18F-Sodium Fluoride PET as a Diagnostic Modality for Metabolic, Autoimmune, and Osteogenic Bone Disorders: Cellular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
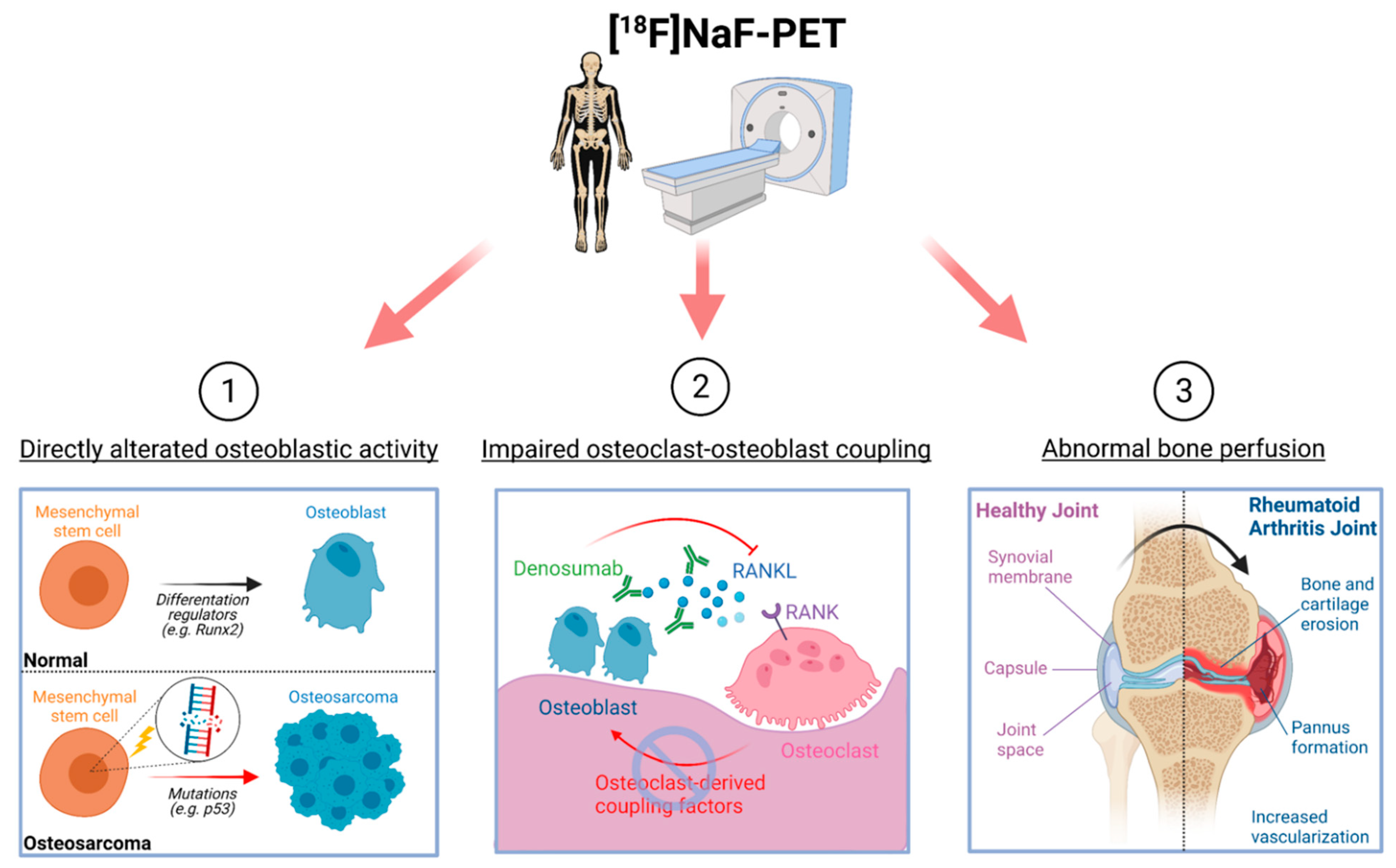
2. Cellular Basis of Detecting Altered Bone Lesions Using 18F-NaF-PET
2.1. Osteoblastic Activity
2.2. Osteoclast–Osteoblast Coupling
2.3. Bone Perfusion
3. 18F-NaF-PET in Metabolic Bone Disorders
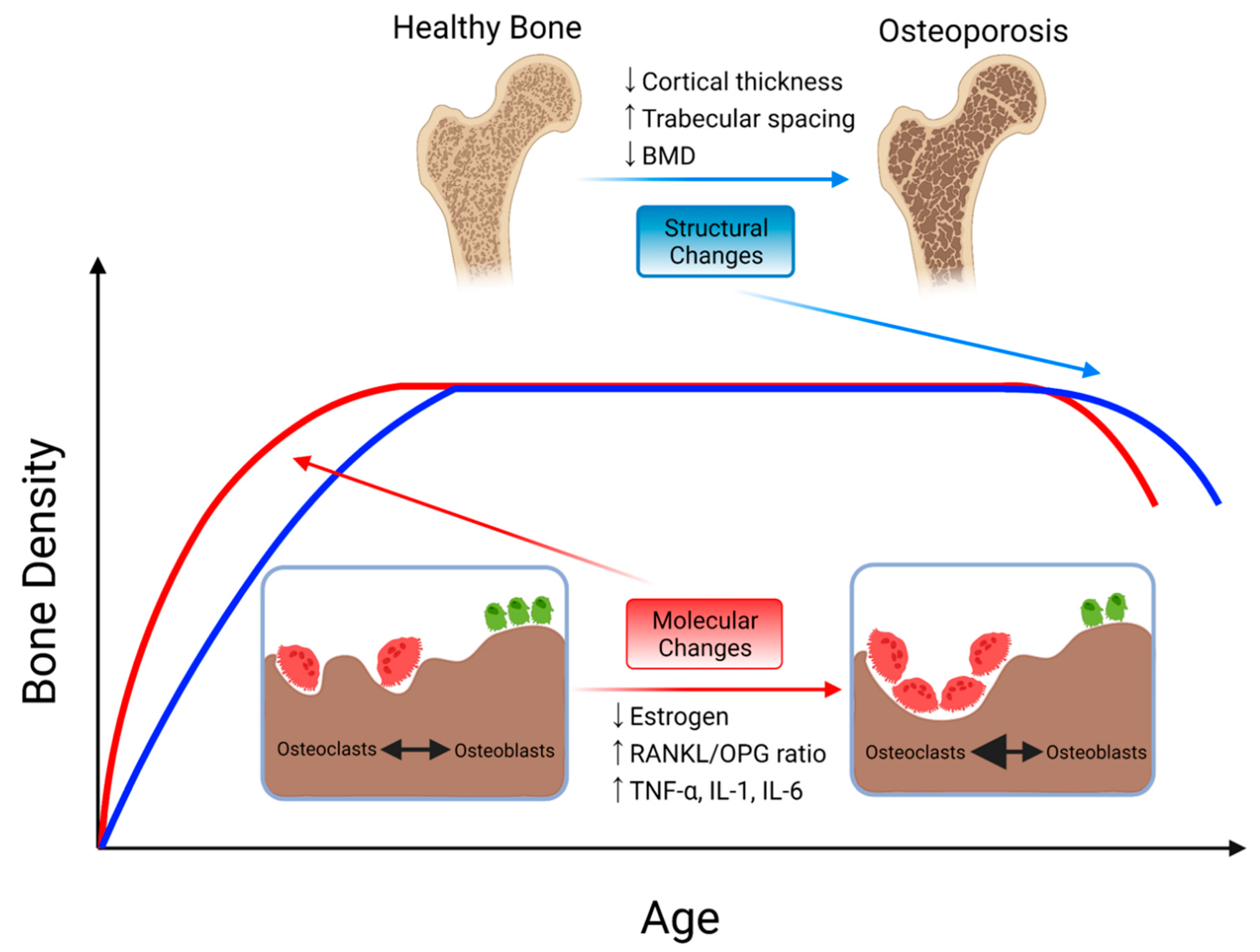
3.1. Osteoporosis
3.2. Paget’s Disease
3.3. Hyperparathyroidism
4. 18F-NaF-PET in Autoimmune Diseases
4.1. Ankylosing Spondylitis
4.2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
5. 18F-NaF-PET in Osteogenic Bone Disorders
5.1. Osteosarcoma
5.2. Melorheostosis
5.3. Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eastell, R.; Szulc, P. Use of bone turnover markers in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 908–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takito, J.; Inoue, S.; Nakamura, M. The Sealing Zone in Osteoclasts: A Self-Organized Structure on the Bone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, H.C.; Larrouture, Q.C.; Li, Y.; Lin, H.; Beer-Stoltz, D.; Liu, L.; Tuan, R.S.; Robinson, L.J.; Schlesinger, P.H.; Nelson, D.J. Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Matrix Formation In Vivo and In Vitro. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2017, 23, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; McDonald, J.M. Disorders of bone remodeling. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarrategi, A.; Tornin, J.; Martinez-Cruzado, L.; Hamilton, A.; Martinez-Campos, E.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Gonzalez, M.V.; Baldini, N.; Garcia-Castro, J.; Rodriguez, R. Osteosarcoma: Cells-of-Origin, Cancer Stem Cells, and Targeted Therapies. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 3631764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, R.; Gravallese, E.M. Impact of inflammation on the osteoblast in rheumatic diseases. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2014, 12, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, C.C.; Raynor, W.Y.; Hong, A.L.; Kargilis, D.C.; Lee, J.S.; Alecxih, A.G.; Gupta, N.; Lim, M.K.; Al-Zaghal, A.; Werner, T.J.; et al. Diagnosis and Monitoring of Osteoporosis With (18)F-Sodium Fluoride PET: An Unavoidable Path for the Foreseeable Future. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 48, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, G.M.; Puri, T.; Siddique, M.; Frost, M.L.; Moore, A.E.B.; Fogelman, I. Site specific measurements of bone formation using [(18)F] sodium fluoride PET/CT. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2018, 8, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, K.; Sotoudeh, H.; Galgano, S.J.; Singh, R.; Gupta, N.; Gaddamanugu, S.; Choudhary, G. (18)F-Sodium Fluoride PET: History, Technical Feasibility, Mechanism of Action, Normal Biodistribution, and Diagnostic Performance in Bone Metastasis Detection Compared with Other Imaging Modalities. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2020, 48, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastawrous, S.; Bhargava, P.; Behnia, F.; Djang, D.S.; Haseley, D.R. Newer PET application with an old tracer: Role of 18F-NaF skeletal PET/CT in oncologic practice. Radiographics 2014, 34, 1295–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even-Sapir, E.; Mishani, E.; Flusser, G.; Metser, U. 18F-Fluoride positron emission tomography and positron emission tomography/computed tomography. