Synergistic Effect of 300 μm Needle-Depth Fractional Microneedling Radiofrequency on the Treatment of Senescence-Induced Aging Hyperpigmentation of the Skin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients
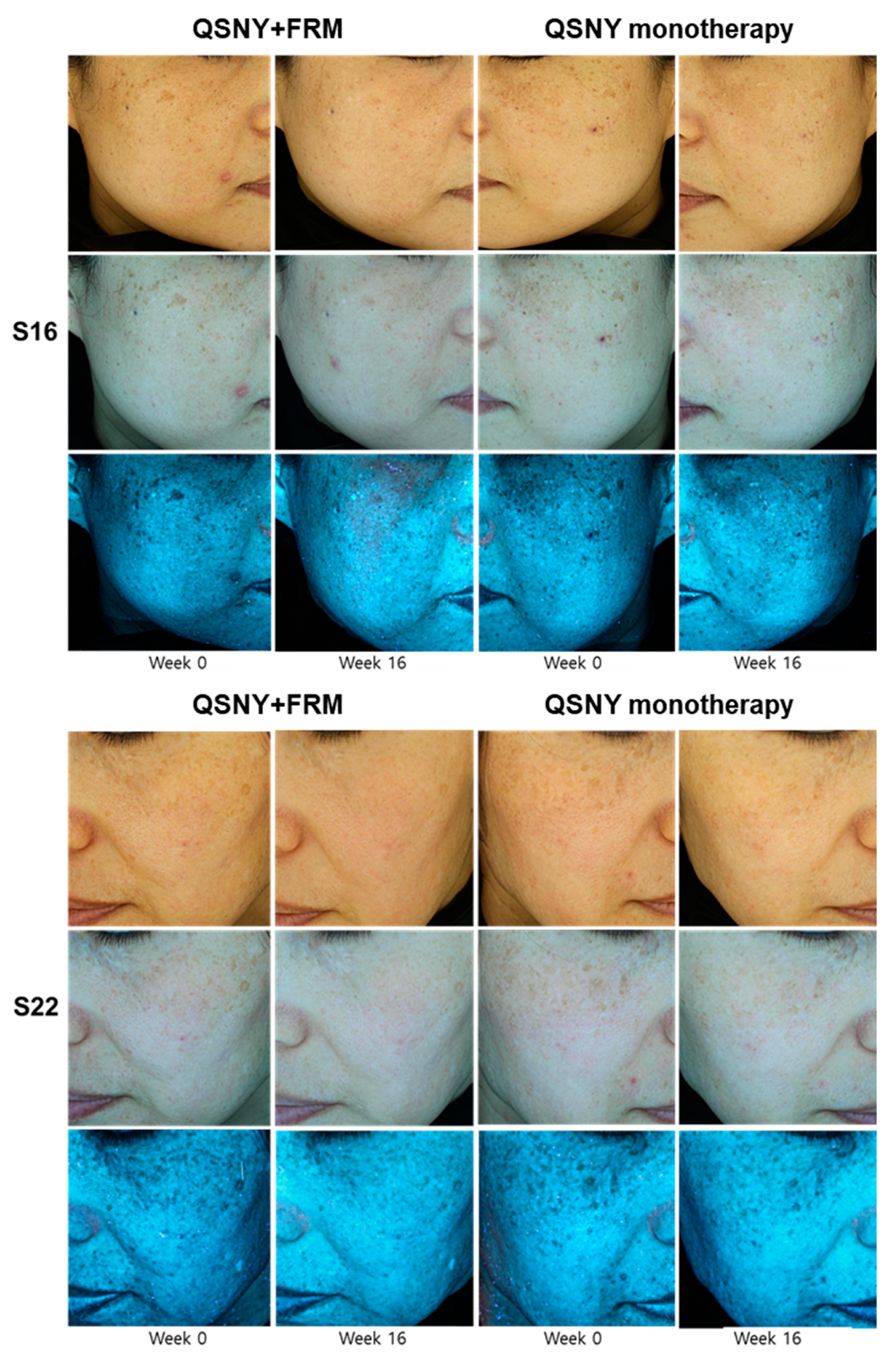
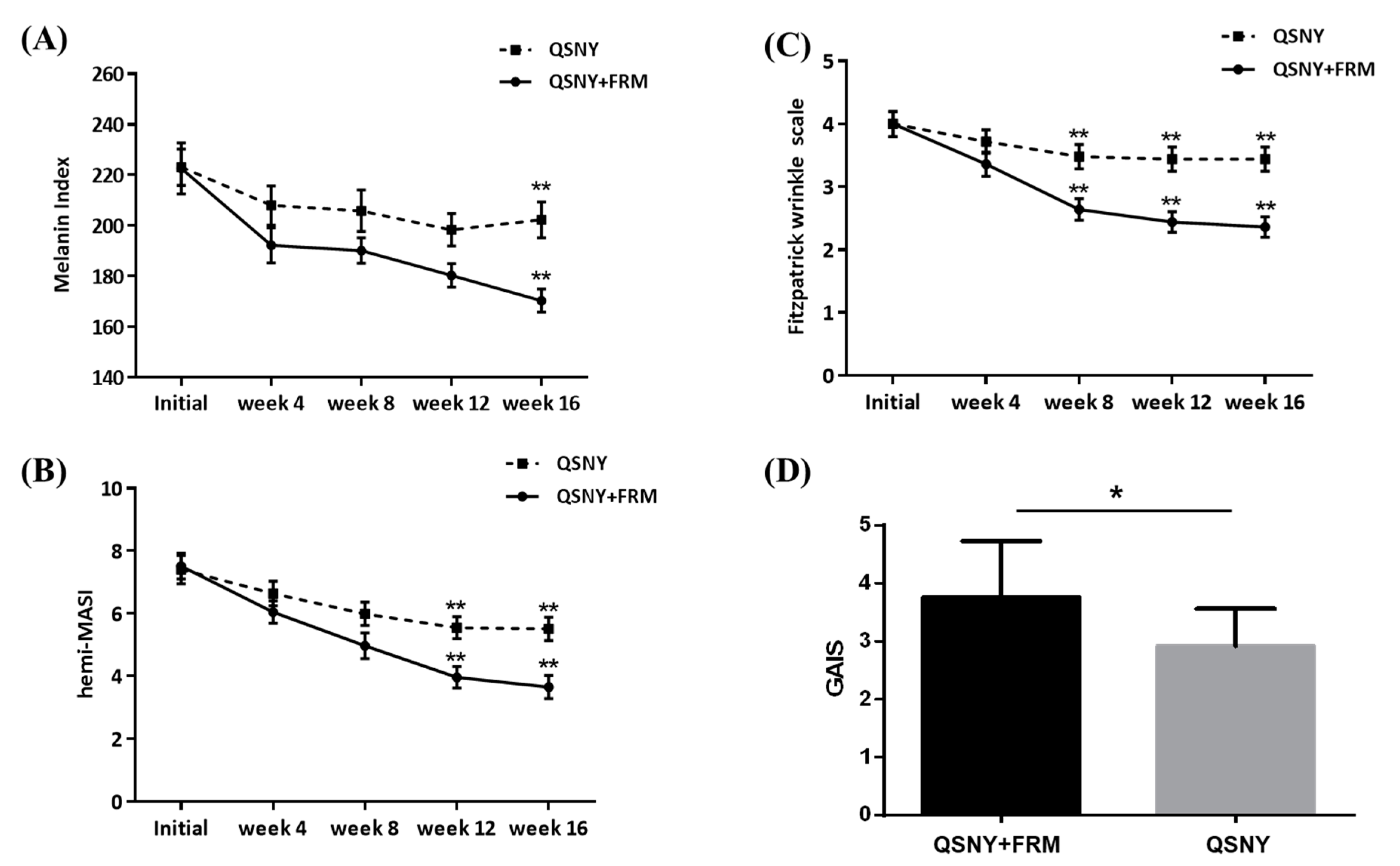
2.2. Clinical Efficacy of Adjuvant FMR Treatment after QSNY for Aging-Associated Hyperpigmentation
2.3. Safety Profile
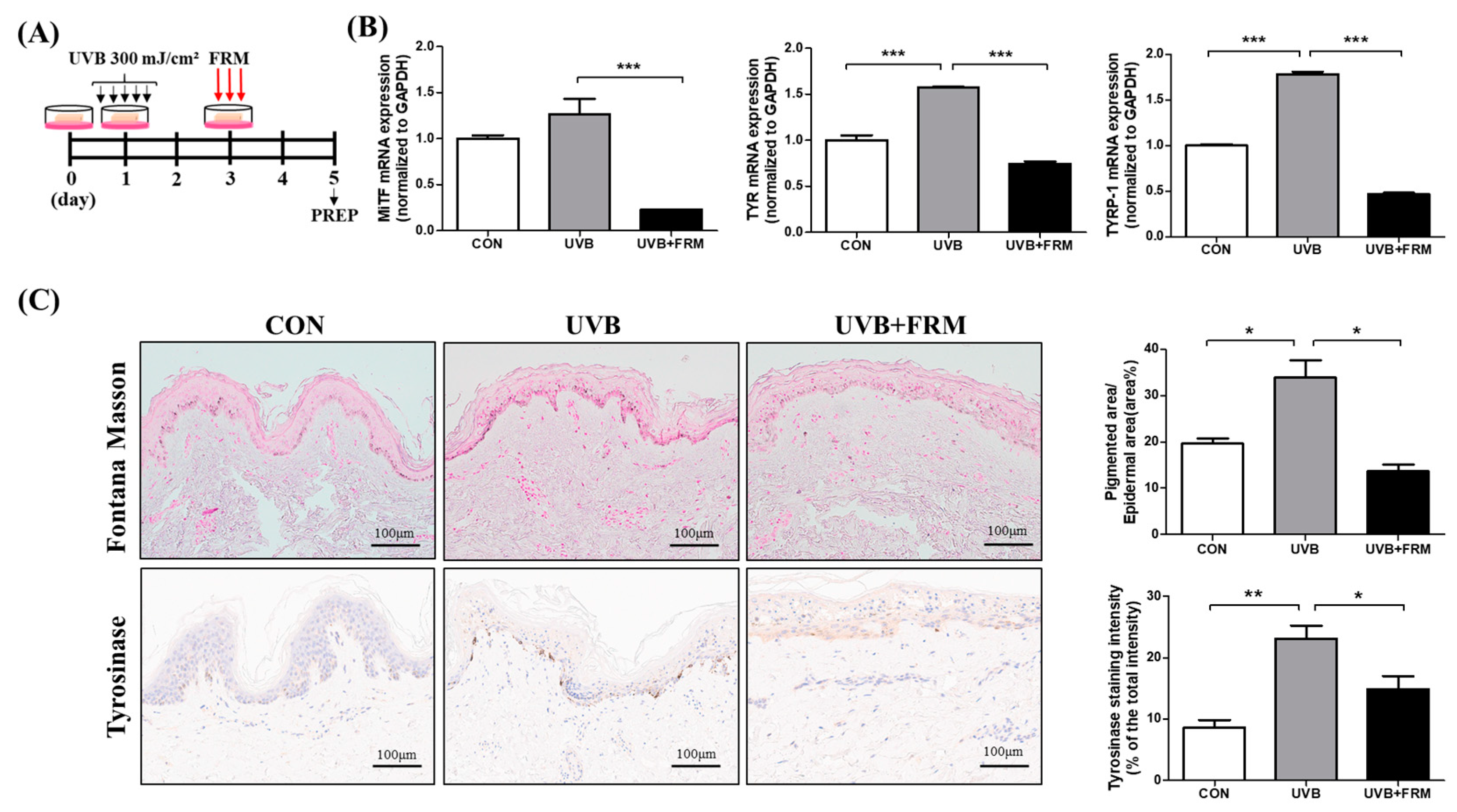
2.4. Effect of FMR Irradiation after UVB Exposure on Skin Pigmentation
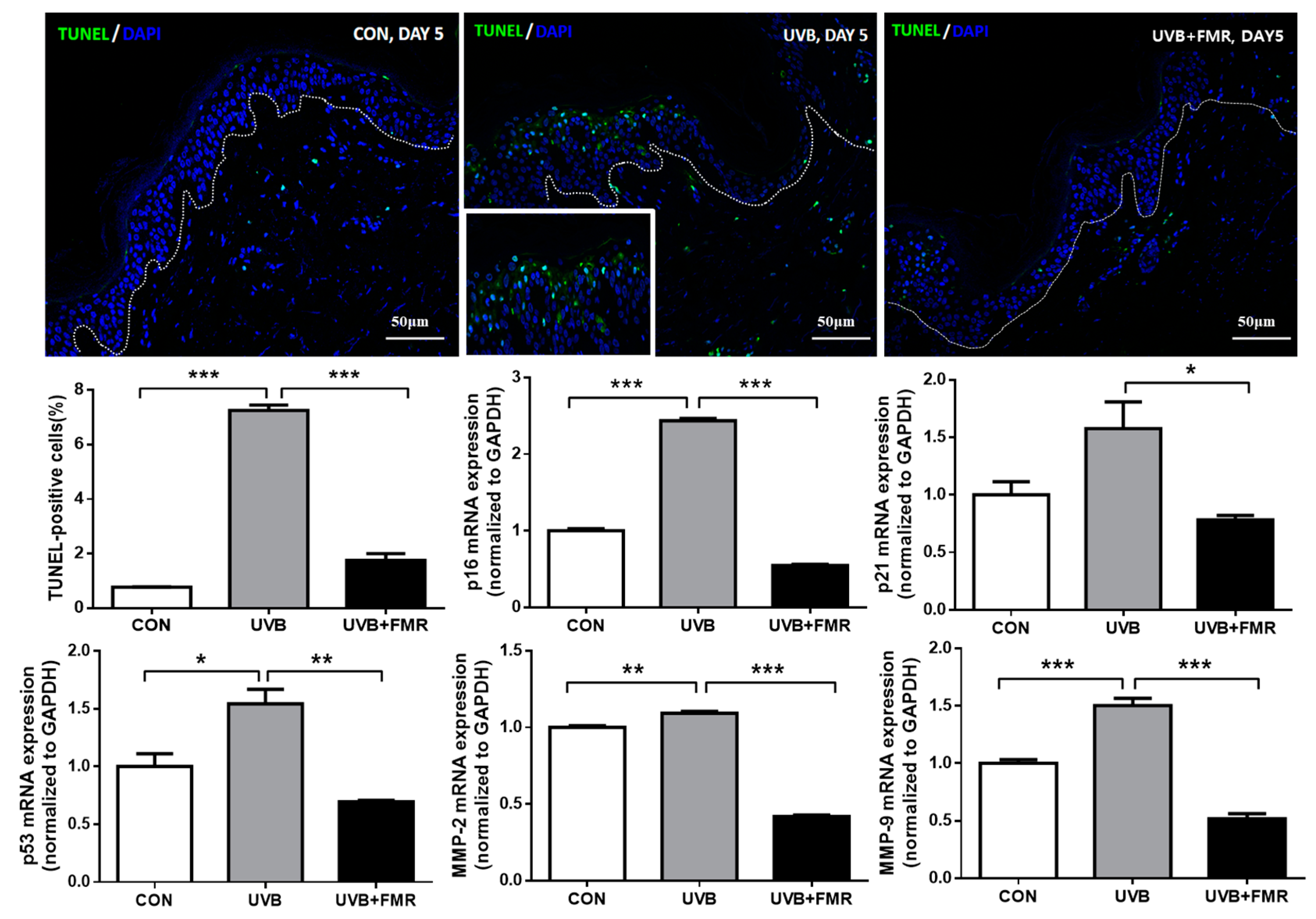
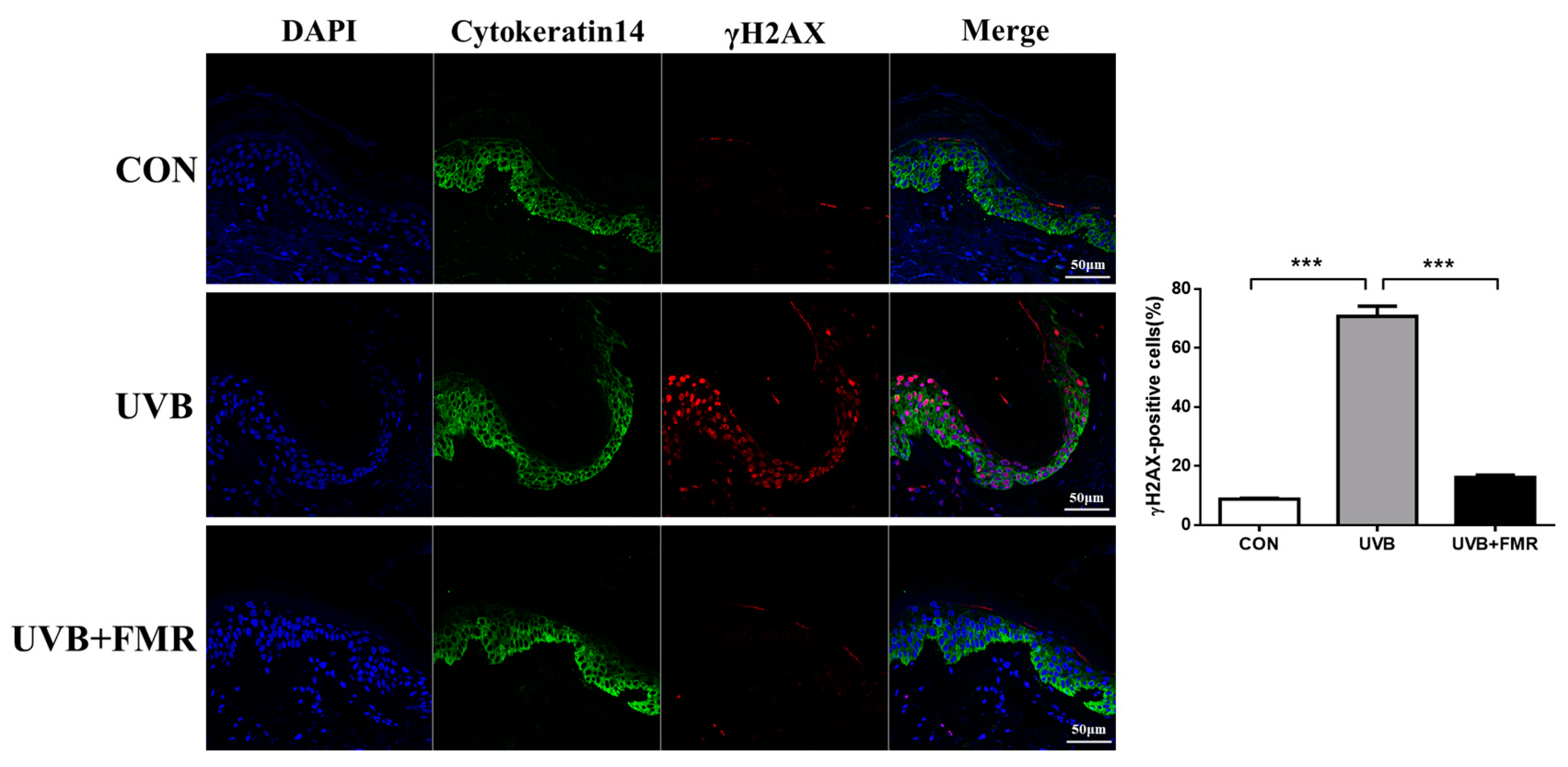
2.5. UVB-Induced Premature Senescence of Epidermal Keratinocytes Rescued by FMR Irradiation
2.6. Restored Expression of Collagen Type IV in the UV-Irradiated Basal Membrane after FMR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical Study Design and Patients
4.2. Treatment Protocol
4.3. Efficacy Evaluation
4.4. Safety Evaluation
4.5. Ex Vivo Skin Organ Culture and UVB/FMR Irradiation Protocol
4.6. Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence
4.7. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase-Mediated dUTP Nick End-Labeling Assay
4.8. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Reverse Transcription–Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.J.; Suh, H.Y.; Choi, M.E.; Jung, C.J.; Chang, S.E. Clinical improvement of photoaging-associated facial hyperpigmentation in korean skin with a picosecond 1064-nm neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser. Lasers Med. Sci. 2020, 35, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Jo, S.