Characterization of Structural Bone Properties through Portable Single-Sided NMR Devices: State of the Art and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
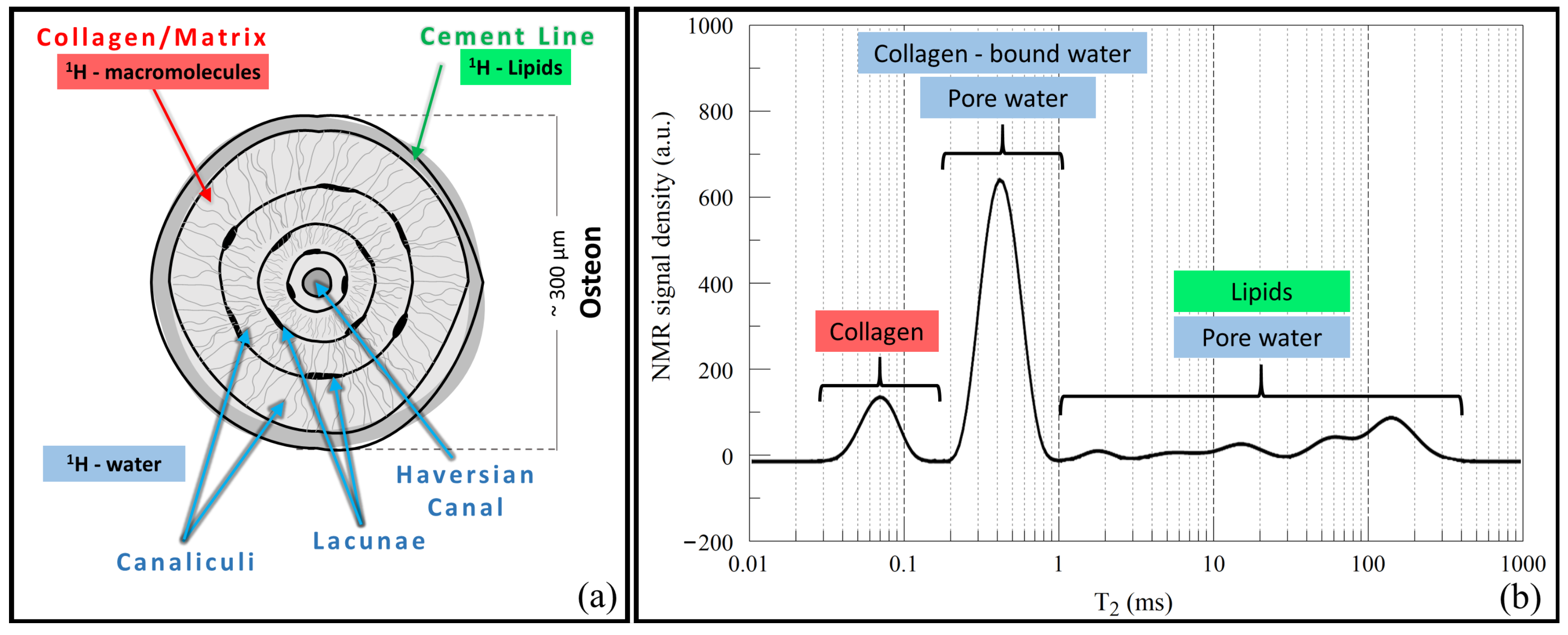
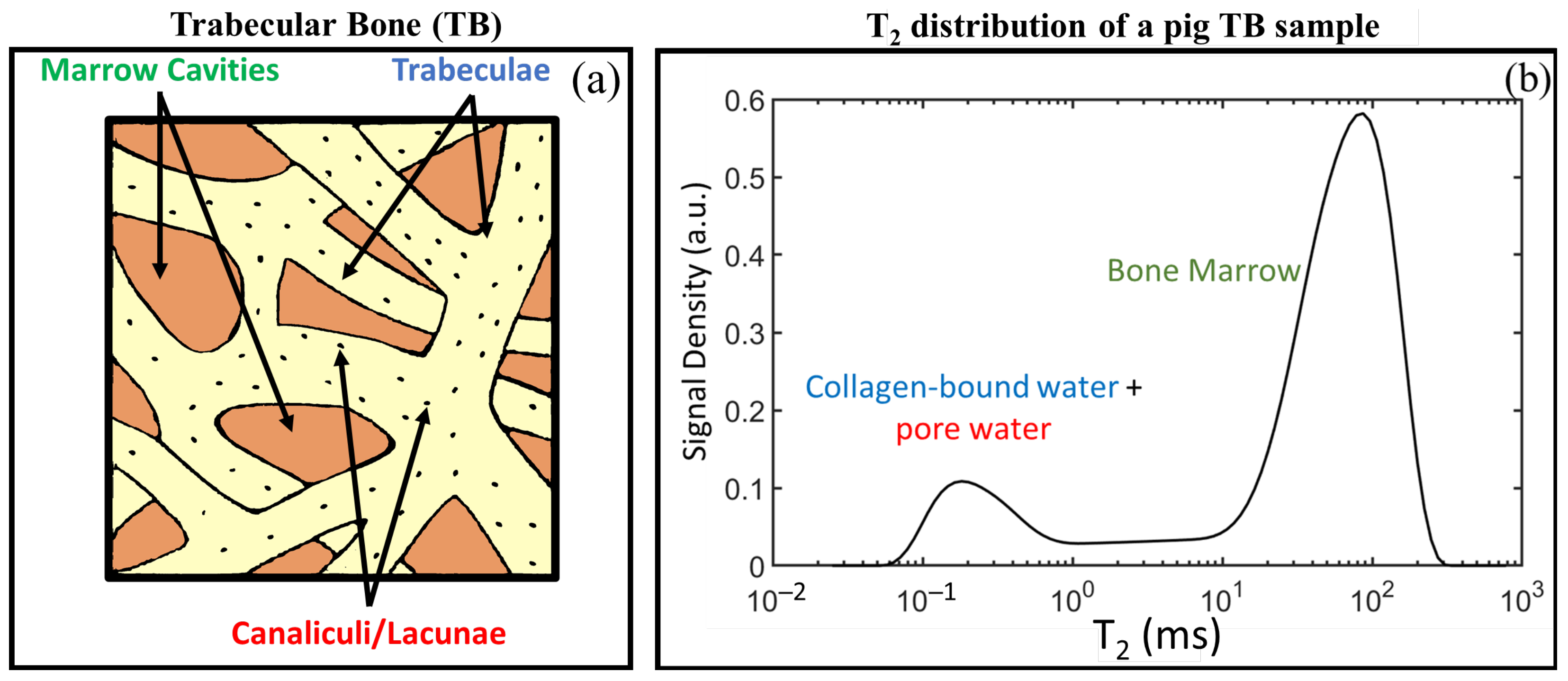
2. NMR Relaxometry Properties of Bone Tissue
2.1. Bone Tissue and Osteoporosis: A Brief Background
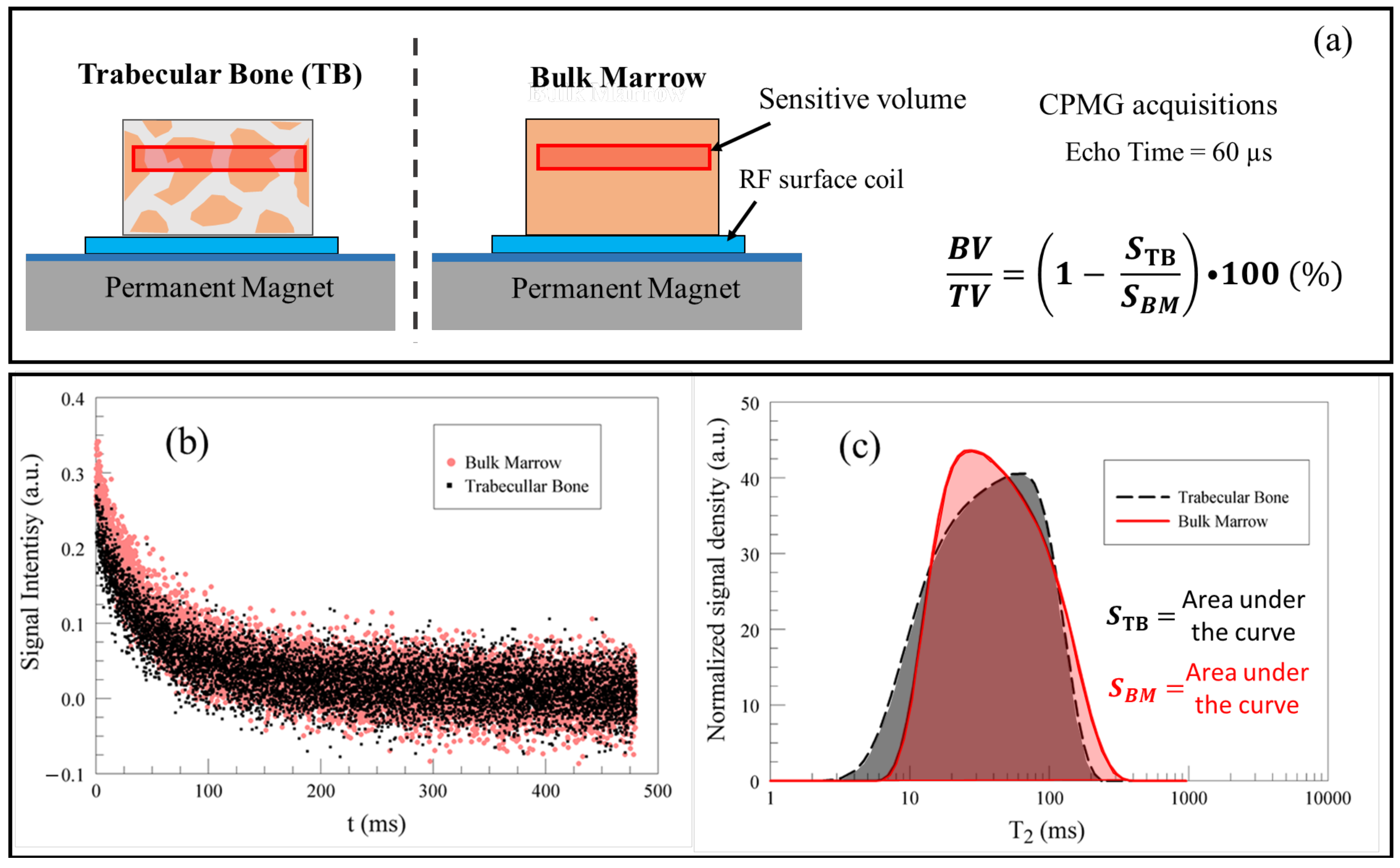
- BONE VOLUME/TOTAL VOLUME, BV/TV (%): % of total volume of the trabeculae with respect to the total volume of the analyzed tissue;
- BONE SURFACE/TOTAL VOLUME, BS/TV (mm−1): total external surface of the trabeculae with respect to the total volume of the analyzed tissue;
- TRABECULAR THICKNESS, Tb.Th (mm): the mean trabecular thickness found in the trabeculae of the analyzed tissue.
