Magnetic Particle Imaging: Current and Future Applications, Magnetic Nanoparticle Synthesis Methods and Safety Measures
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Significance
1.2. Principles and Methods
1.3. Benefits
1.4. Challenges
2. Magnetic Nanoparticle Synthesis Methods
3. MPI Applications
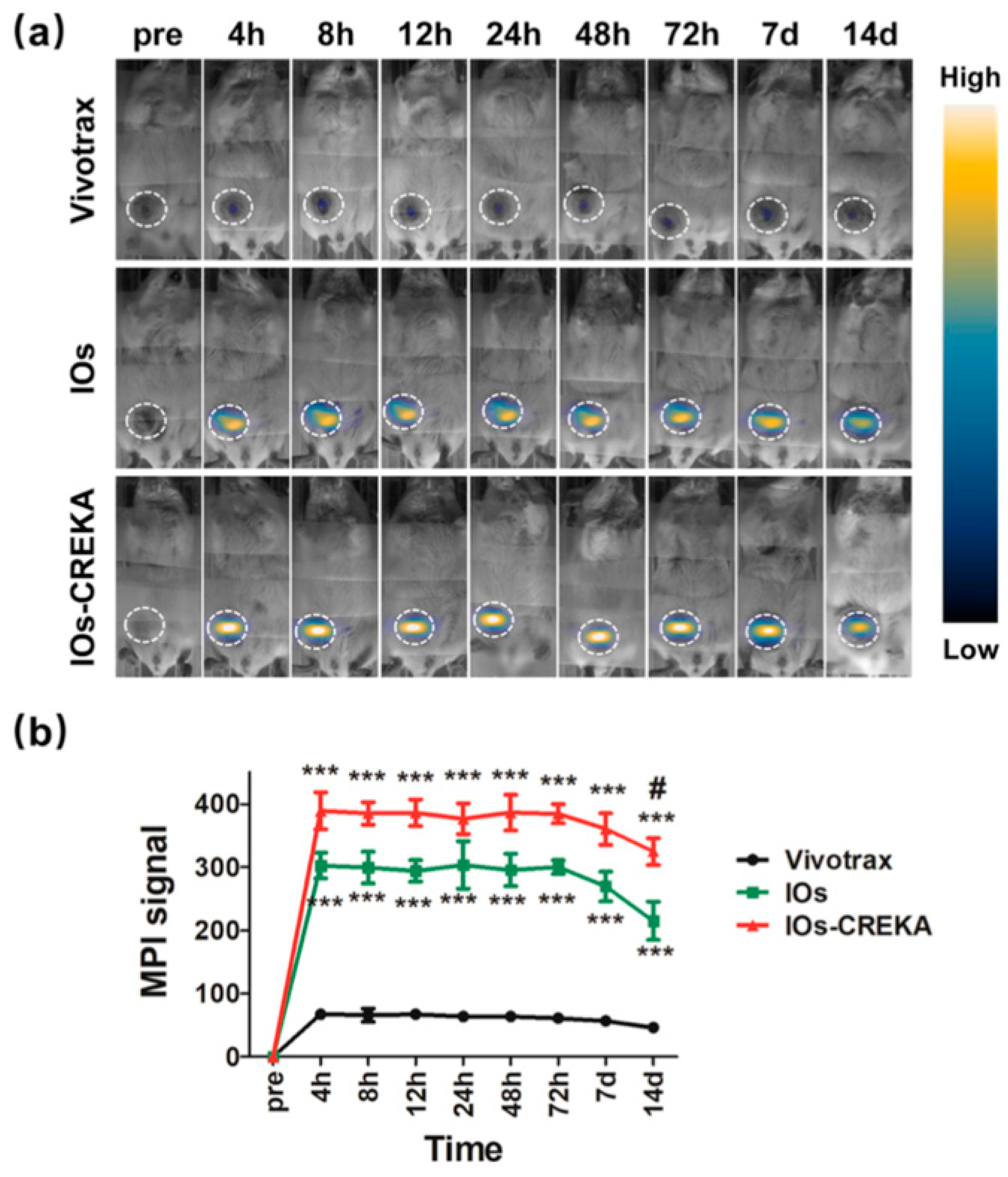
3.1. Cancer Imaging
3.2. Cardiovascular Imaging
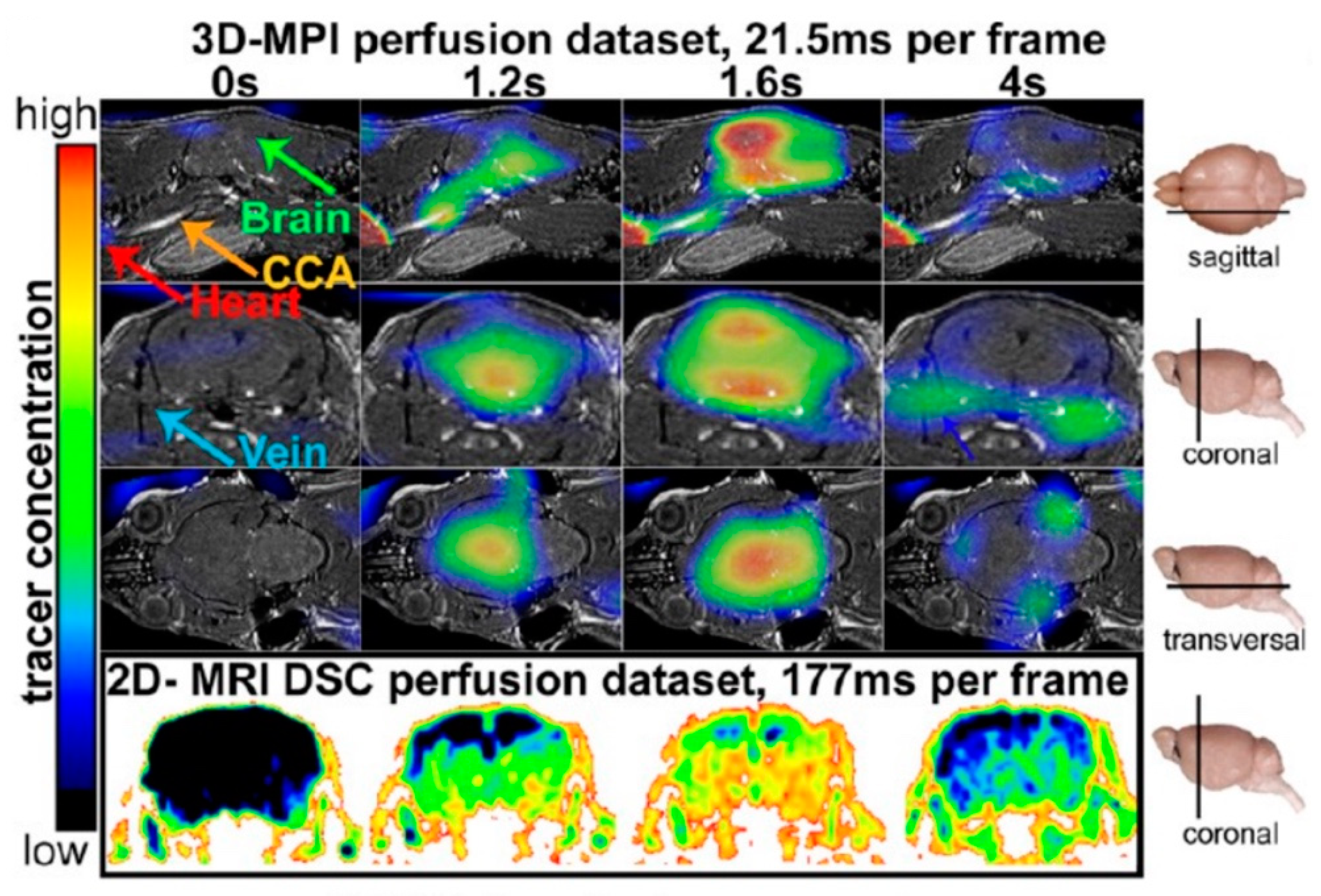
3.3. Neuroimaging
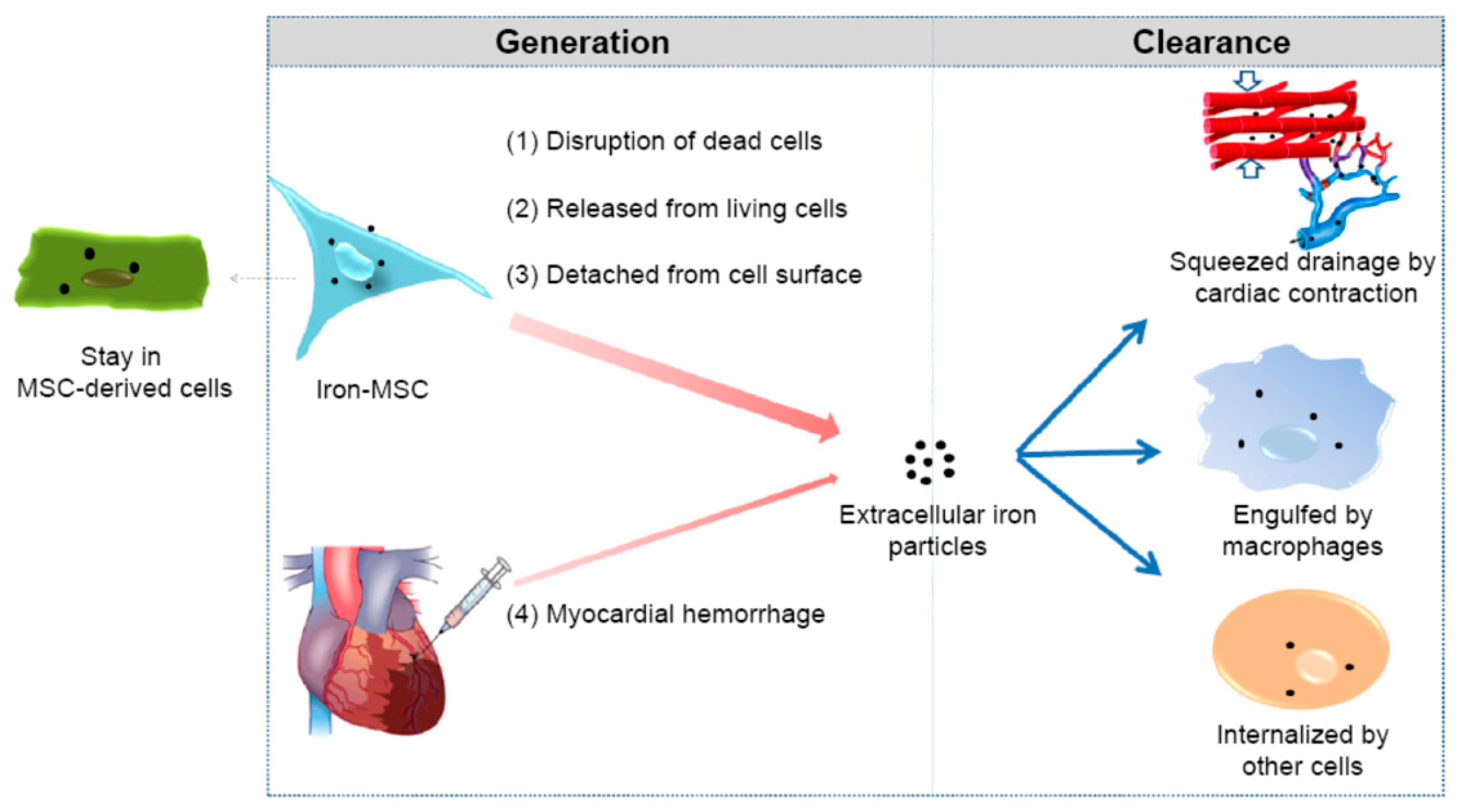
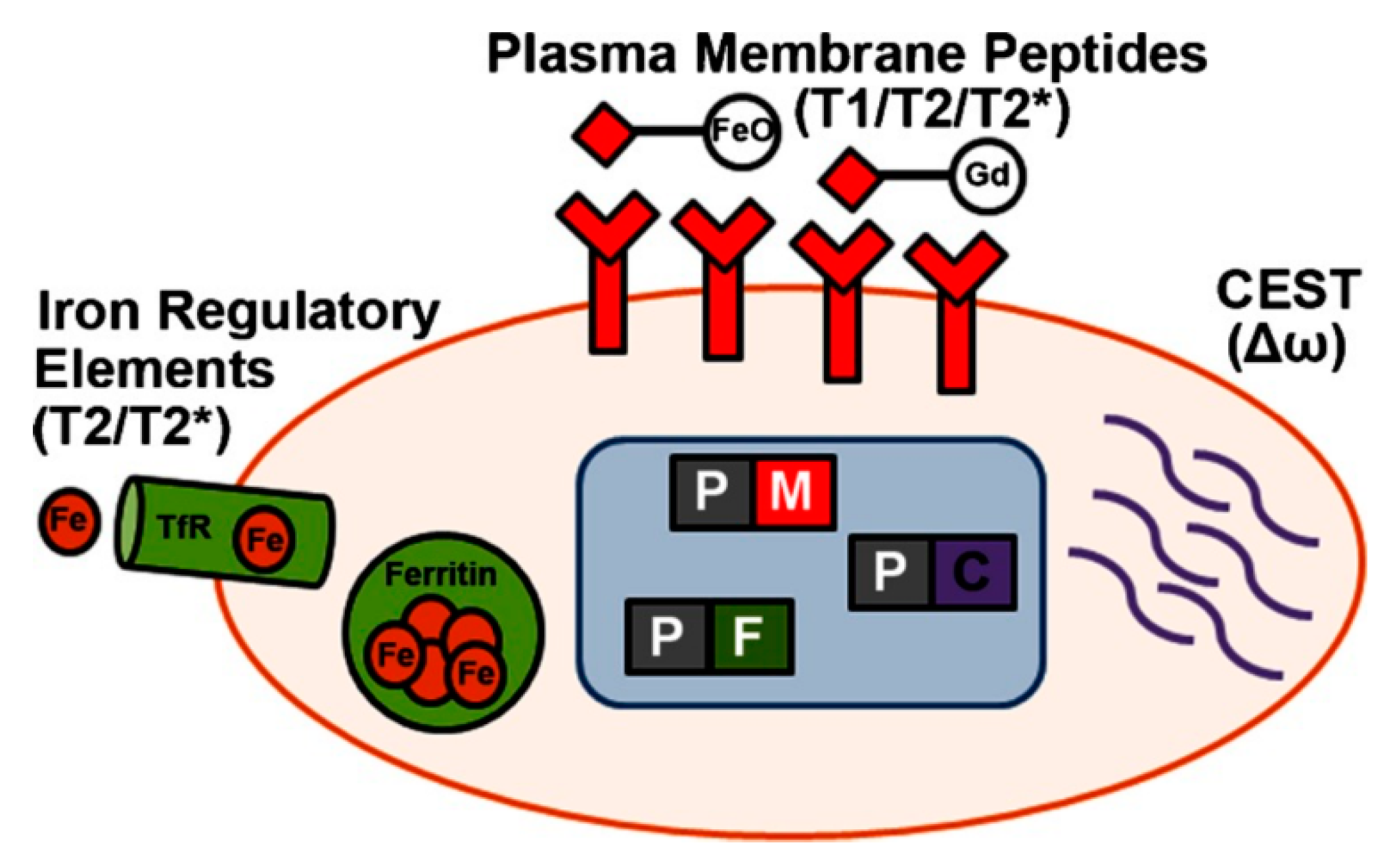
3.4. Cell Tracking
3.5. Magnetic Hyperthermia
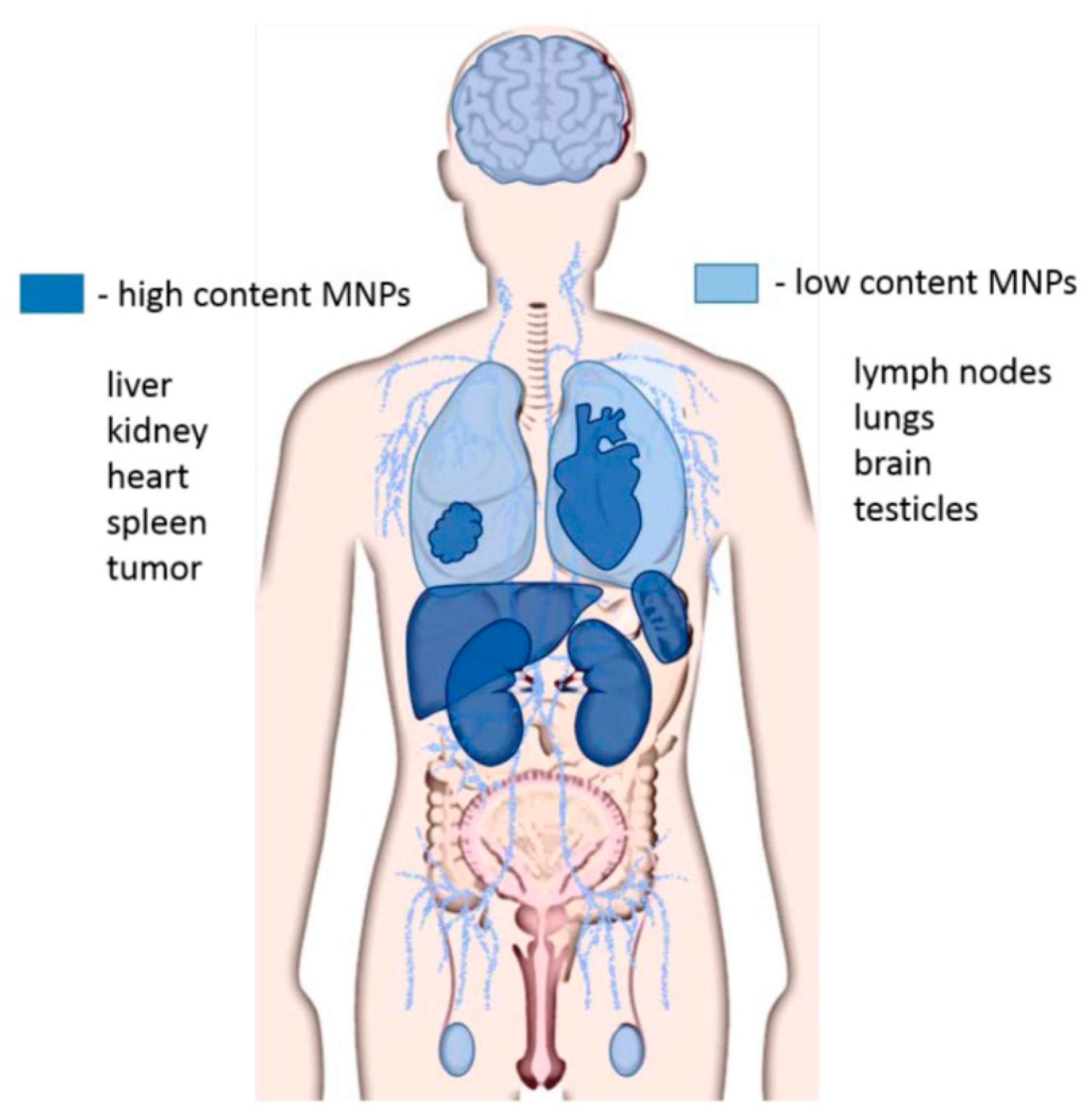
4. Safety and Toxicity
4.1. Background
4.2. Toxicity Mechanisms
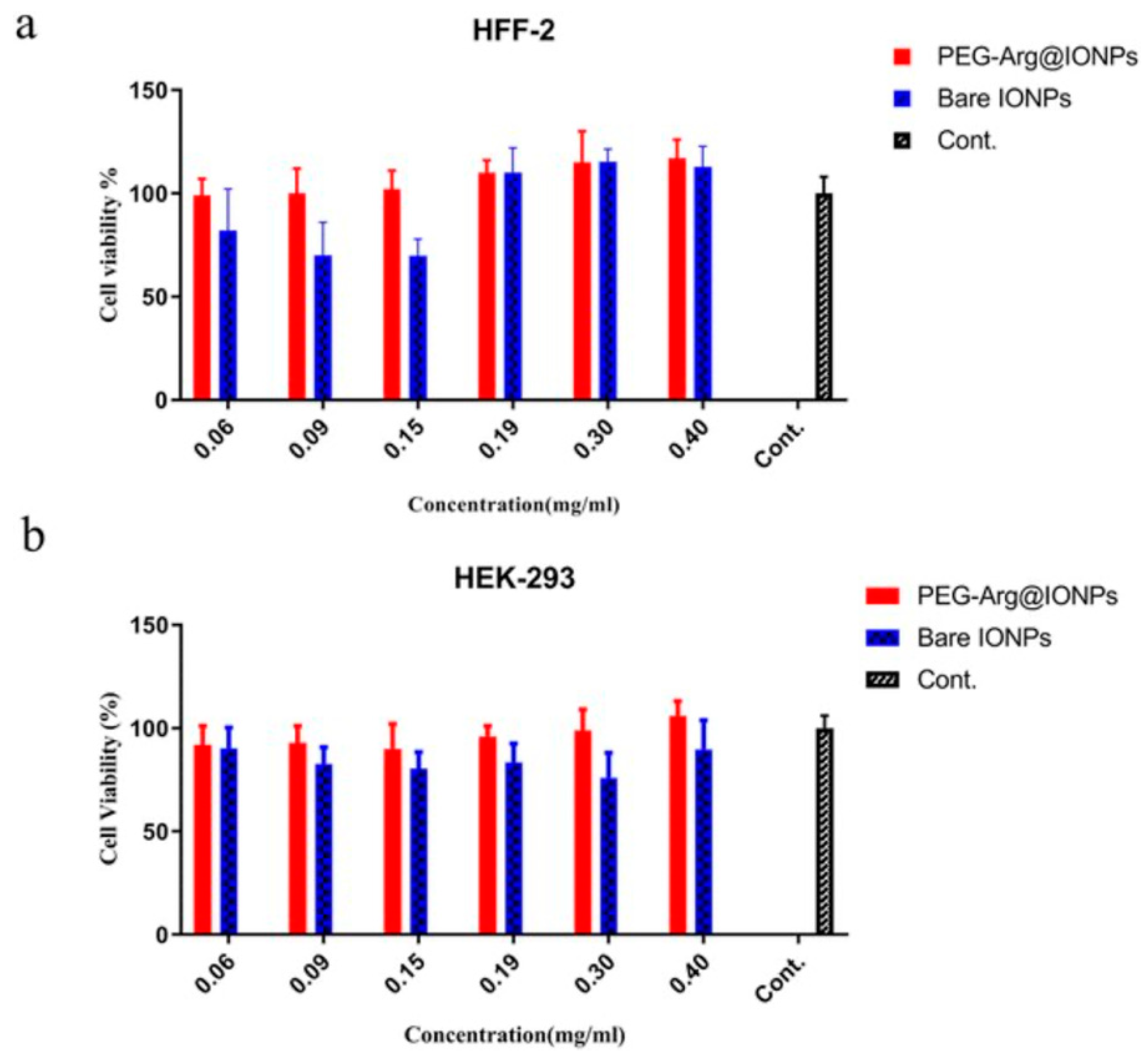
4.3. Methods for Limiting Toxicity
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bulte, J.W.M. Superparamagnetic iron oxides as MPI tracers: A primer and review of early applications. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2019, 138, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Lee, J.S.; Zhang, M. Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1252–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Han, L.; Wang, J.; Wan, J.; Song, G.; Rao, J. Engineering of magnetic nanoparticles as magnetic particle imaging tracers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, T.; Gdaniec, N.; Moddel, M. Magnetic particle imaging: From proof of principle to preclinical applications. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, R124–R178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H. The application of magnetic nanoparticles in the treatment and monitoring of cancer and infectious diseases. Biosci. Horiz. Int. J. Stud. Res. 2017, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleich, B.; Weizenecker, J. Tomographic imaging using the nonlinear response of magnetic particles. Nature 2005, 435, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulos, N.; Vogt, F.; Barkhausen, J.; Buzug, T.M.; Duschka, R.L.; Lüdtke-Buzug, K.; Ahlborg, M.; Bringout, G.; Debbeler, C.; Gräser, M.; et al. Magnetic particle imaging: Current developments and future directions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3097–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, T.; Buzug, T.M. Magnetic Particle Imaging: An Introduction to Imaging Principles and Scanner Instrumentation; Introduction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wáng, Y.X.J.; Idée, J.M. A comprehensive literatures update of clinical researches of superparamagnetic resonance iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2017, 7, 88–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, P.; Markert, J.; Rückert, M.A.; Herz, S.; Keßler, B.; Dremel, K.; Althoff, D.; Weber, M.; Buzug, T.M.; Bley, T.A.; et al. Magnetic particle imaging meets computed tomography: First simultaneous imaging. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwill, P.; Saritas, E.U.; Croft, L.R.; Kim, T.; Krishnan, K.M.; Schaffer, D.V.; Conolly, S.M. X-space MPI: Magnetic nanoparticles for safe medical imaging. Adv. Mater. 2012, 28, 3870–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablico-Lansigan, M.; Situ, S.; Samia, A. Magnetic particle imaging: Advancements and perspectives for real-time in vivo monitoring and image-guided therapy. Nanoscale 2013, 10, 4040–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Z.W.; Chandrasekharan, P.; Chiu-Lam, A.; Hensley, D.W.; Dhavalikar, R.; Zhou, X.Y.; Yu, E.Y.; Goodwill, P.; Zheng, B.; Rinaldi, C.; et al. Magnetic particle imaging–guided heating in vivo using gradient fields for arbitrary localization of magnetic hyperthermia therapy. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3699–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Wen, T.; Samia, A.C.S.; Khandhar, A.P.; Krishnan, K.M. Magnetic nanoparticles: Material engineering and emerging applications in lithography and biomedicine. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 513–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clift, M.J.D.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Brown, D.M.; Duffin, R.; Donaldson, K.; Proudfoot, L.; Guy, K.; Stone, V. Highly stable superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as functional draw solutes for osmotically driven water transport. npj Clean Water 2020, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, M.J.D.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Brown, D.M.; Duffin, R.; Donaldson, K.; Proudfoot, L.; Guy, K.; Stone, V. The impact of different nanoparticle surface chemistry and size on uptake and toxicity in a murine macrophage cell line. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 232, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouly, C.; Pouliquen, D.; Lucet, I.; Jeune, J.J.; Jallet, P. Development of superparamagnetic nanoparticles for MRI: Effect of particle size, charge and surface nature on biodistri- bution. J. Microencapsul. 1996, 13, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Hunter, A.C.; Murray, J.C. Long-circulating and target-specific nanoparticles: Theory to practice. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 283–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lunov, O.; Syrovets, T.; Röcker, C.; Tron, K.; Nienhaus, G.U.; Rasche, V.; Mailänder, V.; Landfester, K.; Simmet, T. Lysosomal degradation of the carboxydextran shell of coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and the fate of professional phagocytes. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9015–9022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebloo, N.; Gudi, M.; Robertson, N.; Wang, P. Magnetic particle imaging: Current applications in biomedical research. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2020, 51, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.C.; Zhang, Y.; Steinberg, G.; Qu, H.; Huang, S.; Cheng, M.; Bliss, T.; Du, F.; Rao, J.; Song, G.; et al. A review of magnetic particle imaging and perspectives on neuroimaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwill, P.W.; Lu, K.; Zheng, B.; Conolly, S.M. An x-space magnetic particle imaging scanner. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 033708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgert, J.; Schmidt, J.D.; Schmale, I.; Rahmer, J.; Bontus, C.; Gleich, B.; David, B.; Eckart, R.; Woywode, O.; Weizenecker, J.; et al. Fundamentals and applications of magnetic particle imaging. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2012, 3, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhavalikar, R.; Rinaldi, C. On the effect of finite magnetic relaxation on the magnetic particle imaging performance of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 074308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeser, M.; Biederer, S.; Gruttner, M. Magnetic Particle Imaging: A Novel SPIO Imaging Technique; Buzug, T.M., Borger, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmer, J.; Weizenecker, B.; Gleich, B.; Borgert, J. Analysis of a 3-D system function measured for magnetic particle imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2012, 31, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakenecker, A.C.; Ahlborg, M.; Debbeler, C.; Kaethner, C.; Buzug, T.; Lüdtke-Buzug, K. Magnetic particle imaging in vascular medicine. Innov. Surg. Sci. 2018, 3, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcu, C.B.; Beek, A.M.; van