Assessing the Role of Lipids in the Molecular Mechanism of Membrane Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Lipids as Regulators of Protein Oligomerization and Complex Assembly
3. Lipids Stabilizing Conformational States
3.1. Measuring Distances
3.2. Looking at High-Resolution Structures
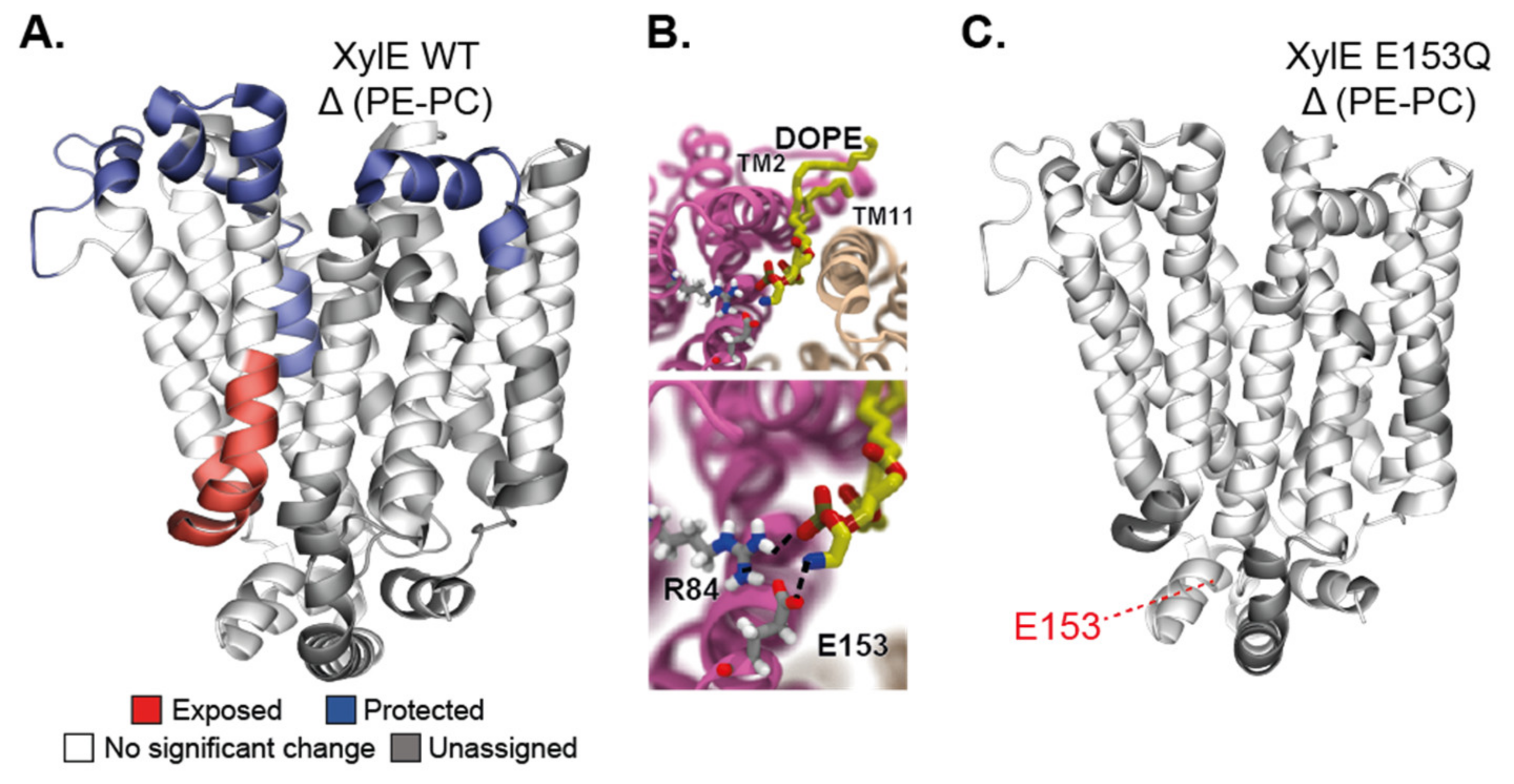
3.3. Measuring Accessibility Changes with H/D Exchange
4. Lipids as Modulators of Ligand Binding
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almén, M.S.; Nordström, K.J.; Fredriksson, R.; Schiöth, H.B. Mapping the Human Membrane Proteome: A Majority of the Human Membrane Proteins Can Be Classified According to Function and Evolutionary Origin. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santos, R.; Ursu, O.; Gaulton, A.; Bento, A.P.; Donadi, R.S.; Bologa, C.G.; Karlsson, A.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Hersey, A.; Oprea, T.I.; et al. A Comprehensive Map of Molecular Drug Targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, M.; Eibl, H.; Barrantes, F.J. Functional Properties of the Acetylcholine Receptor Incorporated in Model Lipid Membranes. Differential Effects of Chain Length and Head Group of Phospholipids on Receptor Affinity States and Receptor-Mediated Ion Translocation. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 9188–9198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, M.; Dowhan, W. Phosphatidylethanolamine Is Required for in Vivo Function of the Membrane-Associated Lactose Permease of Escherichia Coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.G. Lipid-Protein Interactions in Biological Membranes: A Structural Perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1612, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marsh, D. Protein Modulation of Lipids, and Vice-Versa, in Membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 1545–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.G. How Lipids Affect the Activities of Integral Membrane Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2004, 1666, 62–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Findlay, H.E.; Booth, P.J. The Folding, Stability and Function of Lactose Permease Differ in Their Dependence on Bilayer Lipid Composition. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, B.C.; Cater, R.J.; Mancia, F.; Pryor, E.E. A 10-Year Meta-Analysis of Membrane Protein Structural Biology: Detergents, Membrane Mimetics, and Structure Determination Techniques. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganowsky, A.; Reading, E.; Allison, T.M.; Ulmschneider, M.B.; Degiacomi, M.T.; Baldwin, A.J.; Robinson, C.V. Membrane Proteins Bind Lipids Selectively to Modulate Their Structure and Function. Nature 2014, 510, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayburt, T.H.; Sligar, S.G. Membrane Protein Assembly into Nanodiscs. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1721–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flayhan, A.; Mertens, H.D.T.; Ural-Blimke, Y.; Molledo, M.M.; Svergun, D.I.; Löw, C. Saposin Lipid Nanoparticles: A Highly Versatile and Modular Tool for Membrane Protein Research. Structure 2018, 26, 345–355.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angiulli, G.; Dhupar, H.S.; Suzuki, H.; Wason, I.S.; Duong Van Hoa, F.; Walz, T. New Approach for Membrane Protein Reconstitution into Peptidiscs and Basis for Their Adaptability to Different Proteins. eLife 2020, 9, e53530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, M.L.; Young, J.W.; Zhao, Z.; Fabre, L.; Jun, D.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Dhupar, H.S.; Wason, I.; Mills, A.T.; et al. The Peptidisc, a Simple Method for Stabilizing Membrane Proteins in Detergent-Free Solution. eLife 2018, 7, e34085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bada Juarez, J.F.; Harper, A.J.; Judge, P.J.; Tonge, S.R.; Watts, A. From Polymer Chemistry to Structural Biology: The Development of SMA and Related Amphipathic Polymers for Membrane Protein Extraction and Solubilisation. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2019, 221, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, J.; Burmann, B.M. Fake It ‘Till You Make It—The Pursuit of Suitable Membrane Mimetics for Membrane Protein Biophysics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, A.-E.; Vonkova, I.; Gavin, A.-C. The Systematic Analysis of Protein–Lipid Interactions Comes of Age. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, C.-Y.; Richards, M.J.; Daniel, S. A Review of Traditional and Emerging Methods to Characterize Lipid–Protein Interactions in Biological Membranes. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 7076–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, Y.; Ali, A.A.; You, M. Current Methods for Detecting Cell Membrane Transient Interactions. Front. Chem. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, V.; Sejdiu, B.I.; Mesa-Galloso, H.; Abdizadeh, H.; Noskov, S.Y.; Marrink, S.J.; Tieleman, D.P. Emerging Diversity in Lipid–Protein Interactions. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5775–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomasello, G.; Armenia, I.; Molla, G. The Protein Imager: A Full-Featured Online Molecular Viewer Interface with Server-Side HQ-Rendering Capabilities. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2909–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popot, J.L.; Engelman, D.M. Membrane Protein Folding and Oligomerization: The Two-Stage Model. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/bi00469a001 (accessed on 31 May 2021).
