The Neurotrophin Receptor TrkC as a Novel Molecular Target of the Antineuroblastoma Action of Valproic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
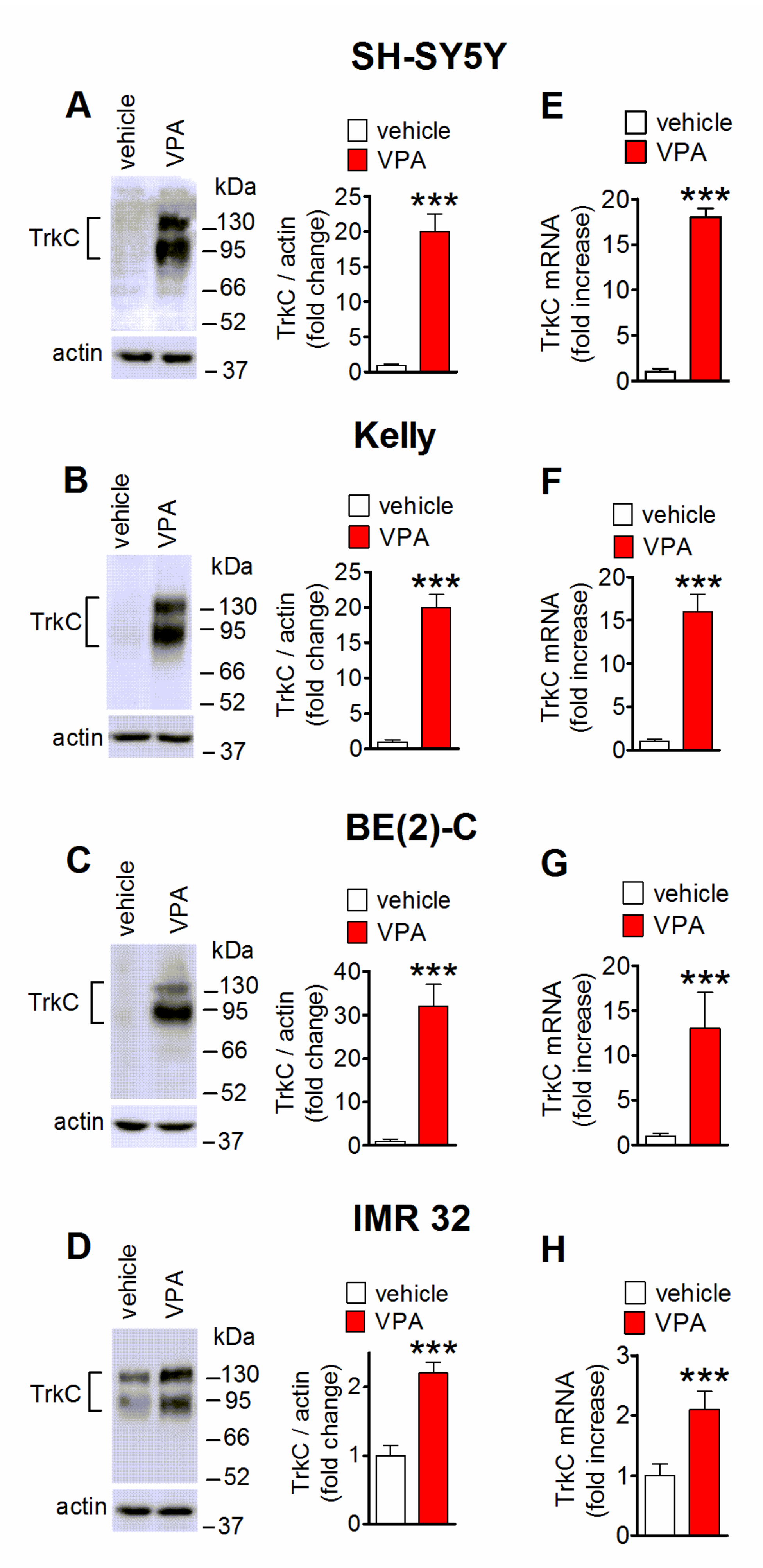
2.1. Induction of TrkC Expression by VPA in Human Neuroblastoma Cells
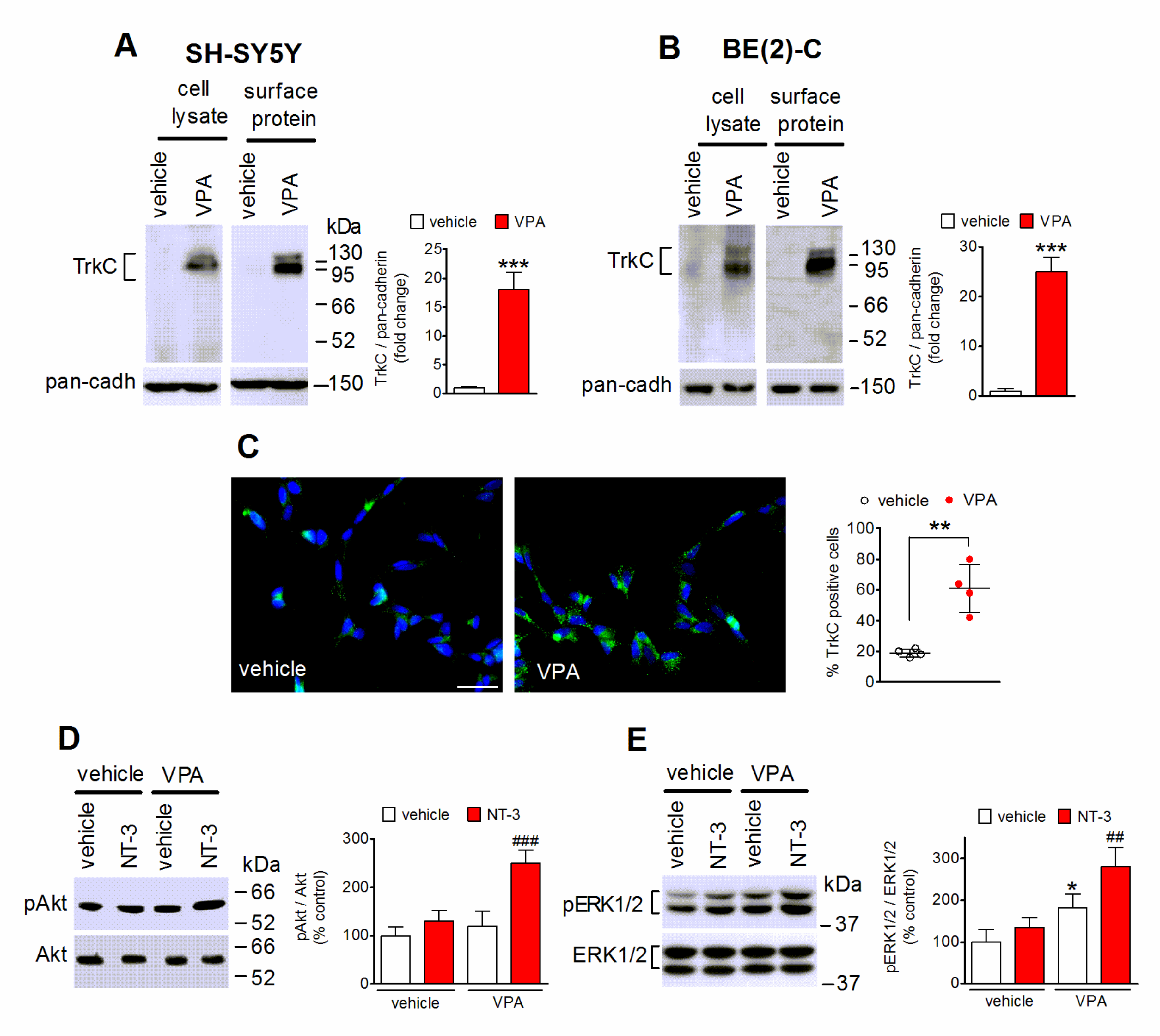
2.2. VPA Enhances the Cell Surface Expression of TrkC and NT-3-Stimulated Intracellular Signaling
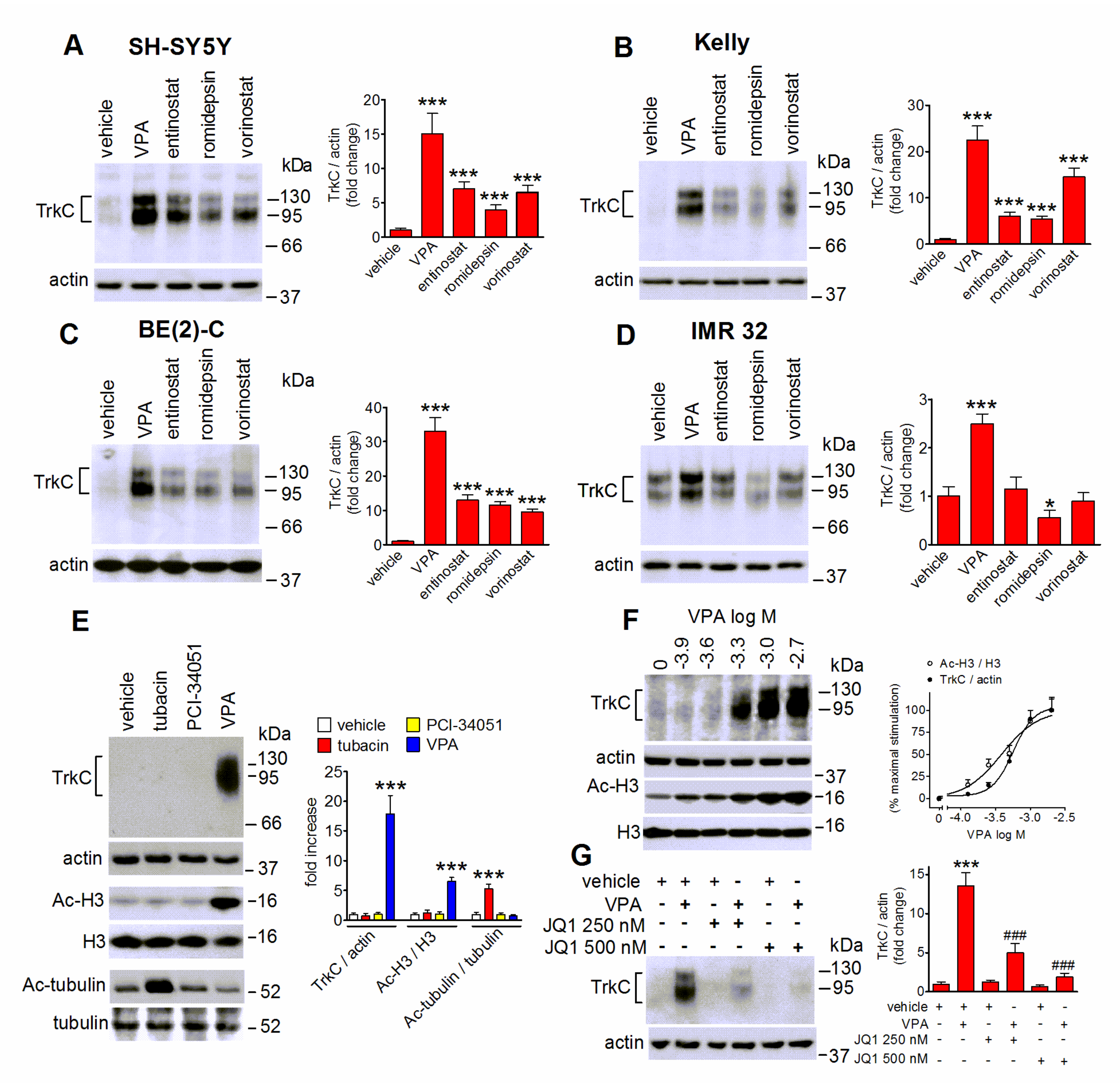
2.3. VPA-Induced TrkC Expression Is Mimicked by Other HDAC Inhibitors and Curtailed by Bromodomain Inhibition
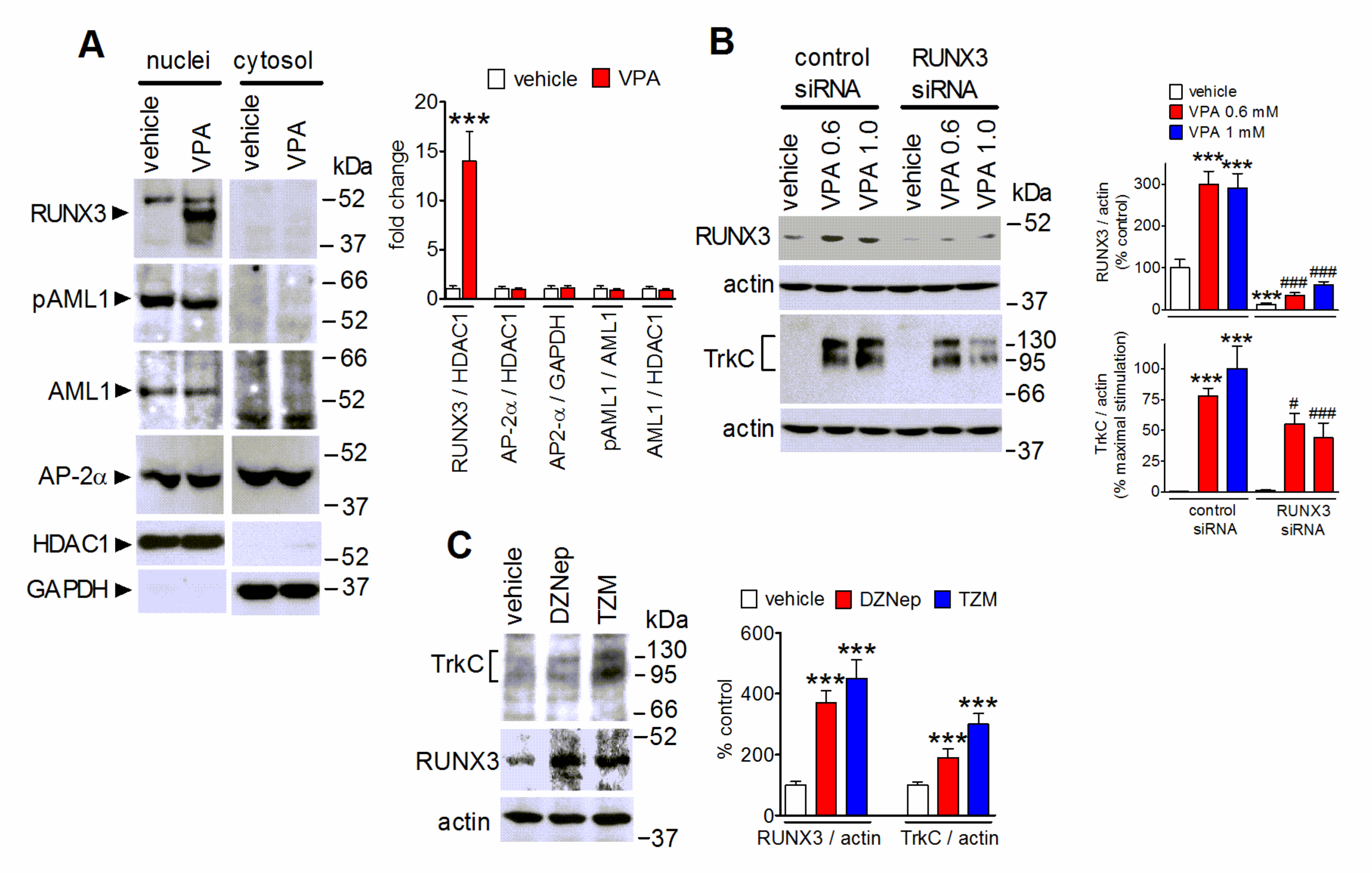
2.4. The Upregulation of the Transcription Factor RUNX3 Contributes to VPA-Induced TrkC Expression
2.5. Role of MAP Kinases in VPA-Induced TrkC Expression
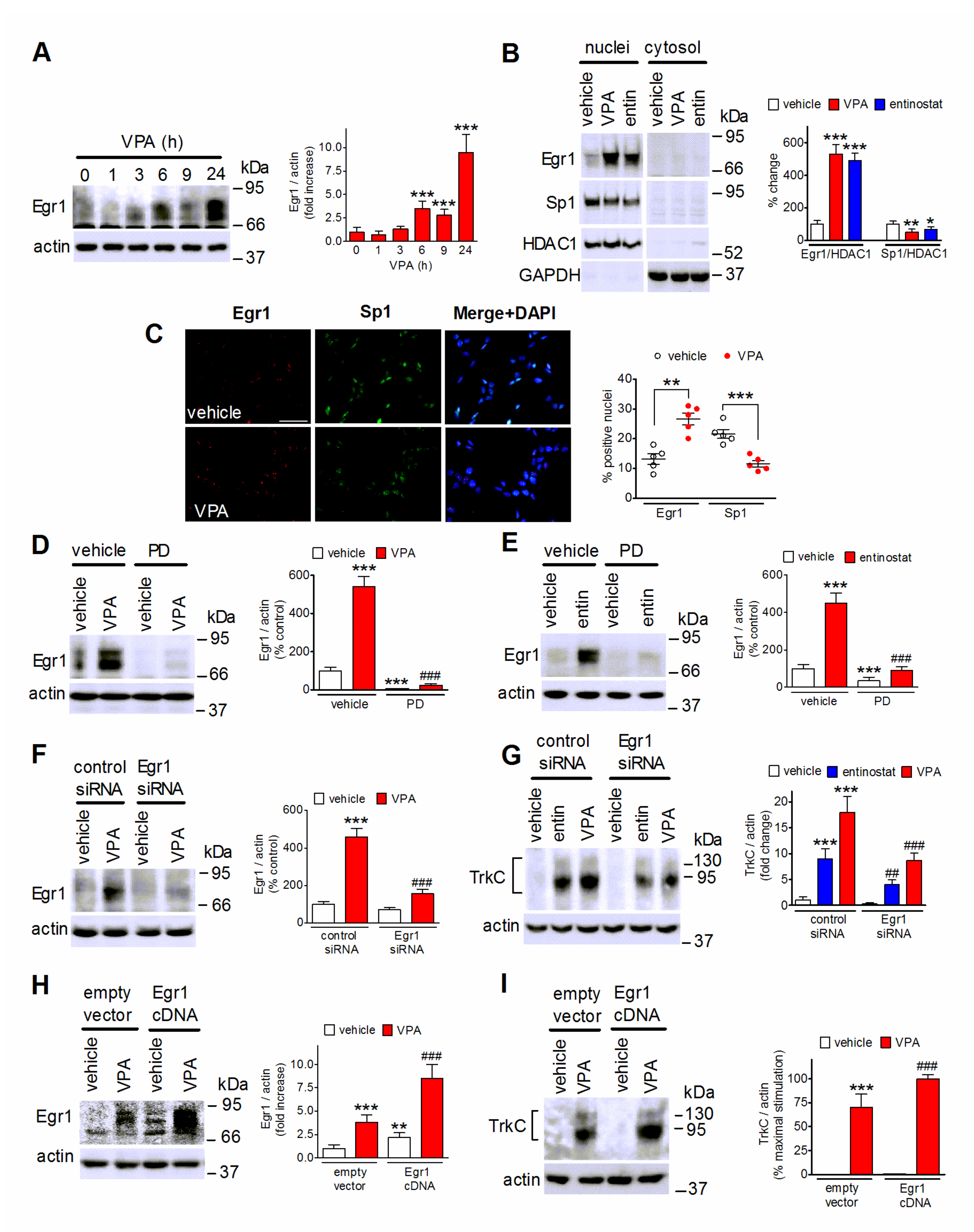
2.6. VPA Upregulates Egr1 to Induce TrkC Expression
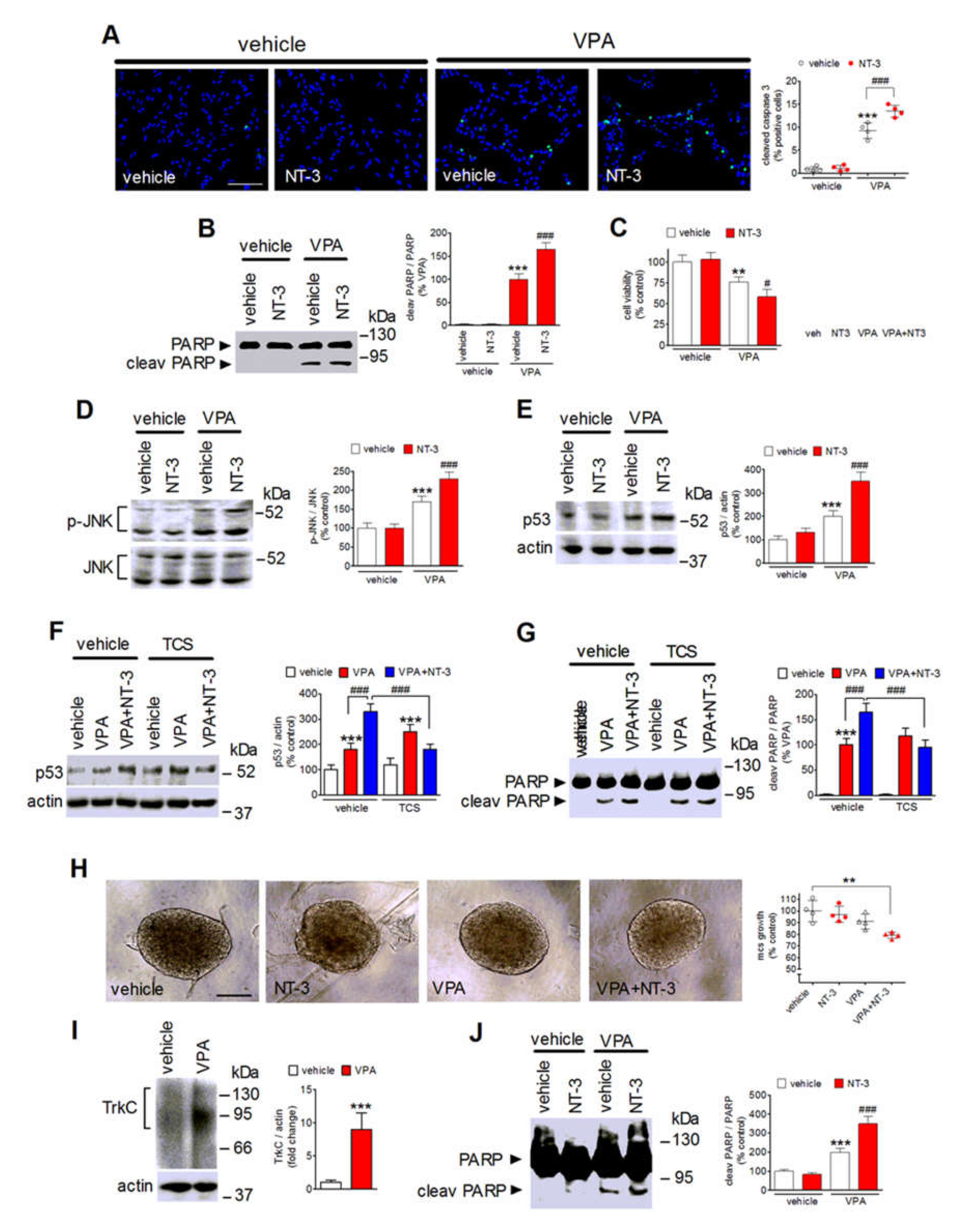
2.7. NT-3 Potentiates Apoptosis in VPA-Treated Neuroblastoma Cells
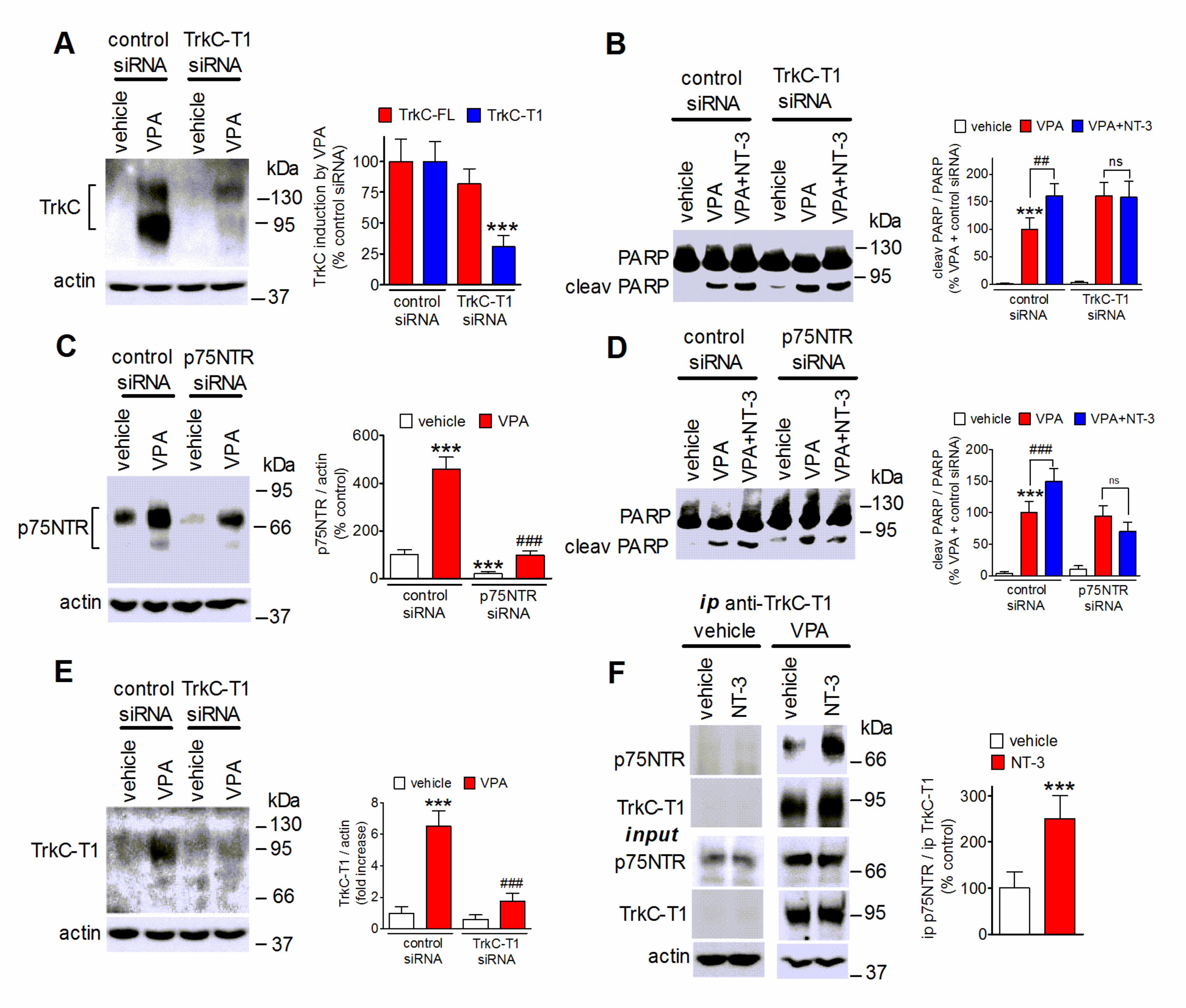
2.8. Role of TrkC-T1 and p75NTR in NT-3 Potentiation of VPA-Induced Neuroblastoma Cell Apoptosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Treatment
4.4. Cell Transfections
4.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.6. Biotinylation of Cell Surface Proteins
4.7. Isolation of Cell Nuclei
4.8. Immunoprecipitation
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.11. Assay of Cell Viability
4.12. Tumor Spheroid Generation and Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Trk receptors: Roles in neuronal signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 609–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamballe, F.; Tapley, P.; Barbacid, M. trkC encodes multiple neurotrophin-3 receptors with distinct biological properties and substrate specificities. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3083–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelton, D.L.; Sutherland, J.; Gripp, J.; Camerato, T.; Armanini, M.P.; Phillips, H.S.; Carroll, K.; Spencer, S.D.; Levinson, A.D. Human trks: Molecular cloning, tissue distribution, and expression of extracellular domain immunoadhesins. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palko, M.E.; Coppola, V.; Tessarollo, L. Evidence for a role of truncated trkC receptor isoforms in mouse development. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, P.F.; Yoon, H.