The Hypoxia–Long Noncoding RNA Interaction in Solid Cancers
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Hypoxia and Hypoxia-Inducible Factors
1.2. Hypoxia and Cancer
1.3. LncRNAs
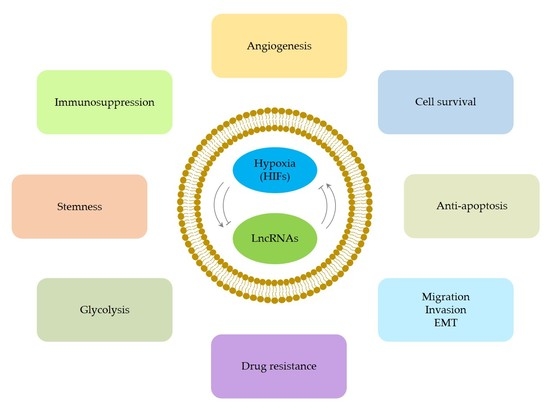
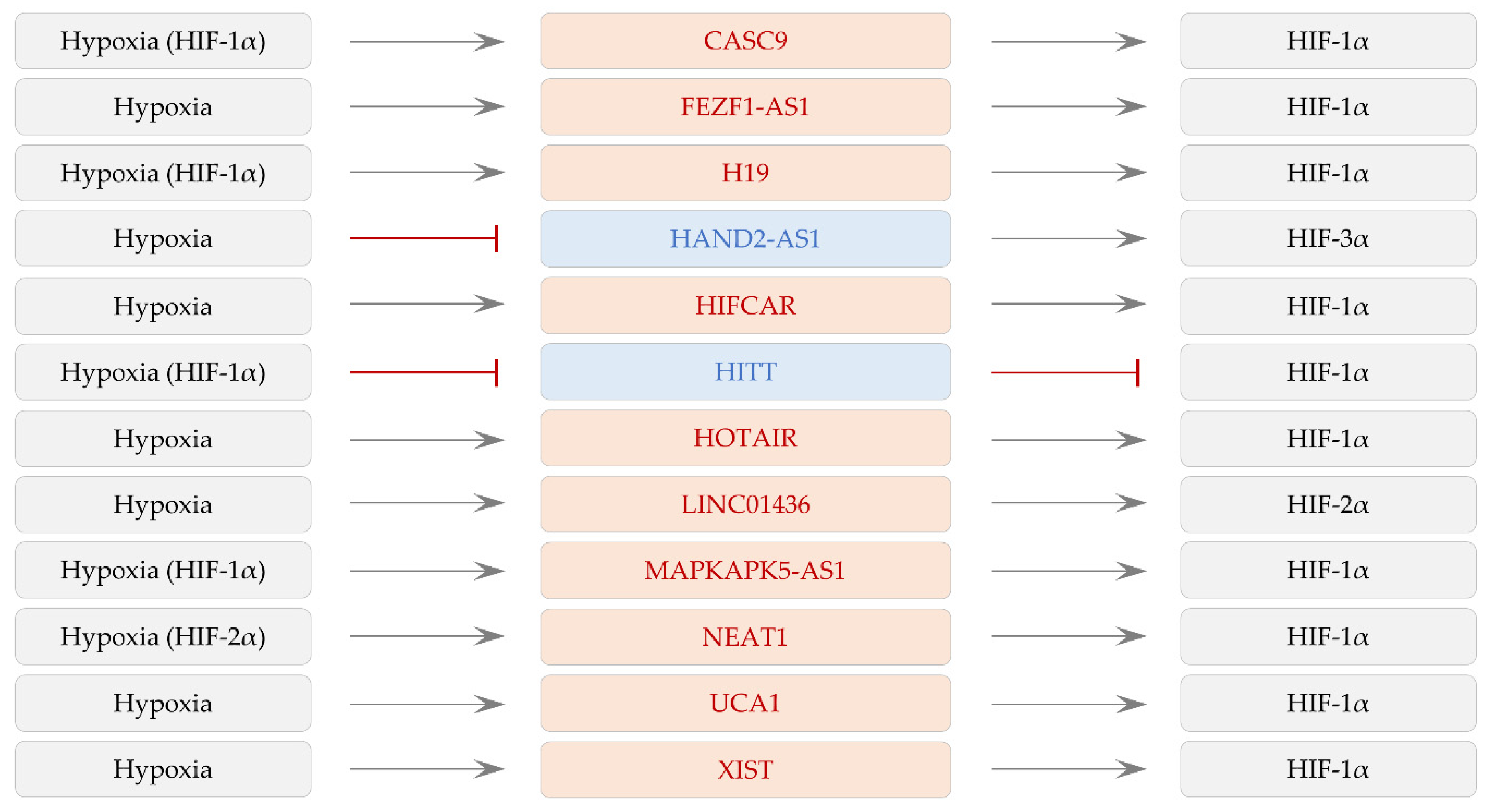
2. LncRNAs Controlled by Hypoxia and HIFs
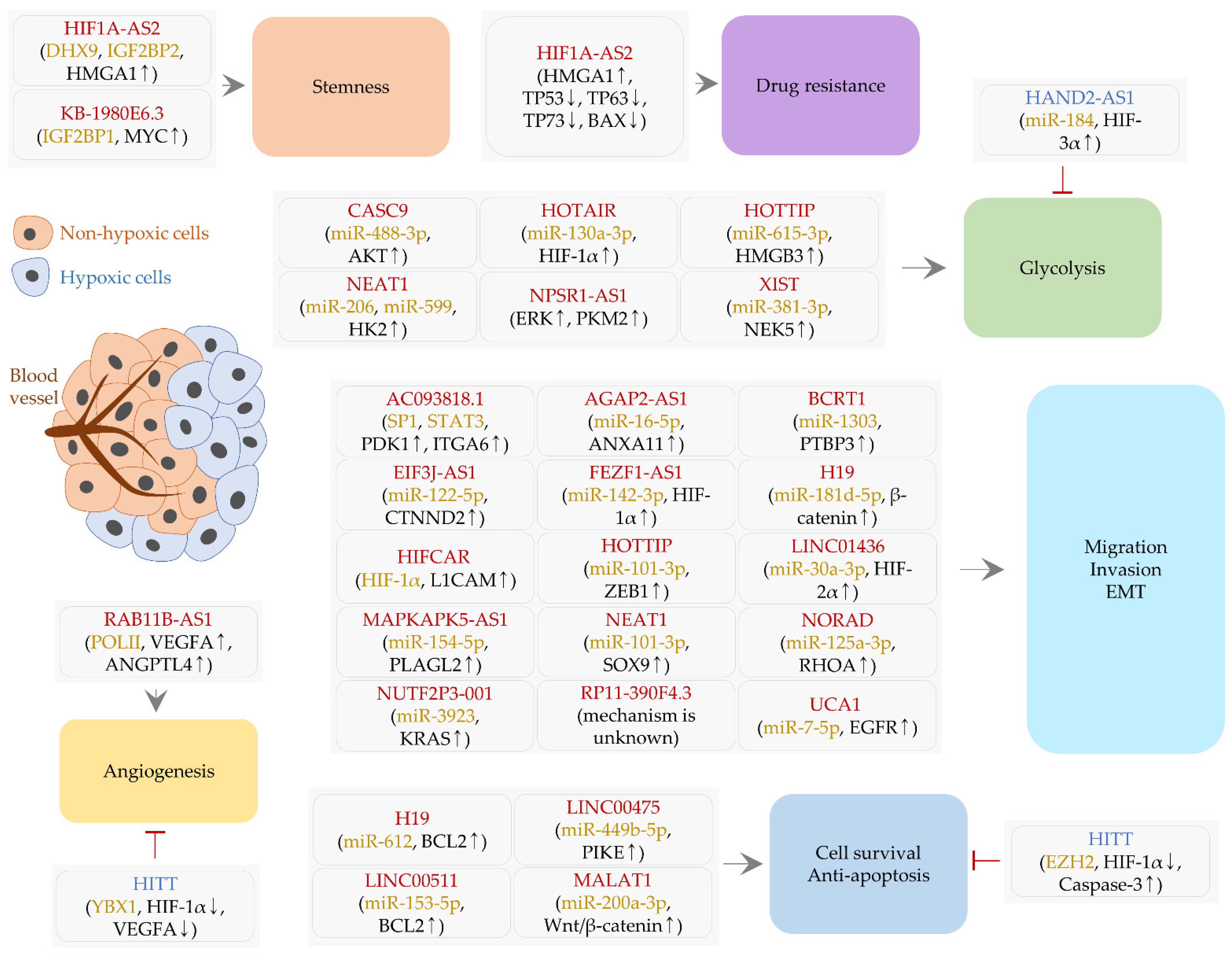
2.1. LncRNAs Regulating Cell Survival and Apoptosis
2.1.1. H19
2.1.2. HITT
2.1.3. LINC00475
2.1.4. LINC00511
2.1.5. MALAT1
2.2. LncRNAs Affecting Cell Migration, Invasion, and EMT
2.2.1. AC093818.1
2.2.2. AGAP2-AS1 and EIF3J-AS1
2.2.3. BCRT1
2.2.4. FEZF1-AS1
2.2.5. H19 and HOTTIP
2.2.6. HIFCAR
2.2.7. LINC01436 and NEAT1
2.2.8. MAPKAPK5-AS1
2.2.9. NORAD and NUTF2P3-001
2.2.10. RP11-390F4.3
2.2.11. UCA1
2.3. A lncRNA Controlling Angiogenesis
2.3.1. RAB11B-AS1
2.3.2. HITT
2.4. LncRNAs Related to Stemness and Drug Resistance
2.4.1. HIF1A-AS2
2.4.2. KB-1980E6.3
2.5. LncRNAs and Glycolysis
2.5.1. CASC9
2.5.2. HAND2-AS1
2.5.3. HOTAIR and NPSR1-AS1
2.5.4. HOTTIP
2.5.5. NEAT1
2.5.6. XIST
3. LncRNAs Regulating HIF-1α Expression
3.1. LncRNAs Affecting Cell Survival and Apoptosis
3.1.1. CDKN2B-AS1
3.1.2. H19 and HOTAIR
3.2. LncRNAs Regulating Cell Migration, Invasion, and EMT
3.2.1. HOXA-AS2
3.2.2. LINC00152
3.2.3. NEAT1 and TUG1
3.2.4. SNHG6
3.2.5. SNHG11 and XIST
3.2.6. TMPO-AS1
3.2.7. ZEB2-AS1
3.3. LncRNAs Modulating Angiogenesis
H19
3.4. LncRNAs Affecting Drug Resistance
3.4.1. FAM201A
3.4.2. UCA1
3.5. A lncRNA and Immunosupression
LINC00301
3.6. LncRNAs and Glycolysis
LINC00518
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3′ UTR | 3′ untranslated region |
| AGAP2 | ArfGAP with GTPase domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 2 |
| AKT2 | AKT serine/threonine kinase 2 |
| ALDH1A1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member A1 |
| ANGPTL4 | Angiopoietin-like 4 |
| ANXA11 | Annexin A11 |
| AXL | AXL receptor tyrosine kinase |
| BAX | BCL2-associated X protein |
| BCL2 | B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 |
| BID | BH3-interacting domain death agonist |
| BRD4 | Bromodomain-containing protein 4 |
| CAFs | Cancer-associated fibroblasts |
| CCL28 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 28 |
| CDH2 | Cadherin 2 |
| CDKN1A | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A |
| CoCl2 | Cobalt chloride |
| CREPT | Cell-cycle related and expression-elevated protein in tumor |
| CTNND2 | Catenin delta 2 |
| DHX9 | DExH-box helicase 9 |
| EAF2 | ELL-associated factor 2 |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EMT | Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| EPAS1 | Endothelial PAS domain-containing protein 1 |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 |
| FOXC1 | Forkhead box C1 |
| GLUT4 | Glucose transporter type 4 |
| HIFs | Hypoxia-inducible factors |
| HK2 | Hexokinase 2 |
| HMGA1 | High-mobility group AT-hook |
| HMGB3 | High-mobility group box 3 |
| IGF2BP2 | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 |
| ITGA6 | Integrin subunit alpha 6 |
| KLF5 | Krueppel-like factor 5 |
| KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| L1CAM | L1 cell adhesion molecule |
| LDHA | Lactate dehydrogenase A |
| LncRNAs | Long noncoding RNAs |
| LONP1 | Mitochondrial ATP-dependent protease Lon |
| MCL1 | Myeloid cell leukemia 1 |
| M-GSCs | Mesenchymal glioma stem cells |
| miRNAs | MicroRNAs |
| MK5 | MAPKAP kinase 5 |
| mRNAs | Messenger RNAs |
| mTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase |
| MYC | V-Myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog |
| NEK2 | Nima-related kinase 2 |
| NFIA | Nuclear factor I/A |
| NFYA | Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit alpha |
| NOB1 | NIN1/PSMD8 binding protein 1 homolog |
| PDK1 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 |
| PFKM | Phosphofructokinase-M |
| PIKE | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase enhancer |
| PKM2 | Pyruvate kinase M2 |
| PLAGL2 | PLAG1-like zinc finger 2 |
| POL II | RNA polymerase II |
| PRC2 | Polycomb repressive complex 2 |
| PTBP3 | Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 3 |
| RAC1 | Rac family small GTPase 1 |
| RHOA | Ras homolog family member A |
| shRNA | Small hairpin RNA |
| SNAI1 | Snail family transcriptional repressor 1 |
| SP1 | Sp1 transcription Factor |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor β |
| TNM | Tumor, node and metastasis |
| TP53 | Tumor suppressor P53 |
| Tregs | Regulatory T cells |
| VASH2 | Vasohibin 2 |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VHL | Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor |
| WNT2B | Wnt family member 2B |
| YBX1 | Y-box binding protein 1 |
| YY1 | Yin and yang 1 |
| ZEB1 | Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 |
| ZEB2 | Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 2 |
References
- Tirpe, A.A.; Gulei, D.; Ciortea, S.M.; Crivii, C.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Hypoxia: Overview on hypoxia-mediated mechanisms with a focus on the role of hif genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, B.S.; Horsman, M.R. Tumor hypoxia: Impact on radiation therapy and molecular pathways. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Jungles, K.; Onder, G.; Samhoun, J.; Gyorffy, B.; Hardiman, K.M. Hif-3alpha1 promotes colorectal tumor cell growth by activation of jak-stat3 signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 11567–11579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizukami, Y.; Kohgo, Y.; Chung, D.C. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 independent pathways in tumor angiogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5670–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsham, A.M.; Howell, J.J.; Simon, M.C. A novel hypoxia-inducible factor-independent hypoxic response regulating mammalian target of rapamycin and its targets. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 29655–29660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iommarini, L.; Porcelli, A.M.; Gasparre, G.; Kurelac, I. Non-canonical mechanisms regulating hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in cancer. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlman, S.; Mohlin, S. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in neuroblastoma. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 372, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flamant, L.; Notte, A.; Ninane, N.; Raes, M.; Michiels, C. Anti-apoptotic role of hif-1 and ap-1 in paclitaxel exposed breast cancer cells under hypoxia. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erler, J.T.; Cawthorne, C.J.; Williams, K.J.; Koritzinsky, M.; Wouters, B.G.; Wilson, C.; Miller, C.; Demonacos, C.; Stratford, I.J.; Dive, C. Hypoxia-mediated down-regulation of bid and bax in tumors occurs via hypoxia-inducible factor 1-dependent and -independent mechanisms and contributes to drug resistance. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 2875–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertout, J.A.; Majmundar, A.J.; Gordan, J.D.; Lam, J.C.; Ditsworth, D.; Keith, B.; Brown, E.J.; Nathanson, K.L.; Simon, M.C. Hif2alpha inhibition promotes p53 pathway activity, tumor cell death, and radiation responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14391–14396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardinocchi, L.; Puca, R.; D’Orazi, G. Hif-1alpha antagonizes p53-mediated apoptosis by triggering hipk2 degradation. Aging 2011, 3, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Shen, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Feng, X.; et al. Hypoxia induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition via activation of snai1 by hypoxia-inducible factor -1alpha in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, D.; Zhou, J. Hif-2alpha promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through regulating twist2 binding to the promoter of e-cadherin in pancreatic cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Q.; Wei, T.; Sun, X.; Chen, Q.; Yang, J.; Bai, X.; Liang, T. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha promotes tumor progression and has crosstalk with wnt/beta-catenin signaling in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, B.; Fu, Z.; Wei, J.; Lu, W. Hypoxic microenvironment induces emt and upgrades stem-like properties of gastric cancer cells. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 15, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Tu, K.; Wang, Y.; Yao, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Dou, C.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, X. Hypoxia accelerates aggressiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells involving oxidative stress, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and non-canonical hedgehog signaling. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 1856–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.W.; Song, M.G.; Yun, B.D.; Park, J.K. Noncoding rnas associated with therapeutic resistance in pancreatic cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.A.; Moeng, S.; Sim, S.; Kuh, H.