The Pivotal Player: Components of NF-κB Pathway as Promising Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Brief View of Colorectal Cancer
1.2. Overview of Types of Biomarkers of CRC
1.2.1. CRC Diagnostic Biomarker Examples
1.2.2. CRC Clinical Biomarker Examples
1.3. Synopsis of Signaling Pathways Related to CRC
2. NF-κB Signaling and Its Important Role in CRC
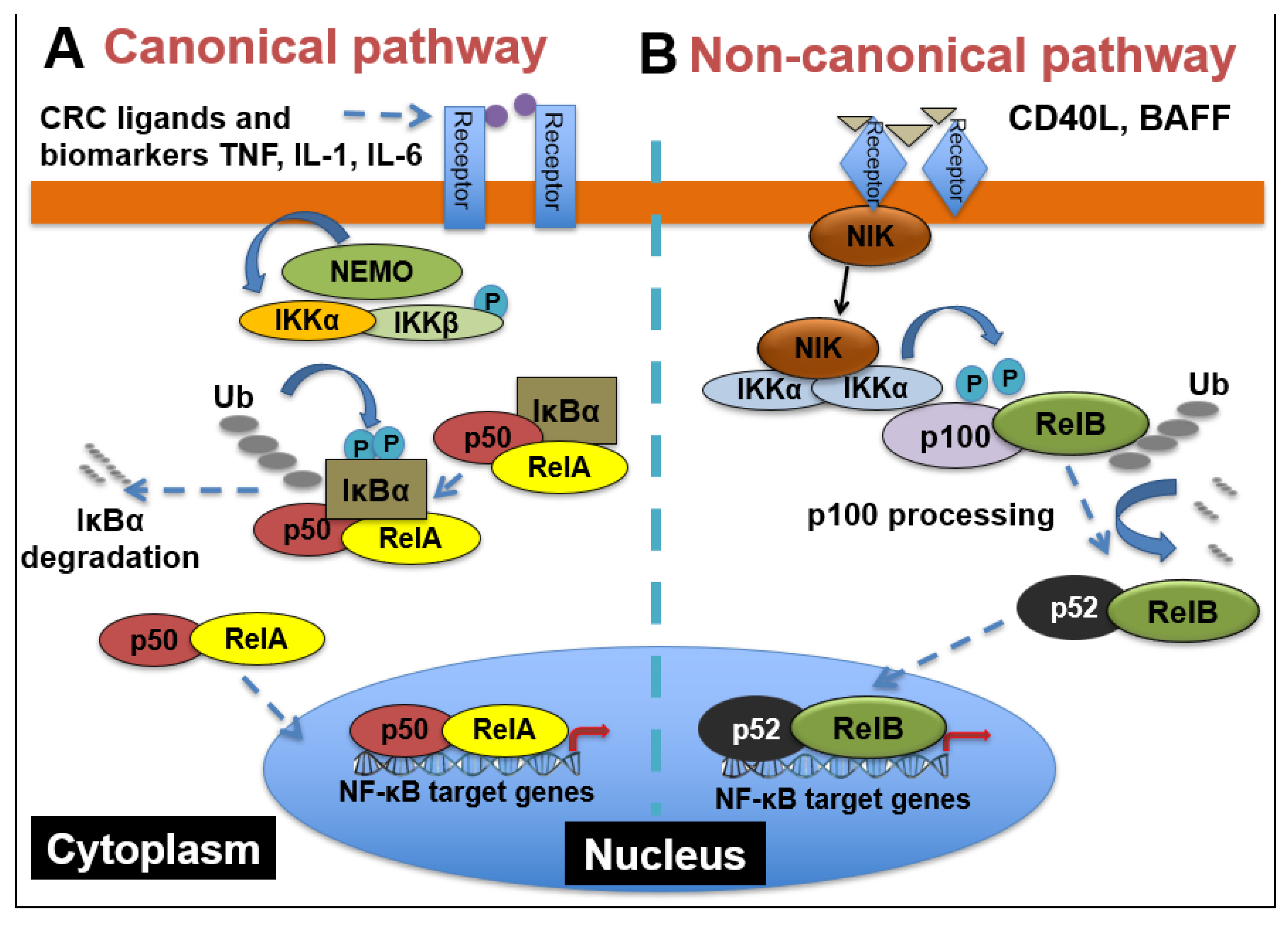
2.1. NF-κB Signaling
2.2. Myriad Functions of NF-κB Signaling and Complex Interactions between Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment (TME) in CRC
3. NF-κB Signaling-Related CRC Biomarkers
4. Effort on Targeting NF-κB Signaling in CRC Treatment and Conclusive Remarks
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alves Martins, B.A.; De Bulhões, G.F.; Cavalcanti, I.N.; Martins, M.M.; de Oliveira, P.G.; Martins, A.M.A. Biomarkers in colorectal cancer: The role of translational proteomics research. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, E.; Tanis, P.J.; Vleugels, J.L.; Kasi, P.M.; Wallace, M.B. Risk factors. Lancet 2019, 394, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuders, E.H.; Ruco, A.; Rabeneck, L.; Schoen, R.E.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Young, G.; Kuipers, E.J. Colorectal cancer screening: A global overview of existing programmes. Gut 2015, 64, 1637–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliore, L.; Migheli, F.; Spisni, R.; Coppedè, F. Genetics, Cytogenetics, and Epigenetics of Colorectal Cancer. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawicki, T.; Ruszkowska, M.; Danielewicz, A.; Niedźwiedzka, E.; Arłukowicz, T.; Przybyłowicz, K. A Review of Colorectal Cancer in Terms of Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Development, Symptoms and Diagnosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fearon, E.R. Molecular Genetics of Colorectal Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2011, 6, 479–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Qiu, T.; Dong, L.; Zhang, F.; Guo, L.; Ying, J. Prevalence and characteristics of PIK3CA mutation in mismatch repair-deficient colorectal cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, K. Colorectal cancer development and advances in screening. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 967. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, S.A. Dynamics of Cancer: Incidence, Inheritance, and Evolution; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lochhead, P.; Chan, A.T.; Giovannucci, E.; Fuchs, C.S.; Wu, K.; Nishihara, R.; O’Brien, M.; Ogino, S. Progress and Opportunities in Molecular Pathological Epidemiology of Colorectal Premalignant Lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carethers, J.M.; Jung, B.H. Genetics and genetic biomarkers in sporadic colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.-Z.; Wang, G.-F.; Cheng, X.-B.; Dong, Z.-H.; Chen, X.; Deng, Y.-J.; Song, X. Relationship between mismatch repair protein, RAS, BRAF, PIK3CA gene expression and clinicopathological characteristics in elderly colorectal cancer patients. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 2458–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velho, S.; Moutinho, C.; Cirnes, L.; Albuquerque, C.; Hamelin, R.; Schmitt, F.; Carneiro, F.; Oliveira, C.; Seruca, R. BRAF, KRAS and PIK3CA mutations in colorectal serrated polyps and cancer: Primary or secondary genetic events in colorectal carcinogenesis? BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pino, M.S.; Chung, D.C. The Chromosomal Instability Pathway in Colon Cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2059–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Li, R.; He, Y.; Yi, Y.; Wu, H.; Liang, Z. Next-generation sequencing reveals heterogeneous genetic alterations in key signaling pathways of mismatch repair deficient colorectal carcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2591–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Advances in Colorectal Cancer Research. National Institutes of Health. Available online: https://www.nih.gov/research-training/advances-colorectal-cancer-research (accessed on 20 August 2015).
