Ubiquitylation of ABA Receptors and Protein Phosphatase 2C Coreceptors to Modulate ABA Signaling and Stress Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Ubiquitylation of ABA Receptors
3. Regulation of Ubiquitylation by Post-Translational Modifications
4. Ubiquitylation of Clade A PP2Cs in the Context of ABA Signaling
5. ABA- and/or Receptor-Dependent Degradation of PP2Cs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABI1 | aba insensitive1 |
| APC | anaphase promoting complex |
| PP2Cs | clade a protein phosphatases type 2c |
| CRL | cullin-ring e3 ubiquitin ligase |
| FLS2 | flagellin sensing 2 |
| HAB1 | hypersensitive to aba1 |
| PUBs | plant u-box type e3 ubiquitin ligases |
| PIR1 | pp2ca interacting ring finger protein 1 |
| RGLG1 | ring domain ligase1 |
| RSL1 | ring finger of seed longevity |
| RFA | ring finger aba-related |
| RBRs | ring1-in between ring-ring2 e3 ubiquitin ligases |
| PYR1 | pyrabactin resistance1 |
| PYL | pyr1-like |
| RCAR | regulatory components of aba receptors |
| PP2CA | protein phosphatase 2ca |
| SnRK2s | snf1-related protein kinases |
References
- Hershko, A.; Ciechanover, A. The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 425–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komander, D.; Rape, M. The ubiquitin code. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Barrios, N.; Vert, G. Proteasome-independent functions of lysine-63 polyubiquitination in plants. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 995–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Pardo, J.M.; Yun, D.J. Desensitization of ABA-Signaling: The swing from activation to degradation. Front Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Xie, Q. Non-26S Proteasome Endomembrane Trafficking Pathways in ABA Signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.K.; Ryu, M.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, J.S.; Oh, T.R.; Kim, W.T.; Yang, S.W. RING E3 ligases: Key regulatory elements are involved in abiotic stress responses in plants. BMB Rep. 2017, 50, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.L. Role of the Ubiquitin Proteasome System in Plant Response to Abiotic Stress. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 343, 65–110. [Google Scholar]
- Bueso, E.; Rodriguez, L.; Lorenzo-Orts, L.; Gonzalez-Guzman, M.; Sayas, E.; Munoz-Bertomeu, J.; Ibanez, C.; Serrano, R.; Rodriguez, P.L. The single-subunit RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase RSL1 targets PYL4 and PYR1 ABA receptors in plasma membrane to modulate abscisic acid signaling. Plant J. 2014, 80, 1057–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irigoyen, M.L.; Iniesto, E.; Rodriguez, L.; Puga, M.I.; Yanagawa, Y.; Pick, E.; Strickland, E.; Paz-Ares, J.; Wei, N.; De Jaeger, G.; et al. Targeted degradation of abscisic acid receptors is mediated by the ubiquitin ligase substrate adaptor DDA1 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 712–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callis, J. The ubiquitination machinery of the ubiquitin system. Arabidopsis. Book. 2014, 12, e0174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.A.; Belda-Palazon, B.; Julian, J.; Coego, A.; Lozano-Juste, J.; Iñigo, S.; Rodriguez, L.; Bueso, E.; Goossens, A.; Rodriguez, P.L. RBR-Type E3 Ligases and the Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme UBC26 Regulate Abscisic Acid Receptor Levels and Signaling. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 1723–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, I. Diversification and Specialization of Plant RBR Ubiquitin Ligases. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Zhuang, X.; Shen, J.; Jiang, L. Plant ESCRT Complexes: Moving Beyond Endosomal Sorting. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Scalf, M.; Smith, L.M.; Vierstra, R.D. Advanced proteomic analyses yield a deep catalog of ubiquitylation targets in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1523–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGurn, J.A.; Hsu, P.C.; Emr, S.D. Ubiquitin and membrane protein turnover: From cradle to grave. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, F.; Horntrich, C.; Blachutzik, J.O.; Scherzer, S.; Reinders, Y.; Kierszniowska, S.; Schulze, W.X.; Harms, G.S.; Hedrich, R.; Geiger, D.; et al. Arabidopsis nanodomain-delimited ABA signaling pathway regulates the anion channel SLAH3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8296–8301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grondin, A.; Rodrigues, O.; Verdoucq, L.; Merlot, S.; Leonhardt, N.; Maurel, C. Aquaporins Contribute to ABA-Triggered Stomatal Closure through OST1-Mediated Phosphorylation. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Lan, W.; Buchanan, B.B.; Luan, S. A protein kinase-phosphatase pair interacts with an ion channel to regulate ABA signaling in plant guard cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21419–21424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belda-Palazon, B.; Rodriguez, L.; Fernandez, M.A.; Castillo, M.C.; Anderson, E.A.; Gao, C.; Gonzalez-Guzman, M.; Peirats-Llobet, M.; Zhao, Q.; De Winne, N.; et al. FYVE1/FREE1 Interacts with the PYL4 ABA Receptor and Mediates its Delivery to the Vacuolar Degradation Pathway. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 2291–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Leon, M.; Cuyas, L.; El Moneim, D.A.; Rodriguez, L.; Belda-Palazon, B.; Sanchez-Quant, E.; Fernandez, Y.; Roux, B.; Zamarreno, A.M.; Garcia-Mina, J.M.; et al. Arabidopsis ALIX Regulates Stomatal Aperture and Turnover of Abscisic Acid Receptors. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 2411–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Lou, L.; Tian, M.; Li, Q.; Ding, Y.; Cao, X.; Wu, Y.; Belda-Palazon, B.; Rodriguez, P.L.; Yang, S.; et al. ESCRT-I Component VPS23A Affects ABA Signaling by Recognizing ABA Receptors for Endosomal Degradation. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 1570–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Yoon, H.J.; Terzaghi, W.; Martinez, C.; Dai, M.; Li, J.; Byun, M.O.; Deng, X.W. DWA1 and DWA2, two Arabidopsis DWD protein components of CUL4-based E3 ligases, act together as negative regulators in ABA signal transduction. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1716–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.I.; Lee, J.H.; Nezames, C.D.; Zhong, S.; Song, E.; Byun, M.O.; Deng, X.W. ABD1 is an Arabidopsis DCAF substrate receptor for CUL4-DDB1-based E3 ligases that acts as a negative regulator of abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabek, N.; Ruble, J.; Waston, C.J.; Garbutt, K.C.; Hinds, T.R.; Li, T.; Zheng, N. Structural insights into DDA1 function as a core component of the CRL4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase. Cell Discov. 2018, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belda-Palazon, B.; Julian, J.; Coego, A.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Batistic, O.; Alquraishi, S.A.; Kudla, J.; An, C.; Rodriguez, P.L. ABA inhibits myristoylation and induces shuttling of the RGLG1 E3 ligase to promote nuclear degradation of PP2CA. Plant J. 2019, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, J.; Coego, A.; Lozano-Juste, J.; Lechner, E.