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, J.K. Microrna-based combinatorial cancer therapy: Effects of micrornas on the efficacy of anti-cancer therapies. Cells 2019, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Francesco, E.M.; Lappano, R.; Santolla, M.F.; Marsico, S.; Caruso, A.; Maggiolini, M. Hif-1alpha/gper signaling mediates the expression of vegf induced by hypoxia in breast cancer associated fibroblasts (cafs). Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morfoisse, F.; Kuchnio, A.; Frainay, C.; Gomez-Brouchet, A.; Delisle, M.B.; Marzi, S.; Helfer, A.C.; Hantelys, F.; Pujol, F.; Guillermet-Guibert, J.; et al. Hypoxia induces vegf-c expression in metastatic tumor cells via a hif-1alpha-independent translation-mediated mechanism. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, N.; Wang, L.; Esko, J.; Giordano, F.J.; Huang, Y.; Gerber, H.P.; Ferrara, N.; Johnson, R.S. Loss of hif-1alpha in endothelial cells disrupts a hypoxia-driven vegf autocrine loop necessary for tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, P.; Osorio, F.G.; Moran, J.; Cabello, E.; Alonso, A.; Freije, J.M.; Gonzalez, C. Loss of glut4 induces metabolic reprogramming and impairs viability of breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.W.; Lin, S.C.; Chen, K.F.; Lai, Y.Y.; Tsai, S.J. Induction of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-3 by hypoxia-inducible factor-1 promotes metabolic switch and drug resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 28106–28114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.C.; Vaira, V.; Caino, M.C.; Tang, H.Y.; Seo, J.H.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Ottobrini, L.; Martelli, C.; Lucignani, G.; Bertolini, I.; et al. Mitochondrial akt regulation of hypoxic tumor reprogramming. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Wang, J.H.; Fan, W.J.; Meng, Y.T.; Li, M.M.; Li, T.T.; Cui, B.; Wang, H.F.; Zhao, Y.; An, F.; et al. Glycolysis gatekeeper pdk1 reprograms breast cancer stem cells under hypoxia. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1062–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milane, L.; Duan, Z.; Amiji, M. Role of hypoxia and glycolysis in the development of multi-drug resistance in human tumor cells and the establishment of an orthotopic multi-drug resistant tumor model in nude mice using hypoxic pre-conditioning. Cancer Cell Int. 2011, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchiq, I.; Pouyssegur, J. Hypoxia, cancer metabolism and the therapeutic benefit of targeting lactate/h(+) symporters. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, A.R.; Cappello, P.; Puppo, M.; Fraone, T.; Vanni, C.; Eva, A.; Musso, T.; Novelli, F.; Varesio, L.; Giovarelli, M. Human dendritic cells differentiated in hypoxia down-modulate antigen uptake and change their chemokine expression profile. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vito, A.; El-Sayes, N.; Mossman, K. Hypoxia-driven immune escape in the tumor microenvironment. Cells 2020, 9, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betts, G.; Jones, E.; Junaid, S.; El-Shanawany, T.; Scurr, M.; Mizen, P.; Kumar, M.; Jones, S.; Rees, B.; Williams, G.; et al. Suppression of tumour-specific cd4(+) t cells by regulatory t cells is associated with progression of human colorectal cancer. Gut 2012, 61, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togashi, Y.; Shitara, K.; Nishikawa, H. Regulatory t cells in cancer immunosuppression—Implications for anticancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, M.J.; Teng, M.W.; Swann, J.; Kyparissoudis, K.; Godfrey, D.I.; Hayakawa, Y. Cd4+cd25+ t regulatory cells suppress nk cell-mediated immunotherapy of cancer. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 1582–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, R.; Yao, Z. Hypoxia-induced ccl28 promotes recruitment of regulatory t cells and tumor growth in liver cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 75763–75773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Zhu, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.T.; Ding, Y.B.; Xiao, W.M.; Lu, G.T.; Bo, P.; Shen, X.Z. Intratumor hypoxia promotes immune tolerance by inducing regulatory t cells via tgf-beta1 in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63777. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, L.W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, Q.X.; Zhang, Q. Long non-coding rna hotair mediates the switching of histone h3 lysine 27 acetylation to methylation to promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.; Wang, Y.; Lin, M.F.; Koegel, A.K.; Kotake, Y.; Grant, G.D.; Horlings, H.M.; Shah, N.; Umbricht, C.; Wang, P.; et al. Extensive and coordinated transcription of noncoding rnas within cell-cycle promoters. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Li, N.; Huang, Z.; Chen, R.; Yi, P.; Kang, R.; Tang, D.; Hu, X.; Fan, X. A novel lncrna, tcons_00006195, represses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting enzymatic activity of eno1. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, S.; Ye, F.; Shen, Y.; Tie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wei, L.; Jin, Y.; Fu, H.; Wu, Y.; et al. Long noncoding rna meg3 interacts with p53 protein and regulates partial p53 target genes in hepatoma cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; An, Y.; Song, L.; Shang, P.; Yue, Z. Long non-coding rna uca1 promotes malignant phenotypes of renal cancer cells by modulating the mir-182-5p/dll4 axis as a cerna. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzler, R.; McGeary, S.E.; Title, A.C.; Agarwal, V.; Bartel, D.P.; Stoffel, M. Impact of microrna levels, target-site complementarity, and cooperativity on competing endogenous rna-regulated gene expression. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.W.; Dinger, M.E. Endogenous microrna sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Kong, F.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Yang, C.; Wu, X.; Zhang, W. Microrna-612 suppresses the malignant development of non-small-cell lung cancer by directly targeting bromodomain-containing protein 4. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 4167–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, L.; He, P.; Yang, X.; Zhou, M.; Feng, Q. Mir-612 negatively regulates colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by targeting akt2. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, M.; Lin, Y. Microrna-612 inhibits cervical cancer progression by targeting nob1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 3149–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.; Zhao, L.; Kang, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, K.; Fu, H. Transcription factor hif1alpha promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma via long noncoding rna h19/microrna-612/bcl-2 axis. Transl. Res. 2020, 224, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Bao, L.; Niu, Y.; Wang, J.E.; Kumar, A.; Xing, C.; Wang, Y.; Luo, W. Lncihat is induced by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and promotes breast cancer progression. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yao, B.; Sun, L.; Liu, R.; Chen, T.; Niu, Y.; Tu, K.; Liu, Q. Long non-coding rna agap2-as1, functioning as a competitive endogenous rna, upregulates anxa11 expression by sponging mir-16-5p and promotes proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Song, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Han, D.; Zhang, N.; et al. Lncrna bcrt1 promotes breast cancer progression by targeting mir-1303/ptbp3 axis. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fang, E.; Rong, Y.; Han, H.; Gong, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Li, H.; Mei, P.; Li, H.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Hypoxia-induced lncrna casc9 enhances glycolysis and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer by a positive feedback loop with akt/hif-1alpha signaling. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 123–137. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yao, B.; Niu, Y.; Chen, T.; Mo, H.; Wang, L.; Guo, C.; Yao, D. Hypoxia-induced lncrna eif3j-as1 accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma progression via targeting mir-122-5p/ctnnd2 axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 518, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.L.; Zhang, M.; Ji, L.D.; Luo, Z.; Han, T.; Lu, Y.B.; Li, Y.X. Long noncoding rna fezf1-as1 predicts poor prognosis and modulates pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and invasion through mir-142/hif-1alpha and mir-133a/egfr upon hypoxia/normoxia. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 15407–15419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Hu, Q.; Nie, E.; Yu, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhi, T.; Jiang, K.; Shen, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Hypoxia induces h19 expression through direct and indirect hif-1alpha activity, promoting oncogenic effects in glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, C.; Chen, S.; Du, Y.; Shi, C.; Cheng, X. Hand2-as1 inhibits gastric adenocarcinoma cells proliferation and aerobic glycolysis via mirnas sponge. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 3053–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineo, M.; Ricklefs, F.; Rooj, A.K.; Lyons, S.M.; Ivanov, P.; Ansari, K.I.; Nakano, I.; Chiocca, E.A.; Godlewski, J.; Bronisz, A. The long non-coding rna hif1a-as2 facilitates the maintenance of mesenchymal glioblastoma stem-like cells in hypoxic niches. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 2500–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Meng, F.; Sun, B.; Jin, X.; Jia, C. The long noncoding rna hif1a-as2 facilitates cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.W.; Chiang, W.F.; Wu, A.T.H.; Wu, M.H.; Wang, L.Y.; Yu, Y.L.; Hung, Y.W.; Wang, W.C.; Chu, C.Y.; Hung, C.L.; et al. Long noncoding rna lnchifcar/mir31hg is a hif-1alpha co-activator driving oral cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Xue, X.; Xie, H.; Shi, H.; Hu, Y. A lncrna coordinates with ezh2 to inhibit hif-1alpha transcription and suppress cancer cell adaption to hypoxia. Oncogene 2020, 39, 1860–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, K.; Lin, Q.; Li, H.; Xue, X.; Ge, W.; He, H.; Liu, D.; Xie, H.; et al. A novel lncrna hitt forms a regulatory loop with hif-1alpha to modulate angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Fu, Q.; Jing, C.; Zhang, X.; Qin, T.; Pan, Y. Lncrna hotair knockdown inhibits glycolysis by regulating mir-130a-3p/hif1a in hepatocellular carcinoma under hypoxia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, G.; Xie, S.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z. Long non-coding rna hottip promotes hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of malignant glioma by regulating the mir-101/zeb1 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, H.; Feng, W.; Huang, S.; An, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, K. Long non-coding rna hottip promotes hypoxia-induced glycolysis through targeting mir-615-3p/hmgb3 axis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 862, 172615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; He, F.; Hou, Y.; Tu, G.; Li, Q.; Jin, T.; Zeng, H.; Qin, Y.; Wan, X.; Qiao, Y.; et al. A novel hypoxic long noncoding rna kb-1980e6.3 maintains breast cancer stem cell stemness via interacting with igf2bp1 to facilitate c-myc mrna stability. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1609–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Gui, S.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, X.; Qiu, B.; Zhang, X.; Pan, J.; Fan, J.; Qi, S.; Zhang, G. Long intergenic non-protein coding rna 00475 silencing acts as a tumor suppressor in glioma under hypoxic condition by impairing microrna-449b-5p-dependent agap2 up-regulation. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920940936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Xia, C.; Xu, Y. Hif-1alpha induced lncrna linc00511 accelerates the colorectal cancer proliferation through positive feedback loop. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 110014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhou, M.; Meng, G.; Liu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Li, C.; Xie, W.; Wu, N.; et al. Hypoxia-sensitive linc01436 is regulated by e2f6 and acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-30a-3p in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.B.; Chen, F.; Bai, X.F. Long noncoding rna malat1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma growth under hypoxia via sponging microrna-200a. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, R.; Mo, H.; Niu, Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Han, S.; Tu, K.; Liu, Q. Long non-coding rna mapkapk5-as1/plagl2/hif-1alpha signaling loop promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Tao, Z.; Hou, M.; Ma, H. Overexpression of hif-2alpha-dependent neat1 promotes the progression of non-small cell lung cancer through mir-101-3p/sox9/wnt/beta-catenin signal pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 52, 368–381. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Wang, P.; Lou, J.; Zhao, J. Knockdown of lncrna neat1 suppresses hypoxia-induced migration, invasion and glycolysis in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells through regulation of mir-206 and mir-599. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.; Wen, C.; Huo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhan, Q.; Cheng, D.; Chen, H.; Deng, X.; Peng, C.; et al. Long noncoding rna norad, a novel competing endogenous rna, enhances the hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Chen, T.; Mo, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, Q.; Guo, C. Hypoxia-inducible long noncoding rna npsr1-as1 promotes the proliferation and glycolysis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating the mapk/erk pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 533, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, S.J.; Zhu, S.; Jin, Y.; Cui, S.P.; Chen, J.Y.; Xiang, C.; Li, Q.Y.; He, C.; Zhao, S.F.; et al. Hypoxia-induced lncrna-nutf2p3-001 contributes to tumorigenesis of pancreatic cancer by derepressing the mir-3923/kras pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 6000–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Bao, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Luo, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, M.; Wang, J.E.; Fang, Y.V.; Kumar, A.; et al. Hif2-induced long noncoding rna rab11b-as1 promotes hypoxia-mediated angiogenesis and breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.H.; Chieh-Yu Lai, J.; Hsu, K.W.; Wu, K.J. Hypoxia-induced lncrna rp11-390f4.3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (emt) and metastasis through upregulating emt regulators. Cancer Lett. 2020, 483, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shi, X.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Hou, K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y.; Qu, X.; Che, X.; et al. Long non-coding rna uca1 upregulation promotes the migration of hypoxia-resistant gastric cancer cells through the mir-7-5p/egfr axis. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 368, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.H.; Bai, X.F.; Hu, X.H. Knockdown of lncrna xist inhibits hypoxia-induced glycolysis, migration and invasion through regulating mir-381-3p/nek5 axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2505–2517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Feng, Y.; Liu, T.; Guo, W. Epigenetic regulation of cancer progression by ezh2: From biological insights to therapeutic potential. Biomark. Res. 2018, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.Y.; Rong, R.; Liu, X.; Ye, K. Pike/nuclear pi 3-kinase signaling mediates the antiapoptotic actions of ngf in the nucleus. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3995–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Q.; Ye, K. The roles of pike in tumorigenesis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hou, W.Z.; Chen, X.L.; Qin, L.S.; Xu, Z.J.; Liao, G.M.; Chen, D.; Hu, L.J.; Mao, Z.M.; Huang, J.-S.; Yuan, Q.; et al. Mir-449b-5p inhibits human glioblastoma cell proliferation by inactivating wnt2b/wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 5549–5557. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Yang, X.; He, X.; Ma, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, M.; Yu, S. Microrna-449b-5p suppresses the growth and invasion of breast cancer cells via inhibiting crept-mediated wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 302, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Han, G. Linc00667/mir-449b-5p/yy1 axis promotes cell proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xi, T.; Zheng, L. Transcriptional factor yin yang 1 promotes the stemness of breast cancer cells by suppressing mir-873-5p transcriptional activity. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Chu, Y.; Song, Y.; Ding, L.; Zhu, B.; Zhai, W.; Wang, X.; Kuang, Y.; Ren, F.; et al. Crept is required for murine stem cell maintenance during intestinal regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, S.Y.; Jun, Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Nam, J.S. Roles of wnt target genes in the journey of cancer stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, R.; Li, S.; Hong, X. Long non-coding rna linc00511/mir-150/mmp13 axis promotes breast cancer proliferation, migration and invasion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 165957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xie, X.; Bi, R.; Ding, F.; Mei, J. Knockdown of linc00511 inhibits tgf-beta-induced cell migration and invasion by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and down-regulating mmps expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Bi, Z.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, Y.; et al. Linc00511 acts as a competing endogenous rna to regulate vegfa expression through sponging hsa-mir-29b-3p in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, M.; Xu, R. Lncrna linc00511 acts as an oncogene in colorectal cancer via sponging mir-29c-3p to upregulate nfia. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 13413–13424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, F.; Han, Y.; Xue, H.; Sun, X.; Jiang, Y.; Tian, Z. Linc00511-dependent inhibition of il-24 contributes to the oncogenic role of hnf4alpha in colorectal cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 320, G338–G350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tan, F.; Wang, L.F.; Liu, D.H.; Wang, R.J.; Yin, X.Z. Mir-153-5p promotes sensibility of colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin via targeting bcl-2-mediated autophagy pathway. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2020, 84, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Piao, H.L.; Kim, B.J.; Yao, F.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Siverly, A.N.; Lawhon, S.E.; Ton, B.N.; et al. Long noncoding rna malat1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhang, G.Q.; Pan, S.H.; Ji, L.; Kong, R.; Wang, G.; Jia, Y.H.; et al. Long noncoding rna malat1 promotes aggressive pancreatic cancer proliferation and metastasis via the stimulation of autophagy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2232–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; He, J.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Huang, W.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, S. Long noncoding rna malat1 inhibits the apoptosis and autophagy of hepatocellular carcinoma cell by targeting the microrna-146a/pi3k/akt/mtor axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, P.R. Mir-200a with cdc7 as a direct target declines cell viability and promotes cell apoptosis in wilm’s tumor via wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 2409–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba, M.C.; Ba, Z.; Long, H.; Cui, S.Z.; Gong, Y.F.; Yan, Z.F.; Lin, K.P.; Wu, Y.B.; Tu, Y.N. Lncrna ac093818.1 accelerates gastric cancer metastasis by epigenetically promoting pdk1 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudreault, M.; Vigneault, F.; Gingras, M.E.; Leclerc, S.; Carrier, P.; Germain, L.; Guerin, S.L. Transcriptional regulation of the human alpha6 integrin gene by the transcription factor nfi during corneal wound healing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 3758–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Expression of delta-catenin is associated with progression of human astrocytoma. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 514. [Google Scholar]
- Nopparat, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, J.P.; Chen, Y.H.; Zheng, D.; Neufer, P.D.; Fan, J.M.; Hong, H.; Boykin, C.; Lu, Q. Delta-catenin, a wnt/beta-catenin modulator, reveals inducible mutagenesis promoting cancer cell survival adaptation and metabolic reprogramming. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Lan, R.; Fu, L.; Zhang, L. Delta-catenin promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 809–817. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, P.; Li, L.; Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Bai, J.; Zheng, J. Ptbp3-mediated regulation of zeb1 mrna stability promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Chen, F.; Yong, H.; Lin, T.; Li, J.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, T.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Song, J.; et al. Ptbp3 contributes to colorectal cancer growth and metastasis via translational activation of hif-1alpha. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Weng, L.; Jia, Y.; Liu, B.; Wu, S.; Xue, L.; Yin, X.; Mao, A.; Wang, Z.; Shang, M. Ptbp3 promotes malignancy and hypoxia-induced chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells by atg12 up-regulation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 2917–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Di, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S. Lncrna fezf1-as1 modulates cancer stem cell properties of human gastric cancer through mir-363-3p/hmga2. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 963689720925059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Sun, X.J.; Yin, J.J.; Yin, M.; Wang, W.; Nie, Z.Q.; Xu, J. Long non-coding rna fezf1-as1 promotes cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through jak2/stat3 signaling pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, C.; Huang, J.; Luo, P.; Mo, D.; Wang, H. Lncrna fezf1-as1 promotes non-small lung cancer cell migration and invasion through the up-regulation of notch1 by serving as a sponge of mir-34a. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yao, S.; Jin, G.; Du, J.; Han, W.; et al. Lncrna-fezf1-as1 promotes tumor proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer by regulating pkm2 signaling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4808–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, S.; Li, G.; Lin, Q.; Ye, L.; Wang, Y.; Wei, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, W.; et al. Fezf1-as1/mir-107/znf312b axis facilitates progression and warburg effect in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Shao, M.Y.; Zou, S.C.; Xiao, Z.F.; Chen, Z.C. Mir-101-3p inhibits emt to attenuate proliferation and metastasis in glioblastoma by targeting trim44. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 141, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Hui, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, L.; Peng, P.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; et al. Long noncoding rna mapkapk5-as1 promotes colorectal cancer proliferation by partly silencing p21 expression. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Chen, W.C.; Shi, P.C.; Liu, M.R.; Jiang, T.; Song, H.; Wang, J.Q.; Fan, R.Z.; Pei, D.S.; Song, J. Long noncoding rna mapkapk5-as1 promotes colorectal cancer progression by cis-regulating the nearby gene mk5 and acting as a let-7f-1-3p sponge. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, X.; Xiong, Y. Incrna mapkapk5-as1 promotes proliferation and migration of thyroid cancer cell lines by targeting mir-519e-5p/ywhah. Eur. J. Histochem. 2020, 64, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.S.; Yang, M.C.; Singh, S.; Chou, Y.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, R.H. Lncrna norad is repressed by the yap pathway and suppresses lung and breast cancer metastasis by sequestering s100p. Oncogene 2019, 38, 5612–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, P.; Qiao, F.; Wu, H.; Cui, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Fan, H. Lncrna uca1 promotes tumor metastasis by inducing mir-203/zeb2 axis in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, Y.; Li, X.; Luan, Y.; Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Hao, Y.; Oleg Vladimir, B.; Jia, L. Circulating lncrna uca1 promotes malignancy of colorectal cancer via the mir-143/myo6 axis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, R.; Huang, B.; Wu, D.; Yang, L.; Lu, H.; Jin, D.; et al. Long non-coding rna rab11b-as1 prevents osteosarcoma development and progression via its natural antisense transcript rab11b. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26770–26786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Puca, F.; Tosti, N.; Federico, A.; Kuzay, Y.; Pepe, A.; Morlando, S.; Savarese, T.; D’Alessio, F.; Colamaio, M.; Sarnataro, D.; et al. Hmga1 negatively regulates numb expression at transcriptional and post transcriptional level in glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elcheva, I.A.; Wood, T.; Chiarolanzio, K.; Chim, B.; Wong, M.; Singh, V.; Gowda, C.P.; Lu, Q.; Hafner, M.; Dovat, S.; et al. Rna-binding protein igf2bp1 maintains leukemia stem cell properties by regulating hoxb4, myb, and aldh1a1. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Lv, M.; Chang, Y.; Peng, J.; et al. Mirna-98-5p targeting igf2bp1 induces mesenchymal stem cell apoptosis by modulating pi3k/akt and p53 in immune thrombocytopenia. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidensdorfer, D.; Stohr, N.; Baude, A.; Lederer, M.; Kohn, M.; Schierhorn, A.; Buchmeier, S.; Wahle, E.; Huttelmaier, S. Control of c-myc mrna stability by igf2bp1-associated cytoplasmic rnps. RNA 2009, 15, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, B. Long noncoding rna casc9/mir-519d/stat3 positive feedback loop facilitate the glioma tumourigenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 6338–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Geng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Z.; Shi, K.Q.; Pan, C.; Wu, J. Lncrna casc9 interacts with cpsf3 to regulate tgf-beta signaling in colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Gu, J.; Feng, W.; Lei, T.; Huang, J.; Pu, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. Long non-coding rna casc9 promotes gefitinib resistance in nsclc by epigenetic repression of dusp1. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, H. Long noncoding rna casc9 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer via sponging mir-488-3p. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 1830–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokulnath, P.; de Cristofaro, T.; Manipur, I.; Di Palma, T.; Soriano, A.A.; Guarracino, M.R.; Zannini, M. Long non-coding rna hand2-as1 acts as a tumor suppressor in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J.; Tong, Z. Hand2-as1 works as a cerna of mir-3118 to suppress proliferation and migration in breast cancer by upregulating phlpp2. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8124570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J. Hand2-as1 inhibits invasion and metastasis of cervical cancer cells via microrna-330-5p-mediated ldoc1. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, Y.; Ji, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, F.