Gap Junction-Mediated Intercellular Communication of cAMP Prevents CDDP-Induced Ototoxicity via cAMP/PKA/CREB Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
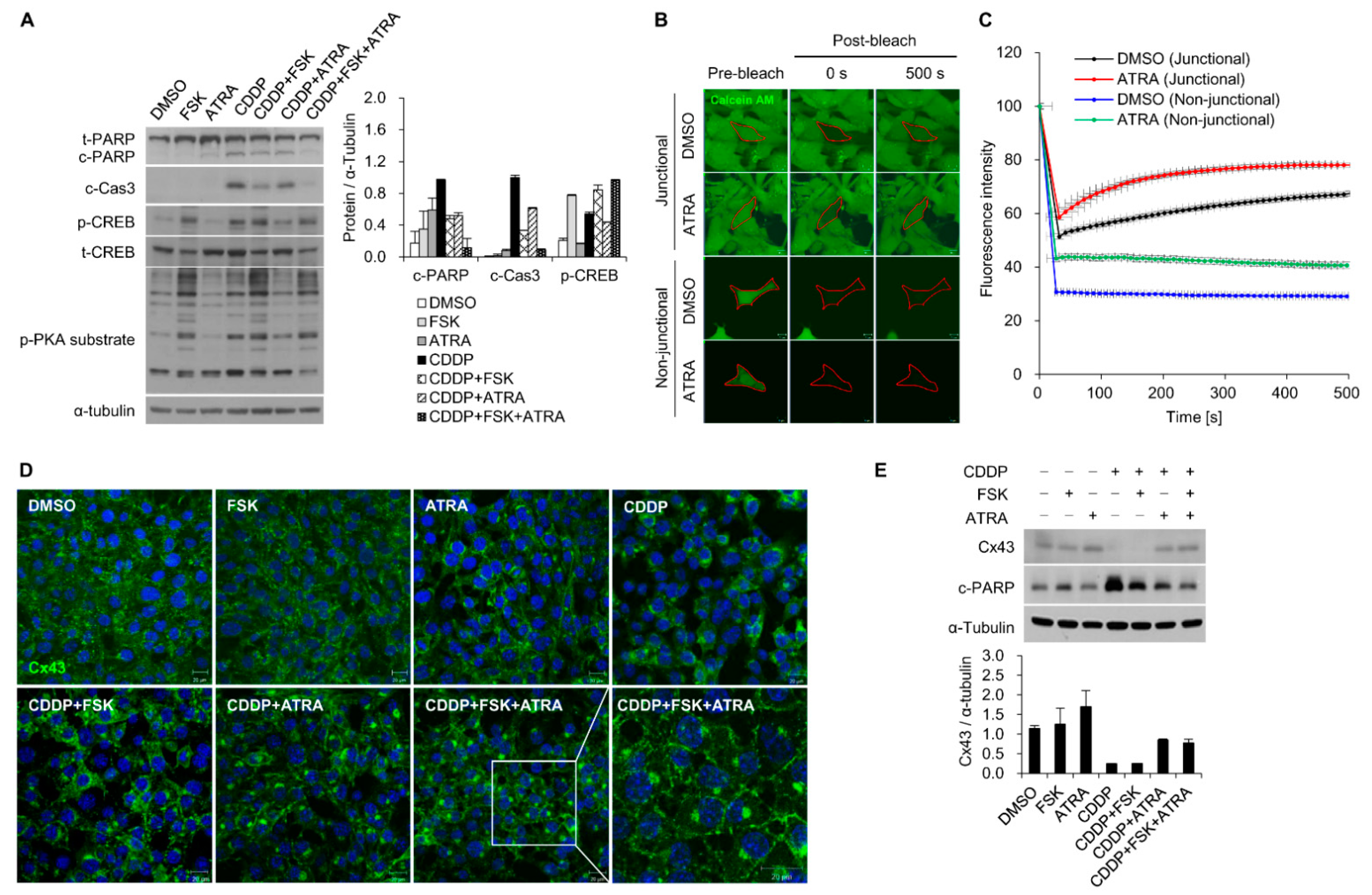
2.1. Increasing cAMP Protects against CDDP-Induced Auditory Cell Death via Activation of the cAMP/PKA/CREB Pathway
2.2. The Gap Junction Enhancer Retinoic Acid Improves the Protective Effect of FSK against CDDP
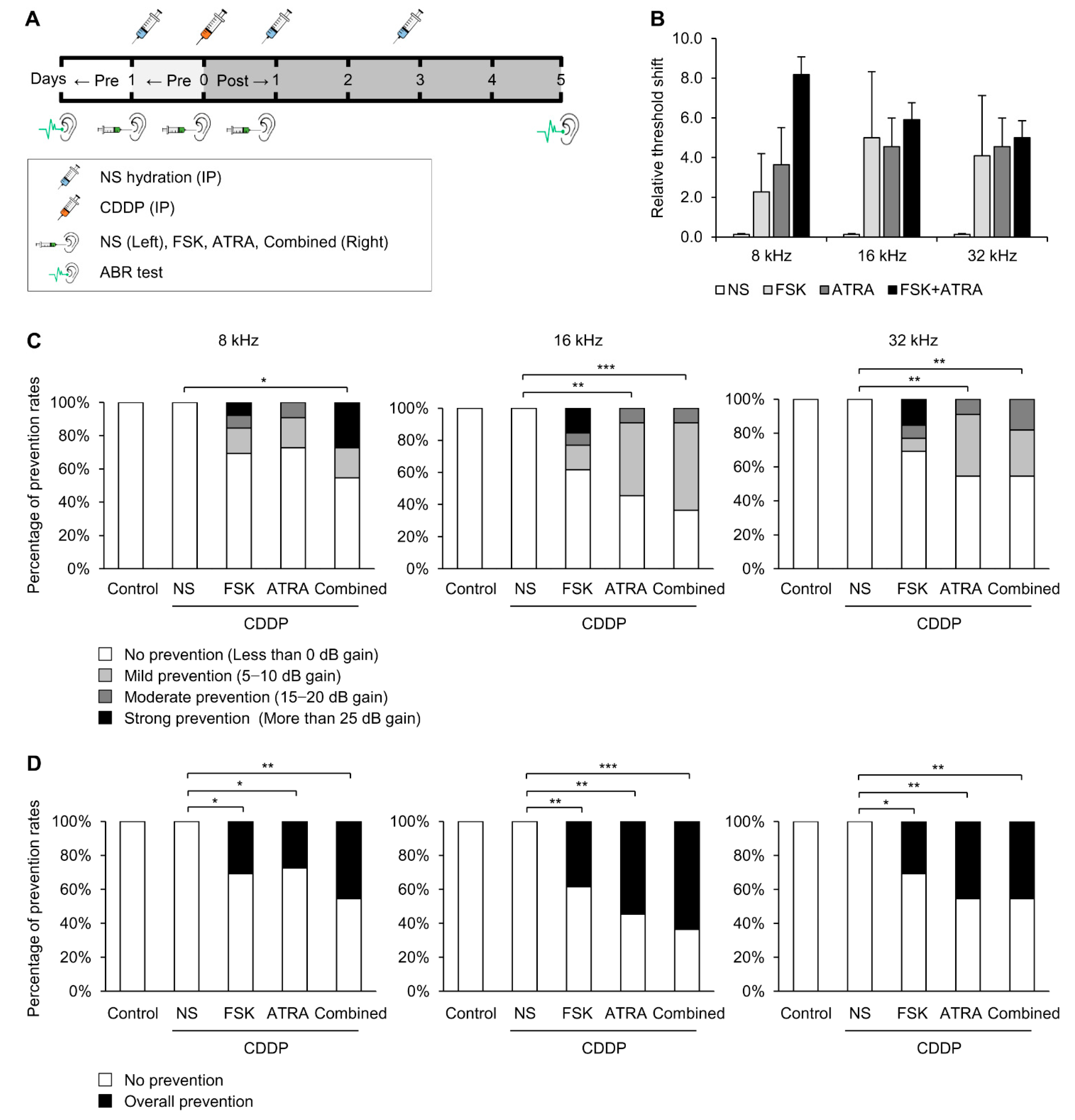
2.3. Combinational Treatment of FSK and ATRA Prevents CDDP-Induced Hearing Loss
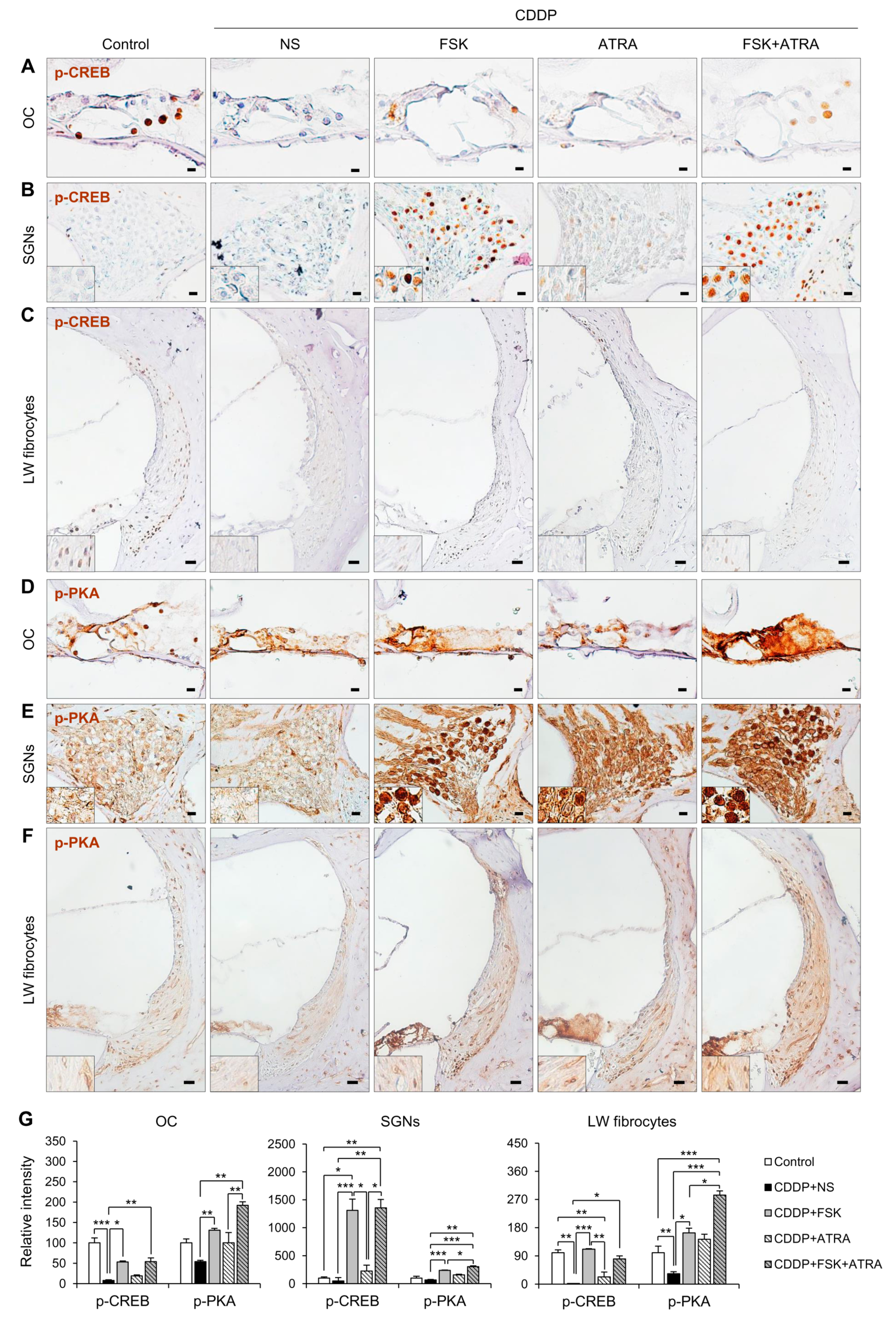
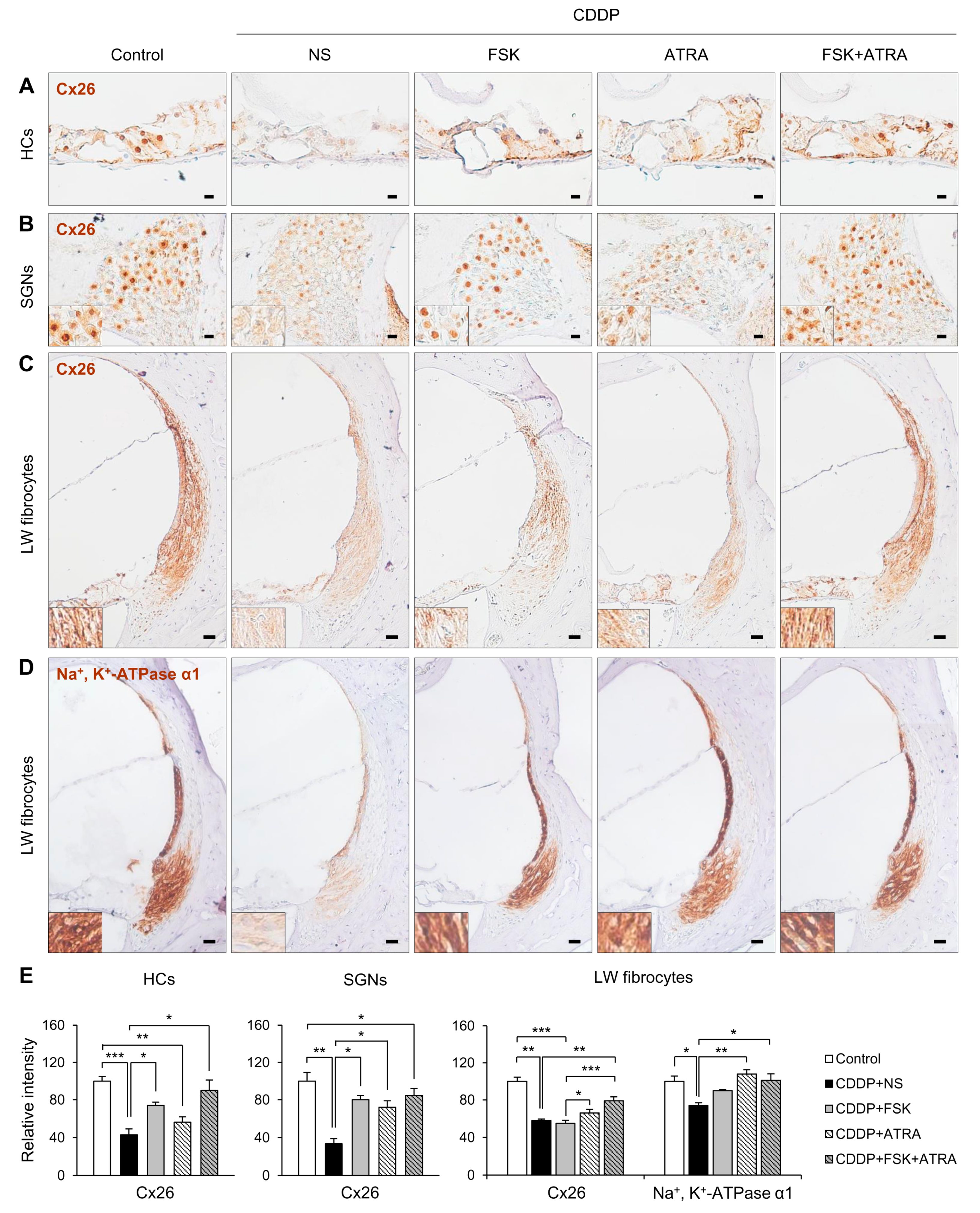
2.4. Treatment with FSK and ATRA Prevents CDDP-Induced Loss of HCs, SGNs and LW Fibrocytes by Improving cAMP and Gap Junction Function
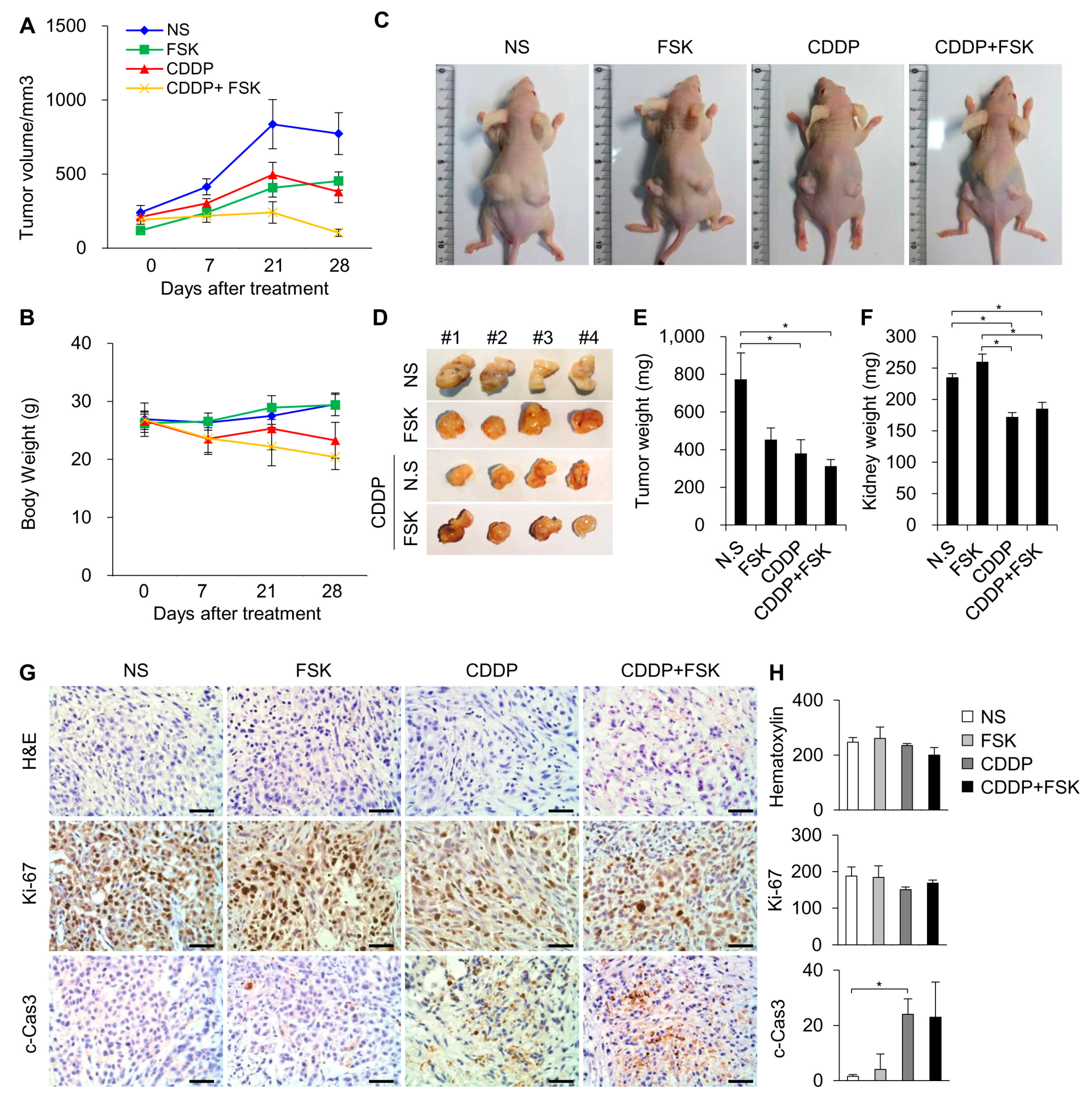
2.5. FSK and ATRA Do Not Attenuate the Anti-Tumor Properties of CDDP
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Organ of Corti Explant Culture and Treatment
4.2. House Ear Institute-Organ of Corti 1 (HEI-OC1) and OC Primary Cell Culture and Treatment
4.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent (ELISA) Assay
4.4. Fluorescence Recovery after Photobleaching (FRAP)
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining and Histological Analysis
4.7. Immunohistochemistry
4.8. Immunofluorescence
4.9. Animal Experiments
4.10. Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Test
4.11. Tumor Xenograft Mouse Model
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, H.-B.; Kikuchi, T.; Ngezahayo, A.; White, T.W. Gap junctions and cochlear homeostasis. J. Membr. Biol. 2006, 209, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, J.J.; Abitbol, J.M.; Hulme, S.; Press, E.R.; Laird, D.W.; Allman, B.L. The connexin 30 A88V mutant reduces cochlear gap junction expression and confers long-term protection against hearing loss. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, jcs224097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, A.D.; Acuña, R.; Figueroa, V.; Maripillan, J.; Nicholson, B. Gap-junction channels dysfunction in deafness and hearing loss. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.Y.; Park, Y.H. Potential of gene and cell therapy for inner ear hair cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8137614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrocal, J.R.G.; Méndez-Benegassi, I.; Martín, C.; Camacho, R.R. Intervention of spiral ligament fibrocytes in the metabolic regulation of the inner ear. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Engl. Ed. 2008, 59, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decrock, E.; Vinken, M.; De Vuyst, E.; Krysko, D.; D’Herde, K.; Vanhaecke, T.; Vandenabeele, P.; Rogiers, V.; Leybaert, L. Connexin-related signaling in cell death: To live or let die? Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugenin, E.A.; Berman, J.W. Cytochrome c dysregulation induced by HIV infection of astrocytes results in bystander apoptosis of uninfected astrocytes by an IP3 and calcium-dependent mechanism. J. Neurochem. 2013, 127, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishii, M.; Rohrer, B. Bystander effects elicited by single-cell photo-oxidative blue-light stimulation in retinal pigment epithelium cell networks. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-J.; Kim, M.-J.; Rothenberger, C.; Kumar, A.; Sampson, E.M.; Ding, D.; Han, C.; White, K.; Boyd, K.; Manohar, S.; et al. GSTA4 mediates reduction of cisplatin ototoxicity in female mice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vlajkovic, S.M.; Thorne, P.R.; Rajan, R.; Gale, J.E. Preventing hearing loss and restoring hearing: A new outlook. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Allman, B.L.; Salvi, R. Review: Ototoxic characteristics of platinum antitumor drugs. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2012, 295, 1851–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Shin, B.; Choo, O.-S.; Lee, J.J.; Choung, Y.-H.; Kim, M.Y.J. Connexin 43 acts as a proapoptotic modulator in cisplatin-induced auditory cell death. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 25, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mughal, W.; Martens, M.; Field, J.; Chapman, D.; Huang, J.; Rattan, S.; Hai, Y.; Cheung, K.G.; Kereliuk, S.; West, A.R.; et al. Myocardin regulates mitochondrial calcium homeostasis and prevents permeability transition. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1732–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, X.; Ding, Y.; Ren, L.; Bai, T.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Inhibition of voltage-dependent potassium channels mediates cAMP-potentiated insulin secretion in rat pancreatic beta cells. Islets 2017, 9, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhargava, P.; Janda, J.; Schnellmann, R.G. Elucidation of cGMP-dependent induction of mitochondrial biogenesis through PKG and p38 MAPK in the kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2020, 318, F322–F328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, L.; Mighty, J.; Zhong, X.; Francis, A.; Mendez, M.; Muharam, H.; Redenti, S.M.; Das, D.; Aktas, B.H.; Sauane, M. IL-24 promotes apoptosis through cAMP-dependent PKA pathways in human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jewell, J.L.; Fu, V.; Hong, A.W.; Yu, F.-X.; Meng, D.; Melick, C.H.; Wang, H.; Lam, W.-L.M.; Yuan, H.-X.; Taylor, S.S.; et al. GPCR signaling inhibits mTORC1 via PKA phosphorylation of Raptor. eLife 2019, 8, e43038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, S.-K.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.-S.; Zheng, R.-S.; Tong, X.-H.; Liu, H.; Tao, L.; He, X.-D. Connexin-dependent gap junction enhancement is involved in the synergistic effect of sorafenib and all-trans retinoic acid on HCC growth inhibition. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Tian, C.; Lim, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Chung, J.H.; Choung, Y.