-Y.; Becker, J.; Dorsey, S.G.; Caprari, P.; Palko, M.E.; Coppola, V.; Saragovi, H.U.; Randazzo, P.A.; Tessarollo, L. A kinase-deficient TrkC receptor isoform activates Arf6-Rac1 signaling through the scaffold protein tamalin. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 173, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhuo, Y.; Liu, J.; Malakhov, A.; Ko, E.; Burgess, K.; Schaefer, H.; Esteban, P.F.; Tessarollo, L.; et al. In glaucoma the upregulated truncated TrkC.T1 receptor isoform in glia causes increased TNF-α production, leading to retinal ganglion cell death. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 6639–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galán, A.; Jmaeff, S.; Barcelona, P.F.; Brahimi, F.; Sarunic, M.V.; Saragovi, H.U. In retinitis pigmentosa TrkC.T1-dependent vectorial Erk activity upregulates glial TNF-α, causing selective neuronal death. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechant, G.; Tsoulfas, P.; Parada, L.F.; Barde, Y.-A. The neurotrophin receptor p75 binds neurotrophin-3 on sympathetic neurons with high affinity and specificity. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 5281–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, P.P.; Barker, P.A. Neurotrophin signaling through the p75 neurotrophin receptor. Progr. Neurobiol. 2002, 67, 203–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, W.J. Neurotrophins induce death of hippocampal neurons via the p75 receptor. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 6340–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nykjaer, A.; Willnow, T.E.; Petersen, C.M. p75NTR–live or let die. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2005, 15, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodeur, G.M.; Minturn, J.E.; Ho, R.; Simpson, A.M.; Iyer, R.; Varela, C.R.; Light, J.E.; Kolla, V.; Evans, A.E. Trk receptor expression in neuroblastomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3244–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maris, J.M. Recent advances in neuroblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnsen, J.I.; Dyberg, C.; Wickstrom, M. Neuroblastoma, a neural crest derived embryonal malignancy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydèn, M.; Sehgal, R.; Dominici, C.; Schilling, F.H.; Ibànez, C.F.; Kogner, P. Expression of mRNA for the neurotrophin receptor trkC in neuroblastomas with favourable tumour stage and good prognosis. Br. J. Cancer 1996, 74, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamashiro, D.J.; Liu, X.