VEGF-R2/Caveolin-1 Pathway of Undifferentiated ARPE-19 Retina Cells: A Potential Target as Anti-VEGF-A Therapy in Wet AMD by Resvega, an Omega-3/Polyphenol Combination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
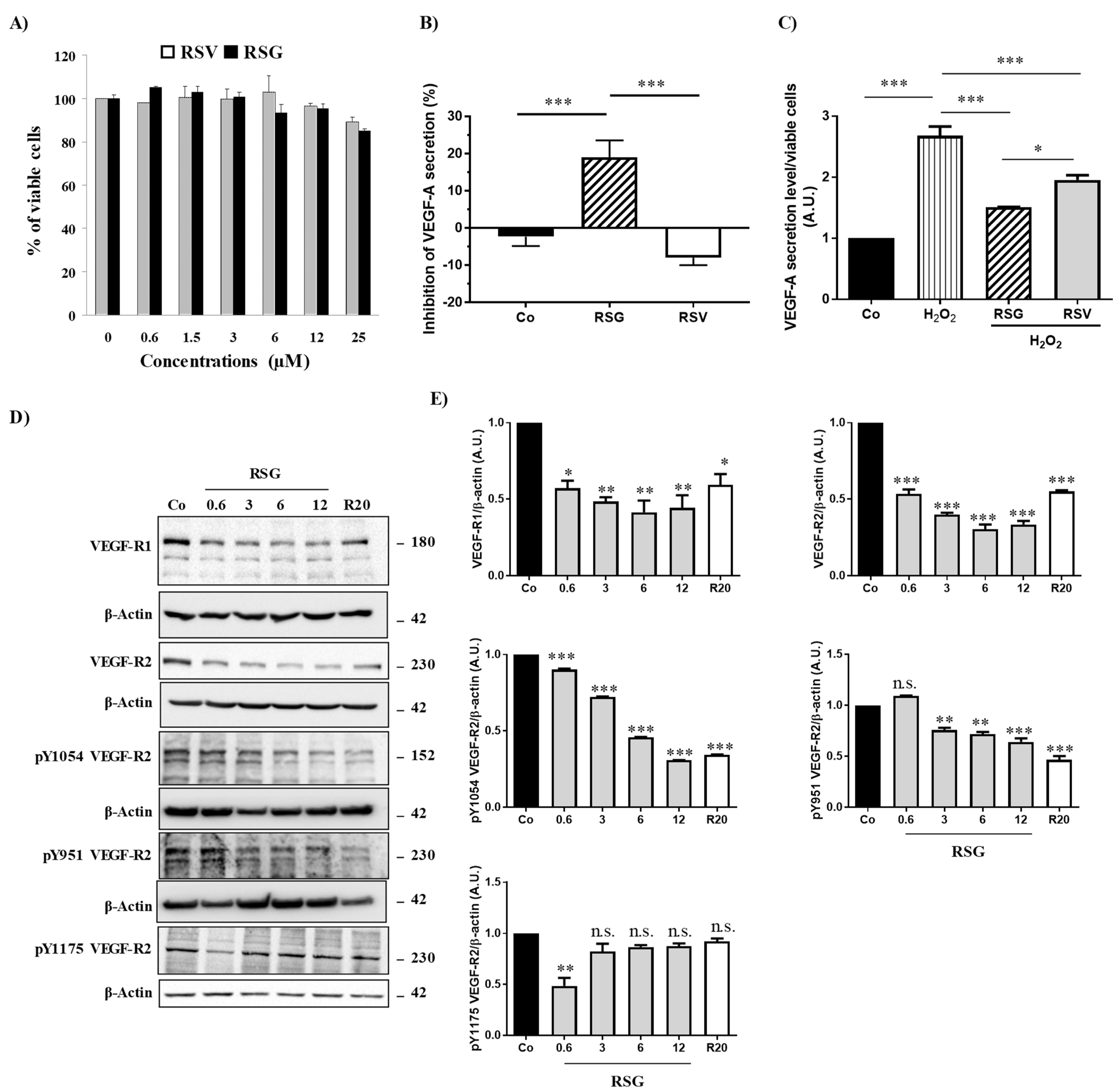
2.1. Combination of Resveratrol/ω3 Fatty Acid Inhibits VEGF Pathway in ARPE-19 Cells
2.2. VEGFR Signaling Pathway Is Disrupted via Lipid Rafts
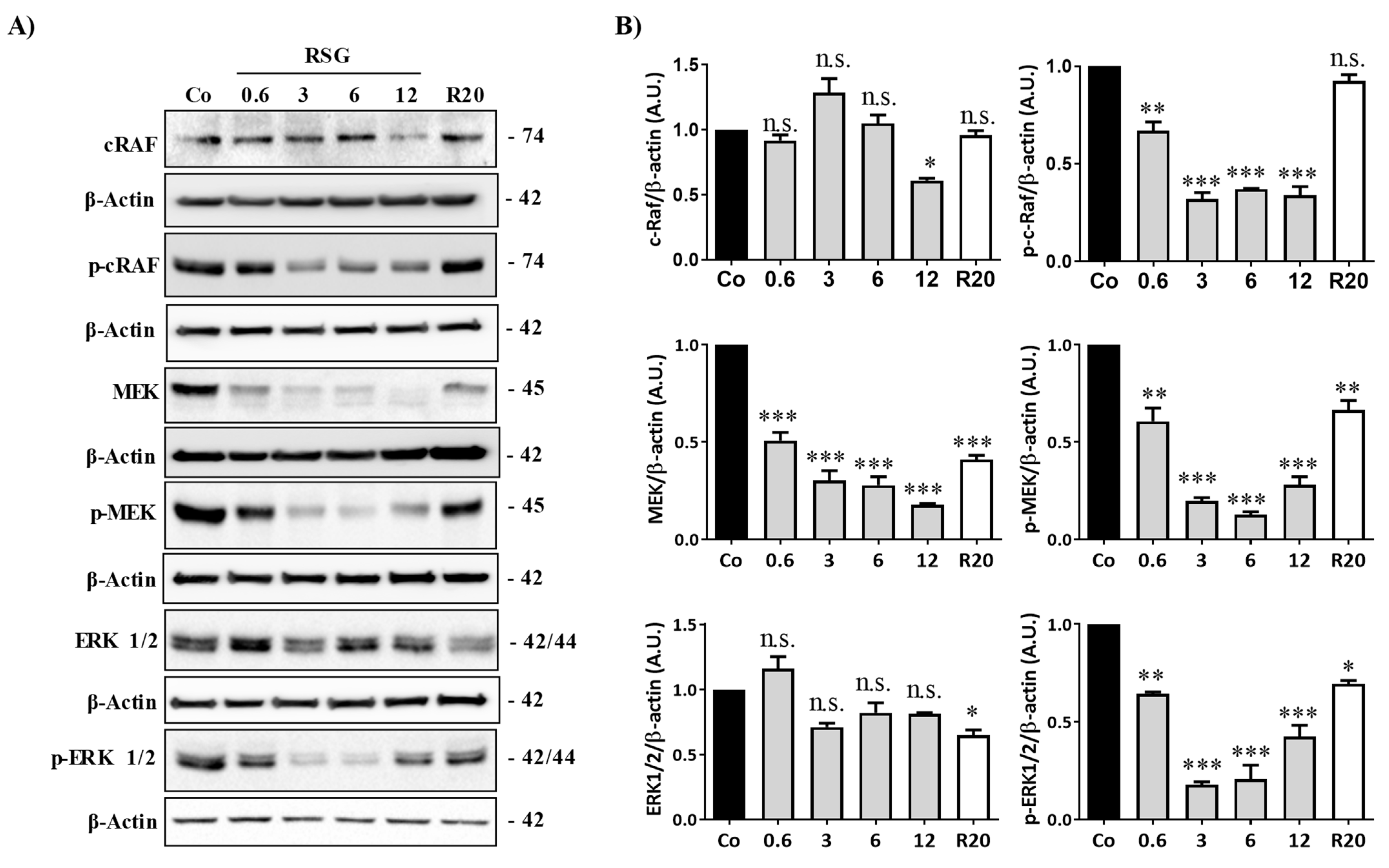
2.3. ω-3. Fatty Acids/RSV Combination-Inhibited VEGF-R2 Activation Is Associated with Disruption of MAPK Pathway Activation
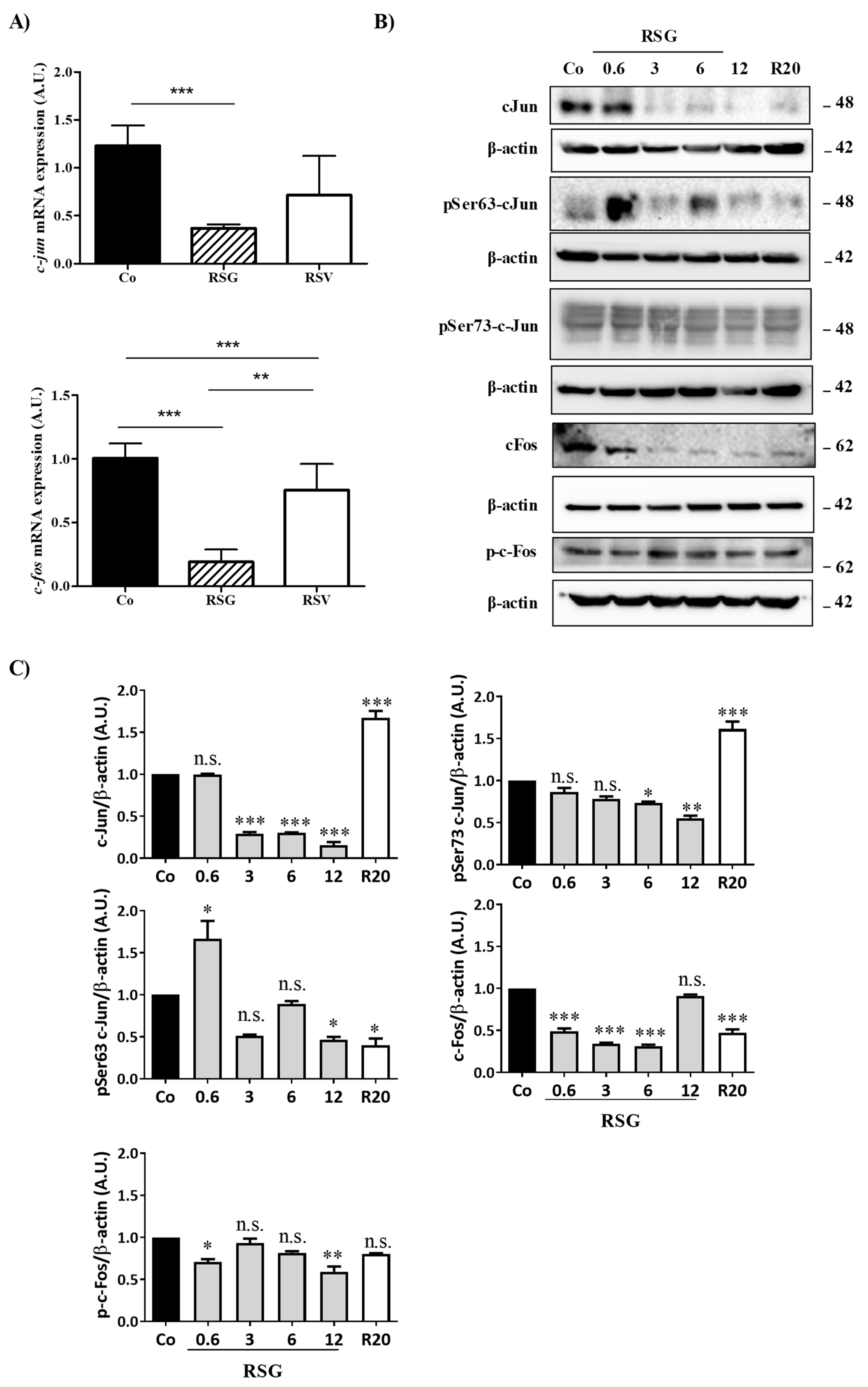
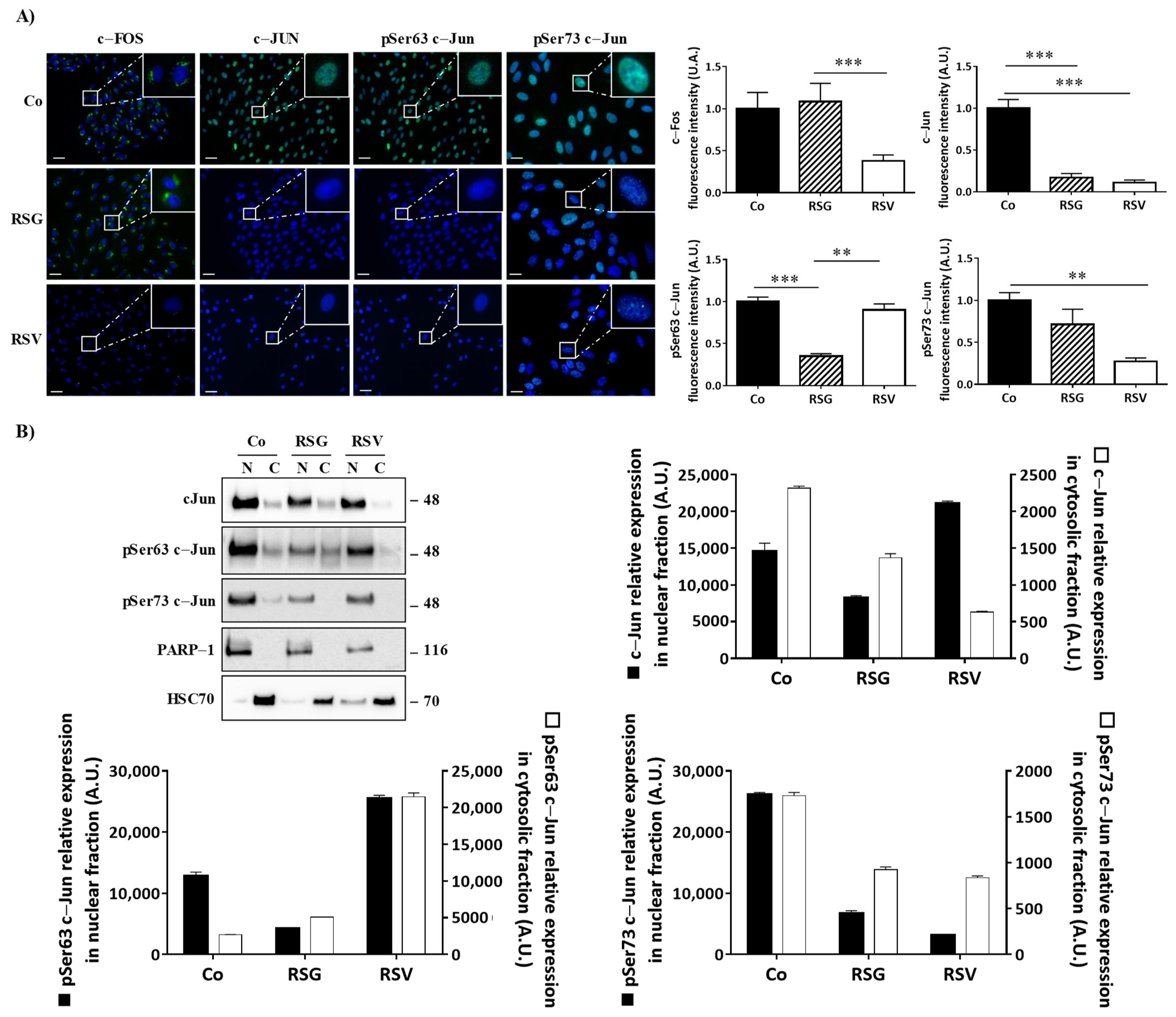
2.4. ω-3. Fatty Acids/RSV Combination Affects c-Jun/c-Fos Signaling Pathways and Their Relocalization into the Nucleus
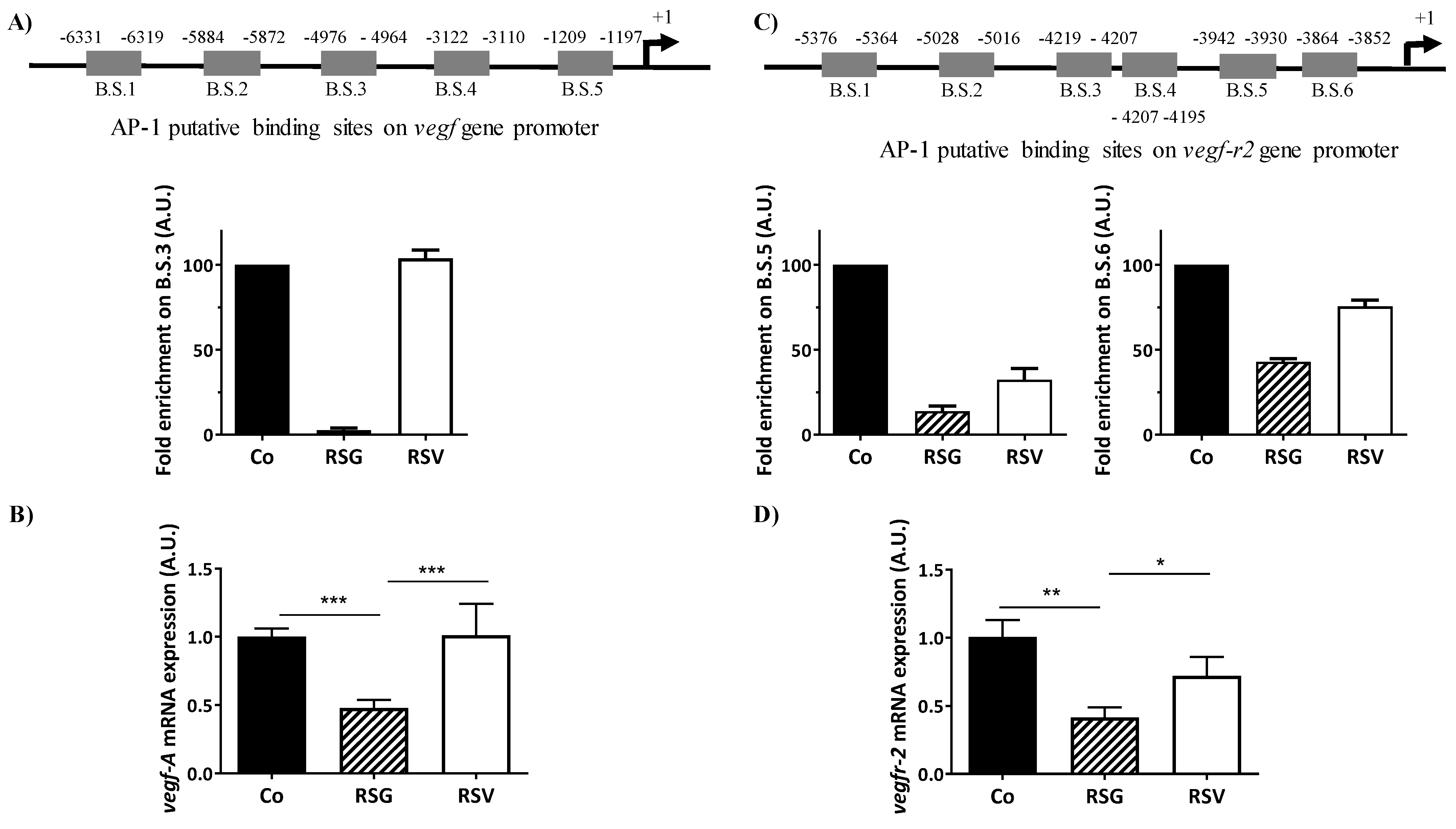
2.5. ω-3. Fatty Acids/RSV Combination Antagonizes AP-1 Binding Sites on VEGF and VEGF-r2 Promoter Genes and Their Transcription
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultured and Viability Assays
4.2. ELISA
4.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.4. Immunofluorescent Labelling and Staining of Cells
4.5. Lipid Rafts Isolation and Biochemical Characterization
4.6. Lipidomic Analysis of Lipid Rafts
4.7. RNA Extraction and Quantitative PCR Analysis
4.8. Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Fraction Isolation
4.9. DNA ChIP Assay
4.10. Densitometry and Statistical Significance
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, L.S.; Mitchell, P.; Seddon, J.M.; Holz, F.G.; Wong, T.Y. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 2012, 379, 1728–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, L.L.; Roach, J.M. Prevention and treatment of age-related macular degeneration: An update for pharmacists. Consult. Pharm. 2013, 28, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querques, G.; Benlian, P.; Chanu, B.; Portal, C.; Coscas, G.; Soubrane, G.; Souied, E.H. Nutritional AMD treatment phase I (NAT-1): Feasibility of oral DHA supplementation in age-related macular degeneration. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 19, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrecque, L.; Royal, I.; Surprenant, D.S.; Patterson, C.; Gingras, D.; Beliveau, R. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 activity by caveolin-1 and plasma membrane cholesterol. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 Research Group. Lutein + zeaxanthin and omega-3 fatty acids for age-related macular degeneration: The Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2) randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Age-Related Eye Disease Study Research Group. The Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS): Design implications. AREDS report no. 1. Control. Clin. Trials 1999, 20, 573–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor and age-related macular degeneration: From basic science to therapy. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, S.; Spee, C.; Ishikawa, K.; Hinton, D.R. SIRT1 mediated inhibition of VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling by Resveratrol and its relevance to choroidal neovascularization. Cytokine 2015, 76, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, H.; Ryu, J.; Jeong, J.Y.; Chung, I.Y.; Han, Y.S.; Hwang, S.H.; Park, J.M.; Kang, S.S.; Seo, S.W. Resveratrol suppresses vascular endothelial growth factor secretion via inhibition of CXC-chemokine receptor 4 expression in ARPE-19 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; He, L.; Shi, J.; Hou, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; An, Q.; Fan, F. Resveratrol inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis in human endothelial cells associated with suppression of aerobic glycolysis via modulation of PKM2 nuclear translocation. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 45, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.W.; Adamis, A.P.; Aiello, L.P. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular neovascularization and proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes. Metab. Rev. 1997, 13, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablonczy, Z.; Dahrouj, M.; Tang, P.H.; Liu, Y.; Sambamurti, K.; Marmorstein, A.D.; Crosson, C.E. Human retinal pigment epithelium cells as functional models for the RPE in vivo. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 8614–8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Korhonen, E.; Toppila, M.; Koskela, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Mysore, Y.; Kauppinen, A. Resvega alleviates hydroquinone-induced oxidative stress in ARPE-19 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, N.; Piippo, N.; Ranta-Aho, S.; Mysore, Y.; Kaarniranta, K.; Kauppinen, A. Effects of resvega on inflammasome activation in conjunction with dysfunctional intracellular clearance in Retinal Pigment Epithelial (RPE) Cells. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugas, B.; Charbonnier, S.; Baarine, M.; Ragot, K.; Delmas, D.; Menetrier, F.; Lherminier, J.; Malvitte, L.; Khalfaoui, T.; Bron, A.; et al. Effects of oxysterols on cell viability, inflammatory cytokines, VEGF, and reactive oxygen species production on human retinal cells: Cytoprotective effects and prevention of VEGF secretion by resveratrol. Eur. J. Nutr. 2010, 49, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Tugues, S.; Li, X.; Gualandi, L.; Claesson-Welsh, L. Signal transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Biochem. J. 2011, 437, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhinand, C.S.; Raju, R.; Soumya, S.J.; Arya, P.S.; Sudhakaran, P.R. VEGF-A/VEGFR2 signaling network in endothelial cells relevant to angiogenesis. J. Cell. Commun. Signal 2016, 10, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Mugishima, H. Signal transduction via vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors and their roles in atherogenesis. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2006, 13, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Reagan, A.; Yen, A.; Bhatti, F.; Cohen, A.W.; Elliott, M.H. Spatial and temporal localization of caveolin-1 protein in the developing retina. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 801, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Lin, X.; Tang, Z.; Lee, C.; Tian, G.; Du, Y.; Yin, X.; Ren, X.; Huang, L.; Ye, Z.; et al. Critical role of caveolin-1 in ocular neovascularization and multitargeted antiangiogenic effects of cavtratin via JNK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10737–10742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, S.; Ushio-Fukai, M.; Zuo, L.; Tojo, T.; Dikalov, S.; Patrushev, N.A.; Alexander, R.W. Novel role of ARF6 in vascular endothelial growth factor-induced signaling and angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Finley, S.D. Mechanistic insight into activation of MAPK signaling by pro-angiogenic factors. BMC Syst. Biol. 2018, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Ye, T.; Cui, P.; Hua, Q.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, D. AP-1 transcription factor mediates VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration and proliferation. Microvasc. Res. 2016, 105, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeal, T.; Binetruy, B.; Mercola, D.A.; Birrer, M.; Karin, M. Oncogenic and transcriptional cooperation with Ha-Ras requires phosphorylation of c-Jun on serines 63 and 73. Nature 1991, 354, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulverer, B.J.; Kyriakis, J.M.; Avruch, J.; Nikolakaki, E.; Woodgett, J.R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature 1991, 353, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanini, J.; Vinals, F.; Pouyssegur, J.; Pages, G. p42/p44 MAP kinase module plays a key role in the transcriptional regulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene in fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 18165–18172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 2011, 473, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keane, P.A.; Sadda, S.R. Development of Anti-VEGF Therapies for Intraocular Use: A Guide for Clinicians. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 2012, 483034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, S.A.; Park, S.; Thompson, T.C. Caveolin-1 regulates VEGF-stimulated angiogenic activities in prostate cancer and endothelial cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 2286–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliceti, C.; Zambonin, L.; Rizzo, B.; Fiorentini, D.; Vieceli Dalla Sega, F.; Hrelia, S.; Prata, C. Role of plasma membrane caveolae/lipid rafts in VEGF-induced redox signaling in human leukemia cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 857504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilsbury, K.; Garrett, K.L.; Shen, W.Y.; Constable, I.J.; Rakoczy, P.E. Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the retinal pigment epithelium leads to the development of choroidal neovascularization. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, E.W.; Kreis, A.J.; Wong, T.Y.; Simpson, J.A.; Guymer, R.H. Dietary omega-3 fatty acid and fish intake in the primary prevention of age-related macular degeneration: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2008, 126, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Cao, R.; Brakenhielm, E. Antiangiogenic mechanisms of diet-derived polyphenols. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiringhelli, F.; Rebe, C.; Hichami, A.; Delmas, D. Immunomodulation and anti-inflammatory roles of polyphenols as anticancer agents. Anticancer. Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 852–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas, D.; Jannin, B.; Latruffe, N. Resveratrol: Preventing properties against vascular alterations and ageing. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, D.; Lancon, A.; Colin, D.; Jannin, B.; Latruffe, N. Resveratrol as a chemopreventive agent: A promising molecule for fighting cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 423–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, D.; Solary, E.; Latruffe, N. Resveratrol, a phytochemical inducer of multiple cell death pathways: Apoptosis, autophagy and mitotic catastrophe. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 1100–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Okuda, H. Resveratrol isolated from Polygonum cuspidatum root prevents tumor growth and metastasis to lung and tumor-induced neovascularization in Lewis lung carcinoma-bearing mice. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 1844–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.B.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.Y.; Xue, H.Z.; Pan, C.E.; Zhao, S.H. Resveratrol inhibits VEGF expression of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through a NF-kappa B-mediated mechanism. Hepatogastroenterology 2010, 57, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Limagne, E.; Thibaudin, M.; Euvrard, R.; Berger, H.; Chalons, P.; Vegan, F.; Humblin, E.; Boidot, R.; Rebe, C.; Derangere, V.; et al. Sirtuin-1 Activation Controls Tumor Growth by Impeding Th17 Differentiation via STAT3 Deacetylation. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richer, S.; Patel, S.; Sockanathan, S.; Ulanski, L.J., 2nd; Miller, L.; Podella, C. Resveratrol based oral nutritional supplement produces long-term beneficial effects on structure and visual function in human patients. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richer, S.; Stiles, W.; Ulanski, L.; Carroll, D.; Podella, C. Observation of human retinal remodeling in octogenarians with a resveratrol based nutritional supplement. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmiere, C.; Clerc, A.; Leconte, L. RESVEGA, by the presence of Resveratrol, inhibits retinal endothelial tube formation. Acta Ophtalmol. 