-H. Prevention of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity by the inhibition of gap junctional intercellular communication in auditory cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 3859–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; You, T.; Yuan, D.; Han, X.; Hong, X.; He, B.; Wang, L.; Tong, X.; Tao, L.; Harris, A.L. Cisplatin and Oxaliplatin inhibit gap junctional communication by direct action and by reduction of connexin expression, thereby counteracting cytotoxic efficacy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 333, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lieberthal, W.; Triaca, V.; Levine, J. Mechanisms of death induced by cisplatin in proximal tubular epithelial cells: Apoptosis vs. necrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1996, 270, F700–F708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, K.; Spicer, S.S.; Schulte, B.A. Ultrastructural localization of Na,K-ATPase in the gerbil cochlea. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1995, 43, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Sheth, S.; Sheehan, K.; Mukherjea, D.; Dhukhwa, A.; Borse, V.; Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. The endocannabinoid/cannabinoid receptor 2 system protects against cisplatin-induced hearing loss. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.-H.; Gudas, L.J. Retinoids, retinoic acid receptors, and cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2011, 6, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, D.-X.; Shi, J.; Gao, H.; Li, J.-J.; Zhao, J.-S.; Qiu, L.; Liu, J.; Li, N.; Guo, W.-X.; et al. All-trans retinoic acid potentiates the chemotherapeutic effect of cisplatin by inducing differentiation of tumor initiating cells in liver cancer. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Lazarovici, P.; Quirion, R.; Zheng, W. cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein (CREB): A possible signaling molecule link in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranz, K.; Warnecke, A.; Lenarz, T.; Durisin, M.; Scheper, V. Phosphodiesterase type 4 inhibitor rolipram improves survival of spiral ganglion neurons in vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, H.L.; Astell, K.J.; Mathai, M.L.; Su, X.Q. Coleus forskohlii extract supplementation in