-G.; Lee, C.P.; Nakagawara, A.; Ikegaki, N.; McGregor, L.M.; Baylin, S.B.; Brodeur, G.M. Expression and function of Trk-C in favourable human neuroblastomas. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 2054–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, R.A.; Goumnerova, L.C.; Kwon, Y.K.; Stiles, C.D.; Pomeroy, S.L. Expression of the neurotrophin receptor TrkC is linked to a favorable outcome in medulloblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12867–12871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawara, A.; Arima, M.; Azar, C.G.; Scavarda, N.J.; Brodeur, G.M. Inverse relationship between trk expression and N-myc amplification in human neuroblastomas. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schulte, J.H.; Pentek, F.; Hartmann, W.; Schramm, A.; Friedrichs, N.; Ora, I.; Koster, J.; Versteeg, R.; Kirfel, J.; Buettner, R.; et al. The low affinity neurotrophin receptor, p75, is upregulated in ganglioneuroblastoma/gaglioneuroma and reduces tumorigenity of neuroblastoma cells in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2488–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunone, G.; Mariotti, A.; Compagni, A.; Morandi, E.; Della Valle, G. Induction of apoptosis by p75 neurotrophin receptor in human neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene 1997, 14, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakagawara, A.; Azar, C.G.; Scavarda, N.J.; Brodeur, G.M. Expression and function of TRK-B and BDNF in human neuroblastomas. Mol. Cell Biol. 1994, 14, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Wada, R.K.; Yamashiro, J.M.; Kaplan, D.R.; Thiele, C.J. Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and p145TrkB affects survival, differentiation, and invasiveness of human neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Middlemas, D.S.; Kihl, B.K.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, X. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes survival and chemoprotection of human neuroblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 16451–16460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Douma, S.; Van Laar, T.; Zevenhoven, J.; Meuwissen, R.; Van Garderen, E.; Peeper, D.S. Suppression of anoikis and induction of metastasis by the neurotrophin receptor TrkB. Nature 2004, 430, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.C.; Johnstone, R.W. New and emerging HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witt, O.; Deubzer, H.E.; Lodrini, M.; Milde, T.; Oehme, I. Targeting histone deacetylases in neuroblastoma. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phimmachanh, M.; Han, J.Z.R.; O’Donnell, Y.E.I.; Latham, S.L.; Croucher, D.R. Histone deacetylases and histone deacetylase inhibitors in neuroblastoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 578770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chateauvieux, S.; Morceau, F.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Molecular and therapeutic potential and toxicity of valproic acid. J. Biomed. Biotech. 2010, 2020, 479364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cinatl, J., Jr.; Cinatl, J.; Driever, P.H.; Kotchetkov, R.; Pouckova, P.; Kornhuber, B.; Schwabe, D. Sodium valproate inhibits in vivo growth of human neuroblastoma cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs 1997, 8, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockhausen, M.-Y.; Sjolund, J.; Manetopoulos, C.; Axelson, H. Effects of the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid on Notch signalling in human neuroblastoma cells. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Tian, Y.; Chlenski, A.; Salwen, H.R.; Lu, Z.; Raj, J.U.; Yang, Q. Valproic acid shows a potent antitumor effect with alteration of DNA methylation in neuroblastoma. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2012, 23, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dedoni, S.; Marras, L.; Olianas, M.C.; Ingianni, A.; Onali, P.L. Downregulation of TrkB expression and signaling by valproic acid and other histone deacetylase inhibitors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedoni, S.; Marras, L.; Olianas, M.C.; Ingianni, A.; Onali, P. Valproic acid upregulates the expression of the p75NTR/sortilin receptor complex to induce neuronal apoptosis. Apoptosis 2020, 25, 697–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggarty, S.J.; Koeller, K.M.; Wong, J.C.; Grozinger, C.M.; Schreiber, S.L. Domain-selective small–molecule inhibitor of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6)-mediated tubulin deacetylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 8, 4389–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Ramos, J.; Luo, W.; Sirisawad, M.; Verner, E.; Buggy, J.J. A novel histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8)-specific inhibitor PCI-34051 induces apoptosis in