Aquatic Training after Joint Immobilization in Rats Promotes Adaptations in Myotendinous Junctions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Fiber Area
2.2. Fractal Dimension (FD)
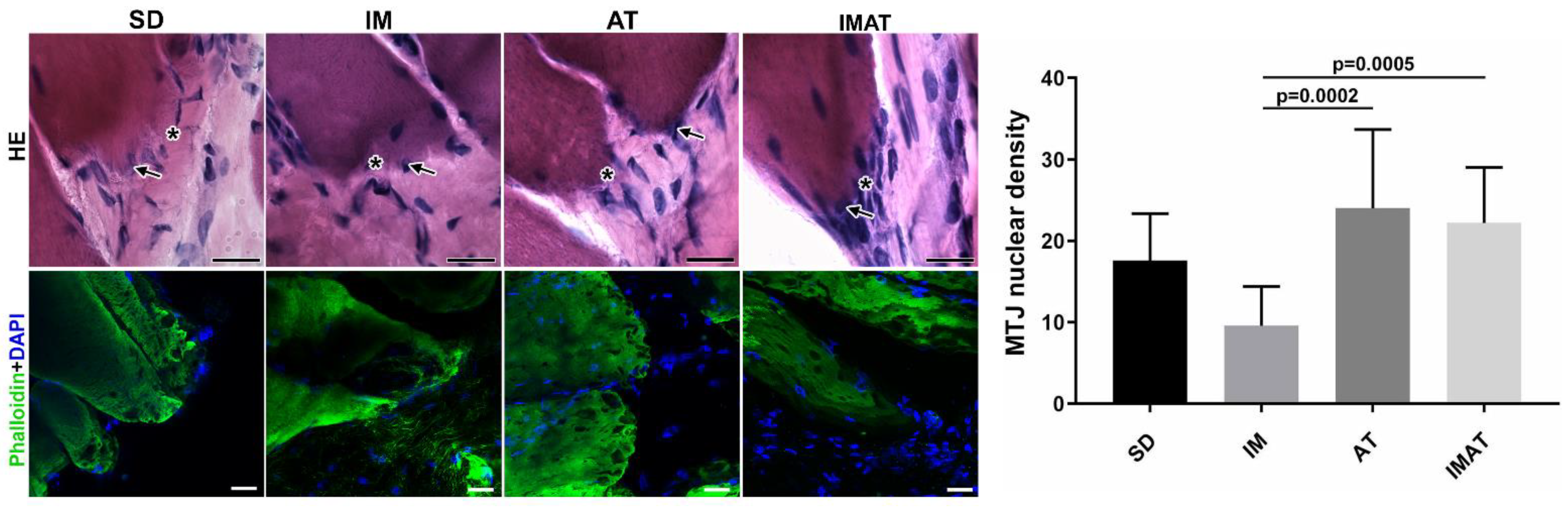
2.3. MTJ Nuclear Density
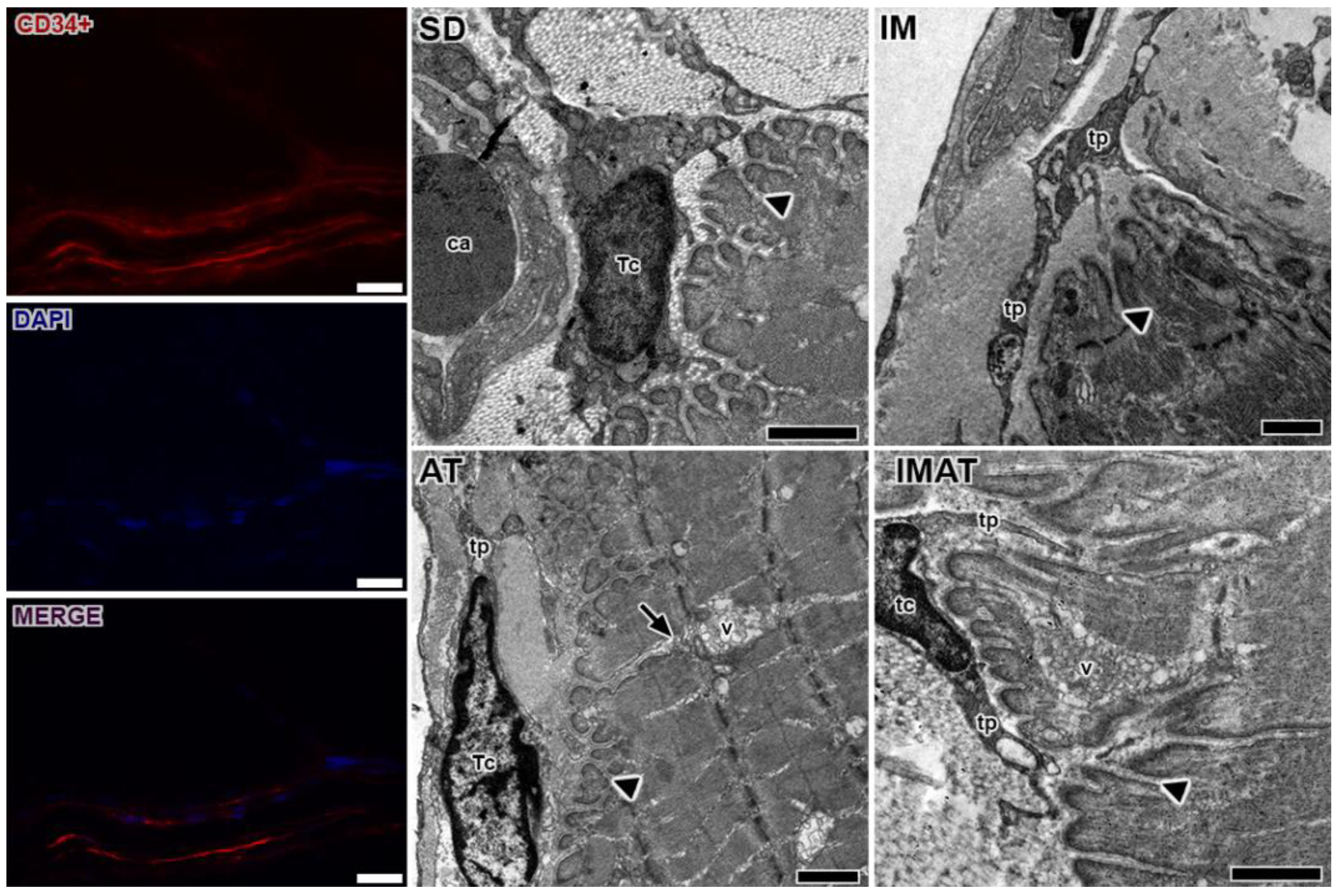
2.4. MTJ Morphology
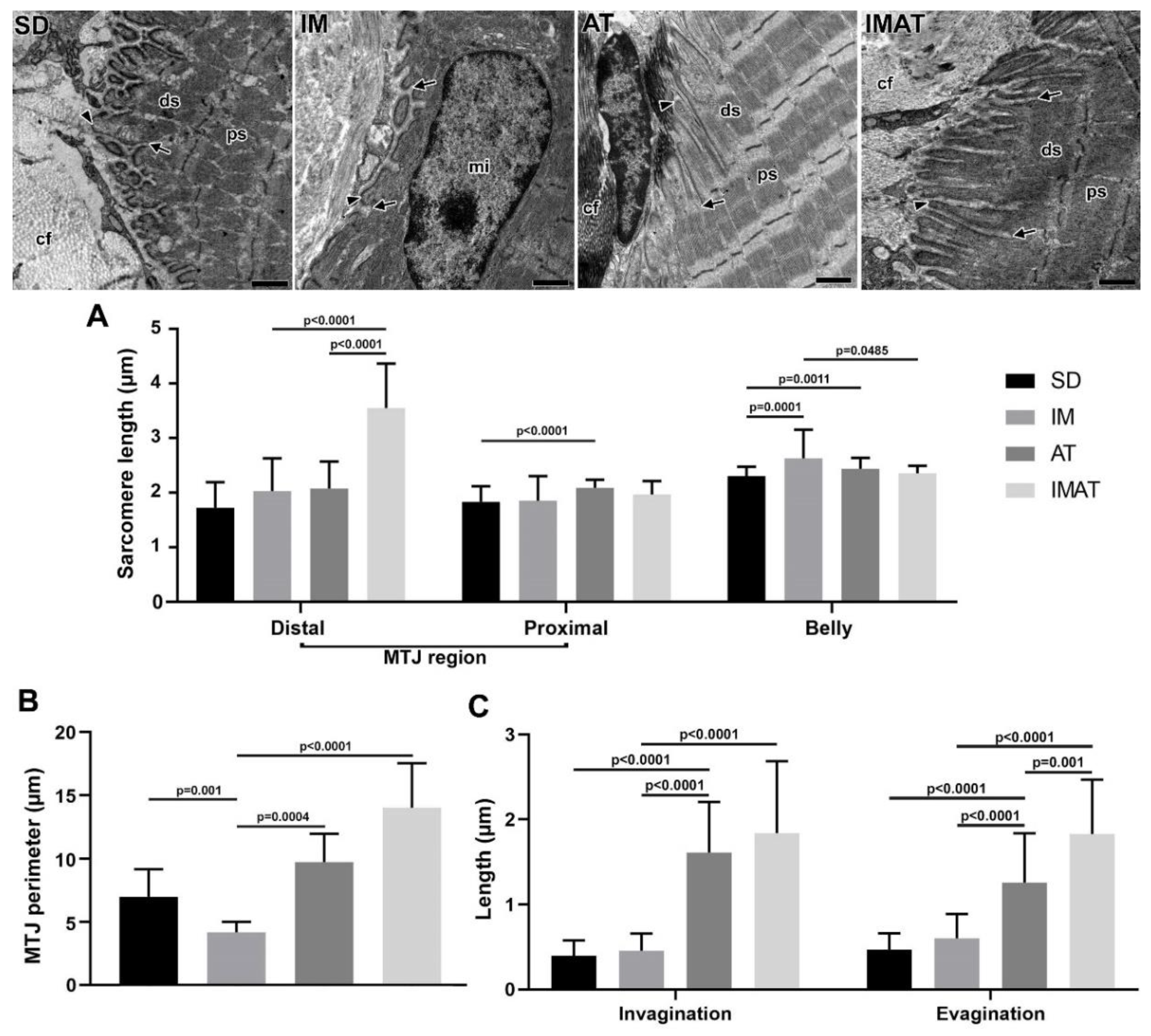
2.5. Sarcomeres
2.6. MTJ Morphometry
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. IM Protocol
4.3. AT Protocol
4.4. Light Microscopy
4.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciena, A.P.; Luques, I.U.; Dias, F.J.; Yokomizo de Almeida, S.R.; Iyomasa, M.M.; Watanabe, I.S. Ultrastructure of the myotendinous junction of the medial pterygoid muscle of adult and aged Wistar rats. Micron 2010, 41, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natali, L.H.; da Silva, T.S.; Ciena, A.P.; Padoin, M.J.; Alves, É.P.B.; Aragão, F.A.; Bertolini, G.R.F. Efeitos da corrida em esteira em músculos sóleos de ratos encurtados por imobilização. Rev. Bras. Med. Do Esporte 2008, 14, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kannus, P.; Jozsa, L.; Kvist, M.; Lehto, M.; Jarvinen, M. The effect of immobilization on myotendinous junction: An ultrastructural, histochemical and immunohistochemical study. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1992, 144, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curzi, D. Ultrastructural study of myotendinous junction plasticity: From disuse to exercise. Sport Sci. Health 2016, 12, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, M.; Folker, E.S. Specialized Positioning of Myonuclei Near Cell-Cell Junctions. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pimentel Neto, J.; Rocha, L.C.; Barbosa, G.K.; Jacob, S.; Krause Neto, W.; Watanabe, I.; Ciena, A.P. Myotendinous junction adaptations to ladder-based resistance training: Identification of a new telocyte niche. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, L. Telocytes-a novel type of interstitial cells. Recent Res. Mod. Med. 2011, 11, 424–432. [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein, L.; Fuxe, K.; Levin, M.; Popescu, B.O.; Smythies, J. Telocytes in their context with other intercellular communication agents. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 55, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, M.; Rosa, I.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Manetti, M. Telocytes in skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle interstitium: Morphological and functional aspects. Histol. Histopathol. 2018, 33, 1151–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.C.; Jacob, C.d.S.; Barbosa, G.K.; Neto, J.P.; Neto, W.K.; Gama, E.F.; Ciena, A.P. Remodeling of the skeletal muscle and postsynaptic component after short-term joint immobilization and aquatic training. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 154, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cação-Benedini, L.O.; Ribeiro, P.G.; Prado, C.M.; Chesca, D.L.; Mattiello-Sverzut, A.C. Immobilization and therapeutic passive stretching generate thickening and increase the expression of laminin and dystrophin in skeletal muscle. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, L.C.; Polizello, J.C.; Padula, N.; Freitas, F.C.; Shimano, A.C.; Mattiello-sverzut, A.C. Mechanical properties of gastrocnemius electro stimulated after immobilization. Acta Ortop Bras 2009, 17, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cação-Benedini, L.O.; Ribeiro, P.G.; Gomes, A.R.S.; Ywazaki, J.L.; Monte-Raso, V.V.; Prado, C.M.; Mattiello-Sverzut, A.C. Remobilization through stretching improves gait recovery in the rat. Acta Histochem. 2013, 115, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaisar, R.; Karim, A.; Elmoselhi, A.B. Muscle unloading: A comparison between spaceflight and ground-based models. Acta Physiol. 2020, 228, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, T.A.; Ozaki, G.A.T.; Castoldi, R.C.; Koike, T.E.; Camargo, R.C.T.; Camargo Filho, J.C.S. Fractal dimension in the evaluation of different treatments of muscular injury in rats. Tissue Cell 2018, 54, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cury, S.S.; Freire, P.P.; Martinucci, B.; dos Santos, V.C.; de Oliveira, G.; Ferretti, R.; Dal-Pai-Silva, M.; Pacagnelli, F.L.; Delella, F.K.; Carvalho, R.F. Fractal dimension analysis reveals skeletal muscle disorganization in mdx mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stankovic, M.; Pantic, I.; De Luka, S.R.; Puskas, N.; Zaletel, I.; Milutinovic-Smiljanic, S.; Pantic, S.; Trbovich, A.M. Quantification of structural changes in acute inflammation by fractal dimension, angular second moment and correlation. J. Microsc. 2016, 261, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.C.; Rosenthal, N. Different modes of hypertrophy in skeletal muscle fibers. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 156, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nascimento, C.C.F.; Padula, N.; Milani, J.G.P.O.; Shimano, A.C.; Martinez, E.Z.; Mattiello-Sverzut, A.C. Histomorphometric analysis of the response of rat skeletal muscle to swimming, immobilization and rehabilitation. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2008, 41, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocha, L.C.; Pimentel Neto, J.; Sant’Ana, J.S.; Jacob, C.S.; Barbosa, G.K.; Krause Neto, W.; Watanabe, I.; Ciena, A.P. Repercussions on sarcomeres of the myotendinous junction and the myofibrillar type adaptations in response to different trainings on vertical ladder. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2020, 83, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.R.S.; Coutinho, E.L.; França, C.N.; Polonio, J.; Salvini, T.F. Effect of one stretch a week applied to the immobilized soleus muscle on rat muscle fiber morphology. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2004, 37, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tinklenberg, J.; Beatka, M.; Bain, J.L.W.; Siebers, E.M.; Meng, H.; Pearsall, R.S.; Lawlor, M.W.; Riley, D.A. Use Of Ankle Immobilization In Evaluating Treatments To Promote Longitudinal Muscle Growth In Mice. Muscle Nerve 2018, 58, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moo, E.K.; Fortuna, R.; Sibole, S.C.; Abusara, Z.; Herzog, W. In vivo sarcomere lengths and sarcomere elongations are not uniform across an intact muscle. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sierra, L.R.; Fávaro, G.; Cerri, B.R.; Rocha, L.C.; de Almeida, S.R.d.Y.; Watanabe, I.-S.; Ciena, A.P. Myotendinous junction plasticity in aged ovariectomized rats submitted to aquatic training. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2018, 81, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caiozzo, V.J.; Utkan, A.; Chou, R.; Khalafi, A.; Chandra, H.; Baker, M.; Rourke, B.; Adams, G.; Baldwin, K.; Green, S. Effects of Distraction on Muscle Length: Sarcomerogenesis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2002, 403, S133–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riley, D.A.; Bain, J.L.W.; Romatowski, J.G.; Fitts, R.H. Skeletal muscle fiber atrophy: Altered thin filament density changes slow fiber force and shortening velocity. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2004, 288, C360–C365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Windner, S.E.; Manhart, A.; Brown, A.; Mogilner, A.; Baylies, M.K. Nuclear Scaling Is Coordinated among Individual Nuclei in Multinucleated Muscle Fibers. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 48–62.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, C.; Yeo, D.; Ji, L.L. Muscle immobilization activates mitophagy and disrupts mitochondrial dynamics in mice. Acta Physiol. 2016, 218, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, K. Muscle memory and a new cellular model for muscle atrophy and hypertrophy. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cadot, B.; Gache, V.; Gomes, E.R. Moving and positioning the nucleus in skeletal muscle-one step at a time. Nucleus 2015, 6, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curzi, D.; Lattanzi, D.; Burattini, S.; Tidball, J.G.; Falcieri, E. Morphological changes of myotendinous junction generated by muscle disuse atrophy. Microscopie 2013, 19, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Palma, L.D.; Marinelli, M.; Pavan, M.; Bertoni-Freddari, C. Involvement of the muscle-tendon junction in skeletal muscle atrophy: An ultrastructural study. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2011, 52, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Machida, S.; Booth, F.W. Regrowth of Skeletal Muscle Atrophied from Inactivity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, C.S.; Rocha, L.C.; Neto, J.P.; Watanabe, I.; Ciena, A.P. Effects of physical training on sarcomere lengths and muscle-tendon interface of the cervical region in an experimental model of menopause. Eur. J. Histochem. 2019, 63, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilceac, F.A.; Renner, A.F.; Teodoro, W.R.; Mattiello-Rosa, S.M. The remodeling of collagen fibers in rats ankles submitted to immobilization and muscle stretch protocol. Rheumatol. Int. 2011, 31, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Sakuma, E.; Mabuchi, Y.; Mizutani, J.; Horiuchi, O.; Wada, I.; Horiba, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Herbert, D.C.; Soji, T.; et al. Ultrastructural changes at the myotendinous junction induced by exercise. J. Orthop. Sci. 2008, 13, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, B.A.C.; Rocha, L.C.; Martinez, G.Z.; Pimentel Neto, J.; Jacob, C.S.; Watanabe, I.; Ciena, A.P. Myotendinous Junction Components of Different Skeletal Muscles Present Morphological Changes in Obese Rats. Microsc. Microanal. 2021, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, E.A. Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical characteristics of telocytes in the skin and skeletal muscle of newborn rats. Acta Histochem. 2016, 118, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, L.M.; Manole, E.; Şerboiu, C.S.; Manole, C.G.; Suciu, L.C.; Gherghiceanu, M.; Popescu, B.O. Identification of telocytes in skeletal muscle interstitium: Implication for muscle regeneration. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1379–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manetti, M.; Tani, A.; Rosa, I.; Chellini, F.; Squecco, R.; Idrizaj, E.; Zecchi-Orlandini, S.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Sassoli, C. Morphological evidence for telocytes as stromal cells supporting satellite cell activation in eccentric contraction-induced skeletal muscle injury. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raquel, H.d.A.; Masson, G.S.; Barna, B.F.; Zanluqui, N.G.; Pinge-Filho, P.; Michelini, L.C.; Martins-Pinge, M.C. Swimming training modulates nitric oxide-glutamate interaction in the rostral ventrolateral medulla in normotensive conscious rats. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiff, R.D.; Miller, C.H.; Munn, R.J. Manual hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse tissue sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2014, 2014, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Rose, J.; Zeller, R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2008, 3, 4986–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parandakh, A.; Tafazzoli-Shadpour, M.; Khani, M.M. Stepwise morphological changes and cytoskeletal reorganization of human mesenchymal stem cells treated by short-time cyclic uniaxial stretch. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2017, 53, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciena, A.P.; Almeida, S.R.Y.; Bolina, C.S.; Bolina-Matos, R.S.; Rici, R.E.G.; Silva, M.C.P.; Miglino, M.A.; Watanabe, I.S. Ultrastructural features of the myotendinous junction of the sternomastoid muscle in Wistar rats: From newborn to aging. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2012, 75, 1292–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolina, C.d.S.; Bolina-Matos, R.D.S.; Alves, P.H.D.M.; Cury, D.P.; Ciena, A.P.; Watanabe, I.S. Three-dimensional aspects of the structural characteristics and kidney angioarchitecture of adult and aged wistar rats: A scanning electron microscopy study. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2013, 76, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rocha, L.C.; Barbosa, G.K.; Pimentel Neto, J.; Jacob, C.d.S.; Knudsen, A.B.; Watanabe, I.-S.; Ciena, A.P. Aquatic Training after Joint Immobilization in Rats Promotes Adaptations in Myotendinous Junctions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136983
Rocha LC, Barbosa GK, Pimentel Neto J, Jacob CdS, Knudsen AB, Watanabe I-S, Ciena AP. Aquatic Training after Joint Immobilization in Rats Promotes Adaptations in Myotendinous Junctions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(13):6983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136983
Chicago/Turabian StyleRocha, Lara Caetano, Gabriela Klein Barbosa, Jurandyr Pimentel Neto, Carolina dos Santos Jacob, Andreas B. Knudsen, Ii-Sei Watanabe, and Adriano Polican Ciena. 2021. "Aquatic Training after Joint Immobilization in Rats Promotes Adaptations in Myotendinous Junctions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 13: 6983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136983
APA StyleRocha, L. C., Barbosa, G. K., Pimentel Neto, J., Jacob, C. d. S., Knudsen, A. B., Watanabe, I. -S., & Ciena, A. P. (2021). Aquatic Training after Joint Immobilization in Rats Promotes Adaptations in Myotendinous Junctions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(13), 6983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136983