Rossum, A.C. Clinical applications of cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. CMAJ 2006, 175, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beek, E.J.; Kuhl, C.; Anzai, Y.; Desmond, P.; Ehman, R.L.; Gong, Q.; Gold, G.; Gulani, V.; Hall-Craggs, M.; Leiner, T.; et al. Value of MRI in medicine: More than just another test? J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, e14–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nievelstein, R.A.J.; Van Ufford, H.M.E.Q.; Kwee, T.C.; Bierings, M.B.; Ludwig, I.; Beek, F.J.A.; De Klerk, J.M.H.; Mali, W.P.T.M.; De Bruin, P.W.; Geleijns, J. Radiation exposure and mortality risk from CT and PET imaging of patients with malignant lymphoma. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Moon, W.J. Gadolinium deposition in the brain: Current updates. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saritas, E.U.; Goodwill, P.; Croft, L.R.; Konkle, J.; Lu, K.; Zheng, B.; Conolly, S.M. Magnetic particle imaging (MPI) for NMR and MRI researchers. J. Magn. Reson. 2013, 229, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.Y.; Bishop, M.; Zheng, B.; Ferguson, R.M.; Khandhar, A.; Kemp, S.J.; Krishnan, K.M.; Goodwill, P.; Conolly, S.M. Magnetic particle imaging: A novel in vivo imaging platform for cancer detection. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, L.; Qu, H.; Zheng, X.; Wintermark, M.; Liu, Z.; Rao, J. Janus iron oxides @ semiconducting polymer nanoparticle tracer for cell tracking by magnetic particle imaging. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, F.; Eberbeck, D.; Löwa, N.; Steinhoff, U.; Wawrzik, T.; Schilling, M.; Trahms, L. Characterization of magnetic nanoparticle systems with respect to their magnetic particle imaging performance. Biomed. Tech. 2013, 6, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Huh, Y.-M.; Jun, Y.-W.; Seo, J.-W.; Jang, J.-T.; Song, H.-T.; Kim, S.; Cho, E.-J.; Yoon, H.-G.Y.; Suh, J.-S.; et al. Artificially engineered magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive molecular imaging. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubia-Rodríguez, I.; Santana-Otero, A.; Spassov, S.; Tombácz, E.; Johansson, C.; De La Presa, P.; Teran, F.; Morales, M.D.P.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; Thanh, N.; et al. Whither magnetic hyperthermia? A tentative roadmap. Materials 2021, 14, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnovik, D.E.; Nahrendorf, M.; Weissleder, R. Magnetic nanoparticles for MR imaging: Agents, techniques and cardiovascular applications. Basic Res. Cardiol 2008, 103, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharan, P.; Tay, Z.W.; Hensley, D.; Zhou, X.Y.; Fung, B.K.; Colson, C.; Lu, Y.; Fellows, B.D.; Huynh, Q.; Saayujya, C.; et al. Using magnetic particle imaging systems to guide magnetic hyperthermia treatment: Tracers, hardware, and future medical applications. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2965–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.; Guérin, B.; Malzacher, M.; Schad, L.R.; Wald, L.L. Predicting magnetostimulation thresholds in the peripheral nervous system using realistic body models. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saritas, E.U.; Goodwill, P.W.; Zhang, G.Z.; Conolly, S.M. Magnetostimulation Limits in Magnetic Particle Imaging. IEEE 2013, 32, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacRitchie, N.; Frleta-Gilchrist, M.; Sugiyama, A.; Lawton, T.; McInnes, I.B.; Maffia, P. Molecular imaging of inflammation—Current and emerging technologies for diagnosis and treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 211, 107550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehl, O.C.; Gevaert, J.J.; Melo, K.P.; Knier, N.N.; Foster, P.J. A perspective on cell tracking with magnetic particle imaging. Tomography 2020, 6, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, B.; Calatayud, M.P.; Cassinelli, N.; Ibarra, M.R.; Goya, G.F. Long term stability and reproducibility of magnetic colloids are key issues for steady values of specific power through time. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 4524–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis and surface functionalization strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, N.; Lee, J.-S.; Liman, R.A.D.; Ruallo, J.M.S.; Villaflores, O.B.; Ger, T.-R.; Hsiao, C.-D. Potential toxicity of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles: A review. Molecules 2020, 25, 3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Lim, H.B. Characterization and analytical application of surface modified magnetic nanoparticles. Microchem. J. 2010, 94, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramimoghadam, D.; Bagheri, S.; Hamid, S.B.A. Stable monodisperse nanomagnetic colloidal suspensions: An overview. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 133, 388–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangioni, J.V. New technologies for human cancer imaging. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4012–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyllenberg, M.; Webb, G.F. Quiescence as an explanation of Gompertzian tumor growth. Growth Dev. Aging 1989, 53, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, L.L.; Galstyan, A.; Holler, E.; Ljubimova, J.Y. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for imaging, targeting and treatment of primary and metastatic tumors of the brain. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilella, A.; Tosi, G.; Grabrucker, A.M.; Ruozi, B.; Belletti, D.; Vandelli, M.A.; Boeckers, T.M.; Forni, F.; Zoli, M. Insight on the fate of CHS-targeted nanoparticles. Part I: Rab5-dependent cell-specific uptake and distribution. J. Control. Release 2014, 174, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, Q.; Liang, X.J.; Tian, J. Optimization and design of magnetic ferrite nanoparticles with uniform tumor distribution for highly sensitive MRI/MPI performance and improved magnetic hyperthermia therapy. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 3618–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arami, H.; Teeman, E.; Troksa, A.; Bradshaw, H.; Saatchi, K.; Tomitaka, A.; Gambhir, S.S.; Häfeli, U.O.; Liggitt, D.; Krishnan, K.M. Tomographic magnetic particle imaging of cancer targeted nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 18723–18730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Hui, H.; Shang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, F.; Ma, Q.; Yang, X.; Tian, J.; Chen, Y. Highly sensitive magnetic particle imaging of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque with active myeloperoxidase-targeted nanoparticles. Theranostics 2021, 11, 506–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Yu, B. Multimodality molecular imaging of cardiovascular disease based on nanoprobes. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.; Joseyphus, R.J.; Ishikawa, T.; Imai, Y.; Yamaguchi, T. Micro-flow visualization of magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. In Single and Two-Phase Flows on Chemical and Biomedical Engineering; Dias, R., Lima Portugal, R., Eds.; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2012; pp. 