T-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munster, P.; Marchion, D.; Bicaku, E.; Lacevic, M.; Kim, J.; Centino, B.; Daud, A.; Neuger, A.; Minton, S.; Sullivan, D. Clinical and biological effects of valproic acid as a histone deacetylase inhibitor on tumor and surrogate tissues: Phase I/II trial of valproic acid and epirubicin/FEC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2488–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belkina, A.C.; Denis, G.V. BET domain co-regulators in obesity, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kramer, I.; Sigrist, M.; de Nooij, J.C.; Taniuchi, I.; Jessell, T.M.; Arber, S. A role for Runx transcription factor signaling in dorsal root ganglion sensory neuron diversification. Neuron 2006, 49, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, K.; Ito, K.; Osato, M.; Lee, B.; Bae, S.-C.; Ito, Y. The transcription factor Runx3 represses the neurotrophin receptor TrkB during lineage commitment of dorsal root ganglion neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24175–24184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ichaso, N.; Rodriguez, R.E.; Martin-Zanca, D.; Gonzales-Sarmiento, R. Genomic characterization of the human trkC gene. Oncogene 1998, 17, 1871–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Biggs, J.R.; Kraft, A.S. Phorbol ester treatment of K562 cells regulates the transcriptional activity of AML1c through phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 53116–53125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Woo, C.-W.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wei, J.S.; Marquez, V.E.; Bates, S.E.; Jin, Q.; Khan, J.; et al. EZH2 mediates epigenetic silencing of neuroblastoma suppressor genes CASZ1, CLU, RUNX3, and NGFR. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, J.; Yang, X.; Zhuang, L.; Jiang, X.; Chen, W.; Lee, P.L.; Karuturi, R.K.M.; Tan, P.B.O.; Liu, E.T.; Yu, Q. Pharmacologic disruption of polycomb–repressive complex 2-mediated gene repression selectively induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1050–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knutson, S.K.; Warholic, N.M.; Wigle, T.J.; Klaus, C.R.; Allain, C.J.; Raimondi, A.; Porter Scott, M.; Chesworth, R.; Moyer, M.P.; Copeland, R.A.; et al. Durable tumor regression in genetically altered malignant rhabdoid tumors by inhibition of methyltransferase EZH2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7922–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, P.-X.; Huang, L.