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Won, C.H.; Lee, M.W.; Choi, J.H.; Chang, S.E. The effect of mcp-1/ccr2 on the proliferation and senescence of epidermal constituent cells in solar lentigo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellei, B.; Picardo, M. Premature cell senescence in human skin: Dual face in chronic acquired pigmentary disorders. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 57, 100981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, K.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, M.H.; Rhee, D.Y.; Yeo, U.C.; Chang, S.E. A prospective, split-face, double-blinded, randomized study of the efficacy and safety of a fractional 1064-nm q-switched nd:Yag laser for photoaging-associated mottled pigmentation in asian skin. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2016, 18, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, L. Laser and laser compound therapy for melasma: A meta-analysis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2020, 31, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, G.Y.; Kim, W.S. Beneficial effect of low fluence 1064 nm q-switched neodymium:Yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser in the treatment of senile lentigo. Ann. Dermatol. 2017, 29, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ho, S.G.; Chan, N.P.; Yeung, C.K.; Shek, S.Y.; Kono, T.; Chan, H.H. A retrospective analysis of the management of freckles and lentigines using four different pigment lasers on asian skin. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2012, 14, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranmanesh, B.; Khalili, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Amiri, R.; Aflatoonian, M. The efficacy of energy-based devices combination therapy for melasma. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, e14927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, T.R.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, A.Y. Cadherin 11 involved in basement membrane damage and dermal changes in melasma. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2016, 96, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passeron, T.; Picardo, M. Melasma, a photoaging disorder. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2018, 31, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.H.; Na, J.I.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, K.C. Melasma: Updates and perspectives. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Alvarez, B.; Mesa-Garza, I.G.; Castanedo-Cazares, J.P.; Fuentes-Ahumada, C.; Oros-Ovalle, C.; Navarrete-Solis, J.; Moncada, B. Histochemical and immunohistochemical study in melasma: Evidence of damage in the basal membrane. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2011, 33, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.H.; Choi, S.C.; Jung, J.Y.; Park, G.H. Combined treatment of melasma involving low-fluence q-switched nd:Yag laser and fractional microneedling radiofrequency. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2019, 30, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzayans, R.; Murray, D. Do tunel and other apoptosis assays detect cell death in preclinical studies? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernadotte, A.; Mikhelson, V.M.; Spivak, I.M. Markers of cellular senescence. Telomere shortening as a marker of cellular senescence. Aging 2016, 8, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyarts, E.; Muizzuddin, N.; Maes, D.; Giacomoni, P.U. Morphological changes associated with aging: Age spots and the microinflammatory model of skin aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1119, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastonini, E.; Kovacs, D.; Picardo, M. Skin pigmentation and pigmentary disorders: Focus on epidermal/dermal cross-talk. Ann. Dermatol. 2016, 28, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, S.; Matsunaga, Y.; Amano, S.; Takada, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Tsunenaga, M.; Nishiyama, T.; Kohno, Y.; Fukuda, M. Possible involvement of gelatinases in basement membrane damage and wrinkle formation in chronically ultraviolet b-exposed hairless mouse. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Park, K.C.; Ortonne, J.P.; Kang, H.Y. Pendulous melanocytes: A characteristic feature of melasma and how it may occur. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.E.; Kim, Y.; Kwon, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, T.J.; Kang, H.Y. Senescent fibroblasts drive ageing pigmentation: A potential therapeutic target for senile lentigo. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4620–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.I.; Choi, S.; Roh, W.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.G. Cellular senescence and inflammaging in the skin microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyter, S.; Coleman, D.J.; Ganguli-Indra, G.; Merrill, G.F.; Ma, S.; Yanagisawa, M.; Indra, A.K. Endothelin-1 is a transcriptional target of p53 in epidermal keratinocytes and regulates ultraviolet-induced melanocyte homeostasis. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2013, 26, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, T.; Kamiya, T.; Kawakami, A.; Ogino, J.; Sohma, H.; Uhara, H.; Jimbow, K. Elucidation of melanogenesis cascade for identifying pathophysiology and therapeutic approach of pigmentary disorders and melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, S.F. Radiofrequency microneedling: Overview of technology, advantages, differences in devices, studies, and indications. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 27, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Widlund, H.R.; Feige, E.; Lin, J.Y.; Wilensky, D.L.; Igras, V.E.; D’Orazio, J.; Fung, C.Y.; Schanbacher, C.F.; Granter, S.R.; et al. Central role of p53 in the suntan response and pathologic hyperpigmentation. Cell 2007, 128, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, D.; Hachiya, A.; Amano, Y.; Ohuchi, A.; Kitahara, T.; Takema, Y. The essential role of p53 in hyperpigmentation of the skin via regulation of paracrine melanogenic cytokine receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4343–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.T.