2013, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Venema, V.J.; Venema, R.C.; Tsai, N.; Caldwell, R.B. VEGF induces nuclear translocation of Flk-1/KDR, endothelial nitric oxide synthase, and caveolin-1 in vascular endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 256, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, R.C.; Bonilha, V.L.; Shin, B.C.; Hu, J.; Cohen-Gould, L.; Bok, D.; Rodriguez-Boulan, E. Bipolar assembly of caveolae in retinal pigment epithelium. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 290, C832–C843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, C.; Ebrahem, Q.; Anand-Apte, B.; Parat, M.O. Altered angiogenesis in caveolin-1 gene-deficient mice is restored by ablation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 1702–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, K.C.; Aotaki-Keen, A.E.; Putkey, F.R.; Hjelmeland, L.M. ARPE-19, a human retinal pigment epithelial cell line with differentiated properties. Exp. Eye Res. 1996, 62, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, D.; Rebe, C.; Lacour, S.; Filomenko, R.; Athias, A.; Gambert, P.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M.; Jannin, B.; Dubrez-Daloz, L.; Latruffe, N.; et al. Resveratrol-induced apoptosis is associated with Fas redistribution in the rafts and the formation of a death-inducing signaling complex in colon cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41482–41490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondelle, J.; Pais de Barros, J.P.; Pilot-Storck, F.; Tiret, L. Targeted Lipidomic Analysis of Myoblasts by GC-MS and LC-MS/MS. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1668, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Forward Sequence | Reverse Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| h-Beta-actin | 5′-TCCACCTTCCAGCAGATGTG-3′ | 5′-GCATTTGCGGTGGACGAT-3′ |
| h-vegf-a | 5′-ATCTTCAAGCCATCCTGTGTG-3′ | 5′-GAGGTTTGATCCGCATAATCTG-3′ |
| h-vegf-r1 | 5′-GAAATCACCTACGTGCCGGA-3′ | 5′-ACGTTCAGATGGTGGCCAAT-3′ |
| h-vegf-r22 | 5′-CCAGCAAAAGCAGGGAGTCTGT-3′ | 5′-TGTCTGTGTCATCGGAGTGATATCC-3′ |