-D.; Jiang, Y.-M.; Gutkind, J.S.; Manji, H.K.; Chen, G. The mood stabilizer valproic acid activates mitogen-activated protein kinases and promotes neurite growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 31674–31683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Zhou, H.; Pan, B.; Li, X.; Fu, Z.; Liu, J.; Shi, Z.; Chu, T.; Wei, Z.; Ning, G.; et al. c-Jun amino-terminal kinase is involved in valproic acid-mediated neuronal differentiation of mouse embryonic NSCs and neurite outgrowth of NSC-derived neurons. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 1254–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, C.S.; Treisman, R. Transcriptional regulation by extracellular signals: Mechanism and specificity. Cell 1995, 80, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qureshi, S.A.; Cao, X.M.; Sukhatme, V.P.; Foster, D.A. v-Src activates mitogen-responsive transcription factor Egr-1 via serum response elements. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 10802–10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naar, A.M.; Ryu, S.; Tjian, R. Cofactor requirements for transcriptional activation by Sp1. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1998, 63, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitmarsh, A.J.; Shore, P.; Sharrocks, A.D.; Davis, R.J. Integration of MAP kinase signal transduction pathways at the serum response element. Science 1995, 269, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutero, A.; Camp, S.; Taylor, P. Promoter elements of the mouse acetylcholinesterase gene. Transcriptional regulation during muscle differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khachigian, L.M.; Williams, A.J.; Collins, T. Interplay of Sp1 and Egr-1 in the proximal platelet-derived growth factor A-chain promoter in cultured vascular endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 27679–27686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iraci, N.; Diolaiti, D.; Papa, A.; Porro, A.; Valli, E.; Ghepardi, S.; Herold, S.; Eilers, M.; Bernardoni, R.; Della Valle, G.; et al. A SP1/MIZ1/MYCN repression complex recruits HDAC1 at the TRKA and p75NTR promoters and affects neuroblastoma malignancy by inhibiting the cell response to NGF. Cancer Res. 2010, 71, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurvich, N.; Tsygankova, O.M.; Meinkoth, J.L.; Klein, P.S. Histone deacetylase is a target of valproic acid-mediated cellular differentiation. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michaelis, M.; Suhan, T.; Michaelis, U.R.; Beek, K.; Rothweiler, F.; Tausch, L.; Werz, O.; Eikel, D.; Zornig, M.; Nau, H.; et al. Valproic acid induces extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation and inhibits apoptosis in endothelial cells. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tessarollo, L. Pleiotropic functions of neurotrophins in development. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1998, 9, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.H.; Sutton, M.E.; Lu, D.J.; Cho, T.A.; Goumnerova, L.C.; Goritchenko, L.; Kaufman, J.R.; Lam, K.K.; Billet, A.L.; Tarbell, N.J.; et al. Activation of neurotrophin-3 receptor TrkC induces apoptosis in medulloblastomas. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 711–719. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzas-Rodriguez, J.; Cabrera, J.R.; Delloye-Bourgeois, C.; Ichim, G.; Delcros, J.-G.; Raquin, M.-A.; Rousseau, R.; Combaret, V.; Bènard, J.; Tauszig-Delamasure, S.; et al. Neurotrophin-3 production promotes human neuroblastoma cell survival by inhibiting TrkC-induced apoptosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrakovcic, M.; Kleinheinz, J.; Fröhlich, L.F. p53 at the crossroads between different types of HDAC inhibitor-mediated cancer cell death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuchs, S.Y.; Adler, V.; Pincus, M.R.; Ronai, Z. MEKK1/JNK signalling stabilizes and activates p53. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 10541–10546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunz-Schughart, L.A.; Freyer, J.P.; Hofstaedter, F.; Ebner, R. The use of 3-D cultures for high-throughput screening: The multicellular spheroid model. J. Biomol. Screen. 2004, 9, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, H.R.; Zhong, X.; Hoelz, D.J.; Rescorla, F.J.; Hickey, R.J.; Malkas, L.H.; Sandoval, J.A. Three-dimensional neuroblastoma cell culture: Proteomic analysis between monolayer and multicellular tumor spheroids. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2008, 24, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dedoni, S.; Olianas, M.C.; Ingianni, A.; Onali, P. Interferon-β inhibits neurotrophin 3 signalling and pro-survival activity by up-regulating the expression of truncated TrkC-T1 receptor. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 1825–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coso, O.A.; Chiariello, M.; Yu, J.