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2007, 37, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarikaya, I.; Elgazzar, A.H.; Sarikaya, A.; Alfeeli, M. Normal bone and soft tissue distribution of fluorine-18-sodium fluoride and artifacts on 18F-NaF PET/CT bone scan: A pictorial review. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2017, 38, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomberg, B.A.; Thomassen, A.; Takx, R.A.; Vilstrup, M.H.; Hess, S.; Nielsen, A.L.; Diederichsen, A.C.; Mickley, H.; Alavi, A.; Hoilund-Carlsen, P.F. Delayed sodium 18F-fluoride PET/CT imaging does not improve quantification of vascular calcification metabolism: Results from the CAMONA study. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2014, 21, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicki, L.M.; Lutje, S.; Baraliakos, X.; Braun, J.; Kirchner, J.; Boos, J.; Heusch, P.; Ruhlmann, V.; Herrmann, K.; Umutlu, L.; et al. Dual-phase hybrid (18) F-Fluoride Positron emission tomography/MRI in ankylosing spondylitis: Investigating the link between MRI bone changes, regional hyperaemia and increased osteoblastic activity. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 62, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czernin, J.; Satyamurthy, N.; Schiepers, C. Molecular mechanisms of bone 18F-NaF deposition. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1826–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, R.A.; Choi, Y.; Huang, S.C.; Hoh, C.K.; Dahlbom, M.; Schiepers, C.; Satyamurthy, N.; Barrio, J.R.; Phelps, M.E. Evaluation of the skeletal kinetics of fluorine-18-fluoride ion with PET. J. Nucl. Med. 1992, 33, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raynor, W.; Houshmand, S.; Gholami, S.; Emamzadehfard, S.; Rajapakse, C.S.; Blomberg, B.A.; Werner, T.J.; Hoilund-Carlsen, P.F.; Baker, J.F.; Alavi, A. Evolving Role of Molecular Imaging with (18)F-Sodium Fluoride PET as a Biomarker for Calcium Metabolism. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2016, 14, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldan, J.D.; Hawkins, A.S.; Chin, B.B. (18)F Sodium Fluoride PET/CT in Patients with Prostate Cancer: Quantification of Normal Tissues, Benign Degenerative Lesions, and Malignant Lesions. World J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 15, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kulshrestha, R.K.; Vinjamuri, S.; England, A.; Nightingale, J.; Hogg, P. The Role of 18F-Sodium Fluoride PET/CT Bone Scans in the Diagnosis of Metastatic Bone Disease from Breast and Prostate Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2016, 44, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ravizzini, G.C.; Gorin, M.A.; Maurer, T.; Eiber, M.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Alemozzaffar, M.; Tollefson, M.K.; Delacroix, S.E.; Chapin, B.F. The use of PET/CT in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018, 21, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadvar, H.; Desai, B.; Conti, P.S. Sodium 18F-fluoride PET/CT of bone, joint, and other disorders. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2015, 45, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komori, T. Regulation of Proliferation, Differentiation and Functions of Osteoblasts by Runx2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.; Kapoor, N.; Bondu, J.D.; Thomas, N.; Paul, T.V. Bone turnover markers: Emerging tool in the management of osteoporosis. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 20, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amarasekara, D.S.; Yun, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, N.; Kim, H.; Rho, J. Regulation of Osteoclast Differentiation by Cytokine Networks. Immune Netw. 2018, 18, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, S.H.; Park, P.S.U.; Park-Min, K.H. The M-CSF receptor in osteoclasts and beyond. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1239–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Duan, N.; Zhu, G.; Schwarz, E.M.; Xie, C. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect. Tissue Res. 2018, 59, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Lin, C.; Stavre, Z.; Greenblatt, M.B.; Shim, J.H. Osteoblast-Osteoclast Communication and Bone Homeostasis. Cells 2020, 9, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, N.A.; Ng, K.W. Implications of osteoblast-osteoclast interactions in the management of osteoporosis by antiresorptive agents denosumab and odanacatib. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2014, 12, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, W.; Vriens, D.; Meier, M.E.; Smit, F.; Winter, E.M.; De Geus-Oei, L.F.; Appelman-Dijkstra, N.M. Denosumab reduces lesional Fluoride skeletal burden on Na[18F]F PET-CT in patients with Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, M.L.; Blake, G.M.; Cook, G.J.; Marsden, P.K.; Fogelman, I. Differences in regional bone perfusion and turnover between lumbar spine and distal humerus: (18)F-fluoride PET study of treatment-naive and treated postmenopausal women. Bone 2009, 45, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, A.; Burger, M.G.; Lunger, A.; Schaefer, D.J.; Banfi, A.; Di Maggio, N. It Takes Two to Tango: Coupling of Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis for Bone Regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2017, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C. VEGF and imaging of vessels in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4, S99–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenzana, M.; Arnett, T.R. The Key Role of the Blood Supply to Bone. Bone Res. 2013, 1, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, J.F.; Yeung, D.K.; Tsang, P.H.; Choi, K.C.; Kwok, T.C.; Ahuja, A.T.; Leung, K.S.; Leung, P.C. Compromised bone marrow perfusion in osteoporosis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2008, 23, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prisby, R.D.; Ramsey, M.W.; Behnke, B.J.; Dominguez, J.M.; Donato, A.J.; Allen, M.R.; Delp, M.D. Aging reduces skeletal blood flow, endothelium-dependent vasodilation, and NO bioavailability in rats. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 1280–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, M.X.; Yu, Q. Primary osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2015, 1, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sozen, T.; Ozisik, L.; Basaran, N.C. An overview and management of osteoporosis. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 4, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.N.; Lie, J.D.; Wan, C.K.V.; Cameron, M.; Austel, A.G.; Nguyen, J.K.; Van, K.; Hyun, D. Osteoporosis: A Review of Treatment Options. Pharm. Ther. 2018, 43, 92–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, V.; Koa, B.; Borja, A.J.; Padmanhabhan, S.; Bhattaru, A.; Raynor, W.Y.; Rojulpote, C.; Seraj, S.M.; Werner, T.J.; Rajapakse, C. Diagnosis and Monitoring of Osteoporosis with Total-Body (18)F-Sodium Fluoride-PET/CT. PET Clin. 2020, 15, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, M.L.; Fogelman, I.; Blake, G.M.; Marsden, P.K.; Cook, G., Jr. Dissociation between global markers of bone formation and direct measurement of spinal bone formation in osteoporosis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2004, 19, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, S.; Batzdorf, A.; Sorci, O.; Peng, M.; Jankelovits, A.; Hornyak, J.; An, J.; Noel, P.B.; Hoilund-Carlsen, P.F.; Alavi, A.; et al. Assessment of femoral neck bone metabolism using (18)F-sodium fluoride PET/CT imaging. Bone 2020, 136, 115351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, M.T.; Clarke, B.L.; Khosla, S. Bisphosphonates: Mechanism of action and role in clinical practice. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, K.; Nakajima, H.; Miyazaki, T.; Yayama, T.; Kawahara, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Tsuchida, T.; Okazawa, H.; Fujibayashi, Y.; Baba, H. Effects of alendronate on bone metabolism in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis measured by 18F-fluoride PET: A prospective study. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazianas, M.; van der Geest, S.; Miller, P. Bisphosphonates and bone quality. Bonekey Rep. 2014, 3, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, M.L.; Cook, G.J.; Blake, G.M.; Marsden, P.K.; Benatar, N.A.; Fogelman, I. A prospective study of risedronate on regional bone metabolism and blood flow at the lumbar spine measured by 18F-fluoride positron emission tomography. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2003, 18, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, M.L.; Siddique, M.; Blake, G.M.; Moore, A.E.; Schleyer, P.J.; Dunn, J.T.; Somer, E.J.; Marsden, P.K.; Eastell, R.; Fogelman, I. Differential effects of teriparatide on regional bone formation using (18)F-fluoride positron emission tomography. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, M.L.; Moore, A.E.; Siddique, M.; Blake, G.M.; Laurent, D.; Borah, B.; Schramm, U.; Valentin, M.A.; Pellas, T.C.; Marsden, P.K.; et al. (1)(8)F-fluoride PET as a noninvasive imaging biomarker for determining treatment efficacy of bone active agents at the hip: A prospective, randomized, controlled clinical study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, M.L.; Siddique, M.; Blake, G.M.; Moore, A.E.; Marsden, P.K.; Schleyer, P.J.; Eastell, R.; Fogelman, I. Regional bone metabolism at the lumbar spine and hip following discontinuation of alendronate and risedronate treatment in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos. Int. 2012, 23, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, S.; Shizukuishi, K.; Tateishi, U.; Yoneyama, T.; Hino, A.; Ishibashi, M.; Inoue, T. Age-related changes in pre- and postmenopausal women investigated with 18F-fluoride PET—A preliminary study. Skeletal Radiol. 2012, 41, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynor, W.Y.; Borja, A.J.; Hancin, E.C.; Werner, T.J.; Alavi, A.; Revheim, M.E. Novel Musculoskeletal and Orthopedic Applications of (18)F-Sodium Fluoride PET. PET Clin. 2021, 16, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul Tuck, S.; Layfield, R.; Walker, J.; Mekkayil, B.; Francis, R. Adult Paget’s disease of bone: A review. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corral-Gudino, L.; Tan, A.J.; Del Pino-Montes, J.; Ralston, S.H. Bisphosphonates for Paget’s disease of bone in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 12, CD004956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, G.J.; Blake, G.M.; Marsden, P.K.; Cronin, B.; Fogelman, I. Quantification of skeletal kinetic indices in Paget’s disease using dynamic 18F-fluoride positron emission tomography. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2002, 17, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Installe, J.; Nzeusseu, A.; Bol, A.; Depresseux, G.; Devogelaer, J.P.; Lonneux, M. (18)F-fluoride PET for monitoring therapeutic response in Paget’s disease of bone. J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.D.; Silverberg, S.J. Primary hyperparathyroidism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, B.C.; Bilezikian, J.P. Parathyroid hormone: Anabolic and catabolic actions on the skeleton. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 22, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.; Suliburk, J.W.; Moron, F.E. Osseous Manifestations of Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Imaging Findings. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 3146535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Hammam, M. Management challenges with brown tumor of primary hyperparathyroidism masked by severe vitamin D deficiency: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2016, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Shen, X.; Lei, L.; Zhang, W. Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica Caused by Hyperparathyroidism Shown on 18F-NaF PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2020, 45, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, C.; Huellner, M.; Tschopp, O.; Bode-Lesniewska, B.; Schmid, C. (18)F-NaF-PET/CT in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism and brown tumors. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2020, 38, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, A.Z.; Aparici, C.M. NaF18-PET/CT Imaging of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 49, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Taurog, J.D.; Chhabra, A.; Colbert, R.A. Ankylosing Spondylitis and Axial Spondyloarthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2563–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.G.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, K.J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, E.K.; Jeon, Y.K.; Yang, B.Y.; Kim, G.T. Assessment of bone synthetic activity in inflammatory lesions and syndesmophytes in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: The potential role of 18F-fluoride positron emission tomography-magnetic resonance imaging. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.K.; Pak, K.; Park, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, G.T.; Lee, S.G. Baseline increased 18F-fluoride uptake lesions at vertebral corners on positron emission tomography predict new syndesmophyte development in ankylosing spondylitis: A 2-year longitudinal study. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbender, C.; Ostendorf, B.; Ruhlmann, V.; Heusch, P.; Miese, F.; Beiderwellen, K.; Schneider, M.; Braun, J.; Antoch, G.; Baraliakos, X. Hybrid 18F-labeled Fluoride Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging of the Sacroiliac Joints and the Spine in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Pilot Study Exploring the Link of MR Bone Pathologies and Increased Osteoblastic Activity. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1631–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Strobel, K.; Fischer, D.R.; Tamborrini, G.; Kyburz, D.; Stumpe, K.D.; Hesselmann, R.G.; Johayem, A.; Von Schulthess, G.K.; Michel, B.A.; Ciurea, A. 18F-fluoride PET/CT for detection of sacroiliitis in ankylosing spondylitis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.M.; Kim, K.; Pak, K.; Kim, S.J.; Goh, T.S.; Lee, J.S. Evaluation of the diagnostic performance of (18)F-NaF positron emission tomography/computed tomography in patients with suspected ankylosing spondylitis according to the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society criteria. Spine J. 2020, 20, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idolazzi, L.; Salgarello, M.; Gatti, D.; Viapiana, O.; Vantaggiato, E.; Fassio, A.; Adami, S.; Rossini, M. 18F-fluoride PET/CT for detection of axial involvement in ankylosing spondylitis: Correlation with disease activity. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2016, 30, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Son, S.M.; Goh, T.S.; Pak, K.; Kim, I.J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.J. Prediction of Response to Tumor Necrosis Value-alpha Blocker Is Suggested by (18)F-NaF SUVmax But Not by Quantitative Pharmacokinetic Analysis in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, Y.Y.; Lee, S.; Joo, Y.B.; Kim, T.H. Predictive value of semi-quantitative index from F-18-fluoride PET/CT for treatment response in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 129, 109048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S. Diagnosis and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review. JAMA 2018, 320, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Nossent, J.; Pavlos, N.J.; Xu, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: Pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Takase-Minegishi, K.; Ihata, A.; Kunishita, Y.; Kishimoto, D.; Kamiyama, R.; Hama, M.; Yoshimi, R.; Kirino, Y.; Asami, Y.; et al. (18)F-FDG and (18)F-NaF PET/CT demonstrate coupling of inflammation and accelerated bone turnover in rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2016, 26, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonnakuti, V.S.; Raynor, W.Y.; Taratuta, E.; Werner, T.J.; Alavi, A.; Baker, J.F. A novel method to assess subchondral bone formation using [18F]NaF-PET in the evaluation of knee degeneration. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2018, 39, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gram, S.B.; Hess, S.; Ahlquist, P.; Hoilund-Carlsen, P.F.; Ellingsen, T. [(18)F]Sodium fluoride positron emission tomography/computed tomography: A predictor of early rheumatoid arthritis? A case report. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 47, 425–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seraj, S.M.; Raynor, W.Y.; Revheim, M.E.; Al-Zaghal, A.; Zadeh, M.Z.; Arani, L.S.; Rojulpote, C.; Werner, T.J.; Gerke, O.; Hoilund-Carlsen, P.F.; et al. Assessing the feasibility of NaF-PET/CT versus FDG-PET/CT to detect abdominal aortic calcification or inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2020, 34, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardi, S.; Corrado, A.; Maruotti, N.; Cici, D.; Cantatore, F.P. Osteoblast role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrado, A.; Maruotti, N.; Cantatore, F.P. Osteoblast Role in Rheumatic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misaghi, A.; Goldin, A.; Awad, M.; Kulidjian, A.A. Osteosarcoma: A comprehensive review. SICOT J. 2018, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velletri, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Hu, M.; Xie, N.; Yang, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Shou, P.; et al. Loss of p53 in mesenchymal stem cells promotes alteration of bone remodeling through negative regulation of osteoprotegerin. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velletri, T.; Xie, N.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Shou, P.; Gan, Y.; Cao, G.; et al. P53 functional abnormality in mesenchymal stem cells promotes osteosarcoma development. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iagaru, A.; Mittra, E.; Dick, D.W.; Gambhir, S.S. Prospective evaluation of (99m)Tc MDP scintigraphy, (18)F NaF PET/CT, and (18)F FDG PET/CT for detection of skeletal metastases. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2012, 14, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wu, J. Incidental Detection of Solitary Hepatic Metastasis by 99mTc-MDP and 18F-NaF PET/CT in a Patient with Osteosarcoma of the Tibia. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2015, 40, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.H.; Ko, K.Y.; Cheng, M.F.; Chen, W.W.; Yen, R.F. 18F-NaF PET/CT Images of Cardiac Metastasis from Osteosarcoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2016, 41, 708–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Purandare, N.; Agrawal, A.; Shah, S.; Rangarajan, V. Unusual Finding of a Tumor Thrombus Arising from Osteosarcoma Detected on 18F-NaF PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2016, 41, e304–e306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usmani, S.; Marafi, F.; Rasheed, R.; Bakiratharajan, D.; Al Maraghy, M.; Al Kandari, F. Unsuspected Metastases to Muscles in Osteosarcoma Detected on 18F-Sodium Fluoride PET-CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 43, e343–e345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohren, E.M.; Etchebehere, E.C.; Araujo, J.C.; Hobbs, B.P.; Swanston, N.M.; Everding, M.; Moody, T.; Macapinlac, H.A. Determination of Skeletal Tumor Burden on 18F-Fluoride PET/CT. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collantes, M.; Martinez-Velez, N.; Zalacain, M.; Marrodan, L.; Ecay, M.; Garcia-Velloso, M.J.; Alonso, M.M.; Patino-Garcia, A.; Penuelas, I. Assessment of metabolic patterns and new antitumoral treatment in osteosarcoma xenograft models by [(18)F]FDG and sodium [(18)F]fluoride PET. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairemo, K.; Rohren, E.M.; Anderson, P.M.; Ravizzini, G.; Rao, A.; Macapinlac, H.A.; Subbiah, V. Development of sodium fluoride PET response criteria for solid tumours (NAFCIST) in a clinical trial of radium-223 in osteosarcoma: From RECIST to PERCIST to NAFCIST. ESMO Open 2019, 4, e000439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Jha, S.; Deng, Z.; Fratzl-Zelman, N.; Cabral, W.A.; Ivovic, A.; Meylan, F.; Hanson, E.P.; Lange, E.; Katz, J.; et al. Somatic activating mutations in MAP2K1 cause melorheostosis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, G.Z.; Jha, S.; Bhattacharyya, T.; Millo, C.; Tu, T.W.; Bagci, U.; Marias, K.; Karantanas, A.H. Patronas, N.J. 18F-NaF PET/CT in Extensive Melorheostosis of the Axial and Appendicular Skeleton with Soft-Tissue Involvement. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2017, 42, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semionov, A.; Jaffer, R.; Kosiuk, J. Melorheostosis of a rib. Radiol. Case Rep. 2018, 13, 886–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, S.; Cowen, E.W.; Lehky, T.J.; Alter, K.; Flynn, L.; Reynolds, J.C.; Lange, E.; Katz, J.D.; Marini, J.C.; Siegel, R.M.; et al. Clinical Evaluation of Melorheostosis in the Context of a Natural History Clinical Study. JBMR Plus 2019, 3, e10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, H.; Slama, J.; Hayem, G.; Ben Ali, K.; Sarda-Mantel, L.; Burg, S.; Le Guludec, D. Melorheostosis associated with peripheral form spondyloarthropathy: New image with 18-fluoride positron emission tomoscintigraphy coupled to computed tomography. Open Access Rheumatol. 2012, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jha, S.; Fratzl-Zelman, N.; Roschger, P.; Papadakis, G.Z.; Cowen, E.W.; Kang, H.; Lehky, T.J.; Alter, K.; Deng, Z.; Ivovic, A.; et al. Distinct Clinical and Pathological Features of Melorheostosis Associated with Somatic MAP2K1 Mutations. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019, 34, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seraj, S.M.; Al-Zaghal, A.; Ostergaard, B.; Hoilund-Carlsen, P.F.; Alavi, A. Identification of Heterotopic Ossification Using 18F-NaF PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mukaddam, M.; Rajapakse, C.S.; Pignolo, R.J.; Kaplan, F.S.; Smith, S.E. Imaging assessment of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: Qualitative, quantitative and questionable. Bone 2018, 109, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, C.S.; Lindborg, C.; Wang, H.; Newman, B.T.; Kobe, E.A.; Chang, G.; Shore, E.M.; Kaplan, F.S.; Pignolo, R.J. Analog Method for Radiographic Assessment of Heterotopic Bone in Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva. Acad. Radiol. 2017, 24, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eekhoff, E.M.W.; Netelenbos, J.C.; De Graaf, P.; Hoebink, M.; Bravenboer, N.; Micha, D.; Pals, G.; De Vries, T.J.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Raijmakers, P.G.; et al. Flare-Up After Maxillofacial Surgery in a Patient With Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva: An [(18)F]-NaF PET/CT Study and a Systematic Review. JBMR Plus 2018, 2, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eekhoff, E.M.W.; Botman, E.; Coen Netelenbos, J.; De Graaf, P.; Bravenboer, N.; Micha, D.; Pals, G.; De Vries, T.J.; Schoenmaker, T.; Hoebink, M.; et al. [18F]NaF PET/CT scan as an early marker of heterotopic ossification in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Bone 2018, 109, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botman, E.; Raijmakers, P.; Yaqub, M.; Teunissen, B.; Netelenbos, C.; Lubbers, W.; Schwarte, L.A.; Micha, D.; Bravenboer, N.; Schoenmaker, T.; et al. Evolution of heterotopic bone in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: An [(18)F]NaF PET/CT study. Bone 2019, 124, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botman, E.; Teunissen, B.P.; Raijmakers, P.; De Graaf, P.; Yaqub, M.; Treurniet, S.; Schoenmaker, T.; Bravenboer, N.; Micha, D.; Pals, G.; et al. Diagnostic Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva. JBMR Plus 2020, 4, e10363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botman, E.; Netelenbos, J.C.; Rustemeyer, T.; Schoonmade, L.J.; Nieuwenhuijzen, J.A.; Teunissen, B.P.; Visser, M.; Raijmakers, P.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Dahele, M.; et al. Radiotherapy in Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva: A Case Report and Systematic Review of the Literature. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, P.S.U.; Raynor, W.Y.; Sun, Y.; Werner, T.J.; Rajapakse, C.S.; Alavi, A. 18F-Sodium Fluoride PET as a Diagnostic Modality for Metabolic, Autoimmune, and Osteogenic Bone Disorders: Cellular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126504
Park PSU, Raynor WY, Sun Y, Werner TJ, Rajapakse CS, Alavi A. 18F-Sodium Fluoride PET as a Diagnostic Modality for Metabolic, Autoimmune, and Osteogenic Bone Disorders: Cellular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(12):6504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126504
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Peter Sang Uk, William Y. Raynor, Yusha Sun, Thomas J. Werner, Chamith S. Rajapakse, and Abass Alavi. 2021. "18F-Sodium Fluoride PET as a Diagnostic Modality for Metabolic, Autoimmune, and Osteogenic Bone Disorders: Cellular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 12: 6504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126504
APA StylePark, P. S. U., Raynor, W. Y., Sun, Y., Werner, T. J., Rajapakse, C. S., & Alavi, A. (2021). 18F-Sodium Fluoride PET as a Diagnostic Modality for Metabolic, Autoimmune, and Osteogenic Bone Disorders: Cellular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(12), 6504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126504