| h-c-fos | 5′-TTATCTCCAGAAGAAGAAGAGAAAAGGAGAATC-3′ | 5′-AGGGCCAGCAGCGTGGGTGAGCTGAGCGAGTCA-3′ |
| h-c-jun | 5′-CAGCCAGGTCGGCAGTATAG-3′ | 5′-GGGACTCTGCCACTTGTCTC-3′ |
| h-c-jun #3 (vegf) | 5′-GAGCAGCGAAAGCGACAG-3′ | 5′-TGTCTGTCTGTCTGTCCGTCA-3′ |
| h-c-jun #5 (vegf-r2) | 5′-CACACCACACAGATGTGCAA-3′ | 5′-CCAATGCCAGTTAATTTCTGA-3′ |
| h-c-jun #6 (vegf-r2) | 5′-TCAGAAATTAACTGGCATTGG-3′ | 5′-AGACCCAGGGATATTCTGACA-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Courtaut, F.; Scagliarini, A.; Aires, V.; Cornebise, C.; Pais de Barros, J.-P.; Olmiere, C.; Delmas, D. VEGF-R2/Caveolin-1 Pathway of Undifferentiated ARPE-19 Retina Cells: A Potential Target as Anti-VEGF-A Therapy in Wet AMD by Resvega, an Omega-3/Polyphenol Combination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126590
Courtaut F, Scagliarini A, Aires V, Cornebise C, Pais de Barros J-P, Olmiere C, Delmas D. VEGF-R2/Caveolin-1 Pathway of Undifferentiated ARPE-19 Retina Cells: A Potential Target as Anti-VEGF-A Therapy in Wet AMD by Resvega, an Omega-3/Polyphenol Combination. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(12):6590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126590
Chicago/Turabian StyleCourtaut, Flavie, Alessandra Scagliarini, Virginie Aires, Clarisse Cornebise, Jean-Paul Pais de Barros, Céline Olmiere, and Dominique Delmas. 2021. "VEGF-R2/Caveolin-1 Pathway of Undifferentiated ARPE-19 Retina Cells: A Potential Target as Anti-VEGF-A Therapy in Wet AMD by Resvega, an Omega-3/Polyphenol Combination" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 12: 6590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126590
APA StyleCourtaut, F., Scagliarini, A., Aires, V., Cornebise, C., Pais de Barros, J.-P., Olmiere, C., & Delmas, D. (2021). VEGF-R2/Caveolin-1 Pathway of Undifferentiated ARPE-19 Retina Cells: A Potential Target as Anti-VEGF-A Therapy in Wet AMD by Resvega, an Omega-3/Polyphenol Combination. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(12), 6590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126590