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Plonka, P.M.; Szaflarski, J.P.; Paus, R. How uv light touches the brain and endocrine system through skin, and why. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 1992–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.T.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Skobowiat, C.; Zbytek, B.; Slominski, R.M.; Steketee, J.D. Sensing the environment: Regulation of local and global homeostasis by the skin’s neuroendocrine system. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 2012, 212, v-115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Plonka, P.M.; Pisarchik, A.; Smart, J.L.; Tolle, V.; Wortsman, J.; Low, M.J. Preservation of eumelanin hair pigmentation in proopiomelanocortin-deficient mice on a nonagouti (a/a) genetic background. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Paus, R. Does p53 regulate skin pigmentation by controlling proopiomelanocortin gene transcription? Pigment. Cell Res. 2007, 20, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Target Gene | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| MITF | Forward: GGCTTGATGGATCCTGCTTTGC Reverse: GAAGGTTGGCTGGACAGGAGTT |
| Tyrosinase | Forward: GCACAGATGAGTACATGGGAGG Reverse: CTGATGGCTGTTGTACTCCTCC |
| TYRP-1 | Forward: TCTCAATGGCGAGTGGTCTGTG Reverse: CCTGTGGTTCAGGAAGACGTTG |
| p16 | Forward: CTCGTGCTGATGCTACTGAGGA Reverse: GGTCGGCGCAGTTGGGCTCC |
| p21 | Forward: AGGTGGACCTGGAGACTCTCAG Reverse: TCCTCTTGGAGAAGATCAGCCG |
| p53 | Forward: CCTCAGCATCTTATCCGAGTGG Reverse: TGGATGGTGGTACAGTCAGAGC |
| MMP-2 | Forward: AGCGAGTGGATGCCGCCTTTAA Reverse: CATTCCAGGCATCTGCGATGAG |