2.2. NMR Relaxation in Porous Media and Bone Tissue
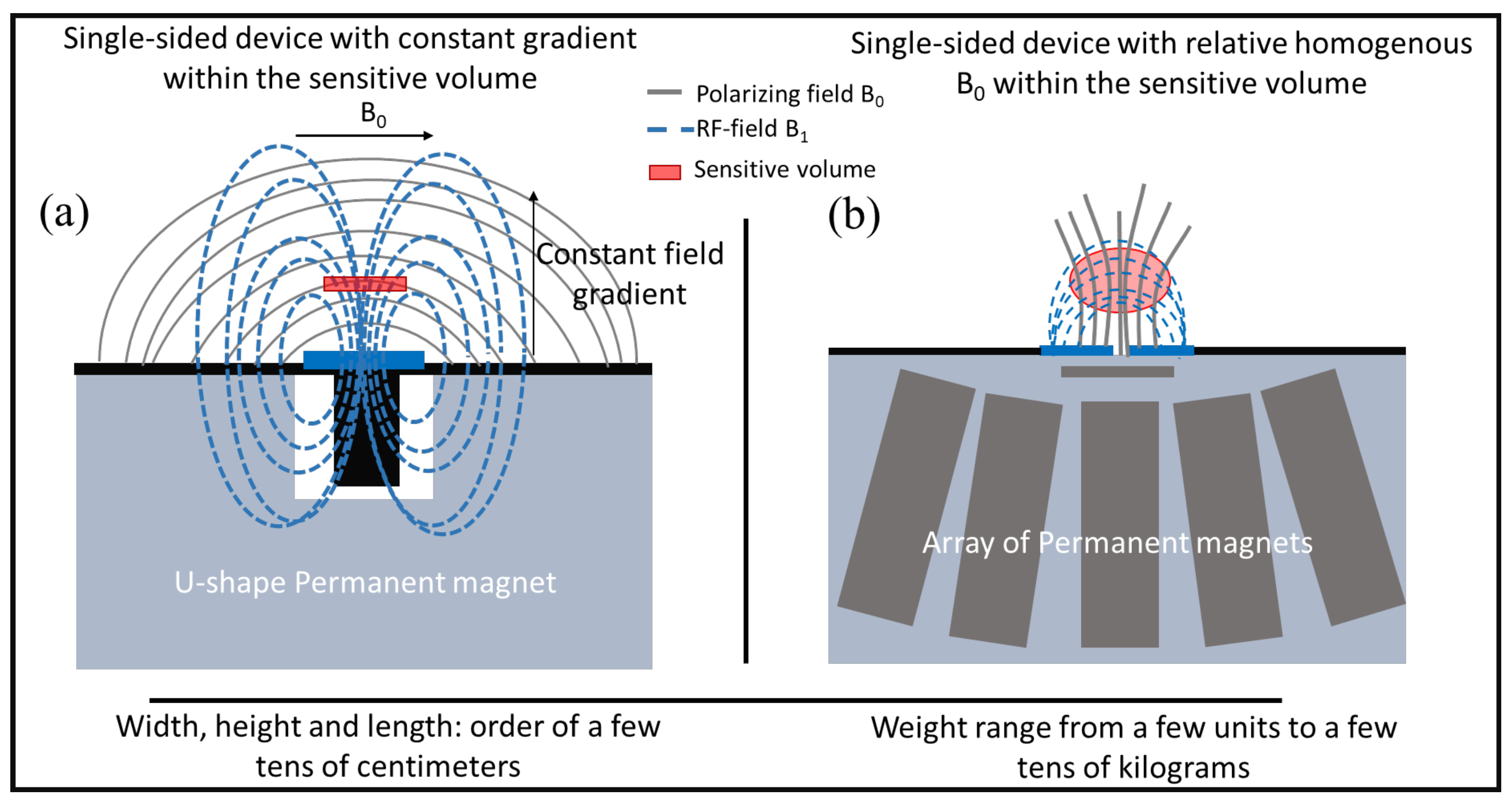
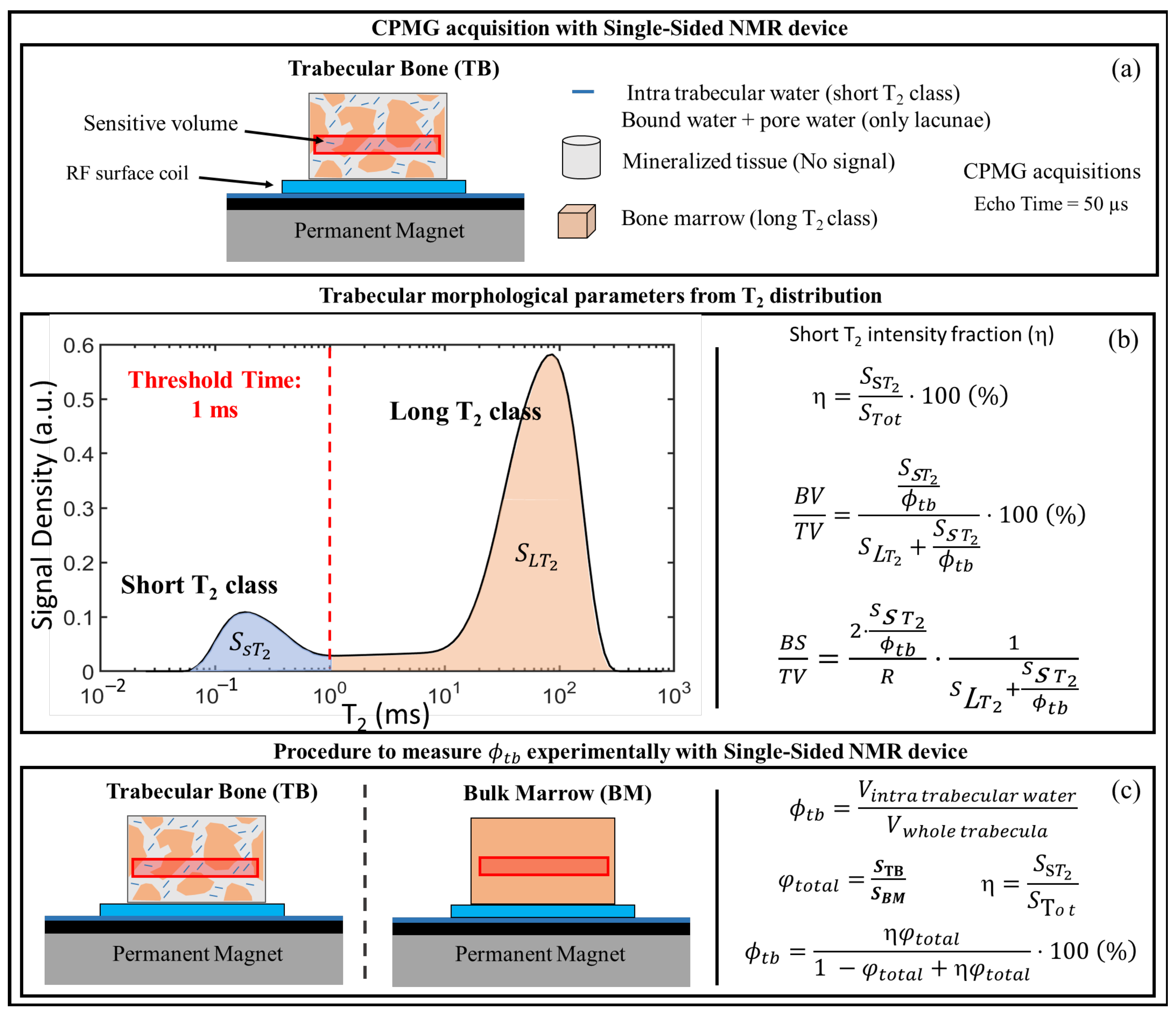
3. Single-Sided NMR Devices
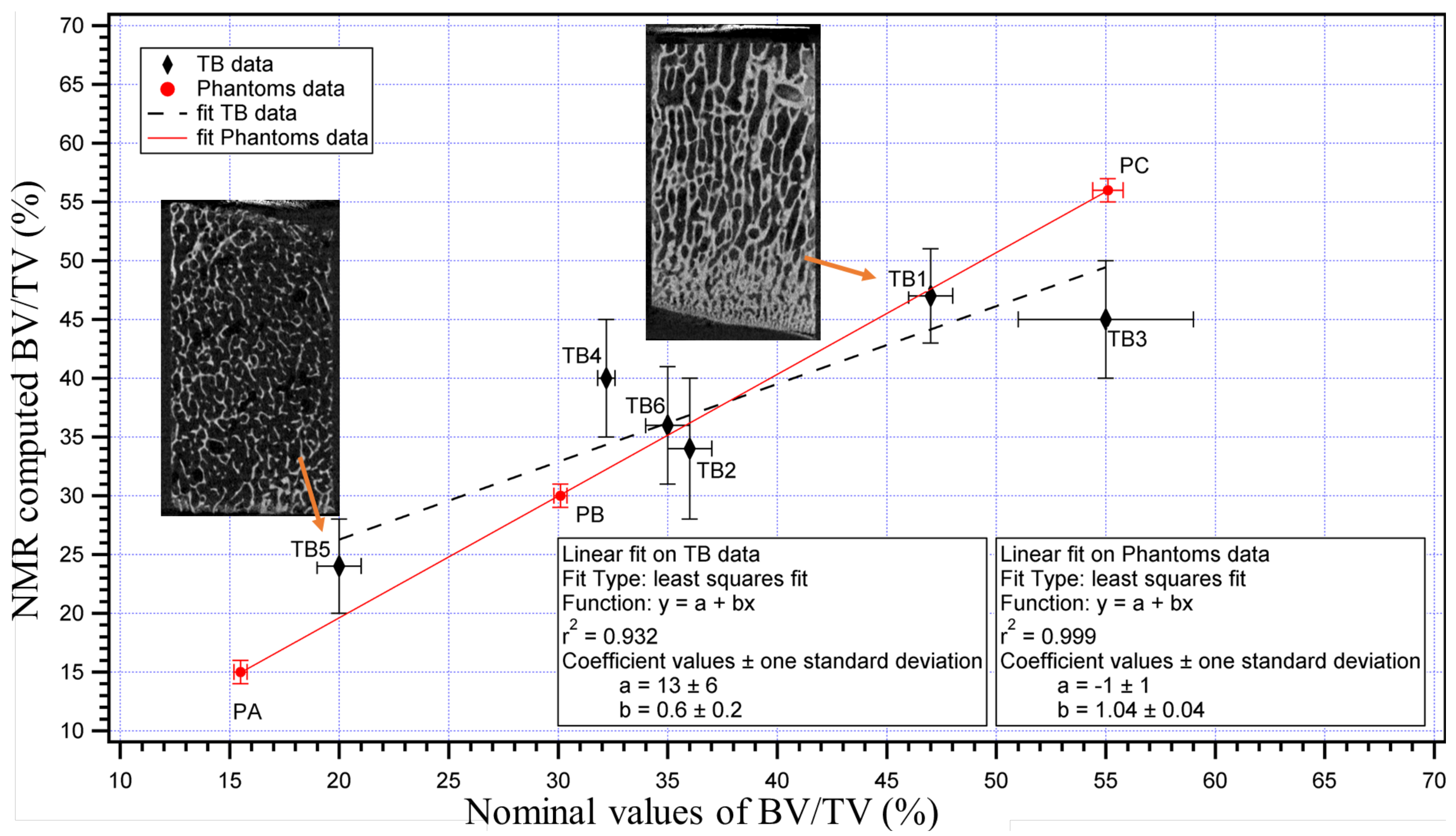
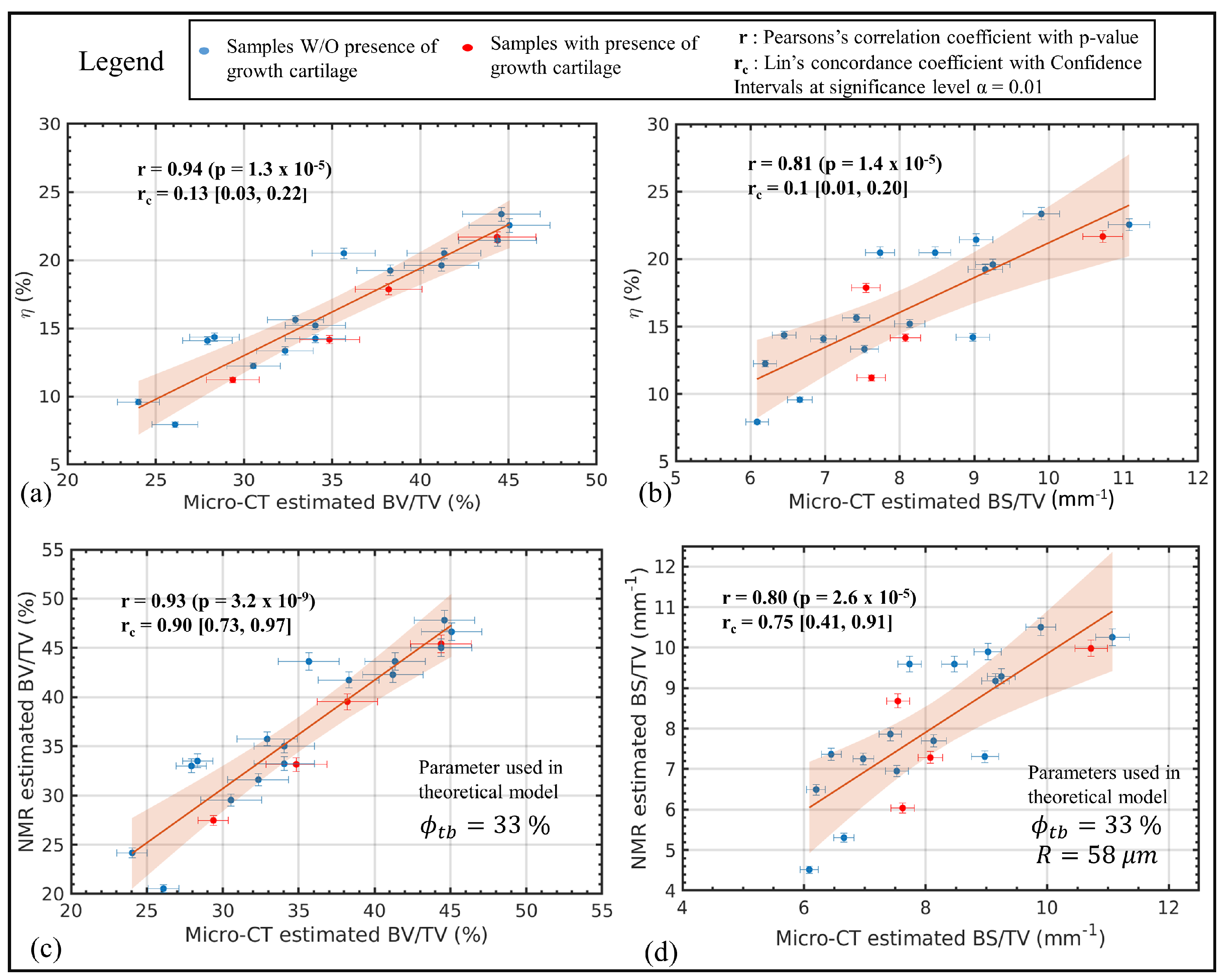
4. Evaluating Trabecular Bone Structural Properties of Animal Samples with Single-Sided NMR
5. Discussion: Current Limitations and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BS/TV | Bone-surface to total-volume ratio |
| BV/TV | Bone-volume to total-volume ratio |
| CB | Cortical Bone |
| CPMG | Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| HRqCT | High-Resolution quantitative Computed Tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| qMRI | quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| qUS | quantitative Ultrasounds |
| TB | Trabecular Bone |
| Tb.Th | Trabecular Thickness |
References
- Avioli, L.V. Significance of osteoporosis: A growing international health care problem. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1991, 49, S5–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krug, R.; Burghardt, A.J.; Majumdar, S.; Link, T.M. High-Resolution Imaging Techniques for the Assessment of Osteoporosis. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 48, 601–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granke, M.; Makowski, A.J.; Uppuganti, S.; Does, M.D.; Nyman, J.S. Identifying Novel Clinical Surrogates to Assess Human Bone Fracture Toughness. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazrun, A.; Tzar, M.; Mokhtar, S.; Mohamed, I. A systematic review of the outcomes of osteoporotic fracture patients after hospital discharge: Morbidity, subsequent fractures, and mortality. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2014, 10, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choksi, P.; Jepsen, K.; Clines, G. The challenges of diagnosing osteoporosis and the limitations of currently available tools. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 4, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blake, G.M.; Fogelman, I. The role of DXA bone density scans in the diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wainwright, S.A.; Marshall, L.M.; Ensrud, K.E.; Cauley, J.A.; Black, D.M.; Hillier, T.A.; Hochberg, M.C.; Vogt, M.T.; Orwoll, E.S. Hip Fracture in Women without Osteoporosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 2787–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanis, J.; Johnell, O.; Oden, A.; Johansson, H.; McCloskey, E. FRAX™ and the assessment of fracture probability in men and women from the UK. Osteoporos. Int. 2008, 19, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, G.S.; Mallett, S.; Altman, D.G. Predicting risk of osteoporotic and hip fracture in the United Kingdom: Prospective independent and external validation of QFractureScores. BMJ 2011, 342. Available online: https://www.bmj.com/content/342/bmj.d3651.full.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antich, P.P.; Anderson, J.A.; Ashman, R.B.; Dowdey, J.E.; Gonzales, J.; Murry, R.C.; Zenvekh, J.E.; Pak, C.Y. Measurement of mechanical properties of bone material in vitro by ultrasound reflection: Methodology and comparison with ultrasound transmission. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1991, 6, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, K.; Jepsen, D.; Matzen, L.; Hermann, A.P.; Masud, T.; Ryg, J. Is calcaneal quantitative ultrasound useful as a prescreen stratification tool for osteoporosis? Osteoporos. Int. 2015, 26, 1459–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans, D.; Baim, S. Quantitative Ultrasound (QUS) in the Management of Osteoporosis and Assessment of Fracture Risk. J. Clin. Densitom. 