Cera Flava Alleviates Atopic Dermatitis by Activating Skin Barrier Function via Immune Regulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CF Improved AD Symptoms
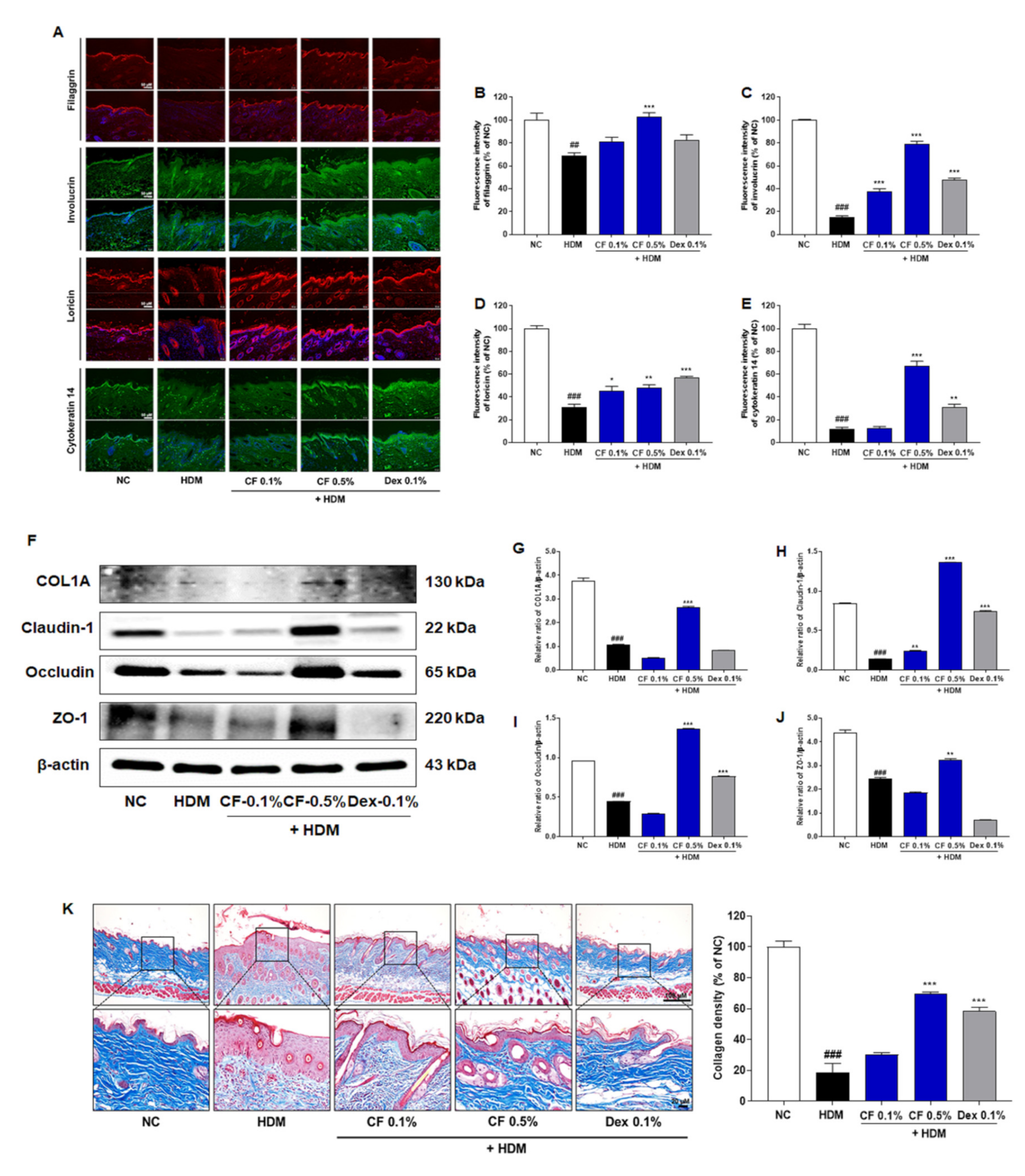
2.2. CF Attenuated HDM-induced Changes in the Expression of Proteins Related to Skin Barrier Function
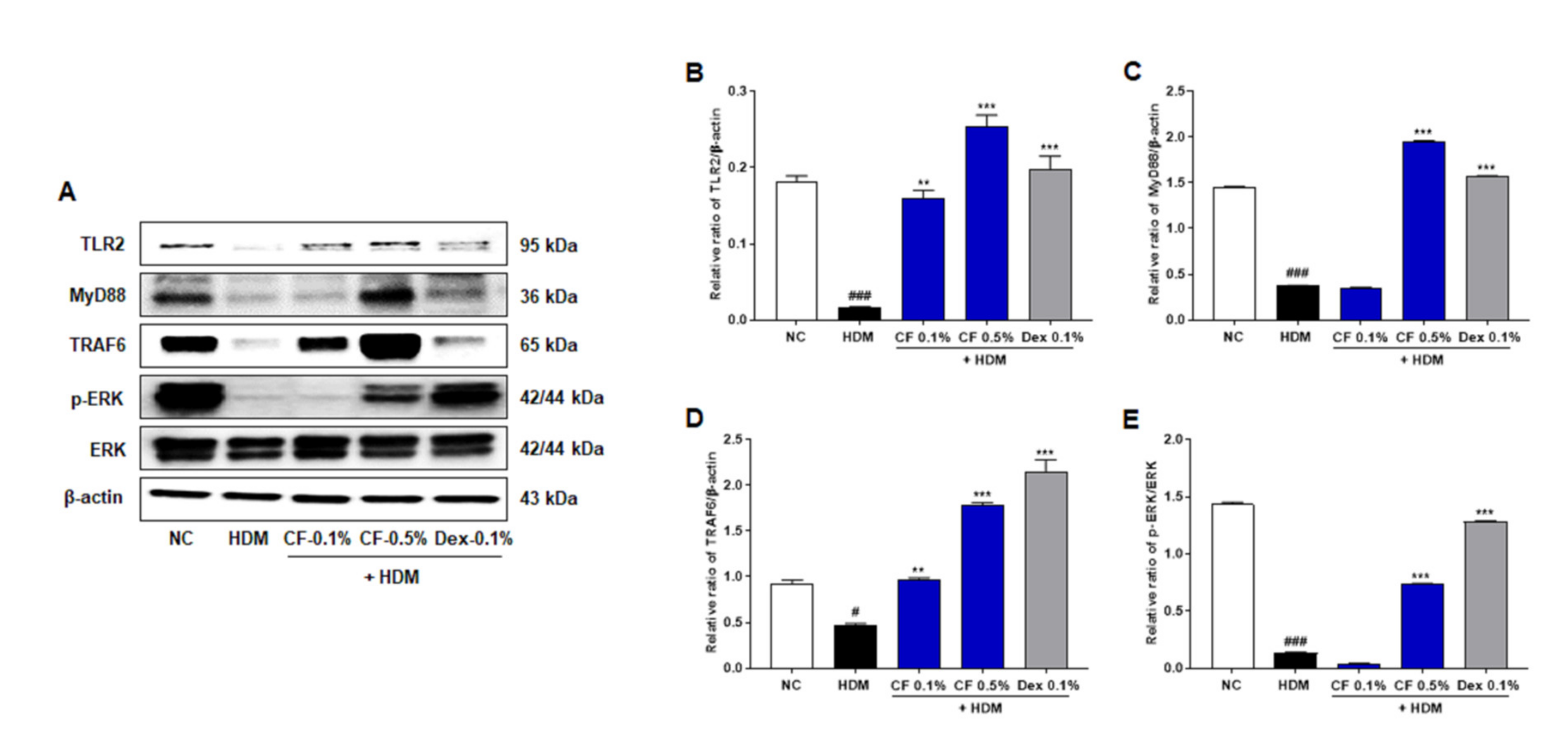
2.3. CF Modulates the TLR2/MyD88/TRAF6/ERK Axis
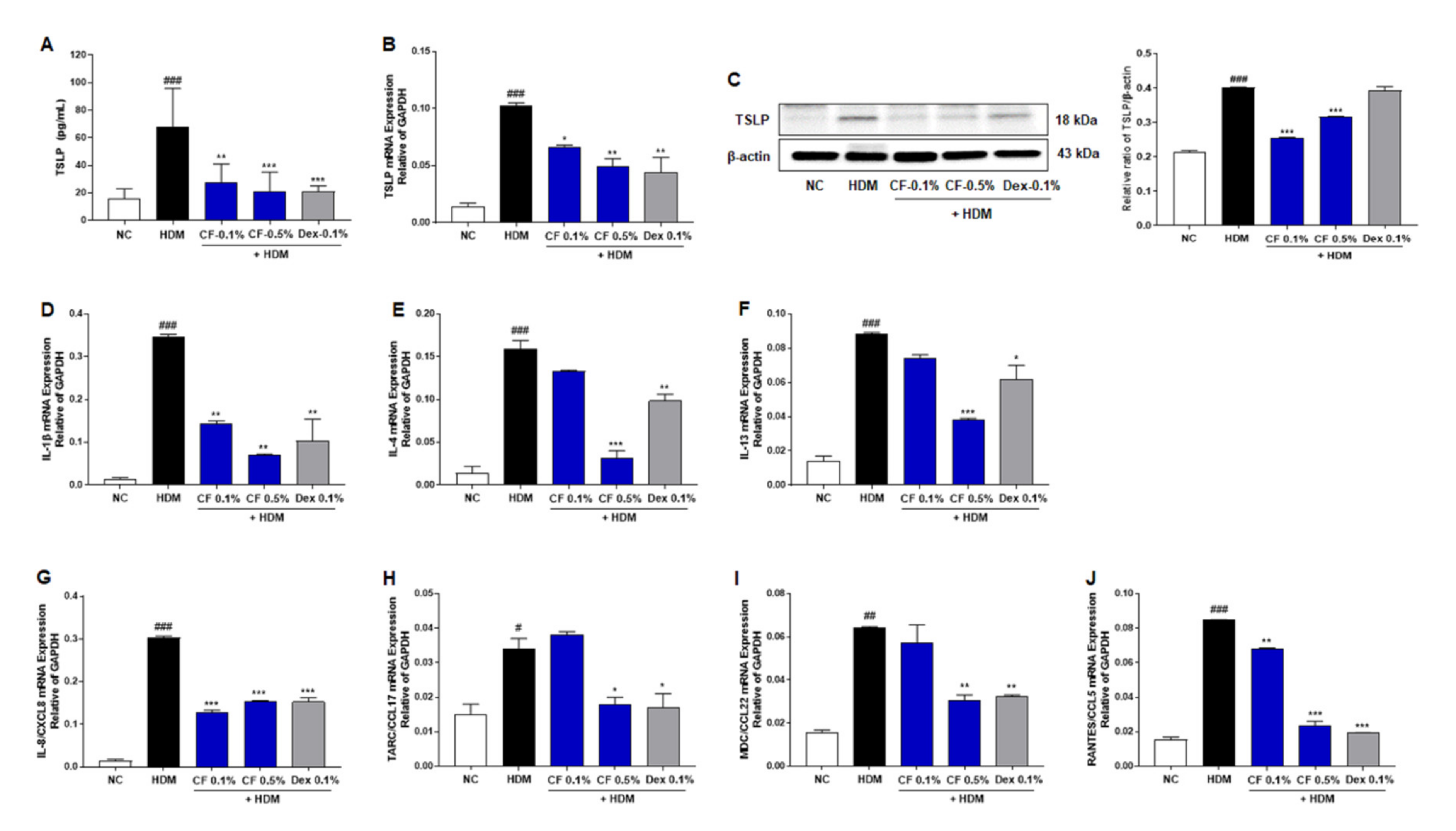
2.4. CF Inhibits the Expression of TSLP and Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines
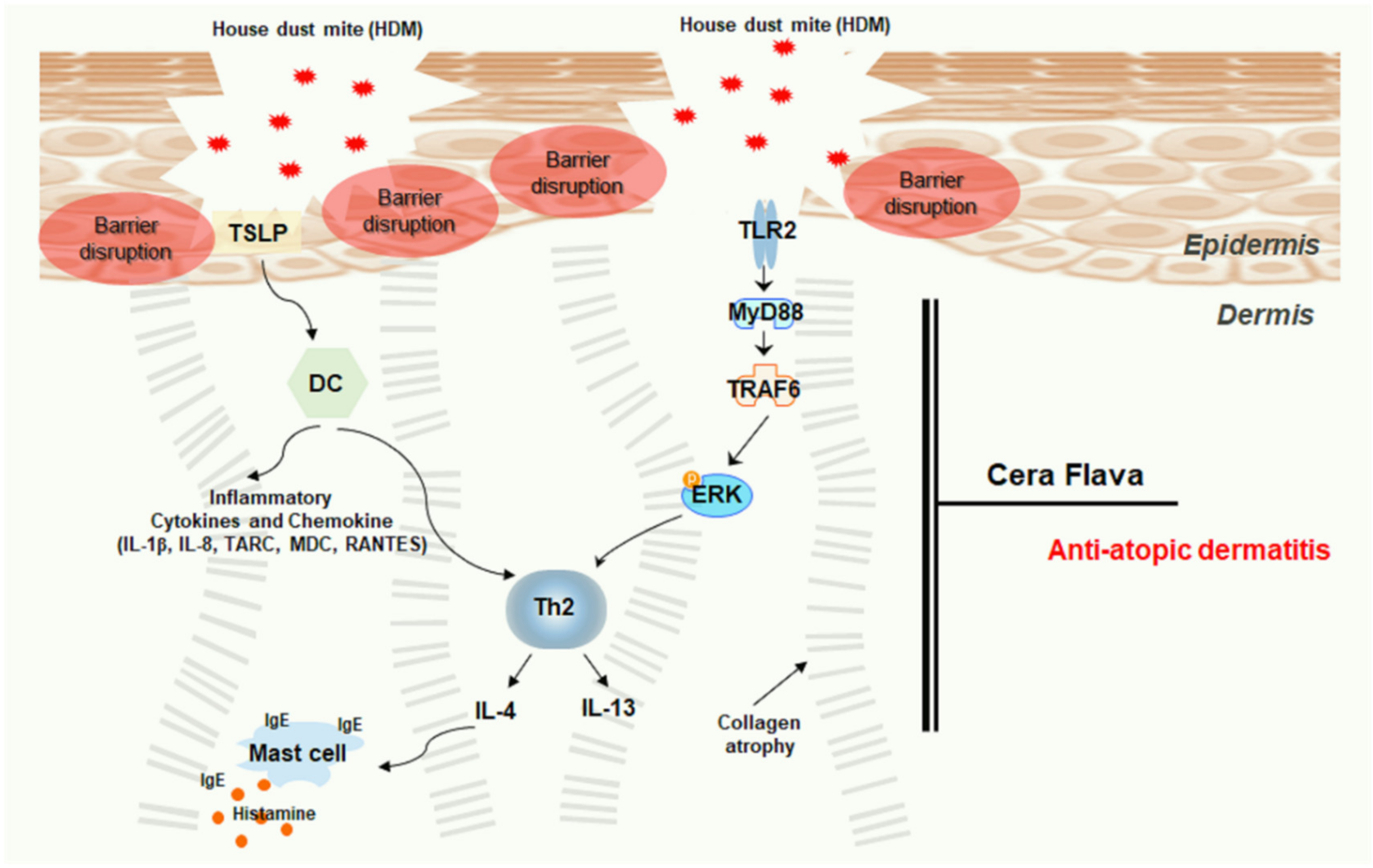
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Preparation of the CF Extract
4.2. Experimental Animals
4.3. Induction of Experimental AD
4.4. Evaluation of Dermatitis Scores
4.5. Evaluation of Scratching Behavior
4.6. Histological Analysis and Measurement of Skin Thickness and Infiltrating Mast Cells
4.7. Evaluation of Moisture Retention
4.8. Measurement of Serum IgE, Histamine, and TSLP Levels
4.9. Quantification of Filaggrin, Involucrin, Loricrin, and Cytokeratin 14 by Immunofluorescence
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations:
| AD | atopic dermatitis |
| CCL | C-C motif chemokine ligand |
| CF | cera flava |
| CXCL8 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8 |
| Dex | dexamethasone |
| ERK | extracellular-signal-regulated kinase |
| HDM | house dust mite |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| IgE | immunoglobulin E |
| IL | interleukin |
| MDC | macrophage-derived chemokine |
| MT | Masson’s trichrome |
| RANTES | regulated activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted |
| TARC | thymus and activation-regulated chemokine |
| TB | toluidine blue |
| TBST | Tris-buffered saline containing Tween 20 |
| Th1 | type II helper T cell |
| Th2 | type II helper T cell |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| TSLP | thymic stromal lymphopoietin |
| ZO-1 | zonula occludens-1 |
References
- Zomer, H.D.; Trentin, A.G. Skin wound healing in humans and mice: Challenges in translational research. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 90, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.E.; Leung, D.Y.M. Significance of Skin Barrier Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furue, M.; Chiba, T.; Tsuji, G.; Ulzii, D.; Kido-Nakahara, M.; Nakahara, T.; Kadono, T. Atopic dermatitis: Immune deviation, barrier dysfunction, IgE autoreactivity and new therapies. Allergol. Int. 2017, 66, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Gallo, R.L. Toll-like receptors in skin infections and inflammatory diseases. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets. 2008, 8, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.J. The Role of Toll-Like Receptors in Skin Host Defense, Psoriasis, and Atopic Dermatitis. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 1824624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek-Górecka, A.; Górecki, M.; Rzepecka-Stojko, A.; Balwierz, R.; Stojko, J. Bee Products in Dermatology and Skin Care. Molecules 2020, 25, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasparaviciene, G.; Savickas, A.; Kalveniene, Z.; Velziene, S.; Kubiliene, L.; Bernatoniene, J. Evaluation of Beeswax Influence on Physical Properties of Lipstick Using Instrumental and Sensory Methods. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 3816460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.; de Freitas, L.A.P.; Maia Campos, P.M.B.G. Topical Formulation Containing Beeswax-Based Nanoparticles Improved In Vivo Skin Barrier Function. AAPS. PharmSciTech. 2017, 18, 2505–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajar, T.; Gontijo, J.R.V.; Hanifin, J.M. New and developing therapies for atopic dermatitis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2018, 93, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Man, G.; Hu, L.Z.; Elias, P.M.; Man, M.Q. Therapeutic Benefits of Natural Ingredients for Atopic Dermatitis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 24, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legat, F.J. Itch in Atopic Dermatitis-What Is New? Front. Med. 2021, 8, 644760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.D.; de Guzman Strong, C. Current understanding of epigenetics in atopic dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rerknimitr, P.; Otsuka, A.; Nakashima, C.; Kabashima, K. The etiopathogenesis of atopic dermatitis: Barrier disruption, immunological derangement, and pruritus. Inflamm. Regen. 2017, 37, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Matsushita, K.; Wang, J.; Kanekura, T. Topical Glucose Induces Claudin-1 and Filaggrin Expression in a Mouse Model of Atopic Dermatitis and in Keratinocyte Culture, Exerting Anti-inflammatory Effects by Repairing Skin Barrier Function. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2018, 98, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bäsler, K.; Bergmann, S.; Heisig, M.; Naegel, A.; Zorn-Kruppa, M.; Brandner, J.M. The role of tight junctions in skin barrier function and dermal absorption. J. Control. Release 2016, 242, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäsler, K.; Brandner, J.M. Tight junctions in skin inflammation. Pflugers. Arch. 2017, 469, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Fricker, K.; Enk, A.H.; Hadaschik, E.N. Altered expression of keratin 14 in lesional epidermis of autoimmune skin diseases. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, T.; Tobiishi, M.; Kusaka-Kikushima, A.; Ota, Y.; Tokura, Y. Impaired Tight Junctions in Atopic Dermatitis Skin and in a Skin-Equivalent Model Treated with Interleukin-17. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0161759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-Castillo, J.M.; Hener, P.; Jiang, H.; Li, M. TSLP produced by keratinocytes promotes allergen sensitization through skin and thereby triggers atopic march in mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boguniewicz, M.; Leung, D.Y. Atopic dermatitis: A disease of altered skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, D.; Wong, C.K.; Qiu, H.N.; Dong, J.; Cai, Z.; Chu, M.; Hon, K.L.; Tsang, M.S.; Lam, C.W. NOD2 and TLR2 ligands trigger the activation of basophils and eosinophils by interacting with dermal fibroblasts in atopic dermatitis-like skin inflammation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, I.H.; Carpenter-Mendini, A.; Yoshida, T.; McGirt, L.Y.; Ivanov, A.I.; Barnes, K.