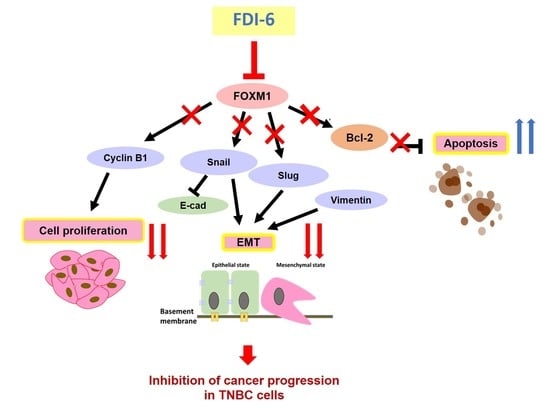
The Anticancer Effects of FDI-6, a FOXM1 Inhibitor, on Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
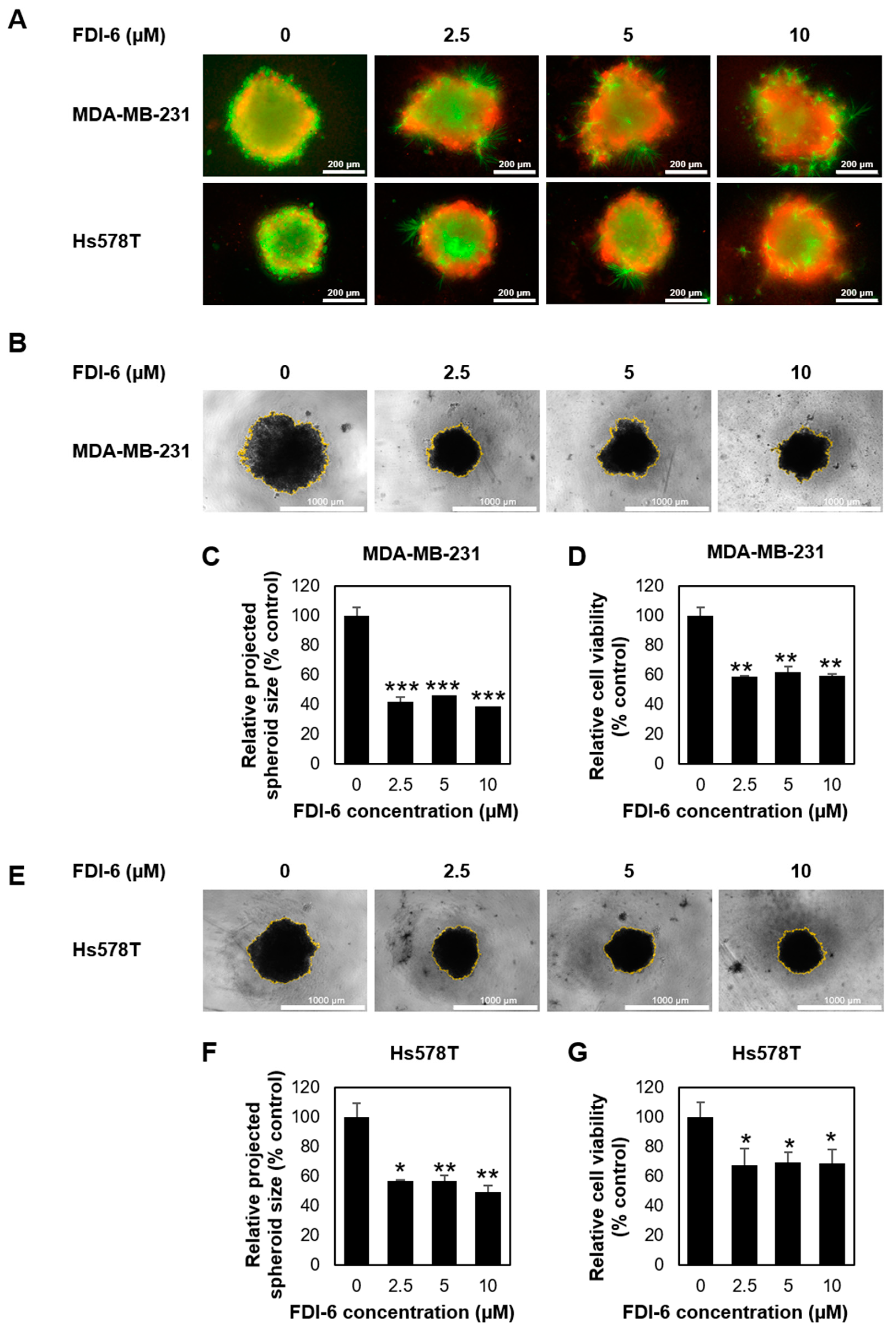
2.1. FDI-6 Inhibits TNBC Cell Proliferation
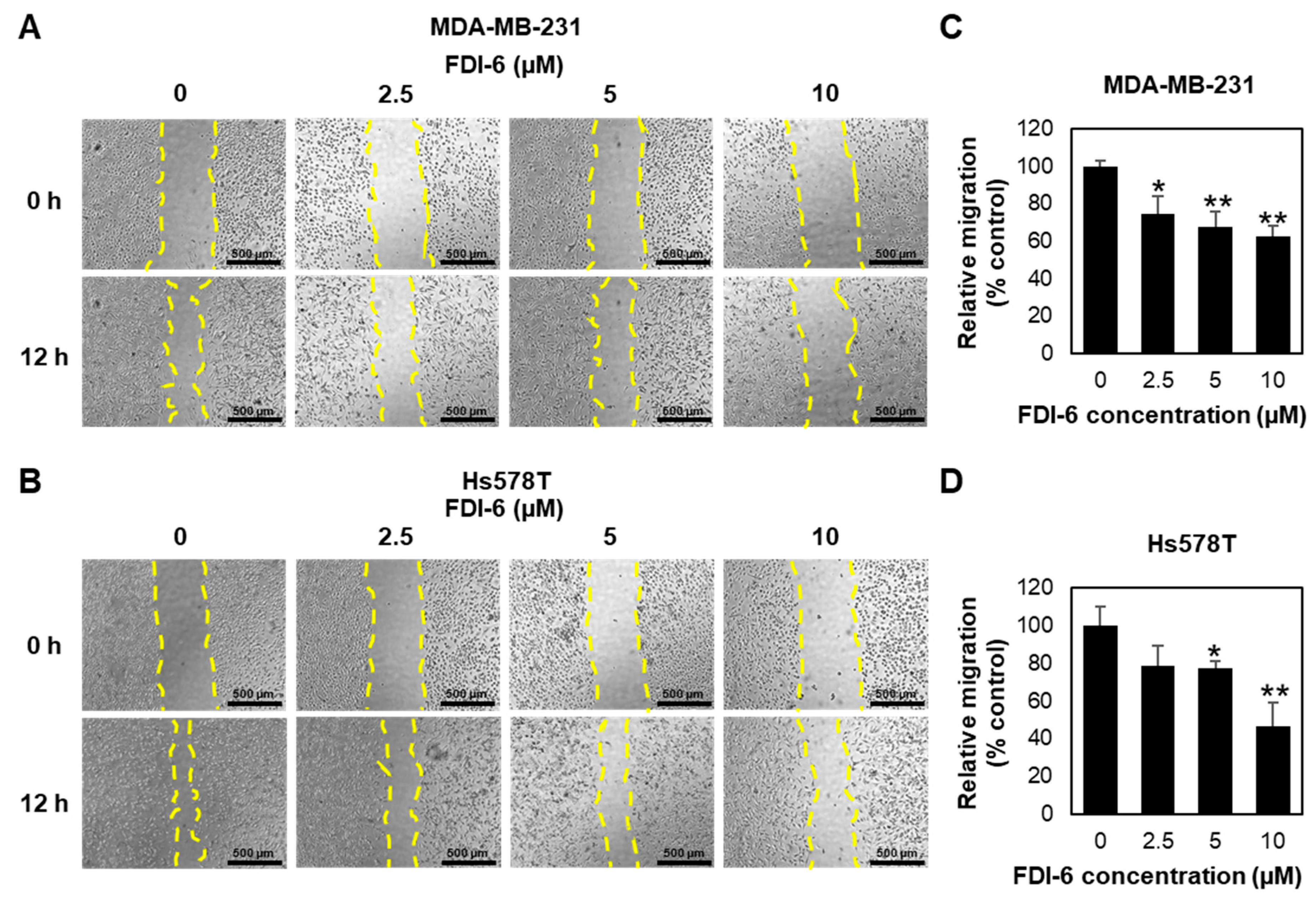
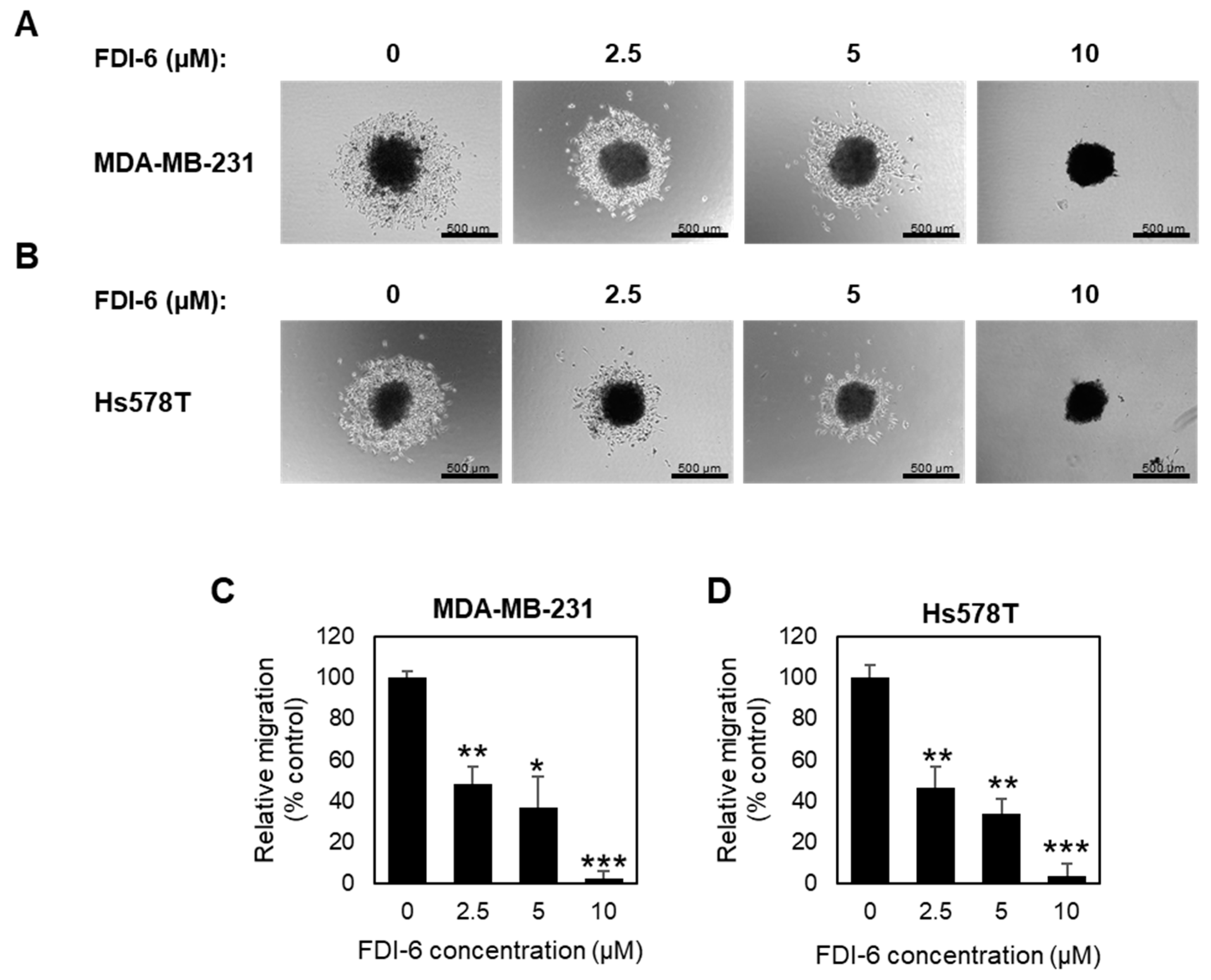
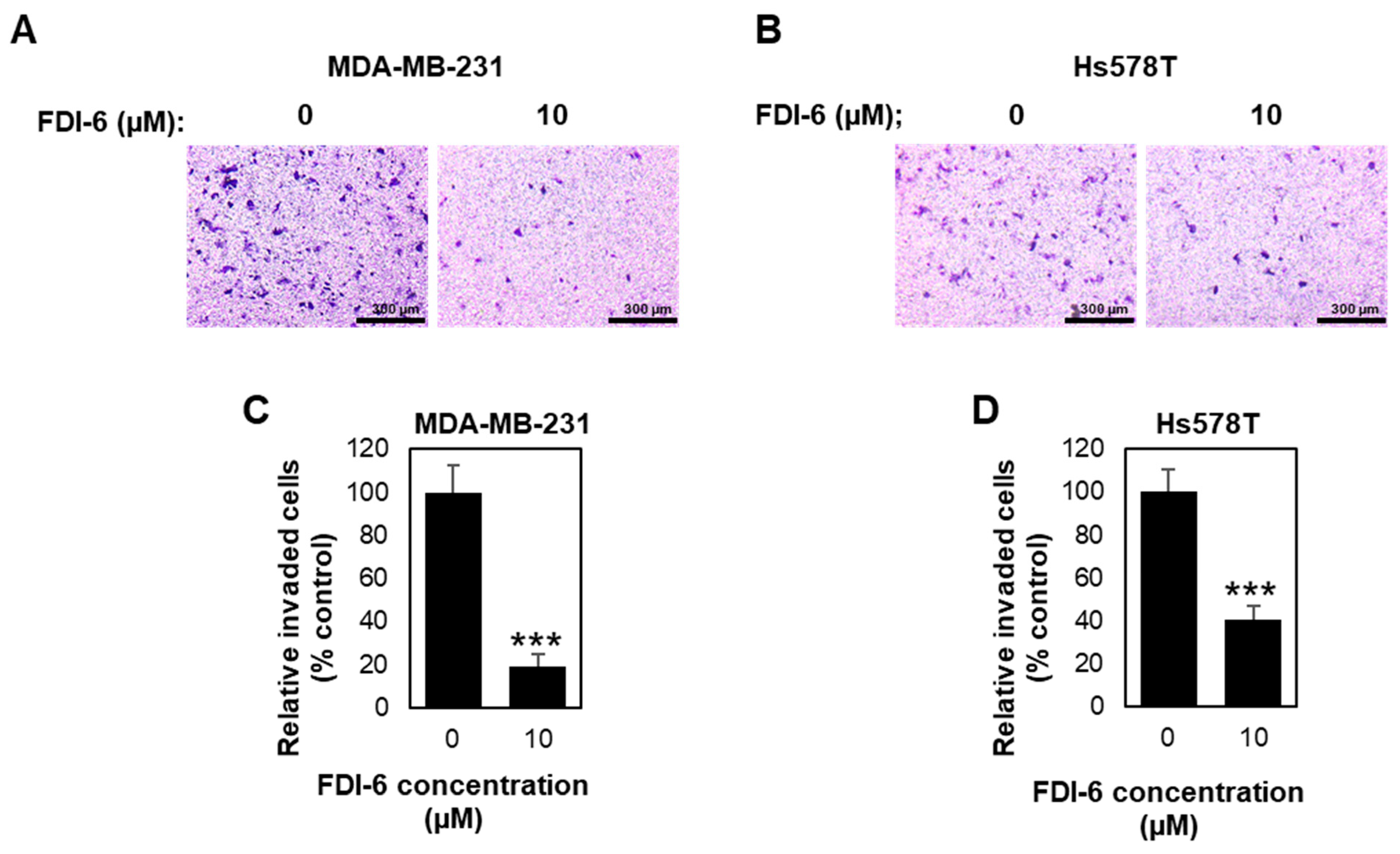
2.2. FDI-6 Inhibits TNBC Cell Migration and Invasion
2.3. FDI-6 Suppressed Gene Expression Related to Tumour Progression of TNBC Cells
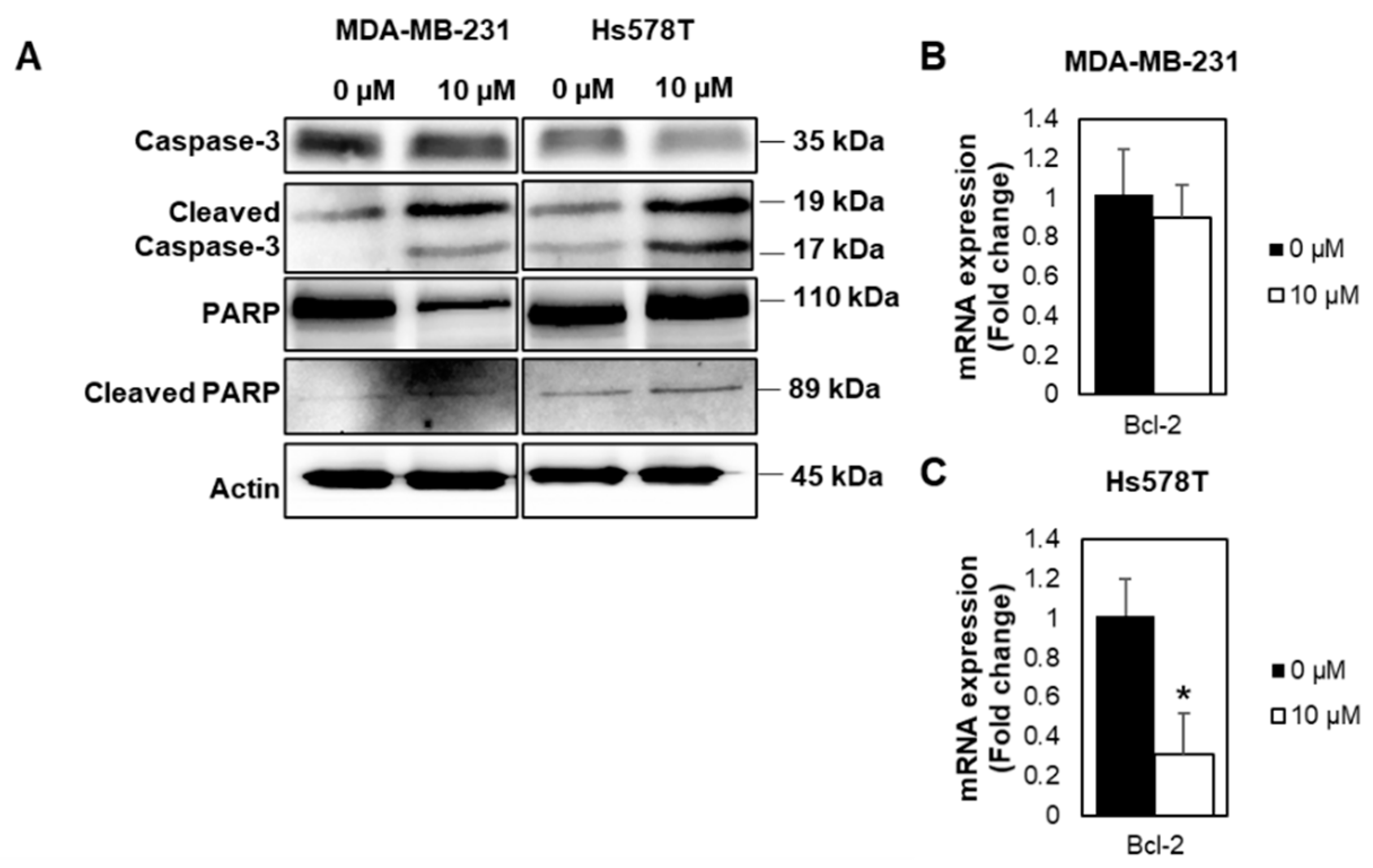
2.4. FDI-6 Promotes Caspase-3 Activation, Cleavage of PARP, and Bcl-2 Expression
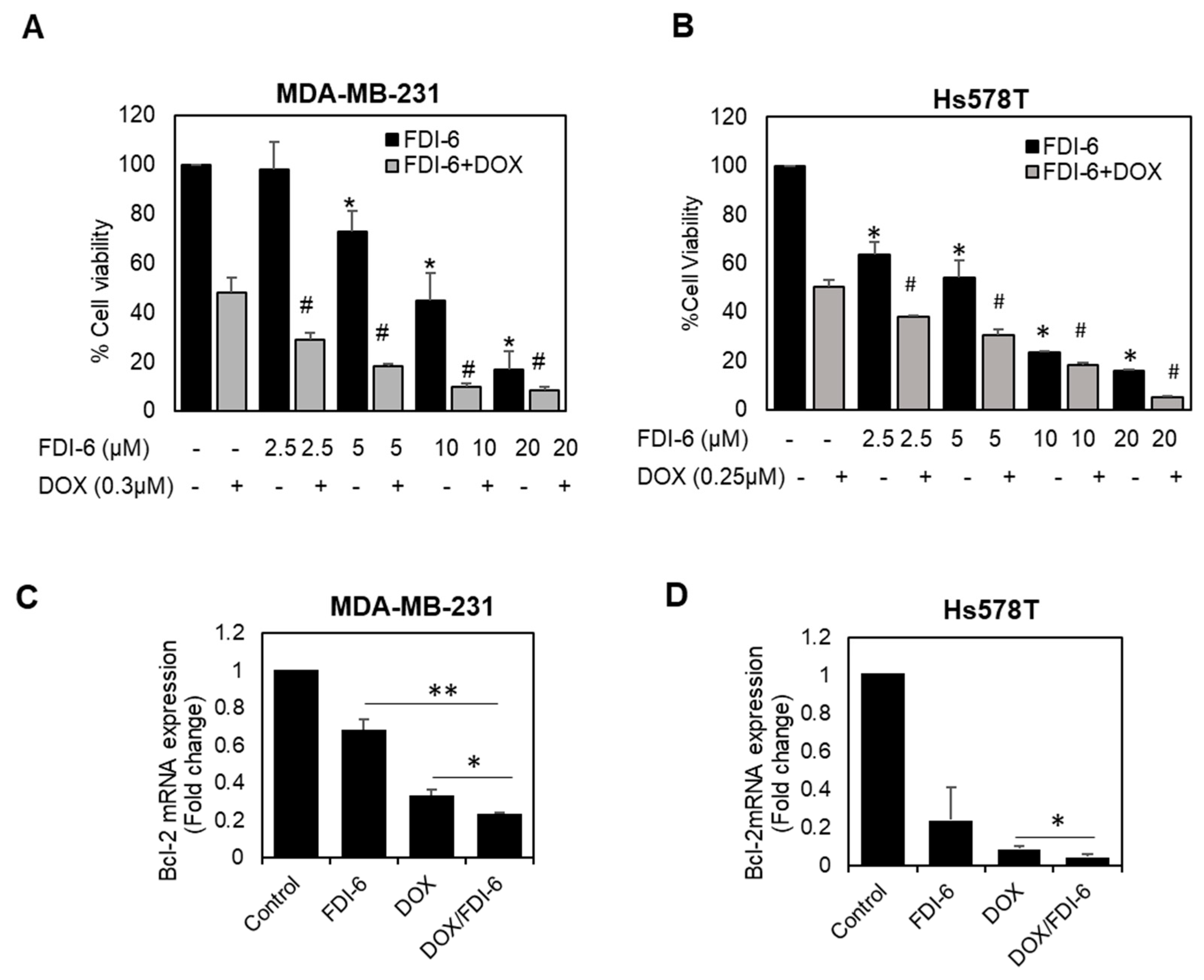
2.5. Synergistic Effect of FDI-6 in Combination with Doxorubicin against TNBC Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. 3D Spheroid Formation
4.3. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay
4.4. Clonogenic Assay
4.5. Wound Healing Assay
4.6. Invasion Assay
4.7. Live/Dead Staining
4.8. 3D Proliferation Assay
4.9. 3D Migration Assay
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Assay
4.12. Quantitative Determination of Drug Synergism
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| DMEM | Dulbecco modified Eagle medium |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FOXM1 | Forkhead box protein M1 |
| G2/M | Gap 2/Mitosis |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| L19 | 60S ribosomal protein L19 |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| Snail | Zinc finger protein SNAI1 |
| SRB | Sulforhodamine B |
| TNBC | Triple negative breast cancer |
| ULA | Ultra-low attachment |
References
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast Cancer Treatment. JAMA 2019, 321, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engebraaten, O.; Vollan, H.K.M.; Børresen-Dale, A.-L. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and the Need for New Therapeutic Targets. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa, R.H. FoxM1 dances with mitosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierstra, I. The Transcription Factor FOXM1 (Forkhead box M1). In Advances in Cancer Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 97–398. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, C.-Y.; Muir, K.W.; Lam, E.W.F. FOXM1: From cancer initiation to progression and treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2012, 1819, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myatt, S.S.; Lam, E.W.F. The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarsky, C.; Wenzig, M.; Specht, T.; Saeger, H.D.; Grützmann, R. Identification and Validation of Commonly Overexpressed Genes in Solid Tumors by Comparison of Microarray Data. Neoplasia 2004, 6, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siraj, A.K.; Pratheeshkumar, P.; Parvathareddy, S.K.; Qadri, Z.; Thangavel, S.; Ahmed, S.; Al-Dayel, F.; Tulbah, A.; Ajarim, D.; Al-Kuraya, K.S. FoxM1 is an independent poor prognostic marker and therapeutic target for advanced Middle Eastern breast cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.-P.; Yu, S.; Shi, L.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.-X.; Wang, Y.-H.; Sun, C.-J.; Liang, J. FoxM1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting Snai1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 5181–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khongkow, P.; Gomes, A.R.; Gong, C.; Man, E.P.S.S.; Tsang, J.W.-H.; Zhao, F.; Monteiro, L.J.; Coombes, R.C.; Medema, R.H.; Khoo, U.S.; et al. Paclitaxel targets FOXM1 to regulate KIF20A in mitotic catastrophe and breast cancer paclitaxel resistance. Oncogene 2016, 35, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khongkow, P.; Karunarathna, U.; Khongkow, M.; Gong, C.; Gomes, A.R.; Yagüe, E.; Monteiro, L.J.; Kongsema, M.; Zona, S.; Man, E.P.S.; et al. FOXM1 targets NBS1 to regulate DNA damage-induced senescence and epirubicin resistance. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4144–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Craig, D.W.; O’Shaughnessy, J.A.; Kiefer, J.A.; Aldrich, J.; Sinari, S.; Moses, T.M.; Wong, S.; Dinh, J.; Christoforides, A.; Blum, J.L.; et al. Genome and Transcriptome Sequencing in Prospective Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Uncovers Therapeutic Vulnerabilities. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narrandes, S.; Huang, S.; Murphy, L.; Xu, W. The exploration of contrasting pathways in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC). BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B. Identification of FOXM1 as a specific marker for triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 54, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamurcu, Z.; Ashour, A.; Kahraman, N.; Ozpolat, B. FOXM1 regulates expression of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase and promotes proliferation, invasion and tumorgenesis of human triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16619–16635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gormally, M.V.; Dexheimer, T.S.; Marsico, G.; Sanders, D.A.; Lowe, C.; Matak-Vinković, D.; Michael, S.; Jadhav, A.; Rai, G.; Maloney, D.J.; et al. Suppression of the FOXM1 transcriptional programme via novel small molecule inhibition. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsico, G.; Gormally, M.V. Small molecule inhibition of FOXM1: How to bring a novel compound into genomic context. Genomics Data 2015, 3, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Center for Biotechnology. 2D Structure Image of CID 5175738. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5175738#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: At the Crossroads of Development and Tumor Metastasis. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aaltonen, K.; Amini, R.-M.; Heikkilä, P.; Aittomäki, K.; Tamminen, A.; Nevanlinna, H.; Blomqvist, C. High cyclin B1 expression is associated with poor survival in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laoukili, J.; Kooistra, M.R.H.; Brás, A.; Kauw, J.; Kerkhoven, R.M.; Morrison, A.; Clevers, H.; Medema, R.H. FoxM1 is required for execution of the mitotic programme and chromosome stability. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, T.W.C.; Lin, S.S.W.; Tsang, A.C.C.; Tong, C.S.W.; Ching, J.C.Y.; Leung, W.Y.; Gimlich, R.; Wong, G.G.; Yao, K.-M. Over-expression of FoxM1 stimulates cyclin B1 expression. FEBS Lett. 2001, 507, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. Targeting FOXM1 in cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, B.; Gartel, A.L. FoxM1 knockdown sensitizes human cancer cells to proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis but not to autophagy. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 3269–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. Suppression of FOXM1 Sensitizes Human Cancer Cells to Cell Death Induced by DNA-Damage. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackman, M.; Lindon, C.; Nigg, E.A.; Pines, J. Active cyclin B1–Cdk1 first appears on centrosomes in prophase. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gartel, A.L. The suppression of FOXM1 and its targets in breast cancer xenograft tumors by siRNA. Oncotarget 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, J.M.-M.; Myatt, S.S.; Marson, C.M.; Coombes, R.C.; Constantinidou, D.; Lam, E.W.-F. Thiostrepton selectively targets breast cancer cells through inhibition of forkhead box M1 expression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2022–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gusarova, G.A.; Wang, I.-C.; Major, M.L.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Ackerson, T.; Petrovic, V.; Costa, R.H. A cell-penetrating ARF peptide inhibitor of FoxM1 in mouse hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wen, T.; Wan, J.; Lei, Y.; Chen, H. Forkhead domain inhibitor-6 (FDI-6) increases apoptosis and inhibits invasion and migration of laryngeal carcinoma cells by down-regulating nuclear FoxM1. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2017, 33, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chatonnet, F.; Pignarre, A.; Sérandour, A.A.A.; Caron, G.; Avner, S.; Robert, N.; Kassambara, A.; Laurent, A.; Bizot, M.; Agirre, X.; et al. The hydroxymethylome of multiple myeloma identifies FAM72D as a 1q21 marker linked to proliferation. Haematologica 2019, 105, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. A novel mode of FoxM1 regulation: Positive auto-regulatory loop. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1966–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, Y.; Laws, M.J.; Sanabria Guillen, V.; Kim, S.H.; Dey, P.; Smith, B.P.; Gong, P.; Bindman, N.; Zhao, Y.; Carlson, K.; et al. Suppression of FOXM1 activities and breast cancer growth in vitro and in vivo by a new class of compounds. NPJ Breast Cancer 2019, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lien, K.; Georgsdottir, S.; Sivanathan, L.; Chan, K.; Emmenegger, U. Low-dose metronomic chemotherapy: A systematic literature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3387–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, S.K.; Bhat, U.G.; Hughes, D.E.; Wang, I.-C.; Costa, R.H.; Gartel, A.L. Identification of a Chemical Inhibitor of the Oncogenic Transcription Factor Forkhead Box M1. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9731–9735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gartel, A.L. FoxM1 inhibitors as potential anticancer drugs. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, R.; Yates, C.; Gary, B.D.; McClellan, S.; Tan, M.; Xi, Y.; Reed, E.; Piazza, G.A.; Owen, L.B.; Dean-Colomb, W. Panepoxydone targets NF-kB and FOXM1 to inhibit proliferation, induce apoptosis and reverse epithelial to mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J. Apoptosis induced by 7-difluoromethoxyl-5,4’-di-n-octyl genistein via the inactivation of FoxM1 in ovarian cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, P.; Chen, L.; Chen, H. Down-regulation of FoxM1 by thiostrepton or small interfering RNA inhibits proliferation, transformation ability and angiogenesis, and induces apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 5450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaei-Dakhili, S.A.; Aguayo-Ortiz, R.; Domínguez, L.; Velázquez-Martínez, C.A. Untying the knot of transcription factor druggability: Molecular modeling study of FOXM1 inhibitors. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2018, 80, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei Dakhili, S.A.; Pérez, D.J.; Gopal, K.; Tabatabaei Dakhili, S.Y.; Ussher, J.R.; Velázquez-Martínez, C.A. A structure-activity relationship study of Forkhead Domain Inhibitors (FDI): The importance of halogen binding interactions. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 93, 103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, L.; Peng, Z.; Jia, Z.; Logsdon, C.D.; Le, X.; Wei, D.; Huang, S.; Xie, K. A Novel FoxM1-Caveolin Signaling Pathway Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Invasion and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, N.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wen, L.; Zhao, S.-H.H.; Ai, Z.-H.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wu, B.; Lu, H.-X.X.; Yang, H.; Liu, W.-C.C.; et al. Overexpression of FOXM1 predicts poor prognosis and promotes cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zou, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Pan, H. Downregulation of FoxM1 inhibits proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis of HeLa cells in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 2355–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Chu, H.; Lv, T.; Wang, L.; Kong, S.; Dai, S. miR-342-3p suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting FOXM1 in human cervical cancer. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 3298–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balli, D.; Ustiyan, V.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, I.-C.; Masino, A.J.; Ren, X.; Whitsett, J.A.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Kalin, T.V. Foxm1 transcription factor is required for lung fibrosis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Chen, H.; Tan, G.; Gao, W.; Cheng, L.; Jiang, X.; Yu, L.; Tan, Y. FOXM1 promotes the epithelial to mesenchymal transition by stimulating the transcription of Slug in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 340, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Craene, B.; Berx, G. Regulatory networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Shen, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Du, X. FOXM1 Promotes Lung Adenocarcinoma Invasion and Metastasis by Upregulating SNAIL. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olmeda, D.; Jordá, M.; Peinado, H.; Fabra, Á.; Cano, A. Snail silencing effectively suppresses tumour growth and invasiveness. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1862–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari-Amorotti, G.; Chiodoni, C.; Shen, F.; Cattelani, S.; Soliera, A.R.; Manzotti, G.; Grisendi, G.; Dominici, M.; Rivasi, F.; Colombo, M.P.; et al. Suppression of Invasion and Metastasis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Lines by Pharmacological or Genetic Inhibition of Slug Activity. Neoplasia 2014, 16, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onder, T.T.; Gupta, P.B.; Mani, S.A.; Yang, J.; Lander, E.S.; Weinberg, R.A. Loss of E-Cadherin Promotes Metastasis via Multiple Downstream Transcriptional Pathways. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3645–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.-Y.; Jung, S.Y.; Jennings, N.B.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Peng, G.; Lee, S.-R.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, K.; Leem, S.-H.; Lin, S.-Y.; et al. FOXM1 mediates Dox resistance in breast cancer by enhancing DNA repair. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abnous, K.; Danesh, N.M.; Ramezani, M.; Charbgoo, F.; Bahreyni, A.; Taghdisi, S.M. Targeted delivery of doxorubicin to cancer cells by a cruciform DNA nanostructure composed of AS1411 and FOXM1 aptamers. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAT Bioquest, I. Quest GraphTM IC50 Calculator. Available online: https://www.aatbio.com/tools/ic50-calculator. (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-C. Theoretical Basis, Experimental Design, and Computerized Simulation of Synergism and Antagonism in Drug Combination Studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Cell Line | [FDI-6] (µM) | [Doxorubicin] (µM) | Fa | CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 | 2.5 | 0.3 | 0.71 | 0.74 |