2017, 20, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, H.H.; Wright, A.C.; Wehrli, F.W. Deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance unambiguously quantifies pore and collagen-bound water in cortical bone. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fantazzini, P.; Brown, R.J.S.; Borgia, G.C. Bone tissue and porous media: Common features and differences studied by NMR relaxation. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2003, 21, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantazzini, P.; Bortolotti, V.; Brown, R.J.; Camaiti, M.; Garavaglia, C.; Viola, R.; Giavaresi, G. Two 1 H-nuclear magnetic resonance methods to measure internal porosity of bone trabeculae: By solid-liquid signal separation and by longitudinal relaxation. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, E.E.; Cho, H.; Song, Y.Q. High-resolution MRI of internal field diffusion-weighting in trabecular bone. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprinkhuizen, S.M.; Ackerman, J.L.; Song, Y.Q. Influence of bone marrow composition on measurements of trabecular microstructure using decay due to diffusion in the internal field MRI: Simulations and clinical studies. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mroue, K.H.; Nishiyama, Y.; Kumar Pandey, M.; Gong, B.; McNerny, E.; Kohn, D.H.; Morris, M.D.; Ramamoorthy, A. Proton-detected solid-state NMR spectroscopy of bone with ultrafast magic angle spinning. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manhard, M.K.; Horch, R.A.; Harkins, K.D.; Gochberg, D.F.; Nyman, J.S.; Does, M.D. Validation of quantitative bound- and pore-water imaging in cortical bone. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 2166–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horch, R.A.; Gochberg, D.F.; Nyman, J.S.; Does, M.D. Clinically compatible MRI strategies for discriminating bound and pore water in cortical bone. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, J.; Bydder, G.M. Qualitative and quantitative ultrashort-TE MRI of cortical bone. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wehrli, F.W. Magnetic resonance of calcified tissues. J. Magn. Reson. 2013, 229, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wehrli, F.W.; Song, H.K.; Saha, P.K.; Wright, A.C. Quantitative MRI for the assessment of bone structure and function. NMR Biomed. 2006, 19, 731–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Q.; King, J.D.; Wang, X. The characterization of human compact bone structure changes by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, A.C.; Wehrli, S.L.; Wehrli, F.W. Bi-component T2* analysis of bound and pore bone water fractions fails at high field strengths. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Seara, M.A.; Song, H.K.; Wehrli, F.W. Trabecular Bone Volume Fraction Mapping by Low-Resolution MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2001, 46, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iita, N.; Handa, S.; Tomiha, S.; Kose, K. Development of a compact MRI system for measuring the trabecular bone microstructure of the finger. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 57, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümich, B.; Blümler, P.; Eidmann, G.; Guthausen, A.; Haken, R.; Schmitz, U.; Saito, K.; Zimmer, G. The NMR-mouse: Construction, excitation, and applications. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1998, 16, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, B.; Coy, A.; Dykstra, R.; Eccles, C.; Hunter, M.; Parkinson, B.; Callaghan, P. A mobile one-sided NMR sensor with a homogeneous magnetic field: The NMR-MOLE. J. Magn. Reson. 2006, 183, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.H.; Chen, J.H.; Hwang, L.P. Single-sided mobile NMR with a Halbach magnet. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 24, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marble, A.E.; Mastikhin, I.V.; Colpitts, B.G.; Balcom, B.J. A compact permanent magnet array with a remote homogeneous field. J. Magn. Reson. 2007, 186, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, P.J.; Blümich, B.; Schmitz, U. One-Dimensional Imaging with a Palm-Size Probe. J. Magn. Reson. 2000, 144, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Naranjo, J.C.; Mastikhin, I.V.; Colpitts, B.G.; Balcom, B.J. A unilateral magnet with an extended constant magnetic field gradient. J. Magn. Reson. 2010, 207, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Galvosas, P.; Teal, P.; Harrison, F.G.; Berry, M.; Tzeng, Y.; Obruchkov, S. Single sided magnet system for relaxometry and diffusion measurement. In Proceedings of the 28th ISMRM Annual Meeting, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–24 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Badea, E.; Şendrea, C.; Carşote, C.; Adams, A.; Blümich, B.; Iovu, H. Unilateral NMR and thermal microscopy studies of vegetable tanned leather exposed to dehydrothermal treatment and light irradiation. Microchem. J. 2016, 129, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehorn, C.; Blümich, B. Cultural Heritage Studies with Mobile NMR. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7304–7312. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/anie.201713009 (accessed on 8 June 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brizi, L.; Camaiti, M.; Bortolotti, V.; Fantazzini, P.; Blümich, B.; Haber-Pohlmeier, S. One and two-dimensional NMR to evaluate the performance of consolidants in porous media with a wide range of pore sizes: Applications to cultural heritage. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 269, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizi, L.; Bortolotti, V.; Marmotti, G.; Camaiti, M. Identification of complex structures of paintings on canvas by NMR: Correlation between NMR profile and stratigraphy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2020, 58, 889–901. [Google Scholar]
- De Boever, E.; Foubert, A.; Oligschlaeger, D.; Claes, S.; Soete, J.; Bertier, P.; Özkul, M.; Virgone, A.; Swennen, R. Multiscale approach to (micro)porosity quantification in continental spring carbonate facies: Case study from the Cakmak quarry (Denizli, Turkey). Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2016, 17, 2922–2939. Available online: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/2016GC006382 (accessed on 8 June 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krüger, M.; Schwarz, A.; Blümich, B. Investigations of silicone breast implants with the NMR-MOUSE. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 25, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navon, G.; Eliav, U.; Demco, D.E.; Blümich, B. Study of order and dynamic processes in tendon by NMR and MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 25, 362–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rössler, E.; Mattea, C.; Stapf, S. Feasibility of high-resolution one-dimensional relaxation imaging at low magnetic field using a single-sided NMR scanner applied to articular cartilage. J. Magn. Reson. 2015, 251, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rössler, E.; Mattea, C.; Saarakkala, S.; Lehenkari, P.; Finnilä, M.; Rieppo, L.; Karhula, S.; Nieminen, M.T.; Stapf, S. Correlations of low-field NMR and variable-field NMR parameters with osteoarthritis in human articular cartilage under load. NMR Biomed. 2017, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landeghem, M.V.; Danieli, E.; Perlo, J.; Blümich, B.; Casanova, F. Low-gradient single-sided NMR sensor for one-shot profiling of human skin. J. Magn. Reson. 2012, 215, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.S.; Tourell, M.C.; Hugo, H.J.; Pyke, C.; Yang, S.; Lloyd, T.; Thompson, E.W.; Momot, K.I. Transverse relaxation-based assessment of mammographic density and breast tissue composition by single-sided portable NMR. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 1199–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühli, F.J.; Böni, T.; Perlo, J.; Casanova, F.; Baias, M.; Egarter, E.; Blümich, B. Non-invasive spatial tissue discrimination in ancient mummies and bones in situ by portable nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Cult. Herit. 2007, 8, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizi, L.; Barbieri, M.; Baruffaldi, F.; Bortolotti, V.; Fersini, C.; Liu, H.; Nogueira d’Eurydice, M.; Obruchkov, S.; Zong, F.; Galvosas, P.; et al. Bone volume–to–total volume ratio measured in trabecular bone by single-sided NMR devices. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, M.; Brizi, L.; Bortolotti, V.; Fantazzini, P.; Nogueira d’Eurydice, M.; Obruchkov, S.; Liu, H.; Galvosas, P. Single-sided NMR for the diagnosis of osteoporosis: Diffusion weighted pulse sequences for the estimation of trabecular bone volume fraction in the presence of muscle tissue. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 269, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizi, L.; Barbieri, M.; Testa, C.; Fantazzini, P. 1H nuclei compartmentalization, exchange and self-diffusion in cortical bone by one- and two-dimensions NMR in homogeneous and inhomogeneous fields. In Proceedings of the 27th ISMRM Annual Meeting, Montréal, QC, Canada, 11–16 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, M.; Fantazzini, P.; Bortolotti, V.; Baruffaldi, F.; Festa, A.; Manners, D.N.; Testa, C.; Brizi, L. Single-sided NMR to estimate morphological parameters of the trabecular bone structure. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 3353–3369. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/mrm.28648 (accessed on 8 June 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haken, R.; Blümich, B. Anisotropy in Tendon Investigated in Vivo by a Portable NMR Scanner, the NMR-MOUSE. J. Magn. Reson. 2000, 144, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, E.; Sarda, Y.; Ritz, N.; Sabo, E.; Navon, G.; Bergman, R.; Nevo, U. In vivo assessment of aged human skin with a unilateral NMR scanner. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterhoff, G.; Morgan, E.F.; Shefelbine, S.J.; Karim, L.; McNamara, L.M. Bone mechanical properties and changes with osteoporosis. Injury 2016, 47, S11–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seeman, E. Bone quality: The material and structural basis of bone strength. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2008, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebaze, R.M.; Ghasem-Zadeh, A.; Bohte, A.; Iuliano-Burns, S.; Mirams, M.; Price, R.I.; Mackie, E.J.; Seeman, E. Intracortical remodelling and porosity in the distal radius and post-mortem femurs of women: A cross-sectional study. Lancet 2010, 375, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appolonia, L.; Borgia, G.C.; Bortolotti, V.; Brown, R.J.S.; Fantazzini, P. Effects of hydrophobic treatments of stone on pore water studied by continuous distribution analysis of NMR relaxation times. Magn Reson. Imaging 2001, 19, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Q. Magnetic Resonance of Porous Media (MRPM): A perspective. J. Magn. Reson. 2013, 229, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horch, R.A.; Gochberg, D.F.; Nyman, J.S.; Does, M.D. Non-invasive Predictors of Human Cortical Bone Mechanical Properties: T2Discriminated 1H NMR Compared with High Resolution X-ray. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horch, R.A.; Nyman, J.S.; Gochberg, D.F.; Dortch, R.D.; Does, M.D. Characterization of1H NMR signal in human cortical bone for magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 64, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carr, H.; Purcell, E. Effects of diffusion on free precession in nuclear magnetic resonance experiments. Phys. Rev. 1954, 94, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiboom, S.; Gill, D. Modified spin-echo method for measuring nuclear relaxation times. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1958, 29, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cowin, S.C. Bone poroelasticity. J. Biomech. 1999, 32, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgia, G.; Brown, R.; Fantazzini, P. Uniform-Penalty Inversion of Multiexponential Decay Data. J. Magn. Reson. 1998, 132, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, D.; Harrison, F.G.; Teal, P.; Galvosas, P.; Berry, M.; Obruchkov, S.; Tzeng, Y. In vivo hypoxia monitoring using a novel single sided NMR device. In Proceedings of the 29th ISMRM Annual Meeting, Concord, CA, USA, 15–20 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, S.L.; Lin, M.A.; Srinivasan, S.; Wheeler, A.J.; Hargreaves, B.A.; Daniel, B.L. A Mixed-Reality System for Breast Surgical Planning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR-Adjunct), Nantes, France, 9–13 October 2017; pp. 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, V.; Megali, G.; Troia, E.; Pietrabissa, A.; Mosca, F. A 3D Mixed-Reality System for Stereoscopic Visualization of Medical Dataset. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 56, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, T.M.; Gregory, J.; Sledge, J.; Allard, R.; Mir, O. Surgery guided by mixed reality: Presentation of a proof of concept. Acta Orthop. 2018, 89, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neves, C.A.; Vaisbuch, Y.; Leuze, C.; McNab, J.A.; Daniel, B.; Blevins, N.H.; Hwang, P.H. Application of holographic augmented reality for external approaches to the frontal sinus. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020, 10, 920–925. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/alr.22546 (accessed on 8 June 2021). [CrossRef]