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaalma, S.; Rahmer, J.; Panagiotopoulos, N.; Duschka, R.L.; Borgert, J.; Barkhausen, J.; Vogt, F.M.; Haegele, J. Magnetic particle imaging (MPI): Experimental quantification of vascular stenosis using stationary stenosis phantoms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, J.; Neverova, N.V.; Nguyen, K.L. USPIOs as targeted contrast agents in cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. Curr. Cardiovasc. Imaging Rep. 2021, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, J.; Baxan, N.; Lehr, H.; Heinen, U.; Reinartz, S.; Schnorr, J.; Heidenreich, M.; Kiessling, F.; Schulz, V. Hybrid MPI-MRI system for dual-modal in situ cardiovascular assessments of real-time 3D blood flow quantification—A pre-clinical in vivo feasibility investigation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 4335–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohtashamdolatshahi, A.; Kratz, H.; Kosch, O.; Hauptmann, R.; Stolzenburg, N.; Wiekhorst, F.; Sack, I.; Hamm, B.; Taupitz, M.; Schnorr, J. In vivo magnetic particle imaging: Angiography of inferior vena cava and aorta in rats using newly developed multicore particles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.Y.; Chandrasekharan, P.; Berzon, R.; Tay, Z.W.; Zhou, X.Y.; Khandhar, A.; Ferguson, R.M.; Kemp, S.J.; Zheng, B.; Goodwill, P.; et al. Magnetic particle imaging for highly sensitive, quantitative, and safe in vivo gut bleed detection in a murine model. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12067–12076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryken, T.C.; Aygun, N.; Morris, J.; Schweizer, M.; Nair, R.; Spracklen, C.; Kalkanis, S.N.; Olson, J.J. The role of imaging in the management of progressive glioblastoma. J. Neuro. Oncol. 2014, 118, 435–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandhar, A.P.; Ferguson, R.M.; Arami, H.; Kemp, S.J.; Krishnan, K.M. Tuning surface coatings of optimized magnetite nanoparticle tracers for in vivo magnetic particle imaging. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomitaka, A.; Arami, H.; Gandhi, S.; Krishnan, K.M. Lactoferrin conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles for targeting brain glioma cells in magnetic particle imaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16890–16898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, E.E.; Cooley, C.Z.; Cauley, S.F.; Griswold, M.A.; Conolly, S.M.; Wald, L.L. Design analysis of an MPI human functional brain scanner. Int. J. Magn. Part. Imaging. 2017, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, M.P.; Le, T.A.; Yoon, J. Development of rat-scale magnetic particle spectroscopy for functional magnetic particle imaging. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2020, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.R.; Taylor, J.J.; Lamb, K.; Hanlon, C.A.; Short, E.B.; George, M.S. Role of functional imaging in the development and refinement of invasive neuromodulation for psychiatric disorders. World J. Radiol. 2014, 6, 756–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szwargulski, P.; Wilmes, M.; Javidi, E.; Thieben, F.; Graeser, M.; Koch, M.; Gruettner, C.; Adam, G.; Gerloff, C.; Magnus, T.; et al. Monitoring intracranial cerebral hemorrhage using multicontrast real-time magnetic particle imaging. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 13913–13923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, C.Z.; Mandeville, J.B.; Mason, E.E.; Mandeville, E.T.; Wald, L.L. Rodent cerebral blood volume (CBV) changes during hypercapnia observed using magnetic particle imaging (MPI) detection. Neuroimage 2018, 178, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludewig, P.; Gdaniec, N.; Sedlacik, J.; Forkert, N.D.; Szwargulski, P.; Gräser, M.; Adam, G.; Kaul, M.G.; Krishnan, K.M.; Ferguson, R.M.; et al. Magnetic particle imaging for real-time perfusion imaging in acute stroke. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10480–10488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.; Riegler, J.; Wu, J. Stem cell imaging: From bench to bedside. Stem Cell Stem 2014, 14, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Von See, M.P.; Yu, E.; Gunel, B.; Lu, K.; Vazin, T.; Schaffer, D.V.; Goodwill, P.; Conolly, S.M. Quantitative magnetic particle imaging monitors the transplantation, biodistribution, and clearance of stem cells in vivo. Theranostics 2016, 6, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehl, O.; Makela, A.; Hamilton, A.; Foster, P. Trimodal cell tracking in vivo: Combining iron- and fluorine-based magnetic resonance imaging with magnetic particle imaging to monitor the delivery of mesenchymal stem cells and the ensuing inflammation. Tomography 2019, 5, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Vazin, T.; Goodwill, P.; Conway, A.; Verma, A.; Saritas, E.U.; Schaffer, D.; Conolly, S.M. Magnetic particle imaging tracks the long-term fate of in vivo neural cell implants with high image contrast. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goradel, N.H.; Hour, F.G.; Negahdari, B.; Malekshahi, Z.V.; Hashemzehi, M.; Masoudifar, A.; Mirzaei, H. Stem cell therapy: A new therapeutic option for cardiovascular diseases. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagno, L.; Hatzistergos, K.E.; Balkan, W.; Hare, J.M. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for cardiovascular disease: Progress and challenges. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 1610–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, P.; Lemcke, H.; David, R. Stem cell therapy in heart diseases–cell types, mechanisms and improvement strategies. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 2607–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jokerst, J.V. Stem cell imaging: Tools to improve cell delivery and viability. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejadnik, H.; Pandit, P.; Lenkov, O.; Lahiji, A.P.; Yerneni, K.; Daldrup-Link, H.E. Ferumoxytol can be used for quantitative magnetic particle imaging of transplanted stem cells. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 65–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Mahmoudi, M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Promises for diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2011, 2, 367–390. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, Y.J.; Kong, T.H.; Choi, J.S.; Yun, W.; Key, J.; Seo, Y.J. Strategies to enhance efficacy of SPION-labeled stem cell homing by magnetic attraction: A systemic review with meta-analysis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4849–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasmin; de Souza, G.T.; Louzada, R.A.; Rosado-De-Castro, P.H.; Mendez-Otero, R.; de Carvalho, A.C.C. Tracking stem cells with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Perspectives and considerations. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 779–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Goodwill, P.; Pandit, P.; Gaudet, J.; Ross, A.; Wang, J.; Yu, E.; Hensley, D.W.; Doyle, T.C.; Contag, C.; et al. Magnetic particle imaging of islet transplantation in the liver and under the kidney capsule in mouse models. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2018, 8, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Shen, D.; Hensley, M.T.; Middleton, R.; Sun, B.; Liu, W.; de Couto, G.; Marbán, E. Magnetic antibody-linked nanomatchmakers for therapeutic cell targeting. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciervo, Y.; Ning, K.; Jun, X.; Shaw, P.J.; Mead, R.J. Advances, challenges and future directions for stem cell therapy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol. Neurodegen. 2017, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoso, M.R.; Yang, P.C. Magnetic nanoparticles for targeting and imaging of stem cells in myocardial infarction. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, F.; Steinke, M.; Kraupner, A.; Grüttner, C.; Hiller, K.-H.; Briel, A.; Westphal, F.; Walles, H.; Jakob, P.M. Stem cell vitality assessment using magnetic particle spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Huang, Z.; Li, C.; Yang, S.; Xu, J.; Shen, Y.; Xie, X.; Dai, Y.; Lu, H.; Gong, H.; et al. Magnetic resonance hypointensive signal primarily originates from extracellular iron particles in the long-term tracking of mesenchymal stem cells transplanted in the infarcted myocardium. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Amsalem, Y.; Mardor, Y.; Feinberg, M.S.; Landa, N.; Miller, L.; Daniels, D.; Ocherashvilli, A.; Holbova, R.; Yosef, O.; Barbash, I.M.; et al. Iron-oxide labeling and outcome of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in the infarcted myocardium. Circulation 2007, 116, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandsburger, M. Cardiac cell tracking with MRI reporter genes: Welcoming a new field. Curr. Cardiovasc. Imaging Rep. 2014, 7, 9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, J.; Kumar, R.; Harilal, S.; Mathew, G.E.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Prabhu, A.; Uddin, S.; Aleya, L.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. Magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia in cancer treatment: An emerging tool. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 19214–19225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley, D.; Tay, Z.W.; Dhavalikar, R.; Zheng, B.; Goodwill, P.; Rinaldi, C.; Conolly, S. Combining magnetic particle imaging and magnetic fluid hyperthermia in a theranostic platform. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 3483–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadhukha, T.; Wiedmann, T.S.; Panyam, J. Inhalable magnetic nanoparticles for targeted hyperthermia in lung cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5163–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milligan, A.J. Whole-body hyperthermia induction techniques. Cancer Res. 1984, 44, 4869s–4872s. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wust, P.; Hildebrandt, B.; Sreenivasa, G. Hyperthermia in combined treatment of cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Sharma, D. Evoution of magnetic hyperthermia for glioblastoma multiforme therapy. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Takata, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Saito, S. Control of the temperature rise in magnetic hyperthermia with use of an external static magnetic field. Phys. Med. 2013, 29, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.B.; Rauwerdink, A.M.; Hansen, E.W. Magnetic nanoparticle temperature estimation. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 1822–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodi, M.B.; Fanti, A.; Muntoni, G.; Mazzarella, G. A multiphysic model for the hyperthermia treatment of residual osteosarcoma in upper limbs using magnetic scaffolds. IEEE J. Multiscale Multiphysics Comput. Tech. 2019, 4, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mues, B.; Bauer, B.; Roeth, A.; Ortega, J.; Buhl, E.; Radon, P.; Wiekhorst, F.; Gries, T.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Slabu, I. Nanomagnetic actuation of hybrid stents for hyperthermia treatment of hollow organ tumors. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Pei, Z.; Zhang, N.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liang, G.; Zhou, J.; Xing, Y. A novel method to enhance magnetic property of bioactive glass-ceramics for hyperthermia. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 4945–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamay, G.S.; Zamay, T.N.; Lukyanenko, K.A.; Kichkailo, A.S. Aptamers increase biocompatibility and reduce the toxicity of magnetic nanoparticles used in biomedicine. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thau, L.; Asuka, E.; Mahajan, K. Physiology, opsonization. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534215/ (accessed on 27 April 2021).
- Markides, H.; Rotherham, M.; El Haj, A.J. Biocompatibility and toxicity of magnetic nanoparticles in regenerative medicine. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubayev, V.I.; Pisanic, T.R.; Jin, S. Magnetic nanoparticles for theragnostics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, P.; Hall, J.B.; McLeland, C.B.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; McNeil, S.E. Nanoparticle interaction with plasma proteins as it relates to particle biodistribution, biocompatibility and therapeutic efficacy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyanina, I.V.; Zamay, T.N.; Zamay, G.S.; Zamay, S.S.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Ivanchenko, T.I.; Denisenko, V.V.; Kirichenko, A.K.; Glazyrin, Y.; Garanzha, I.V.; et al. In vivo cancer cells elimination guided by aptamer-functionalized gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles and controlled with low frequency alternating magnetic field. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3326–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosrati, H.; Salehiabar, M.; Fridoni, M.; Abdollahifar, M.-A.; Manjili, H.K.; Davaran, S.; Danafar, H. New insight about biocompatibility and biodegradability of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles: Stereological and in vivo MRI monitor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keselman, P.; Yu, E.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Goodwill, P.; Chandrasekharan, P.; Ferguson, R.M.; Khandhar, A.; Kemp, S.J.; Krishnan, K.M.; Zheng, B.; et al. Tracking short-term biodistribution and long-term clearance of SPIO tracers in magnetic particle imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Billings, C.; Langley, M.; Warrington, G.; Mashali, F.; Johnson, J.A. Magnetic Particle Imaging: Current and Future Applications, Magnetic Nanoparticle Synthesis Methods and Safety Measures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147651
Billings C, Langley M, Warrington G, Mashali F, Johnson JA. Magnetic Particle Imaging: Current and Future Applications, Magnetic Nanoparticle Synthesis Methods and Safety Measures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(14):7651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147651
Chicago/Turabian StyleBillings, Caroline, Mitchell Langley, Gavin Warrington, Farzin Mashali, and Jacqueline Anne Johnson. 2021. "Magnetic Particle Imaging: Current and Future Applications, Magnetic Nanoparticle Synthesis Methods and Safety Measures" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 14: 7651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147651
APA StyleBillings, C., Langley, M., Warrington, G., Mashali, F., & Johnson, J. A. (2021). Magnetic Particle Imaging: Current and Future Applications, Magnetic Nanoparticle Synthesis Methods and Safety Measures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), 7651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147651