- Mohole, M.; Kumar, G.A.; Sengupta, D.; Chattopadhyay, A. Chapter 6—Molecular Determinants of GPCR Oligomerization. In GPCRs; Jastrzebska, B., Park, P.S.-H., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Valinsky, W.C.; On, N.C.; Houlihan, P.R.; Qu, Q.; Liu, L.; Pan, X.; Clapham, D.E.; Yan, N. Employing NaChBac for Cryo-EM Analysis of Toxin Action on Voltage-Gated Na+ Channels in Nanodisc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14187–14193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGoldrick, L.L.; Singh, A.K.; Demirkhanyan, L.; Lin, T.-Y.; Casner, R.G.; Zakharian, E.; Sobolevsky, A.I. Structure of the Thermo-Sensitive TRP Channel TRP1 from the Alga Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autzen, H.E.; Myasnikov, A.G.; Campbell, M.G.; Asarnow, D.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. Structure of the Human TRPM4 Ion Channel in a Lipid Nanodisc. Science 2018, 359, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koshy, C.; Schweikhard, E.S.; Gärtner, R.M.; Perez, C.; Yildiz, Ö.; Ziegler, C. Structural Evidence for Functional Lipid Interactions in the Betaine Transporter BetP. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 3096–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Essen, L.-O.; Siegert, R.; Lehmann, W.D.; Oesterhelt, D. Lipid Patches in Membrane Protein Oligomers: Crystal Structure of the Bacteriorhodopsin-Lipid Complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11673–11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kern, D.M.; Oh, S.; Hite, R.K.; Brohawn, S.G. Cryo-EM Structures of the DCPIB-Inhibited Volume-Regulated Anion Channel LRRC8A in Lipid Nanodiscs. eLife 2019, 8, e42636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Jiao, H.; Liu, Z. Phospholipid Translocation Captured in a Bifunctional Membrane Protein MprF. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periole, X.; Huber, T.; Marrink, S.-J.; Sakmar, T.P. G Protein-Coupled Receptors Self-Assemble in Dynamics Simulations of Model Bilayers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10126–10132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fotiadis, D.; Liang, Y.; Filipek, S.; Saperstein, D.A.; Engel, A.; Palczewski, K. Rhodopsin Dimers in Native Disc Membranes. Nature 2003, 421, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, X.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Sengupta, D. Cholesterol Modulates the Dimer Interface of the Β2-Adrenergic Receptor via Cholesterol Occupancy Sites. Biophys. J. 2014, 106, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valiyaveetil, F.I.; Zhou, Y.; MacKinnon, R. Lipids in the Structure, Folding, and Function of the KcsA K+ Channel. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 10771–10777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Benlekbir, S.; Venkatakrishnan, P.; Wang, Y.; Hong, S.; Hosler, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Rubinstein, J.L.; Gennis, R.B. Structure of the Alternative Complex III in a Supercomplex with Cytochrome Oxidase. Nature 2018, 557, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobti, M.; Walshe, J.L.; Wu, D.; Ishmukhametov, R.; Zeng, Y.C.; Robinson, C.V.; Berry, R.M.; Stewart, A.G. Cryo-EM Structures Provide Insight into How E. coli F1Fo ATP Synthase Accommodates Symmetry Mismatch. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cao, E.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. TRPV1 Structures in Nanodiscs Reveal Mechanisms of Ligand and Lipid Action. Nature 2016, 534, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, K.; Donlan, J.A.C.; Hopper, J.T.S.; Uzdavinys, P.; Landreh, M.; Struwe, W.B.; Drew, D.; Baldwin, A.J.; Stansfeld, P.J.; Robinson, C.V. The Role of Interfacial Lipids in Stabilizing Membrane Protein Oligomers. Nature 2017, 541, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Li, J.; Liko, I.; Gault, J.; Bechara, C.; Wu, D.; Hopper, J.T.S.; Giles, K.; Benesch, J.L.P.; Robinson, C.V. Identifying Key Membrane Protein Lipid Interactions Using Mass Spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1106–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liko, I.; Degiacomi, M.T.; Mohammed, S.; Yoshikawa, S.; Schmidt, C.; Robinson, C.V. Dimer Interface of Bovine Cytochrome c Oxidase Is Influenced by Local Posttranslational Modifications and Lipid Binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8230–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyle, E.; Kalli, A.C.; Amillis, S.; Hall, Z.; Lau, A.M.; Hanyaloglu, A.C.; Diallinas, G.; Byrne, B.; Politis, A. Structural Lipids Enable the Formation of Functional Oligomers of the Eukaryotic Purine Symporter UapA. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 840–848.