- Sathyanarayana, S.; Leuze, C.; Hargreaves, B.; Daniel, B.; Wetzstein, G.; Etkin, A.; Bhati, M.T.; McNab, J.A. Comparison of head pose tracking methods for mixed-reality neuronavigation for transcranial magnetic stimulation. In Proceedings of the International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Medical Imaging 2020: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling, Huston, TX, USA, 16 March 2020; Volume 11315, pp. 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Humbert, L.; Martelli, Y.; Fonollà, R.; Steghöfer, M.; Di Gregorio, S.; Malouf, J.; Romera, J.; Barquero, L.M.D.R. 3D-DXA: Assessing the Femoral Shape, the Trabecular Macrostructure and the Cortex in 3D from DXA images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väänänen, S.P.; Grassi, L.; Flivik, G.; Jurvelin, J.S.; Isaksson, H. Generation of 3D shape, density, cortical thickness and finite element mesh of proximal femur from a DXA image. Med. Image Anal. 2015, 24, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronczka, M.; Müller-Petke, M. Optimization of CPMG sequences to measure NMR transverse relaxation time T2 in borehole applications. Geosci. Instrum. Methods Data Syst. 2012, 1, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veselinovic, D.; Dick, M.; Green, D. Accurate Pore Size Measurement Via NMR On Unconventionals. In Proceedings of the Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 22–24 July 2019; pp. 1878–1888. Available online: https://library.seg.org/doi/pdf/10.15530/urtec-2019-394 (accessed on 8 June 2021).
- Barbieri, M.; Watkins, L.; Desai, A.D.; Mazzoli, V.; Rubin, E.; Schmidt, A.; Gold, G.E.; Hargreaves, B.A.; Chaudhari, A.S.; Kogan, F. B1 Field Inhomogeneity Correction for qDESS T2 Mapping: Application to Rapid Bilateral Knee Imaging. In Proceedings of the 29th ISMRM Annual Meeting, Concord, CA, USA, 15–20 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, M.; Chaudhari, A.S.; Moran, C.J.; Gold, G.E.; Hargreaves, B.A.; Kogan, F. A Method for Measuring B0 Field Inhomogeneity Using Quantitative DESS (qDESS). In Proceedings of the 29th ISMRM Annual Meeting, Concord, CA, USA, 15–20 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbieri, M.; Fantazzini, P.; Testa, C.; Bortolotti, V.; Baruffaldi, F.; Kogan, F.; Brizi, L. Characterization of Structural Bone Properties through Portable Single-Sided NMR Devices: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147318
Barbieri M, Fantazzini P, Testa C, Bortolotti V, Baruffaldi F, Kogan F, Brizi L. Characterization of Structural Bone Properties through Portable Single-Sided NMR Devices: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(14):7318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147318
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbieri, Marco, Paola Fantazzini, Claudia Testa, Villiam Bortolotti, Fabio Baruffaldi, Feliks Kogan, and Leonardo Brizi. 2021. "Characterization of Structural Bone Properties through Portable Single-Sided NMR Devices: State of the Art and Future Perspectives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 14: 7318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147318
APA StyleBarbieri, M., Fantazzini, P., Testa, C., Bortolotti, V., Baruffaldi, F., Kogan, F., & Brizi, L. (2021). Characterization of Structural Bone Properties through Portable Single-Sided NMR Devices: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), 7318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147318