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Merilo, E.; Belda-Palazon, B.; Park, S.Y.; Cutler, S.R.; et al. The MATH-BTB BPM3 and BPM5 subunits of Cullin3-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases target PP2CA and other clade A PP2Cs for degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 15725–15734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoni, R.; Gonzalez-Guzman, M.; Rodriguez, L.; Peirats-Llobet, M.; Pizzio, G.A.; Fernandez, M.A.; De Winne, N.; De Jaeger, G.; Dietrich, D.; Bennett, M.J.; et al. PYRABACTIN RESISTANCE1-LIKE8 plays an important role for the regulation of abscisic acid signaling in root. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belda-Palazon, B.; Gonzalez-Garcia, M.P.; Lozano-Juste, J.; Coego, A.; Antoni, R.; Julian, J.; Peirats-Llobet, M.; Rodriguez, L.; Berbel, A.; Dietrich, D.; et al. PYL8 mediates ABA perception in the root through non-cell-autonomous and ligand-stabilization-based mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11857–E11863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, D.; Pang, L.; Kobayashi, A.; Fozard, J.A.; Boudolf, V.; Bhosale, R.; Antoni, R.; Nguyen, T.; Hiratsuka, S.; Fujii, N.; et al. Root hydrotropism is controlled via a cortex-specific growth mechanism. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, R.; Yuan, W.; Wang, Y.; Garcia-Maquilon, I.; Dang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Rodriguez, P.L.; Xu, W. Low ABA concentration promotes root growth and hydrotropism through relief of ABA INSENSITIVE 1-mediated inhibition of plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase 2. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Wu, F.; Sheng, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; et al. The SnRK2-APC/C(TE) regulatory module mediates the antagonistic action of gibberellic acid and abscisic acid pathways. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Kong, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Yang, Y. AtRAE1 is involved in degradation of ABA receptor RCAR1 and negatively regulates ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Yang, Y. The Arabidopsis F-box E3 ligase RIFP1 plays a negative role in abscisic acid signaling by facilitating ABA receptor RCAR3 degradation. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, M.; Zafar, S.A.; Fang, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Arabidopsis E3 Ubiquitin Ligases PUB22 and PUB23 Negatively Regulate Drought Tolerance by Targeting ABA Receptor PYL9 for Degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.C.; Rhee, D.Y.; Duda, D.M.; Kelsall, I.R.; Olszewski, J.L.; Paulo, J.A.; de Jong, A.; Ovaa, H.; Alpi, A.F.; Harper, J.W.; et al. Two Distinct Types of E3 Ligases Work in Unison to Regulate Substrate Ubiquitylation. Cell 2016, 166, 1198–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M.C.; Lozano-Juste, J.; Gonzalez-Guzman, M.; Rodriguez, L.; Rodriguez, P.L.; Leon, J. Inactivation of PYR/PYL/RCAR ABA receptors by tyrosine nitration may enable rapid inhibition of ABA signaling by nitric oxide in plants. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, L.; Xie, S.; et al. Initiation and amplification of SnRK2 activation in abscisic acid signaling. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Hsu, C.C.; Liu, X.; Fu, L.; Hou, Y.J.; Du, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, C.; et al. Reciprocal Regulation of the TOR Kinase and ABA Receptor Balances Plant Growth and Stress Response. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Qu, L.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhu, J.K.; Xue, H.W. EL1-like Casein Kinases Suppress ABA Signaling and Responses by Phosphorylating and Destabilizing the ABA Receptors PYR/PYLs in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Y.; Jin, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, G.; Huang, J.; Yan, K.; Wu, C.; et al. CEPR2 phosphorylates and accelerates the degradation of PYR/PYLs in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5457–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Juste, J.; Leon, J. Enhanced abscisic acid-mediated responses in nia1nia2noa1-2 triple mutant impaired in NIA/NR- and AtNOA1-dependent nitric oxide biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Meng, J.