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landreh, M.; Marklund, E.G.; Uzdavinys, P.; Degiacomi, M.T.; Coincon, M.; Gault, J.; Gupta, K.; Liko, I.; Benesch, J.L.P.; Drew, D.; et al. Integrating Mass Spectrometry with MD Simulations Reveals the Role of Lipids in Na+/H + Antiporters. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reading, E.; Walton, T.A.; Liko, I.; Marty, M.T.; Laganowsky, A.; Rees, D.C.; Robinson, C.V. The Effect of Detergent, Temperature, and Lipid on the Oligomeric State of MscL Constructs: Insights from Mass Spectrometry. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winkelmann, I.; Matsuoka, R.; Meier, P.F.; Shutin, D.; Zhang, C.; Orellana, L.; Sexton, R.; Landreh, M.; Robinson, C.V.; Beckstein, O.; et al. Structure and Elevator Mechanism of the Mammalian Sodium/Proton Exchanger NHE9. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e105908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderluh, A.; Hofmaier, T.; Klotzsch, E.; Kudlacek, O.; Stockner, T.; Sitte, H.H.; Schütz, G.J. Direct PIP 2 Binding Mediates Stable Oligomer Formation of the Serotonin Transporter. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderluh, A.; Klotzsch, E.; Reismann, A.W.A.F.; Brameshuber, M.; Kudlacek, O.; Newman, A.H.; Sitte, H.H.; Schütz, G.J. Single Molecule Analysis Reveals Coexistence of Stable Serotonin Transporter Monomers and Oligomers in the Live Cell Plasma Membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 4387–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buchmayer, F.; Schicker, K.; Steinkellner, T.; Geier, P.; Stübiger, G.; Hamilton, P.J.; Jurik, A.; Stockner, T.; Yang, J.-W.; Montgomery, T.; et al. Amphetamine Actions at the Serotonin Transporter Rely on the Availability of Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11642–11647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ardalan, A.; Sowlati-Hashjin, S.; Uwumarenogie, S.O.; Fish, M.; Mitchell, J.; Karttunen, M.; Smith, M.D.; Jelokhani-Niaraki, M. Functional Oligomeric Forms of Uncoupling Protein 2: Strong Evidence for Asymmetry in Protein and Lipid Bilayer Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourkoulou, A.; Grevias, P.; Lambrinidis, G.; Pyle, E.; Dionysopoulou, M.; Politis, A.; Mikros, E.; Byrne, B.; Diallinas, G. Specific Residues in a Purine Transporter Are Critical for Dimerization, ER Exit, and Function. Genetics 2019, 213, 1357–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perozo, E.; Kloda, A.; Cortes, D.M.; Martinac, B. Physical Principles Underlying the Transduction of Bilayer Deformation Forces during Mechanosensitive Channel Gating. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 9, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marty, M.T. Nanodiscs and Mass Spectrometry: Making Membranes Fly. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 458, 116436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ro, S.Y.; Schachner, L.F.; Koo, C.W.; Purohit, R.; Remis, J.P.; Kenney, G.E.; Liauw, B.W.; Thomas, P.M.; Patrie, S.M.; Kelleher, N.L.; et al. Native Top-down Mass Spectrometry Provides Insights into the Copper Centers of Membrane-Bound Methane Monooxygenase. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keener, J.E.; Zambrano, D.E.; Zhang, G.; Zak, C.K.; Reid, D.J.; Deodhar, B.S.; Pemberton, J.E.; Prell, J.S.; Marty, M.T. Chemical Additives Enable Native Mass Spectrometry Measurement of Membrane Protein Oligomeric State within Intact Nanodiscs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, J.A.; Sanders, H.M.; Rolland, A.D.; Prell, J.S.; Wang, J.; Marty, M.T. Influenza A M2 Channel Oligomerization is Sensitive to its Chemical Environment. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoi, K.K.; Bada Juarez, J.F.; Judge, P.J.; Yen, H.-Y.; Wu, D.; Vinals, J.; Taylor, G.F.; Watts, A.; Robinson, C.V. Detergent-Free Lipodisq Nanoparticles Facilitate High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry of Folded Integral Membrane Proteins. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2824–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, M.T.; Baldwin, A.J.; Marklund, E.G.; Hochberg, G.K.A.; Benesch, J.L.P.; Robinson, C.V. Bayesian Deconvolution of Mass and Ion Mobility Spectra: From Binary Interactions to Polydisperse Ensembles. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4370–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, M.-K.; Gayen, A.; Banigan, J.R.; Leninger, M.; Traaseth, N.J. Intrinsic Conformational Plasticity of Native EmrE Provides a Pathway for Multidrug Resistance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8072–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayen, A.; Banigan, J.R.; Traaseth, N.J. Ligand-Induced Conformational Changes of the Multidrug Resistance Transporter EmrE Probed by Oriented Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 10511–10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Cruijsen, E.A.W.; Nand, D.; Weingarth, M.; Prokofyev, A.; Hornig, S.; Cukkemane, A.A.; Bonvin, A.M.J.J.; Becker, S.; Hulse, R.E.; Perozo, E.; et al. Importance of Lipid–Pore Loop Interface for Potassium Channel Structure and Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13008–13013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandala, V.S.; Williams, J.K.; Hong, M. Structure and Dynamics of Membrane Proteins from Solid-State NMR. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2018, 47, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladizhansky, V. Applications of Solid-State NMR to Membrane Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Proteins Proteom. 2017, 1865 (11, Part B), 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, S.J.; Glaubitz, C. Perspectives in Enzymology of Membrane Proteins by Solid-State NMR. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2164–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, E.; Cordes, T.; Ingargiola, A.; Alhadid, Y.; Chung, S.; Michalet, X.; Weiss, S. Toward Dynamic Structural Biology: Two Decades of Single-Molecule Förster Resonance Energy Transfer. Science 2018, 359, eaan1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeschke, G. DEER Distance Measurements on Proteins. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2012, 63, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mchaourab, H.S.; Steed, P.R.; Kazmier, K. Toward the Fourth Dimension of Membrane Protein Structure: Insight into Dynamics from Spin-Labeling EPR Spectroscopy. Structure 2011, 19, 1549–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, R.; Hohng, S.; Ha, T. A Practical Guide to Single-Molecule FRET. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-N.; Jaumann, E.A.; Reichel, K.; Hartmann, J.; Oliver, D.; Hummer, G.; Joseph, B.; Geertsma, E.R. Structural Basis for Functional Interactions in Dimers of SLC26 Transporters. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martens, C.; Stein, R.A.; Masureel, M.; Roth, A.; Mishra, S.; Dawaliby, R.; Konijnenberg, A.; Sobott, F.; Govaerts, C.; Mchaourab, H.S. Lipids Modulate the Conformational Dynamics of a Secondary Multidrug Transporter. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dastvan, R.; Mishra, S.; Peskova, Y.B.; Nakamoto, R.K.; Mchaourab, H.S. Mechanism of Allosteric Modulation of P-Glycoprotein by Transport Substrates and Inhibitors. Science 2019, 364, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardeni, E.H.; Mishra, S.; Stein, R.A.; Bibi, E.; Mchaourab, H.S. The Multidrug Transporter MdfA Deviates from the Canonical Model of Alternating Access of MFS Transporters. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 5665–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husada, F.; Bountra, K.; Tassis, K.; de Boer, M.; Romano, M.; Rebuffat, S.; Beis, K.; Cordes, T. Conformational Dynamics of the ABC Transporter McjD Seen by Single-Molecule FRET. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Livnat Levanon, N.; Acar, B.; Aykac Fas, B.; Masrati, G.; Rose, J.; Ben-Tal, N.; Haliloglu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Lewinson, O. Single-Molecule Probing of the Conformational Homogeneity of the ABC Transporter BtuCD. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasitza-Male, T.; Bartels, K.; Jungwirth, J.; Wiggers, F.; Rosenblum, G.; Hofmann, H.; Löw, C. Membrane Chemistry Tunes the Structure of a Peptide Transporter. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 19121–19128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.C. Single-Molecule Fluorescence Studies on the Conformational Change of the ABC Transporter MsbA. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 4, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jagessar, K.L.; Claxton, D.P.; Stein, R.A.; Mchaourab, H.S. Sequence and Structural Determinants of Ligand-Dependent Alternating Access of a MATE Transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 4732–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masureel, M.; Martens, C.; Stein, R.A.; Mishra, S.; Ruysschaert, J.-M.; Mchaourab, H.S.; Govaerts, C. Protonation Drives the Conformational Switch in the Multidrug Transporter LmrP. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigworth, F.J. Principles of Cryo-EM Single-Particle Image Processing. Microscopy 2016, 65, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; She, J.; Zeng, W.; Guo, J.; Xu, H.; Bai, X.; Jiang, Y. Structure of Mammalian Endolysosomal TRPML1 Channel in Nanodiscs. Nature 2017, 550, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pumroy, R.A.; Samanta, A.; Liu, Y.; Hughes, T.E.; Zhao, S.; Yudin, Y.; Rohacs, T.; Han, S.; Moiseenkova-Bell, V.Y. Molecular Mechanism of TRPV2 Channel Modulation by Cannabidiol. eLife 2019, 8, e48792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Maksaev, G.; Rau, M.; Xie, Z.; Hu, H.; Fitzpatrick, J.A.J.; Yuan, P. Gating of Human TRPV3 in a Lipid Bilayer. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, H.; Kusakizako, T.; Dung Nguyen, T.H.; Nishizawa, T.; Hino, T.; Tominaga, M.; Nureki, O. The Structure of Lipid Nanodisc-Reconstituted TRPV3 Reveals the Gating Mechanism. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.E.; Del Rosario, J.S.; Kapoor, A.; Yazici, A.T.; Yudin, Y.; Fluck, E.C., III; Filizola, M.; Rohacs, T.; Moiseenkova-Bell, V.Y. Structure-Based Characterization of Novel TRPV5 Inhibitors. eLife 2019, 8, e49572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, S.; van Goor, M.K.; Asarnow, D.; Wang, Y.