| MMP-9 | Forward: GCCACTACTGTGCCTTTGAGTC Reverse: CCCTCAGAGAATCGCCAGTACT |
| GAPDH | Forward: TGAGGTCACGGACGATTACT Reverse: GTAGGCCCACGAAACAAATGAT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.I.; Kim, E.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, J.H. Synergistic Effect of 300 μm Needle-Depth Fractional Microneedling Radiofrequency on the Treatment of Senescence-Induced Aging Hyperpigmentation of the Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147480
Lee YI, Kim E, Lee DW, Kim J, Kim J, Lee WJ, Lee JH. Synergistic Effect of 300 μm Needle-Depth Fractional Microneedling Radiofrequency on the Treatment of Senescence-Induced Aging Hyperpigmentation of the Skin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(14):7480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147480
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Young In, Eunbin Kim, Dong Won Lee, Jemin Kim, Jihee Kim, Won Jai Lee, and Ju Hee Lee. 2021. "Synergistic Effect of 300 μm Needle-Depth Fractional Microneedling Radiofrequency on the Treatment of Senescence-Induced Aging Hyperpigmentation of the Skin" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 14: 7480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147480
APA StyleLee, Y. I., Kim, E., Lee, D. W., Kim, J., Kim, J., Lee, W. J., & Lee, J. H. (2021). Synergistic Effect of 300 μm Needle-Depth Fractional Microneedling Radiofrequency on the Treatment of Senescence-Induced Aging Hyperpigmentation of the Skin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), 7480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147480