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; et al. Degradation of the ABA co-receptor ABI1 by PUB12/13 U-box E3 ligases. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, S.; Rodrigues, A.; Saez, A.; Dizon, M.B.; Galle, A.; Kim, T.H.; Santiago, J.; Flexas, J.; Schroeder, J.I.; Rodriguez, P.L. Triple loss of function of protein phosphatases type 2C leads to partial constitutive response to endogenous abscisic acid. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Kim, J.K.; Jan, M.; Khan, H.A.; Khan, I.U.; Shen, M.; Park, J.; Lim, C.J.; Hussain, S.; Baek, D.; et al. Rheostatic Control of ABA Signaling through HOS15-Mediated OST1 Degradation. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 1447–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Zhi, L.; Yao, B.; Su, C.; Liu, L.; Li, X. SCFAtPP2-B11 modulates ABA signaling by facilitating SnRK2.3 degradation in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Lin, W.; Gao, X.; Wu, S.; Cheng, C.; Avila, J.; Heese, A.; Devarenne, T.P.; He, P.; Shan, L. Direct ubiquitination of pattern recognition receptor FLS2 attenuates plant innate immunity. Science 2011, 332, 1439–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Peirats-Llobet, M.; Belda-Palazon, B.; Wang, X.; Cui, S.; Yu, X.; Rodriguez, P.L.; An, C. Ubiquitin Ligases RGLG1 and RGLG5 Regulate Abscisic Acid Signaling by Controlling the Turnover of Phosphatase PP2CA. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 2178–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.L.; Lozano-Juste, J.; Albert, A. PYR/PYL/RCAR ABA receptors. In Advances in Botanical Research, Abscisc Acid in Plants; Seo, M., Marion-Poll, A., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; Volume 92, pp. 51–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kelsall, I.R.; Duda, D.M.; Olszewski, J.L.; Hofmann, K.; Knebel, A.; Langevin, F.; Wood, N.; Wightman, M.; Schulman, B.A.; Alpi, A.F. TRIAD1 and HHARI bind to and are activated by distinct neddylated Cullin-RING ligase complexes. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2848–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, H.; Rittinger, K. RBR ligase-mediated ubiquitin transfer: A tale with many twists and turns. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, W.; Lim, C.W.; Luan, S.; Lee, S.C. The RING finger E3 ligases PIR1 and PIR2 mediate PP2CA degradation to enhance abscisic acid response in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2019, 100, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chico, J.M.; Lechner, E.; Fernandez-Barbero, G.; Canibano, E.; Garcia-Casado, G.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Hammann, P.; Zamarreño, A.M.; GarcÃa-Mina, J.M.; Rubio, V.; et al. CUL3(BPM) E3 ubiquitin ligases regulate MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4 stability and JA responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6205–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, K.; Ohama, N.; Kidokoro, S.; Mizoi, J.; Takahashi, F.; Todaka, D.; Mogami, J.; Sato, H.; Qin, F.; Kim, J.S.; et al. BPM-CUL3 E3 ligase modulates thermotolerance by facilitating negative regulatory domain-mediated degradation of DREB2A in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8528–E8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherel, I.; Michard, E.; Platet, N.; Mouline, K.; Alcon, C.; Sentenac, H.; Thibaud, J.B. Physical and functional interaction of the Arabidopsis K(+) channel AKT2 and phosphatase AtPP2CA. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, W.T. The Arabidopsis RING E3 ubiquitin ligase AtAIRP3/LOG2 participates in positive regulation of high-salt and drought stress responses. Plant Physiol 2013, 162, 1733–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Lin, B.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Xia, R.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Xie, Q. The UBC27-AIRP3 ubiquitination complex modulates ABA signaling by promoting the degradation of ABI1 in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 27694–27702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratelli, R.; Guerra, D.D.; Yu, S.; Wogulis, M.; Kraft, E.; Frommer, W.B.; Callis, J.; Pilot, G. The ubiquitin E3 ligase LOSS OF GDU2 is required for GLUTAMINE DUMPER1-induced amino acid secretion in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1628–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Alvero, M.; Yunta, C.; Gonzalez-Guzman, M.; Lozano-Juste, J.; Benavente, J.L.; Arbona, V.; Menendez, M.; Martinez-Ripoll, M.; Infantes, L.; Gomez-Cadenas, A.; et al. Structure of Ligand-Bound Intermediates of Crop ABA Receptors Highlights PP2C as Necessary ABA Co-receptor. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1250–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
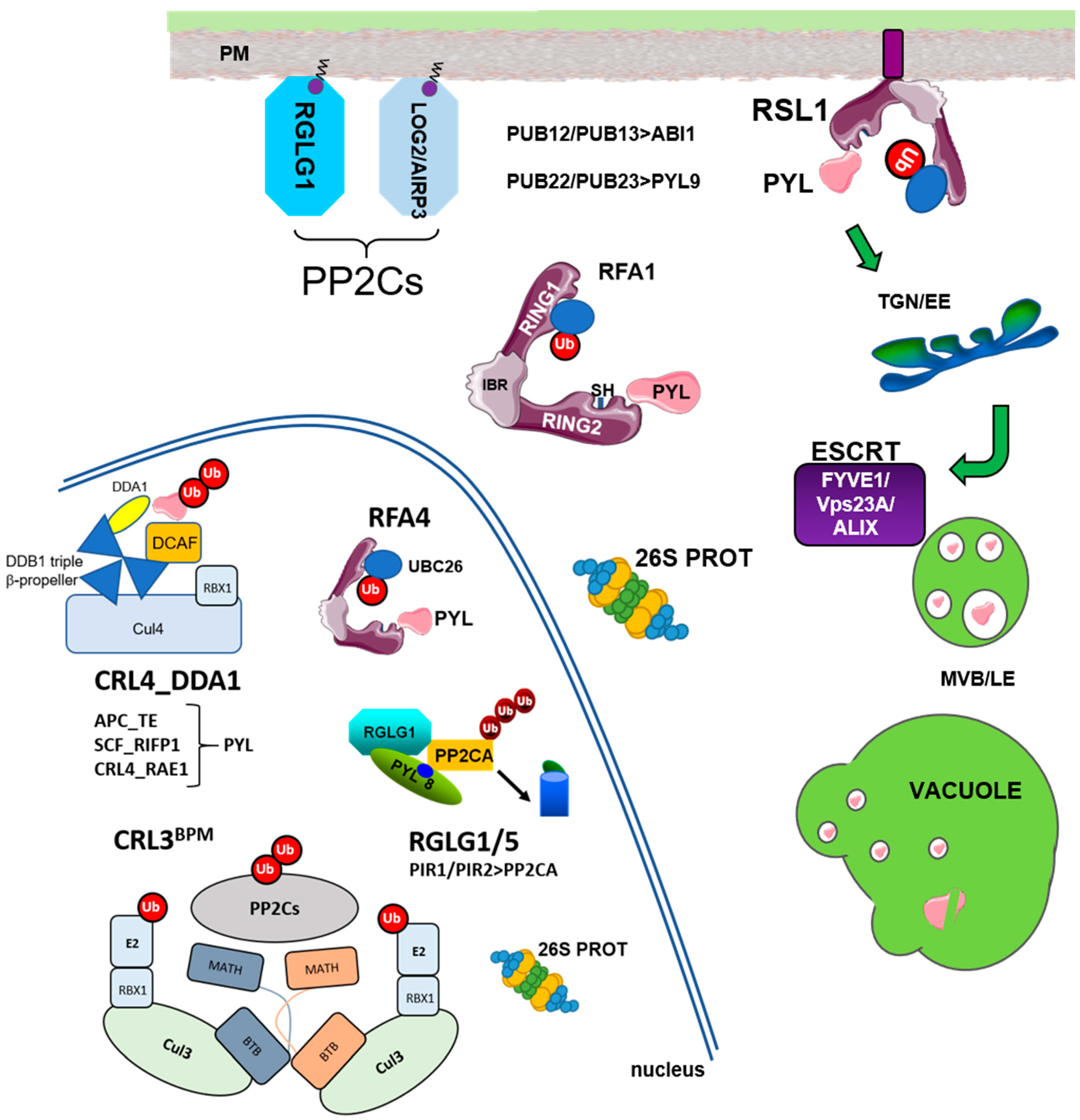
| E3 Ligases_Substrate Adaptor | Localization | Targets | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSL1 | PM | PYR1/PYL4 | Bueso et al., 2014 |
| CRL4_DDA1 | nucleus | PYL8/PYL9 | Irigoyen et al., 2014 |
| APC_TE (rice) | nucleus | OsRCAR10 | Lin et al., 2015 |
| SCF_RIFP1 | nucleus | PYL8/RCAR3 | Li et al., 2016 |
| PUB22/23 | cytosol | PYL9/RCAR1 | Zhao et al., 2017 |
| CRL4_RAE1 | nucleus | PYL9/RCAR1 | Li et al., 2018 |
| RFA1/RFA4 (UBC26) | cytosol, nucleus | PYR1/PYL4 | Fernandez et al., 2020 |
| PUB12/13 | PM for FLS2 | ABI1, FLS2, BRI1 | Kong et al., 2015 Lu et al., 2011; Zhou et al., 2018 |
| RGLG1/RGLG5 | myristoylated PM and nucleus | PP2CA, ABI2, HAB2 | Wu et al., 2016 Belda-Palazon et al., 2019 |
| CRL3_BPM | nucleus | PP2CA, ABI1, HAB1, ABI2 | Julian et al., 2019 |
| PIR1/PIR2 | nucleus | PP2CA | Baek et al., 2019 |
| AIRP3 (UBC27) | myristoylated | ABI1 | Pan et al., 2020 |
| ESCRT Component | ESCRT | Targets Investigated | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| FYVE1/FREE1 | ESCRT-I | PYR1/PYL4 | Belda-Palazon et al., 2016 |
| VPS23A | ESCRT-I | PYR1/PYL4 | Yu et al., 2016 |
| ALIX | ESCRT-III | PYL4 | Garcia-Leon et al., 2019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coego, A.; Julian, J.; Lozano-Juste, J.; Pizzio, G.A.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Rodriguez, P.L. Ubiquitylation of ABA Receptors and Protein Phosphatase 2C Coreceptors to Modulate ABA Signaling and Stress Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137103
Coego A, Julian J, Lozano-Juste J, Pizzio GA, Alrefaei AF, Rodriguez PL. Ubiquitylation of ABA Receptors and Protein Phosphatase 2C Coreceptors to Modulate ABA Signaling and Stress Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(13):7103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137103
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoego, Alberto, Jose Julian, Jorge Lozano-Juste, Gaston A. Pizzio, Abdulwahed F. Alrefaei, and Pedro L. Rodriguez. 2021. "Ubiquitylation of ABA Receptors and Protein Phosphatase 2C Coreceptors to Modulate ABA Signaling and Stress Response" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 13: 7103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137103
APA StyleCoego, A., Julian, J., Lozano-Juste, J., Pizzio, G. A., Alrefaei, A. F., & Rodriguez, P. L. (2021). Ubiquitylation of ABA Receptors and Protein Phosphatase 2C Coreceptors to Modulate ABA Signaling and Stress Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(13), 7103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137103