- Yu, J.; Zhai, X.; Li, X.; Zhong, C.; Guo, C.; Yang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, S. Identification of MST1 as a potential early detection biomarker for colorectal cancer through a proteomic approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, H.; Shen, K.; Li, B.; Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Z. Clinical significance and diagnostic value of serum NSE, CEA, CA19-9, CA125 and CA242 levels in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, A.; Ferrari, P.; Duffy, M.J.; Antonelli, A.; Rossi, G.; Metelli, M.R.; Fulceri, F.; Anselmi, L.; Conte, M.; Berti, P.; et al. Intensive Risk-Adjusted Follow-up With the CEA, TPA, CA19.9, and CA72.4 Tumor Marker Panel and Abdominal Ultrasonography to Diagnose Operable Colorectal Cancer Recurrences. Arch. Surg. 2010, 145, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vallania, F.; Assayag, K.; Warsinske, H.; Ulz, P.; John, J.S.; Brachmann, C.; Patterson, S.D.; Thai, D.; Bhargava, P.; Shah, M.A.; et al. Exploratory longitudinal analysis of cfDNA to reveal potential biomarkers of CRC progression and treatment response. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubeni, C.A.; Jensen, C.D.; Fedewa, S.A.; Quinn, V.P.; Zauber, A.G.; Schottinger, J.E.; Corley, D.A.; Levin, T.R. Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) for Colon Cancer Screening: Variable Performance with Ambient Temperature. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2016, 29, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carethers, J.M. Fecal DNA Testing for Colorectal Cancer Screening. Annu. Rev. Med. 2020, 71, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, Y.; Yamazaki, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Saito, N.; Kakugawa, Y.; Otake, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Matsumura, Y. Fecal miR-106a Is a Useful Marker for Colorectal Cancer Patients with False-Negative Results in Immunochemical Fecal Occult Blood Test. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koga, Y.; Yamazaki, N.; Matsumura, Y. [Fecal Biomarker for Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis]. Rinsho Byori. Jpn. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 63, 361–368. [Google Scholar]
- Califf, R.M. Biomarker definitions and their applications. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhu, C.; Yang, K.; Li, J.; Du, N.; Zong, M.; Zhou, J.; He, J. Poly(C)-binding protein 1 mediates drug resistance in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13312–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gold, P.; Freedman, S.O. Demonstration of tumor-specific antigens in human colonic carcinomata by immunological tolerance and absorption techniques. J. Exp. Med. 1965, 121, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos-Da-Paz, M.; Dórea, J.G.; Galdino, A.S.; Lacava, Z.G.M.; Santos, M.D.F.M.A. Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) and Hepatic Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer: Update on Biomarker for Clinical and Biotechnological Approaches. Recent Patents Biotechnol. 2018, 12, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, E.; Wagner, E.F. AP-1: A double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Hepatology 2011, 3, 1470–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, C.S.; Bernard, J.K.; Demory Beckler, M.; Almohazey, D.; Washington, M.K.; Smith, J.J.; Frey, M.R. ERBB4 is over-expressed in human colon cancer and enhances cellular transformation. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pernicova, I.; Korbonits, M. Metformin—Mode of action and clinical implications for diabetes and cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Medina, R.; Cayuso, J.; Okubo, T.; Takada, S.; Martí, E. Wnt canonical pathway restricts graded Shh/Gli patterning activity through the regulation of Gli3 expression. Development 2008, 135, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.H.; Guo, X.L. Combinational strategies of metformin and chemotherapy in cancers. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrod, J.D.; Matsuno, K.; Artavanis-Tsakonas, S.; Perrimon, N. Interaction between Wingless and Notch signaling pathways mediated by dishevelled. Science 1996, 271, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, S.; Bansal, M.; Guarnieri, P.; Davis, H.; Zen, A.A.H.; Baran, B.; Pinna, C.M.A.; Rahman, H.; Biswas, S.; Bardella, C.; et al. Bone morphogenetic protein and Notch signalling crosstalk in poor-prognosis, mesenchymal-subtype colorectal cancer. J. Pathol. 2017, 242, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Guo, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, H.; Hu, K.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, S.; Pang, X.; Zhou, S.; Dang, Y.; et al. FOXD3 is a tumor suppressor of colon cancer by inhibiting EGFR-Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signal pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 5048–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geissler, K.; Zach, O. Pathways involved in Drosophila and human cancer development: The Notch, Hedgehog, Wingless, Runt, and Trithorax pathway. Ann. Hematol. 2012, 91, 645–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, W.J.; Yoon, J.; Park, J.C.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kaduwal, S.; Choi, K.Y. Ras stabilization through aberrant activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes intestinal tumorigenesis. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, a30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Post-translational modifications and regulation of the RAS superfamily of GTPases as anticancer targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Mu, G.G.; Ding, Q.S.; Li, Y.X.; Shi, Y.B.; Dai, J.F.; Yu, H.G. Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN) Represses Colon Cancer Progression through Inhibiting Paxillin Transcription via PI3K/AKT/NF-κB Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15018–15029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fulbright, L.E.; Ellermann, M.; Arthur, J.C. The microbiome and the hallmarks of cancer. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Prabhu, L.; Hartley, A.V.; Martin, M.; Sun, E.; Jiang, G.; Liu, Y.L.; Lu, T. Methylation of NF-κB and its Role in Gene Regulation. In Gene Expression and Regulation in Mammalian Cells—Transcription from General Aspects; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; p. 291. [Google Scholar]