conjunction with a hypocaloric diet reduces the risk factors of metabolic syndrome in overweight and obese subjects: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9508–9522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girish, B.; Reddy, P.S. Forskolin ameliorates mancozeb-induced testicular and epididymal toxicity in Wistar rats by reducing oxidative toxicity and by stimulating steroidogenesis. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Bai, X.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Wang, H. Forskolin protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity by inhibiting apoptosis and ROS production. BioMed Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Xiong, H.; Sha, S. Noise-induced loss of sensory hair cells is mediated by ROS/AMPKalpha pathway. Redox Biol. 2020, 29, 101406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Anderson, H.; Buo, A.M.; Moorer, M.C.; Ren, M.; Stains, J.P. Communication of cAMP by connexin43 gap junctions regulates osteoblast signaling and gene expression. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Sutton-McDowall, M.; Wang, X.; Sugimura, S.; Thompson, J.; Gilchrist, R. Extending prematuration with cAMP modulators enhances the cumulus contribution to oocyte antioxidant defence and oocyte quality via gap junctions. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Yang, G.-M.; Li, T.; Liu, L.-M. Myoendothelial gap junctions mediate regulation of angiopoietin-2-induced vascular hyporeactivity after hypoxia through connexin 43-gated cAMP transfer. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2017, 313, C262–C273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeunjung Kim, X.L. Effects of retinoid treatment on cochlear development, connexin expression and hearing thresholds in mice. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2017, 1, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, T.J.; Oberholtzer, J.C. cAMP-induced auditory supporting cell proliferation is mediated by ERK MAPK signaling pathway. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2010, 11, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadali, A.; Ying, Y.-L.M.; Kwan, K.Y. Activation of CHK1 in supporting cells indirectly promotes hair cell survival. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- May, L.A.; Kramarenko, I.I.; Brandon, C.S.; Voelkel-Johnson, C.; Roy, S.; Truong, K.; Francis, S.P.; Monzack, E.L.; Lee, F.S.; Cunningham, L.L. Inner ear supporting cells protect hair cells by secreting HSP70. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 3577–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, K.; Song, Y.; Zhou, K.; Yue, B.; Qiu, Y.; Sun, F.; Wang, R.; Zha, D.; Qiu, J. Upregulation of HSP60 expression in the postnatal rat cochlea and rats with drug-induced hearing loss. Cell Stress Chaperones 2018, 23, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.X.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.P. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling was activated in supporting cells during exposure of the zebrafish lateral line to cisplatin. Ann. Anat. 2019, 226, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breglio, A.M.; May, L.A.; Barzik, M.; Welsh, N.C.; Francis, S.P.; Costain, T.Q.; Wang, L.; Anderson, D.E.; Petralia, R.S.; Wang, Y.-X.; et al. Exosomes mediate sensory hair cell protection in the inner ear. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2657–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, A.; Jones, H.; Hiroi, T.; Lam, J.; Zhang, J.; Moss, J.; Vaughan, M.; Levine, S.J. cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) signaling induces TNFR1 exosome-like vesicle release via anchoring of PKA regulatory subunit RIIbeta to BIG2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25364–25371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Ren, J.; Bai, Y.; Pei, X.; Han, Y. Exosomes from hypoxia-treated human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis through VEGF/VEGF-R. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 109, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Hikichi, M.; Yukitake, J.; Wakatsuki, T.; Nishio, E.; Utsumi, T.; Harada, N. Forskolin increases the effect of everolimus on aromatase inhibitor-resistant breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 23451–23461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Illiano, M.; Sapio, L.; Salzillo, A.; Capasso, L.; Caiafa, I.; Chiosi, E.; Spina, A.; Naviglio, S. Forskolin improves sensitivity to doxorubicin of triple negative breast cancer cells via Protein Kinase A-mediated ERK1/2 inhibition. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 152, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvis, A.M.; McCormick, M.L.; Spitz, D.R.; Kiningham, K.K. Redox balance influences differentiation status of neuroblastoma in the presence of all-trans retinoic acid. Redox Biol. 2016, 7, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsson, C.; Moyer, S.M.; Liu, B.; Michel, K.A.; Pant, V.; Yang, P.; Wong, J.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Krahe, R.; Lozano, G. Synergistic and additive effect of retinoic acid in circumventing resistance to p53 restoration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2198–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Najafzadeh, N.; Mazani, M.; Abbasi, A.; Farassati, F.; Amani, M. Low-dose all-trans retinoic acid enhances cytotoxicity of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil on CD44+ cancer stem cells. BioMed Pharmacother. 2015, 74, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, V.D.M.; Gasparotto, J.; Figueiró, F.; Dias, A.D.F.; Rostirolla, D.C.; Somensi, N.; da Rosa, H.T.; Grun, L.K.; Barbé-Tuana, F.M.; Gelain, D.P.; et al. Retinoic acid downregulates thiol antioxidant defences and homologous recombination while promotes A549 cells sensitization to cisplatin. Cell. Signal. 