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Borkowski, A.W.; Yamasaki, K.; Leung, D.Y.; et al. Activation of epidermal toll-like receptor 2 enhances tight junction function: Implications for atopic dermatitis and skin barrier repair. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pastore, S.; Mascia, F.; Mariani, V.; Girolomoni, G. The epidermal growth factor receptor system in skin repair and inflammation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brandt, E.B.; Sivaprasad, U. Th2 Cytokines and Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2011, 2, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.S.; Ha, H.; Lee, M.Y.; Jin, S.E.; Jeong, S.J.; Jeon, W.Y.; Shin, N.R.; Sok, D.E.; Shin, H.K. Saussurea lappa alleviates inflammatory chemokine production in HaCaT cells and house dust mite-induced atopic-like dermatitis in Nc/Nga mice. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 63, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenborg, H.W. Occupational dermatitis in beekeeper due to poplar resins in beeswax. Arch. Dermatol. 1967, 95, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucente, P.; Cavalli, M.; Vezzani, C.; Orlandi, C.; Vincenzi, C. Contact cheilitis due to beeswax. Contact Dermat. 1996, 35, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junghans, V.; Geier, J.; Fuchs, T. Allergy to propolis caused by beeswax-containing ointment. Am. J. Contact Dermat. 2002, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, G.S.A.; Tang, M.; Inerot, A.; Osmancevic, A.; Malmberg, P.; Hagvall, L. Contact allergy to beeswax and propolis among patients with cheilitis or facial dermatitis. Contact Dermat. 2019, 2, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, J.M.; Thurston, M.; Omoto, M.; Cherill, R.; Tofte, S.J.; Graeber, M. The eczema area and severity index (EASI): Assessment of reliability in atopic dermatitis. EASI Evaluator Group. Exp. Dermatol. 2001, 10, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Moon, B.C.; Ryu, S.M.; Kim, W.J.; Lim, H.S. Cicadidae Periostracum Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms and Pathology via the Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8878153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, G.; Moon, B.C.; Choi, G.; Lim, H.-S. Cera Flava Alleviates Atopic Dermatitis by Activating Skin Barrier Function via Immune Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147531
Park G, Moon BC, Choi G, Lim H-S. Cera Flava Alleviates Atopic Dermatitis by Activating Skin Barrier Function via Immune Regulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(14):7531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147531
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Gunhyuk, Byeong Cheol Moon, Goya Choi, and Hye-Sun Lim. 2021. "Cera Flava Alleviates Atopic Dermatitis by Activating Skin Barrier Function via Immune Regulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 14: 7531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147531
APA StylePark, G., Moon, B. C., Choi, G., & Lim, H.-S. (2021). Cera Flava Alleviates Atopic Dermatitis by Activating Skin Barrier Function via Immune Regulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), 7531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147531






