Preproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haßdenteufel, S.; Nguyen, D.; Helms, V.; Lang, S.; Zimmermann, R. ER Import of Small Human Presecretory Proteins: Components and Mechanisms. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 2506–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanovic, S.; Hegde, R.S. Identification of a Targeting Factor for Posttranslational Membrane Protein Insertion into the ER. Cell 2007, 128, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casson, J.; McKenna, M.; Haßdenteufel, S.; Aviram, N.; Zimmerman, R.; High, S. Multiple Pathways Facilitate the Biogenesis of Mammalian Tail-Anchored Proteins. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 3851–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aviram, N.; Ast, T.; Costa, E.A.; Arakel, E.C.; Chuartzman, S.G.; Jan, C.H.; Haßdenteufel, S.; Dudek, J.; Jung, M.; Schorr, S.; et al. The SND Proteins Constitute an Alternative Targeting Route to the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Nature 2016, 540, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakkaraju, A.K.; Thankappan, R.; Mary, C.; Garrison, J.L.; Taunton, J.; Strub, K. Efficient Secretion of Small Proteins in Mammalian Cells Relies on Sec62-Dependent Posttranslational Translocation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 2712–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denecke, J.; De Rycke, R.; Botterman, J. Plant and Mammalian Sorting Signals for Protein Retention in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Contain a Conserved Epitope. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 2345–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Heijne, G. Signal Sequences. The Limits of Variation. J. Mol. Biol. 1985, 184, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Heijne, G. The Signal Peptide. J. Membr. Biol. 1990, 115, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Heijne, G. Patterns of Amino Acids near Signal-Sequence Cleavage Sites. Eur. J. Biochem. 1983, 133, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorkholm, P.; Harish, A.; Hagstrom, E.; Ernst, A.M.; Andersson, S.G. Mitochondrial Genomes Are Retained by Selective Constraints on Protein Targeting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10154–10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodył, A.; Mackiewicz, P. Analysis of the Targeting Sequences of an Iron-Containing Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) of the Dinoflagellate Lingulodinium Polyedrum Suggests Function in Multiple Cellular Compartments. Arch. Microbiol. 2007, 187, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, S.; Longhi, R.; Alcaro, S.; Ortuso, F.; Sprocati, T.; Flora, A.; Borgese, N. N-Myristoylation Determines Dual Targeting of Mammalian NADH-Cytochrome B5 Reductase to ER and Mitochondrial Outer Membranes by a Mechanism of Kinetic Partitioning. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 168, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.; Park, J.; Kim, D.; Jung, K.; Kang, S.; Lee, Y.H. Fungal Secretome Database: Integrated Platform for Annotation of Fungal Secretomes. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Gao, G.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Gu, X.; Luo, J. SPD—A Web-Based Secreted Protein Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D169–D173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wallin, E.; Heijne, G.V. Genome-Wide Analysis of Integral Membrane Proteins from Eubacterial, Archaean, and Eukaryotic Organisms. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome. Science 2015, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesmeyanova, M.A.; Karamyshev, A.L.; Karamysheva, Z.N.; Kalinin, A.E.; Ksenzenko, V.N.; Kajava, A.V. Positively Charged Lysine at the N-Terminus of the Signal Peptide of the Escherichia Coli Alkaline Phosphatase Provides the Secretion Efficiency and Is Involved in the Interaction with Anionic Phospholipids. FEBS Lett. 1997, 403, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karamyshev, A.L.; Karamysheva, Z.N.; Kajava, A.V.; Ksenzenko, V.N.; Nesmeyanova, M.A. Processing of Escherichia Coli Alkaline Phosphatase: Role of the Primary Structure of the Signal Peptide Cleavage Region. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 277, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinin, A.E.; Karamyshev, A.L.; Nesmeianova, M.A. Disruption of processing of alkaline phosphatase as a result of single amino acid changes affects the composition and metabolism of phospholipids from Escherichia coli, secreting mutant proteins. Biokhimiia 1996, 61, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keenan, R.J.; Freymann, D.M.; Walter, P.; Stroud, R.M. Crystal Structure of the Signal Sequence Binding Subunit of the Signal Recognition Particle. Cell 1998, 94, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, I.; Lara, P.; Hessa, T.; Johnson, A.E.; von Heijne, G.; Karamyshev, A.L. The Code for Directing Proteins for Translocation across ER Membrane: SRP Cotranslationally Recognizes Specific Features of a Signal Sequence. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karamyshev, A.L.; Johnson, A.E. Selective SecA association with signal sequences in ribosome-bound nascent chains: A potential role for SecA in ribosome targeting to the bacterial membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37930–37940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schibich, D.; Gloge, F.; Pohner, I.; Bjorkholm, P.; Wade, R.C.; von Heijne, G.; Bukau, B.; Kramer, G. Global Profiling of SRP Interaction with Nascent Polypeptides. Nature 2016, 536, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschke, M.; Le Goff, M.; Koningstein, G.M.; Vischer, N.O.; Abdel-Rehim, A.; High, S.; van Ulsen, P.; Luirink, J. Distinct Requirements for Tail-Anchored Membrane Protein Biogenesis in Escherichia Coli. mBio 2019, 10, e01580–e01619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peschke, M.; Le Goff, M.; Koningstein, G.M.; Karyolaimos, A.; de Gier, J.-W.; van Ulsen, P.; Luirink, J. SRP, FtsY, DnaK and YidC Are Required for the Biogenesis of the E. Coli Tail-Anchored Membrane Proteins DjlC and Flk. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, J.K.; Woolhead, C.A. Hydrophobicity, Rather than Secondary Structure, Is Essential for the SRP Dependent Targeting of GPR35 to the ER Membrane. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2019, 51, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, E.A.; Subramanian, K.; Nunnari, J.; Weissman, J.S. Defining the Physiological Role of SRP in Protein-Targeting Efficiency and Specificity. Science 2018, 359, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chartron, J.W.; Hunt, K.C.; Frydman, J. Cotranslational Signal-Independent SRP Preloading during Membrane Targeting. Nature 2016, 536, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poritz, M.A.; Bernstein, H.D.; Strub, K.; Zopf, D.; Wilhelm, H.; Walter, P. An E. coli ribonucleoprotein containing 4.5S RNA Resembles Mammalian Signal Recognition Particle. Science 1990, 250, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buskiewicz, I.; Kubarenko, A.; Peske, F.; Rodnina, M.V.; Wintermeyer, W. Domain Rearrangement of SRP Protein Ffh upon Binding 4.5S RNA and the SRP Receptor FtsY. RNA 2005, 11, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frasz, C.; Grove Arvidson, C. Role for Both DNA and RNA in GTP Hydrolysis by the Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Signal Recognition Particle Receptor. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, K.; Arslan, S.; Akopian, D.; Ha, T.; Shan, S. Activated GTPase Movement on an RNA Scaffold Drives Co-Translational Protein Targeting. Nature 2012, 492, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, K.; Yahagi, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Yamane, K. Bacillus Subtilis Histone-like Protein, HBsu, Is an Integral Component of a SRP-like Particle That Can Bind the Alu Domain of Small Cytoplasmic RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13569–13576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenblad, M.A.; Larsen, N.; Samuelsson, T.; Zwieb, C. Kinship in the SRP RNA Family. RNA Biol. 2009, 6, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diener, J.L.; Wilson, C. Role of SRP19 in Assembly of the Archaeoglobus Fulgidus Signal Recognition Particle. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 12862–12874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, J.; Moll, R. The Signal Recognition Particle of Archaea. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieb, C.; Bhuiyan, S. Archaea Signal Recognition Particle Shows the Way. Archaea 2010, 2010, 485051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieb, C.; Eichler, J. Getting on Target: The Archaeal Signal Recognition Particle. Archaea 2002, 1, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, W.; Rujan, T.; Richly, E.; Hansen, A.; Cornelsen, S.; Lins, T.; Leister, D.; Stoebe, B.; Hasegawa, M.; Penny, D. Evolutionary Analysis of Arabidopsis, Cyanobacterial, and Chloroplast Genomes Reveals Plastid Phylogeny and Thousands of Cyanobacterial Genes in the Nucleus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12246–12251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raven, J.A.; Allen, J.F. Genomics and Chloroplast Evolution: What Did Cyanobacteria Do for Plants? Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Träger, C.; Rosenblad, M.A.; Ziehe, D.; Garcia-Petit, C.; Schrader, L.; Kock, K.; Richter, C.V.; Klinkert, B.; Narberhaus, F.; Herrmann, C.; et al. Evolution from the Prokaryotic to the Higher Plant Chloroplast Signal Recognition Particle: The Signal Recognition Particle RNA Is Conserved in Plastids of a Wide Range of Photosynthetic Organisms. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4819–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenblad, M.A.; Samuelsson, T. Identification of Chloroplast Signal Recognition Particle RNA Genes. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 1633–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dünschede, B.; Träger, C.; Schröder, C.V.; Ziehe, D.; Walter, B.; Funke, S.; Hofmann, E.; Schünemann, D. Chloroplast SRP54 Was Recruited for Posttranslational Protein Transport via Complex Formation with Chloroplast SRP43 during Land Plant Evolution. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 13104–13114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, R.; van Wijk, K.J. Transient Interaction of CpSRP54 with Elongating Nascent Chains of the Chloroplast-Encoded D1 Protein; ‘CpSRP54 Caught in the Act. FEBS Lett. 2002, 524, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutin, C.; Havaux, M.; Carde, J.-P.; Kloppstech, K.; Meiherhoff, K.; Hoffman, N.; Nussaume, L. Double Mutation CpSRP43–/CpSRP54– Is Necessary to Abolish the CpSRP Pathway Required for Thylakoid Targeting of the Light-Harvesting Chlorophyll Proteins. Plant J. 2002, 29, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krolkiewicz, S.; Sänger, H.L.; Niesbach-KLösgen, U. Structural and Functional Characterisation of the Signal Recognition Particle-Specific 54 KDa Protein (SRP54) of Tomato. Molec. Gen. Genet. 1994, 245, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, P.; Simm, S.; Blaumeiser, A.; Scharf, K.-D.; Fragkostefanakis, S.; Mirus, O.; Schleiff, E. The Protein Translocation Systems in Plants–Composition and Variability on the Example of Solanum Lycopersicum. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lustig, Y.; Goldshmidt, H.; Uliel, S.; Michaeli, S. The Trypanosoma Brucei Signal Recognition Particle Lacks the Alu-Domain-Binding Proteins: Purification and Functional Analysis of Its Binding Proteins by RNAi. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4551–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panchal, M.; Rawat, K.; Kumar, G.; Kibria, K.M.; Singh, S.; Kalamuddin, M.; Mohmmed, A.; Malhotra, P.; Tuteja, R. Plasmodium Falciparum Signal Recognition Particle Components and Anti-Parasitic Effect of Ivermectin in Blocking Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Shuttling of SRP. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zelazny, A.M.; Fedorko, D.P.; Li, L.; Neva, F.A.; Fischer, S.H. Evaluation of 7SL RNA gene sequences for the identification of Leishmania spp. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 72, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Béjà, O.; Ullu, E.; Michaeli, S. Identification of a TRNA-like Molecule That Copurifies with the 7SL RNA of Trypanosoma Brucei. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1993, 57, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, E.S.; Rosenblad, M.A.; Larsen, N.; Westergaard, J.C.; Burks, J.; Wower, I.K.; Wower, J.; Gorodkin, J.; Samuelsson, T.; Zwieb, C. The TmRDB and SRPDB Resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D163–D168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lustig, Y.; Vagima, Y.; Goldshmidt, H.; Erlanger, A.; Ozeri, V.; Vince, J.; McConville, M.J.; Dwyer, D.M.; Landfear, S.M.; Michaeli, S. Down-Regulation of the Trypanosomatid Signal Recognition Particle Affects the Biogenesis of Polytopic Membrane Proteins but Not of Signal Peptide-Containing Proteins. Eukaryot Cell 2007, 6, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hann, B.C.; Walter, P. The Signal Recognition Particle in S. Cerevisiae. Cell 1991, 67, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutka, S.C.; Walter, P. Multifaceted Physiological Response Allows Yeast to Adapt to the Loss of the Signal Recognition Particle-Dependent Protein-Targeting Pathway. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, M.A.; Ravelli, R.B.; McCarthy, A.A.; Strub, K.; Cusack, S. Structure of SRP14 from the Schizosaccharomyces Pombe Signal Recognition Particle. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2009, 65, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birse, D.E.A.; Kapp, U.; Strub, K.; Cusack, S.; Åberg, A. The Crystal Structure of the Signal Recognition Particle Alu RNA Binding Heterodimer, SRP9/14. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 3757–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luirink, J.; Sinning, I. SRP-Mediated Protein Targeting: Structure and Function Revisited. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2004, 1694, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, S.E.; King, S.R.; Telesnitsky, A. 7SL RNA Is Retained in HIV-1 Minimal Virus-like Particles as an S-Domain Fragment. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 9070–9077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menichelli, E.; Isel, C.; Oubridge, C.; Nagai, K. Protein-Induced Conformational Changes of RNA during the Assembly of Human Signal Recognition Particle. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotwinkel, J.T.; Wild, K.; Segnitz, B.; Sinning, I. SRP RNA Remodeling by SRP68 Explains Its Role in Protein Translocation. Science 2014, 344, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, M.M.; Lapouge, K.; Segnitz, B.; Wild, K.; Sinning, I. Structures of Human SRP72 Complexes Provide Insights into SRP RNA Remodeling and Ribosome Interaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rapiejko, P.J.; Gilmore, R. Empty Site Forms of the SRP54 and SR Alpha GTPases Mediate Targeting of Ribosome-Nascent Chain Complexes to the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Cell 1997, 89, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moser, C.; Mol, O.; Goody, R.S.; Sinning, I. The Signal Recognition Particle Receptor of Escherichia Coli (FtsY) Has a Nucleotide Exchange Factor Built into the GTPase Domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11339–11344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legate, K.R.; Andrews, D.W. The β-Subunit of the Signal Recognition Particle Receptor Is a Novel GTP-Binding Protein without Intrinsic GTPase Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 27712–27720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, J.D.; Tajima, S.; Lauffer, L.; Walter, P. The Beta Subunit of the Signal Recognition Particle Receptor Is a Transmembrane GTPase That Anchors the Alpha Subunit, a Peripheral Membrane GTPase, to the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 128, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helmers, J.; Schmidt, D.; Glavy, J.S.; Blobel, G.; Schwartz, T. The Beta-Subunit of the Protein-Conducting Channel of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Functions as the Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor for the Beta-Subunit of the Signal Recognition Particle Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 23686–23690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadhav, B.; Wild, K.; Pool, M.R.; Sinning, I. Structure and Switch Cycle of SRβ as Ancestral Eukaryotic GTPase Associated with Secretory Membranes. Structure 2015, 23, 1838–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilmore, R.; Walter, P.; Blobel, G. Protein Translocation across the Endoplasmic Reticulum. II. Isolation and Characterization of the Signal Recognition Particle Receptor. J. Cell Biol. 1982, 95, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, T.; Blobel, G. Structural Basis for the Function of the β Subunit of the Eukaryotic Signal Recognition Particle Receptor. Cell 2003, 112, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lauffer, L.; Garcia, P.D.; Harkins, R.N.; Coussens, L.; Ullrich, A.; Walter, P. Topology of Signal Recognition Particle Receptor in Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane. Nature 1985, 318, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, K.; Rossman, K.L.; Der, C.J. The Ras Superfamily at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojas, A.M.; Fuentes, G.; Rausell, A.; Valencia, A. The Ras Protein Superfamily: Evolutionary Tree and Role of Conserved Amino Acids. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadhav, B.; McKenna, M.; Johnson, N.; High, S.; Sinning, I.; Pool, M.R. Mammalian SRP Receptor Switches the Sec61 Translocase from Sec62 to SRP-Dependent Translocation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Legate, K.R.; Falcone, D.; Andrews, D.W. Nucleotide-Dependent Binding of the GTPase Domain of the Signal Recognition Particle Receptor β-Subunit to the α-Subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 27439–27446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, P.; Johnson, A.E. Signal Sequence Recognition and Protein Targeting to the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1994, 10, 87–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Mandon, E.C.; Gilmore, R. An Interaction between the SRP Receptor and the Translocon Is Critical during Cotranslational Protein Translocation. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.; Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Shan, G. Signals from Noncoding RNAs: Unconventional Roles for Conventional Pol III Transcripts. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1847–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politz, J.C.; Lewandowski, L.B.; Pederson, T. Signal Recognition Particle RNA Localization within the Nucleolus Differs from the Classical Sites of Ribosome Synthesis. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politz, J.C.; Yarovoi, S.; Kilroy, S.M.; Gowda, K.; Zwieb, C.; Pederson, T. Signal Recognition Particle Components in the Nucleolus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosshans, H.; Deinert, K.; Hurt, E.; Simos, G. Biogenesis of the Signal Recognition Particle (SRP) Involves Import of SRP Proteins into the Nucleolus, Assembly with the SRP-RNA, and Xpo1p-Mediated Export. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederson, T. The Nucleolus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, K.A.; von Ahsen, O.; Gorlich, D.; Fried, H.M. Signal Recognition Particle Protein 19 Is Imported into the Nucleus by Importin 8 (RanBP8) and Transportin. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3479–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpon, L.; Culjkovic-Kraljacic, B.; Osborne, M.J.; Ramteke, A.; Sun, Q.; Niesman, A.; Chook, Y.M.; Borden, K.L. Importin 8 Mediates M7G Cap-Sensitive Nuclear Import of the Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor EIF4E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5263–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egea, P.F.; Napetschnig, J.; Walter, P.; Stroud, R.M. Structures of SRP54 and SRP19, the Two Proteins That Organize the Ribonucleic Core of the Signal Recognition Particle from Pyrococcus Furiosus. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strub, K.; Walter, P. Assembly of the Alu Domain of the Signal Recognition Particle (SRP): Dimerization of the Two Protein Components Is Required for Efficient Binding to SRP RNA. Mol. Cell Biol. 1990, 10, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weichenrieder, O.; Wild, K.; Strub, K.; Cusack, S. Structure and Assembly of the Alu Domain of the Mammalian Signal Recognition Particle. Nature 2000, 408, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maity, T.S.; Fried, H.M.; Weeks, K.M. Anti-Cooperative Assembly of the SRP19 and SRP68/72 Components of the Signal Recognition Particle. Biochem. J. 2008, 415, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwieb, C. Recognition of a Tetranucleotide Loop of Signal Recognition Particle RNA by Protein SRP19. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 15650–15656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittenden, K.; Black, S.D.; Zwieb, C. Systematic Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Protein SRP19. Identification of the Residues Essential for Binding to Signal Recognition Particle RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 20497–20502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieb, C. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Signal-Recognition Particle RNA. Identification of the Nucleotides in Helix 8 Required for Interaction with Protein SRP19. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 222, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuglstatter, A.; Oubridge, C.; Nagai, K. Induced Structural Changes of 7SL RNA during the Assembly of Human Signal Recognition Particle. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 9, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainzl, T.; Huang, S.; Sauer-Eriksson, A.E. Structure of the SRP19–RNA Complex and Implications for Signal Recognition Particle Assembly. Nature 2002, 417, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, S.; Volzeng, C.; Muller, A.; Jung, M.; Zimmermann, R. Protein Transport into Canine Pancreatic Microsomes: A Quantitative Approach. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 3200–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeiwa, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Ohno, M. Exportin-5 Mediates Nuclear Export of SRP RNA in Vertebrates. Genes Cells 2015, 20, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, C.; Yamashita, E.; Lee, S.J.; Shibata, S.; Katahira, J.; Nakagawa, A.; Yoneda, Y.; Tsukihara, T. A High-Resolution Structure of the Pre-MicroRNA Nuclear Export Machinery. Science 2009, 326, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzon, N.; Schlotter, F.; Lefebvre, S.; Dodré, M.; Moreau, A.; Soret, J.; Besse, A.; Barkats, M.; Bordonne, R.; Branlant, C.; et al. Implication of the SMN Complex in the Biogenesis and Steady State Level of the Signal Recognition Particle. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1255–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walter, P.; Blobel, G. Translocation of Proteins across the Endoplasmic Reticulum. II. Signal Recognition Protein (SRP) Mediates the Selective Binding to Microsomal Membranes of in-Vitro-Assembled Polysomes Synthesizing Secretory Protein. J. Cell Biol. 1981, 91, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holtkamp, W.; Lee, S.; Bornemann, T.; Senyushkina, T.; Rodnina, M.V.; Wintermeyer, W. Dynamic Switch of the Signal Recognition Particle from Scanning to Targeting. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noriega, T.R.; Chen, J.; Walter, P.; Puglisi, J.D. Real-Time Observation of Signal Recognition Particle Binding to Actively Translating Ribosomes. Elife 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega, T.R.; Tsai, A.; Elvekrog, M.M.; Petrov, A.; Neher, S.B.; Chen, J.; Bradshaw, N.; Puglisi, J.D.; Walter, P. Signal Recognition Particle-Ribosome Binding Is Sensitive to Nascent Chain Length. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 19294–19305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voorhees, R.M.; Hegde, R.S. Structures of the Scanning and Engaged States of the Mammalian SRP-Ribosome Complex. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mercier, E.; Holtkamp, W.; Rodnina, M.V.; Wintermeyer, W. Signal Recognition Particle Binds to Translating Ribosomes before Emergence of a Signal Anchor Sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 11858–11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Berndt, U.; Gölz, H.; Tais, A.; Oellerer, S.; Wölfle, T.; Fitzke, E.; Rospert, S. NAC Functions as a Modulator of SRP during the Early Steps of Protein Targeting to the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 3027–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raue, U.; Oellerer, S.; Rospert, S. Association of Protein Biogenesis Factors at the Yeast Ribosomal Tunnel Exit Is Affected by the Translational Status and Nascent Polypeptide Sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7809–7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flanagan, J.J.; Chen, J.-C.; Miao, Y.; Shao, Y.; Lin, J.; Bock, P.E.; Johnson, A.E. Signal Recognition Particle Binds to Ribosome-Bound Signal Sequences with Fluorescence-Detected Subnanomolar Affinity That Does Not Diminish as the Nascent Chain Lengthens. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 18628–18637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mary, C.; Scherrer, A.; Huck, L.; Lakkaraju, A.K.K.; Thomas, Y.; Johnson, A.E.; Strub, K. Residues in SRP9/14 Essential for Elongation Arrest Activity of the Signal Recognition Particle Define a Positively Charged Functional Domain on One Side of the Protein. RNA 2010, 16, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halic, M.; Becker, T.; Pool, M.R.; Spahn, C.M.T.; Grassucci, R.A.; Frank, J.; Beckmann, R. Structure of the Signal Recognition Particle Interacting with the Elongation-Arrested Ribosome. Nature 2004, 427, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousset, L.; Mary, C.; Brooks, M.A.; Scherrer, A.; Strub, K.; Cusack, S. Crystal Structure of a Signal Recognition Particle Alu Domain in the Elongation Arrest Conformation. RNA 2014, 20, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, Y.; Bui, N.; Strub, K. A Truncation in the 14 KDa Protein of the Signal Recognition Particle Leads to Tertiary Structure Changes in the RNA and Abolishes the Elongation Arrest Activity of the Particle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 1920–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, V.; Walter, P. Removal of the Alu Structural Domain from Signal Recognition Particle Leaves Its Protein Translocation Activity Intact. Nature 1986, 320, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkaraju, A.K.; Mary, C.; Scherrer, A.; Johnson, A.E.; Strub, K. SRP Keeps Polypeptides Translocation-Competent by Slowing Translation to Match Limiting ER-Targeting Sites. Cell 2008, 133, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolin, S.L.; Walter, P. Ribosome Pausing and Stacking during Translation of a Eukaryotic MRNA. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 3559–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandon, E.C.; Jiang, Y.; Gilmore, R. Dual Recognition of the Ribosome and the Signal Recognition Particle by the SRP Receptor during Protein Targeting to the Endoplasmic Reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Jomaa, A.; Lee, J.H.; Chandrasekar, S.; Boehringer, D.; Shan, S.O.; Ban, N. Structure of a Prehandover Mammalian Ribosomal SRP-SRP Receptor Targeting Complex. Science 2018, 360, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jomaa, A.; Fu, Y.-H.H.; Boehringer, D.; Leibundgut, M.; Shan, S.; Ban, N. Structure of the Quaternary Complex between SRP, SR, and Translocon Bound to the Translating Ribosome. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainprize, I.L.; Vulcu, F.; Andrews, D.W. The signal. recognition particle and its receptor in er protein targeting. In The Enzymes: Molecular Machines Involved in Protein Transport; Dalbey, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- Bacher, G.; Pool, M.; Dobberstein, B. The Ribosome Regulates the GTPase of the Beta-Subunit of the Signal Recognition Particle Receptor. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 146, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Raden, D.; Mandon, E.C.; Gilmore, R. Role of Sec61alpha in the Regulated Transfer of the Ribosome-Nascent Chain Complex from the Signal Recognition Particle to the Translocation Channel. Cell 2000, 100, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fulga, T.A.; Sinning, I.; Dobberstein, B.; Pool, M.R. SRβ Coordinates Signal Sequence Release from SRP with Ribosome Binding to the Translocon. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2338–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oubridge, C.; Kuglstatter, A.; Jovine, L.; Nagai, K. Crystal Structure of SRP19 in Complex with the S Domain of SRP RNA and Its Implication for the Assembly of the Signal Recognition Particle. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, K.; Bange, G.; Motiejunas, D.; Kribelbauer, J.; Hendricks, A.; Segnitz, B.; Wade, R.C.; Sinning, I. Structural Basis for Conserved Regulation and Adaptation of the Signal Recognition Particle Targeting Complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 2880–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, Z.; Tian, W.; Tang, J.; Wu, W.; Tong, Y.; et al. Human Apo-SRP72 and SRP68/72 Complex Structures Reveal the Molecular Basis of Protein Translocation. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 9, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.3.3; Schrodinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019.
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, D.W.; Walter, P.; Ottensmeyer, F.P. Evidence for an Extended 7SL RNA Structure in the Signal Recognition Particle. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3471–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.N.; Doudna Cate, J.H. The Structure and Function of the Eukaryotic Ribosome. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, P.; Blobel, G. Purification of a Membrane-Associated Protein Complex Required for Protein Translocation across the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 7112–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahl, V.; Keller, H.; Schmidt, S.; Weichenrieder, O. Retrotransposition and Crystal Structure of an Alu RNP in the Ribosome-Stalling Conformation. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gongadze, G.M. 5S RRNA and Ribosome. Biochem. Mosc. 2011, 76, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, N.; Wolff, N.; Cusack, S.; Strub, K. Mutational Analysis of the Protein Subunits of the Signal Recognition Particle Alu-Domain. RNA 1997, 3, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Das, A.K.; Cohen, P.W.; Barford, D. The Structure of the Tetratricopeptide Repeats of Protein Phosphatase 5: Implications for TPR-Mediated Protein-Protein Interactions. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utz, P.J.; Hottelet, M.; Le, T.M.; Kim, S.J.; Geiger, M.E.; van Venrooij, W.J.; Anderson, P. The 72-KDa Component of Signal Recognition Particle Is Cleaved during Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 35362–35370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clemons, W.M.; Gowda, K.; Black, S.D.; Zwieb, C.; Ramakrishnan, V. Crystal Structure of the Conserved Subdomain of Human Protein SRP54M at 2.1 A Resolution: Evidence for the Mechanism of Signal Peptide Binding. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 292, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lutcke, H.; High, S.; Romisch, K.; Ashford, A.J.; Dobberstein, B. The Methionine-Rich Domain of the 54 KDa Subunit of Signal Recognition Particle Is Sufficient for the Interaction with Signal Sequences. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, C.Y.; Li, J.; Oubridge, C.; Hernández, H.; Robinson, C.V.; Nagai, K. Recognition of a Signal Peptide by the Signal Recognition Particle. Nature 2010, 465, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Abdulrahman, S.; Yin, J.; Zwieb, C. Systematic Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Human Protein SRP54: Interactions with Signal Recognition Particle RNA and Modes of Signal Peptide Recognition. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 11362–11371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, S.O.; Chandrasekar, S.; Walter, P. Conformational Changes in the GTPase Modules of the Signal Reception Particle and Its Receptor Drive Initiation of Protein Translocation. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadian, M.R.; Stege, P.; Scheffzek, K.; Wittinghofer, A. Confirmation of the Arginine-Finger Hypothesis for the GAP-Stimulated GTP-Hydrolysis Reaction of Ras. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainzl, T.; Huang, S.; Sauer-Eriksson, A.E. Interaction of Signal-Recognition Particle 54 GTPase Domain and Signal-Recognition Particle RNA in the Free Signal-Recognition Particle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14911–14916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, E.A.; Keller, H.; Mills, R.E.; Schmidt, S.; Moran, J.V.; Weichenrieder, O.; Devine, S.E. Active Alu Retrotransposons in the Human Genome. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talhouarne, G.J.S.; Gall, J.G. 7SL RNA in Vertebrate Red Blood Cells. RNA 2018, 24, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamyshev, A.L.; Patrick, A.E.; Karamysheva, Z.N.; Griesemer, D.S.; Hudson, H.; Tjon-Kon-Sang, S.; Nilsson, I.; Otto, H.; Liu, Q.; Rospert, S.; et al. Inefficient SRP Interaction with a Nascent Chain Triggers a MRNA Quality Control Pathway. Cell 2014, 156, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tikhonova, E.B.; Karamysheva, Z.N.; von Heijne, G.; Karamyshev, A.L. Silencing of Aberrant Secretory Protein Expression by Disease-Associated Mutations. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 2567–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamysheva, Z.N.; Tikhonova, E.B.; Karamyshev, A.L. Granulin in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: Molecular Mechanisms of the Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinarbasi, E.S.; Karamyshev, A.L.; Tikhonova, E.B.; Wu, I.-H.; Hudson, H.; Thomas, P.J. Pathogenic Signal Sequence Mutations in Progranulin Disrupt SRP Interactions Required for MRNA Stability. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2844–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamyshev, A.L.; Karamysheva, Z.N. Lost in Translation: Ribosome-Associated MRNA and Protein Quality Controls. Front. Genet. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amm, I.; Sommer, T.; Wolf, D.H. Protein Quality Control and Elimination of Protein Waste: The Role of the Ubiquitin–Proteasome System. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loedige, I.; Gaidatzis, D.; Sack, R.; Meister, G.; Filipowicz, W. The Mammalian TRIM-NHL Protein TRIM71/LIN-41 Is a Repressor of MRNA Function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Species | SRP RNA | Alu Domain | S Domain | Additional Subunits | Receptor | Source | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | 7SL RNA | SRP9 | SRP14 | SRP19 | SRP54 | SRP68 | SRP72 | - | SR | [97] |
| Trypanosoma brucei | 7SL RNA | sRNA76 | SRP19 | SRP54 | SRP68 | SRP72 | - | SR | [69,74] | |
| S. pombe | s1r1 RNA | SRP14p | SRP14p | SRP19p | SRP54p | SRP68p | SRP72p | SRP21p | SR | [77,98] |
| Archaeoglobus fulgidus | 7S RNA | - | - | SRP19 | Ffh | - | - | - | FtsY | [55,56,57,58] |
| Escherichia coli | 4.5S RNA | - | - | - | Ffh | - | - | - | FtsY | [50] |
| Bacillus subtilis | 6S RNA | HBSu | HBSu | - | Ffh | - | - | - | FtsY | [54,55] |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | - | - | - | - | cpSRP54 | - | - | cpSRP43 | cpFtsY | [57,58,62,63] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kellogg, M.K.; Miller, S.C.; Tikhonova, E.B.; Karamyshev, A.L. SRPassing Co-translational Targeting: The Role of the Signal Recognition Particle in Protein Targeting and mRNA Protection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126284
Kellogg MK, Miller SC, Tikhonova EB, Karamyshev AL. SRPassing Co-translational Targeting: The Role of the Signal Recognition Particle in Protein Targeting and mRNA Protection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(12):6284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126284
Chicago/Turabian StyleKellogg, Morgana K., Sarah C. Miller, Elena B. Tikhonova, and Andrey L. Karamyshev. 2021. "SRPassing Co-translational Targeting: The Role of the Signal Recognition Particle in Protein Targeting and mRNA Protection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 12: 6284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126284
APA StyleKellogg, M. K., Miller, S. C., Tikhonova, E. B., & Karamyshev, A. L. (2021). SRPassing Co-translational Targeting: The Role of the Signal Recognition Particle in Protein Targeting and mRNA Protection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(12), 6284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126284