- Motolani, A.; Martin, M.; Sun, M.; Lu, T. Phosphorylation of the Regulators, a Complex Facet of NF-κB Signaling in Cancer. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Hartley, A.V.; Jin, J.; Sun, M.; Lu, T. Phosphorylation of NF-κB in Cancer. Adenosine Triphosphate Health Dis. 2019, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.-C. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soleimani, A.; Rahmani, F.; Ferns, G.A.; Ryzhikov, M.; Avan, A.; Hassanian, S.M. Role of the NF-κB signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Gene 2020, 726, 144132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, W.; Feng, J.; Qin, H.; Ma, Y. Molecular therapy of colorectal cancer: Progress and future directions. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 136, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C.; Edwards, J. NF-κB pathways in the development and progression of colorectal cancer. Transl. Res. 2018, 197, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartley, A.-V.; Wang, B.; Jiang, G.; Wei, H.; Sun, M.; Prabhu, L.; Martin, M.; Safa, A.; Sun, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Regulation of a PRMT5/NF-κB Axis by Phosphorylation of PRMT5 at Serine 15 in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, L.; Wei, H.; Chen, L.; Demir, Ö.; Sandusky, G.; Sun, E.; Lu, T. Adapting AlphaLISA high throughput screen to discover a novel small-molecule inhibitor targeting protein arginine methyltransferase 5 in pancreatic and colorectal cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 39963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prabhu, L.; Chen, L.; Wei, H.; Demir, Ö.; Safa, A.; Zeng, L.; Lu, T. Development of an AlphaLISA high throughput technique to screen for small molecule inhibitors targeting protein arginine methyltransferases. Mol. Biosyst. 2017, 13, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Huang, J.; Zhong, H.; Shen, N.; Faggioni, R.; Fung, M.; Yao, Y. Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 141, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marelli, G.; Sica, A.; Vannucci, L.; Allavena, P. Inflammation as target in cancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 35, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Wei, H.; Lu, T. Targeting microenvironment in cancer therapeutics. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52575–52583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.W.; Wang, S.R.; Chao, M.F.; Wu, T.C.; Lui, W.Y.; P’eng, F.K. Chi CW. Serum interleukin-6 levels reflect disease status of gastric cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1996, 91, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stanilov, N.; Miteva, L.; Dobreva, Z.; Stanilova, S. Colorectal cancer severity and survival in correlation with tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2014, 28, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Karin, M. Dangerous liaisons: STAT3 and NF-κB collaboration and crosstalk in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cammarota, R.; Bertolini, V.; Pennesi, G.; Bucci, E.; Gottardi, O.; Garlanda, C.; Laghi, L.; Barberis, M.C.; Sessa, F.; Noonan, D.M.; et al. The tumor microenvironment of colorectal cancer: Stromal TLR-4 expression as a potential prognostic marker. J. Transl. Med. 2010, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- West, N.; McCuaig, S.; Franchini, F.; Powrie, F. Emerging cytokine networks in colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, P.T.; Beswick, E.J.; Coronado, Y.A.; Johnson, P.; O’Connell, M.R.; Watts, T.; Pinchuk, I.V. CD 90+ stromal cells are the major source of IL-6, which supports cancer stem-like cells and inflammation in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1971–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ismail, N.I.; Othman, I.; Abas, F.; Lajis, N.H.; Naidu, R. Mechanism of Apoptosis Induced by Curcumin in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neil, B.H.; Funkhouser, W.K.; Calvo, B.F.; Meyers, M.O.; Kim, H.J.; Goldberg, R.M.; Tepper, J.E. NF-κB is activated by radiotherapy and is prognostic for overall survival in patients with rectal cancer treated with preoperative fluorouracil-based chemoradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holley, A.K.; Miao, L.; Clair, D.K.S.; Clair, W.H.S. Redox-Modulated Phenomena and Radiation Therapy: The Central Role of Superoxide Dismutases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1567–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.Y.; Cusack, J.C.; Liu, R.; Baldwin, A.S. Control of inducible chemoresistance: Enhanced anti-tumor therapy through increased apoptosis by inhibition of NF-κB. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Villalona-Calero, M.A. Irinotecan: Mechanisms of tumor resistance and novel strategies for modulating its activity. Ann. Oncol. 