An Ancestry Perspective of the Evolution of PBS1 Proteins in Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
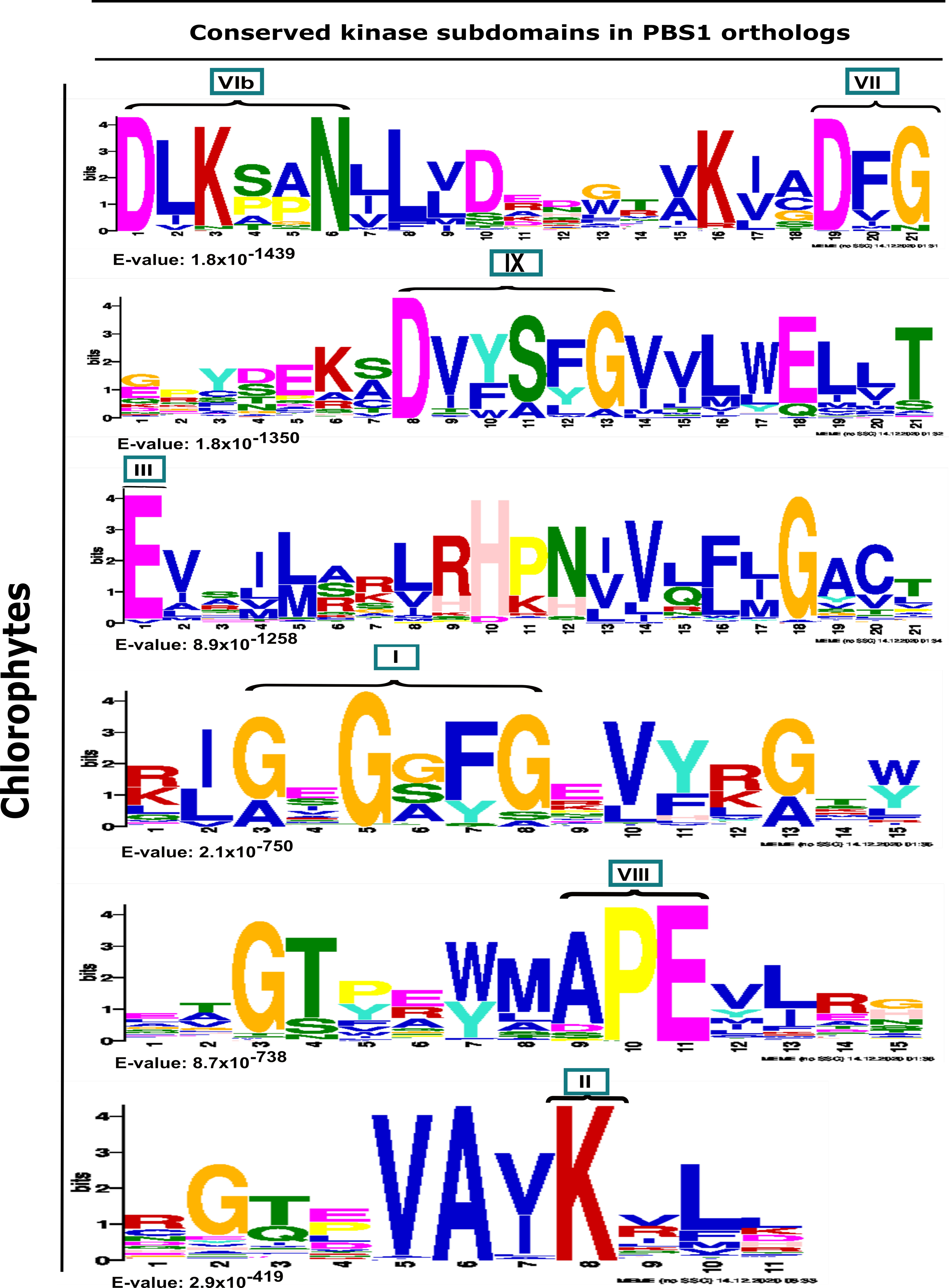
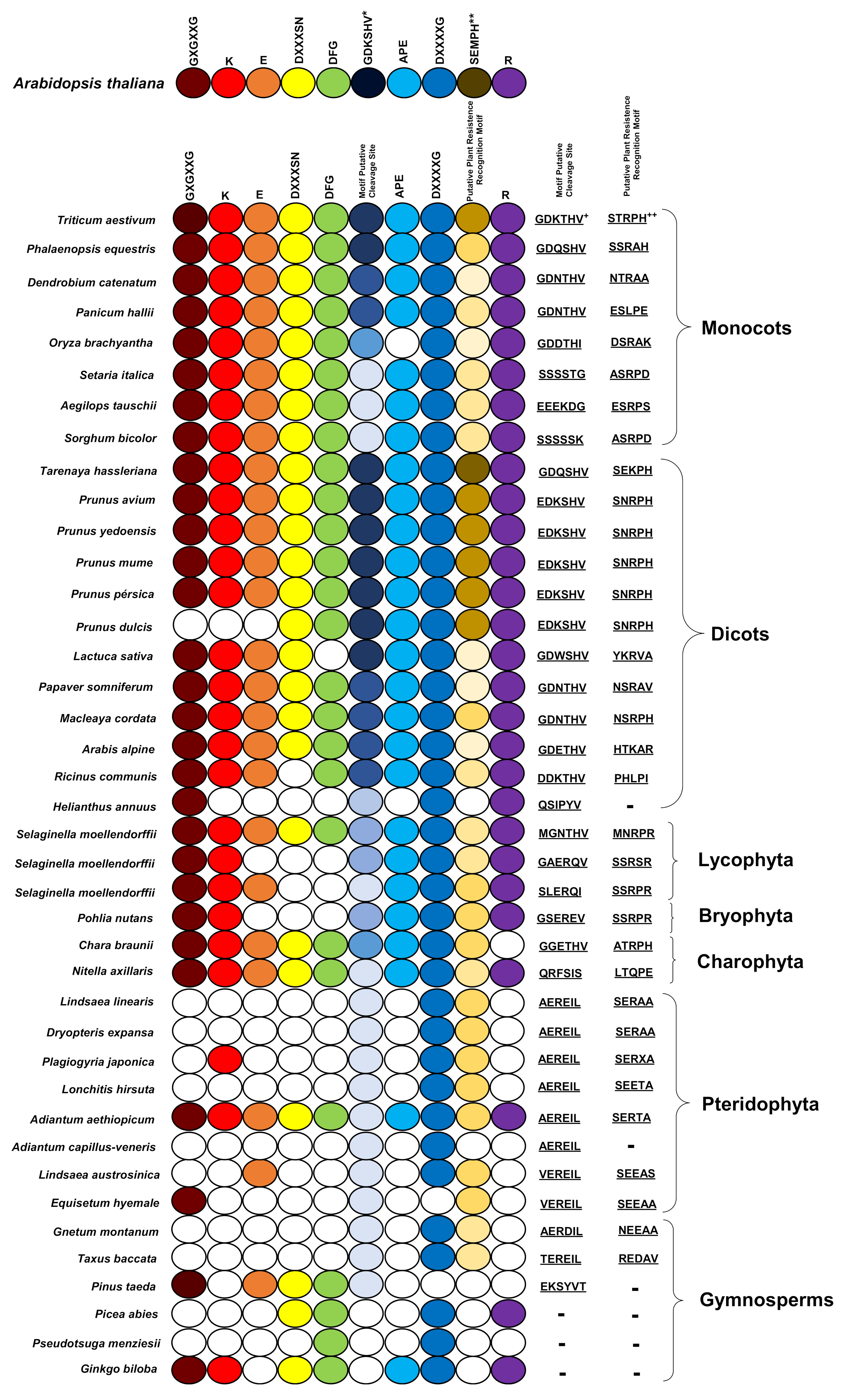
2.1. Identification of PBS1 Proteins, Conserved Kinase Subdomains and Motifs Involved in the Indirect Immune Response in PBS1 in the Plant Kingdom
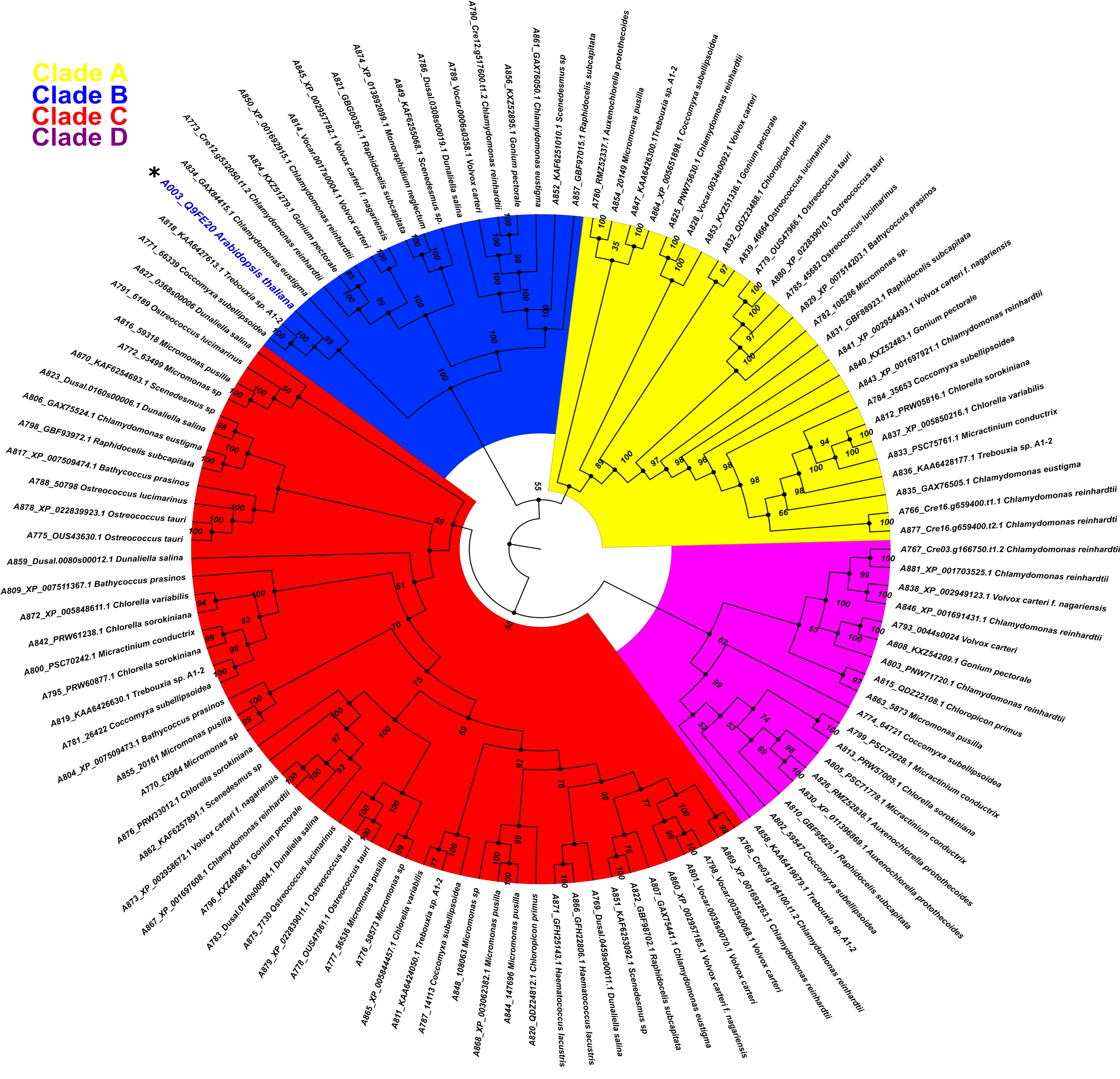
2.2. Phylogeny of PBS1 Orthologs in Chlorophytes
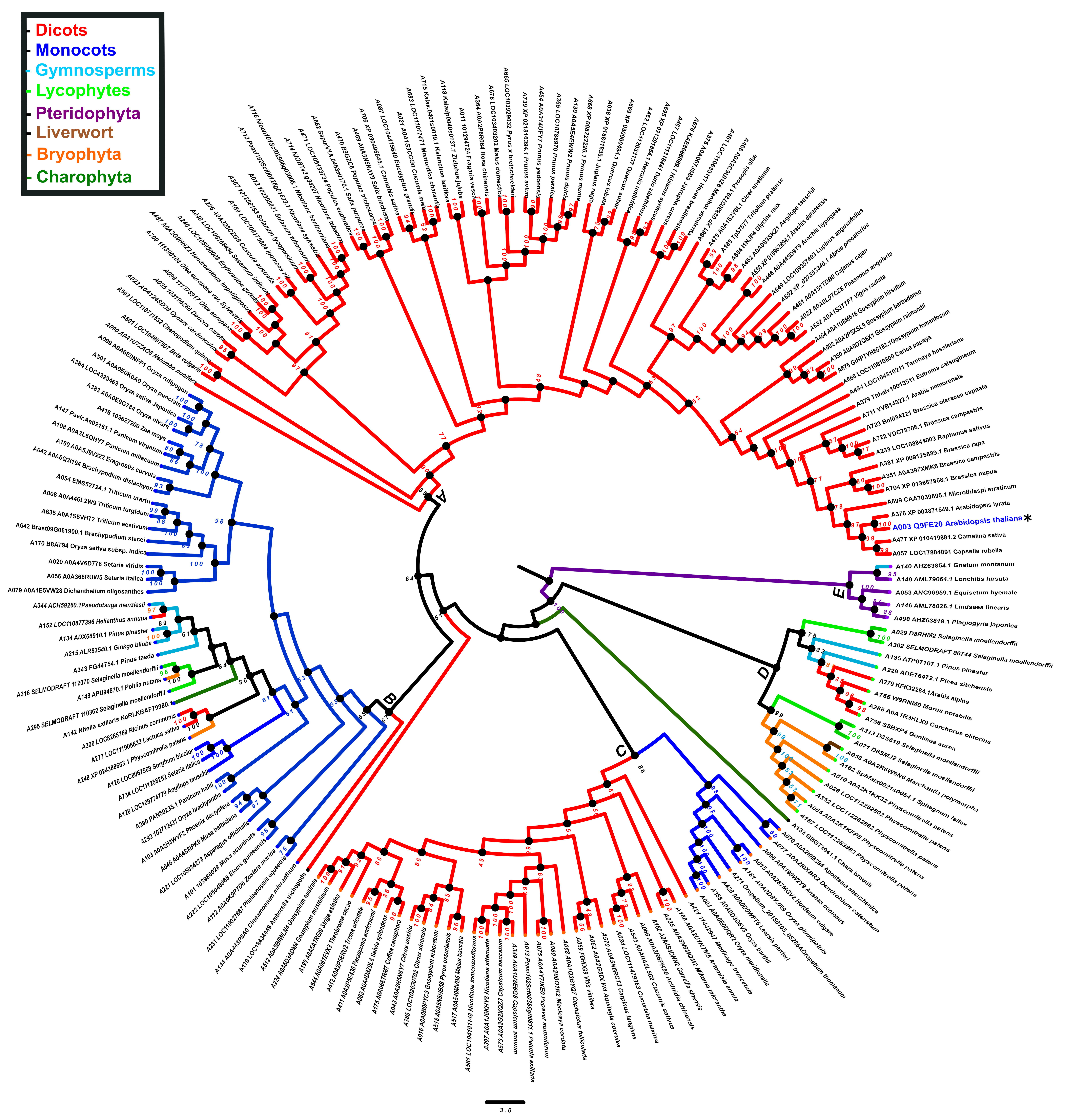
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of PBS1 Orthologs from Different Plant Lineages
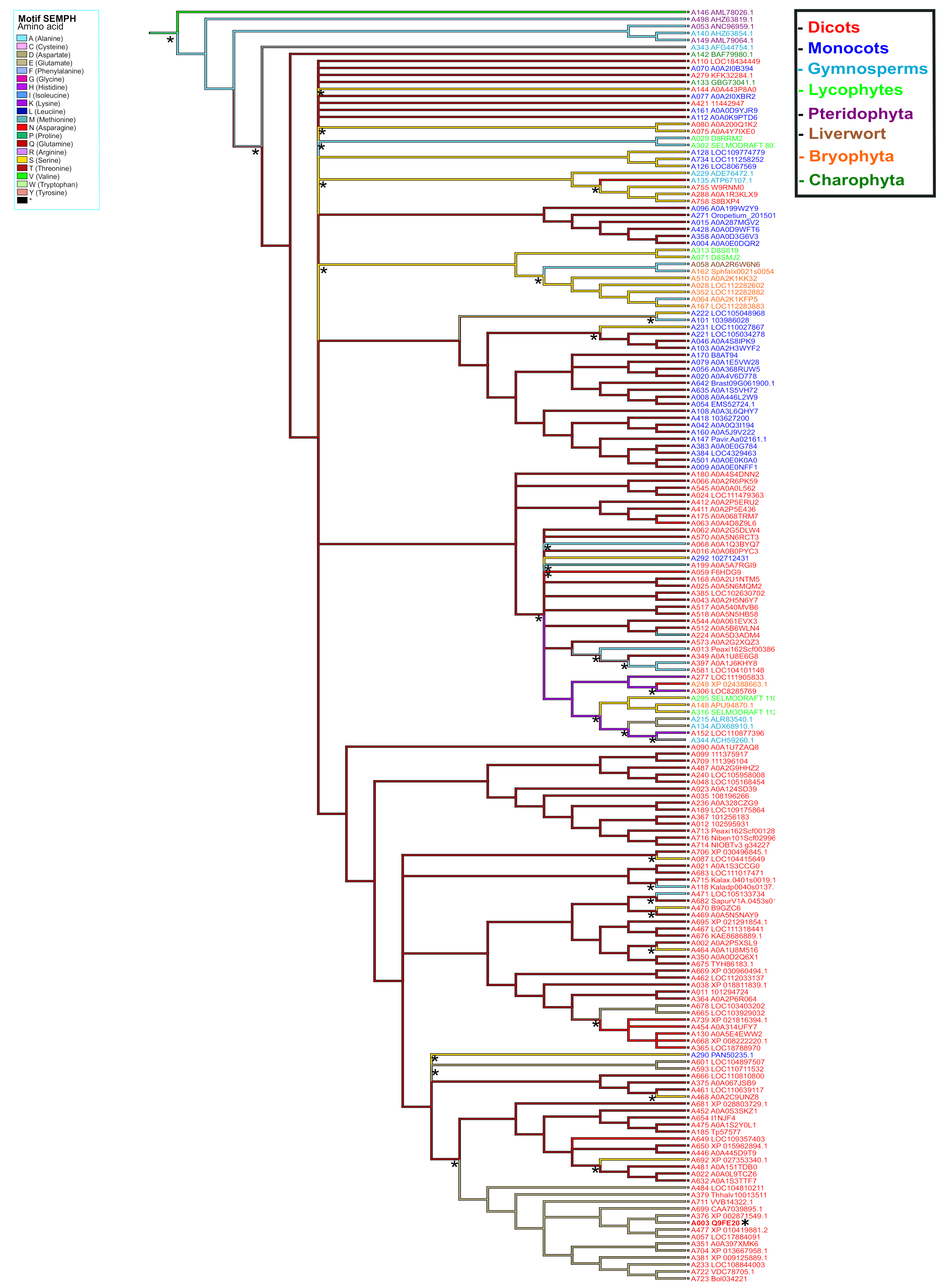
2.4. Ancestral State Reconstruction of PBS1 Orthologs in Terrestrial Plants
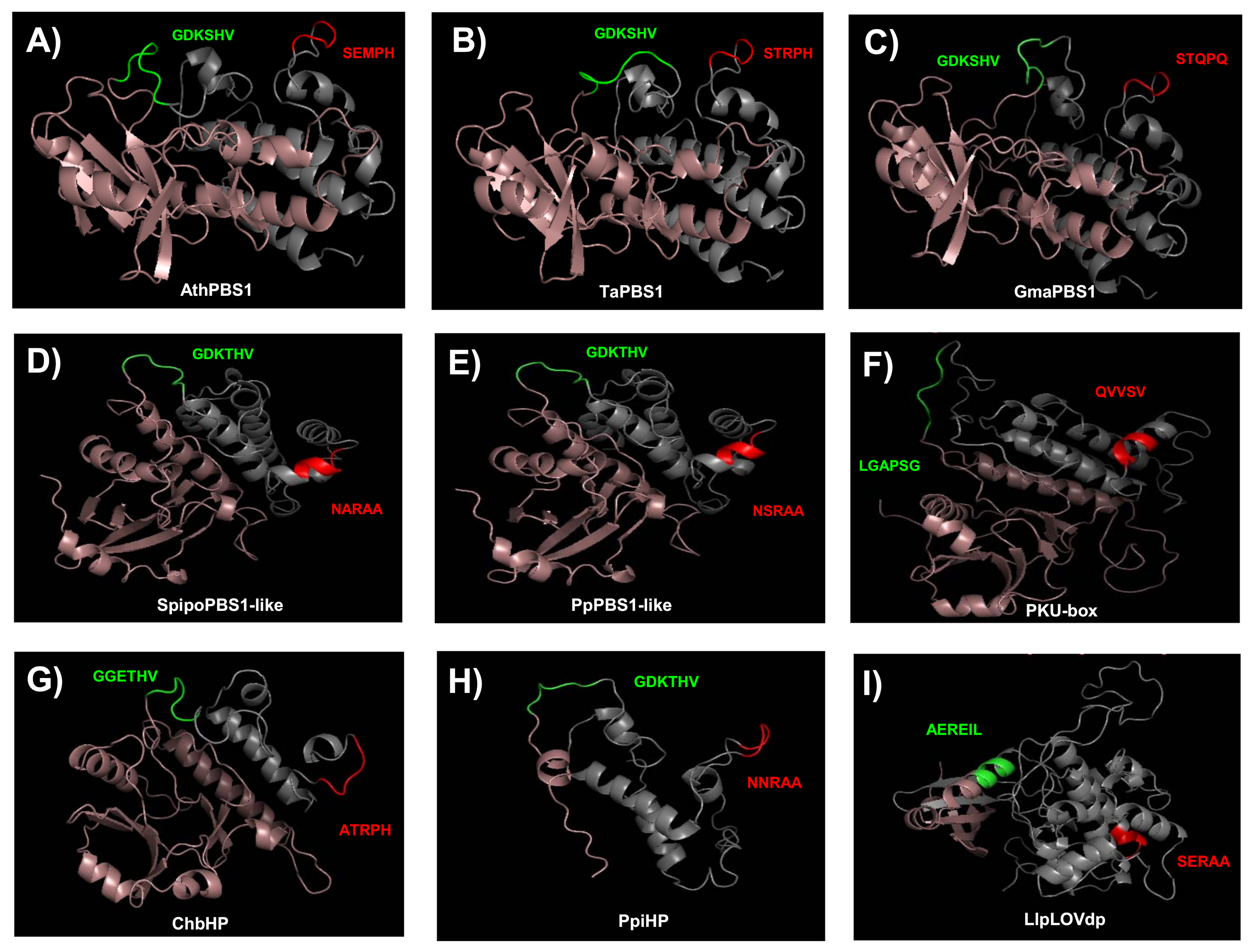
2.5. Structure Modeling of PBS1 Orthologs
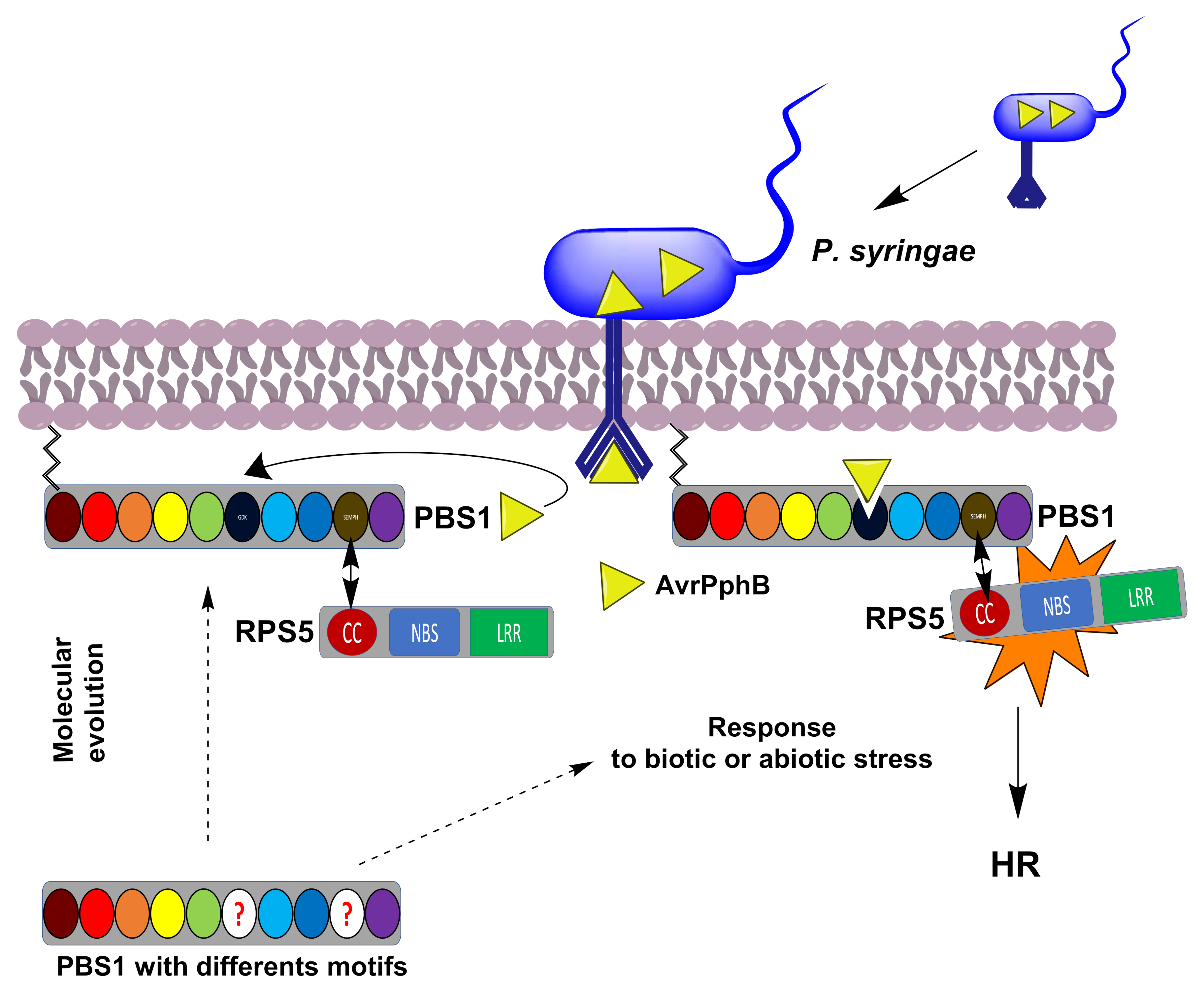
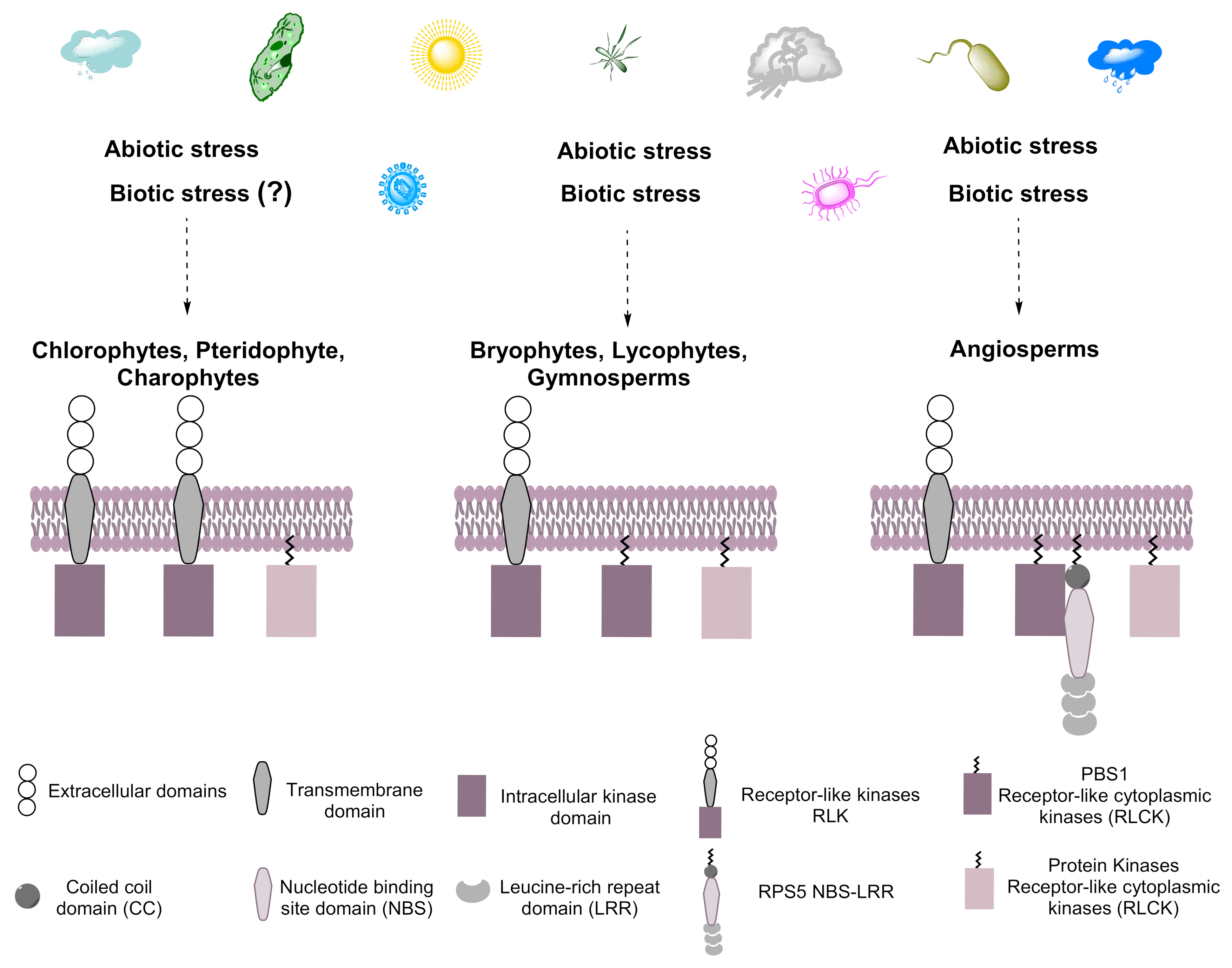
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bioinformatic Identification of PBS1 Proteins in Plant Species
4.2. Identification of Subdomains in PBS1 Orthologs
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of PBS1
4.4. Ancestral State Reconstruction of PBS1 Orthologs
4.5. PBS1 Structure Modeling
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, G.Z. Origin and evolution of the plant immune system. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chisholm, S.T.; Coaker, G.; Day, B.; Staskawicz, B.J. Host-microbe interactions: Shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 2006, 124, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, J.D.