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Aldape, K.; Cantley, L.C.; Lu, Z. Erk1/2-dependent phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of pkm2 promotes the warburg effect. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Peng, S.; Li, P.; Ma, L.; Gan, X. High expression of nek2 promotes lung cancer progression and drug resistance and is regulated by mutant egfr. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 475, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Xia, J.; Xu, H.; Frech, I.; Tricot, G.; Zhan, F. Nek2 promotes aerobic glycolysis in multiple myeloma through regulating splicing of pyruvate kinase. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Hmgb3 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of glioblastoma and is negatively regulated by mir-200b-3p and mir-200c-3p. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2018, 36, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lin, F.; Wan, T.; Chen, A.; Wang, H.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, W.; Liao, S.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; et al. Zeb1 enhances warburg effect to facilitate tumorigenesis and metastasis of hcc by transcriptionally activating pfkm. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5926–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Zeng, Z.; Xiong, W.; et al. The role of wnt signaling pathway in tumor metabolic reprogramming. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 3789–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferezin, C.C.; Basei, F.L.; Melo-Hanchuk, T.D.; de Oliveira, A.L.; Peres de Oliveira, A.; Mori, M.P.; de Souza-Pinto, N.C.; Kobarg, J. Nek5 interacts with lonp1 and its kinase activity is essential for the regulation of mitochondrial functions and mtdna maintenance. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 546–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, B.; Wang, M.; Hou, N.; Hu, X.; Jia, G.; Qin, X.; Zuo, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, K.; Song, W.; et al. Atp-dependent lon protease contributes to helicobacter pylori-induced gastric carcinogenesis. Neoplasia 2016, 18, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xu, G.; Wang, W. Long noncoding rna cdkn2b-as1 facilitates lung cancer development through regulating mir-378b/nr2c2. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 10641–10649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Li, Y.; He, F.; Kong, J. Lncrna cdkn2b-as1 promotes cell viability, migration, and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma via sponging mir-424-5p. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 6807–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Su, D.; Luo, F.; Zhou, F. Long noncoding rna cdkn2b-as1 interacts with mir-411-3p to regulate ovarian cancer in vitro and in vivo through hif-1a/vegf/p38 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 514, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandrika, L.; Lieberman, R.; Koul, S.; Kumar, B.; Maroni, P.; Chandhoke, R.; Meacham, R.B.; Koul, H.K. Hypoxia-associated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated androgen receptor activation and increased hif-1alpha levels contribute to emergence of an aggressive phenotype in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2009, 28, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, S.; Jain, P.; So, J.; Shahidi, S.; Chung, S.; Koritzinsky, M. P38 mapk inhibition mitigates hypoxia-induced ar signaling in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.M.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, Z.W.; Lei, L.; Fu, S.Z.; Chen, Y. Long noncoding rna fam201a involves in radioresistance of non-small-cell lung cancer by enhancing egfr expression via mir-370. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5802–5814. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Jin, Y.M.; Lyu, X.M.; Fan, L.M.; Wu, F. Long noncoding rna h19 regulates hif-1alpha/axl signaling through inhibiting mir-20b-5p in endometrial cancer. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 2454–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Z.; Tian, Y.F.; Wu, H.; Ouyang, S.Y.; Kuang, W.L. Lncrna h19 promotes glioma angiogenesis through mir-138/hif-1alpha/vegf axis. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Li, O.; Zheng, W.; Xiao, W.Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Cai, G.Y.; He, J.C.; Chen, X.M. Lncrna hotair regulates hif-1alpha/axl signaling through inhibition of mir-217 in renal cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; You, H.; Yu, S. Long non-coding rna hoxa-as2 promotes the expression levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and programmed death-ligand 1, and regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression via mir-519. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Weng, M.; Zhou, D.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, E.; Quan, Z. Long non-coding rna linc00152 promotes gallbladder cancer metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating hif-1alpha via mir-138. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 160247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.C.; Zhu, W.; Li, S.J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhuo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.X.; et al. Foxc1-mediated linc00301 facilitates tumor progression and triggers an immune-suppressing microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating the hif1alpha pathway. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; He, D.; Xiao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Cao, K. Long noncoding rna linc00518 induces radioresistance by regulating glycolysis through an mir-33a-3p/hif-1alpha negative feedback loop in melanoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Zhao, L. Lncrna nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion by targeting mir-186-5p/hif-1alpha in osteosarcoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 6502–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.; Guo, T.; Cao, C. Silencing of long noncoding rna snhg6 inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via mir-186-5p/hif1alpha axis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 2844–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhao, Z.; Song, J.; Zhang, D.; Wu, F.; Tu, J.; Xu, M.; Ji, J. Lncrna-snhg6 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting mir-6509-5p and hif1a. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Deng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, C. Long noncoding rna snhg6 promotes carcinogenesis by enhancing ybx1-mediated translation of hif1alpha in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Huan, L.; Guo, T.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, S.; Xu, Y.; Liang, L.; He, X. Lncrna snhg11 facilitates tumor metastasis by interacting with and stabilizing hif-1alpha. Oncogene 2020, 39, 7005–7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Yan, J.; Cheng, F. Lncrna tmpo-as1 up-regulates the expression of hif-1alpha and promotes the malignant phenotypes of retinoblastoma cells via sponging mir-199a-5p. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Hu, L.; Li, S.; Shen, J.; Wang, D.; Xu, R.; Yang, H. Long non-coding rna taurine upregulated gene 1 promotes osteosarcoma cell metastasis by mediating hif-1alpha via mir-143-5p. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, A.; Tang, X. Long non-coding rna uca1 enhances tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells through a mir-18a-hif1alpha feedback regulatory loop. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 14733–14743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.G.; Cao, M.Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.Y.; Sun, Q.L. Lncrna xist modulates hif-1a/axl signaling pathway by inhibiting mir-93-5p in colorectal cancer. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Gao, H.; Liu, K.; Gao, B.; Ren, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, F. The lncrna zeb2-as1 is upregulated in gastric cancer and affects cell proliferation and invasion via mir-143-5p/hif-1alpha axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linger, R.M.; Cohen, R.A.; Cummings, C.T.; Sather, S.; Migdall-Wilson, J.; Middleton, D.H.; Lu, X.; Baron, A.E.; Franklin, W.A.; Merrick, D.T.; et al. Mer or axl receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition promotes apoptosis, blocks growth and enhances chemosensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3420–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, E.S.; Cichon, M.A.; Vyas, J.J.; Patel, N.; Ghali, L.; Cerio, R.; Storey, A.; O’Toole, E.A. Axl promotes cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma survival through negative regulation of pro-apoptotic bcl-2 family members. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, E.B.; Fuh, K.C.; Castellini, L.; Viswanathan, K.; Finger, E.C.; Diep, A.N.; LaGory, E.L.; Kariolis, M.S.; Chan, A.; Lindgren, D.; et al. Direct regulation of gas6/axl signaling by hif promotes renal metastasis through src and met. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13373–13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tan, J.; Li, E.; Li, F. Overexpression of microrna-519d-3p suppressed the growth of pancreatic cancer cells by inhibiting ribosomal protein s15a-mediated wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 304, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Qi, Y.; Wang, X.L.; Gu, J.J.; Shi, T.M. Down-regulation of lncrna blacat1 inhibits ovarian cancer progression by suppressing the wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway via regulating mir-519d-3p. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 467, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, W.; Qiu, H.; Yu, H.; Du, J. Mir-519d-3p overexpression inhibits p38 and pi3k/akt pathway via targeting vegfa to attenuate the malignant biological behavior of non-small cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 10257–10266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Shi, S.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Y.; Zhong, T. Microrna-519d-3p inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis by targeting hif-2alpha in cervical cancer under hypoxic conditions. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhu, L.; Xu, L.; Pei, Q.; Cao, Y. Linc00152 knock-down suppresses esophageal cancer by egfr signaling pathway. Open Med. 2020, 15, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liao, W.; Wu, Q.; Huang, X.; Pan, Z.; Chen, W.; Gu, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X.; et al. Linc00152 upregulates zeb1 expression and enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition and oxaliplatin resistance in esophageal cancer by interacting with ezh2. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhong, G.; Xu, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. A positive feedback loop of long noncoding rna linc00152 and klf5 facilitates breast cancer growth. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 619915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Xie, M.; Ni, W.; Chen, S. Klf5 promotes hypoxia-induced survival and inhibits apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells via hif-1alpha. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. Long non-coding rna snhg6 promotes tumorigenesis in melanoma cells via the microrna-101-3p/rap2b axis. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Xu, J.; Deng, R.; Wei, W.; Zhou, B.; Yue, C.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, H. Snhg 6 promotes the progression of colon and rectal adenocarcinoma via mir-101-3p and wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lai, Q.; He, J.; Li, Q.; Ding, J.; Lan, Z.; Gu, C.; Yan, Q.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, X.; et al. Lncrna snhg6 promotes proliferation, invasion and migration in colorectal cancer cells by activating tgf-beta/smad signaling pathway via targeting upf1 and inducing emt via regulation of zeb1. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.; Xiao, G.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Hui, Z.; Sun, X.; Qin, S.; Zhang, B.; Du, N.; et al. Snhg6 functions as a competing endogenous rna to regulate e2f7 expression by sponging mir-26a-5p in lung adenocarcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1434–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamura, T.; Sato, S.; Iwai, K.; Czyzyk-Krzeska, M.; Conaway, R.C.; Conaway, J.W. Activation of hif1alpha ubiquitination by a reconstituted von hippel-lindau (vhl) tumor suppressor complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10430–10435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; White, S.B.; Zhao, Q.; Lee, F.S. Hif-1alpha binding to vhl is regulated by stimulus-sensitive proline hydroxylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9630–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Dong, S.; Cha, Y.; Yuan, X. Snhg11 promotes cell proliferation in colorectal cancer by forming a positive regulatory loop with c-myc. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 527, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doe, M.R.; Ascano, J.M.; Kaur, M.; Cole, M.D. Myc posttranscriptionally induces hif1 protein and target gene expression in normal and cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y. Long non-coding rna xist sponges mir-34a to promotes colon cancer progression via wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Gene 2018, 665, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Song, X.; Zhang, S.; Niu, M.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, T. Long non-coding rna tmpo-as1 serves as a tumor promoter in pancreatic carcinoma by regulating mir-383-5p/sox11. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, M.; Xu, R. Long noncoding rna tmpo-as1/mir-126-5p/brcc3 axis accelerates gastric cancer progression and angiogenesis via activating pi3k/akt/mtor pathway. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Y. Lncrna tmpo-as1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion through sponging mir-329-3p to stimulate foxk1-mediated akt/mtor signaling pathway. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 5235–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, P.; Ge, H.; Song, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J. Overexpression of zeb2-as1 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by stabilizing zeb2 mrna in head neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4269–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Li, H.; Sun, R.; Li, P.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yin, C. Long non-coding rna zeb2-as1 promotes the proliferation, metastasis and epithelial mesenchymal transition in triple-negative breast cancer by epigenetically activating zeb2. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3271–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, W.; Yang, R.; Xie, W.; Wang, D. Lncrna zeb2-as1 contributes to the tumorigenesis of gastric cancer via activating the wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 456, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Cai, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xue, Y. Long non-coding rna h19 regulates glioma angiogenesis and the biological behavior of glioma-associated endothelial cells by inhibiting microrna-29a. Cancer Lett. 2016, 381, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, Z.Z.; Wu, H.; Kuang, W.L. Lncrna h19 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of glioma by regulating wnt5a/beta-catenin pathway via targeting mir-342. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Zhong, Z.; Huang, M.; Tian, Q.; Jiang, R.; Chen, J. Lncrna h19 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of bladder cancer by mir-29b-3p as competing endogenous rna. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 1887–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.M.; Bock, J.M.; Harari, P.M. Epidermal growth factor receptor blockade with c225 modulates proliferation, apoptosis, and radiosensitivity in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 1935–1940. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandru, O.; Purcaru, S.O.; Tataranu, L.G.; Lucan, L.; Castro, J.; Folcuti, C.; Artene, S.A.; Tuta, C.; Dricu, A. The influence of egfr inactivation on the radiation response in high grade glioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, F.G., 2nd; Simmons, M.L.; Chang, S.M.; Prados, M.D.; Larson, D.A.; Sneed, P.K.; Wara, W.M.; Berger, M.S.; Chen, P.; Israel, M.A.; et al. Egfr overexpression and radiation response in glioblastoma multiforme. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 51, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuneo, K.C.; Nyati, M.K.; Ray, D.; Lawrence, T.S. Egfr targeted therapies and radiation: Optimizing efficacy by appropriate drug scheduling and patient selection. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 154, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, H. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-mediated characteristic features of cancer cells for tumor radioresistance. J. Radiat. Res. 2016, 57 (Suppl. S1), i99–i105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabakov, A.E.; Yakimova, A.O. Hypoxia-induced cancer cell responses driving radioresistance of hypoxic tumors: Approaches to targeting and radiosensitizing. Cancers 2021, 13, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Qiu, Q.; Li, Z.; Sachdeva, M.; Min, H.; Cardona, D.M.; DeLaney, T.F.; Han, T.; Ma, Y.; Luo, L.; et al. Hif-1 alpha regulates the response of primary sarcomas to radiation therapy through a cell autonomous mechanism. Radiat. Res. 2015, 183, 594–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Luo, J. Long non-coding rna (lncrna) urothelial carcinoma-associated 1 (uca1) enhances tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells via inhibiting mtor signaling pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 3860–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.J.; Shyu, W.C.; Chang, C.W.; Wang, C.C.; Wu, C.P.; Lee, H.T.; Chen, L.J.; Hsieh, C.H. Tumor hypoxia regulates forkhead box c1 to promote lung cancer progression. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, C.; Caltabiano, R.; Broggi, G.; Russo, A.; Puzzo, L.; Avitabile, T.; Longo, A.; Reibaldi, M.; Barbagallo, D.; Di Pietro, C.; et al. Lncrna linc00518 acts as an oncogene in uveal melanoma by regulating an rna-based network. Cancers 2020, 12, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhu, H.; Han, S. Linc00518 interference inhibits non-small cell lung cancer by upregulating mir216b-5p expression. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 11041–11050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, W.; Ding, Y.; Ma, S.; Ruan, H.; Wang, J.; Lu, F. Long noncoding rna linc00518 acts as a competing endogenous rna to promote the metastasis of malignant melanoma via mir-204-5p/ap1s2 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.B.; Wei, H.; Wang, J.S.; Li, L.; Chen, A.Y.; Li, Z.G. Down-regulated expression of linc00518 prevents epithelial cell growth and metastasis in breast cancer through the inhibition of cdx2 methylation and the wnt signaling pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Sun, M.; Geng, H.; Tian, S. Long non-coding rna linc00518 promotes paclitaxel resistance of the human prostate cancer by sequestering mir-216b-5p. Biol. Cell 2019, 111, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H. Linc00518 contributes to multidrug resistance through regulating the mir-199a/mrp1 axis in breast cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadari, N.; Deng, S.; Li, W. The transcriptional factors hif-1 and hif-2 and their novel inhibitors in cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.T.; Harris, A.L. Small-molecule inhibitors of the hif pathway and synthetic lethal interactions. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hill, H.; Christie, A.; Kim, M.S.; Holloman, E.; Pavia-Jimenez, A.; Homayoun, F.; Ma, Y.; Patel, N.; Yell, P.; et al. Targeting renal cell carcinoma with a hif-2 antagonist. Nature 2016, 539, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, Y.; Konno, M.; Asai, A.; Koseki, J.; Kawamoto, K.; Miyoshi, N.; Takahashi, H.; Nishida, N.; Haraguchi, N.; Sakai, D.; et al. Hypoxia stimulates the cytoplasmic localization of oncogenic long noncoding rna linc00152 in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, X.; Xue, X.; Li, L.; Hu, Y. A long noncoding rna sensitizes genotoxic treatment by attenuating atm activation and homologous recombination repair in cancers. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, J.; Tang, H.; Zhai, D.; Huang, D.; Ling, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Lncrna snord3a specifically sensitizes breast cancer cells to 5-fu by sponging mir-185-5p to enhance umps expression. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeng, S.; Son, S.W.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Kuh, H.J.; Park, J.K. Extracellular vesicles (evs) and pancreatic cancer: From the role of evs to the interference with ev-mediated reciprocal communication. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, K.; Teng, B.; Huang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Qiu, Z. Hypoxic tumor-derived exosomal long noncoding rna uca1 promotes angiogenesis via mir-96-5p/amotl2 in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, J.J.; Marrades, R.M.; Molins, L.; Vinolas, N.; Moises, J.; Canals, J.; Han, B.; Li, Y.; Martinez, D.; Monzo, M.; et al. Extracellular vesicle lincrna-p21 expression in tumor-draining pulmonary vein defines prognosis in nsclc and modulates endothelial cell behavior. Cancers 2020, 12, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Xu, F.; Li, X. Inhibition of hif1a-as1 promoted starvation-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis by reducing hif-1alpha/mtor-mediated autophagy. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, W.; Du, Q.; Xu, T.; Xu, W. Long noncoding rna hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha-antisense rna 1 promotes tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis through caspase 3 in kupffer cells. Medicine 2018, 97, e9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.H.; Kuo, W.W.; Shih, H.N.; Cheng, S.F.; Yang, C.K.; Chen, M.C.; Tu, C.C.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Liao, P.H.; Huang, C.Y. Foxc1 regulation of mir-31-5p confers oxaliplatin resistance by targeting lats2 in colorectal cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xue, M. Long noncoding rna linc00511 regulates the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and autophagy of trophoblast cells to mediate pre-eclampsia progression through modulating the mir-31-5p/homeobox protein a7 axis. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2020, 46, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniue, K.; Akimitsu, N. The functions and unique features of lncrnas in cancer development and tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Son, S.W.; Moeng, S.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, J.K. The role of noncoding rnas in the regulation of anoikis and anchorage-independent growth in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hompland, T.; Fjeldbo, C.S.; Lyng, H. Tumor hypoxia as a barrier in cancer therapy: Why levels matter. Cancers 2021, 13, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LncRNA | Type of Cancer | Expression (Cell Lines and/or Tissues) | Induction Condition | In Vivo Experiment | Clinical Relevance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC093818.1 | Breast cancer | Overexpressed in triple-negative breast cancer tissues and cell lines (BT-20, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468, and SUM159) | Upregulated in MDA-MB-231 and SUM159 cells by hypoxia (1% O2) | Orthotopic implantation of MDA-MB-231 cells stably knocking down AC093818.1 | – | [46] |
| AGAP2-AS1 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Abundantly expressed in cancer tissues and cell lines (Hep3B, SMCC-7721, Huh7, HCCLM3, and MHCC-97H) | Increased in Hep3B cells under hypoxia | Tail vein injections of AGAP2-AS1-overexpressing Hep3B cells or AGAP2-AS1-silencing HCCLM3 cells | Poor overall survival of patients with high AGAP2-AS1 expression | [47] |
| BCRT1 | Breast cancer | Upregulated in cancer tissues compared to normal controls | Increased in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells under hypoxic stress | Subcutaneous or tail vein injections of MDA-MB-231 cells stably overexpressing BCRT1 | High expression of BCRT1 is correlated with poor overall survival and disease-free survival | [48] |
| CASC9 | Pancreatic cancer | – | Increased in PANC-1 and SW1990 cells by hypoxia (1% O2) | Subcutaneous or tail vein injections of CASC9-depleted SW1990 cells | [49] | |
| EIF3J-AS1 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Upregulated in cancer tissues and cell lines (HepG2, SMCC-7721, HCCLM3, and MHCC-97H) | Induced by hypoxia in SMCC-7721 cells | – | Prognostic features (size, invasion and stages) are associated with EIF3J-AS1 levels | [50] |
| FEZF1-AS1 | Pancreatic cancer | Upregulated in cancer tissues and cell lines (PANC-1, SW1990, HuP, and CFPAC-1) | Induced by hypoxia (1% O2) in PANC-1 and SW1990 cells | – | Positively associated with advanced TNM stages | [51] |
| H19 | Cholangiocarcinoma | Upregulated in carcinoma tissues compared to normal bile duct tissues | Increased by HIF-1α overexpression | Subcutaneous injections of cholangiocarcinoma cells transduced with lentiviral vectors encoding small hairpin RNA (shRNA) against HIF-1α | – | [45] |
| Glioblastoma | – | Increased in U87 and U251 cells following exposure to hypoxia (2% O2) | Subcutaneous injections of U87 cells stably knocking down HIF-1α | Patients with high H19 levels show poor overall survival | [52] | |
| HAND2-AS1 | Gastric cancer | Downregulated in cancer tissues compared to adjacent control tissues | Reduced by hypoxia (1% O2) in AGS cells | – | – | [53] |
| HIF1A-AS2 | Glioblastoma multiforme | Abundantly expressed in cancer tissues | Upregulated in mesenchymal glioblastoma stem cells exposed to hypoxic conditions (1% O2) | Intracranial xenografts generated by implanting HIF1A-AS2-depleted mesenchymal glioblastoma stem cells | – | [54] |
| Bladder cancer | Increased in cancer tissues from patients treated with cisplatin | Upregulated in cisplatin-resistant and cobalt chloride (CoCl2)-treated cells | – | – | [55] | |
| HIFCAR | Oral cancer | Overexpressed in cancer tissues compared to non-cancerous tissues | Induced by hypoxia (1% O2) and CoCl2 treatment in HeLa cells | Tail vein injections of HIFCAR-depleted SAS cells | High HIFCAR levels are associated with worse overall survival, tumor differentiation, and lymph node metastasis | [56] |
| HITT | Colorectal cancer | Downregulated in cancer tissues compared to normal controls | Decreased by hypoxia (1% O2) in HCT116 and HeLa cells | Subcutaneous injections of HCT116 cells stably overexpressing HITT | Negatively associated with TNM classification | [57,58] |
| HOTAIR | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Upregulated in cancer tissues | Augmented in HepG2 and Huh7 cells after hypoxic exposure (1% O2) | – | – | [59] |
| HOTTIP | Glioblastoma | Upregulated in metastatic glioma tissues compared to non-metastatic tissues | Increased in U87 and U251 cells under hypoxia (1% O2) | – | Negatively correlated with the survival rate of patients | [60] |
| Lung cancer | Abundant in cancer tissues compared to normal controls | Induced in A549 and H1299 cells following hypoxic exposure (1% O2) | – | – | [61] | |