-C.; Teramoto, H.; Crespo, P.; Xu, N.; Miki, T.; Gutkind, J.S. The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell 1995, 81, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aloyz, R.S.; Bamji, S.X.; Pozniak, C.D.; Toma, J.G.; Atwal, J.; Kaplan, D.R.; Miller, F.D. P53 is essential for developmental neuron death as regulated by the TrkA and p75 neurotrophin receptors. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hapner, S.J.; Boeshore, K.L.; Large, T.H.; Lefcort, F. Neural differentiation promoted by truncated trkC receptors in collaboration with p75NTR. Dev. Biol. 1998, 201, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guidi, M.; Muiños-Gimeno, M.; Kagerbauer, B.; Martí, E.; Estivill, X.; Espinosa-Parrilla, Y. Overexpression of miR-128 specifically inhibits the truncated isoform of NTRK3 and upregulates BCL2 in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. BMC Mol. Biol. 2010, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dedoni, S.; Olianas, M.C.; Ingianni, A.; Onali, P. Type I interferons impair BDNF-induced cell signaling and neurotrophic activity in differentiated human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells and mouse primary cortical neurons. J. Neurochem. 2012, 122, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dedoni, S.; Marras, L.; Olianas, M.C.; Ingianni, A.; Onali, P. The Neurotrophin Receptor TrkC as a Novel Molecular Target of the Antineuroblastoma Action of Valproic Acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157790
Dedoni S, Marras L, Olianas MC, Ingianni A, Onali P. The Neurotrophin Receptor TrkC as a Novel Molecular Target of the Antineuroblastoma Action of Valproic Acid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(15):7790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157790
Chicago/Turabian StyleDedoni, Simona, Luisa Marras, Maria C. Olianas, Angela Ingianni, and Pierluigi Onali. 2021. "The Neurotrophin Receptor TrkC as a Novel Molecular Target of the Antineuroblastoma Action of Valproic Acid" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 15: 7790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157790
APA StyleDedoni, S., Marras, L., Olianas, M. C., Ingianni, A., & Onali, P. (2021). The Neurotrophin Receptor TrkC as a Novel Molecular Target of the Antineuroblastoma Action of Valproic Acid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(15), 7790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157790