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwessinger, B.; Zipfel, C. News from the frontline: Recent insights into PAMP-triggered immunity in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gómez, L.; Boller, T. FLS2: An LRR receptor–like kinase involved in the perception of the bacterial elicitor flagellin in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, H.; Nishizawa, Y.; Ishii-Minami, N.; Akimoto-Tomiyama, C.; Dohmae, N.; Takio, K.; Minami, E.; Shibuya, N. Plant cells recognize chitin fragments for defense signaling through a plasma membrane receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11086–11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boller, T.; Felix, G. A renaissance of elicitors: Perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, S.-H.; Bleecker, A.B. Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10763–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Huang, G.; Fan, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Zou, Y.; Lu, D. Comparative study of Arabidopsis PBS1 and a wheat PBS1 homolog helps understand the mechanism of PBS1 functioning in innate immunity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Wang, G.; Zhou, J.M. Receptor Kinases in Plant-Pathogen Interactions: More than Pattern Recognition. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 618–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiu, S.H.; Karlowski, W.M.; Pan, R.; Tzeng, Y.H.; Mayer, K.F.; Li, W.H. Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1220–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pottinger, S.E.; Innes, R.W. RPS5-Mediated disease resistance: Fundamental insights and translational applications. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2020, 58, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balint-Kurti, P. The plant hypersensitive response: Concepts, control and consequences. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caldwell, K.S.; Michelmore, R.W. Arabidopsis thaliana genes encoding defense signaling and recognition proteins exhibit contrasting evolutionary dynamics. Genetics 2009, 181, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Afzal, A.J.; Wood, A.J.; Lightfoot, D.A. Plant receptor-like serine threonine kinases: Roles in signaling and plant defense. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ade, J.; DeYoung, B.J.; Golstein, C.; Innes, R.W. Indirect activation of a plant nucleotide binding site–leucine-rich repeat protein by a bacterial protease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2531–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, D.; Dubiella, U.; Kim, S.H.; Sloss, D.I.; Dowen, R.H.; Dixon, J.E.; Innes, R.W. Recognition of the protein kinase AVRPPHB SUSCEPTIBLE1 by the disease resistance protein RESISTANCE TO PSEUDOMONAS SYRINGAE5 is dependent on s-acylation and an exposed loop in AVRPPHB SUSCEPTIBLE1. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Qi, D.; Ashfield, T.; Helm, M.; Innes, R.W. Using decoys to expand the recognition specificity of a plant disease resistance protein. Science 2016, 351, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Xiang, T.; Liu, Z.; Laluk, K.; Ding, X.; Zou, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; et al. Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases integrate signaling from multiple plant immune receptors and are targeted by a Pseudomonas syringae effector. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, F.; Golstein, C.; Ade, J.; Stoutemyer, M.; Dixon, J.E.; Innes, R.W. Cleavage of Arabidopsis PBS1 by a bacterial type III effector. Science 2003, 301, 1230–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.E.; Helm, M.; Chapman, A.V.; Wan, E.; Restrepo Sierra, A.M.; Innes, R.W.; Bogdanove, A.J.; Wise, R.P. Convergent evolution of effector protease recognition by Arabidopsis and barley. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiderski, M.; Innes, R. The Arabidopsis PBS1 resistance gene encodes a member of a novel protein kinase subfamily. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2001, 26, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, A.; Agrawal, N.; Sharma, M.; Pandey, A.; Pandey, G.K. Role of protein tyrosine phosphatases in plants. Curr. Genom. 2015, 16, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaux, P.-M.; Radhakrishnan, G.V.; Jayaraman, D.; Cheema, J.; Malbreil, M.; Volkening, J.D.; Sekimoto, H.; Nishiyama, T.; Melkonian, M.; Pokorny, L. Algal ancestor of land plants was preadapted for symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13390–13395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jose, J.; Ghantasala, S.; Roy Choudhury, S. Arabidopsis Transmembrane Receptor-Like Kinases (RLKs): A Bridge between Extracellular Signal and Intracellular Regulatory Machinery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehti-Shiu, M.D.; Zou, C.; Hanada, K.; Shiu, S.-H. Evolutionary history and stress regulation of plant receptor-like kinase/pelle genes. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Wu, S.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, L.; He, P. A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase, BIK1, associates with a flagellin receptor complex to initiate plant innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeYoung, B.J.; Qi, D.; Kim, S.H.; Burke, T.P.; Innes, R.W. Activation of a plant nucleotide binding-leucine rich repeat disease resistance protein by a modified self protein. Cell Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albers, P.; Üstün, S.; Witzel, K.; Kraner, M.; Börnke, F. A Remorin from Nicotiana benthamiana Interacts with the Pseudomonas Type-III Effector Protein HopZ1a and is Phosphorylated by the Immune-Related Kinase PBS1. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 1229–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.; Bohnert, H.J. Integration of Arabidopsis thaliana stress-related transcript profiles, promoter structures, and cell-specific expression. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Block, A.; Li, G.; Fu, Z.Q.; Alfano, J.R. Phytopathogen type III effector weaponry and their plant targets. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.S.; Park, S.-C.; Ji, C.Y.; Park, S.; Jeong, J.C.; Lee, H.-S.; Kwak, S.-S. Molecular characterization of biotic and abiotic stress-responsive MAP kinase genes, IbMPK3 and IbMPK6, in sweetpotato. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 108, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Song, Y.H.; Josephson-Day, A.R.; Miller, R.J.; Breton, G.; Olmstead, R.G.; Imaizumi, T. FLOWERING BHLH transcriptional activators control expression of the photoperiodic flowering regulator CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3582–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christie, J.M. Phototropin blue-light receptors. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, R.; Toma, W.; Yamazaki, K.; Akanuma, S. Ancestral sequence reconstruction produces thermally stable enzymes with mesophilic enzyme-like catalytic properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joy, J.B.; Liang, R.H.; McCloskey, R.M.; Nguyen, T.; Poon, A.F.Y. Ancestral Reconstruction. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garrido-Bigotes, A.; Valenzuela-Riffo, F.; Figueroa, C.R. Evolutionary Analysis of JAZ Proteins in Plants: An Approach in Search of the Ancestral Sequence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thornton, J.W. Resurrecting ancient genes: Experimental analysis of extinct molecules. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amborella Genome Project. The Amborella genome and the evolution of flowering plants. Science 2013, 342, 1241089. [Google Scholar]
- Harms, M.J.; Thornton, J.W. Evolutionary biochemistry: Revealing the historical and physical causes of protein properties. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeYoung, B.J.; Innes, R.W. Plant NBS-LRR proteins in pathogen sensing and host defense. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Gong, Z.; Zhao, H.; Han, G.-Z. Out of water: The origin and early diversification of plant R-genes. Plant Physiol. 2018, 177, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, Z.-Q.; Xue, J.-Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.-Q. Revisiting the origin of plant NBS-LRR genes. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, B.C.; Kozik, A.; Griego, A.; Kuang, H.; Michelmore, R.W. Genome-wide analysis of NBS-LRR–encoding genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 809–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Upson, J.L.; Zess, E.K.; Białas, A.; Wu, C.H.; Kamoun, S. The coming of age of EvoMPMI: Evolutionary molecular plant-microbe interactions across multiple timescales. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 44, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, S.; Brunk, B.P.; Chen, F.; Gao, X.; Harb, O.S.; Iodice, J.B.; Shanmugam, D.; Roos, D.S.; Stoeckert, C.J., Jr. Using OrthoMCL to assign proteins to OrthoMCL-DB groups or to cluster proteomes into new ortholog groups. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, T.L.; Williams, N.; Misleh, C.; Li, W.W. MEME: Discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34 (Suppl. 2), W369–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villegas-Vázquez, E.Y.; Xoconostle-Cázares, B.; Ruiz-Medrano, R. An Ancestry Perspective of the Evolution of PBS1 Proteins in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136819
Villegas-Vázquez EY, Xoconostle-Cázares B, Ruiz-Medrano R. An Ancestry Perspective of the Evolution of PBS1 Proteins in Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(13):6819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136819
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillegas-Vázquez, Edgar Yebrán, Beatriz Xoconostle-Cázares, and Roberto Ruiz-Medrano. 2021. "An Ancestry Perspective of the Evolution of PBS1 Proteins in Plants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 13: 6819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136819
APA StyleVillegas-Vázquez, E. Y., Xoconostle-Cázares, B., & Ruiz-Medrano, R. (2021). An Ancestry Perspective of the Evolution of PBS1 Proteins in Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(13), 6819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136819