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y.; van der Wijst, J. Structural Insight into TRPV5 Channel Function and Modulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8869–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGoldrick, L.L.; Singh, A.K.; Saotome, K.; Yelshanskaya, M.V.; Twomey, E.C.; Grassucci, R.A.; Sobolevsky, A.I. Opening of the Human Epithelial Calcium Channel TRPV6. Nature 2018, 553, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Bavi, N.; Lu, A.; Park, Y.; Perozo, E. Molecular Basis of Force-from-Lipids Gating in the Mechanosensitive Channel MscS. eLife 2019, 8, e50486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, T.; Flegler, V.J.; Rasmussen, A.; Böttcher, B. Structure of the Mechanosensitive Channel MscS Embedded in the Membrane Bilayer. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Daday, C.; Gu, R.-X.; Cox, C.D.; Martinac, B.; de Groot, B.L.; Walz, T. Visualization of the Mechanosensitive Ion Channel MscS under Membrane Tension. Nature 2021, 590, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jojoa-Cruz, S.; Saotome, K.; Murthy, S.E.; Tsui, C.C.A.; Sansom, M.S.; Patapoutian, A.; Ward, A.B. Cryo-EM Structure of the Mechanically Activated Ion Channel OSCA1.2. eLife 2018, 7, e41845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthies, D.; Bae, C.; Toombes, G.E.; Fox, T.; Bartesaghi, A.; Subramaniam, S.; Swartz, K.J. Single-Particle Cryo-EM Structure of a Voltage-Activated Potassium Channel in Lipid Nanodiscs. eLife 2018, 7, e37558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintzer, A.F.; Green, E.M.; Dominik, P.K.; Bridges, M.; Armache, J.-P.; Deneka, D.; Kim, S.S.; Hubbell, W.; Kossiakoff, A.A.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Structural Basis for Activation of Voltage Sensor Domains in an Ion Channel TPC1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E9095–E9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, P.S.; Yang, X.; DeCaen, P.G.; Liu, X.; Bulkley, D.; Clapham, D.E.; Cao, E. The Structure of the Polycystic Kidney Disease Channel PKD2 in Lipid Nanodiscs. Cell 2016, 167, 763–773.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, S.; Dang, S.; Han, T.W.; Ye, W.; Jin, P.; Cheng, T.; Li, J.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, L.Y.; Cheng, Y. Cryo-EM Studies of TMEM16F Calcium-Activated Ion Channel Suggest Features Important for Lipid Scrambling. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 567–579.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Fu, Z.; Xu, G.G.; Grassucci, R.A.; Zhang, Y.; Frank, J.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Guo, Y. Structure and Activity of Lipid Bilayer within a Membrane-Protein Transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12985–12990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofmann, S.; Januliene, D.; Mehdipour, A.R.; Thomas, C.; Stefan, E.; Brüchert, S.; Kuhn, B.T.; Geertsma, E.R.; Hummer, G.; Tampé, R.; et al. Conformation Space of a Heterodimeric ABC Exporter under Turnover Conditions. Nature 2019, 571, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.M.I.; Manolaridis, I.; Jackson, S.M.; Kowal, J.; Stahlberg, H.; Locher, K.P. Structure of the Human Multidrug Transporter ABCG2. Nature 2017, 546, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; McGoldrick, L.L.; Demirkhanyan, L.; Leslie, M.; Zakharian, E.; Sobolevsky, A.I. Structural Basis of Temperature Sensation by the TRP Channel TRPV3. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubcevic, L.; Herzik, M.A.; Wu, M.; Borschel, W.F.; Hirschi, M.; Song, A.S.; Lander, G.C.; Lee, S.-Y. Conformational Ensemble of the Human TRPV3 Ion Channel. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zubcevic, L.; Borschel, W.F.; Hsu, A.L.; Borgnia, M.J.; Lee, S.-Y. Regulatory Switch at the Cytoplasmic Interface Controls TRPV Channel Gating. eLife 2019, 8, e47746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegler, V.J.; Rasmussen, T.; Böttcher, B. More Than Just Closed and Open: Unraveling a Mechanosensor. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englander, S.W.; Kallenbach, N.R. Hydrogen Exchange and Structural Dynamics of Proteins and Nucleic Acids. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1983, 16, 521–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konermann, L.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y.-H. Hydrogen Exchange Mass Spectrometry for Studying Protein Structure and Dynamics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wales, T.E.; Eggertson, M.J.; Engen, J.R. Considerations in the Analysis of Hydrogen Exchange Mass Spectrometry Data. In Mass Spectrometry Data Analysis in Proteomics; Matthiesen, R., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 263–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.L.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Z. Probing the Non-Covalent Structure of Proteins by Amide Hydrogen Exchange and Mass Spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 32, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engen, J.R. Analysis of Protein Conformation and Dynamics by Hydrogen/Deuterium Exchange MS. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7870–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martens, C.; Shekhar, M.; Lau, A.M.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Politis, A. Integrating Hydrogen–Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry with Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Probe Lipid-Modulated Conformational Changes in Membrane Proteins. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 3183–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, C.; Politis, A. A Glimpse into the Molecular Mechanism of Integral Membrane Proteins through Hydrogen–Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 1285–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komolov, K.E.; Du, Y.; Duc, N.M.; Betz, R.M.; Rodrigues, J.P.G.L.M.; Leib, R.D.; Patra, D.; Skiniotis, G.; Adams, C.M.; Dror, R.O.; et al. Structural and Functional Analysis of a Β2-Adrenergic Receptor Complex with GRK5. Cell 2017, 169, 407–421.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Kim, H.R.; Deepak, R.N.V.K.; Wang, L.; Chung, K.Y.; Fan, H.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, C. Orthosteric and Allosteric Action of the C5a Receptor Antagonists. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkle, P.S.; Gotfryd, K.; Cuendet, M.A.; Leth-Espensen, K.Z.; Gether, U.; Loland, C.J.; Rand, K.D. Substrate-Modulated Unwinding of Transmembrane Helices in the NSS Transporter LeuT. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adhikary, S.; Deredge, D.J.; Nagarajan, A.; Forrest, L.R.; Wintrode, P.L.; Singh, S.K. Conformational Dynamics of a Neurotransmitter:Sodium Symporter in a Lipid Bilayer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E1786–E1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martens, C.; Shekhar, M.; Borysik, A.J.; Lau, A.M.; Reading, E.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Booth, P.J.; Politis, A. Direct Protein-Lipid Interactions Shape the Conformational Landscape of Secondary Transporters. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, S.; Domene, C.; Forest, E.; Jault, J.-M. Dynamics of a Bacterial Multidrug ABC Transporter in the Inward- and Outward-Facing Conformations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10832–10836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaptal, V.; Zampieri, V.; Wiseman, B.; Orelle, C.; Martin, J.; Nguyen, K.-A.; Magnard, S.; Gobet, A.; Cesare, M.D.; Javed, W.; et al. Drug-Bound and -Free Outward-Facing Structures of a Multidrug ABC Exporter Point to a Swing Mechanism. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebling, C.M.; Morgan, C.R.; Stafford, D.W.; Jorgenson, J.W.; Rand, K.D.; Engen, J.R. Conformational Analysis of Membrane Proteins in Phospholipid Bilayer Nanodiscs by Hydrogen Exchange Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5415–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamashita, A.; Singh, S.K.; Kawate, T.; Jin, Y.; Gouaux, E. Crystal Structure of a Bacterial Homologue of Na+/Cl−-Dependent Neurotransmitter Transporters. Nature 2005, 437, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penmatsa, A.; Gouaux, E. How LeuT Shapes Our Understanding of the Mechanisms of Sodium-Coupled Neurotransmitter Transporters. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.J.; Guttman, M.; Atkins, W.M. Conformational Dynamics of P-Glycoprotein in Lipid Nanodiscs and Detergent Micelles Reveal Complex Motions on a Wide Time Scale. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 6297–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reading, E.; Hall, Z.; Martens, C.; Haghighi, T.; Findlay, H.; Ahdash, Z.; Politis, A.; Booth, P.J. Interrogating Membrane Protein Conformational Dynamics within Native Lipid Compositions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15654–15657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Mao, C.; Zhou, X.E.; Cheng, X.; Simon, I.A.; Shen, D.-D.; Yen, H.-Y.; Robinson, C.V.; et al. Structural Insights into the Lipid and Ligand Regulation of Serotonin Receptors. Nature 2021, 592, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawaliby, R.; Trubbia, C.; Delporte, C.; Masureel, M.; Van Antwerpen, P.; Kobilka, B.K.; Govaerts, C. ALLOSTERIC REGULATION OF GPCR ACTIVITY BY PHOSPHOLIPIDS. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Hamada-Nakahara, S.; Itoh, Y.; Takemura, K.; Shimada, A.; Ueda, Y.; Kitamata, M.; Matsuoka, R.; Hanawa-Suetsugu, K.; Senju, Y.; et al. TRPV4 Channel Activity Is Modulated by Direct Interaction of the Ankyrin Domain to PI(4,5)P2. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Gui, M.; Wang, Z.-F.; Gorgulla, C.; Yu, J.J.; Wu, H.; Sun, Z.J.; Klenk, C.; Merklinger, L.; Morstein, L.; et al. Cryo-EM Structure of an Activated GPCR–G Protein Complex in Lipid Nanodiscs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staus, D.P.; Hu, H.; Robertson, M.J.; Kleinhenz, A.L.W.; Wingler, L.M.; Capel, W.D.; Latorraca, N.R.