| 5 | 0.3 | 0.82 | 0.62 | |
| 10 | 0.3 | 0.90 | 0.58 | |
| 20 | 0.3 | 0.92 | 0.84 | |
| Hs578T | 2.5 | 0.25 | 0.66 | 0.99 |
| 5 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.98 | |
| 10 | 0.25 | 0.84 | 0.97 | |
| 20 | 0.25 | 0.95 | 0.58 |
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′ > 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′ > 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| FOXM1 | TGCAGCTAGGGATGTGAATCTTC | GGAGCCCAGTCCATCAGAACT |
| Cyclin B1 | AAGAACAGCTCTTGGGGACA | CACTGGCACCAGCATAGGTA |
| Snail | GGTTCTTCTGCGCTACTGCT | TAGGGCTGCTGGAAGGTAAA |
| Slug | GCCAAACTACAGCGAACTGG | GATGGGGCTGTATGCTCCTG |
| Bcl-2 | CTTTGAGTTCGGTGGGGTCA | GGGCCGTACAGTTCCACAAA |
| L19 | GCGGAAGGGTACAGCCAAT | GCAGCCGGCGCAAA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ulhaka, K.; Kanokwiroon, K.; Khongkow, M.; Bissanum, R.; Khunpitak, T.; Khongkow, P. The Anticancer Effects of FDI-6, a FOXM1 Inhibitor, on Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136685
Ulhaka K, Kanokwiroon K, Khongkow M, Bissanum R, Khunpitak T, Khongkow P. The Anticancer Effects of FDI-6, a FOXM1 Inhibitor, on Triple Negative Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(13):6685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136685
Chicago/Turabian StyleUlhaka, Karan, Kanyanatt Kanokwiroon, Mattaka Khongkow, Rassanee Bissanum, Thanaporn Khunpitak, and Pasarat Khongkow. 2021. "The Anticancer Effects of FDI-6, a FOXM1 Inhibitor, on Triple Negative Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 13: 6685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136685
APA StyleUlhaka, K., Kanokwiroon, K., Khongkow, M., Bissanum, R., Khunpitak, T., & Khongkow, P. (2021). The Anticancer Effects of FDI-6, a FOXM1 Inhibitor, on Triple Negative Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(13), 6685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136685