| KB-1980E6.3 | Breast cancer | Highly expressed in cancer tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues | Elevated in multiple cell lines (e.g., BT549 and Hs578T) under hypoxic conditions (1% O2) | Subcutaneous injections of stem cells from Hs578T in which KB-1980E6.3 is silenced | Negatively correlated with the overall survival of patients | [62] |
| LINC00475 | Glioblastoma | – | Upregulated in LN229 cells exposed to hypoxia (1% O2) | Injections of lentiviral vectors encoding shRNA against LINC00475 into mice bearing LN229 cells | High expression is correlated with the stage of cancer | [63] |
| LINC00511 | Colorectal cancer | Abundantly expressed in cancer tissues compared to normal tissues | Transcription is promoted by HIF-1α overexpression | – | The level of LINC00511 is negatively correlated with the overall survival of patients | [64] |
| LINC01436 | Lung cancer | Overexpressed in cancer tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues | Increased in H1299 cells under hypoxic conditions (1% O2) | Subcutaneous or tail vein injections of A549 cells stably overexpressing LINC01436 | High levels are associated with worse overall survival of patients | [65] |
| MALAT1 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | – | Increased in several cell lines (Huh7, SNU-423, PLC, and Hep3B) under hypoxic conditions | – | – | [66] |
| MAPKAPK5-AS1 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Highly expressed in cancer tissues | Increased by hypoxia (1% O2) in Hep3B cells | Subcutaneous or tail vein injections of MAPKAPK5-AS1-knockdown HCCLM3 cells or MAPKAPK5-AS1-overexpressing Hep3B cells | Positively associated with poor prognosis and pathological stages | [67] |
| NEAT1 | Lung cancer | Abundantly expressed in cancer tissues | Upregulated by hypoxia (1% O2) in A549 and SPCA1 cells | – | Positively associated with the tumor, node and metastasis (TNM) classification | [68] |
| Anaplastic thyroid cancer | Upregulated in cancer tissues | Increased in several cell lines (SW1736 and KAT-18) under hypoxic conditions (1% O2) | Subcutaneous injections of SW1736 cells stably knocking down NEAT1 | – | [69] | |
| NORAD | Pancreatic cancer | Upregulated in cancer tissues | Increased in SW1990 cells under hypoxia (1% O2) | Orthotopic implantation of SW1990 cells stably knocking down NORAD | Poor overall and recurrence-free survival in patients with high NORAD levels | [70] |
| NPSR1-AS1 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Overexpressed in cancer tissues compared to control specimens | Increased in Hep3B and Huh7 cells by hypoxia and HIF-1α | – | – | [71] |
| NUTF2P3-001 | Pancreatic cancer | Overexpressed in cancer tissues compared to noncancerous tissues | Increased in hypoxia (1% O2)-exposed and CoCl2-treated PANC-1 cells | Subcutaneous injections of NUTF2P3-001-depleted PANC-1 cells | Strong expression is correlated with distant metastasis and worse prognosis | [72] |
| RAB11B-AS1 | Breast cancer | Upregulated in cancer tissues | Induced by hypoxia (1% O2) in multiple cell lines (e.g., MDA-MB-231 and BT474) | Orthotopic implantation of MDA-MB-231 cells stably knocking down RAB11B-AS1 | – | [73] |
| RP11-390F4.3 | Multiple types (hypopharyngeal, breast, osteosarcoma, prostate, and lung cancer) | – | Induced by hypoxia (1% O2) in FADU, MCF-7, and U2-OS cells. Decreased by HIF-1α silencing in H1299, MDA-MB-231, and PC3 cells | Tail vein or orthotopic injections of FADU cells (RP11-390F4.3 overexpressed) and H1299/MDA-MB-231 cells (RP11-390F4.3 depleted) | – | [74] |
| UCA1 | Gastric cancer | – | Increased in hypoxia-resistant cell lines (MGC-803 and BGC-823 cells) | – | – | [75] |
| XIST | Nasopharyngeal cancer | Overexpressed in cancer tissues | Increased by hypoxia (1% O2) in HK-1 and C666-1 cells | Subcutaneous injections of XIST-depleted HK-1 cells | – | [76] |
| LncRNA | Type of Cancer | Expression (Cell Lines and/or Tissues) | In Vivo Experiment | Clinical Relevance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDKN2B-AS1 | Ovarian cancer | Highly expressed in cancer cells (e.g., SKOV-3 cells) compared to normal ovarian epithelial cells | Subcutaneous injections of SKOV-3 cells following the knockdown of CDKN2B-AS1 | – | [138] |
| FAM201A | Lung cancer | Highly expressed in cancer tissues from patients responding poorly to radiotherapy | Subcutaneous injections of A549 and SK-MES-1 cells following FAM201A silencing | Unfavorable prognosis in patients with high FAM201A levels | [141] |
| H19 | Endometrial cancer | Overexpressed in cancer tissues compared to normal controls | Subcutaneous injections of H19-silencing HHUA cells | – | [142] |
| Glioblastoma | Abundant in cancer cell lines (U373, A172, and U87) compared to normal glial cells (HEB) | – | – | [143] | |
| HOTAIR | Renal cancer | Upregulated in cancer tissues and cell lines compared to adjacent normal tissues and normal renal cells, respectively | Subcutaneous injections of 769-P cells transfected with HOTAIR small interfering RNA | High expression of HOTAIR is correlated with tumor stages and metastasis | [144] |
| HOXA-AS2 | Nasopharyngeal cancer | Highly expressed in cancer tissues as well as cell lines (SUNE1 and SUNE2) | – | – | [145] |
| LINC00152 | Gallbladder cancer | Abundant in cancer tissues and cell lines (NOZ and GBC-SD) | Intraperitoneal injections of GBC-SD cells stably overexpressing LINC00152 | Positively associated with short overall survival and lymph node invasion | [146] |
| LINC00301 | Lung cancer | Upregulated in cancer tissues compared to normal counterparts | Implantations of LINC00301-overexpressing LA-4 and KLN-205 cells | Positively associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis, and worse overall survival | [147] |
| LINC00518 | Melanoma | Overexpressed in cancer tissues compared to normal skin controls | Subcutaneous injections of LINC00518-depleted WM451 and A375 cells + irradiation (2Gy) | Worse survival in patients with high LINC00518 levels | [148] |
| NEAT1 | Osteosarcoma | Enriched in cancer tissues and various cell lines (HOS, U2OS, SaOS2, and MG63) | Subcutaneous injections of HOS cells following NEAT1 depletion | Significantly associated with distant metastasis, advanced clinical stage, and poor overall survival | [149] |
| SNHG6 | Esophageal cancer | Upregulated in cancer tissues and cell lines (EC109, EC9706, KYSE30, and KYSE150) | – | – | [150] |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | Increased in cancer tissues compared to control tissues | Subcutaneous injections of Huh7 cells stably knocking down SNHG6 | Associated with overall and progression-free survival | [151] | |
| Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Highly expressed in cancer tissues compared to normal tissues | Subcutaneous injections of A498 cells stably expressing SNHG6 | Short overall survival in patients with high SNHG6 levels | [152] | |
| SNHG11 | Colorectal cancer | Highly expressed in cancer tissues compared to normal tissues | Tail vein injections of HCT116 cells stably overexpressing SNHG11 | Positively associated with lymphatic invasion, metastasis, distant recurrence, and short overall survival | [153] |
| TMPO-AS1 | Retinoblastoma | Overexpressed in cancer tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues | – | Positively associated with the stages of cancer | [154] |
| TUG1 | Osteosarcoma | Highly expressed in cancer tissues compared to normal controls. Higher in several cancer cell lines (e.g., U2OS and 143B cells) than in NHOst (normal osteoplastic cells) | Subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, or intravenous injections of TUG1-depleted U2OS cells | Positively associated with poor prognosis | [155] |
| UCA1 | Breast cancer | Abundant in tamoxifen-resistant cell lines (LCC2, LCC9, and BT474) compared to a tamoxifen-sensitive cell line (MCF-7) | – | – | [156] |
| XIST | Colorectal cancer | Upregulated in cancer tissues compared to normal controls | Subcutaneously inject XIST-silencing LoVo cells or SW480 cells overexpressing XIST | Positively associated with the TNM stage | [157] |
| ZEB2-AS1 | Gastric cancer | Overexpressed in cancer cell lines (SGC-7901, BGC-823, and MKN-28) compared to normal gastric epithelial cells (GES-1) | Subcutaneous injections of SGC-7901 cells depleted of ZEB2-AS1 | – | [158] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, S.W.; Yun, B.D.; Song, M.G.; Lee, J.K.; Choi, S.Y.; Kuh, H.J.; Park, J.K. The Hypoxia–Long Noncoding RNA Interaction in Solid Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147261
Son SW, Yun BD, Song MG, Lee JK, Choi SY, Kuh HJ, Park JK. The Hypoxia–Long Noncoding RNA Interaction in Solid Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(14):7261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147261
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Seung Wan, Ba Da Yun, Mun Gyu Song, Jin Kyeong Lee, Soo Young Choi, Hyo Jeong Kuh, and Jong Kook Park. 2021. "The Hypoxia–Long Noncoding RNA Interaction in Solid Cancers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 14: 7261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147261
APA StyleSon, S. W., Yun, B. D., Song, M. G., Lee, J. K., Choi, S. Y., Kuh, H. J., & Park, J. K. (2021). The Hypoxia–Long Noncoding RNA Interaction in Solid Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), 7261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147261