2002, 13, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scartozzi, M.; Bearzi, I.; Pierantoni, C.; Mandolesi, A.; Loupakis, F.; Zaniboni, A.; Cascinu, S. Nuclear factor-kB tumor expression predicts response and survival in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab-irinotecan therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 3930–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.L.; Hawke, N.A.; Kashatus, D.; Baldwin, A.S. The nuclear factor κB subunits RelA/p65 and c-Rel potentiate but are not required for Ras-induced cellular transformation. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7248–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, G.; Tang, Z.; Ye, Y.B.; Chen, Q. NF-κB activity is downregulated by KRAS knockdown in SW620 cells via the RAS-ERK-IκBα pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Okugawa, Y.; Yang, J.; Liang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Han, H.; et al. Novel evidence for an oncogenic role of microRNA-21 in colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Gut 2015, 65, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, D.; Noorbakhsh, F.; Delavari, A.; Tavakkoli-Bazzaz, J.; Farashi-Bonab, S.; Abdollahzadeh, R.; Rezaei, N. Expression level of long noncoding RNA NKILA-miR103-miR107 inflammatory axis and its clinical significance as potential biomarker in patients with colorectal cancer. J. Res. Med Sci. 2020, 25, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Qiao, C.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; Wu, S.; Hu, S.; Qiu, Z.; Qian, M.; Tian, D.; et al. Forkhead box K2 promotes human colorectal cancer metastasis by upregulating ZEB1 and EGFR. Theranostics 2019, 9, 3879–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calik, I.; Calik, M.; Turken, G.; Ozercan, I.H. A promising independent prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer: P2X7 receptor. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 107–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Guan, X.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, X.; Lin, H.; Yang, M.; Li, C.; Yang, R.; et al. GADD45B as a Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker in Stage II Colorectal Cancer. Genes 2018, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viennois, E.; Chen, F.; Merlin, D. NF-κB pathway in colitis-associated cancers. Transl. Gastrointest. Cancer 2013, 2, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Prasad, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Regulation of survival, proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis of tumor cells through modulation of inflammatory pathways by nutraceuticals. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 405–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, J. Proteasome inhibition: A novel approach to cancer therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, S49–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Methotrexate suppresses NF-κB activation through inhibition of IκBα phosphorylation and degradation. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 2911–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weber, C.K.; Liptay, S.; Wirth, T.; Adler, G.; Schmid, R.M. Suppression of NF-κB activity by sulfasalazine is mediated by direct inhibition of IκB kinases α and β. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.K.; Llanes, S.; Schumer, W. Effect of dexamethasone on NF-κB activation, tumor necrosis factor formation, and glucose dyshomeostasis in septic rats. J. Surg. Res. 1997, 72, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, A.; Deepa, N.; Chennazhi, K.; Lakshmanan, V.K.; Kumar, A.S.; Anitha, A.; Deepa, N.; Chennazhi, K.; Lakshmanan, V.K.; Kumar, A.S. Combinatorial anticancer effects of curcumin and 5-fluorouracil loaded thiolated chitosan nanoparticles towards colon cancer treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 2730–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Symbol | Description | Type of Biomarker (Diagnostic or Clinical) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| p65 | P65 subunit of NF-κB | Diagnostic | [63,65,66,67,68,69] |
| p50 | P50 subunit of NF-κB | Clinical (radiation) | [64,67,68] |
| KRas | Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog | Clinical/diagnostic (chemotherapeutic) | [70] |
| mir-21 | microRNA 21 | Diagnostic | [71] |
| NKILA | NF-κB interacting lncRNA | Diagnostic | [72] |
| mir-103 | microRNA 103 | Diagnostic | [72] |
| mir-107 | microRNA 107 | Diagnostic | [72] |
| FOXK2 | Protein forkhead box K2 | Diagnostic | [73] |
| P2 × 7R | P2 × 7 receptor | Diagnostic | [74] |
| GADD45B | Growth arrest and DNA damage inducible Beta | Clinical/diagnostic (chemotherapeutic) | [75] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin, M.; Sun, M.; Motolani, A.; Lu, T. The Pivotal Player: Components of NF-κB Pathway as Promising Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147429
Martin M, Sun M, Motolani A, Lu T. The Pivotal Player: Components of NF-κB Pathway as Promising Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(14):7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147429
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin, Matthew, Mengyao Sun, Aishat Motolani, and Tao Lu. 2021. "The Pivotal Player: Components of NF-κB Pathway as Promising Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 14: 7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147429
APA StyleMartin, M., Sun, M., Motolani, A., & Lu, T. (2021). The Pivotal Player: Components of NF-κB Pathway as Promising Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), 7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147429