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Skiniotis, G. Structure of the M2 Muscarinic Receptor–β-Arrestin Complex in a Lipid Nanodisc. Nature 2020, 579, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.J.; Baenziger, J.E. Structural Basis for the Modulation of Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channel Function by Lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquet, N.; Nury, H.; Baaden, M.; Le Poupon, C.; Changeux, J.-P.; Delarue, M.; Corringer, P.-J. X-Ray Structure of a Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channel in an Apparently Open Conformation. Nature 2009, 457, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Cymes, G.D.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Grosman, C. Cryo-EM Structures of a Lipid-Sensitive Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channel Embedded in a Phosphatidylcholine-Only Bilayer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Gharpure, A.; Teng, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Howard, R.J.; Zhu, S.; Noviello, C.M.; Walsh, R.M.; Lindahl, E.; Hibbs, R.E. Shared Structural Mechanisms of General Anaesthetics and Benzodiazepines. Nature 2020, 585, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guixà-González, R.; Albasanz, J.L.; Rodriguez-Espigares, I.; Pastor, M.; Sanz, F.; Martí-Solano, M.; Manna, M.; Martinez-Seara, H.; Hildebrand, P.W.; Martín, M.; et al. Membrane Cholesterol Access into a G-Protein-Coupled Receptor. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paila, Y.D.; Chattopadhyay, A. The Function of G-Protein Coupled Receptors and Membrane Cholesterol: Specific or General Interaction? Glycoconj. J. 2008, 26, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gault, J.; Donlan, J.A.C.; Liko, I.; Hopper, J.T.S.; Gupta, K.; Housden, N.G.; Struwe, W.B.; Marty, M.T.; Mize, T.; Bechara, C.; et al. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry of Small Molecules Bound to Membrane Proteins. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcoux, J.; Wang, S.C.; Politis, A.; Reading, E.; Ma, J.; Biggin, P.C.; Zhou, M.; Tao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, G.; et al. Mass Spectrometry Reveals Synergistic Effects of Nucleotides, Lipids, and Drugs Binding to a Multidrug Resistance Efflux Pump. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9704–9709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yen, H.-Y.; Hoi, K.K.; Liko, I.; Hedger, G.; Horrell, M.R.; Song, W.; Wu, D.; Heine, P.; Warne, T.; Lee, Y.; et al. PIP2 Stabilises Active States of GPCRs and Enhances the Selectivity of G-Protein Coupling. Nature 2018, 559, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Liang, X.; Laganowsky, A. Allosteric Modulation of Protein-Protein Interactions by Individual Lipid Binding Events. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrecke, S.; Zhu, Y.; McCabe, J.W.; Bartz, M.; Packianathan, C.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, M.; Russell, D.; Laganowsky, A. Selective Regulation of Human TRAAK Channels by Biologically Active Phospholipids. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, J.W.; Boone, C.D.; Liu, W.; Conover, G.M.; Liu, Y.; Cong, X.; Laganowsky, A. Allostery Revealed within Lipid Binding Events to Membrane Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2976–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; LoCaste, C.E.; Liu, W.; Poltash, M.L.; Russell, D.H.; Laganowsky, A. Selective Binding of a Toxin and Phosphatidylinositides to a Mammalian Potassium Channel. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolla, J.R.; Sauer, J.B.; Wu, D.; Mehmood, S.; Allison, T.M.; Robinson, C.V. Direct Observation of the Influence of Cardiolipin and Antibiotics on Lipid II Binding to MurJ. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.-C.; Klenotic, P.A.; Bolla, J.R.; Purdy, G.E.; Robinson, C.V.; Yu, E.W. MmpL3 Is a Lipid Transporter That Binds Trehalose Monomycolate and Phosphatidylethanolamine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11241–11246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bechara, C.; Nöll, A.; Morgner, N.; Degiacomi, M.T.; Tampé, R.; Robinson, C.V. A Subset of Annular Lipids Is Linked to the Flippase Activity of an ABC Transporter. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liko, I.; Degiacomi, M.T.; Lee, S.; Newport, T.D.; Gault, J.; Reading, E.; Hopper, J.T.S.; Housden, N.G.; White, P.; Colledge, M.; et al. Lipid Binding Attenuates Channel Closure of the Outer Membrane Protein OmpF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6691–6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehmood, S.; Corradi, V.; Choudhury, H.G.; Hussain, R.; Becker, P.; Axford, D.; Zirah, S.; Rebuffat, S.; Tieleman, D.P.; Robinson, C.V.; et al. Structural and Functional Basis for Lipid Synergy on the Activity of the Antibacterial Peptide ABC Transporter McjD. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 21656–21668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hariharan, P.; Tikhonova, E.; Medeiros-Silva, J.; Jeucken, A.; Bogdanov, M.V.; Dowhan, W.; Brouwers, J.F.; Weingarth, M.; Guan, L. Structural and Functional Characterization of Protein–Lipid Interactions of the Salmonella Typhimurium Melibiose Transporter MelB. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, F.; Habeck, M.; Kanai, R.; Toyoshima, C.; Karlish, S.J.D. General and Specific Lipid–Protein Interactions in Na,K-ATPase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 1729–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinoda, T.; Ogawa, H.; Cornelius, F.; Toyoshima, C. Crystal Structure of the Sodium–Potassium Pump at 2.4 Å Resolution. Nature 2009, 459, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeck, M.; Kapri-Pardes, E.; Sharon, M.; Karlish, S.J.D. Specific Phospholipid Binding to Na,K-ATPase at Two Distinct Sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2904–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schur, F.K. Toward High-Resolution in Situ Structural Biology with Cryo-Electron Tomography and Subtomogram Averaging. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigal, Y.M.; Zhou, R.; Zhuang, X. Visualizing and Discovering Cellular Structures with Super-Resolution Microscopy. Science 2018, 361, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chorev, D.S.; Baker, L.A.; Wu, D.; Beilsten-Edmands, V.; Rouse, S.L.; Zeev-Ben-Mordehai, T.; Jiko, C.; Samsudin, F.; Gerle, C.; Khalid, S.; et al. Protein Assemblies Ejected Directly from Native Membranes Yield Complexes for Mass Spectrometry. Science 2018, 362, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaledhonkar, S.; Fu, Z.; White, H.; Frank, J. Time-Resolved Cryo-Electron Microscopy Using a Microfluidic Chip. In Protein Complex Assembly: Methods and Protocols; Marsh, J.A., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaledhonkar, S.; Fu, Z.; Caban, K.; Li, W.; Chen, B.; Sun, M.; Gonzalez, R.L.; Frank, J. Late Steps in Bacterial Translation Initiation Visualized Using Time-Resolved Cryo-EM. Nature 2019, 570, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäeots, M.-E.; Lee, B.; Nans, A.; Jeong, S.-G.; Esfahani, M.M.N.; Ding, S.; Smith, D.J.; Lee, C.-S.; Lee, S.S.; Peter, M.; et al. Modular Microfluidics Enables Kinetic Insight from Time-Resolved Cryo-EM. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Fan, X.; Yan, N. Cryo-EM Analysis of a Membrane Protein Embedded in the Liposome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18497–18503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Biophysical Techniques | Information Obtained | |
|---|---|---|
| X-ray crystallography extrapolates the position and arrangement of atoms in single crystals from the diffraction pattern of X-ray. |  | High-resolution structure. |
| Cryo-electron microscopy images flash frozen protein solutions with an electron beam. Single particles are aligned and classified in two-dimensional classes. The 3D structure is determined by reconstruction software. |  | High-resolution structure. |
| Native mass spectrometry (nMS) retains in the gas-phase non-covalent interactions pre-existing in solution. Protein-protein and protein-ligand complexes can be observed. |  | Protein–protein interactions, protein–ligand interactions. |
| Hydrogen–deuterium exchange (HDX) MS measures the rate of deuterium exchange of labile protons of the backbone amide. The exchange depends on stability of the H-bond and solvent accessibility. |  | Structural dynamics, protein–protein interactions, protein–ligand interactions. |
| Single-molecule FRET measures the amount of energy transfer between a pair of fluorophores, a donor and an acceptor to perform small distances measurements (1–10 nanometers). |  | Conformational changes, kinetics. |
| Double electron–electron resonance measures the dipolar spin coupling between a pair of spin labels. The modulated spin echo contains distance information. |  | Conformational changes. |
| Electron paramagnetic resonance (cw-EPR) provides a read-out of the environment and the mobility of a paramagnetic probe within a protein, typically a nitroxide spin label. |  | Mobility, environment, tertiary fold. |
| Multidimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) provides details about the local molecular environment of the nuclei of an isotopically labelled protein, allowing to deduce chemical bonds, distance and relative motions between nuclei. |  | High-resolution structure, dynamics, protein–protein interactions, protein–ligand interactions. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jodaitis, L.; van Oene, T.; Martens, C. Assessing the Role of Lipids in the Molecular Mechanism of Membrane Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147267
Jodaitis L, van Oene T, Martens C. Assessing the Role of Lipids in the Molecular Mechanism of Membrane Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(14):7267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147267
Chicago/Turabian StyleJodaitis, Léni, Thomas van Oene, and Chloé Martens. 2021. "Assessing the Role of Lipids in the Molecular Mechanism of Membrane Proteins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 14: 7267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147267
APA StyleJodaitis, L., van Oene, T., & Martens, C. (2021). Assessing the Role of Lipids in the Molecular Mechanism of Membrane Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), 7267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147267