2019, 62, 109356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, C.; Yucel, E.E.; Arslan, F.D.; Ekmekci, S.; Kisa, E.; Ülker, V.; Ucar, M.; Ilbey, Y.O.; Celik, O.; Basok, B.I.; et al. All-trans retinoic acid prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Naunyn Schmiedeberg Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yucel, C.; Arslan, F.D.; Ekmekci, S.; Ulker, V.; Kisa, E.; Yucel, E.E.; Ucar, M.; Ilbey, Y.O.; Celik, O.; Basok, B.I.; et al. Protective effect of all-trans retinoic acid in cisplatin-induced testicular damage in rats. World J. Men Health 2019, 37, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rah, Y.C.; Park, S.; Koun, S.; Park, H.-C.; Choi, J. In vivo assay of the ethanol-induced embryonic hair cell loss and the protective role of the retinoic and folic acid in zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio). Alcohol 2019, 75, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.-J.; Kang, H.; Lee, Y.Y.; Choo, O.-S.; Jang, J.H.; Park, S.-H.; Moon, J.-S.; Choi, S.J.; Choung, Y.-H. Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in rats is driven by RIP3-dependent necroptosis. Cells 2019, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, H.; Jang, J.H.; Choung, Y.-H. Gap Junction-Mediated Intercellular Communication of cAMP Prevents CDDP-Induced Ototoxicity via cAMP/PKA/CREB Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126327
Kim YJ, Lee J-S, Kim H, Jang JH, Choung Y-H. Gap Junction-Mediated Intercellular Communication of cAMP Prevents CDDP-Induced Ototoxicity via cAMP/PKA/CREB Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(12):6327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126327
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yeon Ju, Jin-Sol Lee, Hantai Kim, Jeong Hun Jang, and Yun-Hoon Choung. 2021. "Gap Junction-Mediated Intercellular Communication of cAMP Prevents CDDP-Induced Ototoxicity via cAMP/PKA/CREB Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 12: 6327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126327
APA StyleKim, Y. J., Lee, J.-S., Kim, H., Jang, J. H., & Choung, Y.-H. (2021). Gap Junction-Mediated Intercellular Communication of cAMP Prevents CDDP-Induced Ototoxicity via cAMP/PKA/CREB Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(12), 6327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126327






